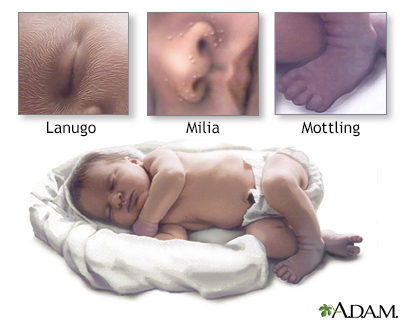
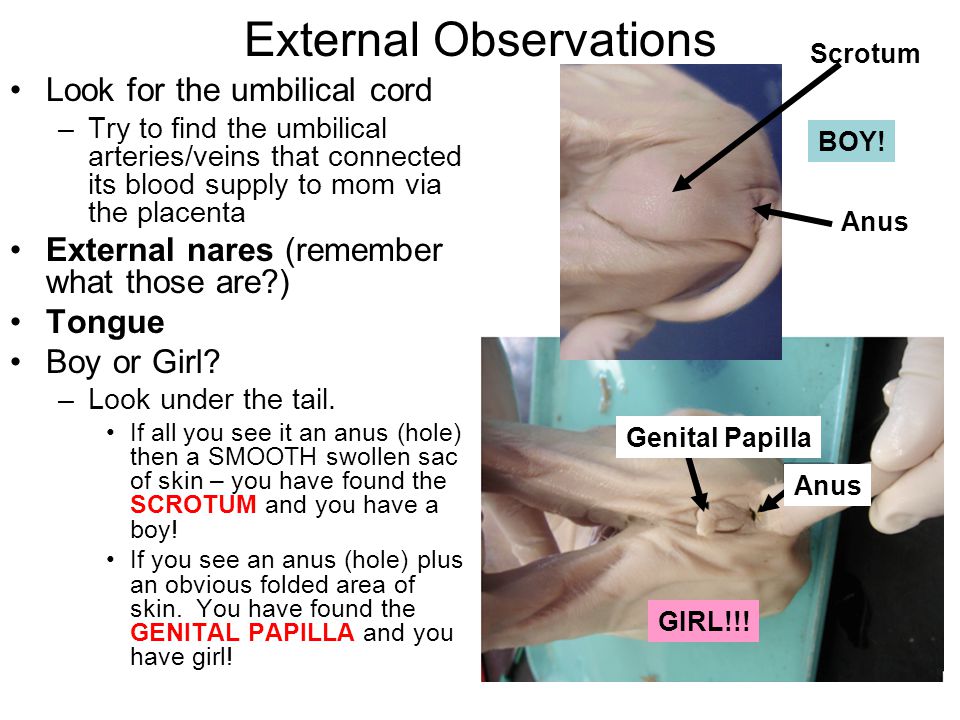
Straining in newborn
Constipation
Is this your child's symptom?
- Can't pass a stool or pain when passing a stool
- Crying when passing a stool (bowel movement or BM) or
- Can't pass a stool after straining or pushing longer than 10 minutes or
- 3 or more days without passing a stool (Exception: Breastfed and over 1 month old)
- Caution: any belly pain from constipation comes and goes. Most often, it is mild. Use the Abdominal Pain (Stomach Pain) care guide if there is constant belly pain.
Causes of Constipation
- High Milk Diet. Milk and cheese are the only foods that in high amounts can cause constipation. It causes hard pale stools. This is why you want your child to eat a well-balanced diet.
- Low Fiber Diet. Fiber is found in vegetables, fruits and whole grains. Fiber keeps stools soft, bulky and easy to pass. A low fiber diet causes hard, small stools.
- Low Fluid Intake. This can also cause stools to be dry and harder to pass.
It's rarely the only cause of constipation.
- Lack of Exercise. Exercise also keeps the bowel from slowing down. Not a cause in children unless they are confined to bed.
- Holding Back Stools Because of Pain. If passing a stool causes pain, many children will hold back the next one. This can happen with a Strep infection around the anus. It can also occur with a bad diaper rash or anal fissure (tear).
- Holding Back Stools Because of Power Struggles. This is the most common cause of recurrent constipation in children. Most often it's a battle around toilet training. If they are already trained, it may begin with the start of school. Reason: some children refuse to use public toilets. Some children postpone stools because they are too busy to sit down.
- Slow passage of food through the intestines. Most often, this type runs in families. Called slow transit time.
Stools: How Often is Normal?
- Normal Range: 3 per day to 1 every 2 days.
 Once children are on normal table foods, their stool pattern is like adults.
Once children are on normal table foods, their stool pattern is like adults. - Kids who go every 4 or 5 days almost always have pain with passage. They also have a lot of straining.
- Kids who go every 3 days often drift into longer times. Then, they also develop symptoms.
- Passing a stool should be free of pain.
- Any child with pain during stool passage or lots of straining needs treatment. At the very least, the child should be treated with changes in diet.
Imitators of Constipation: Normal Patterns and Stools
- Breastfed and Over 1 Month Old. Stools every 4-7 days that are soft, large and pain-free can be normal. Caution: before 1 month old, not stooling enough can mean not getting enough breast milk.
- Straining in Babies. Grunting or straining while pushing out a stool is normal in young babies. They are learning to relax their anus after 9 months of keeping it closed. It's also hard to pass stool lying on their back with no help from gravity.
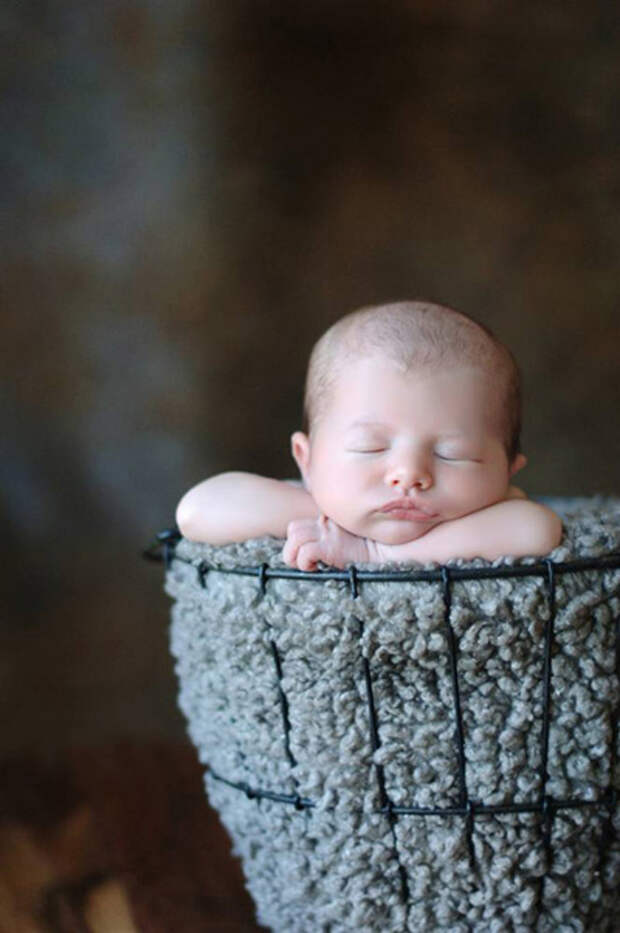 Babies also become red in the face and draw up their legs during straining. This is normal. Key: they continue to pass normal size stools every day. Just not every time they have some straining.
Babies also become red in the face and draw up their legs during straining. This is normal. Key: they continue to pass normal size stools every day. Just not every time they have some straining. - Brief straining under 10 minutes can occur at times at any age.
- Large Stools. Size relates to the amount of food eaten. Large eaters have larger stools.
- Hard or Dry Stools. Also can be normal if passed easily without too much straining. Often, this relates to poor fiber intake. Some children even have small, dry rabbit-pellet-like stools.
When to Call for Constipation
Call Doctor or Seek Care Now
- Stomach pain goes on more than 1 hour (includes crying) after using care advice
- Rectal pain goes on more than 1 hour (includes straining) after using care advice
- Vomits 2 or more times and stomach looks more swollen than normal
- Age less than 1 month old and breastfed
- Age less than 12 months with recent onset of weak suck or weak muscles
- Your child looks or acts very sick
- You think your child needs to be seen, and the problem is urgent
Contact Doctor Within 24 Hours
- Age less than 2 months.
 Exception: normal straining and grunting.
Exception: normal straining and grunting. - Bleeding from anus
- Needs to pass a stool but afraid to or refuses to let it out
- Child may be "blocked up"
- Suppository or enema was given but did not work
- You think your child needs to be seen, but the problem is not urgent
Contact Doctor During Office Hours
- Leaking stool
- Suppository or enema was needed to get the stool out
- Infrequent stools do not get better after changes to diet. Exception: normal if breastfed infant more than 1 month old and stools are not painful.
- Stool softeners are being used and have not been discussed with your doctor
- Toilet training is in progress
- Painful stools occur 3 or more times after changes to diet
- Constipation is a frequent problem
- You have other questions or concerns
Self Care at Home
- Mild constipation
Seattle Children's Urgent Care Locations
If your child’s illness or injury is life-threatening, call 911.
- Bellevue
- Everett
- Federal Way
- Seattle
- Virtual Urgent Care
Care Advice for Constipation
- What You Should Know about Constipation:
- Constipation is common in children.
- Most often, it's from a change in diet. It can also be caused by waiting too long to stool.
- Passing a stool should be pleasant and free of pain.

- Any child with pain during stool passage or lots of straining needs treatment. At the very least, they need changes in diet.
- Here is some care advice that should help.
- Normal Stools:
- Normal range: 3 per day to 1 every 2 days. Once children are on a regular diet, their stool pattern is like adults.
- Kids who go every 3 days often drift into longer times. Then symptoms start.
- Kids who go every 4 and 5 days almost always have pain with passage. They also have lots of straining.
- Diet for Infants Under 1 Year Old:
- Age over 1 month old only on breast milk or formula, add fruit juice.
- Amount. Give 1 ounce (30 mL) per month of age per day. Limit amount to 4 ounces (120 mL).
- Pear and apple juice are good choices. After 3 months, can use prune (plum) juice. Reason for fruit juice: approved for babies in treating a symptom.
- Age over 4 months old, also add baby foods with high fiber.
 Do this twice a day. Examples are peas, beans, apricots, prunes, peaches, pears, or plums.
Do this twice a day. Examples are peas, beans, apricots, prunes, peaches, pears, or plums. - Age over 8 months old on finger foods, add cereals and small pieces of fresh fruit.
- Diet for Children Over 1 Year Old:
- Increase fruit juice (apple, pear, cherry, grape, prune). Note: citrus fruit juices are not helpful.
- Add fruits and vegetables high in fiber content. Examples are peas, beans, broccoli, bananas, apricots, peaches, pears, figs, prunes, or dates. Offer these foods 3 or more times per day.
- Increase whole grain foods. Examples are bran flakes or muffins, graham crackers, and oatmeal. Brown rice and whole wheat bread are also helpful. Popcorn can be used if over 4 years old.
- Limit milk products (milk, ice cream, cheese, yogurt) to 3 servings per day.
- Fluids. Give enough fluids to stay well-hydrated. Reason: keep the stool soft.
- Stop Toilet Training:
- Put your child back in diapers or pull-ups for a short time.

- Tell him that the poops won't hurt when they come out.
- Praise him for passing poops into a diaper.
- Holding back stools is harmful. Use rewards to help your child give up this bad habit.
- Avoid any pressure or punishment. Also, never force your child to sit on the potty against his will. Reason: it will cause a power struggle.
- Treats and hugs always work better.
- Put your child back in diapers or pull-ups for a short time.
- Encourage Sitting on the Toilet (if toilet trained):
- Set up a normal stool routine, if your child agrees to sitting.
- Have your child sit on the toilet for 5 minutes after meals.
- This is especially important after breakfast.
- If you see your child holding back a stool, also take to the toilet for a sit (if cooperates).
- During sits, stay with your child and be a coach. Just focus on helping the poop come out.
- Do not distract your child. Do not allow your child to play with video devices, games or books during sits.

- Once he passes a normal size stool, he doesn't need to sit anymore that day.
- Warm Water to Relax the Anus:
- Warmth helps many children relax the anus and release a stool.
- For straining too long, have your child sit in warm water.
- You can also put a warm wet cotton ball on the anus. Vibrate it side to side for about 10 seconds to help relax the anus.
- Flexed Position to Help Stool Release for Babies:
- Help your baby by holding the knees against the chest. This is like squatting for your baby. This is the natural position for pushing out a stool. It's hard to have a stool lying down.
- Gently pump on the lower belly with your fingers. If no stool release in a few minutes, stop.
- Squatting Position to Help Stool Release for Older Children:
- The squatting position gives faster stool release and less straining.
- Squatting means that the knees are above the hips.

- For most children who sit on the toilet, a foot stool is needed.
- It is an important part of treating constipation.
- Stool Softeners (Age Over 1 Year Old):
- If a change in diet doesn't help, you can add a stool softener. Must be over 1 year of age.
- Use a stool softener (such as Miralax). It is available without a prescription. Give 1-3 teaspoons (5-15 mL) powder each day with dinner. Mix the powder in 2 to 6 ounces (60-180 mL) of water.
- Fiber products (such as Benefiber) are also helpful. Give 1 teaspoon (5 mL) twice a day. Mix it in 2 ounces (60 mL) of water or fruit juice.
- Stool softeners and fiber should produce regular soft stools in 1 to 3 days.
- Discuss dosage and how long to use with your doctor.
- What to Expect:
- Most often, changes in diet helps constipation.
- After your child is better, be sure to keep him on high fiber foods.
- Also, have your child sit on the toilet at the same time each day.
- These tips will help to prevent the symptoms from coming back.
- Call Your Doctor If:
- Constipation lasts more than 1 week after making changes to diet
- You think your child needs to be seen
- Your child becomes worse
And remember, contact your doctor if your child develops any of the 'Call Your Doctor' symptoms.
Disclaimer: this health information is for educational purposes only. You, the reader, assume full responsibility for how you choose to use it.
Last Reviewed: 04/06/2023
Last Revised: 12/30/2022
Copyright 2000-2023. Schmitt Pediatric Guidelines LLC.
Dyschezia: Types, Causes & Treatment
Overview
What is dyschezia?
Dyschezia literally means difficulty pooping. Another name for dyschezia is disordered defecation. Healthcare providers use the term “dyschezia” differently when talking about infants or adults, which can be confusing.
- Dyschezia in adults is more of a description than a condition. It means that you can’t poop without having some type of difficulty, straining or pain. This could be for a lot of reasons. Constipation often relates to dyschezia in adults, either as the cause of your difficulties or as a side effect.
- Infant dyschezia is a specific condition. Another name for infant dyschezia is grunting baby syndrome. Infants with dyschezia appear to have difficulty pooping, but they have no signs of constipation. They might strain, grunt or cry for 10 to 30 minutes before they poop, but when the poop comes out, it's normal.
Infant dyschezia is a muscle coordination problem. It means that your baby is having trouble coordinating the different muscle groups necessary to poop. This is a learned reflex, and some babies struggle a bit more than others to learn it. They usually figure it out within a week or two.
It’s upsetting for parents to watch their babies struggle, but infants with dyschezia aren’t sick or suffering. Pediatricians believe these infants cry to produce the necessary abdominal pressure to poop, not because they’re in pain. No treatment is necessary or recommended.
Pediatricians believe these infants cry to produce the necessary abdominal pressure to poop, not because they’re in pain. No treatment is necessary or recommended.
Symptoms and Causes
What symptoms are associated with adult dyschezia?
Your healthcare provider might use the term “dyschezia” to describe your condition if you experience:
- Obstructed defecation.
- Straining to poop.
- Pain with pooping.
What symptoms are associated with infant dyschezia?
Infants with dyschezia may show symptoms such as:
- Struggling to poop for at least 10 minutes.
- Grunting, crying or screaming while they try to poop.
- Turning red in the face with effort.
- Squirming or kicking their feet.
- Not succeeding in pooping every time.
- Poop that looks “normal” — soft or pasty — when it comes out.
How can I tell if my baby has dyschezia vs. constipation?
Parents of babies with infant dyschezia often mistake it for constipation at first.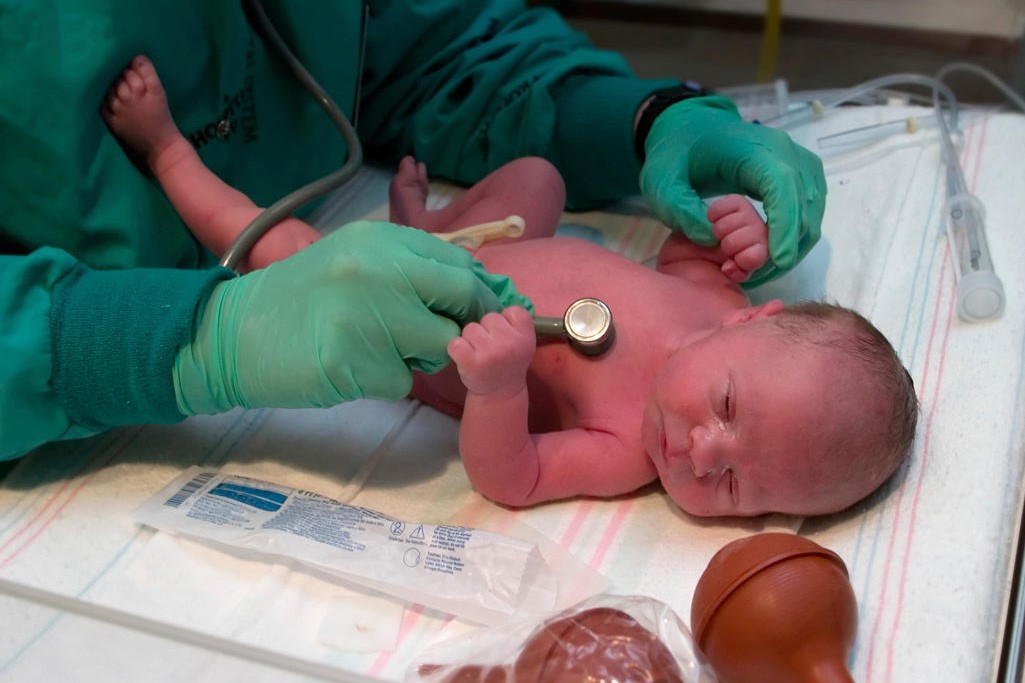 They see their baby straining to poop, and they assume that’s because the poop is too hard to pass. This is, after all, usually the reason why adults strain to poop. Adults don’t remember that they once had to learn how to do it.
They see their baby straining to poop, and they assume that’s because the poop is too hard to pass. This is, after all, usually the reason why adults strain to poop. Adults don’t remember that they once had to learn how to do it.
Straining to poop looks the same, whether they’re straining against hard poop or against their own muscles. But you can tell which kind of struggle it is from the poop that comes out. If the poop is hard or bloody, that’s a sign of constipation. If the poop looks normal, the poop itself isn’t the problem.
How can I tell if my baby has infant dyschezia vs. colic?
Colic is another condition that causes babies to cry inconsolably for no discernible reason. Babies with colic often appear to be in gastrointestinal distress. They might arch their backs, clench their fists or pull their legs up to their tummies while crying, and sometimes they turn red in the face.
Parents and doctors alike once assumed digestive system issues such as gas, reflux, indigestion or difficulty pooping might relate to colic. But evidence of this is scarce, and parents have observed that colic episodes don’t necessarily correspond with feeding cycles.
But evidence of this is scarce, and parents have observed that colic episodes don’t necessarily correspond with feeding cycles.
Colic is still a mystery, but some now believe that it may be, like infant dyschezia, a developmental phase — one that you just have to wait out. This doesn’t stop either colic or infant dyschezia from causing parents a lot of distress. We want to know what’s going on and how to fix it.
In general, doctors diagnose colic when they can’t find any other explanation for your baby’s fussiness. Infant dyschezia is one possibility they might try to exclude first. If you notice that your baby is fussy before pooping in particular, and that it ends when they poop, they might have infant dyschezia.
What causes dyschezia in adults?
Several conditions can cause dyschezia in adults, including:
- Anismus: This condition can cause adults to struggle with their pooping muscles, similar to the way babies with infant dyschezia do.
 Another name for anismus is dyssynergic defecation.
Another name for anismus is dyssynergic defecation. - Endometriosis: People with endometriosis may have difficulty, pain or rectal bleeding during pooping if their endometriosis spreads to their lower bowel, near their rectum.
- Constipation: Hard, impacted poop can be difficult and painful to pass. Prolonged constipation can also damage the muscles and nerves that control pooping, causing further problems.
- Inflammatory bowel disease: Chronic conditions such as ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease can cause chronic inflammation and bleeding in your lower large bowel (your rectum and anus).
- Anorectal lesions: Temporary wounds or growths can cause pain or obstruction while pooping, including hemorrhoids, anal fissures, anal abscesses, colon polyps and tumors.
What causes infant dyschezia?
Infants and children are constantly developing, and they take their time with different skills. Pooping, believe it or not, is one of those skills. It takes a lot of coordination between the brain, nerves and different muscle groups to synchronize the act of pooping, especially without gravity on their side.
Pooping, believe it or not, is one of those skills. It takes a lot of coordination between the brain, nerves and different muscle groups to synchronize the act of pooping, especially without gravity on their side.
Normally, poop entering your rectum triggers your anus muscles to release and let it through. Since infants can’t sit up yet, the pressure in their rectum might be weaker, and it may take more abdominal pressure to push it through. They also have to figure out how to push and release at the same time.
Infants who are trying to push poop out against a clenched anus will struggle and possibly cry with frustration until they learn to relax it. Infants may also cry because they sense that crying helps them contract their abdominal muscles. It may be part of their process of figuring out how to push poop out.
Diagnosis and Tests
How is dyschezia diagnosed in adults?
Dyschezia in adults is a symptom, and your symptoms are what you say they are. If you tell a healthcare provider that you have difficulty pooping, they’ll write it down and ask you more about it. It may relate to a condition you already know that you have, or it may lead you to discover an underlying condition.
It may relate to a condition you already know that you have, or it may lead you to discover an underlying condition.
How is infant dyschezia diagnosed?
Your pediatrician will ask you about your baby’s symptoms and what their poop is like. They may ask for a poop sample. They’ll also give your baby a basic physical exam. If their anatomy looks normal, their poop looks normal and their symptoms only involve the act of pooping, they’ll diagnose infant dyschezia.
Management and Treatment
How do you relieve dyschezia in adults?
Dyschezia in adults can mean different things, and it can have many different causes. Your healthcare provider will need to isolate the cause in order to recommend the right treatment. Possible treatments for pooping difficulties include medications, physical therapy, biofeedback and sometimes surgery.
How can I help my baby with dyschezia?
There’s no treatment for infant dyschezia, and pediatricians don’t advise interfering. This is hard to hear for parents who want to relieve their babies’ struggles. It may be tempting to try to help by stimulating their rectum. But this delays their own learning process and may make them dependent on stimulation.
This is hard to hear for parents who want to relieve their babies’ struggles. It may be tempting to try to help by stimulating their rectum. But this delays their own learning process and may make them dependent on stimulation.
There’s some research to suggest that infant massage can help stimulate your baby’s nervous system and their physical development. While not a direct treatment for dyschezia, regular massage may improve the brain-body coordination they need to develop in order to learn how to poop.
Outlook / Prognosis
What is the outlook for adults with dyschezia?
Some pooping problems are relatively easy to treat, and others can be more elusive, especially when they involve your brain and nervous system. In these cases, healthcare providers often take a holistic approach that combines diet and lifestyle changes with various therapies. This approach takes time.
If you have a chronic disease or a physical lesion that causes pain and difficulty pooping, surgery might have a place in your treatment plan. Surgery is usually the last resort for people with severe symptoms that don’t respond to other treatments or complementary medicine. But it’s often successful.
Surgery is usually the last resort for people with severe symptoms that don’t respond to other treatments or complementary medicine. But it’s often successful.
When do babies grow out of infant dyschezia?
The good news is that infant dyschezia is usually a brief problem, lasting a few days to weeks. Even this can feel like forever when you witness your baby’s daily struggles. But you can rest assured that they’ll overcome it. Most have outgrown dyschezia by the time they’re two to three months old.
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Pooping difficulties will make you miserable, whether you’re an infant, child or adult. Fortunately, infant dyschezia is short-lived and resolves on its own. Adult dyschezia can be more complicated and can take longer to resolve. If you have dyschezia, don’t delay seeing a qualified healthcare provider about it.
What to do with constipation in a newborn?
Constipation in a newborn or infant is an extremely unpleasant problem for parents. And it is not always possible to quickly determine what is the cause of constipation in an infant. Most often, problems with bowel movements in babies are functional in nature and are directly related to the nutrition of the child.
And it is not always possible to quickly determine what is the cause of constipation in an infant. Most often, problems with bowel movements in babies are functional in nature and are directly related to the nutrition of the child.
Signs of constipation in a child of the first year of life
- Infrequent dry and hard stools
- Sleep disorder
- Troubled state
- Pungent odor of feces and flatus
Causes of constipation in a newborn child
Causes of constipation in newborns and infants, as a rule, are not associated with a serious pathology of the internal organs or the central nervous system. The main cause of constipation in a baby is malnutrition, early transfer of a child to supplementary feeding with infant formula, frequent changes in products during artificial feeding.
When breastfeeding, the formation of constipation in children of the first year of life is affected by poor nutrition of the mother, for example, the use of large amounts of animal fats and a lack of fiber in the diet. One possible cause of constipation in newborns is dehydration.
One possible cause of constipation in newborns is dehydration.
What to do if a child has problems with stool
- If a child under one year old has acute constipation and there is anxiety, straining and arching, we actively massage the abdomen in a clockwise direction so that hand marks remain on the skin (but not bruises!) . We spread it on the stomach, do the exercise - legs to the head, children under one year old can massage the anus, if all this does not help - a children's candle with glycerin from the refrigerator.
- If such situations are repeated often - a mandatory consultation with a pediatrician.
- When introducing complementary foods to a baby with a tendency to constipation, introduce fruits and vegetables into the diet first.
- If the child is older than a year and the process is chronic - evaluate nutrition - whether there are the necessary 5 servings of vegetables and fruits per day (portion - from the palm or fist of the baby).
 Estimate - how much water does the child drink per day? Is there enough physical activity during the day? What is the psychological climate in the family and the attitude - not to demand a chair from the child, not to swear and not to shout, not to discuss problems with other people in his presence, not to force him to sit on the potty, not to scold him for dirty panties when anointing.
Estimate - how much water does the child drink per day? Is there enough physical activity during the day? What is the psychological climate in the family and the attitude - not to demand a chair from the child, not to swear and not to shout, not to discuss problems with other people in his presence, not to force him to sit on the potty, not to scold him for dirty panties when anointing. - It is better to choose laxatives based on macrogol or lactulose with the help of a doctor.
- In parallel with laxatives, we conduct psychological work with the child at home and with a specialist - books about defecation, toilet games, etc.
In what case should you be very worried about constipation in a child? Namely:
- if there is no meconium discharge in the first days of life;
- retardation and constipation;
- vomiting and tense abdomen;
- blood in stool;
- changes in hair growth and pigmentation of the sacrum and coccyx,
- violation of the development of the sacrum;
- changes in the anus - fistulas with discharge, hematomas, inflammation;
- change in the muscular skeleton of the anterior abdominal wall - lack of muscles or insufficient development.
If a baby up to a year old is breastfed for several days (3-5 days, but not weeks!) Does not poop and does not worry - if he is cheerful and cheerful, eats well, does not spit up and does not stain the diaper, and farts well, in this no parental intervention required! The stool should be soft and not cause trouble during bowel movements.
In the treatment of constipation, toilet training is important - every day at the same time, preferably after eating and drinking - calmly and kindly go to the potty (if the toilet is, then there should be a support under the feet so that the knees are above the level of the priests) and try to poop. If there was no stool for several days, you can pre-put a glycerin suppository.
In the presence of painful defecation, fissures and blood, urgently show the child to a doctor (gastroenterologist or proctologist) and start treatment - local baths, suppositories and laxatives are applied. This is absolutely necessary in order to soften the stool and prevent the formation of persistent fear of defecation, which is then very difficult to remove. Before defecation with a dense stool, you can additionally lubricate the anus with baby oil. 9+7 (423) 267-61-30; +7 (423) 274-32-22; +7 914-704-32-22.
Before defecation with a dense stool, you can additionally lubricate the anus with baby oil. 9+7 (423) 267-61-30; +7 (423) 274-32-22; +7 914-704-32-22.
Make an appointment online:
PediatricianGeneral practitionerUltrasound doctorGastroenterologistHematologistGynecologistImmunologist-allergistInfectionistCardiologistNeurologistOtorhinolaryngologist (ENT)Orthopedist-traumatologistOphthalmologistPsychiatristUrologist-andrologistPhysiotherapistPhthisiatricianSurgeonEndocrinologistHouse doctorVaccinationMedical examinationTestsOnline consultation Conclude an observation agreement (subscription)
I agree to the processing of data
Please enable JavaScript to pass the CAPTCHA test
If you have any questions, ask them in the comment form below↓↓↓
Leave This Blank:Leave This Blank Too:Do Not Change This: Your email:
Constipation in a child while breastfeeding 9002 You need to act based on the cause of constipation.
 With diagnosed organic constipation, the treatment of the underlying disease is prescribed by a doctor. Solving the problem leads to the normalization of bowel movements.
With diagnosed organic constipation, the treatment of the underlying disease is prescribed by a doctor. Solving the problem leads to the normalization of bowel movements. For functional constipation, doctors recommend:
1. Breastfeed
2 .Breast milk, containing the mother's immune factors, provides the baby's natural protection against infections, promotes the formation of its intestinal microflora and the development of the digestive system as a whole 2 . With weak lactation and lack of breast milk and unstable stool with a tendency to constipation in a child, doctors recommend supplementary feeding with adapted milk formulas with the addition of prebiotics 2 . They contribute to the maintenance of the intestinal microflora, which is partly responsible for digestion 2 .
2. Follow the diet of a nursing mother
The composition of breast milk directly depends on the mother's nutrition, therefore, by changing the diet, it is possible to influence the baby's diet 4 . For the work of the gastrointestinal tract of the baby, it is important to observe the water regime, vegetables, fruits, cereals eaten by the mother, wholemeal bread, that is, foods high in fiber 4 . You should limit the consumption of foods that provoke increased gas formation: cabbage, onions, tomatoes, rice, legumes, black bread, pears, grapes, mushrooms, pickles, smoked meats and spices 3 .
For the work of the gastrointestinal tract of the baby, it is important to observe the water regime, vegetables, fruits, cereals eaten by the mother, wholemeal bread, that is, foods high in fiber 4 . You should limit the consumption of foods that provoke increased gas formation: cabbage, onions, tomatoes, rice, legumes, black bread, pears, grapes, mushrooms, pickles, smoked meats and spices 3 .
Prunes, dried apricots and simple boiled beets can be used as a natural laxative during breastfeeding for constipation in a newborn - you just need to include them in the diet.
Fermented milk products are useful for maintaining the intestinal microflora 2 . But if a child is diagnosed with intolerance to cow's milk, a nursing mother will have to completely abandon dairy products made from it 4 .
3. Maintain the child's physical activity
A well-organized daily routine and physical activity is the most important factor in the treatment of constipation in a child 2 . Physical activity is selected individually according to the age of the child 2 . For newborns and infants during the first 5 months of life, their natural activity and special gymnastics are sufficient 2 . It is very important that the clothes do not hamper the movement of the child and allow him to independently improve his motor skills in the process of learning the world.
Physical activity is selected individually according to the age of the child 2 . For newborns and infants during the first 5 months of life, their natural activity and special gymnastics are sufficient 2 . It is very important that the clothes do not hamper the movement of the child and allow him to independently improve his motor skills in the process of learning the world.
4. Massage the abdomen
First of all, after feeding, it is necessary to hold the baby in an upright position so that he burps air, and then lay him down on his tummy.
Abdominal massage involves gentle strokes on the tummy in a clockwise direction, that is, in a circle, starting from the right iliac region and ending with the left iliac region. In this case, the child should lie on the back. At the end of the procedure, holding the ankles, alternately press the baby's legs to the tummy. This stimulates the passage of gases and defecation.
5. It is wise to use drugs that reduce flatulence
A large amount of gas stretches the walls of the intestine, weakens its peristalsis and leads to colic. Dill water, light fennel tea, and simethicone preparations may relieve symptoms associated with constipation 4 .
Dill water, light fennel tea, and simethicone preparations may relieve symptoms associated with constipation 4 .
Means to help mechanically remove gases from the intestines, such as a gas tube or enemas, are sometimes useful. 4 . However, their frequent use exacerbates the problem of constipation: the baby’s gastrointestinal tract begins to “get lazy” and ceases to perform its functions independently 3 .
6. Microclysters MICROLAX®
Microclysters
occupy a special place in the complex treatment of constipation in breastfed newborns . They promote bowel movements and thereby alleviate the suffering of the baby. MICROLAX® for children from 0 years is designed for the smallest children, equipped with a special short nose and can be used from birth up to 3 years 6 . The composition of the drug includes sodium citrate, which displaces water from the feces, sodium lauryl sulfoacetate, which thins the contents of the rectum, and sorbitol, which stimulates the flow of water into the intestines 6 .