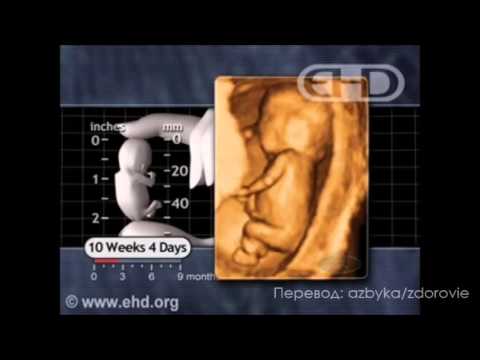
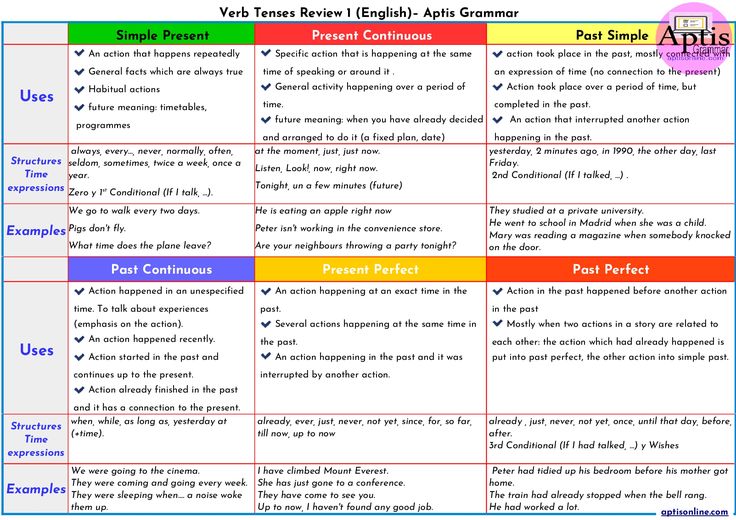
Will a pap smear detect pregnancy
Can a Pap Smear Detect Pregnancy? Here’s What You Need to Know - Lona Sasser
Can a pap smear detect pregnancy? We discuss gynecological screenings and answer your questions here.
It’s so important to take interest in routine medical screenings and what they are for. Having an understanding of procedures will make you an empowered patient. You will be in partnership with your care providers for optimal health and well-being. Today, we look at the question, “can a pap smear detect pregnancy?” and break down what to expect from a pap smear, and what it is for.
When it comes to your gynecological health, you may have questions, especially if you are pregnant or trying to conceive. You should always bring questions and concerns about your health to your medical provider.
Dr. Lona Sasser and Dr. Mary Squire-De Leon are highly skilled, compassionate gynecologists in Coral Springs, Florida, who offer an array of services for patients of all ages.
To make an appointment, you can easily book online or give us a call at (954) 340-1050.
Can a pap smear detect pregnancy?
You came here to get some questions answered. So, can a pap smear detect pregnancy?
The answer is no.
A pap smear is a screening test used to detect and prevent cervical cancer, the most common gynecologic cancer. On the other hand, the only way to detect pregnancy is by measuring your human chorionic gonadotropic (HCG) hormone. So your gynecologist cannot use a pap smear to detect pregnancy.
What you need to know about pap smears
A Papanicolaou or “pap” smear is usually a routine part of a pelvic examination at your obgyn’s office. Your “well-woman visit” takes place every year, and includes routine testing and more.
Your well-woman visit includes a physical exam. Usually, this means taking measurements of your weight and height, a blood pressure check, a breast exam, a pelvic exam, and pap smear.
Pap smears won’t happen every time. They are generally recommended every 3 years for women ages 21 to 65, but you should have a comprehensive wellness exam annually.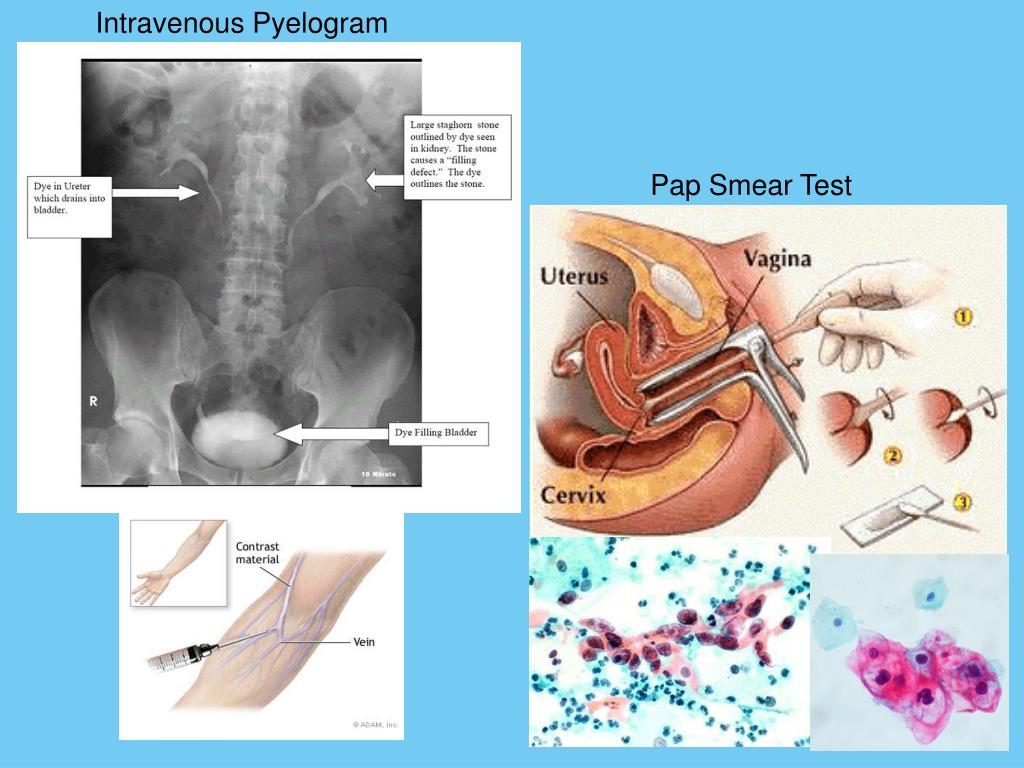
What do they detect?
The pap smear identifies the presence of abnormal cervical cells. The presence of abnormal cells may require further testing, follow-up care, or treatment to avoid the development of cancer. Detecting cervical cancer early with a pap smear gives you a greater chance of a cure.
Here’s what to expect:
With your consent, your doctor will place a speculum inside your vagina to help them see the cervix, the lower, narrow end of your uterus.
A device that resembles a tiny spatula will collect cervical cells, which are then sent to a pathologist to examine under a microscope.
Your doctor should keep you aware of what to expect and tell you what’s coming next and where you will feel their hands and instruments at any point.
The Pap smear may be combined with a test for human papillomavirus (HPV), the biggest risk factor for developing cervical cancer or genital warts.
In review
Can a pap smear detect pregnancy? Nope.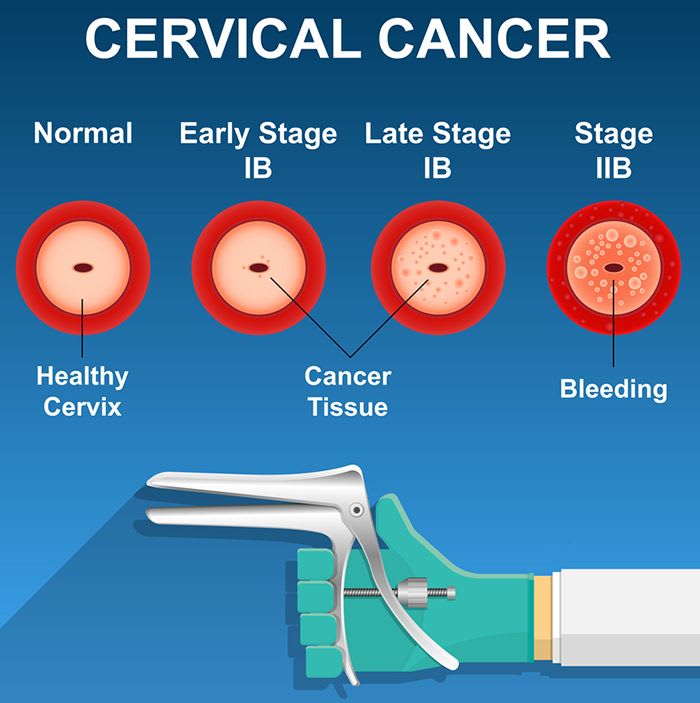
But a pap smear can detect changes in your cervical cells that suggest cancer may develop in the future. And, regular pap smear testing puts you at a much lower risk of developing invasive cervical cancer.
Pregnancy tests work by detecting HCG, often called the pregnancy hormone because it is made by cells formed in the placenta. Levels can first be detected by a blood test at your obgyn’s office about 11 days after conception.
Compassionate care
If you are pregnant, trying to conceive, or just need a doctor for routine visits, choose compassionate care from providers you can trust.
For caring, experienced, and attentive doctors, Lona Sasser Obstetrics and Gynecology is South Florida’s choice. Schedule your appointment today!
Easily book online or give us a call at (954) 340-1050.
Photo by nappy
Can A Pap Smear Detect Early Pregnancy? [Everything You Need To Know]
Are you pregnant or trying to conceive and wondering if your pap smear can detect early pregnancy?
You’re in the right place.
A pap smear cannot detect early pregnancy. It is a screening test used to prevent the most common gynecologic cancer worldwide.
After reading this post, you’ll learn:
- The pros and cons of getting a pap smear in pregnancy,
- If and how a pap smear can affect your pregnancy, and
- What to do if you have an abnormal pap smear result during pregnancy.
Let’s get started!
Disclaimer
Although I am a doctor, I am not your doctor. This information is for informational purposes only and should not substitute the advice from your healthcare professional. All kinds of exercise and dietary changes are potentially dangerous, and those who do not seek counsel from the appropriate health care authority assume the liability of any injury which may occur. Please read my full Disclaimer for more information. Also, this post may contain affiliate links: meaning I may receive a commission if you use them.
Do Pap smears detect pregnancy?
Pap smears cannot detect early pregnancy.
The only way to detect an early pregnancy is by measuring your beta-human chorionic gonadotropic (or bHCG for short) hormone.
Pap smears on the other hand detect abnormal cells in your cervix.
What does a pap smear detect?
A Papanicolaou or “pap” smear test is a cervical cancer screening test to determine if you have any abnormal cells on your cervix.
This test is done in your OBGYN’s office at the time of the pelvic exam.
A speculum will be placed inside your vagina to help your doctor visualize the cervix.
A small spatula-like device will then be used to collect some cervical cells which will then be sent to a pathologist to examine under a microscope.
An abnormal result will require further testing.
The sample may be also be tested for HPV infection (human papillomavirus)- which is the biggest risk factor for developing cervical cancer and/or genital warts.
Can a smear test affect early pregnancy?
Pap smears collect cells from the outermost part of the cervix, which is at least 2-3 cm away from the lower segment of the uterus.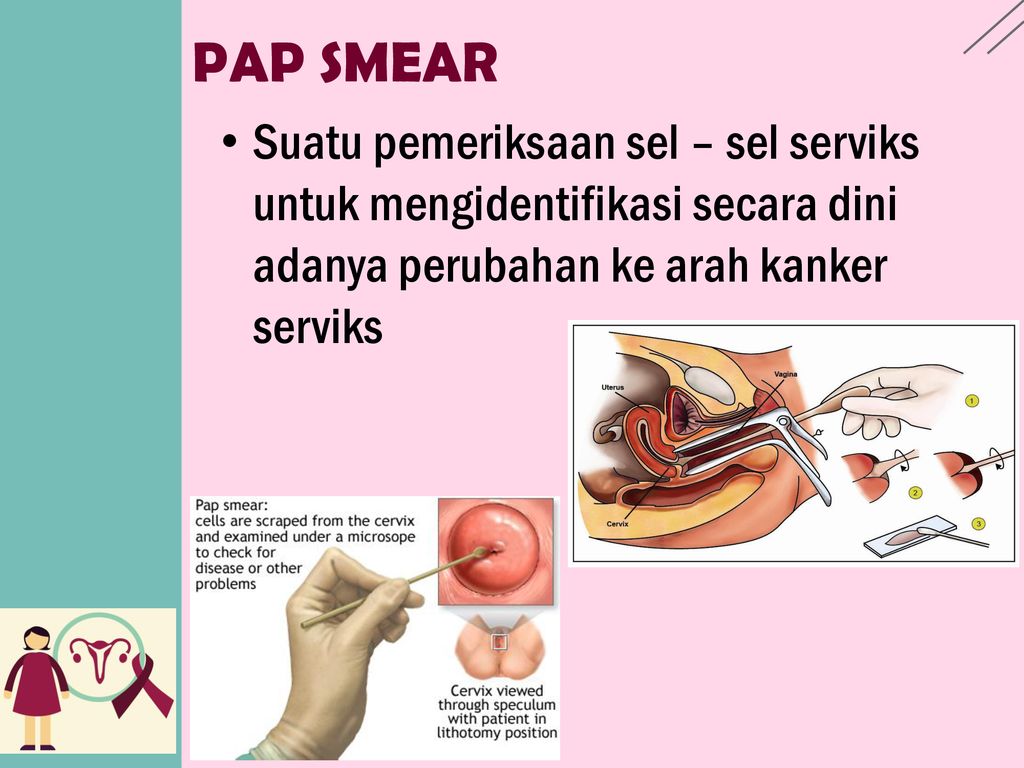 As such, collecting a pap should not affect an early pregnancy as it lies beyond the innermost part of the cervix.
As such, collecting a pap should not affect an early pregnancy as it lies beyond the innermost part of the cervix.
You can think of a cervix like a tube.
There is:
- the outermost part of the cervix aka the ectocervix,
- the endocervix (which is the 2-3cm canal), and
- the internal cervix, which is the entry into the uterus.
A pap smear done on pregnant women should only collect cells from the ectocervix.
However, a pap smear can also collect cells from the endocervix by using an instrument known as the cytobrush. This brush can enter the external cervix and be inserted all the way into the lower uterus.
Therefore, a cytobrush is NOT used during a pap smear in pregnancy as there is a potential for the pregnancy to be affected.
Are they safe? Can Pap smears cause miscarriage?
Pap smears are safe and do not cause miscarriage as long as it is done properly.
However, it is important to note that vaginal bleeding/spotting can occur after a pap smear as the cervix is very vascular.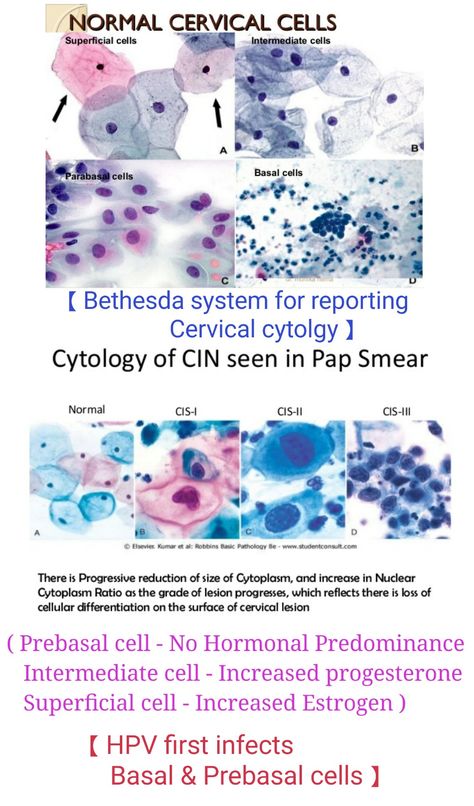
This bleeding is coming from the OUTSIDE of the uterus, and not from the pregnancy.
The good news is- any spotting caused by a pap is self-limited and stops fairly quickly.
If you experience anything heavier than light bleeding, you should speak with your provider immediately.
Most miscarriages occur very early in the 1st trimester, typically before 7 weeks gestation, and before you would get a pap smear.
Can I refuse a Pap smear during pregnancy?
You can refuse to do a pap smear during pregnancy. In fact, you can refuse anything you want while pregnant.
It is your body and your choice.
With that said information is power. Make informed choices after weighing the pros and cons of accepting or refusing treatment.
In the case of a pap smear, it is always better to identify and treat cervical dysplasia sooner rather than later.
Women who get regular pap smear testing are at a much lower risk of developing invasive cervical cancer as it can detect precancerous cells before it is too late.
Do you get tested for HPV when pregnant?
You will get tested for HPV during pregnancy if:
- you are due for a Pap smear, and
- you are over 30 years of age.
The HPV test is done together at the time of the pap smear. This is called a co-test.
If you are under 30 years of age, you will not be tested.
It is also important to note that there are many different strains of the human papillomavirus. This virus can cause cervical cancer/cervical intraepithelial neoplasia and/or genital warts depending on the type of strain that you become infected with.
We are most concerned about the high-risk HPV strains, which are 16 and 18.
You will be tested for HPV even if you have gotten the HPV vaccine.
What Happens If You Have An Abnormal Pap Test?
If your pap test comes back with abnormal cells, or your HPV test comes back positive for high-risk strains, you will likely have a colposcopy done in the 2nd trimester.
A colposcopy is a procedure that is done by your OBGYN in the office in which a colposcope (kind of like a telescope) is used to examine the cervix more closely for suspicious lesions.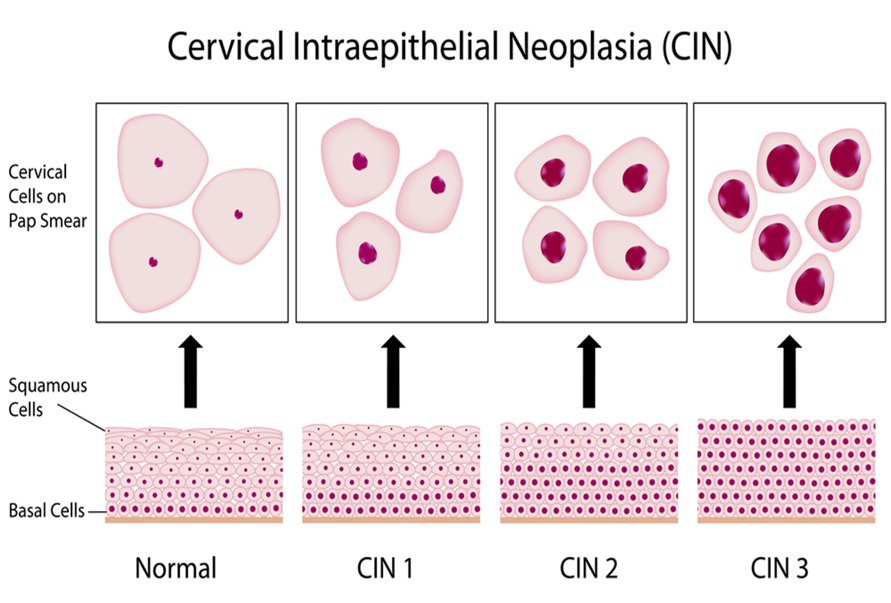
If there is a highly suspicious lesion, a cervical biopsy of that area may be considered.
Any other findings that are less concerning, or ones that might require further treatment like a cone biopsy are often handled in the postpartum period in the operating room.
Other Related Questions
Can a doctor tell if you are pregnant by looking at your cervix?
In general, a doctor cannot tell you are pregnant just by looking at your cervix. The only definitive way to tell if you are pregnant is by:
- performing a urine pregnancy test,
- performing a blood pregnancy test, or
- performing a sonogram once you are at least 5-6 weeks pregnant.
A doctor can tell if you’ve had a vaginal delivery before by looking at your cervix, but not if you are pregnant.
How early can a gynecologist detect pregnancy?
A gynecologist can detect pregnancy typically 6-10 days after you ovulate by taking a blood sample.
Ovulation occurs when one of the follicles in your ovary releases an egg to be fertilized.
This usually occurs around day 14 in a 28-day menstrual cycle. (Check out my post on Ovulation to learn more.)
The blood sample looks for the amount of beta human chorionic gonadotropin hormone or bHCG for short.
Most women refer to this as the “pregnancy hormone.”
bHCG is released by the placenta and the level will double every 48 hours in early pregnancy.
How long does it take to know if you are pregnant?
If you are using a home pregnancy test, you can typically find out you are pregnant after you miss a period, which is around the time that you are 4-5 weeks pregnant. Usually, your bHCG needs to be at 25 mIU/mL to be detected in the urine.
If your doctor has obtained a blood sample, you can find out much earlier as the blood test is more sensitive than the urine test.
If you have a sonogram performed, you will start to see some pregnancy-related changes in the uterus (such as a gestational sac and/or a yolk sac) around 5 weeks gestation.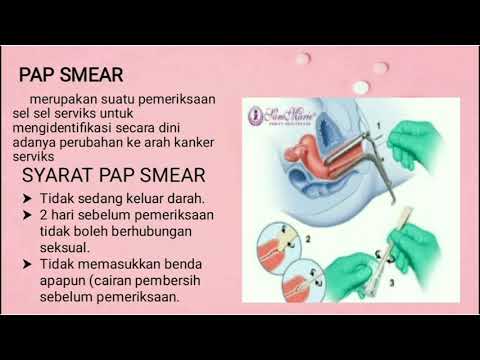
Typically the fetal pole and the heart beat can be seen around 5-6 weeks.
Does a Pap smear detect fertility potential?
Unfortunately, a pap test does not detect your fertility potential. In addition, abnormal pap test results do not make you less fertile.
There is no definitive way of measuring your fertility.
A common misconception is thinking that an anti-mullerian hormone or AMH predicts fertility.
AMH only tells you about your ovarian reserve, which is the number of eggs left in your body.
The AMH does not tell you how fertile you are but rather how your body might respond to fertility treatment.
Can a Pap smear affect implantation?
A pap smear has nothing to do with implantation.
Implantation requires a precise combination of an appropriately developed embryo reaching the uterus at the time that there is a receptive endometrium to receive it.
Implantation occurs before you can detect that you are pregnant, and is not affected by having a cervical cancer screening test.
Final Words on Pap Smear and early pregnancy
Although a pap smear cannot detect early pregnancy, there are three other effective ways to know you are pregnant.
However, if you are due for a pap smear, it is a good idea to get one done- even if you are pregnant. It is safe and effective as a cervical screening test, and will not interrupt an early pregnancy.
Now I want to hear from you.
Did you have a pap smear test in pregnancy?
What was your experience like?
Comment below and let me know!
Get Four Free Workouts To Help Strengthen Your Pelvic Floor & Heal Your Mommy Tummy!
YES- I WANT THE PDF!
Brittany Robles, MD, MPH, CPT
Brittany Robles is a full-time OBGYN physician, a NASM certified trainer, and a prenatal and postnatal fitness specialist. She holds a Master of Public Health degree in maternal health with a special interest in exercise and nutrition. She is also the co-author of The White Coat Trainer. Learn more about her here.
She is also the co-author of The White Coat Trainer. Learn more about her here.
Sharing is Caring – Send This To A Mom In Need!
References:
- Zhang S, Xu H, Zhang L, Qiao Y. Cervical cancer: Epidemiology, risk factors and screening. Chin J Cancer Res. 2020;32(6):720-728. doi:10.21147/j.issn.1000-9604.2020.06.05
- ASCCP- Cervical Cancer Screening Guidelines
Flora smear during pregnancy - when and why to take it
- When to take a flora smear
- What a flora smear shows
- Flora smear preparation rules
The flora smear is the most common test prescribed by an obstetrician-gynecologist. To conduct this study, the doctor, while examining a woman in a gynecological chair, takes the contents of the vagina from the posterior fornix (this is the space that is located between the back wall of the vagina and the cervix), the cervical canal and the discharged urethra, applies the material to the glass slide and directs him to the lab.
Smear examination for flora in the laboratory is carried out by a doctor of laboratory diagnostics under a microscope. This study allows you to determine the nature of the microflora (types of microorganisms) of the vagina, cervical canal and urethra, to identify the inflammatory process in the genitals of a woman, in some cases it also allows you to determine the causative agent of this inflammatory process (for example, gonococcus, Trichomonas).
When to take a smear for flora
It is mandatory for all pregnant women to take a swab twice - at registration and at 30 weeks of pregnancy, often another swab for flora is taken at 36-37 weeks to assess the state of the vaginal microflora before childbirth. During these periods, the analysis is given even in cases where the patient is not bothered by anything. This is carried out in order to identify a hidden inflammatory process that can lead to serious complications during pregnancy. During pregnancy, due to changes in hormonal levels and a decrease in immunity, exacerbation of chronic infections, as well as candidiasis (thrush), is much more likely. Any inflammatory process in the vagina during pregnancy can lead to serious complications of pregnancy - premature rupture of amniotic fluid, premature birth, oligohydramnios or polyhydramnios, intrauterine growth retardation and others.
Any inflammatory process in the vagina during pregnancy can lead to serious complications of pregnancy - premature rupture of amniotic fluid, premature birth, oligohydramnios or polyhydramnios, intrauterine growth retardation and others.
If a pregnant woman has complaints - the appearance of copious discharge from the genital tract, itching, burning or discomfort in the genital area, a swab for flora is also taken. In some pathological conditions, for example, in the presence of past miscarriages associated with infectious complications of pregnancy, cervical incompetence, a smear for flora is taken once a month, and after 30 weeks once every two weeks. Smear sampling is an absolutely safe procedure and does not lead to any complications, therefore it can be performed at any stage of pregnancy.
Learn more about the services:
- Pregnancy tests
What a flora smear shows
A flora smear is evaluated according to the following indicators:
Epithelium
Squamous epithelium is the cells of the surface layer of the mucous membrane of the vagina and cervix.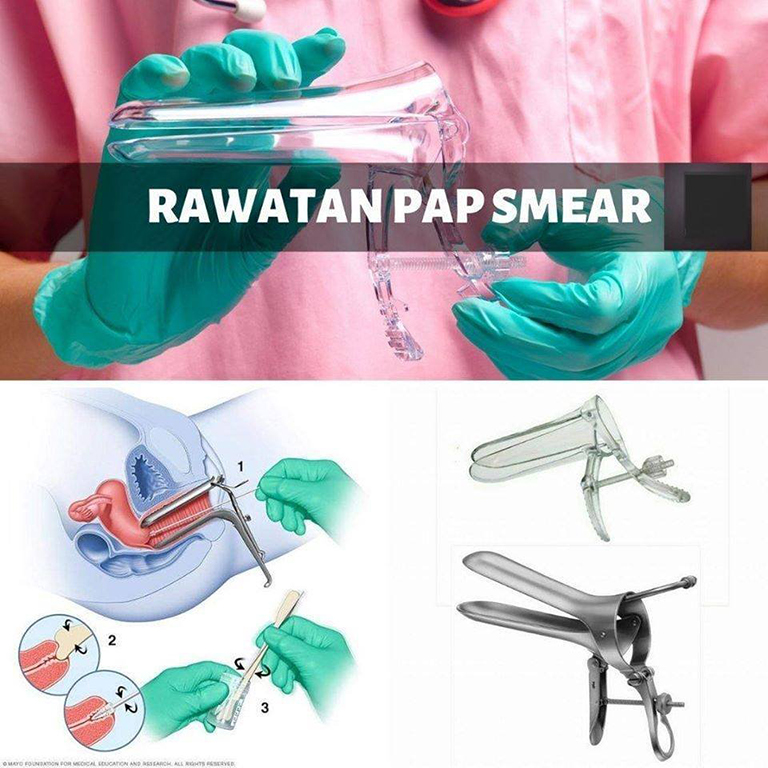 The presence of a large amount of squamous epithelium in a smear may indicate an inflammatory process. The absence of epithelium in the smear indicates a violation of the hormonal background.
The presence of a large amount of squamous epithelium in a smear may indicate an inflammatory process. The absence of epithelium in the smear indicates a violation of the hormonal background.
Leukocytes
These are blood cells involved in the destruction of pathogenic bacteria. Leukocytes are able to actively penetrate through the wall of blood vessels into the tissues of the body and participate in the fight against infectious agents. Normally, no more than 10 leukocytes are present in a smear for flora from the vagina, no more than 15 leukocytes per field of view from the cervical canal, and up to 2 leukocytes per field of view from the urethra. An increase in the content of leukocytes in a smear is a sign of inflammation, while the higher the content of leukocytes in a smear, the more pronounced the inflammatory process.
Erythrocytes
These are red blood cells. Normally, single erythrocytes (1-2 in the field of view) can be found in a flora smear. An increase in the number of red blood cells indicates the presence of a chronic inflammatory process, and also be a sign of injury or occult bleeding, for example, in the presence of cervical ectopia (the so-called erosion, when the vaginal part of the cervix is covered with a cylindrical epithelium normally lining the inside of the cervix).
An increase in the number of red blood cells indicates the presence of a chronic inflammatory process, and also be a sign of injury or occult bleeding, for example, in the presence of cervical ectopia (the so-called erosion, when the vaginal part of the cervix is covered with a cylindrical epithelium normally lining the inside of the cervix).
Slime
Normally, there is no mucus in the urethra, a moderate amount of mucus is detected in the vagina, and there may be a large amount of mucus in the cervix. An increase in the amount of mucus may be a sign of an inflammatory process, but this criterion does not have great diagnostic value, and doctors rarely rely on it when making a diagnosis.
Bacteria
Normally, flora should not be detected in the urethra, rod flora is detected in a moderate amount in the vagina and cervix. Rod flora is most often lactobacilli, which are 95% are normal vaginal biocenosis. Lactobacilli actively colonize the vagina and create an acidic environment in it, thereby preventing the growth and reproduction of pathogenic bacteria.
In addition to lactobacilli, other rod bacteria, such as E. coli, bacteroids, and various cocci, may also be present in the vagina. These are bacteria that, under microscopy, have the shape of balls. This group of bacteria includes streptococci, staphylococci, enterococci. In a small amount, they are normally present in the vagina. If their number increases sharply against the background of the death of normal lactobacilli, this can lead to the development of an inflammatory process. Unfortunately, according to the results of a routine smear on the flora, it is impossible to determine which specific bacteria and in what quantity are present in the vagina. Therefore, with a pronounced inflammatory process, as well as when a large amount of coccal flora is found in a smear on the flora, the doctor prescribes an additional analysis to make the correct diagnosis - sowing on the flora with the determination of sensitivity to antibiotics.
Opportunistic flora
These are micro-organisms that live in the human body in small numbers without causing harm, but under certain conditions can lead to an inflammatory process. Such microorganisms found in a smear on the flora include fungi of the genus Candida and gardnerella.
Such microorganisms found in a smear on the flora include fungi of the genus Candida and gardnerella.
Gardnerella ("key cells")
Gardnerella and other bacteria living in anoxic conditions (so-called anaerobic bacteria) normally live in the vagina in small numbers, without causing symptoms of an inflammatory process. With a decrease in local immunity, which is quite common during pregnancy, there is an increase in the proportion of these bacteria in the vaginal microflora, a disease occurs - bacterial vaginosis (vaginal dysbiosis). At the same time, “key” cells are found in a smear on the flora - these are cells of the vaginal mucosa, covered with gardnerella and other anaerobic bacteria. The gardnerella themselves are not visible in a normal unstained smear. They can only be detected by staining smears with special dyes.
Mushrooms
Microorganisms of the genus Candida are part of the normal microflora of the mouth, vagina and colon of most healthy people. Normally, the number of these microorganisms is small and they do not cause an inflammatory process. Normally, in some women, a small amount of spores of the fungus may be detected in a vaginal smear. In the absence of an inflammatory reaction and complaints of the patient, the treatment of this condition is not carried out. The detection of a large number of spores or mycelium of a yeast-like fungus of the genus Candida in a smear on the flora makes it possible to diagnose candidiasis (or thrush)
Normally, the number of these microorganisms is small and they do not cause an inflammatory process. Normally, in some women, a small amount of spores of the fungus may be detected in a vaginal smear. In the absence of an inflammatory reaction and complaints of the patient, the treatment of this condition is not carried out. The detection of a large number of spores or mycelium of a yeast-like fungus of the genus Candida in a smear on the flora makes it possible to diagnose candidiasis (or thrush)
Pathogenic flora
There are microorganisms that should not normally be present in the vagina of a healthy woman and the detection of which in a flora smear indicates the presence of a serious sexually transmitted disease. Of these infections in the smear, Trichomonas and gonococci are most often detected.
Trichomonas
These are the simplest microorganisms that have a flagellum and are capable of movement. Detection in a smear on the flora of Trichomonas indicates the presence of a sexually transmitted disease - trichomoniasis.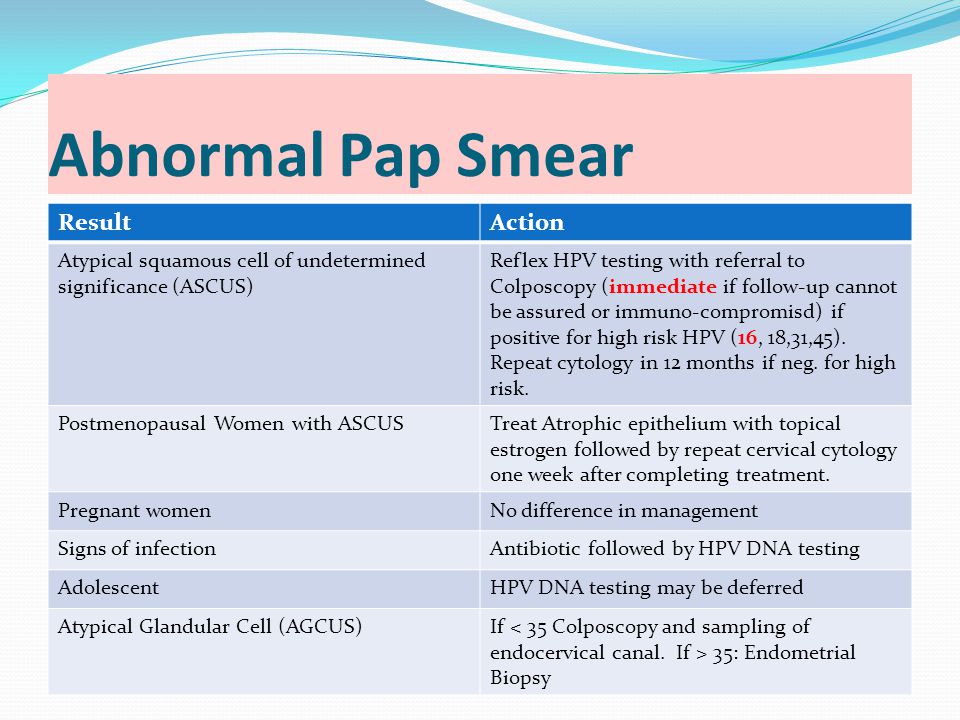 Trichomoniasis in a pregnant woman increases the risk of preterm birth, premature rupture of amniotic fluid, intrauterine growth retardation. In addition, there is a risk of infection of the baby when passing through the birth canal, therefore, if Trichomonas is found in a smear, antibacterial treatment is mandatory during pregnancy.
Trichomoniasis in a pregnant woman increases the risk of preterm birth, premature rupture of amniotic fluid, intrauterine growth retardation. In addition, there is a risk of infection of the baby when passing through the birth canal, therefore, if Trichomonas is found in a smear, antibacterial treatment is mandatory during pregnancy.
Gonococci
These are bacteria that look like double bean-shaped balls in the smear, adjacent to each other with a concave side. Detection of gonococci in a smear allows the doctor to make a diagnosis - gonorrhea. This is a sexually transmitted disease, which must also be cured during pregnancy. The inflammatory process caused by gonococcus significantly complicates the course of pregnancy, can lead to miscarriage, premature birth, premature rupture of amniotic fluid, infection of the placenta and membranes, and in addition, when the baby passes through the birth canal, the eyes of the newborn are affected by gonococcus.
Detection of pathogens of other sexually transmitted infections in a smear on the flora is very difficult.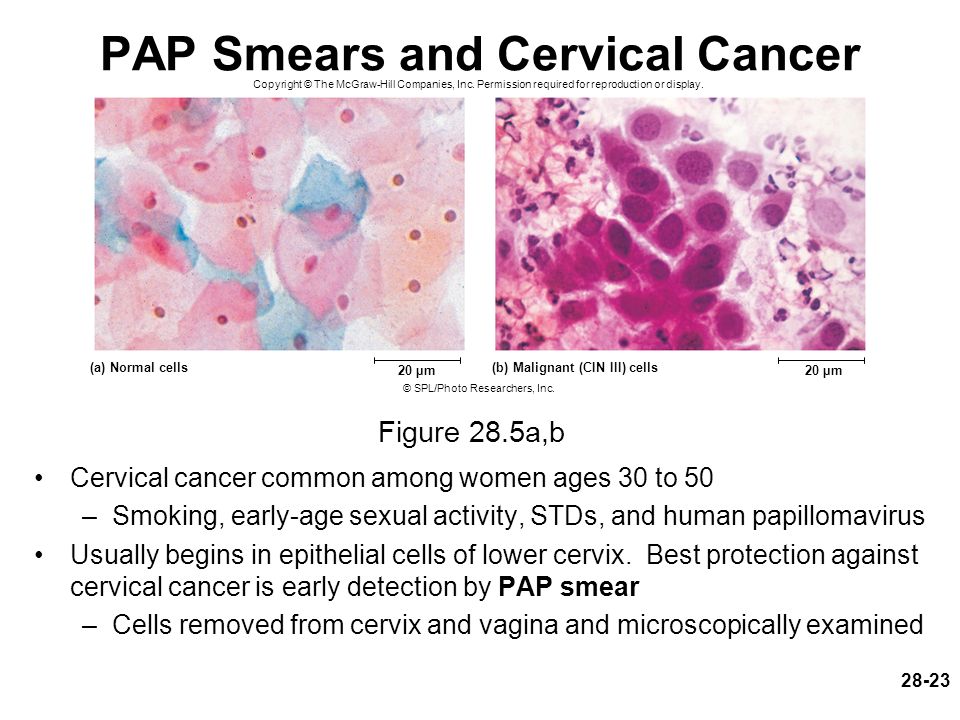 Therefore, in the presence of an inflammatory process according to the smear, the doctor usually recommends testing for sexual infections by another, more sensitive method - a PCR smear.
Therefore, in the presence of an inflammatory process according to the smear, the doctor usually recommends testing for sexual infections by another, more sensitive method - a PCR smear.
Rules for preparation for taking a smear for flora
In order for the result of a smear for flora to be reliable, a number of important conditions must be observed before taking this analysis. Within 2-3 days, you can not use any vaginal suppositories or creams, douching with any solutions is contraindicated, since they change the composition of the vaginal microflora, making it difficult to identify the causative agent of inflammation. In addition, within 2 days it is desirable to refrain from sexual intercourse. This is also due to the fact that spermatozoa and residual semen in the vagina can lead to an incorrect smear result for flora.
Why is a smear taken? - Dafina
Ruslan Karagulyan
Head of the women's consultation at the Khimki Central District Hospital, obstetrician-gynecologist of the highest category
Magazine "9 months"
№10 2002
The genital tract swab is one of the most common diagnostic methods in obstetrics and gynecology. This study is completely safe for a woman and very informative for a doctor. Based on such smears, two analyzes can be carried out: a study of the microbial flora of the vagina and an indicative cytological diagnosis. We will only talk about the first, because it is he who is mandatory for any woman during pregnancy.
This study is completely safe for a woman and very informative for a doctor. Based on such smears, two analyzes can be carried out: a study of the microbial flora of the vagina and an indicative cytological diagnosis. We will only talk about the first, because it is he who is mandatory for any woman during pregnancy.
How and when to examine the microflora of the vagina
Smears, which determine the state of the microflora, are taken from a woman during pregnancy at least three times: at the initial visit to the gynecologist, at 30 weeks at the time of issuing an exchange card and at 36-37 weeks. The need for additional research arises if a pregnant woman complains of itching, burning in the vulva and / or vagina, a change in the amount, color or smell of discharge: such symptoms may be a sign of inflammation. In order for the result of the study to be reliable, it is necessary to exclude the use of antibacterial drugs 7-10 days before taking a smear. In addition, douching, treatment with vaginal suppositories, etc.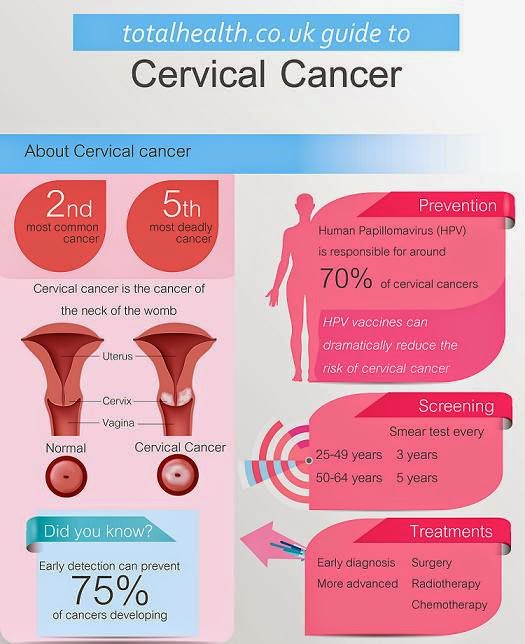 should be stopped 24 hours before the analysis.
should be stopped 24 hours before the analysis.
For examination, the doctor takes three smears: from the cervical canal (cervical canal), from the vaginal wall and from the mouth of the paraurethral passages (a separate spatula is used for each of these smears). Taking a smear is a simple and painless procedure. So that the gynecological mirror is not cold and does not give you discomfort, the doctor can heat it with hot water before manipulation. The contents of the smears are applied to a glass slide, which is then sent to the laboratory, where the analysis material is stained using a special technique and examined under a microscope. In some situations, doctors not only examine the smear with a microscope, but also place the resulting material in a nutrient medium in a Petri dish. During reproduction, bacteria form colonies, the appearance of which depends on the type of bacteria. By the way, using this method, the sensitivity of microbes to various antibiotics is also determined.
Bacteria - good neighbors or irreconcilable enemies?
After reviewing the results of the study, the doctor can obtain information about the composition of the vaginal microflora, the total number of microbes, the presence and severity of inflammation, and, finally, the state of the vaginal epithelium.
The microflora of the vagina is the microbes that inhabit it. In the vagina of a healthy woman, beneficial microorganisms predominate. The leading place among them is occupied by lactobacilli, which form a kind of barrier to the spread of pathogenic (pathogenic) microbes. In addition, lactic acid, which is formed during their life, largely determines the acidity (pH) of the vaginal environment. With a sufficient number of lactobacilli, the acidic environment of the vagina inhibits the growth of pathogenic microbes. Under conditions when lactobacilli die, the acidity of the medium decreases and the number of pathogenic bacteria increases.
Bacteria that have disease-causing properties live side by side with beneficial ones, but these properties do not have the opportunity to manifest themselves as long as their beneficial neighbors interfere with this.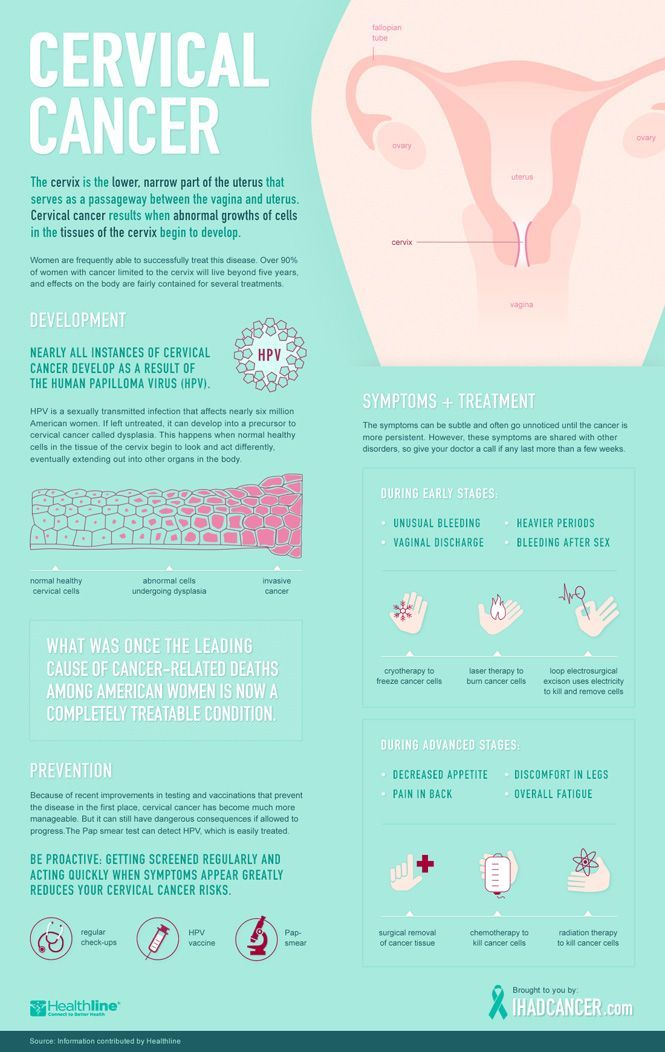 With normal immunity, as a rule, various microorganisms that inhabit the vagina are in a state of truce. When immunity is weakened, favorable conditions are created for expanding the sphere of influence of pathogenic microbes. The microflora of the vagina is sensitive to both external and internal changes occurring in the body of a woman. The use of antibiotics, hormonal fluctuations, chemotherapy or hormone therapy, radiation therapy, surgical interventions, stressful situations and other factors can have a negative impact on the normal flora of the vagina. Pregnancy also affects the microflora of the vagina, since during this period the hormonal background and immunity change significantly. These changes reach their peak in the third trimester. Therefore, it is during this period that women are very often concerned about the symptoms of inflammation, which were mentioned above. The most common cause of this condition during pregnancy is the yeast-like fungus Candida albicans, and the disease itself is called candidiasis, candidiasis, or simply thrush.
With normal immunity, as a rule, various microorganisms that inhabit the vagina are in a state of truce. When immunity is weakened, favorable conditions are created for expanding the sphere of influence of pathogenic microbes. The microflora of the vagina is sensitive to both external and internal changes occurring in the body of a woman. The use of antibiotics, hormonal fluctuations, chemotherapy or hormone therapy, radiation therapy, surgical interventions, stressful situations and other factors can have a negative impact on the normal flora of the vagina. Pregnancy also affects the microflora of the vagina, since during this period the hormonal background and immunity change significantly. These changes reach their peak in the third trimester. Therefore, it is during this period that women are very often concerned about the symptoms of inflammation, which were mentioned above. The most common cause of this condition during pregnancy is the yeast-like fungus Candida albicans, and the disease itself is called candidiasis, candidiasis, or simply thrush.
The fungus Candida albicans lives on the skin and mucous membranes of any person, but it is activated only when the immune system is weakened or the bacteria that inhibit its reproduction, including lactobacilli, die. Thrush manifests itself with signs of inflammation and a milky white coating on the mucosa; such a plaque resembles grains of cottage cheese or the remains of dairy food.
Balance control
Why is the study of the microflora of the vagina necessary for every pregnant woman? The fact is that an infectious process that affects the birth canal (cervix, vagina, external genitalia) is fraught with infection of the child during childbirth. The microflora of the mother's vagina has a significant impact on the formation of microbiocenosis of the intestines and skin of the newborn. In addition, in some situations, intrauterine infection of the fetus is possible. Sometimes the altered microflora adversely affects the course of the postpartum period: the recovery process may slow down, the development of infectious complications in a woman is not excluded.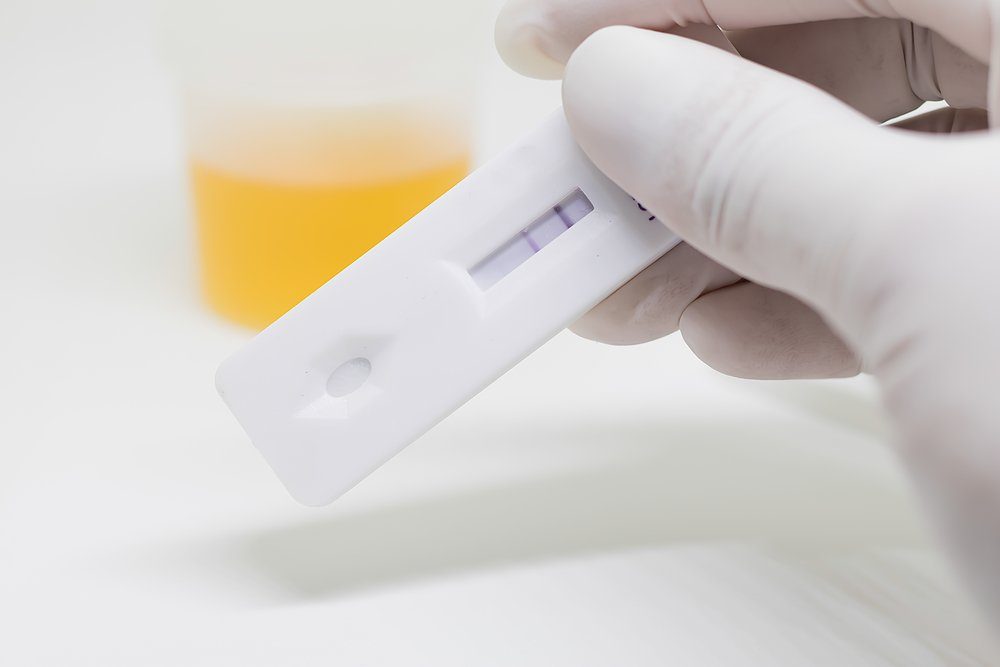 A control smear after a course of therapy will help evaluate the effectiveness of the treatment. A decrease in the percentage of lactic acid bacteria and an increase in the number of pathogenic microbes is one of the signs of inflammation. The presence of inflammation is also confirmed by a large number of leukocytes - defender cells that fight for health. To assess the state of the microflora of the vagina, doctors use the concept of "degree of purity". There are four such levels. The first characterizes the optimal state: lactobacilli predominate in the microbial "landscape", the acidity of the medium is normal, there are no signs of inflammation. At the fourth degree, there are no lactobacilli, many pathogenic microbes, signs of inflammation are pronounced, it turns from an acidic environment into an alkaline one. The second and third degrees are intermediate between the first and fourth. When choosing a treatment, the doctor will focus on the general condition of the pregnant woman and the results of the examination.
A control smear after a course of therapy will help evaluate the effectiveness of the treatment. A decrease in the percentage of lactic acid bacteria and an increase in the number of pathogenic microbes is one of the signs of inflammation. The presence of inflammation is also confirmed by a large number of leukocytes - defender cells that fight for health. To assess the state of the microflora of the vagina, doctors use the concept of "degree of purity". There are four such levels. The first characterizes the optimal state: lactobacilli predominate in the microbial "landscape", the acidity of the medium is normal, there are no signs of inflammation. At the fourth degree, there are no lactobacilli, many pathogenic microbes, signs of inflammation are pronounced, it turns from an acidic environment into an alkaline one. The second and third degrees are intermediate between the first and fourth. When choosing a treatment, the doctor will focus on the general condition of the pregnant woman and the results of the examination. Of course, he will choose the method of treatment that in a particular situation will be safer for the fetus.
Of course, he will choose the method of treatment that in a particular situation will be safer for the fetus.
In situations where signs of inflammation are present, but the cause is not clear from the results of conventional smears, doctors may resort to additional research methods, such as PCR smear diagnostics. The PCR method (polymerase chain reaction) is based on a multiple increase in the number of DNA of pathogenic microbes to such an amount that it is possible to determine the type of pathogen even if the smear contained a very small amount of pathogenic bacteria. This analysis requires special equipment, so it can only be done in well-equipped laboratories. The results of vaginal smears are of great importance during hospitalization in the maternity hospital: if the results are absent or a large number of leukocytes or pathogenic microflora are found in them, and also if the results are obtained more than 40 days ago, the pregnant woman is hospitalized in the II maternity ward, intended for women with infectious diseases and pathology of pregnancy, which is in all maternity hospitals.