How long are you in the hospital after a miscarriage
Treating miscarriage | The Royal Women's Hospital
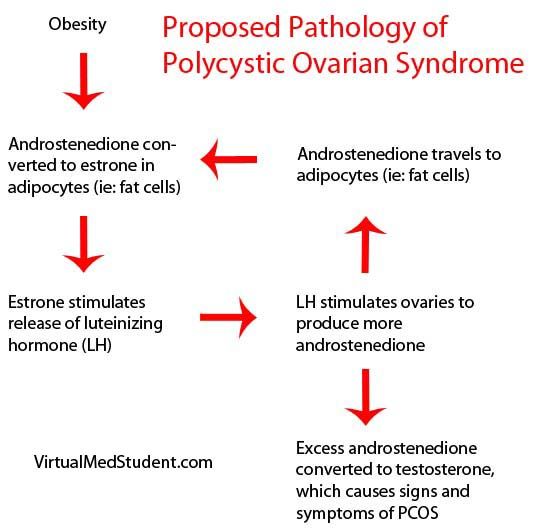
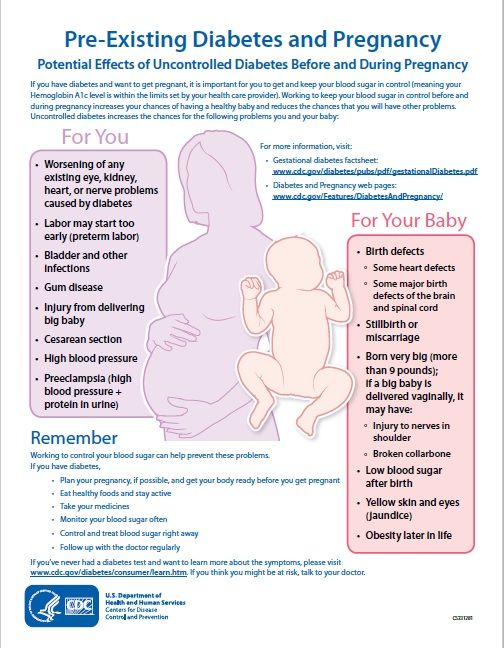
If a miscarriage has begun, there is nothing that can be done to stop it. Any treatment you have will be aimed at avoiding heavy bleeding and infection.
A discussion with the doctor or nurse will help you to work out which treatment options are best and safest for you.
On this page:
- No treatment (expectant management)
- Treatment with medicine
- Surgical treatment (curette)
- Waiting for treatment
- After a miscarriage
No treatment (expectant management)
You can choose to wait and see what will happen. This is called 'expectant management'. If nothing is done, sooner or later the pregnancy tissue will pass naturally. If it is an incomplete miscarriage (where some but not all pregnancy tissue has passed) it will often happen within days, but for a missed miscarriage (where the fetus or embryo has stopped growing but no tissue has passed) it might take as long as three to four weeks.
While you are waiting you may have some spotting or bleeding, much like a period. When the pregnancy tissue passes, you are likely to have heavier bleeding with crampy, period-like pains. You can use sanitary pads and take pain relieving tablets, such as paracetamol.
If your miscarriage is incomplete, with just a small amount of pregnancy tissue remaining, it’s probably best to take a wait and see approach. But if there is heavy bleeding or signs of infection you will need treatment.
If the tissue does not pass naturally or you have signs of infection, the doctor will recommend a dilatation and curettage (D&C). You and the doctor can discuss and decide the preferred option for you.
Things to know
- There are many reasons why some women prefer to wait and see. It may feel more natural, it may help with the grieving process or it may give you more of a sense of control.
- Some women become worried or frightened when the bleeding gets heavier, especially if blood clots, tissue or even a recognisable embryo is passed.
- Usually, the wait and see approach takes longer than any other approaches such as surgery or medication. Sometimes bleeding can last for up to four weeks.
- Although excessive bleeding and blood transfusion are very rare, they are slightly more common with expectant management than with surgery.
- A few women still need to have surgery – sometimes urgently – if they develop infection, bleed heavily or if the tissue does not pass naturally.
- The waiting time can be emotionally draining for some women.
Treatment with medicine
Medicine is available that can speed up the process of passing the pregnancy tissue. For an incomplete miscarriage, the medicine will usually encourage the pregnancy tissue to pass within a few hours. At most it will happen within a day or two. For a missed miscarriage, it may happen quickly, but it can take up to two weeks and, occasionally, longer.
- Medication is not suitable if there is very heavy bleeding or signs of infection.
 It is usually not recommended for pregnancies that are older than about nine weeks.
It is usually not recommended for pregnancies that are older than about nine weeks. - If the tissue does not pass naturally, eventually your doctor will recommend a dilatation and curettage (D&C).
Things to know
- The pregnancy tissue will pass between four to six hours after taking the medicine, during which time you may be in hospital. After a few hours, if the pregnancy hasn’t passed, you may be sent home to wait. This will depend on where you are and which hospital you are in.
- The medicine has side effects which usually pass in a few hours but can be unpleasant, such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea, fever and chills. The tablets can be swallowed or dissolved under the tongue, or inserted in the vagina.
- After receiving the medication there may be some spotting or bleeding like a period. When the pregnancy tissue passes, you are likely to notice heavier bleeding and clots with strong cramping, period-like pains. You can use sanitary pads and take pain relieving tablets such as paracetamol.
- Some women may need stronger pain killers or a pain relieving injection.
- A few women still need to have surgery, sometimes urgently, if they develop infection, bleed heavily or if the tissue does not pass.
Surgical treatment (curette)
A D&C (or ‘curette’) is a minor operation. The full name is dilatation and curettage. It is done in an operating theatre, usually under general anaesthetic. There is no cutting involved because the surgery happens through the vagina. The cervix (neck of the uterus) is gently opened and the remaining pregnancy tissue is removed so that the uterus is empty. Usually the doctor is not able to see a recognisable embryo.
The actual procedure usually only takes five to ten minutes, but you will usually need to be in the hospital for around four to five hours. Most of this time will be spent waiting and recovering.
You may have to wait a day or two to have a curette and sometimes, while you are waiting, the pregnancy tissue will pass on its own. If this happens and all of the tissue is passed you may not need to have a curette.
If this happens and all of the tissue is passed you may not need to have a curette.
A curette is done in the following circumstances:
- You have heavy or persistent bleeding and/or pain.
- The medical staff advise that this is a better option for you; this may be because of the amount of tissue present, especially with a missed miscarriage.
- This is an option you prefer.
Things to know
The risks of a D&C are very low, but include:
- some pregnancy tissue remains in uterus. This can cause prolonged or heavy bleeding and the operation may need to be repeated
- infection needing antibiotics
- damage to the cervix or uterus. This is very rare (around 1 in 1000) and, when it does happen, it is usually a small hole or tear which will heal itself
- excessive bleeding (very rare)
- anaesthetic risks. These are very low for healthy women, but no anaesthetic or operation is without risk.
Waiting for treatment
If you have heavy bleeding with clots and crampy pain, it is likely that you are passing the pregnancy tissue. The bleeding, clots and pain will usually settle when most of the pregnancy tissue has been passed. Sometimes the bleeding will continue to be heavy and you may need further treatment.
The bleeding, clots and pain will usually settle when most of the pregnancy tissue has been passed. Sometimes the bleeding will continue to be heavy and you may need further treatment.
You should go to your nearest emergency department if you have:
- increased bleeding, for instance soaking two pads per hour and/or passing golf ball sized clots
- severe abdominal pain or shoulder pain
- fever or chills
- dizziness or fainting
- vaginal discharge that smells unpleasant
- diarrhoea or pain when you open your bowels.
What to do while you are waiting
- You can try to rest and relax at home.
- Usual activity that is not too strenuous will not be harmful. You can go to work if you feel up to it.
- If you have pain you can take paracetamol.
- If there is bleeding, use sanitary pads rather than tampons.
After a miscarriage
- It is usual to have pain and bleeding after a miscarriage.
 It will feel similar to a period and will usually stop within two weeks. You can take ordinary painkillers for the pain. Your next period will usually come in four to six weeks after a miscarriage.
It will feel similar to a period and will usually stop within two weeks. You can take ordinary painkillers for the pain. Your next period will usually come in four to six weeks after a miscarriage. - See a doctor or attend a hospital emergency department if you have strong pain and bleeding (stronger than period pain), abnormal discharge, (especially if it is smelly), or fever. These symptoms may mean that you have an infection or that tissue has been left behind.
- Try and avoid vaginal sex until the bleeding stops and you feel comfortable.
- Use sanitary pads until the bleeding stops (do not use tampons).
- All contraceptive methods are safe after a miscarriage
- See a GP (local doctor) in four to six weeks for a check-up.
Anti-D injection after a miscarriage
It is important to have your blood group checked. If you’re RhD negative and the fetus is RhD positive this can cause problems for future pregnancies. This is because the fetus’s blood cells have RhD antigen attached to them, whereas yours do not. If small amounts of the fetus’s blood mixes with your blood, your immune system may perceive this difference in blood cells as a threat and produce antibodies to fight against the fetus’s blood. Once your body has made these antibodies they can’t be removed. This is unlikely to have caused your miscarriage and is more likely to affect future pregnancies. Women with a negative blood type usually need an Anti-D injection, which will stop the antibodies forming.
If small amounts of the fetus’s blood mixes with your blood, your immune system may perceive this difference in blood cells as a threat and produce antibodies to fight against the fetus’s blood. Once your body has made these antibodies they can’t be removed. This is unlikely to have caused your miscarriage and is more likely to affect future pregnancies. Women with a negative blood type usually need an Anti-D injection, which will stop the antibodies forming.
Future pregnancies after a miscarriage
One of the most common concerns following a miscarriage is that it might happen again. However, if you have had one miscarriage the next pregnancy will usually be normal.
If you do try for another pregnancy, try and avoid smoking, alcohol and excess caffeine as they increase the risk of miscarriage. It is recommended that all women take folic acid while trying to conceive, and continue until three months of pregnancy. In your next pregnancy you are encouraged to see your GP and have an ultrasound at about seven weeks. If ultrasound is done too early in pregnancy the findings are often uncertain and cause unnecessary worry.
If ultrasound is done too early in pregnancy the findings are often uncertain and cause unnecessary worry.
Feelings and reactions
There is no ‘right’ way to feel following a miscarriage. Some degree of grief is very common, even if the pregnancy wasn’t planned. Partners may react quite differently, just as people can respond differently to a continuing pregnancy. Feelings of loss may persist for some time and you may have mixed feelings about becoming pregnant again. Some friends and family may not understand the depth of emotion that can be attached to a pregnancy and may unreasonably expect for you to move on before you are ready.
Some couples decide that they want to try for a pregnancy straight away, while others need time to adjust to their loss. If you feel anxious about a possible loss in future pregnancies, you may find it helpful to talk to someone about this. If it’s difficult to speak with your friends and family about these issues, your doctor, community support group and counsellors can provide information and assistance.
Related Health Topics
-
- Treatment for miscarriage
Treatment for miscarriage is aimed at avoiding heavy bleeding and infection. It is also aimed at looking after you, physically and emotionally.
-
- (English) PDF (302 KB)
- Treatment for miscarriage
The Women’s does not accept any liability to any person for the information or advice (or use of such information or advice) which is provided on the Website or incorporated into it by reference. The Women’s provide this information on the understanding that all persons accessing it take responsibility for assessing its relevance and accuracy. Women are encouraged to discuss their health needs with a health practitioner.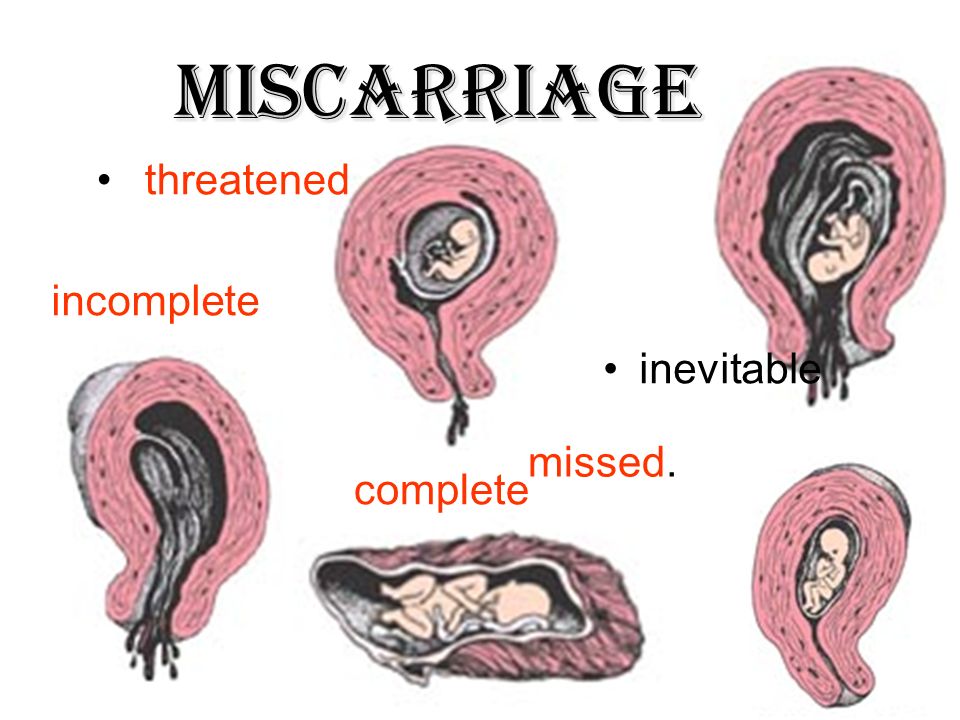 If you have concerns about your health, you should seek advice from your health care provider or if you require urgent care you should go to the nearest Emergency Dept.
If you have concerns about your health, you should seek advice from your health care provider or if you require urgent care you should go to the nearest Emergency Dept.
What happens after miscarriage | Pregnancy Birth and Baby
What happens after miscarriage | Pregnancy Birth and Baby beginning of content7-minute read
Listen
It can be very distressing to have a miscarriage. But aside from the emotional sides of things, there are practical things to decide on and your health to consider.
What should I do if I’ve miscarried at home?
If you wish to, you may decide to collect your baby in a container to show your doctor. Depending on your circumstances, your doctor may send the baby to a laboratory for testing to try to find out why it happened.
What will happen if I miscarry in hospital?
If you miscarry in hospital, you may decide that you wish to see your baby. Whether or not this is possible depends on:
- the stage of your pregnancy
- when the baby died
- whether you had a dilatation and curettage (also called a D&C or curette)
Sometimes your baby may no longer be recognisable, and the staff may advise you not to view the remains.
If you think you would like to see your baby, discuss your wishes with the hospital staff.
Are there any legal obligations?
Legal obligations following your miscarriage may vary according to your state or territory. Your hospital should inform you of any requirements.
Generally, if you lose your baby in the first 20 weeks of pregnancy (defined as a miscarriage), the birth and death of your baby cannot be formally registered. This means that you will not receive a birth or a death certificate.
Some state governments, such as NSW and Queensland, offer optional certificates recognising early pregnancy loss to support parents grieving a miscarriage. If this interests you, please contact the Births, Deaths and Marriage Registry in your state or territory to find out if similar certificates are available.
If this interests you, please contact the Births, Deaths and Marriage Registry in your state or territory to find out if similar certificates are available.
You are not legally required to have a funeral, burial or cremation, although you may choose to do so.
What services will the hospital offer?
The services offered for miscarriage vary between different hospitals.
Some hospitals offer services such as:
- saving the pregnancy tissue from a D&C where possible (provided you have explicitly requested this)
- arranging to have pregnancy tissue cremated at your request
- giving you back the pregnancy tissue for your own private burial or cremation
If you do not make any specific requests, the pregnancy tissue is commonly examined in a laboratory and then cremated according to the hospital protocol.
Some hospitals raise these issues with you. If they do not, it is important to raise these issues yourself.
Can I have a memorial service?
Some hospitals offer shared memorial services to commemorate the loss of all babies.
Your hospital may also offer bereavement support.
Can I have a funeral?
While there is no legal obligation to have a funeral, burial or cremation after a miscarriage, you may choose to make your own arrangements to mark the loss of your baby.
You may choose to engage a private funeral director or approach your religious leader for advice about having a funeral, burial or cremation. Alternatively, you may decide to bury your baby at home.
How long will it take to physically recover from a miscarriage?
How long recovery takes depends on how far along you were in your pregnancy, the treatment you needed and whether or not you had any complications.
Bleeding and discomfort
You may have discomfort and bleeding for up to 2 weeks.
Things to consider:
- use pads for the bleeding, not tampons
- use medication such as paracetamol for the discomfort
- avoid sex and swimming until the bleeding stops
See your doctor or go to your nearest emergency department if:
- the bleeding becomes heavy (soaking 1 to 2 pads in an hour) or goes on for longer than 2 weeks
- you pass large blood clots
- you have severe pain
- you have a temperature
- you have signs of infection, such as a temperature or a smelly vaginal discharge
Other changes
You may find the nausea gets better, and your breasts decrease in size and become less tender.
If you have had a miscarriage near 20 weeks, your breasts may produce milk. Please talk to your doctor or midwife if you have any questions or concerns.
When should I follow up with my doctor or midwife?
You should have a check-up with your doctor or midwife no later than 6 weeks after you miscarry. Your doctor or midwife can provide support, answer questions and advise about contraception.
Your doctor may want to order further tests, including:
- your blood group — if you have a negative blood group, your doctor may recommend an anti-D injection
- your haemoglobin level — if you have anaemia (low blood haemoglobin), your doctor may recommend a diet to follow and iron tablets
What does this mean for future pregnancies?
If you have had a miscarriage, the next pregnancy will usually be normal. After a miscarriage, the chance of you miscarrying again is low (1 in 5 women). If you have had 3 or more miscarriages, your doctor may recommend you that you see a fertility specialist.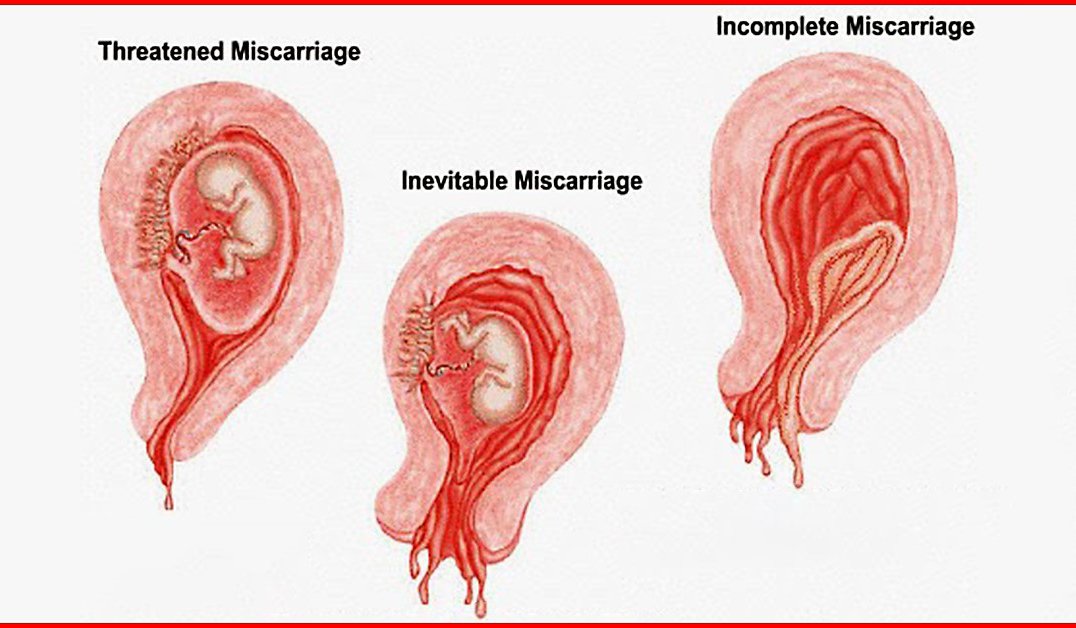
How soon can I fall pregnant again?
Fertility can return immediately after a miscarriage, so consider using contraception until you are ready to start trying again.
If you fall pregnant straight after having a miscarriage, the risk that you will miscarry again is slightly higher. For this reason, doctors recommend that you wait until you have had at least one period before trying to get pregnant again.
How do I plan for another pregnancy?
Planning for pregnancy after a miscarriage can be confronting. It is important that both you and your partner are physically and emotionally ready for another pregnancy. Your doctor or midwife can provide advice about emotional support, falling pregnant again and lifestyle changes that may help you have a successful pregnancy.
Who can I talk to for advice and support?
Talk to your doctor or midwife for information and advice on what do and how to look after yourself if you experience a miscarriage.
Your hospital should be able to provide details of available support services, such as bereavement support.
SANDS is an independent organisation that provides support for miscarriage, stillbirth and newborn death. You can call them on 1300 072 637 or visit www.sands.org.au.
Speak to a maternal child health nurse
Call Pregnancy, Birth and Baby to speak to a maternal child health nurse on 1800 882 436 or video call. Available 7am to midnight (AET), 7 days a week.
Sources:
NSW Registry of Birth Deaths & Marriages (Recognition of early pregnancy loss), Miscarriage Association (Management of miscarriage: your options), Queensland Government (Early pregnancy loss recognition certificate), The Royal Women's Hospital (After a miscarriage), The Royal Women's Hospital (Miscarriage), NSW Health (Early pregnancy - when things go wrong), SANDS (Miscarriage), SANDS (Early pregnancy loss brochure), Raising Children Network (Miscarriage: what it is and what to expect), Women's and Children's Health Network (Miscarriage), Red Nose (Women's physical health after a miscarriage)Learn more here about the development and quality assurance of healthdirect content.
Last reviewed: March 2022
Back To Top
Related pages
- Fathers and miscarriage
- Emotional support after miscarriage
- Miscarriage
- What really happens during a miscarriage
- Experiencing a pregnancy loss
Need more information?
Miscarriage
Miscarriage Despite being common and widespread, miscarriage can be a heartbreaking experience – with up to one in five pregnancies ending before week 20
Read more on Gidget Foundation Australia website
Miscarriage
A miscarriage is the loss of a baby, usually during the first three months or first trimester of pregnancy.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Fathers and miscarriage
A miscarriage can be a time of great sadness for the father as well as the mother.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Emotional support after miscarriage
It is important to know that there is no right or wrong way to feel after experiencing a miscarriage.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Miscarriage | SANDS - MISCARRIAGE STILLBIRTH NEWBORN DEATH SUPPORT
Helping you understand the complex range of emotions you may experience during fertility treatment or after miscarriage or early pregnancy loss
Read more on Sands Australia website
Miscarriage: a guide for men | Raising Children Network
This Dads Guide to Pregnancy covers miscarriage, the grief men might experience after miscarriage, and how to support partners after pregnancy loss.
Read more on raisingchildren.net.au website
The Pink Elephants Support Network - Medical Options for Recurrent Miscarriage
In some cases, a medical reason for miscarriage or recurrent miscarriage can be found through testing
Read more on Pink Elephants Support Network website
What really happens during a miscarriage
Understand what actually happens during a miscarriage and what you might see and feel. Please be warned that this article contains some graphic descriptions.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
New research on vitamin B3 and miscarriages
Pregnant women are being warned not to start taking vitamin B3 supplements, despite a recent study that suggests it might reduce the risk of miscarriages and birth defects.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Pregnancy: miscarriage & stillbirth | Raising Children Network
Have you experienced a miscarriage or stillbirth? Find articles and videos about coping with the grief of losing a pregnancy or having a stillbirth.
Read more on raisingchildren.net.au website
Disclaimer
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is not responsible for the content and advertising on the external website you are now entering.
OKNeed further advice or guidance from our maternal child health nurses?
1800 882 436
Video call
- Contact us
- About us
- A-Z topics
- Symptom Checker
- Service Finder
- Linking to us
- Information partners
- Terms of use
- Privacy
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is funded by the Australian Government and operated by Healthdirect Australia.
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is provided on behalf of the Department of Health
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby’s information and advice are developed and managed within a rigorous clinical governance framework. This website is certified by the Health On The Net (HON) foundation, the standard for trustworthy health information.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
This information is for your general information and use only and is not intended to be used as medical advice and should not be used to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any medical condition, nor should it be used for therapeutic purposes.
The information is not a substitute for independent professional advice and should not be used as an alternative to professional health care. If you have a particular medical problem, please consult a healthcare professional.
Except as permitted under the Copyright Act 1968, this publication or any part of it may not be reproduced, altered, adapted, stored and/or distributed in any form or by any means without the prior written permission of Healthdirect Australia.
Support this browser is being discontinued for Pregnancy, Birth and Baby
Support for this browser is being discontinued for this site
- Internet Explorer 11 and lower
We currently support Microsoft Edge, Chrome, Firefox and Safari. For more information, please visit the links below:
- Chrome by Google
- Firefox by Mozilla
- Microsoft Edge
- Safari by Apple
You are welcome to continue browsing this site with this browser. Some features, tools or interaction may not work correctly.
Treatment and prevention of miscarriage
Miscarriage. Symptoms
Causes of a miscarriage
Questions to ask your doctor about a miscarriage
Diagnosis of a miscarriage
If there is a risk of a miscarriage, your doctor may recommend rest until the bleeding or pain stops. Your doctor may also recommend that you abstain from sports and sexual activity. It is better not to travel, and especially not to travel to places where it is difficult to get emergency medical care.
It is better not to travel, and especially not to travel to places where it is difficult to get emergency medical care.
Thanks to the widespread use of ultrasound, it is much easier these days to know if an embryo has died or not formed at all, and to know for sure that a miscarriage will occur. In this case, there are several options:
Expectant tactics. Before ultrasound was used in early pregnancy, most women had no idea that they were going to have a miscarriage. Some women allow the process to develop naturally. Usually a miscarriage occurs a few weeks after the death of the embryo is established. Unfortunately, this process can take three to four weeks. From an emotional point of view, this can be quite a difficult period.
Conservative treatment for miscarriage. If, after diagnosing a miscarriage, a woman decides to speed up the process, then the removal of the embryonic tissue and placenta from the body can be provoked by taking certain drugs.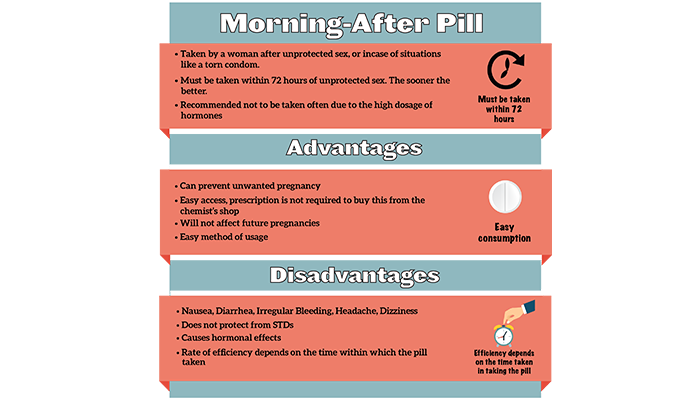 Some medications are taken by mouth, but your doctor may prescribe intravaginal medications to increase their effectiveness and reduce the risk of side effects such as nausea, abdominal pain, and diarrhea. Most likely, a miscarriage will occur at home. The time of action of the drug may vary. You may also need more than one dose of the drug. In 70% of cases, the drug begins to act within a day, and a miscarriage occurs in the next few days or weeks.
Some medications are taken by mouth, but your doctor may prescribe intravaginal medications to increase their effectiveness and reduce the risk of side effects such as nausea, abdominal pain, and diarrhea. Most likely, a miscarriage will occur at home. The time of action of the drug may vary. You may also need more than one dose of the drug. In 70% of cases, the drug begins to act within a day, and a miscarriage occurs in the next few days or weeks.
Surgical treatment. Another treatment option is vacuum aspiration and curettage. During this procedure, the doctor opens the cervix and, using a special device, gently sucks tissue from the uterus. Sometimes a special metal surgical instrument with a loop at the end (curette) is used to scrape the walls of the uterus after vacuum aspiration. Complications are rare, but the connective tissue of the cervix or the wall of the uterus may be damaged.
In the event of an unavoidable miscarriage, surgery is necessary to stop the bleeding.
Lifestyle and home care
Physical recovery
In most cases, physical recovery after a miscarriage takes a few hours to a few days. It will take 4-6 weeks to return to a normal lifestyle. During this period, if you experience heavy bleeding, fever, chills or severe pain, you should contact your doctor. These signs and symptoms may indicate an infection. For two weeks after a miscarriage, you should not have sex, use tampons, or flush your vagina.
Subsequent pregnancy
It is possible to become pregnant during your period immediately after a miscarriage. If you and your partner decide to try for a baby, make sure you are emotionally and physically ready for it. The doctor may recommend to postpone this process until the next menstruation, and maybe even more.
More than three miscarriages in a row should be investigated to determine the underlying causes, such as uterine abnormalities, coagulation problems, or abnormalities at the chromosomal level. In some cases, the doctor will suggest that you get tested after two miscarriages in a row, but two miscarriages still may not have hidden medical reasons. If the cause of miscarriages cannot be determined, do not lose hope. 60-70% of women who have had consecutive miscarriages can become pregnant in the future, even without treatment.
In some cases, the doctor will suggest that you get tested after two miscarriages in a row, but two miscarriages still may not have hidden medical reasons. If the cause of miscarriages cannot be determined, do not lose hope. 60-70% of women who have had consecutive miscarriages can become pregnant in the future, even without treatment.
Coping with illness and finding support
Psychological recovery can take much longer than physical recovery. A miscarriage is a painful loss that others will not be able to fully understand. You can experience completely different feelings: from anger to despair. Give yourself time to process this grief and find support from loved ones. Don't blame yourself for what happened. You may not be able to forget all the hopes and dreams you had for this pregnancy, but over time, acceptance will ease the pain. Talk to your healthcare provider if you are experiencing deep sadness or depression.
Prevention
With so many possible causes of miscarriage, there is simply no way to prevent it. It is better to concentrate all your energy on taking care of yourself and your unborn child. Seek medical attention and avoid known risk factors such as smoking and drinking alcohol. In the presence of chronic diseases, you need to consult with your doctor in order to monitor your health.
It is better to concentrate all your energy on taking care of yourself and your unborn child. Seek medical attention and avoid known risk factors such as smoking and drinking alcohol. In the presence of chronic diseases, you need to consult with your doctor in order to monitor your health.
You can get more detailed information about miscarriage from the gynecologists of the Health 365 clinic in Yekaterinburg.
Prices
Gynecologist, initial appointment
2300 i
Miscarriage. What to do after a miscarriage?
When a woman finds out about her pregnancy, she changes her rhythm of life, especially if the pregnancy is desired. However, depending on many circumstances, miscarriage may occur, that is, a natural termination of pregnancy. Statistics say that up to 20 percent of pregnancies end in pathological abortions. Often a woman may not know that she was pregnant, as a miscarriage sometimes occurs at a very early stage and seems to be just a normal delay in menstruation followed by heavy discharge.
If a woman finds out that she is pregnant and wants to become a mother, she should be very attentive to her condition. The threat of miscarriage often occurs in the early stages of pregnancy and therefore it is necessary to know what symptoms and signs precede a sudden miscarriage.
Signs
The main sign of a suspected miscarriage is bleeding from the uterus. They happen not abundant, pale scarlet or gray-brown. The discharge most often gradually increases and is characterized by sudden spasms or pulling pains in the lower abdomen. These symptoms may last for some time.
The pains are often so mild that the woman simply does not pay attention to them. They are able to be interrupted, and the woman simply forgets about them, especially if the discharge also stopped, and before that they were insignificant. Meanwhile, the very first symptoms should alert you and you should urgently go to the gynecologist for examination and consultation. Even if the process has stopped, after a few days you can feel a sharp deterioration in health, and then you can no longer save the life of the unborn child. Be sure to pay attention to what exactly comes out with the discharge, if there are tissue fragments, it means that miscarriage has already occurred. Therefore, one should not hesitate to go to the doctor, the fetus may come out, in whole or in parts, there may be white particles or a round gray bubble. When the body is completely cleansed, the pain will subside, but before that it may continue for some time.
Even if the process has stopped, after a few days you can feel a sharp deterioration in health, and then you can no longer save the life of the unborn child. Be sure to pay attention to what exactly comes out with the discharge, if there are tissue fragments, it means that miscarriage has already occurred. Therefore, one should not hesitate to go to the doctor, the fetus may come out, in whole or in parts, there may be white particles or a round gray bubble. When the body is completely cleansed, the pain will subside, but before that it may continue for some time.
Terms of miscarriage
A miscarriage is classified as early if it occurred before twelve weeks from the onset of pregnancy. Starting from the 22nd week, if a spontaneous miscarriage has occurred, it is considered late. If the termination of pregnancy occurred before thirty-seven weeks, then this is already called premature birth. All subsequent fetal rejections are called term births and are generally considered normal, since during this period, mostly able-to-survive children are born. In modern medicine, children born after 22 weeks are nursed and subsequently do not differ from those born at term with normal weight.
In modern medicine, children born after 22 weeks are nursed and subsequently do not differ from those born at term with normal weight.
Types of miscarriages
Specialists have identified several types of miscarriages.
- Complete or unavoidable – characterized by lower back pain and dilatation of the cervix, hemorrhages from it. The fetal membrane necessarily bursts, and the pregnancy is terminated. The fetus comes out of the uterus, and all discomfort in the form of pain and bleeding stops.
- Miscarriage is different in that the fetus died, but remained in the mother's body. This can be detected by a doctor when examining a woman and when listening to the fetal heartbeat.
- Repeated miscarriage is rare, it occurs only some time after the first and can occur up to three times in a row in the early stages.
Causes of spontaneous abortion
The vast majority of women, having learned about their pregnancy, want to give birth to a healthy baby. And if a spontaneous miscarriage occurs, then for a failed mother this is a real tragedy. Many, having experienced an abortion, try to conceive a child faster again, but first you need to know the reasons for what happened in order to save the fetus in the future. According to statistics, the largest number of miscarriages occurs precisely in the early stages.
And if a spontaneous miscarriage occurs, then for a failed mother this is a real tragedy. Many, having experienced an abortion, try to conceive a child faster again, but first you need to know the reasons for what happened in order to save the fetus in the future. According to statistics, the largest number of miscarriages occurs precisely in the early stages.
There are several reasons for this:
- Violations in genetics.
This is the most common cause of miscarriage. This is not due to heredity, it is a consequence of the mutation of parent germ cells, which accidentally ended up in unfavorable conditions. This is also the influence of radiation, poisoning, viruses, that is, temporary situations that affected the quality of germ cells. The body thus gets rid of a weak non-viable fetus. It is impossible and unnecessary to prevent such spontaneous abortion. It is only necessary, having decided to become pregnant, to try to cleanse your body of possible harmful influences.
- Hormonal disorders
The cause of a miscarriage at a very early stage also lies in the lack of the hormone progesterone, or in the fact that a woman has an excess of male sex hormones that suppress the production of estrogen and progesterone in her body. In this case, the fetus can be saved medically by administering the necessary medicines to the woman. The work of the adrenal glands, as well as the thyroid gland, affects the production of hormones, so a lot depends on the work of these glands throughout the pregnancy process.
- Immunological causes .
In this case, the vitality of the fetus is directly affected by the Rh conflict. The embryo will inherit the positive Rh of the man, and if the partner has a negative Rh, then her body simply rejects cells that are foreign to him. A similar situation can be prevented by injecting the expectant mother with a variety of progesterone, a process called immunomodulation.
Sexually transmitted infections such as toxoplasmosis, syphilis, trichomoniasis, chlamydia and others are of great danger. External infection: bacteria and viruses infect the fetal membranes, and the body will inevitably reject the embryo. Therefore, before becoming pregnant, you should be examined to know for sure that there are no infections, and if the result is positive, undergo treatment.
In addition, all inflammatory processes, various diseases of the internal organs, which are accompanied by a persistent high temperature, can also lead to unexpected rejection of the fetus. Rubella is especially dangerous, and viral hepatitis is common. But even a sore throat, mild pneumonia, appendicitis sometimes play a key role and lead to a miscarriage, so the expectant mother must undergo a thorough examination even before the child is conceived, and then beware of all kinds of infections and weakening of the body.
- Medical abortion.
If a woman had an abortion in a hospital and then became pregnant and decided to give birth, there is a risk that she will have a miscarriage. Abortion is a stress factor for the body, ovarian dysfunction is often observed, inflammatory processes in the female genital organs can begin, and all this will lead, at best, to miscarriage and subsequent repeated miscarriages, and at worst, to infertility. Therefore, you need to think very seriously before going for an abortion.
- Medicines and certain herbs.
Pregnant women should not take any medication at all, especially during the first three calendar months. Medicines and herbs can cause various defects in the fetus, which in turn will lead to its rejection. Analgesics and uncontrolled hormonal contraceptives are especially dangerous. Parsley and nettle should be eaten with caution - they cause a high tone of the uterus, which in turn can reject the fetus.:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/hemorrhage-in-miscarriage-meaning-2371523-FINAL-f2ab04cab1cc491e964a45e682f93da5.png)
- Stress.
It is no coincidence that in ancient times, pregnant women were protected from unrest, they were created comfortable conditions, they tried to give as many positive emotions as possible. Now the direct dependence of the health of the unborn baby on the mental state during pregnancy has already been proven. Any stress, fear and overstrain can cause an unexpected termination of pregnancy. If you have a problem (death of a loved one, divorce, etc.), you need to find sedatives with the help of a doctor, they will help you cope with this period.
- Unhealthy lifestyle.
Of course, the intake of alcoholic beverages, an unhealthy lifestyle, smoking, even coffee consumption in large quantities, improper diet - all this can lead to a transient miscarriage. Therefore, the expectant mother should prioritize and change her rhythm of life in advance in order to give birth to a healthy child.
- Sexual intercourse, falling, heavy lifting.
All of these factors can affect the fetus, so you should protect yourself and your baby by avoiding these activities.
What to do after a miscarriage?
Having experienced the tragedy of losing a child, parents often intend to immediately conceive a new baby, but they are afraid that everything will happen again. In this case, you do not need to make independent decisions, but consult a doctor. And first of all, it is necessary to identify the cause that led to the miscarriage. For this, the expectant mother needs to undergo as thorough an examination as possible.
If no obvious cause is found, the fetus most likely has a chromosomal abnormality. In this case, you should not worry, since the next conception will occur with a different set of chromosomes, which means that there will be no repeated miscarriage. If the miscarriage was repeated, it is necessary to contact a geneticist and conduct a study of the set of chromosomes of both parents. If it turns out that the cause was an infection, then it is necessary to fully recover. If we are talking about sexual infections, then both parents need to undergo therapy. It is necessary to take tests for hormonal studies, hemostasis systems and determine the immune status.
If it turns out that the cause was an infection, then it is necessary to fully recover. If we are talking about sexual infections, then both parents need to undergo therapy. It is necessary to take tests for hormonal studies, hemostasis systems and determine the immune status.
After a miscarriage, should be treated, if necessary, and pause between conceptions. During pregnancy, you should not take medications to prevent re-spontaneous pathological termination of pregnancy. Therefore, you can become pregnant only after the end of the course of treatment. If the cause was hormonal abnormalities, then the expectant mother should take special drugs to stabilize the background, and at this time she should never become pregnant. During the pause, you need to choose contraceptives with the help of a doctor. You can go to a specialized clinic where you will be prescribed a full course of rehabilitation.
During the first week after a miscarriage women often experience pain in the lower abdomen, heavy bleeding, so you should refrain from sexual intercourse with a man. If there is severe bleeding, acute pain in the lower abdomen, convulsions, high fever, palpitations, nausea, vomiting, then you should immediately consult a doctor to identify the cause of this condition. It is necessary to plan a subsequent pregnancy not earlier than three months after this situation, but preferably six months later. Until that time, it is worth reconsidering your outlook on life, giving up hard work, eating right and wisely, taking vitamins, exercising, losing weight if you are overweight, stop smoking, drinking alcohol, think over your daily routine.
If there is severe bleeding, acute pain in the lower abdomen, convulsions, high fever, palpitations, nausea, vomiting, then you should immediately consult a doctor to identify the cause of this condition. It is necessary to plan a subsequent pregnancy not earlier than three months after this situation, but preferably six months later. Until that time, it is worth reconsidering your outlook on life, giving up hard work, eating right and wisely, taking vitamins, exercising, losing weight if you are overweight, stop smoking, drinking alcohol, think over your daily routine.
It is very important during this recovery period to have a positive attitude and confidence that the next attempt will be successful. It is more difficult to do than to say, because after a miscarriage the woman is in a depressed state and is afraid of a repetition of the situation. You can’t get hung up on your problem, during this period it’s better to do some favorite thing, relax, change the situation, travel, visit the city more often.