Pregnancy and travelling by air
Air Travel During Pregnancy | ACOG
By reading this page you agree to ACOG's Terms and Conditions. Read terms
Number 746 (Replaces Committee Opinion Number 443, October 2009. Reaffirmed 2019)
Committee on Obstetric Practice
INTERIM UPDATE: This Committee Opinion is updated as highlighted to reflect a limited, focused change regarding the addition of a report on occupational exposure to ionizing radiation.
ABSTRACT: In the absence of obstetric or medical complications, occasional air travel is safe for pregnant women. Pregnant women can fly safely, observing the same precautions for air travel as the general population. Because severe air turbulence cannot be predicted and the subsequent risk for trauma is significant should this occur, pregnant women should be instructed to use their seat belts continuously while seated. Despite a lack of evidence associating lower extremity edema and venous thrombotic events with air travel during pregnancy, certain preventive measures can be used to minimize these risks, including use of support stockings and periodic movement of the lower extremities, avoidance of restrictive clothing, occasional ambulation, and maintenance of adequate hydration. For most air travelers, the risks to the fetus from exposure to cosmic radiation are negligible. However, aircrew or frequent flyers may exceed these limits. The Federal Aviation Administration and the International Commission on Radiological Protection consider aircrew to be occupationally exposed to ionizing radiation and recommend that they be informed about radiation exposure and health risks.
Occasional air travel during pregnancy is generally safe. Recent cohort studies suggest no increase in adverse pregnancy outcomes for occasional air travelers 1 2. Most commercial airlines allow pregnant women to fly up to 36 weeks of gestation. Some restrict pregnant women from international flights earlier in gestation and some require documentation of gestational age. For specific airline requirements, women should check with the individual carrier. Civilian and military aircrew members who become pregnant should check with their specific agencies for regulations or restrictions to their flying duties.
Air travel is not recommended at any time during pregnancy for women who have medical or obstetric conditions that may be exacerbated by flight or that could require emergency care. The duration of the flight also should be considered when planning travel. Pregnant women should be informed that the most common obstetric emergencies occur in the first and third trimesters.
In-craft environmental conditions, such as changes in cabin pressure and low humidity, coupled with the physiologic changes of pregnancy, do result in adaptations, including increased heart rate and blood pressure, and a significant decrease in aerobic capacity 3 4. The risks associated with long hours of air travel immobilization and low cabin humidity, such as lower extremity edema and venous thrombotic events, recently have been the focus of attention for all air travelers. Despite a lack of evidence associating these events with air travel during pregnancy, certain preventive measures can be used to minimize these risks, including use of support stockings and periodic movement of the lower extremities, avoidance of restrictive clothing, occasional ambulation, and maintenance of adequate hydration.
Because severe air turbulence cannot be predicted and the subsequent risk for trauma is significant should this occur, pregnant women should be instructed to use their seatbelts continuously while seated. The seatbelt should be belted low on the hipbones, between the protuberant abdomen and pelvis. Several precautions may ease discomfort for pregnant air travelers. For example, gas-producing foods or drinks should be avoided before scheduled flights because entrapped gases expand at altitude 5. Preventive antiemetic medication should be considered for women with increased nausea.
Available information suggests that noise, vibration, and cosmic radiation present a negligible risk for the occasional pregnant air traveler 6 7. Both the National Council on Radiation Protection and Measurements and the International Commission on Radiological Protection recommend a maximum annual radiation exposure limit of 1 millisievert (mSv) (100 rem) for members of the general public and 1 mSv over the course of a 40-week pregnancy 7. For most air travelers, the risks to the fetus from exposure to cosmic radiation are negligible. Even the longest available intercontinental flights will expose passengers to no more than 15% of this limit 7; therefore, it is unlikely that the occasional traveler will exceed current exposure limits during pregnancy. However, aircrew or frequent flyers may exceed these limits. The Federal Aviation Administration and the International Commission on Radiological Protection consider aircrew to be occupationally exposed to ionizing radiation and recommend that they be informed about radiation exposure and health risks 8 9. The reader is referred to What Aircrews Should Know About Their Occupational Exposure to Ionizing Radiation 10 and In-flight Radiation Exposure 11 for additional details.
For most air travelers, the risks to the fetus from exposure to cosmic radiation are negligible. Even the longest available intercontinental flights will expose passengers to no more than 15% of this limit 7; therefore, it is unlikely that the occasional traveler will exceed current exposure limits during pregnancy. However, aircrew or frequent flyers may exceed these limits. The Federal Aviation Administration and the International Commission on Radiological Protection consider aircrew to be occupationally exposed to ionizing radiation and recommend that they be informed about radiation exposure and health risks 8 9. The reader is referred to What Aircrews Should Know About Their Occupational Exposure to Ionizing Radiation 10 and In-flight Radiation Exposure 11 for additional details.
In the absence of obstetric or medical complications, occasional air travel is safe for pregnant women. Pregnant women can fly safely, observing the same precautions for air travel as the general population. Women should check with specific carriers for airline requirements.
Women should check with specific carriers for airline requirements.
- Chibber R, Al-Sibai MH, Qahtani N. Adverse outcome of pregnancy following air travel: a myth or a concern? Aust N Z J Obstet Gynaecol 2006;46:24–8.
Article Locations:Article Location
- Freeman M, Ghidini A, Spong CY, Tchabo N, Bannon PZ, Pezzullo JC. Does air travel affect pregnancy outcome? Arch Gynecol Obstet 2004;269:274–7.
Article Locations:Article Location
- Huch R, Baumann H, Fallenstein F, Schneider KT, Holdener F, Huch A. Physiologic changes in pregnant women and their fetuses during jet air travel. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1986;154:996–1000.
Article Locations:Article Location
- Artal R, Fortunato V, Welton A, Constantino N, Khodiguian N, Villalobos L, et al. A comparison of cardiopulmonary adaptations to exercise in pregnancy at sea level and altitude. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1995;172:1170–8; discussion 1178–80.
Article Locations:Article Location
- Bia FJ.
 Medical considerations for the pregnant traveler. Infect Dis Clin North Am 1992;6:371–88.
Medical considerations for the pregnant traveler. Infect Dis Clin North Am 1992;6:371–88.
Article Locations:Article Location
- Morrell S, Taylor R, Lyle D. A review of health effects of aircraft noise. Aust N Z J Public Health 1997;21:221–36.
Article Locations:Article Location
- Barish RJ. In-flight radiation exposure during pregnancy. Obstet Gynecol 2004;103:1326–30.
Article Locations:Article LocationArticle LocationArticle Location
- Federal Aviation Administration. In-flight radiation exposure. Advisory Circular No. 120–61A . Washington, DC: FAA; 2006.
Article Locations:Article Location
- The 2007 recommendations of the International Commission on Radiological Protection. International Commission on Radiological Protection. IRCP Publication 103. Ann IRCP 2007;37:1–332.
Article Locations:Article Location
- Office of Aerospace Medicine, Federal Aviation Administration. What aircrews should know about their occupational exposure to ionizing radiation .
 Washington, DC: FAA; 2003. Available at: https://www.faa.gov/data_research/research/med_humanfacs/oamtechreports/2000s/media/0316.pdf. Retrieved May 1, 2018.
Washington, DC: FAA; 2003. Available at: https://www.faa.gov/data_research/research/med_humanfacs/oamtechreports/2000s/media/0316.pdf. Retrieved May 1, 2018.
Article Locations:Article Location
- Federal Aviation Administration. In-flight radiation exposure. Advisory Circular . Washington, DC: FAA; 2014. Available at: https://www.faa.gov/documentLibrary/media/Advisory_Circular/AC_120-61B.pdf. Retrieved May 2, 2018.
Article Locations:Article Location
Published online on July 25, 2018.
Copyright 2018 by the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, posted on the Internet, or transmitted, in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording, or otherwise, without prior written permission from the publisher.
Requests for authorization to make photocopies should be directed to Copyright Clearance Center, 222 Rosewood Drive, Danvers, MA 01923, (978) 750-8400.
American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists 409 12th Street, SW, PO Box 96920, Washington, DC 20090-6920
Air travel during pregnancy. ACOG Committee Opinion No. 746. American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Obstet Gynecol 2018;132:e64–6.
This information is designed as an educational resource to aid clinicians in providing obstetric and gynecologic care, and use of this information is voluntary. This information should not be considered as inclusive of all proper treatments or methods of care or as a statement of the standard of care. It is not intended to substitute for the independent professional judgment of the treating clinician. Variations in practice may be warranted when, in the reasonable judgment of the treating clinician, such course of action is indicated by the condition of the patient, limitations of available resources, or advances in knowledge or technology. The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists reviews its publications regularly; however, its publications may not reflect the most recent evidence. Any updates to this document can be found on www.acog.org or by calling the ACOG Resource Center.
Any updates to this document can be found on www.acog.org or by calling the ACOG Resource Center.
While ACOG makes every effort to present accurate and reliable information, this publication is provided “as is” without any warranty of accuracy, reliability, or otherwise, either express or implied. ACOG does not guarantee, warrant, or endorse the products or services of any firm, organization, or person. Neither ACOG nor its officers, directors, members, employees, or agents will be liable for any loss, damage, or claim with respect to any liabilities, including direct, special, indirect, or consequential damages, incurred in connection with this publication or reliance on the information presented.
All ACOG Committee members and authors have submitted a conflict of interest disclosure statement related to this published product. Any potential conflicts have been considered and managed in accordance with ACOG's Conflict of Interest Disclosure Policy. The ACOG policies can be found on acog.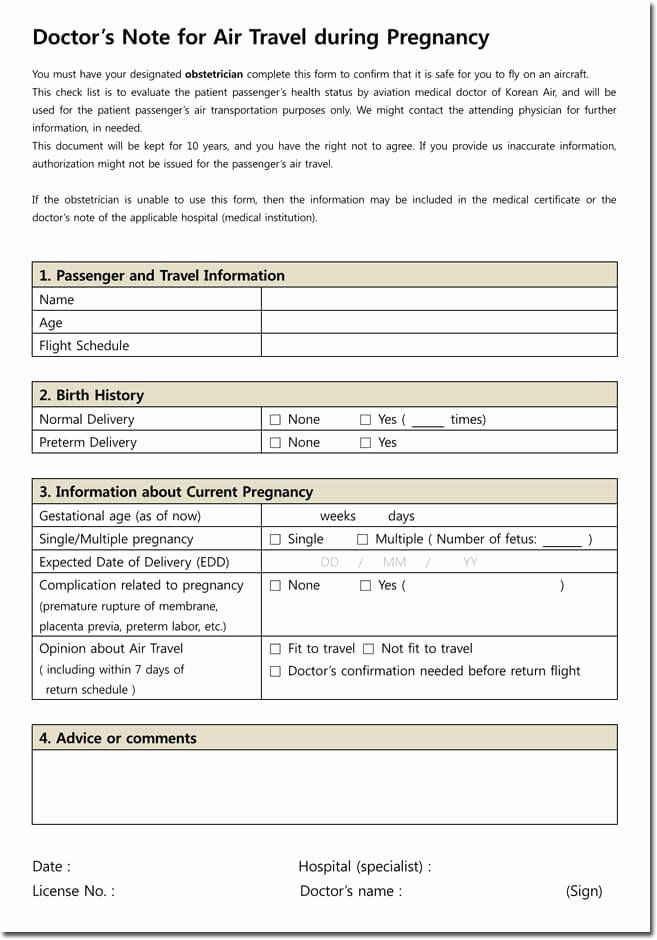 org. For products jointly developed with other organizations, conflict of interest disclosures by representatives of the other organizations are addressed by those organizations. The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists has neither solicited nor accepted any commercial involvement in the development of the content of this published product.
org. For products jointly developed with other organizations, conflict of interest disclosures by representatives of the other organizations are addressed by those organizations. The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists has neither solicited nor accepted any commercial involvement in the development of the content of this published product.
Topics
Environmental exposure Pregnancy Pregnancy complications Public health Radiation effects Radiologic health
Pregnancy and travel - Better Health Channel
Actions for this page
Summary
Read the full fact sheet- If you are pregnant, the safest time for you to travel is during the second trimester, provided you aren’t experiencing any complications.
- If you are pregnant and considering travel, you must consult with your doctor, especially if your pregnancy is high risk.

- Avoid travelling to developing nations during pregnancy.
- Be wary of taking medications of any kind, including those commonly used to treat traveller’s diarrhoea.
If you are pregnant, the safest time for you to travel, generally speaking, is during the second trimester, provided you aren’t experiencing any complications. If you are pregnant and considering travel, you must consult with your doctor, especially if your pregnancy is high risk. Consider the standard of medical care at your chosen destination, just in case you need help.
Some countries have reciprocal healthcare arrangements with Australia – check with Medicare. Travelling to developing nations is not encouraged during pregnancy for various reasons, including the risk of disease and the lower standard of medical facilities compared to Australia.
High-risk pregnancies and travel
Pregnant women experiencing complications are advised not to travel. Some complications include:
Some complications include:
- cervical problems, such as 'incompetent cervix'
- vaginal bleeding
- multiple pregnancy
- gestational diabetes, past or present
- high blood pressure, past or present
- pre-eclampsia (a toxic condition sometimes occurring in pregnancy), past or present
- abnormalities of the placenta, past or present
- prior miscarriage
- prior ectopic pregnancy (a pregnancy that develops outside the womb)
- prior premature labour.
If you are aged 35 years or over and pregnant for the first time, you are also advised not to travel.
Travel immunisation warnings for pregnant women
Travellers to most developing nations need to be immunised against diseases such as typhoid. Most vaccines are either dangerous to unborn babies or haven't been adequately tested for safety on pregnant women.
The important exception to this is the influenza vaccine, which can be safely given during pregnancy. It is strongly recommended for all pregnant women, as influenza in pregnancy can be a very serious illness. Generally, all live virus vaccines (such as mumps and measles) should be avoided during pregnancy.
It is strongly recommended for all pregnant women, as influenza in pregnancy can be a very serious illness. Generally, all live virus vaccines (such as mumps and measles) should be avoided during pregnancy.
Some vaccines, such as for yellow fever, may cautiously be given after the first trimester. Be advised by your doctor. It is recommended that pregnant women delay any travel to developing nations until after their babies are born.
Travel and the risk of malaria during pregnancy
Malaria is an infection carried by particular species of mosquito. A pregnant woman who catches malaria risks miscarriage, premature labour and stillbirth. Some antimalarial drugs (such as chloroquine) are considered safe to take during pregnancy, but others (such as doxycycline) are potentially harmful to the unborn baby. It is recommended that pregnant women avoid travelling to areas where malaria is present.
Risks of long-distance travel during pregnancy
Long periods of not moving during car, bus, rail and air travel increases the risk of clots forming in the deep veins of the leg, known as deep vein thrombosis (DVT). These clots can circulate and lodge in parts of the body such as the lungs.
These clots can circulate and lodge in parts of the body such as the lungs.
The risk of DVT is increased in pregnancy if:
- you had a DVT in the past
- you weigh more than 100 kg
- you have a multiple pregnancy
- a family member has had a DVT.
One in 1,000 pregnant women will develop DVT. Research indicates the risk of DVT can increase by two or three times in a long-distance flight.
There is no research-based advice on travel for pregnant women. However, if you choose to travel long distances, you should:
- Do frequent leg exercises.
- Walk regularly (in the case of air travel, walk around the aircraft cabin if the flight is smooth).
- Avoid dehydration by drinking plenty of water.
- Minimise alcohol and caffeine intake.
If you have an increased risk of DVT, you are advised to:
- Discuss travel plans with your doctor.
- Wear well-fitting elastic below-knee compression stockings during the journey.

- Receive heparin injections before and after any journey longer than four hours.
Air travel and pregnancy
Before you decide to travel by plane:
- Discuss any potential risks particular to your pregnancy with your doctor. For example, a woman with gestational diabetes or a multiple pregnancy is generally advised not to fly.
- Be aware that air travel in the last six weeks of pregnancy could trigger premature labour.
- Check with the airline – some airlines won't allow a woman over 35 weeks to fly at all, or they require a doctor’s note.
- Check the fine print of your travel insurance – some policies may not cover pregnancy.
- Arrange with the airline for a bulkhead seat or a seat near an exit for extra leg room.
- Consider booking an aisle seat – going to the toilet will be a little easier.
Before you leave, discuss with your doctor whether you need to travel with a medical kit. Remember to pack this kit in your carry-on luggage so you can access it during the flight.
Items your medical kit could contain:
- preparations to help you treat common pregnancy complaints such as heartburn, thrush, constipation and haemorrhoids
- oral rehydration preparations in case of traveller’s diarrhoea
- multivitamins formulated for pregnant women
- urine dipsticks to check glucose levels (if required).
During the flight:
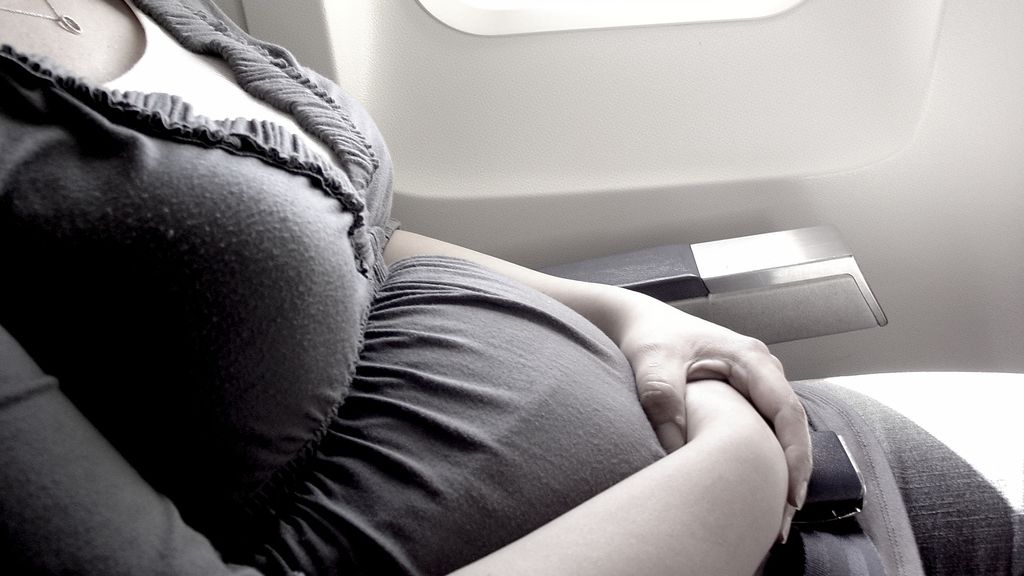
- Wear your seatbelt under your bump and across your lap.
- Stretch and move your legs regularly while seated. Consider wearing support stockings for the duration of the flight. A pregnant woman's circulation is already under strain – the lower cabin pressure inside a plane can theoretically increase the risk of blood clots.
- Drink plenty of water to reduce the risk of dehydration. Keeping up your fluid intake will also reduce the risk of DVT.
- If the flight is smooth, walk up and down the aisles every half hour.
- If the flight has turbulence, stay in your seat, but flex and extend your ankles frequently.

- If you are feeling short of breath or light-headed, ask one of the flight attendants to give you breathing oxygen.
Car travel and pregnancy
If travelling by car:
- Make frequent breaks to stretch your legs and visit the toilet.
- Always wear a seatbelt. Fasten the lap sash across your lap and under your bump, fit the shoulder sash above your bump and between your breasts.
- Avoid wearing the lap sash across your bump as a sudden jolt could cause your placenta to separate from your uterus.
- If you are sitting in the front passenger seat, move your seat well back from the dashboard to reduce airbag impact in case of a collision.
- If you are driving, have your seat as far back from the steering wheel as possible, while still being able to drive safely and comfortably. It may help to tilt the steering wheel downwards, away from your belly.
- If you are involved in a collision, however minor, see your doctor.
- If you have contractions, pain or bleeding after an accident, see a doctor as soon as possible.
 Let them know if you have a rhesus negative blood group, as you may need to have an anti-D injection.
Let them know if you have a rhesus negative blood group, as you may need to have an anti-D injection. - Consider joining a roadside assistance program that can help you in case of a breakdown, and always carry a mobile phone.
Heat and sun exposure and pregnancy
If travelling in hot weather:
- Carry a water bottle with you and drink water frequently.
- Stay in the shade or inside during the hottest part of the day.
- Protect your skin by wearing loose-fitting clothing, a hat and sunscreen.
- Avoid rushing or overexertion – plan your activities and give yourself plenty of time.
Overheating during pregnancy
If you feel weak and dizzy, light-headed or even slightly nauseous, it may be a sign that you are overheating and dehydrated. Remember:
- to seek shade or go inside, drink a glass of cool water and lie down
- to bring down your temperature by using a fan, placing a cool, wet cloth on your forehead and the back of your neck, or running cool water over your wrists.

- that dizziness may also indicate a drop in blood sugar, so have a light snack such as a banana or a piece of toast.
Sporting activities and pregnancy
Certain sporting activities carry an increased risk to your unborn baby. Activities to avoid include:
- Water-skiing – coming off the skis could force water into the vagina.
- Scuba diving – the changes in blood gases may harm your baby. Snorkelling is fine and scuba diving to depths of less than 18 metres (60 feet) is reasonably safe, but check with your doctor first.
- Saunas and hot tubs – raising your body temperature can harm your baby.
- Horseback riding – the motion of horseback riding carries a risk of placental abruption (separating the placenta from the uterus). Falling from or being kicked by a horse carries a high risk of trauma to your baby, or even death.
- High-altitude activities such as mountain climbing – at heights over 3,000 metres, the oxygen level in the air is low.
 This reduces the oxygen available to your baby. Pregnant women are also more vulnerable to developing altitude sickness.
This reduces the oxygen available to your baby. Pregnant women are also more vulnerable to developing altitude sickness.
Traveller’s diarrhoea and pregnancy
Be careful to avoid food poisoning, as certain infections can harm the baby or trigger miscarriage. Remember to:
- Avoid food buffets, seafood, undercooked meats, soft cheeses and pâtés.
- Wash your hands thoroughly after going to the toilet, before preparing food and before eating.
- In developing nations, only eat fruit that you have peeled yourself. Avoid leafy greens and salads because they could have been washed in contaminated water.
- Drink bottled water if you are unsure of the water supply. Use bottled water when brushing your teeth. Make sure that all eating utensils are thoroughly dried after washing.
- Avoid ice.
- If you must use the local water, boil the water thoroughly for five minutes before using.
- Avoid treating unsafe water with iodine. If consumed over a few weeks, iodine can cause your unborn baby to develop a goitre (enlarged thyroid gland).

Medications to avoid during pregnancy
Pregnant women should be wary of taking medications of any kind. Some medications can pass to the baby through the placenta and cause birth defects or miscarriage.
- Avoid taking any over-the-counter medication unless advised by your doctor, who knows you are pregnant.
- Medications that are commonly used to treat traveller’s diarrhoea are dangerous during pregnancy.
- Avoid alcohol.
- Avoid using 'social' or 'recreational' drugs.
Where to get help
- Your doctor
- NURSE-ON-CALL Tel. 1300 60 60 24 – for expert health information and advice (24 hours, 7 days)
Things to remember
- If you are pregnant, the safest time for you to travel is during the second trimester, provided you aren’t experiencing any complications.
- If you are pregnant and considering travel, you must consult with your doctor, especially if your pregnancy is high risk.
- Avoid travelling to developing nations during pregnancy.

- Be wary of taking medications of any kind, including those commonly used to treat traveller’s diarrhoea.
- Getting there by car, babycenter.com.au. More information here.
- Pregnancy and overheating, 2011, netdoctor, More information here.
- ‘Influenza’, 2013, The Australian Immunisation Handbook 10th Edition 2013, Australian Government Department of Health. More information here.
- Reyes N, Grosse S, Grant A, Deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. More information here.
This page has been produced in consultation with and approved by:
This page has been produced in consultation with and approved by:
Give feedback about this page
Was this page helpful?
More information
Content disclaimer
Content on this website is provided for information purposes only. Information about a therapy, service, product or treatment does not in any way endorse or support such therapy, service, product or treatment and is not intended to replace advice from your doctor or other registered health professional. The information and materials contained on this website are not intended to constitute a comprehensive guide concerning all aspects of the therapy, product or treatment described on the website. All users are urged to always seek advice from a registered health care professional for diagnosis and answers to their medical questions and to ascertain whether the particular therapy, service, product or treatment described on the website is suitable in their circumstances. The State of Victoria and the Department of Health shall not bear any liability for reliance by any user on the materials contained on this website.
Information about a therapy, service, product or treatment does not in any way endorse or support such therapy, service, product or treatment and is not intended to replace advice from your doctor or other registered health professional. The information and materials contained on this website are not intended to constitute a comprehensive guide concerning all aspects of the therapy, product or treatment described on the website. All users are urged to always seek advice from a registered health care professional for diagnosis and answers to their medical questions and to ascertain whether the particular therapy, service, product or treatment described on the website is suitable in their circumstances. The State of Victoria and the Department of Health shall not bear any liability for reliance by any user on the materials contained on this website.
Reviewed on: 31-03-2015
Flying on vacation while pregnant. Rules, recommendations, tips
ATOR Bulletin, with the help of gynecologists and insurers, has compiled a set of the most important tips and recommendations that pregnant women will need when planning, preparing, flying and staying on a summer beach holiday - from choosing insurance to the rules of safe tanning and nutrition.
Vestnik ATOR was told about the details and nuances of organizing summer vacation during pregnancy:
Natalya Badikova , obstetrician-gynecologist with 13 years of experience, urogynecologist, PhD
Yulia Alcheeva , executive director of the insurance company ERV, the largest monotourism insurance company in Russia
From our review you will find out:
- At what period of pregnancy can you fly on vacation, and when is it better to stay at home
- Until what week of pregnancy can you fly on vacation abroad
- Which insurance to choose for pregnant women
- What needs to be done before a vacation for a pregnant woman and what documents to take
- What are the symptoms of a pregnant woman to postpone the trip
- Plane, car, train - which is safer for pregnant women?
- Is it possible for pregnant women to pass the scanner during security screening at the airport
- Air travel during pregnancy: how to behave and what to take with you
- Which country to choose for a beach vacation during pregnancy
- How to sunbathe during pregnancy
- Where it is safe to swim while pregnant - sea or swimming pool
- How to eat while pregnant on vacation
- What to do if you find out you are pregnant while on vacation
I.
 PLANNING A PREGNANCY HOLIDAY
PLANNING A PREGNANCY HOLIDAY
WHEN PREGNANT WOMAN CAN GO ON HOLIDAY AND WHEN IT IS BETTER TO STAY AT HOME
during pregnancy, exclude pathological conditions.
To eliminate the risks of early booking, pregnant women should always take extended insurance when buying a tour - with the trip cancellation insurance option included. If you found out about pregnancy after buying the tour, you should purchase such insurance separately, as well as special medical insurance (but more on that later).
According to doctors and insurers, if there are no medical contraindications, it is best to go on a beach vacation with air travel in the second trimester of pregnancy, with some restrictions - in the first and first half of the third trimester (up to 31 weeks)
“The gestation period is from 14 weeks to 23 weeks, according to medical practice, the most “calm” and relatively safe period for flights and any travel,” says Natalya Badikova, obstetrician-gynecologist.
Pregnancy from 14 weeks to 23 weeks, according to medical practice, the most "calm" and relatively safe period for flights and any travel
According to doctors, it's not just that before the 12th week, pregnant women often experience toxicosis, which manifests itself in fatigue, nausea, poor health, changes in taste preferences, etc., which, of course, does not contribute to a peaceful rest. But also in the fact that until the 14th week inclusive, in the body of a woman there is an intensive main "laying" of all the systems and organs of the baby - and it is important not to interfere with her. In addition, in Russia, the most important screening during pregnancy is performed just at the end of the first trimester - from 11 to 14 weeks. This screening includes specialized ultrasound diagnostics, calculation of the individual risk of having a child with a chromosomal pathology, and a number of other complex studies. It is highly undesirable to miss it, so traveling far from the place of medical observation from the 11th to the 14th week of pregnancy is best excluded altogether.
The same rule applies to 18-21 weeks - at this time, pregnant women undergo a second screening (perinatal diagnosis of fetal anomalies, a very important study), so you need to be within reach of the clinic where it is carried out and plan the start and end dates correctly tour so as to have time to pass this examination.
TILL WHAT WEEK OF PREGNANCY CAN YOU FLY ON A VACATION ABROAD PREGNANCY
Note that the third trimester of pregnancy is generally not recommended for travel with air travel and climate change. In particular, doctors consider it highly undesirable to fly on vacation from the 28th week of pregnancy until childbirth if:
- aggravated obstetric and gynecological history (earlier termination of pregnancy, miscarriages, miscarriages, serious gynecological diseases, etc.)
- there are serious somatic comorbidities, including autoimmune diseases
- we are talking about a multiple pregnancy (twins or triplets).
However, if the pregnancy proceeds normally, without complications, then the tourist can go on a beach holiday abroad, but so that it ends no later than 31 weeks of pregnancy.
Why this period? The point is not only the increased risk at this stage, but also the fact that all special insurance products existing in Russia with options for pregnant women provide insurance coverage for medical expenses for pregnant women only up to 31 weeks as a maximum. Therefore, all trips of pregnant women, starting from the 32nd week, will not be insured by any insurance company. There are simply no such policies - which means that complications or premature births abroad threaten with huge amounts billed for treatment.
After 32 weeks, both doctors and insurers give good advice to everyone: do not travel abroad, unless it is about some difficult life situations. This advice should be taken very seriously. The statistics of the largest travel insurer, ERV, are disappointing: 9 out of 10 women who seek medical assistance abroad for pregnancy complications lose a child.
Finally, let's recall one more factor. At a gestational age of 30-34 weeks, ultrasound is performed at the place of observation of a pregnant woman. That is, during this period it is also better to be within the reach of the health facility, where pregnancy monitoring takes place.
WHICH INSURANCE TO CHOOSE FOR PREGNANT WOMEN
“The first thing tourists should understand is that pregnant women traveling abroad need special and separate insurance with options specifically for pregnant women. No basic insurance policy on the market that comes "by default" in a regular tour package covers any risks of pregnancy complications at 12-31 weeks. In this case, the tourist must ask a travel agent or take out additional insurance under a special program himself, ”says the executive director of the ERV insurance company.
Pregnant women traveling abroad need special and separate insurance with options specifically for pregnant women - this is not the same insurance that is already included in the tour package
The vast majority of Russian insurance companies do not include the risks of pregnancy complications up to 12 weeks into their basic programs. The only exception on the market is ERV insurance, which even in the “basic” version recognizes pregnancy complications for up to 12 weeks as an insured event, since there is a possibility that the insured might not have known about her pregnancy in the early stages.
Insurance products for pregnant women, starting from 12-13 weeks, are available in the range of all major players in the insurance market, the tourist can choose such insurance according to the set of options, the amount of insurance coverage or price.
As for insurances that cover risks up to 31 weeks of pregnancy (this is the maximum period), there are relatively few of them. The most “complete” insurance is again with ERV (Optima tariff): in addition to the period up to 31 weeks inclusive, the coverage here includes medical expenses not only for women, but also 10 thousand euros for nursing a child in a medical institution in case of premature birth (other companies cover mother's medical expenses only). This amount is enough for long-term care of the baby using special equipment in Europe or Turkey.
And of course, the insurance must necessarily include the option “cancellation of the trip” (in everyday life this is also called “non-departure insurance”). The condition of a pregnant woman changes, and it may happen that right before the trip she will have contraindications to the flight. It is important to remember that if a tourist flies with her husband, children, or other relatives, then they will all receive the full amount of the entire tour only if the “insurance against non-departure” is issued for all of them (and not just for the pregnant woman herself).
WHAT SHOULD A PREGNANT WOMAN NEED TO DO BEFORE HOLIDAY AND WHAT DOCUMENTS TO TAKE
Before the trip (3-7 days in advance) it is necessary to visit a therapist and attending gynecologist, get a consultation and, if necessary, undergo the prescribed tests and procedures.
You need to ask the doctor to issue a certificate for the airline about the duration of pregnancy and the absence of medical contraindications (without it, if there are external signs of pregnancy, some air carriers may not allow you to board the aircraft).
“In addition to insurance, travel documents and passports, you should also take an exchange card - especially if you are going to Russia. For the convenience and peace of mind of the vacationer, you can also take an extract from the attending physician with your medical history, appointments, the results of the last ultrasound, screening, etc., and translate them, if not into the language of the host country, then at least into English, ”advises the doctor gynecologist Natalya Badikova.
It would also be nice if the attending physician could be in touch with the tourist during the holidays. Modern telemedicine services allow this. For example, before traveling, you can check with your doctor if he consults remotely in a special application, or purchase a subscription to several telemedicine consultations from a trusted telemedicine operator. By the way, gynecologists also consult remotely.
WHAT SYMPTOMS OF A PREGNANT WOMEN IT IS BETTER TO POSTPONE A TRIP
“Drawing pains in the lower abdomen in the first trimester of pregnancy, pulling, cramping pains or tension (false and true contractions) – in the second and third trimester of pregnancy before a trip – an alarm call. These are unconditional reasons for immediate medical attention. Brownish spotting or, moreover, scarlet spotting at any stage of pregnancy, watery - in the second and third trimester - is also a reason to immediately consult a doctor, and not go to the airport, ”says Natalya Badikova.
Among other "bad" signs that indicate the need for prompt consultation of a tourist with a doctor is a sharp headache accompanied by tinnitus. This may be the first signs of preeclampsia or preeclampsia. Reasons to postpone a trip for a pregnant woman are vomiting, diarrhea, as well as exacerbation of concomitant diseases.
In order for a pregnant woman to painlessly cancel a trip for health reasons and not lose money, when buying a tour or separately (but maximum 5 days before departure), you need to take out travel insurance for all tour participants, which we have already talked about. As a rule, its cost is 5% of the total tour.
II. AIR TRAVELING IN PREGNANCY
PLANE, CAR, TRAIN – WHICH IS SAFE FOR PREGNANT WOMEN?
Contrary to popular belief, the plane is not the most "risky" mode of transport for pregnant women.
“Many people think that the safest way for pregnant women to travel is by car because you can stop wherever you want. But it's not. The way it shakes in a car, it doesn't shake anywhere, even on a train. Bumps, sudden braking, emergency situations on the road - all this has a very negative effect on the state of pregnancy. Plus, prolonged physical inactivity, motion sickness, the smell of gasoline - this can trigger a cascade of pathological reactions, ”says Dr. Badikova.
As for the train, if it is a comfortable express, and especially if the journey is not long (3-4 hours, "Sapsan"), then it is quite possible to consider it. You can also consider the new double-decker express trains "Moscow-Sochi". In other cases, especially if the train is old, with age-appropriate bathrooms, doctors recommend considering an airplane instead of a train.
IS IT POSSIBLE FOR PREGNANT WOMEN TO PASS THE SCANNER WHEN INSPECTION AT THE AIRPORT
Only X-ray devices are dangerous - therefore, you should find out what type of scanner is at the airport. If there is a corresponding icon on the device, then you should present a certificate of pregnancy to the airport employee and go through other screening procedures.
However, modern devices at airports are not dangerous for pregnant women. “Modern airport scanners use a low-frequency electromagnetic field. This is not ionizing radiation, there is no harm to the body of the pregnant woman and the baby from him, as well as from ultrasound, ”says Natalya Badikova.
FLIGHT IN PREGNANCY: HOW TO BE AND WHAT TO BRING WITH YOU
Air travel also has its own factors that can negatively affect the health of pregnant women. There are risks, but if the pregnant woman feels well, and the doctors have no objection to the vacation, you can fly.
Firstly, these are changes in blood pressure during takeoff and landing. This is usually fought by creating a state of rest (you need to take a special pillow with an adjustable boost, disposable ear plugs, an eye mask for the flight), and drinking plenty of water (plain water without gas). You can easily buy water at the airport after crossing the border. It is also a good idea to take a bar of dark chocolate with you on a flight (in case of pressure drops and just for a snack).
Secondly, this is hypodynamia and a long stay in a sitting position, so pregnant women should, if possible, choose destinations for recreation with a short flight (3-5 hours) during this period of their lives
Pregnant women should, if possible, choose holiday destinations during this period of their lives with a short flight (3-5 hours)
Why? “Long stay in a sitting position leads to congestion in the pelvis. This can disrupt blood flow in the pelvic organs, including the uterus, and cause changes in bowel function. Swollen intestinal loops can put pressure on the uterus, this can cause hypertonicity, which, in some cases, can cause abortion, ”explains Natalia Badikova. How to deal with this risk? It's simple: during the flight, you should try to walk around the cabin more often, get up, change the position of the body, do light gymnastics for the legs and arms.
A pregnant woman should not forget to take hygiene products (wet wipes, disposable pads, etc.), micellar water (no more than 100 ml to be allowed on the plane) with her on the flight (in hand luggage) - to moisturize the skin during the flight, a set of drugs (if the drugs are rare and prescription, it is better to take a prescription for them, sometimes with a notarized translation - in order to avoid difficulties at the border).
Pregnant women should also take care of compression stockings during the flight. These must be stockings or stockings (compression class must be determined by the attending physician). In the second and third trimester, a prenatal bandage should be worn for flying. During the flight, a woman should wear cotton underwear and a bra with wide straps.
During the flight, it is better for pregnant women to wear comfortable shoes - light, breathable moccasins or slippers.
III. PREGNANCY BEACH HOLIDAY
WHICH COUNTRY TO CHOOSE FOR A PREGNANT BEACH HOLIDAY
The list of such countries is determined by a combination of three main factors. Firstly, as we have already said, these should be destinations with a short flight (up to 5 hours as a maximum).
Secondly, it should be Russia or foreign non-exotic countries with a relatively temperate climate and a diet adapted to our cuisine. Countries with excessively hot climates and exotic cuisine should be avoided.
“Water and food that is not typical for our diet, for example, in the countries of South and Central America, Southeast Asia, can provoke toxicosis of pregnant women in the first trimester, even if you do not have it. It is also provoked by heat. The fact is that hypoglycemia (lack of glucose) can serve as an impetus for the development of toxicosis in pregnant women. And it occurs in hot climates due to increased evaporation of moisture from the skin, heavy drinking and, as a result, lack of appetite and long intervals in eating,” says Dr. Badikova.
Doctors advise pregnant women to choose for a beach vacation those countries where the average daily (attention - not daily, but average daily) temperature in the place and during the rest period does not exceed 30. 5 degrees Celsius.
Pregnant women should choose for a beach holiday those countries where the average daily (not daily, but average daily) temperature during the holidays does not exceed 30.5 degrees Celsius
Definitely, pregnant women should not choose countries where there is a risk of contracting giardia infections and, in general, infectious diseases (Japanese encephalitis, Dengue fever, Zika, etc.). It should be clearly excluded from visiting countries in which it is recommended to be vaccinated in advance (the list can be found on the website of Rospotrebnadzor). Doctors strongly recommend that pregnant women not be vaccinated against any diseases - this can be fatal for the child, since any vaccine passes through the placental barrier.
Thirdly, besides the climate and food, pregnant women should take into account one more factor when choosing a vacation destination: the availability and level of medicine in the country and in the hotel. Preference during pregnancy should be given to countries with developed medicine (at least in resorts), and when choosing a hotel, you should ask the travel agent if there is a doctor in the hotel (as a rule, he happens in high-level hotels).
The choice of a pregnant woman in the first and second trimester, therefore, comes down to the following list of destinations: Russia, worthy hotels in Turkey, Spain, Italy, Greece, Cyprus, Croatia, Bulgaria, Montenegro, Slovenia, Czech Republic. You can also go to the countries of the Persian Gulf (preferably to the developed emirates of the UAE - Dubai and Abu Dhabi, or to Qatar), and carefully choosing a hotel, preferring high-level ones.
The countries of Equatorial Africa, South-East Asia and the Americas should be excluded from your list during pregnancy due to the long flight, hot climate, unusual cuisine, the risk of infectious diseases, and in some cases the need for vaccinations.
HOW TO BATH WHEN PREGNANT
All is well, and the pregnant tourist is at a beach resort. Summer and the beach mean the sun, and here the doctors also have their advice. The sun, of course, brings positive to the pregnant woman (more endorphins are released), replenishes the vitamin D deficiency, which is typical for residents of northern countries.
Firstly, exposure to the sun and even swimming in the sea (due to the reflection of the sun's rays from the water surface) should be avoided by pregnant women from 12.00 to 16.00.
Secondly, and the rest of the time you need to be careful about protection from sunlight. “During pregnancy, a woman often has hyperpigmentation. Taking into account being in the sun during the holidays, there is a very high probability that age spots, freckles that appeared during pregnancy on exposed parts of the body will not disappear. Therefore, a pregnant woman needs to take sun protection with her on vacation, with a protection factor of at least 50 - more is better. It is desirable that such a product contains vitamin E. And immediately after exposure to the sun, you need to apply a special after-sun product, it will additionally moisturize the skin, ”says Natalya Badikova.
Pregnant women should take sun protection with a protection factor of at least 50, preferably more. It is desirable that the composition contains vitamin E
In particular, doctors consider such lines of protective equipment as Sanosan, Lierak, Uriage, from budget ones, for example, Garnier, to be well-established products. But everything is individual, and in choosing the brand and, most importantly, the composition of the product, it is better to follow the advice of the attending gynecologist.
Gynecologists strongly recommend tourists to take a closed swimsuit to the beach, excluding direct sunlight on the abdomen. “It will also be very good to take a cap with a large visor or a hat with a brim - to exclude sun exposure on the face, since the risks of age spots in pregnant women are very high,” advises Dr. Natalya Badikova.
WHERE IT IS SAFE TO BATH FOR A PREGNANT WOMAN - SEA OR POOL
Pregnant women can safely swim in the sea if it is warm and comfortable for the woman. The duration of stay in it is until the first moment when the pregnant woman feels “chillness”. Another tip - pregnant women should not stay in a wet bathing suit for a long time. At the first uncomfortable sensations, it is better to change clothes, and therefore take more than one set with you.
At the same time, experts say, the sea for pregnant women is definitely preferable to the pool.
“Excessively chlorinated water in some pools can lead to changes in the microflora of the vagina, and eventually to bacterial vaginosis or inflammation of this area,” says Natalya Badikova. After the pool, it is also better for a pregnant woman to make an external (only external!) Treatment of intimate places with Miramistin or similar means.
HOW TO EAT FOR A PREGNANT WOMAN ON HOLIDAY
It is better to leave the diet in the hotel the same, close to the set of products that a woman eats at home, doctors say. The advice is feasible, especially with the all-inclusive system - the buffet at the hotel allows you to choose almost any type of food.
However, there are restrictions: for example, any carbonated drinks should be excluded, it is better to drink black tea instead of green tea. And any exotic products for us, including southern fruits and vegetables, should be added to the diet gradually, in small portions, starting from 3-4 days of vacation.
“You shouldn't eat more than two unusual fruits a day (for example, mango). If we are talking about freshly squeezed juices, then this is a replacement for fruits (or fruits - or juices from them). Such juices should be drunk strictly after meals, not on an empty stomach, in order to avoid increased secretion of hydrochloric acid and heartburn, ”explains doctor Badikova.
WHAT TO DO IF YOU FIND OUT YOUR PREGNANCY DURING VACATION
A tourist found out about her pregnancy while on vacation and she has to fly back. It happens. If there are no disturbing moments (bleeding, pain, etc.) - you do not need to contact a local doctor. What should be done during this period?
Doctors advise in this case to immediately change the diet to a more fractional one, exclude alcohol, coffee, smoking (if there is such a habit), include more meat, fish, chicken in the diet. At the same time, it is necessary to limit the consumption of bright orange and red vegetables and fruits - so as not to form an allergic syndrome.
With regard to the transfer to the airport and the flight itself, a pregnant woman in the early stages should not lift weights. Photos provided by pixabay.com
You can read the news by subscribing to the ATOR channel in Telegram or to updates of our Facebook page.
You will find free online courses, webinars and electronic catalogs of tour operators on the ATOR Academy portal.
Actual SPECIAL OFFERS of tour operators for tours abroad and in Russia see the SPO section of the ATOR portal .
Flights during pregnancy: answers, tips and tricks
Modern way of life, worldview and generally accepted canons do not make pregnant women stop before any difficulties. Often, no warnings and risks can affect their choice and actions, but when it comes to the health or life of the unborn baby, everything is serious. That is why issues related to the travel of women in position by air cause a lot of discussion and require detailed consideration.
Can you fly while pregnant?
This question worries many of the fair sex, who are in an interesting position, who are faced with a choice - to fly or not to fly? It is impossible to give a single answer that will suit every woman. In general, there are no restrictions regarding air travel during pregnancy. However, there are many factors that affect the final verdict. One of the first things to consider is the requirements of the airlines. If you have already booked an air ticket, then check the conditions for the flight of passengers in the position. If you are in the process of searching for air tickets, then check out the requirements of different aviation companies and choose the option that suits you best.
UIA, airBaltic - women from 28 to 35 weeks of pregnancy inclusive, when checking in for a flight, an appropriate certificate from a doctor must be attached to the ticket.
Lufthansa - Moms-to-be can book flights and travel with this airline until the end of the 36th week (or four weeks before the due date) without providing a medical certificate from a doctor. After 36 weeks - a woman should contact the Lufthansa medical center. In the case of multiple pregnancies, air travel after the 28th week is not allowed.
Alitalia – when checking in for a flight with a ticket, a pregnant woman must have a completed special medical form (MEDIF) signed and stamped by the attending physician after 36 weeks of pregnancy or in case of multiple pregnancy.
Air France - you do not need to obtain official medical approval to fly with Air France.
Turkish Airlines - women are allowed to travel by air for a period not exceeding 28 weeks with medical permission from a gynecologist.
Etihad Airways - From the 29th week until the end of the 36th week pregnant women traveling are required to present a medical certificate. From the 37th week, the flight is not allowed. If a woman is expecting more than one child, then the flight until the 32nd week is allowed with a medical certificate, after the 33rd - air travel is prohibited.
Air Moldova - after 28 and up to 32 weeks inclusive - a woman in the position when checking in for a flight must provide, along with the ticket, a medical certificate with a seal and a doctor's signature, which clearly reflects the permission to fly. After 32 and until the end of 35 weeks, as well as in cases of complications, a MEDIF form filled out by the attending physician and confirmed by the airline doctor is provided with a medical certificate. From the 36th - air travel is prohibited.
What is the safest pregnancy for flying?
Everyone knows that each period of pregnancy is special in its own way, so when planning a trip and purchasing air tickets, it is necessary to take into account not only the general condition, but the specific trimester of pregnancy.
- first trimester: 1-13 weeks
It is best to refrain from traveling during this period. If there is an urgent need for a flight, then issue air tickets for a plane with a departure date corresponding to the 7th or 8th week of pregnancy, which are considered the safest for air travel in the first trimester. - second trimester: 14-27 weeks
This period is considered the most favorable for future mothers and babies to travel by air. However, some experts advise not to buy tickets for flights from 18 to 22 weeks, arguing that during this period there is a risk of late miscarriage. But if the pregnancy proceeds without any complications, the woman feels great and there are no risks to the fetus - feel free to issue an air ticket and go on a long-awaited vacation. - third trimester: 28-40 weeks
This period requires great care and attention when traveling. Most airlines will only allow you to board an aircraft if you have a certificate from your doctor, and some carriers may also require a document from the airline's medical center.Also, in most cases, female passengers will have to fill out and sign a document indicating that the airline is not responsible for possible adverse consequences.
In what situations is it better for a pregnant woman to refrain from flying?
In order to protect yourself and your unborn baby, you should consult your personal doctor before issuing air tickets. There are a number of contraindications to flying during pregnancy, even if the woman feels well, such as anemia, hypertension, severe toxicosis, etc.
How to make your flight comfortable?
If you have decided to fly, the doctor has given his consent, and you have already booked air tickets, then it's time to start preparing for the trip. There are a number of recommendations that will help expectant mothers feel comfortable during air travel and minimize the risks of possible complications:
- book a business class ticket. In the business class, there are wider seats and an increased distance between them.
If you still booked an economy class ticket, then choose a seat in the first row (enough legroom) or, in extreme cases, an aisle seat
- to reduce the risk of vascular complications, wear compression stockings on the plane
- fasten seat belts under the tummy
- take an orthopedic neck and back pillow
- recline the seat back to reduce back strain
- periodically walk around the cabin of the liner to avoid swelling of the legs
- drink plenty of fluids - about 500 ml per hour (avoid carbonated drinks and coffee)
Flights train tickets Bus tickets
- Tickets
- Railway tickets
- Bus tickets
Similar news
27th of spring
Travel news digest
New clients,
Still not subscribed to our telegram channel, in which we rarely publish the latest news related to the travel industry, aviation and other assistance to the people from Ukraine, we have importantly prepared the TOP-news for you
May 13
Airline traffic in the world of cities 83% pre-pandemic
The UK was expected to have the largest increase in capacity for the remaining river - up to 3 million months - 690% more, lower on the cob of May 2021.