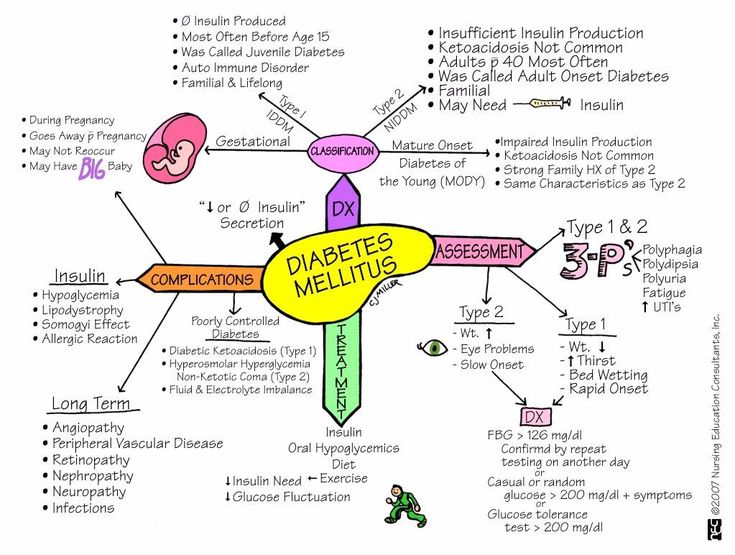
Women going in labor
Labor and birth | Office on Women's Health
Cesarean delivery, also called c-section, is surgery to deliver a baby. The baby is taken out through the mother's abdomen. Most cesarean births result in healthy babies and mothers. But c-section is major surgery and carries risks. Healing also takes longer than with vaginal birth.
Most healthy pregnant women with no risk factors for problems during labor or delivery have their babies vaginally. Still, the cesarean birth rate in the United States has risen greatly in recent decades. Today, nearly 1 in 3 women have babies by c-section in this country. The rate was 1 in 5 in 1995.
Public heath experts think that many c-sections are unnecessary. So it is important for pregnant women to get the facts about c-sections before they deliver. Women should find out what c-sections are, why they are performed, and the pros and cons of this surgery.
Reasons for c-sections
Your doctor might recommend a c-section if she or he thinks it is safer for you or your baby than vaginal birth. Some c-sections are planned. But most c-sections are done when unexpected problems happen during delivery. Even so, there are risks of delivering by c-section. Limited studies show that the benefits of having a c-section may outweigh the risks when:
- The mother is carrying more than one baby (twins, triplets, etc.)
- The mother has health problems including HIV infection, herpes infection, and heart disease
- The mother has dangerously high blood pressure
- The mother has problems with the shape of her pelvis
- There are problems with the placenta
- There are problems with the umbilical cord
- There are problems with the position of the baby, such as breech
- The baby shows signs of distress, such as a slowed heart rate
- The mother has had a previous c-section
Patient-requested c-section: Can a woman choose?
A growing number of women are asking their doctors for c-sections when there is no medical reason. Some women want a c-section because they fear the pain of childbirth. Others like the convenience of being able to decide when and how to deliver their baby. Still others fear the risks of vaginal delivery including tearing and sexual problems.
Some women want a c-section because they fear the pain of childbirth. Others like the convenience of being able to decide when and how to deliver their baby. Still others fear the risks of vaginal delivery including tearing and sexual problems.
But is it safe and ethical for doctors to allow women to choose c-section? The answer is unclear. Only more research on both types of deliveries will provide the answer. In the meantime, many obstetricians feel it is their ethical obligation to talk women out of elective c-sections. Others believe that women should be able to choose a c-section if they understand the risks and benefits.
Experts who believe c-sections should only be performed for medical reasons point to the risks. These include infection, dangerous bleeding, blood transfusions, and blood clots. Babies born by c-section have more breathing problems right after birth. Women who have c-sections stay at the hospital for longer than women who have vaginal births. Plus, recovery from this surgery takes longer and is often more painful than that after a vaginal birth. C-sections also increase the risk of problems in future pregnancies. Women who have had c-sections have a higher risk of uterine rupture. If the uterus ruptures, the life of the baby and mother is in danger.
C-sections also increase the risk of problems in future pregnancies. Women who have had c-sections have a higher risk of uterine rupture. If the uterus ruptures, the life of the baby and mother is in danger.
Supporters of elective c-sections say that this surgery may protect a woman's pelvic organs, reduces the risk of bowel and bladder problems, and is as safe for the baby as vaginal delivery.
The National Institutes of Health (NIH) and American College of Obstetricians (ACOG) agree that a doctor's decision to perform a c-section at the request of a patient should be made on a case-by-case basis and be consistent with ethical principles. ACOG states that "if the physician believes that (cesarean) delivery promotes the overall health and welfare of the woman and her fetus more than vaginal birth, he or she is ethically justified in performing" a c-section. Both organizations also say that c-section should never be scheduled before a pregnancy is 39 weeks, or the lungs are mature, unless there is medical need.
The c-section experience
Most c-sections are unplanned. So, learning about c-sections is important for all women who are pregnant. Whether a c-section is planned or comes up during labor, it can be a positive birth experience for many women. The overview that follows will help you to know what to expect during a nonemergency c-section and what questions to ask.
Before surgery
Cesarean delivery takes about 45 to 60 minutes. It takes place in an operating room. So if you were in a labor and delivery room, you will be moved to an operating room. Often, the mood of the operating room is unhurried and relaxed. A doctor will give you medicine through an epidural or spinal block, which will block the feeling of pain in part of your body but allow you to stay awake and alert. The spinal block works right away and completely numbs your body from the chest down. The epidural takes away pain, but you might be aware of some tugging or pushing. See Medical methods of pain relief for more information. Medicine that makes you fall asleep and lose all awareness is usually only used in emergency situations. Your abdomen will be cleaned and prepped. You will have an IV for fluids and medicines. A nurse will insert a catheter to drain urine from your bladder. This is to protect the bladder from harm during surgery. Your heart rate, blood pressure, and breathing also will be monitored. Questions to ask:
Medicine that makes you fall asleep and lose all awareness is usually only used in emergency situations. Your abdomen will be cleaned and prepped. You will have an IV for fluids and medicines. A nurse will insert a catheter to drain urine from your bladder. This is to protect the bladder from harm during surgery. Your heart rate, blood pressure, and breathing also will be monitored. Questions to ask:
- Can I have a support person with me during the operation?
- What are my options for blocking pain?
- Can I have music played during the surgery?
- Will I be able to watch the surgery if I want?
During surgery
The doctor will make two incisions. The first is about 6 inches long and goes through the skin, fat, and muscle. Most incisions are made side to side and low on the abdomen, called a bikini incision. Next, the doctor will make an incision to open the uterus. The opening is made just wide enough for the baby to fit through. One doctor will use a hand to support the baby while another doctor pushes the uterus to help push that baby out. Fluid will be suctioned out of your baby's mouth and nose. The doctor will hold up your baby for you to see. Once your baby is delivered, the umbilical cord is cut, and the placenta is removed. Then, the doctor cleans and stitches up the uterus and abdomen. The repair takes up most of the surgery time. Questions to ask:
One doctor will use a hand to support the baby while another doctor pushes the uterus to help push that baby out. Fluid will be suctioned out of your baby's mouth and nose. The doctor will hold up your baby for you to see. Once your baby is delivered, the umbilical cord is cut, and the placenta is removed. Then, the doctor cleans and stitches up the uterus and abdomen. The repair takes up most of the surgery time. Questions to ask:
- Can my partner cut the umbilical cord?
- What happens to my baby right after delivery?
- Can I hold and touch my baby during the surgery repair?
- When is it okay for me to try to breastfeed?
- When can my partner take pictures or video?
After surgery
You will be moved to a recovery room and monitored for a few hours. You might feel shaky, nauseated, and very sleepy. Later, you will be brought to a hospital room. When you and your baby are ready, you can hold, snuggle, and nurse your baby. Many people will be excited to see you. But don't accept too many visitors. Use your time in the hospital, usually about four days, to rest and bond with your baby. C-section is major surgery, and recovery takes about six weeks (not counting the fatigue of new motherhood). In the weeks ahead, you will need to focus on healing, getting as much rest as possible, and bonding with your baby — nothing else. Be careful about taking on too much and accept help as needed. Questions to ask:
Many people will be excited to see you. But don't accept too many visitors. Use your time in the hospital, usually about four days, to rest and bond with your baby. C-section is major surgery, and recovery takes about six weeks (not counting the fatigue of new motherhood). In the weeks ahead, you will need to focus on healing, getting as much rest as possible, and bonding with your baby — nothing else. Be careful about taking on too much and accept help as needed. Questions to ask:
- Can my baby be brought to me in the recovery room?
- What are the best positions for me to breastfeed?
Vaginal birth after c-section (VBAC)?
Some women who have delivered previous babies by c-section would like to have their next baby vaginally. This is called vaginal delivery after c-section or VBAC. Women give many reasons for wanting a VBAC. Some want to avoid the risks and long recovery of surgery. Others want to experience vaginal delivery.
Today, VBAC is a reasonable and safe choice for most women with prior cesarean delivery, including some women who have had more than one cesarean delivery. Moreover, emerging evidence suggests that multiple c-sections can cause serious harm. If you are interested in trying VBAC, ask your doctor if you are a good candidate. A key factor in this decision is the type of incision made to your uterus with previous c-sections.
Moreover, emerging evidence suggests that multiple c-sections can cause serious harm. If you are interested in trying VBAC, ask your doctor if you are a good candidate. A key factor in this decision is the type of incision made to your uterus with previous c-sections.
Your doctor can explain the risks of both repeat cesarean delivery and VBAC. With VBAC, the most serious danger is the chance that the c-section scar on the uterus will open up during labor and delivery. This is called uterine rupture. Although very rare, uterine rupture is very dangerous for the mother and baby. Less than 1 percent of VBACs lead to uterine rupture. But doctors cannot predict if uterine rupture is likely to occur in a woman. This risk, albeit very small, is unacceptable to some women.
The percent of VBACs is dropping in the United States for many reasons. Some doctors, hospitals, and patients have concerns about the safety of VBAC. Some hospitals and doctors are unwilling to do VBACs because of fear of lawsuits and insurance or staffing expenses. Many doctors, however, question if this trend is in the best interest of women's health.
Many doctors, however, question if this trend is in the best interest of women's health.
Choosing to try a VBAC is complex. If you are interested in a VBAC, talk to your doctor and read up on the subject. Only you and your doctor can decide what is best for you. VBACs and planned c-sections both have their benefits and risks. Learn the pros and cons and be aware of possible problems before you make your choice.
Signs, Progression & What To Expect
What to expect during labor and delivery.How does labor work?
As your pregnancy begins to wrap up, your body will prepare for labor and delivery. This is the process through which your baby will be born. Labor is often different for each person. Some have quick labors and some long, difficult labors. Other people may even experience labor that stalls or stops, leading to medical intervention.
Early labor
The average labor lasts 12 to 24 hours for a first birth and is typically shorter (eight to 10 hours) for other births. Throughout this time, you’ll experience three stages of labor. The first stage of labor is usually the longest and it ranges from when you first go into labor until your cervix is open. The beginning of this stage is called early labor. Early labor is described as dilating from 0 to 6 centimeters.
Active labor
As you progress and your contractions become stronger, you’ll move into the second part of the first stage of labor called active labor. Active labor is dilating from 6 to 8 centimeters and then transitioning into the second stage as you dilate 8 to 10 centimeters. Your contractions will become even stronger during active labor and your cervix will open up quickly. The second stage of labor is when you push. This is the phase of your labor when you will actually give birth to your baby.
Afterbirth
The third stage is the point when you deliver the placenta. This is also called afterbirth.
This is also called afterbirth.
During these stages, your body prepares for childbirth by going through dilation and effacement.
- Dilation: This is a process where your cervix stretches and opens to make way for your baby’s birth. Dilation is measured from 1 to 10 centimeters. Your provider will do a vaginal exam to check how dilated you are throughout your labor. You’ll be 10 centimeters dilated in the second stage of labor for the delivery of your baby.
- Effacement: The cervix not only stretches during labor but it also becomes thinner. The shortening and thinning of your cervix are measured in percentages. You’ll progress from 0% to 100% effacement during your labor.
Think of your cervix as a round doorway that needs to stretch outward and get thinner before your baby can pass through it. This stretching and thinning are caused by contractions. Contractions can be described in a variety of ways ranging from uncomfortable, period-like cramps to a painful tightening of your abdomen. You might also feel a dull ache in your back and lower abdomen, as well as pressure in your pelvis.
You might also feel a dull ache in your back and lower abdomen, as well as pressure in your pelvis.
When you have a contraction, it’s actually the muscles of your uterus tightening at regular intervals to dilate and efface (open and thin) your cervix. During contractions, your abdomen becomes hard. Between contractions, your uterus relaxes and your abdomen becomes soft. Even though they can be painful, each contraction helps move you forward through your labor.
How will I know I’m in labor?
It can be difficult to know when you’re in true labor. First-time parents, in particular, might mistake other symptoms or irregular practice contractions (called Braxton Hicks contractions) for true labor. True labor has a pattern and progresses steadily over time.
When you’re in true labor, you’ll notice a pattern in your contractions. Instead of the irregular Braxton Hicks contractions you might have felt during your pregnancy that showed up and then went away randomly, these contractions will keep coming for an extended period of time. There are three things you’ll want to look for when you are in true labor.
There are three things you’ll want to look for when you are in true labor.
- Frequency: How often are your contractions happening? Keep track of them with a journal or labor app on your phone to make sure they're coming at regular intervals.
- Duration: How long are each of your contractions? As your labor continues, your contractions will last longer and longer. Use a stopwatch, watch a clock or keep the timer on your phone handy so you can record the length of each contraction.
- Intensity: Are your contractions getting stronger? Contractions can get stronger and you might feel them more intensely as you move through the stages of labor. Keep track of how your contractions feel over time.
Are there any signs that I will go into labor soon?
Many women have several pre-labor signs that might hint that labor will start soon. These signs of labor include:
- Backaches.
- Diarrhea.

- Weight loss.
- Nesting (cleaning and organizing your home).
No one knows for sure what causes labor to start, but several hormonal and physical changes may point to the beginning of labor.
What are Braxton Hicks contractions?
Often called practice contractions, Braxton Hicks are irregular contractions that don’t cause cervical change. Think of them as a test run for the real thing. They can start happening at the end of your pregnancy and can startle people into thinking they’re in labor. This is called false labor.
A Braxton Hicks contraction will feel like a sudden, sharp tightening of your abdominal muscles. Even though this is very similar to how a contraction feels, Braxton Hicks contractions don’t follow a pattern or progress over time. They may also stop when you lay down or relax. When you start to experience these practice contractions, keep track of them. Writing them down is the best way to tell the difference between true and false labor.
What is lightening?
Lightening is the process where your baby settles or lowers into your pelvis. This can happen a few weeks or a few hours before labor. When this happens, you may experience some increased lower pelvic pressure. Because your uterus rests on your bladder more after lightening, you might also feel the need to urinate more frequently. You might notice that you’re not as short of breath once your baby drops.
What’s the mucus plug and what does it mean when it falls out?
During pregnancy, a thick piece of mucus called a plug blocks the cervical opening. This plug keeps your uterus closed off from the birth canal and the outside of your body and prevents bacteria from traveling into your uterus. When your cervix begins to soften, thin, and open, the mucus is expelled into your vagina. Not every mucus plug will look the same. Possible colors of the mucus plug can include:
- Clear.
- Pink.
- Slightly bloody.
Labor could start shortly after you lose your mucus plug or it could begin several weeks later.
How do I time my contractions?
Once you’re in labor, it’s important to keep track of your contractions. Your healthcare provider will need to know how long your contractions are lasting (duration), how often they’re happening (frequency) and how intense they are. When you’re timing your contractions, you will want to have a way to record each one – pen and paper or through an app on your phone – and a timer or clock. Make sure you keep track of each contraction from start to end, as well as the time between each contraction. This second measurement will help your provider know the frequency of your contractions.
It can be difficult to record the intensity of your contractions. This can really vary from person to person. Often, an easy way to keep track of the intensity of your contractions is to record when you cannot walk, talk or laugh during contractions.
Is there anything I can do to cope with contractions?
As you approach the end of your pregnancy, it’s a good idea to talk to your healthcare provider about different ways to deal with pain and discomfort during labor. There are several options your provider will discuss with you to relieve pain.
There are several options your provider will discuss with you to relieve pain.
There are also ways to deal with the discomforts of labor at home or without medication, including:
- Distract yourself by taking a walk, going shopping or watching a movie.
- Soak in a warm tub or take a warm shower. Make sure to ask your healthcare provider if you should take a tub bath if your bag of water has broken.
- Sit on a birth ball.
- Listen to music.
- Dim the lights.
- Use aromatherapy.
- Get a massage.
- Stay in an upright position. This can help with the descent and rotation of your baby.
- Try to sleep if it’s evening. You’ll want to store up your energy before active labor and delivery.
How will I know when my water breaks?
You may be familiar with the common phrase “my water broke.” This is actually the rupturing of your amniotic membrane. During pregnancy, your baby is inside a fluid-filled sac, also called your bag of water. When this membrane breaks, you might feel a sudden gush or trickle of fluid. Like many parts of labor and childbirth, this experience can be different for each person. The fluid is usually odorless and may look clear or straw-colored.
When this membrane breaks, you might feel a sudden gush or trickle of fluid. Like many parts of labor and childbirth, this experience can be different for each person. The fluid is usually odorless and may look clear or straw-colored.
Unlike urine leakage that some pregnant women experience, this won’t stop. The amniotic fluid will often continue to leak.
If your water breaks, call your healthcare provider. Let your provider know what time your water broke, the amount (trickle or gush), the color of the fluid and the odor. Don't use tampons if your water has broken. Your labor might start right after your water breaks. Some women are already in labor when their water breaks while others don’t experience the first stage of labor for a while after their water breaks.
When should I call my healthcare provider or go to the hospital?
If you ever have any questions, it’s always a good idea to call your healthcare provider. Your provider can answer any questions you have about true labor versus false labor and discuss how you’re feeling. When you start to notice that you’re having regular contractions, call your provider to talk about when you should go to the hospital. Some women are able to stay home throughout early labor, while others may need to come in sooner.
When you start to notice that you’re having regular contractions, call your provider to talk about when you should go to the hospital. Some women are able to stay home throughout early labor, while others may need to come in sooner.
You should also call your healthcare provider if you:
- Think your water has broken. This could be a sudden gush of fluid or a trickle of fluid that leaks steadily.
- Are bleeding (more than spotting).
- Experience contractions that are very uncomfortable and have been coming every five minutes, lasting for one minute and have been like this for one hour.
What happens when I get to the hospital?
When you get to the hospital, you will check in at the labor and delivery desk. Most people will be seen in a triage room first. This is part of the admission process. It’s usually recommended that you only bring one person with you to the triage room.
From the triage room, you will be taken to the labor, delivery and recovery (LDR) room. You’ll be asked to wear a hospital gown. Your pulse, blood pressure and temperature will be checked. An external fetal monitor will be placed on your abdomen for a short time to check for uterine contractions and measure your baby’s heart rate. Your healthcare provider will also examine your cervix to see how far labor has progressed. An intravenous (IV) line might be placed into a vein in your arm to deliver fluids and medications.
You’ll be asked to wear a hospital gown. Your pulse, blood pressure and temperature will be checked. An external fetal monitor will be placed on your abdomen for a short time to check for uterine contractions and measure your baby’s heart rate. Your healthcare provider will also examine your cervix to see how far labor has progressed. An intravenous (IV) line might be placed into a vein in your arm to deliver fluids and medications.
What does it mean to have labor induced?
Labor doesn’t always start naturally or progress as it should. In these cases, your provider might talk to you about inducing labor. This is a medical procedure where labor is started by your healthcare provider. This could happen if you:
- Are past your due date.
- Have health complications like high blood pressure, preeclampsia, infection or diabetes.
- Had your water break but labor didn’t start.
- Have low levels of amniotic fluid.
Your labor can be advanced or induced in several ways. Your provider will advise you about the best and safest option depending on your health. Inducing labor can be done by using:
Your provider will advise you about the best and safest option depending on your health. Inducing labor can be done by using:
- Medications (oxytocin) given through an IV (directly into your vein).
- Breaking your amniotic sac (water).
- Separating the amniotic membrane (the sac of fluid the baby is inside within your uterus) from your uterine wall. This is also called sweeping the membrane.
- Softening your cervix and encouraging it to open with a medication that can be placed directly in your vagina.
Labor induction can take longer than spontaneous labor because the cervical ripening process takes time.
What are the different types of delivery?
There are two main types of delivery: vaginal and cesarean section (C-section). During vaginal birth, your baby will pass naturally through the birth canal. A C-section is a surgical procedure where your provider makes an incision (cut) in your abdomen and delivers the baby in an operating room. Vaginal delivery is the most common type of birth. However, sometimes you might need a C-section for a variety of reasons, including:
Vaginal delivery is the most common type of birth. However, sometimes you might need a C-section for a variety of reasons, including:
- If your baby is not in the head-down position.
- If your baby is too large to naturally pass through your pelvis.
- If your baby is in distress.
- If the placenta blocks your cervix (a condition called placenta previa).
- If you have health issues or complications that make a C-section the safest option.
- If there’s an emergency situation that requires your baby to be delivered quickly.
In many cases, a cesarean delivery is not determined until after labor begins.
How long will I be in the hospital?
The length of your hospital stay can depend on the hospital where you deliver your baby and the type of delivery you have. Typically, you will stay in the hospital longer if you have a C-section delivery because it's a surgical procedure. You may also need to stay in the hospital for a longer period of time if you experience any complications or health issues during your delivery.
A note from Cleveland Clinic:
You're bound to a lot of feelings as you prepare to deliver your baby. It's normal to feel both excited and nervous. Discussing the signs and symptoms with your healthcare provider can help you know what to expect. Your partner and healthcare team are here to support you and will help you remain as comfortable as possible through the delivery process.
Why is it much harder for women to give birth than their distant ancestors?
- Helen Briggs
- BBC
Image copyright, Getty Images
Childbirth in modern women, as a rule, is painful and lasts quite a long time, sometimes more than one day, and a woman in labor often needs help.
So why do the closest biological relatives of humans, such as chimpanzees, give birth easily, they last only a few hours and the woman in labor does not need anyone's help?
- Why childbirth is so difficult and dangerous
- "I was always afraid to go crazy, but it happened after the birth of my son"
To answer this question, scientists tried to find out how the most ancient human ancestors gave birth.
Two million years ago, it was relatively easy for human ancestors to give birth. This was revealed during the study of ancient fossils.
The Australopithecus sediba, who lived 1.95 million years ago in what is now South Africa, had a relatively easy birth process, anthropologist Natalie Lauditsina, a participant in the study, said.
"The head and shoulders of the fetus had enough room to fit through even the tightest of the maternal birth canals," she said.
Today the situation has changed. Due to the size and shape of the modern human pelvis (the trade-off required to walk upright) and the large size of the baby's head, the fetus is difficult to deliver.
During childbirth, the baby has to turn several times in the birth canal.
By studying the pelvic bones of our ancient humanoid relatives, scientists can roughly understand what the births were at the base of the human family tree.
Photo copyright, Laudicina et al, 2019
Photo caption,Australopithecus sediba birth reconstruction
But this is not to say that childbirth has steadily become more difficult as human evolution has progressed.
According to Lauditsina, when studying the fossils of a female Australopithecus of Afar, named Lucy, it turned out that her birth was more difficult than that of Australopithecus sediba, because in her case the fetus was more crowded in the birth canal.
At the same time, Australopithecus Afar lived a million years earlier.
"Many believe that the evolution of childbirth is a transition from easy in monkeys to difficult today. But we see that this is not so," said Lauditsina.
It's difficult to tell when childbirth became difficult and entered the modern phase, she says, because each fossil from the human family tree shows its own birth problems.
And even today, women give birth in different ways: for some, childbirth is relatively easy and fast, while others give birth in agony for more than 20 hours.
Experts explained why Russian women are in no hurry to give birth
The average age of the birth of the first child in Russia is rapidly shifting - now it is already 28 years old. This is due, among other things, to the fact that women are focused on a career, the Ministry of Labor reported. Experts interviewed by Gazeta.Ru also point to other reasons: pressure from society has decreased, people want to live for themselves and prolong their youth due to the late birth of their first child.
The increase in the age at which girls give birth to their first child is associated with a general trend towards careerism and a desire to increase income levels. Family and procreation have receded into the background, Vladimir Dashevsky, a candidate of psychological sciences, family psychotherapist, told Gazeta.Ru.
“It used to be customary to give birth to many children, because they were needed to help in the family household. These social considerations formed stereotypes in society, pushing to give birth earlier. Now there is no such need, since people do not need to survive, with an increase in living standards, stereotypes have also changed,” he said.
Now there is no such need, since people do not need to survive, with an increase in living standards, stereotypes have also changed,” he said.
Modern women live more consciously, it is important for them to get an education and develop a career in order to be financially ready for the birth of a child.
“This significant increase in age is partly due to the desire of people to receive higher education and additional skills, as well as the desire for financial stability and securing a job before leaving on maternity leave,” a demographer, professor at the Department of Family Sociology and Demography at the Faculty of Sociology told Gazeta.Ru Moscow State University Alexander Sinelnikov.
But there is also an opposite trend - many women, looking at the "cult of children", fear that they are not ready to bear maternal responsibility and postpone the decision, Dashevsky noted.
“Women ask themselves if they will be good mothers, they look for a maternal instinct in themselves that does not really exist. And the child-centricity of other people increases the fear of those who have not yet decided on the birth of a child. Therefore, women are starting to create financial insurance, trying to prepare for this, ”the expert clarified.
And the child-centricity of other people increases the fear of those who have not yet decided on the birth of a child. Therefore, women are starting to create financial insurance, trying to prepare for this, ”the expert clarified.
The second factor is the development of medicine and reproductive technologies, continued Dashevsky.
“Now the so-called “ticking clock” has eased, as women can have IVF or adopt a child – this has become the norm in society, and women feel freer. Thanks to medicine, they can do it later, and at 40 they can be considered a young mother, thus prolonging their youth,” he said.
The third factor is the desire of young couples to prolong a comfortable relationship.
“A child greatly changes the life of parents in everyday, financial terms, not everyone is ready for this and strives to live for each other as long as possible. The childfree movement also played a role: some couples immediately agree that they do not want to have children.