First postpartum ovulation symptoms
5 Signs of Ovulation After Giving Birth
5 Signs of Ovulation After Giving Birth | NatalistHome > Learn > Postpartum > >5 Signs of Ovulation After Giving Birth
Jan 09, 23 ● 10 min
Wondering how to tell the signs of ovulation after giving birth? Read on to learn more about what to look for.
By OBGYN and fertility expert Dr. Kenosha Gleaton
There are many changes in the body throughout pregnancy, childbirth, and postpartum. These changes also vary greatly from person to person and can depend on a few different factors.
Postnatal care
Postnatal care is just as important as prenatal care. Childbirth puts your body through a lot of stress and it’s important to care for it however possible, including taking a postnatal vitamin and prioritizing self care. You may be experiencing hair loss, sore nipples, dehydration, and if you’re planning on breastfeeding, you’ll likely need to up your caloric intake an extra 400-500 calories a day. Now, let’s talk about ovulating after giving birth!
Why doesn’t ovulation occur immediately after giving birth?
There is about a six week period following birth known as the puerperium, which is full of changes in the body to get back to pre-pregnancy functioning. Organs like the uterus reduce down to their original sizes and functions, hormone changes are occuring, the placenta is lost, and lactation is beginning. This is the process one goes through to transition from being pregnant to postpartum and potentially breastfeeding.
Lactation has a huge impact on ovulation because of the body’s natural hormonal response. Prolactin is a hormone that is released during pregnancy and while breastfeeding, it’s responsible for lactation, tissue development, and many other processes. Prolactin levels will increase and remain fairly constant during breastfeeding, but if someone chooses not to breastfeed or is unable to breastfeed, levels will drop.
This is important to note as the presence of prolactin actually inhibits the release of luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) which are two vital hormones for ovulation. LH is the hormone that is measured when using ovulation tests, and is responsible for the release of a mature egg during ovulation, FSH is the hormone that helps the egg grow. When prolactin is present in high amounts, LH and FSH are much less likely to circulate in the body and trigger ovulation.
LH is the hormone that is measured when using ovulation tests, and is responsible for the release of a mature egg during ovulation, FSH is the hormone that helps the egg grow. When prolactin is present in high amounts, LH and FSH are much less likely to circulate in the body and trigger ovulation.
How soon do you ovulate after giving birth?
Not everyone has the same timeline on resuming their menstrual cycle after giving birth, and menstruation and ovulation restarting following childbirth vary greatly depending on the person and whether or not they’re breastfeeding. For those that do not lactate, the first period can occur around 45 to 64 days following birth and ovulation can occur between 45 and 94 days postpartum. It’s not uncommon for some to have a few anovulatory cycles (a menstrual cycle without the release of an egg) before ovulation begins again. Earlier ovulation is possible in nonlactating people and has happened before, with ovulation occurring as soon as 25 to 27 days postpartum.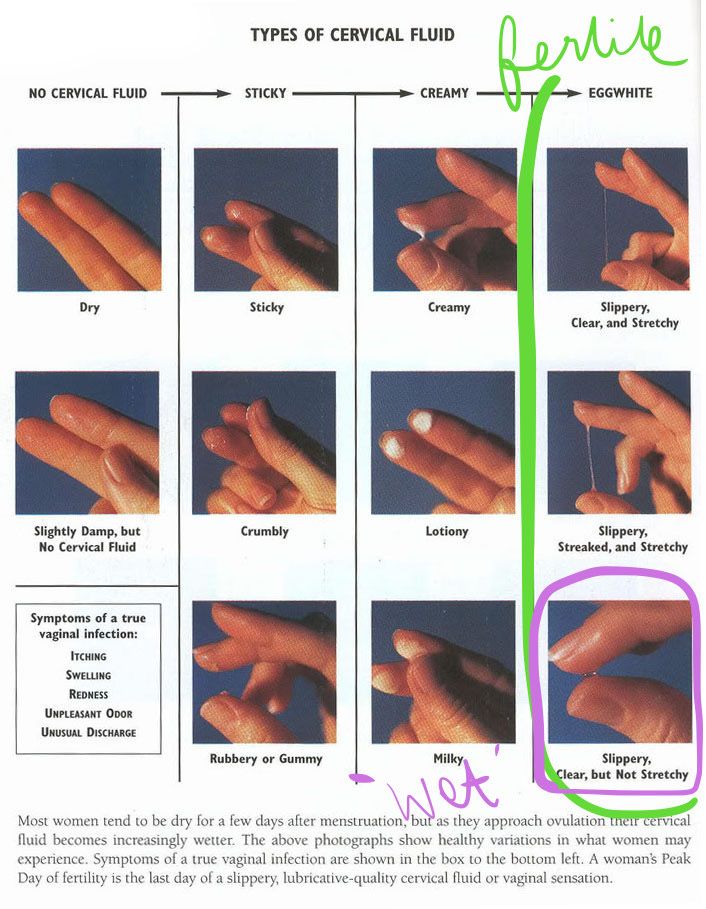
For those who breastfeed, ovulation and menstruation are much more delayed. Lactational amenorrhea (LAM) is a method of birth control that relies on regular breastfeeding to suppress ovulation and menstruation from restarting and is effective until about six months postpartum. If breastfeeding frequency or duration is reduced, there is a risk that ovulation can begin earlier, so back up contraception should be used if there is no intention to conceive. It’s also unclear whether or not pumping has an effect on LAM. It is possible to ovulate before your period starts, so keep this in mind when thinking about family planning and contraceptive methods. Read more about postpartum contraception on ACOGs website, or check out the Natalist blog for more information on postpartum, ovulation, and more.
What are signs of ovulation after giving birth?
The best and most effective way to know when you’re ovulating is by measuring luteinizing hormone using ovulation tests. If you’re not breastfeeding or have stopped breastfeeding and are expecting ovulation to begin again, try testing regularly to keep track of your hormone levels. When the time does come for ovulation to restart postpartum, there are a few signs that you may notice, including:
When the time does come for ovulation to restart postpartum, there are a few signs that you may notice, including:
1. Changes in cervical mucus
Your cervical mucus can give you some insight into where you are in your cycle. When nearing ovulation, cervical mucus typically changes to an egg-white consistency, it will be slippery, translucent, and slippery. This is a sign of fertile cervical mucus and is an indicator of ovulation.
2. Basal body temperature
Your lowest resting body temperature is known as your basal body temperature (BBT), and research shows that there is a slight increase in BBT around ovulation. This isn’t always the case for everyone, as about 20% of those studied didn’t have noticeable differences in temperature despite ovulating, but it can be a good way to track ovulation along with ovulation tests, cervical mucus tracking, or when accompanied by other symptoms.
3. Ovulation pain
Ovulatory pain or cramping is experienced in about 40% of people and is often a noticeable one-sided pain in the abdomen or lower back.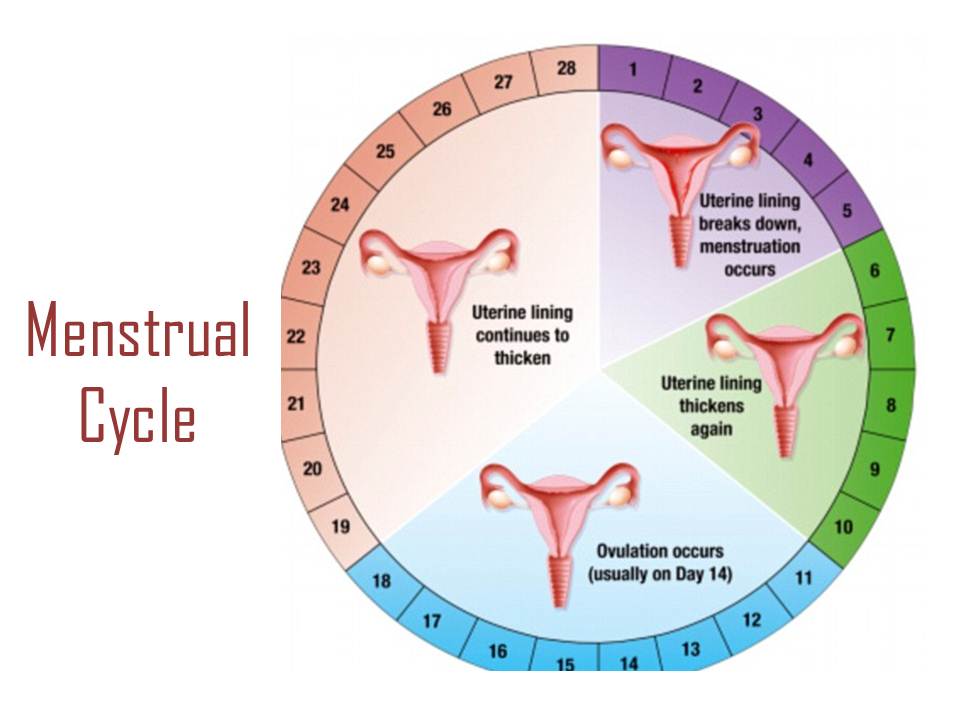 Ovulation pain can be dull or sharp and may last for a few hours to a few days. Pain may also be accompanied by bloating. If you’re experiencing extreme pain coupled with nausea, fever, heavy bleeding, or if pain lasts for longer than a few days, you should see your healthcare provider to rule out other conditions.
Ovulation pain can be dull or sharp and may last for a few hours to a few days. Pain may also be accompanied by bloating. If you’re experiencing extreme pain coupled with nausea, fever, heavy bleeding, or if pain lasts for longer than a few days, you should see your healthcare provider to rule out other conditions.
4. Painful or sore breasts
Breast pain is known as mastalgia and is a common symptom throughout the menstrual cycle as well as during ovulation, occurring in up to 66% of people.
5. Increased sex drive
It’s also a researched symptom of ovulation that some women experience an increased sex drive.
Shop Postpartum Products
What are signs of early pregnancy after giving birth?
Although it’s rare, it is possible for pregnancy to occur as soon as a few weeks postpartum. It’s more likely in non-lactating women for pregnancy to be possible about a month and a half to three months postpartum. For breastfeeding women, pregnancy may occur as early as six months, potentially sooner if breastfeeding frequency or duration decreases.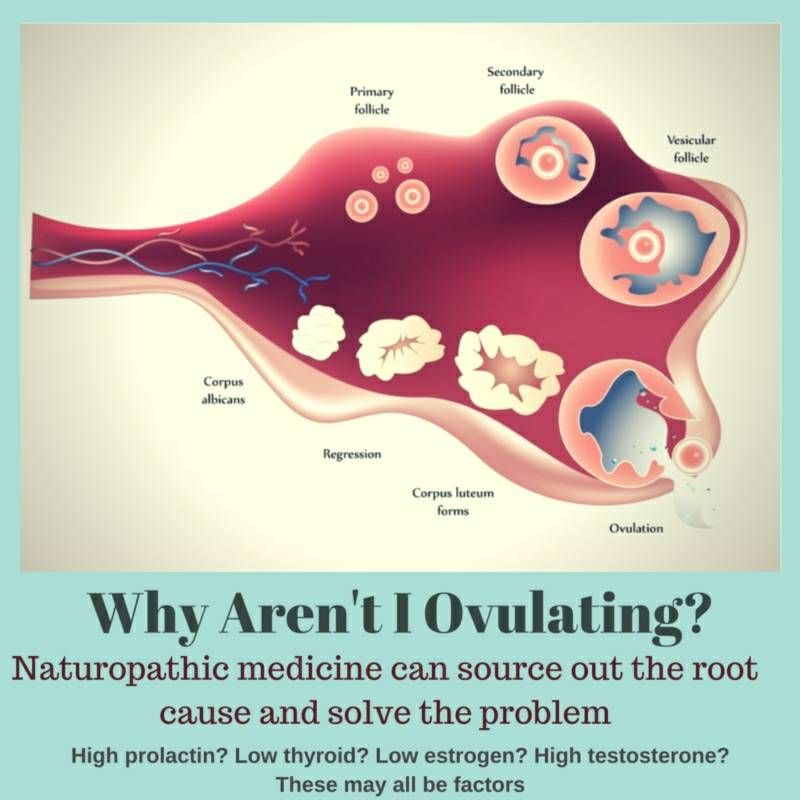 Most experts advise women to wait at least 18 months between pregnancies, so you may want to discuss contraception options with your healthcare provider after giving birth.
Most experts advise women to wait at least 18 months between pregnancies, so you may want to discuss contraception options with your healthcare provider after giving birth.
Early signs of pregnancy after giving birth include:
1. Missed period
Having a late or missed period is one of the most obvious signs of pregnancy. When postpartum, pregnancy can occur before menstruation ever begins, so it’s important that you keep track of your cycle, regularly use pregnancy tests and ovulation tests if you are sexually active, and keep an eye out for other symptoms.
2. Exhaustion
It’s normal to feel some fatigue while recovering from childbirth and breastfeeding, but if you’re noticing that you feel more tired than usual or need more sleep than usual, you could be experiencing some pregnancy fatigue. This is caused by increased levels of hormones like progesterone during early pregnancy.
3. Frequent urination
Having to use the bathroom frequently is a result of increased blood supply during pregnancy and can be a very early symptom of pregnancy.
4. Morning sickness
Another common sign of pregnancy is nausea or vomiting at any time of the day, despite the common term “morning sickness.” If you’re experiencing extreme vomiting and can’t keep water down, be sure to see a doctor immediately to avoid dehydration and get confirmation of pregnancy or another condition.
5. Sore breasts
Mastalgia can be a sign of ovulation, an incoming period, or pregnancy. A change in the color of the areolas is a likely sign of pregnancy as well.
6. Implantation bleeding
Some bleeding may occur as an early sign of pregnancy as well and is the result of implantation bleeding. It can be easy to confuse this as period spotting, so be sure to take a pregnancy test or see your doctor to confirm the cause of any bleeding.
If you suspect you could be pregnant, it’s important to act fast and find out as soon as you can using early pregnancy tests and visiting your healthcare provider.
What to expect for the first period postpartum
Your first period postpartum is likely to be different from your normal menstruation, and you may even have some abnormal menstrual cycles for a few months after giving birth. This could include anovulatory cycles when no ovulation occurs, or irregular periods that are longer or shorter than usual or don’t occur every month. It’s also common to experience cramping, heavier bleeding, and small blood clots in the first few periods following birth. Be sure to mention any clotting, pain, or irregularities to your healthcare provider just in case.
This could include anovulatory cycles when no ovulation occurs, or irregular periods that are longer or shorter than usual or don’t occur every month. It’s also common to experience cramping, heavier bleeding, and small blood clots in the first few periods following birth. Be sure to mention any clotting, pain, or irregularities to your healthcare provider just in case.
Key Takeaways
-
It’s common to experience sore nipples, hair loss, postpartum depression, and potentially dehydration after birth and while breastfeeding. Be sure to let your doctor know of any symptoms you’re experiencing.
-
Ovulation typically does not occur immediately after birth due to a change in hormones and the body slowly adjusting back to its pre-pregnancy conditions.
-
Prolactin is a hormone that is released during pregnancy and lactation that inhibits the release of two key hormones responsible for ovulation: FSH and LH. The longer someone breastfeeds regularly, the longer it will take for menstruation and ovulation to occur, although every one’s experience is unique.

-
In those that do not breastfeed, ovulation can occur as early as a few weeks postpartum to two or more months postpartum.
-
In those that do breastfeed, the lactational amenorrhea method is a way of preventing pregnancy for up to or around six months postpartum.
-
Signs of ovulation after giving birth include a change in body temperature, cervical mucus, ovulation pain, painful breasts, and an increased sex drive.
-
You can get pregnant before having a period after giving birth, so be sure to have a backup method of contraception ready when you are sexually active again.
Shop Products From This Article
Subscribe & Save $7.00
Postpartum Essentials Bundle
Bundle & save on postpartum support
$75 $68
Share on:
Related Blogs
Postpartum 8 min
Can You Take Biotin While Breastfeeding?
Read MorePostpartum 9 min
5 Benefits of Taking Collagen Postpartum
Read MorePostpartum 5 min
How Long Do Cracked Nipples Take to Heal When Breastfeeding?
Read MorePostpartum 17 min
Breastfeeding Cracked Nipples: Causes and Remedies
Read MoreShop Products
Subscribe & Save $5.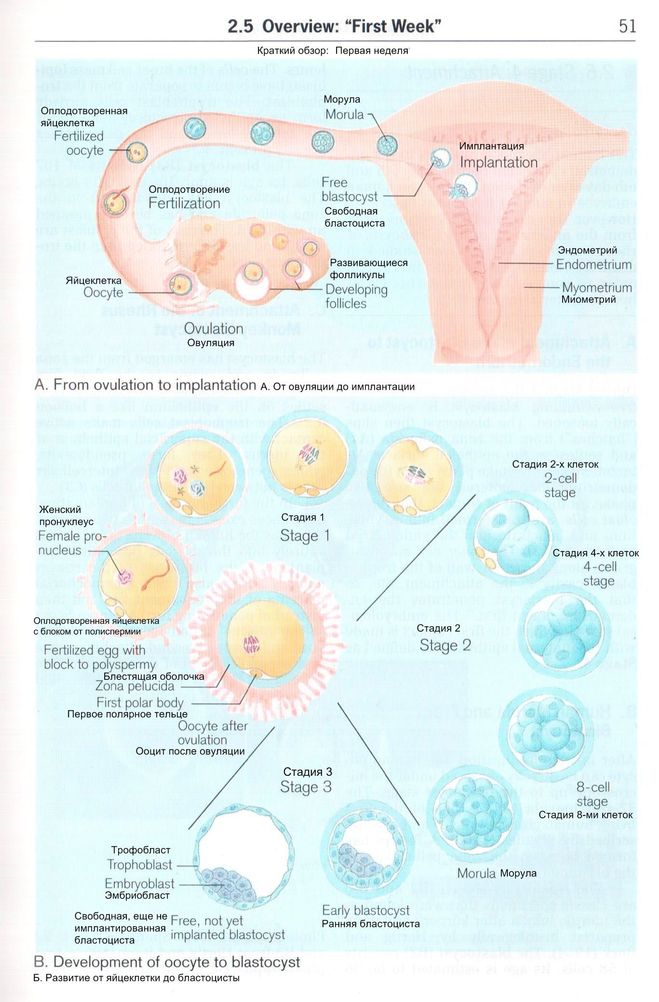 00
00
Prenatal Daily Packets
Vegan prenatal daily packets
$60 $55
Subscribe & Save $3.00
Magnesium Plus
Pregnancy-safe drink mix to support relaxation‡
$35 $32
Subscribe & Save $2. 00
00
Prenatal Gummies
Doctor-formulated & delicious prenatal gummies
$35 $33
Shop All
Subscribe & Save $5.00
Prenatal Daily Packets
Vegan prenatal daily packets
$60 $55
Subscribe & Save $3. 00
00
Magnesium Plus
Pregnancy-safe drink mix to support relaxation‡
$35 $32
Subscribe & Save $2.00
Prenatal Gummies
Doctor-formulated & delicious prenatal gummies
$35 $33
Subscribe & Save $3. 00
00
CoQ10 Liquid Capsules
Antioxidant fertility supplement
$35 $32
Shop All
Subscribe & Save $4.00
The Test Pack
Pregnancy & ovulation tests
$40 $36
Shop All
Sign Up For 10% Off Your First Order!
Sign up for insider access, exclusive deals, and OBGYN insights!
Signs of Ovulation While Breastfeeding: Can You Get Pregnant?
Skip to contentIn general, there’s no ovulation while breastfeeding. Actually, breastfeeding your baby exclusively for the first six months is generally considered to be natural birth control. Namely, to produce milk, your body also produces high levels of a hormone called prolactin. This hormone, in turn, suppresses the production of ovulation hormones. However, it’s not recommended to rely only on breastfeeding as birth control as you could still get pregnant. It’s nice to give your baby a little sibling soon, but getting pregnant sooner than two years postpartum is not recommended in terms of the mother’s health. Therefore, you should also use some other form of birth control during this period. The thing with breastfeeding is that it’s rarely ever exclusive for the entirety of six months. What’s more, your body’s production of prolactin might start decreasing sooner than expected.
Actually, breastfeeding your baby exclusively for the first six months is generally considered to be natural birth control. Namely, to produce milk, your body also produces high levels of a hormone called prolactin. This hormone, in turn, suppresses the production of ovulation hormones. However, it’s not recommended to rely only on breastfeeding as birth control as you could still get pregnant. It’s nice to give your baby a little sibling soon, but getting pregnant sooner than two years postpartum is not recommended in terms of the mother’s health. Therefore, you should also use some other form of birth control during this period. The thing with breastfeeding is that it’s rarely ever exclusive for the entirety of six months. What’s more, your body’s production of prolactin might start decreasing sooner than expected.
To get rid of any doubts or worries you may have as you start planning to expand your family, it would be best to see a preconception and obstetrics specialist.
6 Signs of Ovulation While BreastfeedingIf you start ovulating while still breastfeeding, you can get pregnant. Every woman is different, meaning that when and what signs of ovulation after giving birth will show depend on the individual.
Every woman is different, meaning that when and what signs of ovulation after giving birth will show depend on the individual.
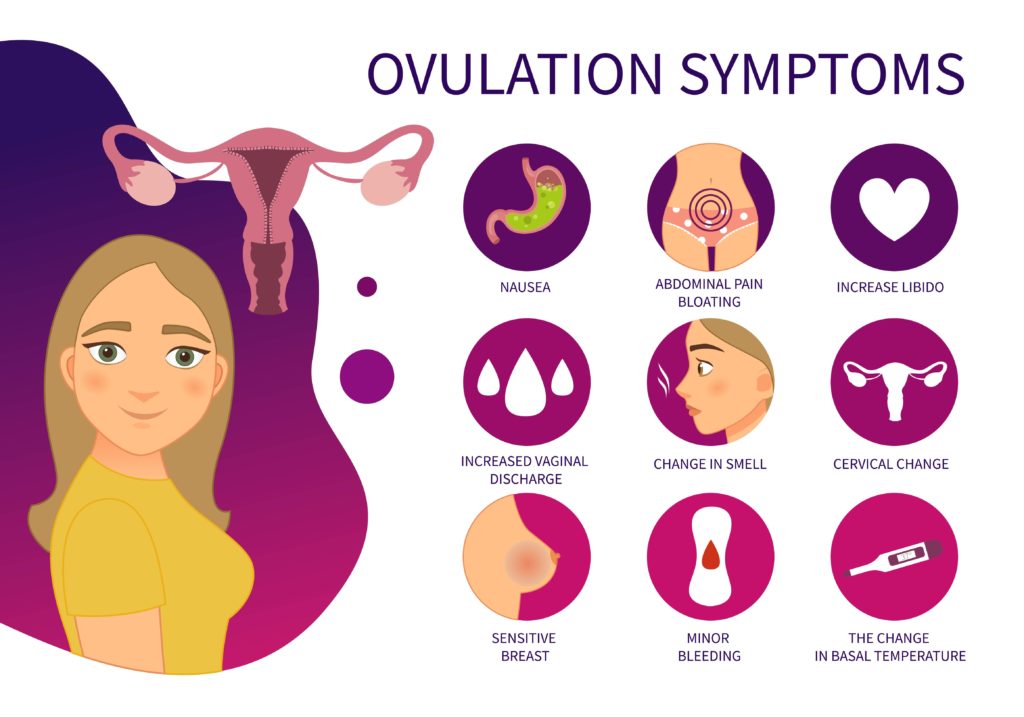
Getting your period is a clear sign of returning fertility while breastfeeding. If the egg is released and you bleed, you can expect ovulation to follow as well. If you don’t want to get pregnant again so soon after giving birth, start using some other form of birth control. Of course, if you so desire, you could use this chance to start planning another pregnancy, but, as mentioned, that’s not the best health decision. Pregnancies in such short intervals do carry certain risks.
2. Cervical Mucus Gets LighterPay attention to your discharge. If suddenly the cervical mucus goes from sticky and thick to being rather light and clear to the point of making you feel wet, you are ovulating, and pregnancy after ovulation is more than possible.
3. Slight Temperature RiseIf it was common for you to feel a bit feverish post ovulation before you got pregnant, and you start feeling seemingly random increases in temperature again, this could be one of the signs of ovulation while breastfeeding. Obviously, this slight increase is nothing concerning, as long as it’s not a really high fever, but it should tell you it’s time to start tracking your menstrual patterns again.
Obviously, this slight increase is nothing concerning, as long as it’s not a really high fever, but it should tell you it’s time to start tracking your menstrual patterns again.
Another one of the signs of ovulation after giving birth is probably not the one you missed. Once you start feeling the cramps in your abdomen again, you’re probably resuming your menstrual cycle. Cramps actually stop when the egg gets released, which is when you’re at your most fertile phase of the cycle.
5. A Libido BoostSome of the signs of returning fertility while breastfeeding will present themselves in the body’s desire to put that fertility to good use. With estrogen surging again, you will probably notice that your inclination for sexual intercourse is higher than before. And with a boost in estrogen and libido, also comes ovulation.
6. Tender BreastsJust like cramps, breast tenderness is part of the menstrual cycle that could also signal ovulation while breastfeeding. Of course, breasts will be tender because of breastfeeding too, which is why you should also pay attention to other signs of ovulation while breastfeeding. You should differentiate breast tenderness from actual breast pain; if you feel like something’s wrong and the pain doesn’t seem to subside, make sure to talk to your doctor.
Of course, breasts will be tender because of breastfeeding too, which is why you should also pay attention to other signs of ovulation while breastfeeding. You should differentiate breast tenderness from actual breast pain; if you feel like something’s wrong and the pain doesn’t seem to subside, make sure to talk to your doctor.
Even if you recognize signs of returning fertility while breastfeeding, that doesn’t necessarily mean you should rush to get pregnant again. You may want a big family, and that’s perfectly fine and possible, but patience is recommended as it will generally be safer and healthier for both you and the fetus.
Basically, going through labor causes bodily trauma, especially in the case of women who went through a C-section. As such, the body needs time in order to recover. Even if your previous pregnancy went perfectly, forcing your body through another pregnancy so soon could lead to complications with both your and your child’s health. Sometimes, the complications can be so serious that they can lead to worst-case scenarios. For some women, just dealing with the early signs of pregnancy again so fast could be dangerous.
Sometimes, the complications can be so serious that they can lead to worst-case scenarios. For some women, just dealing with the early signs of pregnancy again so fast could be dangerous.
When you look at the bigger picture, it pays off to be patient. What’s more, your kids will get along just fine with a couple of years of an age difference. It will also be a lot easier for you to take care of a baby and a toddler at the same time, instead of two babies.
How to Exclusively Breastfeed?You can try and avoid ovulation while breastfeeding by committing yourself to exclusively breastfeed your baby for the first six months. However, keep in mind that, in practice, this is actually rather difficult. Less than 33% of women manage to exclusively breastfeed during just the first three months. But, if you’re set on this goal, there are some practices that could help you reach it:
- Educate yourself about the process of breastfeeding even before it’s time to give birth.
 That way, you’ll be more prepared for it once the baby comes.
That way, you’ll be more prepared for it once the baby comes. - After you give birth, you’ll have a chance to consult with a lactation specialist in the hospital. Make sure to have them explain every single detail to you. Don’t hesitate to ask whether they make home visits as well.
- If you want to breastfeed exclusively, and there’s no medical reason not to, then you obviously cannot use anything else in your baby’s diet. So, no formula or water is allowed.
- You have to listen to your baby during this period. Whenever your child wants to eat, you should feed them. The more frequent you breastfeed, the better your breast milk production will be. In general, anywhere between eight and twelve feedings in 24 hours are ideal.
- The fact is that prolactin production is the highest during the night. Milk pumping or feeding your child at night will further boost prolactin levels.
- Make sure not to use any pacifiers or bottles during this period in order to stimulate oxytocin production through the baby’s sucking.
Following these tips is likely to postpone the return of your ovulation and menstrual cycle. On the other hand, if you’re looking for signs of ovulation after giving birth with anticipation, you should change your habits. In that case, you should minimize the number of breastfeeds, start introducing formula and bottles, and ultimately, avoid getting too stressed about it.
It’s true that things can get a bit confusing in regards to the menstrual cycle after you give birth. However, in most cases, it’s your habits and choices that can affect just how fast you’ll start ovulating again. Still, it’s important to mention that it’s not a good idea to rely just on breastfeeding as birth control if you don’t want another pregnancy.
Of course, don’t hesitate to get in touch with us at University Park OBGYN if you’re in need of any advice or medical help when it comes to your reproductive health. You’ll be in the hands of the best gynecologist in Florida whom you can fully trust and open up to.
Search for:
Recent Posts
- Remedies For Vaginal Dryness
- Low Estrogen Levels: How Low Estrogen Effects Your Body
- Signs You Might Have a Vaginal Yeast Infection
- Gynecology Procedures: Most common Gynecologic Surgeries
- The Ways In Which The Body Changes During Pregnancy
Archives
- December 2022
- November 2022
- October 2022
- September 2022
- August 2022
- July 2022
- June 2022
- May 2022
- April 2022
- March 2022
- February 2022
- January 2022
- December 2021
- November 2021
- October 2021
- September 2021
- August 2021
- July 2021
- June 2021
- May 2021
When menstruation starts after childbirth: how long after the birth of the child will menstruation
When does menstruation begin after childbirth
In women who do not breastfeed, the first menstruation occurs 7-8 weeks after childbirth. In the vast majority of nursing mothers, the menstrual cycle is restored later 3 . If the child is transferred to artificial feeding, ovulation can be observed as early as 27 days after the last breastfeeding 3 .
In the vast majority of nursing mothers, the menstrual cycle is restored later 3 . If the child is transferred to artificial feeding, ovulation can be observed as early as 27 days after the last breastfeeding 3 .
Let's see why this happens and what changes are observed in the uterus and ovaries during this period.
Menstruation after childbirth
The uterus, the weight of which during pregnancy, excluding the fetus, increased to a kilogram, and the length - up to 39 cm, begins to decrease 2 . Its muscle fibers contract and undergo physiological decay and rebirth 2 . By the end of the postpartum period, it becomes the same as before conception - weighing about 50 g and a length of 8-9see 1 .
The inner surface of the uterus, to which the placenta was attached, gradually heals.

It is believed that the inner layer of the uterus (endometrium) is completely restored by 6-8 weeks and “freezes” in anticipation of the first menstrual cycle after childbirth 1.2 .
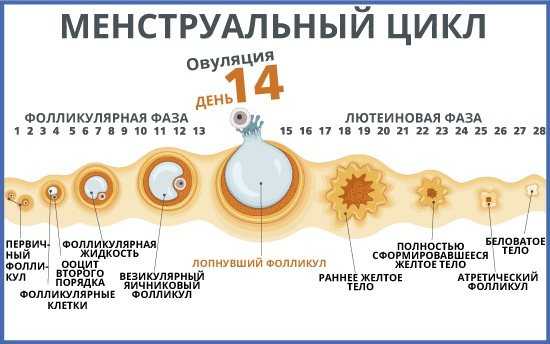
Active changes are also taking place in the ovaries. The follicles begin to mature in them. The accompanying hormonal changes lead to the resumption of menstruation 3 .
What determines the onset of menstruation after childbirth
The process of restoring the menstrual cycle is primarily affected by lactation - the formation of milk in the mammary glands 3 . The hormone prolactin, which is responsible for this process, inhibits the onset of cyclic processes in the ovaries 3.4 .
Breastfeeding an infant supports lactation and prolactin release. Therefore, if a mother breastfeeds her baby exclusively and at least 6-10 times a day (with an interval of 4 hours during the day and 6 at night), postpartum lactational amenorrhea is usually observed, that is, the absence of menstruation 3.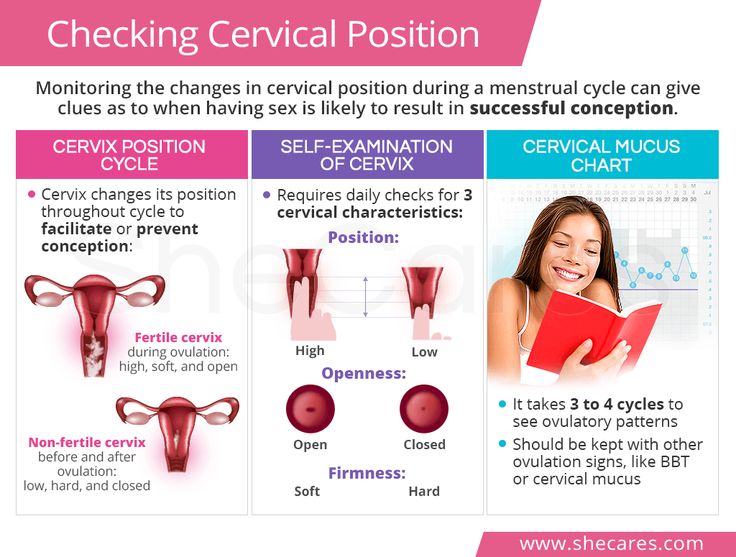 4 .
4 .
According to some reports, in lactating women, the first menstruation is observed on average 4.5 months after childbirth. Some do not have them until the end of lactation 3 .
How long after childbirth does menstruation begin if the woman had a caesarean section?
If milk is scarce and the woman is not breastfeeding, the first menstruation may start as early as 4 weeks after the caesarean section 3 . This is 2-4 weeks earlier than after natural childbirth 3 . Preservation and enhancement of lactation postpones the start of the cycle indefinitely 3 .
How can the cycle and nature of menstruation change after childbirth
The body needs time to return all organs and functions to the state it was before pregnancy. Therefore, the restoration of the ovaries may be delayed 4 .
In 40% of women, a new egg matures already in the first menstrual cycle after the birth of a child 4 . However, more often at the beginning of the postpartum period, ovulation - the release of a mature egg from the follicle - does not occur. Such cycles are called anovulatory. Their typical manifestation is irregular periods 4 . The duration of anovulatory cycles can be from 1.5 to 6 months 5 .
However, more often at the beginning of the postpartum period, ovulation - the release of a mature egg from the follicle - does not occur. Such cycles are called anovulatory. Their typical manifestation is irregular periods 4 . The duration of anovulatory cycles can be from 1.5 to 6 months 5 .
How long do periods last after childbirth if there is no ovulation?
Periods that occur during anovulatory cycles are called dysfunctional uterine bleeding. They are abundant and sometimes last more than 10 days 5 . As soon as ovulation is restored, the cycle becomes what it was before the conception of the child 3 .
When to see a doctor
In the postpartum period, a woman should be especially attentive to her health. The slightest disturbances in well-being and the appearance of suspicious symptoms are a reason for contacting an obstetrician-gynecologist.
Below we will explain in which cases a doctor's consultation is urgently needed.
Postpartum hemorrhage
In the first months after childbirth, attention should be paid to the amount of discharge. Abundant discharge of blood or its impurities in the lochia - signs of postpartum hemorrhage 2 .
Bleeding in the late postpartum period, that is, after 24 hours and within 6 weeks after delivery 6 , occurs much less frequently than on the first day after the birth of a child - in 0.2-3% of cases 7 .
They may be caused by 6 :
- pieces of placenta in the uterus;
- too slow recovery of the size of the uterus;
- penetration into the uterine cavity of pathogens causing inflammation; nine0028
- bleeding disorder 6 .
Postpartum endometritis
According to statistics, postpartum endometritis is diagnosed in 4-5% of women who gave birth spontaneously, and after cesarean section, endometritis is detected in 10-15% 9 .
After the birth of a child, the inner surface of the uterus resembles an open wound, so pathogens from the vagina, penetrating into the uterine cavity, can easily cause inflammation 8 .
Signs of postpartum endometritis or inflammation of the lining of the uterus include:
- purulent lochia;
- fever;
- lower abdominal pain 1 .
What is important to know?
Not only the inner surface of the uterus, but also cracks, abrasions on the surface of the soft tissues of the cervix, vagina and perineum can become entry gates for infection to enter the body 2 . Therefore, in the postpartum period, it is extremely important to observe special rules of intimate hygiene.
During the first 8 weeks it is better to use special postpartum sanitary napkins. When menstruation returns after childbirth, you can replace the pads with tampons, for example, o.b.® ExtraDefence 10 . With soft, bi-directional SilkTouch® wings, these tampons adapt to your body shape and provide reliable protection during your period, day and night 10 .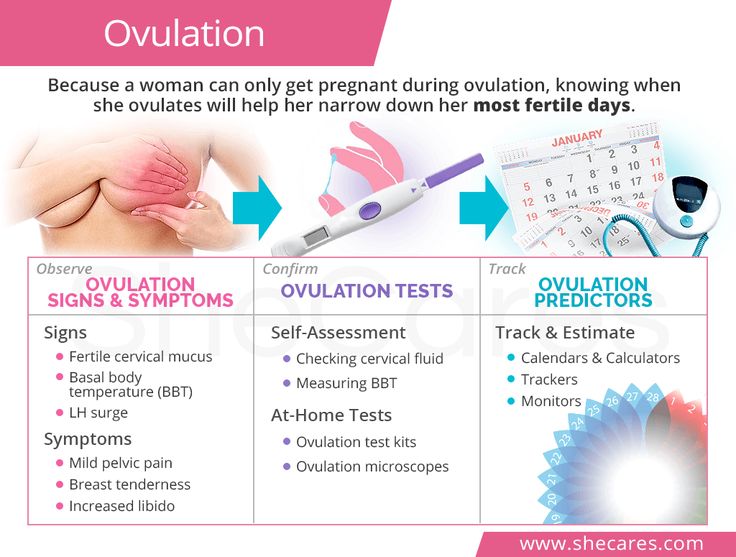
The processes of restoring the reproductive system after childbirth can proceed in different ways. They are influenced by the individual characteristics of the body, the course of pregnancy and childbirth, the nature of lactation and feeding the baby 2.3 . For example, after a caesarean section, recovery is 3 times slower than after a natural birth 3 . If the mother is breastfeeding, the uterus returns to normal faster 1 . Proper postpartum hygiene is an important part of caring for the female body.
The information in this article is for reference only and does not replace professional medical advice. For diagnosis and treatment, contact a qualified specialist.
Literature
- Zanko S. N., Radetskaya L. E., Zhukova N. P. Obstetrics / Vitebsk. - 2017. - 383 p. / ISBN 978-985-466-891-8
- Tayupova I. M., Sakhautdinova I. V., Kuleshova T. P. Physiology and pathology of the postpartum period // Ufa: BashNIPIneft.
 - 2014. - 59 p.
- 2014. - 59 p. - Khaskhanova L. Kh., Musaeva Ya. V. Physiological and pathological postpartum period // Grozny: Chechen State University Publishing House, 2016. – 96 p.
- Nazarova NM, Prilepskaya VN, Nekrasova ME Postpartum contraception: efficiency and safety // Gynecology. – 2018. - 20(2). - P. 5-8. nine0193 DOI: 10.26442/2079-5696_2018.2.5-8
- Zaidieva Ya. Z. Dysfunctional uterine bleeding in the age aspect // Medical Council / №3. - 2012. - S. 78-83. Belousova A. A., Aryutin D. G., Toktar L. R. Late postpartum hemorrhage // Obstetrics and gynecology: opinion news, training. 2019. V. 7, No. 3. S. 64-69. doi: 10.24411/2303-9698-2019-13009.
- Adamyan L. V, Kan N. E, Lomova N. A Postpartum endometritis // Clinical recommendations / 2016.
- Shulzhenko E.V., Zaritskaya E.N., Mirlas E.M., Borzunov M.N. -one hundred.
- O.B.® EXTRA DEFENCE Tampons / https://www.
 obtampons.ru/produkty/ob-extradefence.
obtampons.ru/produkty/ob-extradefence.
Postpartum hygiene
Congratulations! You have become a mother!
The postpartum period is no less important and responsible stage in the life of a family than pregnancy.
The postpartum period lasts 6-8 weeks (begins after the birth of the placenta and ends when the organs and systems that have changed during pregnancy return to their original state).
In the process of healing the inner surface of the uterus, postpartum discharge appears - lochia, which is a wound secret. Their character during the postpartum period changes: in the first days, lochia has a bloody character; from the 4th day, their color changes to reddish-brown; by the 10th day they become light, liquid, without blood, and after 3 weeks there is practically no discharge. There may be discomfort due to uterine contractions. To relieve discomfort, bend forward and gently massage your belly. If discomfort in the uterine area occurs during feeding, try choosing a different position. It is convenient to feed lying on your side. The stomach may ache for another reason. It hurts the abdominal muscles that were actively involved during childbirth, try to relax or do a light massage. nine0193 In most non-nursing women, menstruation occurs on the 6-8th week after childbirth, more often it comes without the release of an egg from the ovary. However, ovulation and pregnancy may occur during the first months after childbirth. In lactating women, the time of the onset of the first menstruation after childbirth can be delayed for many months.
It is convenient to feed lying on your side. The stomach may ache for another reason. It hurts the abdominal muscles that were actively involved during childbirth, try to relax or do a light massage. nine0193 In most non-nursing women, menstruation occurs on the 6-8th week after childbirth, more often it comes without the release of an egg from the ovary. However, ovulation and pregnancy may occur during the first months after childbirth. In lactating women, the time of the onset of the first menstruation after childbirth can be delayed for many months.
The normal postpartum period is characterized by a good general condition of the woman, normal temperature, sufficient lactation. For the prevention of infectious complications, strict adherence to sanitary and epidemiological requirements and personal hygiene rules is important. nine0009
POSTPARTUM HYGIENE
The strictest cleanliness is essential.
- The mother should take a shower twice a day (morning and evening), then wash the mammary gland with soap and brush her teeth.
- Particular attention should be paid to the cleanliness of hands. Nails should be cut short, hands should be washed more often with soap and be sure before each feeding of the child (if the hands are dirty, you can infect the child, infect the nipples). nine0028
- Among the hygienic measures of particular importance in the postpartum period is the maintenance of cleanliness of the external genitalia and the surrounding skin.
- Should be washed with warm water and soap (liquid with a dispenser, because microbes feel great on lumps) with a fluid stream, washing the genitals should be from front to back (from the pubis to the anus) after each visit to the toilet at least 4-5 times a day (you need to go to the toilet exactly at such a frequency that the filled bladder does not interfere with uterine contraction). nine0193 Wash hands cleanly before washing.
- Keep the pads clean, change them every 3-4 hours, regardless of fullness. Remove pads from front to back to prevent microorganisms from entering the vagina from the anus.
 If there are seams on the perineum, they should be washed thoroughly enough - you can simply direct a jet of water at it. After washing, you need to dry the perineum and the seam area by blotting the towel from front to back. nine0028
If there are seams on the perineum, they should be washed thoroughly enough - you can simply direct a jet of water at it. After washing, you need to dry the perineum and the seam area by blotting the towel from front to back. nine0028 - Do not take a bath for the first 6 weeks after giving birth. This is due to the fact that the entrance to the vagina is not yet closed enough and pathogenic microbes can penetrate into it along with water. It is clear that at this time you can not swim in the pool, river, lake, sea.
- The use of tight underwear is strictly excluded, as it puts significant pressure on the perineum, which disrupts blood circulation, preventing healing.
- If there are stitches on the perineum, a woman should not sit down for 7-14 days (depending on the degree of damage). At the same time, you can sit on the toilet already on the first day after childbirth. By the way, about the toilet. Many women are afraid of severe pain and try to skip bowel movements, as a result, the load on the muscles of the perineum increases and the pain intensifies.
 nine0028
nine0028
To avoid constipation after childbirth, do not eat foods that have a fixative effect. If the problem of constipation is not new to you, drink a tablespoon of vegetable oil before each meal. The stool will be soft and will not affect the healing process of the stitches.
- Underwear and bed linen must be cotton. We change underwear daily, bedding - at least once every three to five days.
- Stitches after caesarean section do not require special care. After the stitches and bandage are removed, you can take a shower. Do not scrub the seam area with a washcloth. With painful sensations in the anterior abdominal wall, a postpartum or postoperative bandage, which must be worn for 4 months, will help to cope. Young mothers are often interested in: will the seams come apart if you carry a baby in your arms? For the first 2-3 months after surgery, it is recommended to lift no more than your child's weight. nine0028
It happens that redness, irritation, bloody or purulent discharge occurs at the suture site.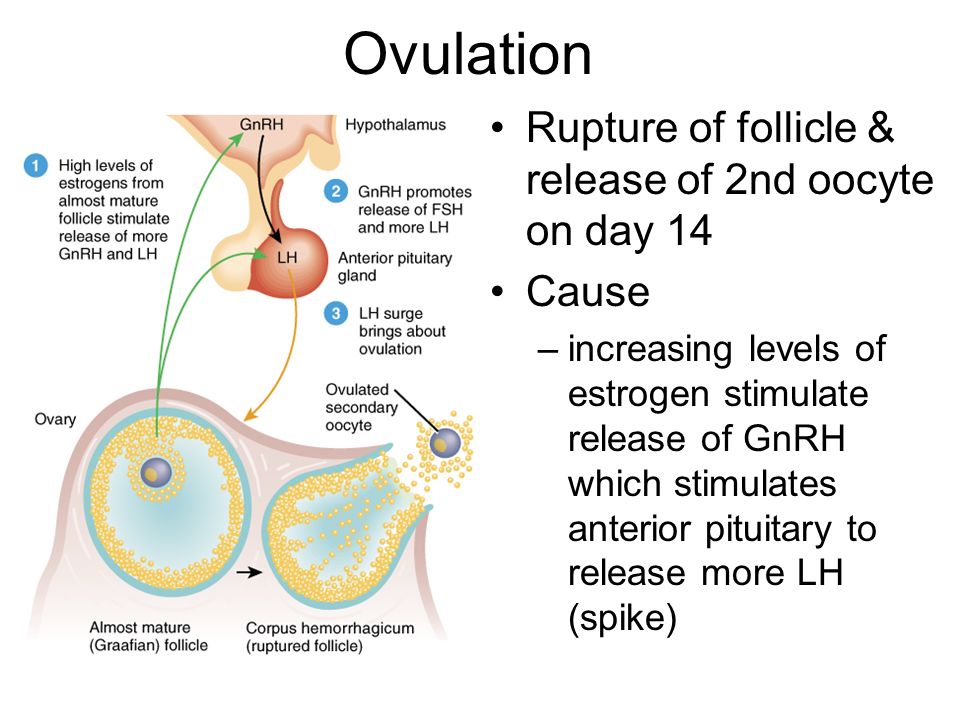 This indicates suppuration or divergence of the seams. Then you should immediately consult a doctor in a antenatal clinic.
This indicates suppuration or divergence of the seams. Then you should immediately consult a doctor in a antenatal clinic.
Sexual life after childbirth can be resumed after 6-8 weeks. By this time, the woman's body is already completely back to normal. Your doctor will advise you on contraceptives.
To fully recover from childbirth, at least two years must pass before the next pregnancy. nine0009
BREASTFEEDING
Breastfeeding should not be done according to the clock, but on demand, incl. in nighttime. At one feeding, put the baby on one breast so that he suckles for a long time and receives later milk, which contains brain and intelligence development factors, growth factors and immunoglobulins. Later, the milk comes in droplets like colostrum, the child sucks it intermittently. Sometimes the mother at this moment thinks that the child is indulging and tearing him off the breast. You don't need to do this. Let him let her go. nine0193 Breast milk is the best food for a baby!
- After the baby has had enough, the mother should carefully feel the mammary gland.
 If the breast is soft and there is no soreness and seals anywhere, then pumping is not necessary. If necessary, you can wash the mammary glands with warm water after feeding, starting from the nipple and ending with the armpit, and dry with a clean towel.
If the breast is soft and there is no soreness and seals anywhere, then pumping is not necessary. If necessary, you can wash the mammary glands with warm water after feeding, starting from the nipple and ending with the armpit, and dry with a clean towel.
Very useful for the breasts after childbirth and air baths, which are best taken after feeding, to give the breast the opportunity to rest, "breathe". The duration of such an air bath may not exceed 15-20 minutes, but the benefits of it are enormous. nine0009
- The nipple should be carefully inspected daily, the surface of which should not be cracked, and as a preventive measure, leave a drop of milk on the nipple and let it dry in the open air.
Only breast milk should be used as the main and only product for feeding a newborn. The use of nipples, horns and "pacifiers" is unacceptable, as this leads to a weakening of sucking in newborns and, accordingly, to incomplete emptying of the mammary gland, a decrease in prolactin production. nine0193 Are you worried about the question - do I have enough milk?
nine0193 Are you worried about the question - do I have enough milk?
To resolve this issue, you need to observe the child, if he urinates more than 6 times a day, then he receives a sufficient amount of milk. The reason for a decrease in the amount of milk can be:
- rare feeding break (3 or more hours)
- if you do not feed at night
- short feedings or by the hour
To increase the amount of milk, you need to rearrange the feeding regimen, feed often and for as long as you want child. Try to feed with one breast so that the baby sucks out milk later, you can strain the empty breast for 10 minutes, thereby increasing the flow of milk. It is necessary to improve the mother's nutrition or use herbal teas to increase lactation. nine0009
NUTRITION
Nursing mother's nutrition should be rich in calories (3200 kcal), balanced with the proper amount of proteins, fats, carbohydrates, vitamins and microelements. This diet will be dominated by lactic acid, protein foods, fresh fruits and vegetables.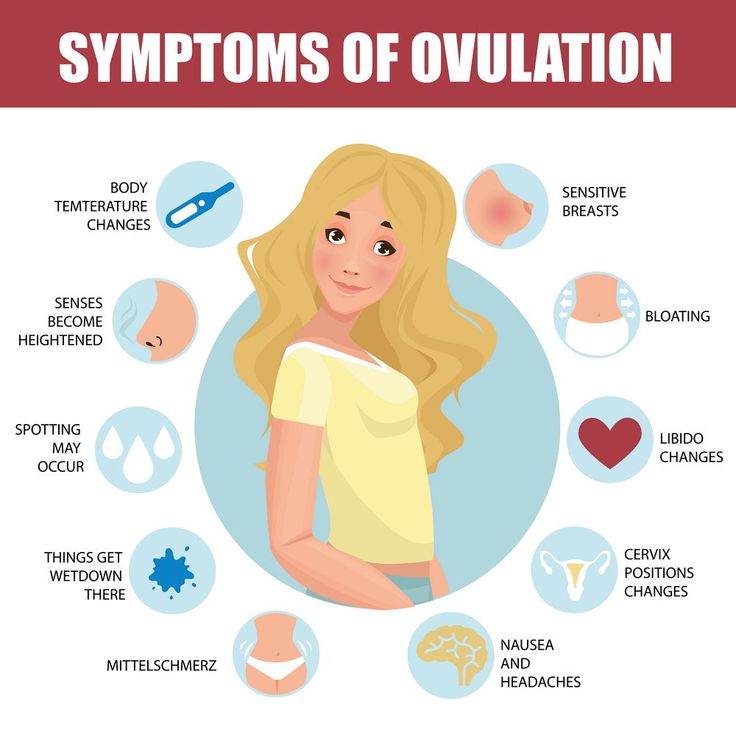 Food should be rich in vitamins and minerals. Spicy, fatty, fried, smoked foods, canned food, sausages, alcohol and potential allergens for the child (chocolate, citrus fruits, coffee) should be excluded from the diet. nine0193 The food of the puerperal should be 5-6 times a day. It is necessary to distribute products in the daily menu in such a way that those that are rich in protein and are much more difficult to digest in the gastrointestinal tract (meat, fish, cereals) would be used during the first half of the day, and in the second half it is advisable to give preference to milk. - vegetable food.
Food should be rich in vitamins and minerals. Spicy, fatty, fried, smoked foods, canned food, sausages, alcohol and potential allergens for the child (chocolate, citrus fruits, coffee) should be excluded from the diet. nine0193 The food of the puerperal should be 5-6 times a day. It is necessary to distribute products in the daily menu in such a way that those that are rich in protein and are much more difficult to digest in the gastrointestinal tract (meat, fish, cereals) would be used during the first half of the day, and in the second half it is advisable to give preference to milk. - vegetable food.
Conditions requiring special attention
Unfortunately, the first month after childbirth does not always go smoothly. Situations may arise, when medical attention is needed . Monitor your well-being, regularly measure your body temperature, as fever is most often the first sign of complications in the postpartum period.
All complications of the postpartum period can be divided into several groups:
1. Complications of the uterus.
Complications of the uterus.
Subinvolution of the uterus - a decrease in the rate of contraction of the uterus, due to a delay in the uterus of postpartum discharge. The disease often occurs 5-7 days after childbirth, due to the closure of the cervical canal with a blood clot or a piece of membranes, as well as the inflection of the uterus due to relaxation of the ligamentous apparatus. nine0193 Infection of the contents of the uterus can lead to inflammation of the uterine mucosa - endometritis. Predisposing factors for the occurrence of endometritis are difficult childbirth, violations of the separation of the placenta during childbirth, infections of the genital tract during pregnancy, impaired immunity, abortion. Symptoms of the disease are: fever, unpleasant odor in lochia, aching pain in the lower abdomen. If these symptoms appear, you should consult an obstetrician-gynecologist at the place of residence. To clarify the diagnosis, an ultrasound examination is performed and, if necessary, surgery, during which the contents are removed from the uterine cavity (washing or curettage of the uterus).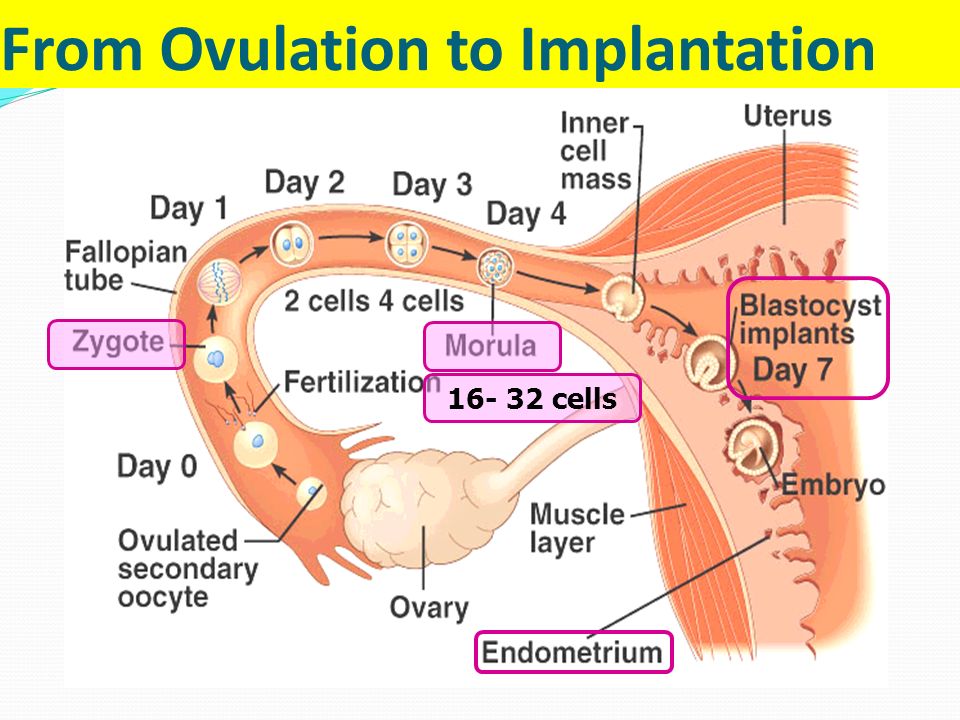 After surgery, antibiotics must be prescribed. nine0009
After surgery, antibiotics must be prescribed. nine0009
2. Breast complications.
Laktostasis - stagnation of milk in the mammary gland. At the same time, the chest swells and becomes painful, foci of seals appear, a short-term rise in body temperature is possible. In itself, lactostasis is not a disease, requiring only gentle pumping of the breast, restriction of fluid intake, and frequent feeding of painful breasts. However, when an infection joins, it turns into lactational mastitis, requiring immediate medical attention , antibiotic therapy, and sometimes surgery. The question of the possibility of breastfeeding with mastitis is decided individually, depending on the stage of the disease.
Another complication of the chest is the appearance of cracks in the nipples. The main reason for their appearance is improper attachment of the baby to the breast, when the baby captures only the nipple, and not the entire areola. Such a seizure is very painful for the mother - and this is the main danger signal.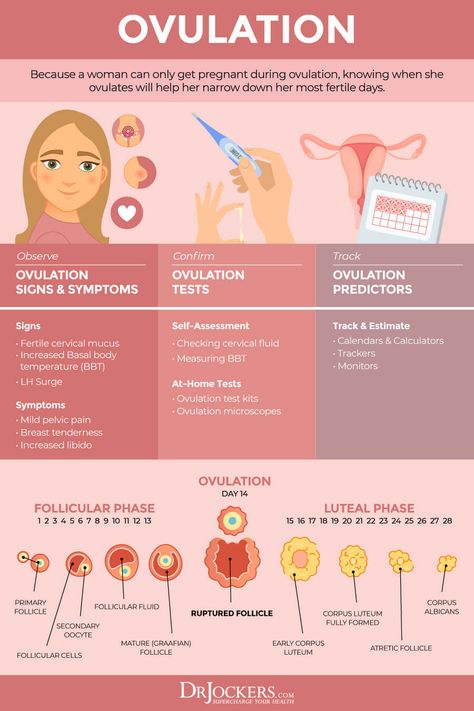 Breastfeeding doesn't have to be painful. Good advisory and practical help for lactostasis and cracked nipples is provided by breastfeeding consultants. Treatment of cracks consists in treating the nipple with wound healing drugs. nine0193 Hypogalactia - insufficient milk production. In order to increase the amount of milk, a mother needs to increase the frequency of feedings, not skip night feedings, offer her baby both breasts in one feeding, drink more, eat well and sleep a lot.
Breastfeeding doesn't have to be painful. Good advisory and practical help for lactostasis and cracked nipples is provided by breastfeeding consultants. Treatment of cracks consists in treating the nipple with wound healing drugs. nine0193 Hypogalactia - insufficient milk production. In order to increase the amount of milk, a mother needs to increase the frequency of feedings, not skip night feedings, offer her baby both breasts in one feeding, drink more, eat well and sleep a lot.
3. Complications from the tissues of the cervix, vagina and skin.
Inflamed wounds of these tissues are called postpartum ulcers. When an infection is attached, these wounds swell, become covered with a purulent coating, and their edges are painful. For the purpose of treatment, they are treated with various antiseptics, sometimes they require surgical treatment. nine0009
4. Complications of the venous system.
Hemorrhoids (varicose veins of the rectum) also cause pain. When infringed, they increase, become swollen, tense and painful. Thorough hygiene helps to reduce pain (shower after each visit to the toilet), applying ice to the perineum. Certain medications can be used as prescribed by a doctor.
When infringed, they increase, become swollen, tense and painful. Thorough hygiene helps to reduce pain (shower after each visit to the toilet), applying ice to the perineum. Certain medications can be used as prescribed by a doctor.
Thrombophlebitis is a disease of the veins characterized by inflammation of the venous wall and thrombosis of the vein. After childbirth, thrombophlebitis of the pelvic veins most often occurs. Usually this disease occurs in the third week after childbirth. In terms of symptoms, it is very similar to endometritis, but requires a different treatment. Surgeons are involved in the treatment of complications from the venous system. nine0193 Complications after childbirth require immediate treatment, as they can lead to a generalization of the process - postpartum peritonitis or sepsis. Therefore, if something bothers you in your condition, be sure to consult a doctor.
You must come to the antenatal clinic for the first time 10 days after discharge from the maternity hospital.