Woman pregnant with twins
Pregnant with twins? About twin pregnancy
Finding out you’re pregnant with twins
If you have very early and noticeable pregnancy symptoms like tiredness, emotional ups and downs, nausea, vomiting and constipation, you might wonder whether you’re having twins.
You might also suspect you’re having twins if you had fertility treatment – especially if you had more than one embryo transferred – or used certain fertility drugs to help with getting pregnant.
The only definite way to find out whether you’re having twins or other multiples is to have an ultrasound scan.
The best time to have this ultrasound is at 10-12 weeks of pregnancy. This is usually when your health professional can say for sure how many fetuses, placentas and amniotic sacs there are. This information can tell you whether you have identical or fraternal twins. And the information also helps your health professionals recommend the right pregnancy care for you.
Hormone tests can’t tell you for sure whether you’re pregnant with twins.
Pregnant with twins: antenatal care and birth options
Because a twin pregnancy can be more complicated than a single pregnancy, health professionals usually recommend specialist antenatal care. Specialist antenatal care usually involves seeing an obstetrician and a midwife in a hospital twins clinic.
Specialist antenatal checks can pick up any complications early, which means they can be treated early too.
Also, health professionals will usually recommend that you give birth in a hospital, rather than in a birth centre or at home. Hospitals have facilities to manage any complications of a twin pregnancy, like premature birth.
Tests, checks and appointments during twin pregnancy
If you’re pregnant with twins, you’ll need a higher level of care, which means more appointments and tests during your pregnancy.
You probably won’t need a lot of extra blood tests, but you will need more ultrasounds.
If you have twins with separate placentas, it’s generally recommended that you have ultrasounds at 12-13 weeks, 20 weeks, and then every 4 weeks until your babies are born. You might have more frequent ultrasounds than this.
A twin pregnancy with babies sharing one placenta might be more complicated. It’s generally recommended that you have ultrasounds about every 2 weeks from 12 weeks.
If you’re pregnant with twins, you’ll have more frequent antenatal appointments. Antenatal appointments are a good chance to get health and lifestyle support if you need it. You can also get information about pregnancy, labour, birth and early parenting.
Potential health complications in a twin pregnancy
Women with twin pregnancies are more likely to have pregnancy health problems and complications like gestational diabetes, pre-eclampsia, premature labour and bleeding.
Twins who share a placenta might have extra complications. Sometimes their blood supply is shared unequally, which can cause health problems for both twins. Or if the placenta itself is shared unequally, this can mean that one twin doesn’t get enough nutrients and doesn’t grow as well.
Or if the placenta itself is shared unequally, this can mean that one twin doesn’t get enough nutrients and doesn’t grow as well.
You can reduce the risk of complications – or stop them from getting worse – by going to your antenatal appointments. At these appointments it’s important to tell your obstetrician, doctor or midwife if you have any physical symptoms or you feel that something is wrong.
Pregnancy health problems can be both physical and emotional. If you have emotional changes that last longer than 2 weeks or that get in the way of your daily life, it could be a sign of antenatal depression, antenatal anxiety or another problem. Talk with your midwife or doctor about any emotional changes. You can also call Lifeline on 131 114, Beyond Blue on 1300 224 636 or PANDA on 1300 726 306.
Physical changes during a twin pregnancy
Physical changes with a twin pregnancy are more obvious than with a single pregnancy.
If you’re pregnant with twins, you might gain 16-20 kg (compared to 10-15 kg with a single pregnancy).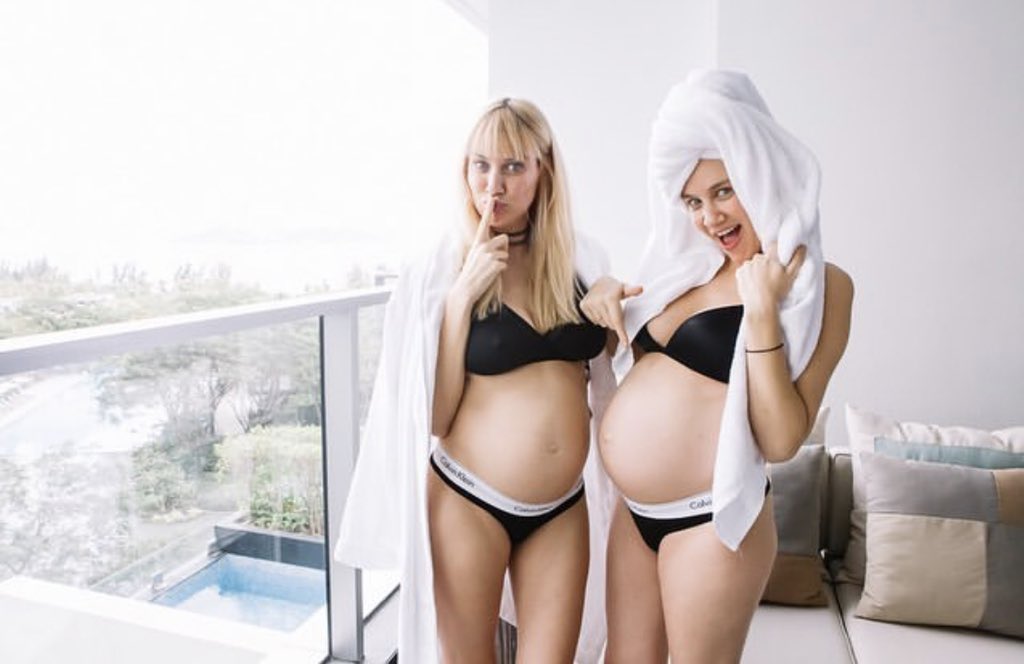 Also, stretch marks, bloating, varicose veins and haemorrhoids are common. These changes might affect the way you feel about your body.
Also, stretch marks, bloating, varicose veins and haemorrhoids are common. These changes might affect the way you feel about your body.
You can talk with your doctor or midwife about the changes in your body and how you feel about these changes.
Keep up to date with the changes in your body and your babies’ development with our week-by-week pregnancy emails.
Healthy eating and twin pregnancy
Healthy eating in pregnancy involves a healthy, well-balanced diet, full of vitamins and minerals.
When you’re pregnant with twins, your doctor or midwife might recommend that you get expert advice about your dietary intake of protein, carbohydrates, folate, iron, calcium, iodine, fats and overall nutrients. Dietitians have qualifications and skills to give you expert nutrition and dietary advice.
Will your twins be born early?
Health professionals usually aim for twins to be born at 37-38 weeks unless problems develop earlier or there’s a good reason to delay birth.
About 60% of twins are born before 37 weeks, while single babies are born at around 40 weeks.
If you know your twins will be born early, you can get ready for premature birth.
Vaginal or caesarean birth
It’s good to talk with your obstetrician and midwife about whether vaginal birth or caesarean birth will be better for you and your twins.
If you’re having twins, you’re almost twice as likely to have a caesarean birth.
You can discuss with your obstetrician the most appropriate time and ‘way’ to give birth to your twins.
Preparing for raising twins
Raising twins can be very rewarding and very challenging at times too. Here are ways to get ready for parenting twins:
- Work on communication with your partner, if you have one. Communication is an essential part of continuing a healthy relationship. Pregnancy is a great time to discuss and share your thoughts and expectations for the future. You might like to watch our video on relationships in pregnancy and early parenting and read about pregnancy and healthy relationships.

- Look at our resources on breastfeeding. You can breastfeed your twins, and it’s good for you and your babies. You can ask for help from a lactation consultant or your midwife. You can also ask your birth hospital if there are classes specifically for expectant parents of twins.
- Read about services and support. As parents of twins, you and your partner will find that life is very busy, so it’ll help to have support from family and friends.
- Enrol with the Australian Multiple Birth Association (AMBA). The AMBA offers a range of support services and links to other services for new parents of twins. You might also like to register your twins with Twins Research Australia.
Being pregnant with twins, triplets and other multiples
If you’re pregnant with multiples, you and your babies are more likely to have health complications than if you’re pregnant with one baby.
You may need to go to extra prenatal care checkups so your health care provider can check you and your babies closely during pregnancy.

The most common complication of being pregnant with multiples is premature birth (before 37 weeks of pregnancy).
What causes you to get pregnant with multiples?
A multiple pregnancy means you’re pregnant with more than one baby.
Multiple pregnancy usually happens when more than one egg is fertilized. It also can happen when one egg is fertilized and then splits into 2 or more embryos that grow into 2 or more babies.
When one fertilized egg splits into 2, the babies are called identical twins. They look almost exactly alike and share the exact same genes. When two separate eggs are fertilized by two separate sperm, the babies are called fraternal twins. They don’t share the same genes and are no more alike than any siblings from different pregnancies with the same parents.
Singletons, or one baby, are the most common type of pregnancy. However, more people are getting pregnant with multiples now than in the past. This is mostly because more people are having babies later in life, and multiples are more common among parents who are older than 30. Also, more people are using fertility treatments to get pregnant. Multiples are also more common among people who use fertility treatment.
Also, more people are using fertility treatments to get pregnant. Multiples are also more common among people who use fertility treatment.
How do you know if you’re pregnant with multiples?
You may be pregnant with multiples if:
- Your breasts are very sore.
- You’re very hungry or you gain weight quickly in the first trimester.
- You feel movement in different parts of your belly at the same time.
- You have severe morning sickness. Morning sickness is nausea (feeling sick to your stomach) and vomiting that happens in the first few months of pregnancy.
- Your health care provider hears more than one heartbeat or finds that your uterus is larger than usual.
- You have high levels of a hormone called human chorionic gonadotrophin (also called hCG) or a protein called alpha-fetoprotein in your blood. HCG is a hormone your body makes during pregnancy. Alpha-fetoprotein is a protein that a developing baby makes during pregnancy.

Your provider can use ultrasound to find out for sure if you’re pregnant with multiples. Ultrasound uses sound waves and a computer screen to show a picture of a baby.
What kind of prenatal care do you need if you’re pregnant with multiples?
If you’re pregnant with multiples, you may need extra medical care during pregnancy, labor and birth. You may need to go to extra prenatal care checkups so your provider can watch you and your babies for problems. You also may need more prenatal tests (such as ultrasounds) to check on your growing babies throughout your pregnancy.
If you’ve had pregnancy complications in the past or if you have health conditions that put you at risk for pregnancy complications, your provider may refer you to a maternal-fetal medicine specialist. This is a doctor who specializes in high-risk pregnancies. High-risk means you’re more likely than most pregnant people to have problems with your pregnancy. If you’re referred to this kind of doctor, it doesn’t mean you’ll have problems during pregnancy. It just means they can check you and your babies more closely to help prevent or treat any conditions that may happen.
It just means they can check you and your babies more closely to help prevent or treat any conditions that may happen.
How can a multiple pregnancy affect your health?
The following complications are more common in people who are pregnant with multiples:
- Preterm labor. This is labor that happens too early, before 37 weeks of pregnancy. Preterm labor can lead to premature birth (birth before 37 weeks of pregnancy).
- Anemia. Anemia is when you don’t have enough healthy red blood cells to carry oxygen to the rest of your body. A condition called iron-deficiency anemia is common in multiple pregnancies and can increase your chances of premature birth. Your provider may prescribe an iron supplement for you to make sure you’re getting enough iron.
- Gestational diabetes. This is a kind of diabetes that only pregnant people can get. If untreated, it can cause serious health problems for you and your babies.
 Diabetes is when you have too much sugar (called blood sugar or glucose) in your blood.
Diabetes is when you have too much sugar (called blood sugar or glucose) in your blood. - Gestational hypertension or preeclampsia. These are types of high blood pressure that only pregnant people can get. High blood pressure is when the force of blood against the walls of your blood vessels is too high. It can cause problems during pregnancy. Preeclampsia is a condition that can happen after the 20th week of pregnancy or right after pregnancy. It’s when a pregnant person has high blood pressure and signs that some of their organs, like the kidneys and liver, may not be working properly.
- Hyperemesis gravidarum. This is severe nausea and vomiting.
- Intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy (also called ICP). ICP is a liver condition that slows the normal flow of bile, causing bile to build up in the liver. Bile is a fluid that helps your body break down fats and helps the liver get rid of toxins (poisonous substances).
 This buildup can cause chemicals called bile acids to spill into your blood and tissues, leading to severe itching.
This buildup can cause chemicals called bile acids to spill into your blood and tissues, leading to severe itching. - Polyhydramnios. This is when there’s too much amniotic fluid. Amniotic fluid is the fluid that surrounds the baby in the uterus.
- Miscarriage or stillbirth. Miscarriage is when a baby dies before 20 weeks of pregnancy. Stillbirth is when a baby dies after 20 weeks of pregnancy. Some people who are pregnant with multiples have a condition called vanishing twin syndrome. This is when one or more babies die during the pregnancy and one baby survives.
- Postpartum depression (also called PPD). This is a kind of depression that some parents get after having a baby. PPD is strong feelings of sadness that last for a long time. These feelings can make it hard for you to take care of your baby.
- Postpartum hemorrhage. This is heavy bleeding after giving birth.
 It’s a serious but rare condition.
It’s a serious but rare condition.
How can being pregnant with multiples affect your babies’ health?
If you’re pregnant with multiples, your babies are more likely to have health complications, including:
- Preterm birth. Premature babies (born before 37 weeks of pregnancy) may have more health problems or need to stay in the hospital longer than babies who are born close to their due date. Some may spend time in a hospital’s newborn intensive care unit (also called NICU). Premature babies also may have health problems that can affect them later in life. More than half of twins and nearly all triplets and other higher-order multiples are born earlier than they should be.
- Birth defects. Birth defects are health conditions that are present at birth. They change the shape or function of one or more parts of the body. Birth defects can cause problems in overall health, how the body develops or how the body works.
 Multiples are about twice as likely as singleton babies to have birth defects, including neural tube defects (such as spina bifida), cerebral palsy, congenital heart defects and birth defects that affect the digestive system.
Multiples are about twice as likely as singleton babies to have birth defects, including neural tube defects (such as spina bifida), cerebral palsy, congenital heart defects and birth defects that affect the digestive system. - Growth problems. Multiples are usually smaller than singleton babies. Your provider can use ultrasound to check your babies’ growth at prenatal care checkups. When one twin is much smaller than the other, they’re called discordant twins. Discordant twins are more likely to have health problems during pregnancy and after birth.
- Low birthweight. This is when your baby is born weighing less than 5 pounds, 8 ounces. Babies whose weight is lower than it should be at birth are more likely than babies born at a normal weight to have certain health problems, such as retinopathy of prematurity. They’re also more likely to have health problems later in life, like high blood pressure. More than half of twins and nearly all higher order multiples weigh less than they should at birth.

- Twin-twin transfusion syndrome. This condition happens when identical twins share a placenta and one baby gets too much blood flow, while the other baby doesn’t get enough. The placenta grows in the uterus and supplies your babies with food and oxygen through the umbilical cord. Twin-twin transfusion syndrome can be treated with laser surgery to seal off the connection between the babies’ blood vessels and amniocentesis to drain off extra fluid.
- Neonatal death. This is when a baby dies in the first 28 days of life. Preterm birth is the most common cause of neonatal death.
What makes you more likely to get pregnant with multiples?
You may be more likely to get pregnant with more than one baby if:
- You have fertility treatment. If you’re having fertility treatment, it’s important to try to get pregnant with just one baby. For example, if you’re having a treatment called in vitro fertilization (also called IVF), you can have just one embryo placed in your uterus.
 This is called single embryo transfer. In IVF, an egg and sperm are combined in a lab to create an embryo (fertilized egg) which is then placed in the uterus. If you’re having any kind of fertility treatment, talk with your provider about ways to lower the chance of getting pregnant with multiples.
This is called single embryo transfer. In IVF, an egg and sperm are combined in a lab to create an embryo (fertilized egg) which is then placed in the uterus. If you’re having any kind of fertility treatment, talk with your provider about ways to lower the chance of getting pregnant with multiples. - You’re in your 30s, especially your late 30s. If you’re 30 or older, you’re more likely than younger people to release more than one egg during a menstrual cycle.
- You have relatives who have had multiples. If you or other people in your family have had fraternal twins, you may be more likely to have twins, too. You’re also more likely to have multiples if you’ve been pregnant before, especially if you’ve been pregnant with multiples.
- You’re a person who has obesity. If your body mass index (also called BMI) is 30 or higher. To find out your BMI, go to cdc.gov/bmi.
- You’re Black or White. Black people are more likely to have twins than other parents.
 White people, especially those older than 35 years old, are most likely to have higher-order multiples.
White people, especially those older than 35 years old, are most likely to have higher-order multiples.
How are multiples born?
Vaginal birth is the way most babies are born. During vaginal birth, the uterus contracts to help push the baby out.
If you’re pregnant with multiples, you’re more likely to have a cesarean birth (also called c-section) than if you’re pregnant with one baby. During a c-section, the doctor makes a cut in the belly and uterus to remove the baby. Most triplets and higher-order multiples are born by c-section.
If you’re pregnant with twins, you may need a c-section if neither baby is in the head-down position or if you have other complications. You may be able to have a vaginal birth if:
- Both babies are in the head-down position and you have no other complications
- The lower twin is in the head-down position but the higher twin isn’t.
Do you need to eat special foods if you’re pregnant with multiples?
No. But you do need more of certain nutrients, such as folic acid, protein, iron and calcium. You can get the right amount of these nutrients by eating healthy foods and taking your prenatal vitamin every day. Prenatal vitamins are multivitamins made just for pregnant people. Compared to a regular multivitamin, they have more of some nutrients that you need during pregnancy. Your provider can prescribe a prenatal vitamin for you at your first prenatal care checkup. Even when you’re pregnant with multiples, you only need to take one prenatal vitamin each day.
But you do need more of certain nutrients, such as folic acid, protein, iron and calcium. You can get the right amount of these nutrients by eating healthy foods and taking your prenatal vitamin every day. Prenatal vitamins are multivitamins made just for pregnant people. Compared to a regular multivitamin, they have more of some nutrients that you need during pregnancy. Your provider can prescribe a prenatal vitamin for you at your first prenatal care checkup. Even when you’re pregnant with multiples, you only need to take one prenatal vitamin each day.
How much weight should you gain if you’re pregnant with multiples?
If you’re pregnant with multiples, you need to gain more weight than if you were pregnant with one baby. The amount of weight to gain depends on your weight before pregnancy and how many babies you have. Talk with your provider about how much weight to gain.
Here’s what you should know about gaining weight if you’re pregnant with twins:
- If you were at a healthy weight before pregnancy, you want to gain about 37 to 54 pounds during pregnancy.
- If you were overweight before pregnancy, you want to gain about 31 to 50 pounds during pregnancy.
- If you were affected by obesity before pregnancy, you want to gain about 25 to 42 pounds during pregnancy.
Do you need to limit physical activity if you’re pregnant with multiples?
Talk with your provider about what kind of activities are safe for you to do. You may need to cut out any high-impact activities, such as aerobics or jogging, that make you jump or put stress on your joints. You may be able to do some activities, such as swimming, prenatal yoga or walking.
Later in pregnancy, you may need to limit physical activity, including travel and work. Many people who are pregnant with multiples go on bed rest. Bed rest means reducing your activities while you’re pregnant. Bed rest may mean staying in bed all day or just resting a few times each day.
More information
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)
- Show Your Love Preconception Health
Updated June, 2021
articles from the specialists of the clinic "Mother and Child"
Arifullina Claudia Viktorovna
Gastroenterologist
Clinical Hospital "AVICENNA" GC "Mother and Child"
There is data on the frequency of twins in case of anomalies in the development of the uterus, characterized by its bifurcation (bicornuate uterus, having a septum in the cavity, etc. ). The cause of polyembryony may be the separation of blastomeres (in the early stages of crushing), resulting from hypoxia, cooling, acidity and ionic composition of the medium, exposure to toxic and other factors. Multiple pregnancy can occur: as a result of the fertilization of two or more simultaneously mature eggs, as well as the development of two or more embryos from one fertilized egg. nine0003
). The cause of polyembryony may be the separation of blastomeres (in the early stages of crushing), resulting from hypoxia, cooling, acidity and ionic composition of the medium, exposure to toxic and other factors. Multiple pregnancy can occur: as a result of the fertilization of two or more simultaneously mature eggs, as well as the development of two or more embryos from one fertilized egg. nine0003
Twins formed from two (three, etc.) eggs are called dizygotic (polyzygotic), those arising from one are called identical. The origin of fraternal twins (polyzygotic twins): the simultaneous maturation (and ovulation) of two or more follicles in one ovary is possible. There may be maturation of two or more follicles and ovulation in both ovaries.
A third way of the origin of fraternal (multi-ovular) twins is possible - the fertilization of two or more eggs that have matured in one follicle. The origin of identical twins: most often, the occurrence of identical twins is associated with the fertilization of an egg that has two or more nuclei. a single embryonic germ in the stage of crushing is divided into two parts; from each part an embryo (fruit) is formed. Twin twin. Fertilized eggs develop on their own. After penetration into the mucous membrane, each embryo develops its own aqueous and fleecy membranes; in the future, each twin forms its own placenta with an independent network of vessels, each fetal egg, except for the chorion and amnion, has an independent capsular membrane (decidua capsularis). In some cases, anastomoses are formed between the vessels of independent placentas. Twins can be same-sex (both boys or both girls) or different-sex (boy and girl). Their blood type can be the same or different. Identical twin. Identical twins have a common capsular and fleecy membrane and a common placenta; the vessels (both arterial and venous) of both twins in the placenta communicate with the help of numerous anastomoses. The water membrane of each twin is separate, the septum between the fetal sacs consists of two water membranes (biamniotic twins).
a single embryonic germ in the stage of crushing is divided into two parts; from each part an embryo (fruit) is formed. Twin twin. Fertilized eggs develop on their own. After penetration into the mucous membrane, each embryo develops its own aqueous and fleecy membranes; in the future, each twin forms its own placenta with an independent network of vessels, each fetal egg, except for the chorion and amnion, has an independent capsular membrane (decidua capsularis). In some cases, anastomoses are formed between the vessels of independent placentas. Twins can be same-sex (both boys or both girls) or different-sex (boy and girl). Their blood type can be the same or different. Identical twin. Identical twins have a common capsular and fleecy membrane and a common placenta; the vessels (both arterial and venous) of both twins in the placenta communicate with the help of numerous anastomoses. The water membrane of each twin is separate, the septum between the fetal sacs consists of two water membranes (biamniotic twins). nine0003
nine0003
Identical twins always belong to the same sex (both boys or both girls), look alike, have the same blood type.
In fraternal twins, the membranes in the septum are arranged as follows: amnion - chorion, chorion - amnion; with monozygotic amnion-amnion.
Important signs for the diagnosis are: blood type (and other blood factors), eye color, hair color, skin texture of the fingertips, shape and location of teeth. In identical twins, these signs are completely the same. Fraternal twins share the same similarities as normal siblings. nine0017
MULTIPLE PREGNANCY
With multiple pregnancy, increased demands are made on the woman's body: the cardiovascular system, lungs, liver, nights and other organs function with great stress. In this regard, multiple pregnancies are more difficult than single pregnancies.
- Pregnant women often complain of fatigue and shortness of breath, which increases towards the end of pregnancy.
 The cause of shortness of breath is a difficulty in the activity of the heart due to a significant displacement of the diaphragm by the bottom of the uterus, the size of which is larger in multiple pregnancy than in singleton. nine0031
The cause of shortness of breath is a difficulty in the activity of the heart due to a significant displacement of the diaphragm by the bottom of the uterus, the size of which is larger in multiple pregnancy than in singleton. nine0031 - Often there is a dilation of the veins of the lower extremities. By the end of pregnancy, there is often an increase in the urge to urinate due to the pressure of a large fetus on the bladder.
- Pregnant women often complain of heartburn and constipation.
- In multiple pregnancies, toxicosis occurs more often than in singleton pregnancies: vomiting, salivation, edema, nephropathy, eclampsia.
- With twins, polyhydramnios of one of the fetuses is often found, which leads to a sharp increase and hyperextension of the uterus, shortness of breath, tachycardia and other disorders. Polyhydramnios is more common in one of the identical twins. In some cases, the polyhydramnios of one twin is accompanied by an oligohydramnios of the other fetus.
 nine0031
nine0031 - Premature termination of multiple pregnancies often occurs.
- With twins, preterm birth occurs in at least 25% of women.
- Prematurity is more common in triplets than in twins. The greater the number of gestated fetuses, the more often preterm births are observed.
- Development of term twins is normal in most cases. However, their body weight is usually less than that of single fetuses. Often there is a difference in body weight of twins by 200-300 g, and sometimes more. nine0031
- Uneven development of twins is associated with unequal intake of nutrients from a single placental circulation.
- Often there is a difference not only in weight, but also in the length of the body of the twins. In connection with this, the theory of supergenesis (superfoetatio) was put forward. Proponents of this hypothesis believe that fertilization of eggs of different ovulation periods is possible, i.e., the onset of a new pregnancy in the presence of an already existing, previously occurring, pregnancy.
 nine0031
nine0031 - Due to the uneven delivery of nutrients and oxygen, a significant developmental disorder and even death of one of the twins can occur. This is more commonly seen in identical twins. The dead fetus is squeezed by the second, well-growing fetus, the amniotic fluid is absorbed, the placenta undergoes regression. The compressed mummified fetus ("paper fetus") is released from the uterus along with the placenta after the birth of a live twin. Polyhydramnios of one fetus, which occurs during multiple pregnancies, often also prevents the other twin from developing correctly. With pronounced polyhydramnios, certain anomalies in the development of the fetus, which grows with an excess of amniotic fluid, are often observed. Rarely, fused twins are born (fusion can be in the head, chest, abdomen, pelvis) and twins with other malformations. nine0031
- The position of the fetus in the uterine cavity in most cases (about 90%) is normal. In the longitudinal position, different presentation options are observed: both fetuses are presented with the head, both with the pelvic end, one with the head, and the other with the pelvic end.
 With longitudinal presentation, one fetus may be behind the other, which makes diagnosis difficult. Less commonly observed is the longitudinal position of one fetus and the transverse position of the other. The most rare is the transverse position of both twins. nine0031
With longitudinal presentation, one fetus may be behind the other, which makes diagnosis difficult. Less commonly observed is the longitudinal position of one fetus and the transverse position of the other. The most rare is the transverse position of both twins. nine0031 - Position of the twins in the uterus, both fetuses are presented with the head, one fetus is presented with the head, the second - with the pelvic end, both fetuses are in the transverse position
- In case of multiple pregnancies, women are taken to a special account and carefully monitored. When the earliest signs of complications appear, the pregnant woman is sent to the pregnancy pathology department of the maternity hospital. Given the frequent occurrence of preterm birth, it is recommended that a pregnant woman with twins be sent to the maternity hospital 2 to 3 weeks before delivery, even in the absence of complications. nine0031
RECOGNITION OF MULTIPLE PREGNANCY
Diagnosis of multiple pregnancy often presents significant difficulties, especially in its first half. In the second half, towards the end of pregnancy, the recognition of twins (triplets) is facilitated. However, diagnostic errors occur during the study at the end of pregnancy and even during childbirth.
In the second half, towards the end of pregnancy, the recognition of twins (triplets) is facilitated. However, diagnostic errors occur during the study at the end of pregnancy and even during childbirth.
When recognizing a multiple pregnancy, the following signs are taken into account: nine0017
- The enlargement of the uterus in multiple pregnancy occurs faster than in pregnancy with one fetus, so the size of the uterus does not correspond to the gestational age. The bottom of the uterus is usually high, especially at the end of pregnancy, the circumference of the abdomen during this period reaches 100-110 cm or more.
- The following signs are unstable and not sufficiently reliable: a) deepening of the uterine fundus (saddle uterus), the formation of which is associated with protrusion of the corners of the uterus with large parts of the fetus; b) the presence of a longitudinal depression on the anterior wall of the uterus, which is formed as a result of the fruits that are in a longitudinal position adjacent to each other; c) the presence of a horizontal groove on the anterior wall of the uterus with the transverse position of the fetus.
 nine0031
nine0031 - The small size of the presenting head with a significant volume of the pregnant uterus and the high standing of its bottom also make it possible to suspect a multiple pregnancy. The presence of this sign is explained by the fact that the study determines the head of one and the pelvic end (in the bottom of the uterus) of another fetus, which lies slightly higher.
- Feeling the movement of the fetus in different places and probing the parts of the fetus in different parts of the abdomen (both on the right and on the left) also indicate multiple pregnancies. nine0031
Make an appointment
to the doctor - Arifullina Claudia Viktorovna
Clinical Hospital "AVICENNA" GC "Mother and Child"
GastroenterologyPediatric Gastroenterology
By clicking on the submit button, I consent to the processing of personal data
Attention! Prices for services in different clinics may vary. To clarify the current cost, select a clinic
nine0002 Clinical Hospital "AVICENNA" GC "Mother and Child"Novosibirsk Center for Reproductive MedicineAll directionsGynecological proceduresSpecialist consultations (adults)Specialist consultations (children)Laboratory of molecular geneticsGeneral clinical studiesProcedure roomTherapeutic studiesUltrasound examinations for adults
nine0002 01.
Gynecological procedures
02.
Consultations of specialists (adults)
03.
Consultations of specialists (children's)
04.
Laboratory of molecular genetics
05.
General clinical studies
06 06.
Treatment Room
07.
Therapeutic Research
08.
Adult Ultrasound
Nothing found
The administration of the clinic takes all measures to update the price list posted on the website in a timely manner, however, in order to avoid possible misunderstandings, we advise you to clarify the cost of services and the timing of the tests by calling
How is the pregnancy of twins | gently sloping booth "Leleka"
Before describing the course of multiple pregnancy, it should be noted that the course of pregnancy has individual characteristics for each woman. There are no universal recommendations that would suit absolutely all pregnant women with one fetus or with several. Therefore, in this article we have tried to describe the general points that are most common, and which should be paid attention to the expectant mother. nine0003
Therefore, in this article we have tried to describe the general points that are most common, and which should be paid attention to the expectant mother. nine0003
How to detect twin pregnancy
Thanks to modern diagnostic methods, multiple pregnancy can be detected at an early stage. First, a doctor can diagnose twins during a routine examination - by noting the rapid increase in the size of the uterus or by hearing a double heartbeat. An experienced specialist can diagnose twins after 4 weeks of pregnancy. Secondly, twins are diagnosed during an ultrasound examination. This usually happens after 12 weeks. Prior to this, the expectant mother can only assume that she is carrying twins - for example, based on family history and the frequent occurrence of twins in the family. Blood tests are not yet a reliable way to determine twins. nine0003
How twin pregnancy proceeds
All stages of fetal development in a multiple pregnancy occur at the same time as in a single fetus. Therefore, the expectant mother can focus on the usual calendar for pregnant women. There are two main risks that a woman must take into account: this is the burden on the mother's body and the increased likelihood of complications.
Therefore, the expectant mother can focus on the usual calendar for pregnant women. There are two main risks that a woman must take into account: this is the burden on the mother's body and the increased likelihood of complications.
Great burden on the mother's body
Two fetuses develop in a woman's body at once. They require more oxygen, more nutrients, their vital activity leads to an increased load on the excretory system. Any infection or pathology immediately creates a risk for three at once: for the mother and for the second fetus. nine0003
Therefore, during multiple pregnancy, it is especially important for a woman to walk a lot in the fresh air, eat right and regularly, monitor body hygiene, and consult a doctor at the first alarming signs.
Increased likelihood of complications
Alas, not all women can bear two children normally. Approximately in the fifth part, the involution of the second fetal egg occurs: even in the first trimester, it freezes and decreases in size, while the second fetus continues to develop. nine0003
nine0003
If both fetuses develop evenly, the difficulties do not end there. Due to the lack of iron in the mother's body, anemia, or anemia, can develop. Therefore, in multiple pregnancies, iron preparations are often prescribed.
Due to the large weight of the abdomen in the later stages, placenta or fetal previa may form. The placenta blocks the exit from the uterus, or the position of the fetus makes natural childbirth impossible. In these cases, resort to caesarean section. nine0003
Premature aging of the placenta and premature birth - due to the fact that the placenta has to provide oxygen and nutrients to two fetuses at once, it quickly wears out and ages. Because of this, and also because of a number of similar reasons, premature birth can begin. To reduce the risk of preterm labor, pregnant women may be prescribed drugs that relax the muscles.
Is a caesarean section mandatory during pregnancy with twins
No.