Whooping cough vaccine for babies
Your Baby Needs Whooping Cough Vaccines on Time
Once your baby is old enough (2 months), he needs to get his whooping cough vaccines. That will be the best way to protect him from whooping cough as he gets older. DTaP is the name of the whooping cough vaccine for children (2 months through 6 years). DTaP vaccine combines protection against diphtheria, tetanus, and pertussis (whooping cough).
Vaccinate your baby on time to continue protecting against whooping cough
It is very important for your baby to get the DTaP vaccine on time so he can start building his own protection against the disease. Your baby needs to get DTaP vaccines even if you received the whooping cough vaccine for adults (called Tdap) while pregnant. The antibodies you shared with your baby before birth provide short-term protection, but his DTaP shots provide protection during childhood.
Your baby will need several doses of DTaP vaccine to best protect him. CDC recommends the first dose when he is 2 months old. One recent study showed that parents and doctors can prevent many whooping cough deaths among babies. They can do this by making sure all babies receive the first DTaP dose on time. Your baby will need 2 more doses after that, given at 4 months and 6 months, to build up high levels of protection. He will then need booster shots at 15 through 18 months and at 4 through 6 years to maintain that protection.
Most whooping cough deaths are among babies younger than 3 months old.
Newborns cannot get the whooping cough vaccine
In the United States, there are currently no whooping cough vaccines licensed or recommended for newborns. Therefore, babies do not get the whooping cough vaccine at birth. This leaves babies unprotected in the first few months of life. This is when they are at greatest risk for catching whooping cough and having severe, potentially life-threating complications from the infection.
The best way you can protect your baby is to:
- Get the whooping cough vaccine while you are pregnant
- Encourage those around your baby to be up to date with their whooping cough vaccine
- Have your baby get DTaP vaccines on time according to CDC’s immunization schedule [2 pages] starting at 2 months
Your vaccine during pregnancy could affect your baby’s response to his vaccine
There is a chance that your baby’s immune response to the first few doses of his DTaP vaccine may not be as strong after you get your whooping cough vaccine while pregnant. However, based on a recent study looking at this issue, this interference does not seem to cause any problems when it comes to protecting your baby. Researchers are still working to better understand this issue. The benefits of you getting the vaccine while pregnant outweigh this potential risk. Babies younger than 2 months old only have the antibodies they get from their mother to help protect them. Any protection that you can provide at this age is critical because young babies are most vulnerable to severe disease and death from whooping cough.
However, based on a recent study looking at this issue, this interference does not seem to cause any problems when it comes to protecting your baby. Researchers are still working to better understand this issue. The benefits of you getting the vaccine while pregnant outweigh this potential risk. Babies younger than 2 months old only have the antibodies they get from their mother to help protect them. Any protection that you can provide at this age is critical because young babies are most vulnerable to severe disease and death from whooping cough.
When you get your vaccine while pregnant, it is still critical that your baby gets all his vaccines according to the recommended schedule [2 pages].
Whooping Cough (Pertussis) Vaccines for Children
How to pronounce pertussis: [per-tuhs-is] or Listen
Five doses of a DTaP shot for children and one Tdap shot for preteens are recommended by doctors as the best way to protect against whooping cough (pertussis).
When should my child get a whooping cough shot?
One dose of DTaP at each of the following ages:
One dose of Tdap at the following ages:
Why should my child get a whooping cough shot?
- Helps protect your child from whooping cough, a potentially serious and even deadly disease, as well as diphtheria and tetanus.
- Helps prevent your child from having violent coughing fits from whooping cough.
- Helps protect your newborn when they are most vulnerable to serious disease and complications.
- Keeps your child from missing school or child care and you from missing work.
What vaccines protect against whooping cough?
There are 2 vaccines that help protect children against whooping cough: DTaP and Tdap. Both also protect against diphtheria and tetanus. These shots do not offer lifetime protection.
Whooping cough shots are safe.
Whooping cough shots are safe and effective at preventing whooping cough. Vaccines, like any medicine, can have side effects. These are usually mild and go away on their own.
Vaccines, like any medicine, can have side effects. These are usually mild and go away on their own.
What are the side effects?
Most children don’t have any side effects from DTaP or Tdap. The side effects that do occur with DTaP are usually mild, and may include:
- Soreness or swelling where the shot was given
- Fever
- Fussiness
- Feeling tired
- Loss of appetite
- Vomiting
More serious side effects are very rare but with DTaP can include:
- A fever over 105 degrees
- Nonstop crying for 3 hours or more
- Seizures (jerking, twitching of the muscles, or staring)
The side effects from Tdap are usually mild, and may include:
- Pain, redness, or swelling where the shot was given
- Mild fever
- Headache
- Feeling tired
- Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and stomachache
Some preteens and teens might faint after getting Tdap or any other shot.:no_upscale()/imgs/2018/04/24/07/2141577/a9599dd4712b38e86a9e83def0f139ee5c9d9ad1.jpg)
To prevent fainting and injuries related to fainting, people should be seated or lying down during vaccination and remain in that position for 15 minutes after the vaccine is given.
Prepare for your child's vaccine visit and learn about how you can:
- Research vaccines and ready your child before the visit
- Comfort your child during the appointment
- Care for your child after the shot
Before, During, and After Shots
What is whooping cough?
- Whooping cough is a very serious respiratory illness.
- It is caused by Bordetella pertussis bacteria.
- It can cause violent coughing fits.
- Whooping cough is most harmful for young babies and can be deadly.
What are the symptoms of whooping cough?
Whooping cough usually starts with the following symptoms:
- Runny nose
- Low-grade fever (less than 100.
 4 degrees)
4 degrees) - Mild cough (babies do not do this)
- Apnea (life-threatening pause in breathing in babies) and cyanosis (turning blue or purple) in babies and young children
Children and babies may then begin to develop these more serious problems:
- Coughing very hard, over and over. These coughing fits happen more at night.
- Gasping for breath after a coughing fit. They may make a “whooping” sound. This sound is where the name “whooping cough” comes from. Babies may not cough or make this sound—they may gag, gasp, or stop breathing.
- Difficulty breathing, eating, drinking, or sleeping.
- Turning blue from lack of oxygen.
- Vomiting after coughing fits.
Coughing fits can last for up to 10 weeks or more, and sometimes happen again the next time the child has a respiratory illness.
Is it serious?
Whooping cough is most dangerous for babies and young children. In fact, babies younger than 1 year old who have whooping cough may:
- Need to be cared for in the hospital
- Develop pneumonia (a serious lung infection)
- Have seizures
- Suffer brain damage
Women can get Tdap during pregnancy to pass whooping cough protection to their babies. This helps protect babies until they can start getting their own whooping cough shots. Get vaccinated while pregnant.
This helps protect babies until they can start getting their own whooping cough shots. Get vaccinated while pregnant.
Whooping cough can even be deadly. About 1 in 2 deaths from whooping cough are among babies younger than 2 months old. These babies are too young to get whooping cough shots.
How does whooping cough spread?
The bacteria that cause whooping cough spread easily through the air when a person who has whooping cough breathes, coughs, or sneezes. Almost everyone who is not immune to whooping cough will get sick if exposed to it. A person can spread the disease from the very beginning of the sickness (which may begin as cold-like symptoms) and for at least 2 weeks after coughing starts.
Since symptoms can be mild for some people, a baby can catch whooping cough from adults, grandparents, or older brothers or sisters who don’t know they have the disease.
Do people still get whooping cough in the United States?
Before the whooping cough vaccines were recommended for all infants, about 8,000 people in the United States died each year from whooping cough.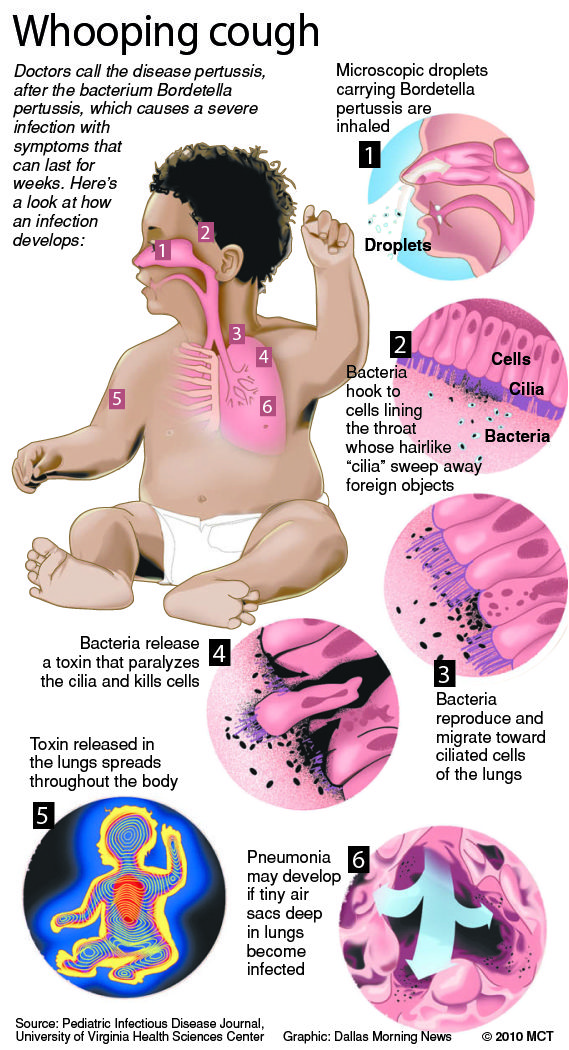 Today, because of the vaccine, this number has dropped to fewer than 20 per year.
Today, because of the vaccine, this number has dropped to fewer than 20 per year.
But, cases of whooping cough have been increasing since the late 1980s, and outbreaks of whooping cough can occur.
Whooping cough vaccine for children | When to do?
Whooping cough is an infectious disease of the respiratory tract, the causative agent of Bordetella pertussis, the most characteristic symptom of which is a dry paroxysmal cough. The greatest number of infected is detected among children under the age of two. The disease is transmitted by airborne droplets, the attacks of suffocation that appear during the disease are very dangerous, as they provoke malfunctions in the vital systems: cardiovascular and nervous. In addition, this infection is dangerous because it can cause complications such as pneumonia, emphysema, pleurisy, hemorrhage in the conjunctiva or retina, diseases of the ENT organs. In the severe stage of the disease, hemorrhage in the brain and respiratory arrest can occur.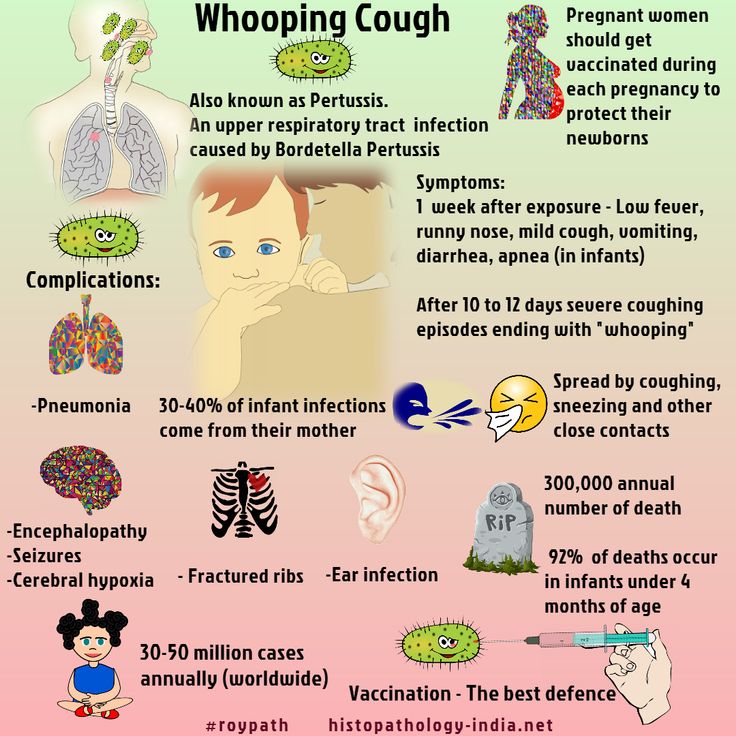
For pertussis vaccination, combined vaccines are used, which, in addition to the pertussis component, contain antigens of other infectious diseases and contain either a whole-cell pertussis component or an acellular pertussis component: Whole cell pertussis vaccines
- DPT for pertussis, diphtheria and tetanus
- Infarix (pertussis, diphtheria and tetanus),
- Adasel (pertussis, diphtheria and tetanus for schoolchildren and adults)
- Pentaxim (pertussis, diphtheria, tetanus, polio and Haemophilus influenzae type B)
- Infarix Hexa (against whooping cough, diphtheria, tetanus, poliomyelitis, Haemophilus influenzae type B, hepatitis B)
Preparations that include a cell-free pertussis component have an advantage over vaccines with a whole-cell pertussis component in terms of tolerability, but according to the results of studies, they are equally effective in forming stable immunity to infection caused by Bordetella pertussis.
If you are looking for a paid clinic in Moscow where you can get your child vaccinated against whooping cough, contact Miracle Doctor. At the pre-vaccination examination, the pediatrician will recommend the vaccine necessary for your baby, taking into account previous vaccinations.
Vaccination schedule
Children are vaccinated against whooping cough at the age of 3, 4.5 and 6 months. Revaccination is performed at 18 months and at 6-7 years. Between the first three injections, the interval is 45 days, between the 3rd and 4th from 6-12 months (according to indications), 5 years between the 4th and 5th.
The first 4 vaccinations contribute to the formation of an immune response. If the vaccination is not done on time, it is necessary to consult with the pediatrician of the clinic "Miracle Doctor" to draw up an individual vaccination schedule. Adults are vaccinated against whooping cough according to indications.
Preparation for vaccination
Before being vaccinated, the pediatrician conducts an examination of the baby in order to determine contraindications for vaccination: it is necessary to undergo a full medical examination with an examination by specialists, ultrasound diagnostics, before vaccination, it is necessary to pass a general blood test and a general urine test
Also before vaccination:
- it is not recommended to introduce new foods and citrus fruits into the child's diet 7 days before vaccination;
- do not change the normal daily routine of the baby, try to limit contact with strangers in order to avoid contact with infectious diseases;
- in the post-vaccination period, the doctor may recommend an antipyretic drug.

Any acute infectious diseases are a contraindication for vaccination, other contraindications can only be determined by a pediatrician at the examination before vaccination
Vaccination
The vaccine is administered intramuscularly into the anterolateral region of the thigh. After vaccination, observation by a pediatrician for half an hour is recommended in case of post-vaccination reactions.
Benefits of the clinic
The Miracle Doctor clinic uses only certified vaccines that are stored in accordance with established requirements. Qualified pediatricians will examine your child before vaccination, choose the most appropriate drug, provide all the necessary recommendations, and draw up an individual vaccination schedule.
You can sign up for whooping cough vaccination on the website or by calling the clinic.
Possible reactions to the vaccine
It should be remembered that the chance of side effects increases if DTP combination preparations are used for pertussis vaccination. On average, complications develop in a third of those vaccinated. Preparations based on live pathogens are the most reactogenic. Side effects most often occur within a day after vaccination. Patients typically experience:
On average, complications develop in a third of those vaccinated. Preparations based on live pathogens are the most reactogenic. Side effects most often occur within a day after vaccination. Patients typically experience:
- hyperemia and itching at the injection site,
- mild fever,
- slight malaise.
In most cases, the reaction to the introduction of the DTP vaccine lasts no more than 48 hours. Inactivated pertussis vaccines are considered less reactogenic. They do not contain a live pathogen, so the vaccine is easier to tolerate. When using acellular vaccines, fever and skin reactions at the injection site are less common. The incidence of post-vaccination complications is also much lower.
Risks of complications after vaccination
Specific complications of DTP vaccines include neurological disorders. Clinicians and scientists assume that diseases develop due to pertussis toxins that are contained in combination vaccines, even inactivated ones. A small part of children susceptible to these components is at risk. Toxins irritate the meninges and lead to encephalopathic disorders. However, dangerous complications are extremely rare, less than 1 case per 300,000 vaccinated.
A small part of children susceptible to these components is at risk. Toxins irritate the meninges and lead to encephalopathic disorders. However, dangerous complications are extremely rare, less than 1 case per 300,000 vaccinated.
Seizures are not considered a complication of pertussis immunization unless accompanied by fever. Medical studies have shown that this symptom occurs with equal frequency in both vaccinated and unvaccinated children. At the same time, convulsions accompanying epilepsy and organic brain damage appear just at the age of 3-4 months, when routine vaccination is carried out. Due to the coincidence of temporal factors, they have long been mistaken for a reaction to the vaccine.
The development of afebrile seizures is a symptom of organic brain damage, which for objective reasons cannot be diagnosed before vaccination. If a child has such seizures, not vaccinating alone is not enough. To prescribe adequate treatment, a comprehensive neurological examination is required.
Contraindications to vaccination
Prevention of mass morbidity involves immunization of all infants, including HIV-positive ones. Pertussis vaccination restrictions are:
- severe adverse reactions to primary vaccination;
- inflammatory processes accompanied by fever or intoxication;
- exacerbation of chronic diseases;
- severe immunodeficiency conditions;
- SARS and acute respiratory infections;
- progressive diseases of the nervous system;
- history of afebrile convulsions.
There is no evidence to support the view that previous encephalitis may be a contraindication for pertussis vaccination.
Whooping cough vaccine. Where to get vaccinated against whooping cough with an imported vaccine in Moscow
+7 (495) 780-07-71
Call center open 24/7
Ambulancearound the clock
Cashback 1000 rubles for all services for a visit in November More All promotions
Whooping cough vaccine
JSC Family Doctor - Whooping cough vaccine
Whooping cough vaccine is included in the National Immunization Schedule. Whooping cough is an infectious disease of the respiratory tract, especially dangerous for children under the age of 2 years. In accordance with the Calendar, pertussis vaccination consists of 3 vaccinations, which are given at the age of 3, 4.5 and 6 months. Revaccination is carried out once at the age of 18 months.
Whooping cough is an infectious disease of the respiratory tract, especially dangerous for children under the age of 2 years. In accordance with the Calendar, pertussis vaccination consists of 3 vaccinations, which are given at the age of 3, 4.5 and 6 months. Revaccination is carried out once at the age of 18 months.
For pertussis vaccination, complex vaccines are used, including imported ones - Infarix (against pertussis, diphtheria and tetanus), Pentaxim (immunization against poliomyelitis and Haemophilus influenzae type B is added), Infarix Hexa (also includes a component that promotes the development of immunity against hepatitis B) . All vaccines create stable immunity to the causative agent of whooping cough.
If you are looking for a paid polyclinic in Moscow where you can get your child vaccinated against whooping cough, contact JSC "Family Doctor". At the pre-vaccination consultation, the doctor will help you choose a vaccine, taking into account the vaccinations that your baby has already received. Below you can specify the prices for vaccination with various vaccines, as well as make an appointment with a pediatrician by choosing a clinic that is located in the most convenient area of Moscow for you.
Dear patients! Please note that pre-vaccination and post-vaccination examinations of the patient by a general practitioner / pediatrician are paid separately. You can specify the price of the service below.
Prices
- Doctor visit
- Manipulations and procedures
| Name | Cost |
|---|---|
| Pediatrician's appointment KMN/leading specialist primary | 2550 |
| Pediatrician primary appointment | 2 100 |
| Appointment with a primary care physician/leading specialist | 2900 |
| General practitioner primary appointment | 2 250 |
| Designation | Cost |
|---|---|
| Vaccination against whooping cough, diphtheria, tetanus, poliomyelitis as part of a complex imported vaccine (from the Pentaxim vaccine, once) | 4000 |
| Vaccination against diphtheria-tetanus-pertussis-poliomyelitis-hemophilic infection type B-hepatitis B (Infanrix Hexa, single dose) | 5 990 |
| Vaccination against diphtheria, whooping cough, tetanus with Adasel vaccine (single dose) | 5 500 |
| Vaccination against diphtheria, tetanus, whooping cough, poliomyelitis, Haemophilus influenzae type B (Pentaxim, single dose) | 5,000 |
| Childhood pertussis, diphtheria and tetanus vaccination (Infanrix) (single dose) Involvement from influenza Dipheria vaccination Benching from whooping cough Caria vaccination Rubber Vaccination Vacore A to Z Whooping cough Answers to questions Persistent fever in a child All answers Probably, the proposed time does not suit you, or there is no free time for online in the schedule records. You can leave a request and we will do our best to organize your appointment. {{formatRecordDate(visitData.date)}} {{visitData.doctor_fio_short}} {{visitData.specialization_name}} {{visitData. |