Baby with tooth
Baby’s First Tooth: 7 Facts Parents Should Know
By: Dina DiMaggio, MD, FAAP & Julie Cernigliaro, DMD
1. Most babies will develop teeth between 6 and 12 months.
There is a wide range of variability of when a first tooth may appear—some babies may not have any teeth by their first birthday! Around 3 months of age, babies will begin exploring the world with their mouth and have increased saliva and start to put their hands in their mouth. Many parents question whether or not this means that their baby is teething, but a first tooth usually appears around 6 months old.
Typically, the first teeth to come in are almost always the lower front teeth (the lower central incisors), and most children will usually have all of their baby teeth by age 3.
2. Fluoride should be added to your child's diet at 6 months of age.
Fluoride is a mineral that helps prevent tooth decay by hardening the enamel of teeth. The good news is that fluoride is often added to tap water. Give your baby a few ounces of water in a sippy or straw cup when you begin them on solid foods (about 6 months of age). Speak with your pediatrician to see if your tap water contains fluoride or whether your child needs fluoride supplements. Fluoride is not typically found in most bottled water. See FAQ: Fluoride and Children for more information.
3. Massaging sore gums, offering something cold, or acetaminophen, on an occasional rough night, can help soothe your baby's teething pain.
Usually teething doesn't cause children too much discomfort, however, many parents can tell when their baby is teething. Babies may show signs of discomfort in the area where the tooth is coming in, the gums around the tooth may be swollen and tender, and the baby may drool a lot more than usual.
Parents can help ease teething pain by massaging their baby's gums with clean fingers, offering solid, not liquid-filled, teething rings or a clean frozen or wet washcloth. If you offer a teething biscuit, make sure to watch your baby while they are eating it. Chunks can break off easily and can lead to choking. Also, these biscuits are not very nutritious and most contain sugar and salt.
If you offer a teething biscuit, make sure to watch your baby while they are eating it. Chunks can break off easily and can lead to choking. Also, these biscuits are not very nutritious and most contain sugar and salt.
A baby's body temperature may slightly rise when teething; however, according to a 2016 study in Pediatrics, a true fever (temperature over 100.4 degrees Fahrenheit or 38 degrees Celsius) is not associated with teething and is actually a sign of an illness or infection that may require treatment. If your baby is clearly uncomfortable, talk with your pediatrician about giving a weight-appropriate dose of acetaminophen (e.g., Tylenol) or if over 6 months, ibuprofen (e.g., Advil, Motrin). Make sure to ask your pediatrician for the right dose in milliliters (mL) based on your child's age and weight.
Many children, however, will have no problems at all when their teeth come in!
4. Do not use teething tablets, gels with benzocaine, homeopathic teething gels or tablets, or amber teething necklaces.

Stay away from teething tablets that contain the plant poison belladonna and gels with benzocaine. Belladonna and benzocaine are marketed to numb your child's pain, but the FDA has issued warnings against both due to potential side effects.
In addition, amber teething necklaces are not recommended. Necklaces placed around an infant's neck can pose a strangulation risk or be a potential choking hazard. There is also no research to support the necklace's effectiveness. See Teething Necklaces and Beads: A Caution for Parents for more information.
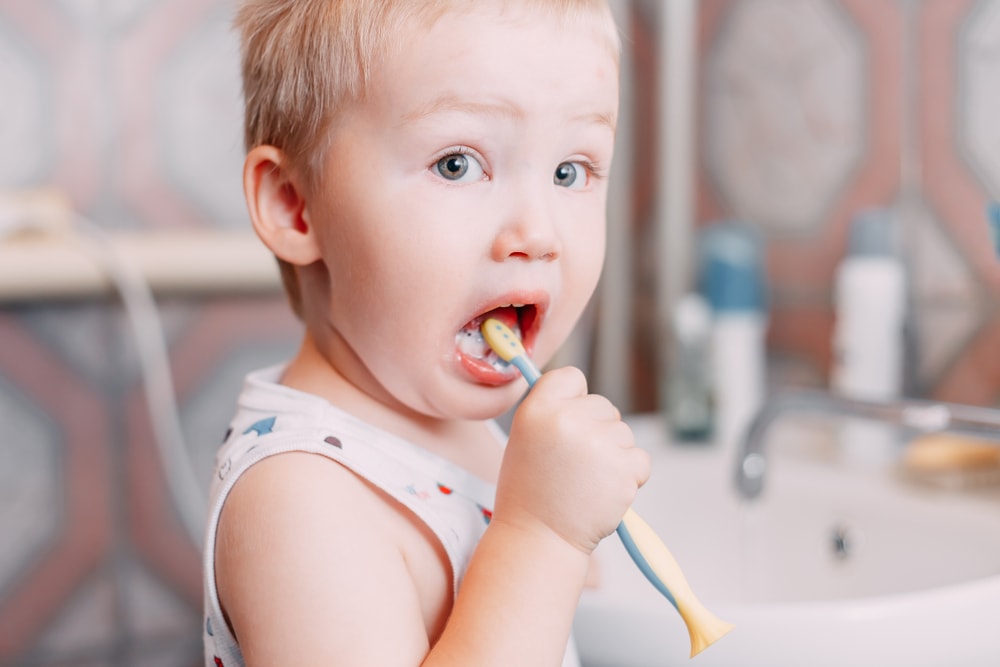
5. You should brush your child's teeth twice a day with fluoride toothpaste.
Once your child has a tooth, you should be brushing them twice a day with a smear of fluoride toothpaste the size of a grain of rice, especially after the last drink or food of the day. Remember not to put your baby to bed with a bottle—it can lead to tooth decay.
Once your child turns 3, the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP), the American Dental Association (ADA), and the American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry (AAPD)recommend that a pea-sized amount of fluoride toothpaste be used when brushing.
When your child is able, teach them to spit out the excess toothpaste. It is best if you put the toothpaste on the toothbrush until your child is about age 6. Parents should monitor and assist their child while brushing until they are around 7 or 8 years old. When your child can write their name well, he or she also has the ability to brush well.
6. Ask your pediatrician about your baby's teeth and fluoride varnish.
During regular well-child visits, your pediatrician will check your baby's teeth and gums to ensure they are healthy and talk to you about how to keep them that way. The AAP and the United States Preventive Services Task Force also recommend that children receive fluoride varnish once they have teeth.
If your child does not yet have a dentist, ask your pediatrician if they can apply fluoride varnish to your baby's teeth. Once your child has a dentist, the varnish can be applied in the dental office. The earlier your child receives fluoride varnish the better to help prevent tooth decay.
7. Make your first dental appointment when the first tooth appears.
Try to make your baby's first dental appointment after the eruption of the first tooth and by his or her first birthday.
Both the AAP and the AAPD recommend that all children see a pediatric dentist and establish a "dental home" by age one. A pediatric dentist will make sure all teeth are developing normally and that there are no dental problems. They will also give you further advice on proper hygiene. If you don't have a pediatric dentist in your community, find a general dentist who is comfortable seeing young children.
Additional Information:
Brushing Up On Oral Health: Never Too Early to Start
How to Prevent Tooth Decay in Your Baby
Brush, Book, Bed: How to Structure Your Child's Nighttime Routine
Give Your Baby the Best Possible Start
About Dr.
 DiMaggio:
DiMaggio: Dina DiMaggio, MD, FAAP, is a board certified pediatrician at Pediatric Associates of NYC and at NYU Langone Medical Center. She is the co-author of The Pediatrician's Guide to Feeding Babies and Toddlers, a comprehensive manual written by a team of medical, nutrition, and culinary experts. Follow her on Instagram @Pediatriciansguide.
About Dr. Cernigliaro:
Julie Cernigliaro, DMD, is a board certified pediatric dentist and the Associate Director of the Pediatric Dental Residency Program at Lutheran Medical Center in Brooklyn, NY. She holds a faculty position at NYU College of Dentistry and currently works in private practice at Happy Smile Pediatric Dentistry, PC in NYC.
The information contained on this Web site should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your pediatrician. There may be variations in treatment that your pediatrician may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances.
Teething Tots (for Parents) - Nemours KidsHealth
What Is Teething?
Teething is when teeth first come through a baby's gums. It can be a frustrating time for babies and their parents. Knowing what to expect during teething and how to make it a little less painful can help.
When Does Teething Start?
While teething can begin as early as 3 months, most likely you'll see the first tooth start pushing through your baby's gum line when your little one is between 4 and 7 months old.
The first teeth to appear usually are the two bottom front teeth, also known as the central incisors. They're usually followed 4 to 8 weeks later by the four front upper teeth (central and lateral incisors). About a month later, the lower lateral incisors (the two teeth flanking the bottom front teeth) will appear.
Next to break through are the first molars (the back teeth used for grinding food), then finally the eyeteeth (the pointy teeth in the upper jaw). Most kids have all 20 of their primary teeth by their third birthday. (If your child's teeth come in much slower than this, speak to your doctor.)
(If your child's teeth come in much slower than this, speak to your doctor.)
In some rare cases, kids are born with one or two teeth or have a tooth emerge within the first few weeks of life. Unless the teeth interfere with feeding or are loose enough to pose a choking risk, this is usually not a cause for concern.
What Are the Signs of Teething?
As kids begin teething, they might drool more and want to chew on things. For some babies, teething is painless. Others may have brief periods of irritability, while some may seem cranky for weeks, with crying spells and disrupted sleeping and eating patterns. Teething can be uncomfortable, but if your baby seems very fussy, talk to your doctor.
Although tender and swollen gums could cause your baby's temperature to be a little higher than normal, teething doesn't usually cause high fever or diarrhea. If your baby does develop a fever during the teething phase, something else is probably causing the fever and you should contact your doctor.
How Can I Make Teething Easier?
Here are some tips to keep in mind when your baby is teething:
- Gently wipe your baby's face often with a cloth to remove the drool and prevent rashes from developing.
- Rub your baby's gums with a clean finger.
- Give your baby something to chew on. Make sure it's big enough that it can't be swallowed or choked on and that it can't break into small pieces. A wet washcloth placed in the freezer for 30 minutes makes a handy teething aid. Be sure to take it out of the freezer before it becomes rock hard — you don't want to bruise those already swollen gums — and be sure to wash it after each use.
Rubber teething rings are also good, but avoid ones with liquid inside because they may break or leak. If you use a teething ring, chill it in the refrigerator, but NOT the freezer. Also, never boil to sterilize it — extreme changes in temperature could cause the plastic to get damaged and leak chemicals.
- Teething biscuits and frozen or cold food are only OK for kids who already eat solid foods.
 Don't use them if your child has not yet started solids. And make sure to watch your baby to make sure that no pieces break off or pose a choking hazard.
Don't use them if your child has not yet started solids. And make sure to watch your baby to make sure that no pieces break off or pose a choking hazard. - If your baby seems irritable, ask your doctor if it is OK to give a dose of acetaminophen or ibuprofen (for babies older than 6 months) to ease discomfort.
- Never place an aspirin against the tooth, and don't rub alcohol on your baby's gums.
- Never tie a teething ring around a baby's neck or any other body part — it could get caught on something and strangle the baby.
- Don't use teething necklaces made of amber. These can lead to strangulation or choking if pieces break off.
- Don't use teething gels and tablets because they may not be safe for babies.
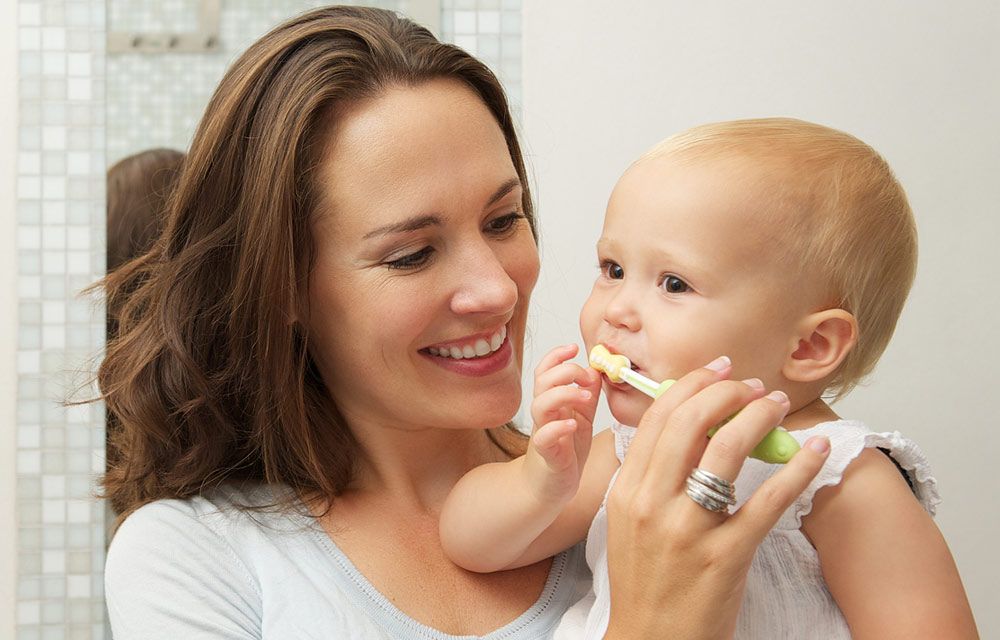
How Should I Care for My Baby's Teeth?
The care and cleaning of your baby's teeth is important for long-term dental health. Even though the first set of teeth will fall out, tooth decay makes them fall out more quickly, leaving gaps before the permanent teeth are ready to come in. The remaining primary teeth may then crowd together to attempt to fill in the gaps, which may cause the permanent teeth to come in crooked and out of place.
The remaining primary teeth may then crowd together to attempt to fill in the gaps, which may cause the permanent teeth to come in crooked and out of place.
Daily dental care should begin even before your baby's first tooth comes in. Wipe your baby's gums daily with a clean, damp washcloth or gauze, or brush them gently with a soft, infant-sized toothbrush and water (no toothpaste!).
As soon as the first tooth appears, brush it with water and fluoridated toothpaste, using only a tiny amount.
It's OK to use a little more toothpaste once a child is old enough to spit it out — usually around age 3. Choose one with fluoride and use only a pea-sized amount or less in younger kids. Don't let your child swallow the toothpaste or eat it out of the tube because an overdose of fluoride can be harmful to kids.
By the time all your baby's teeth are in, try to brush them at least twice a day and especially after meals. It's also important to get kids used to flossing early on. A good time to start flossing is when two teeth start to touch. Talk to your dentist for advice on flossing those tiny teeth. You also can get toddlers interested in the routine by letting them watch and imitate you as you brush and floss.
A good time to start flossing is when two teeth start to touch. Talk to your dentist for advice on flossing those tiny teeth. You also can get toddlers interested in the routine by letting them watch and imitate you as you brush and floss.
Another important tip for preventing tooth decay: Don't let your baby fall asleep with a bottle. The milk or juice can pool in a baby's mouth and cause tooth decay and plaque.
The American Dental Association (ADA) recommends that kids see a dentist by age 1, or within 6 months after the first tooth appears, to spot any potential problems and advise parents about preventive care.
Reviewed by: Larissa Hirsch, MD
Date reviewed: January 2018
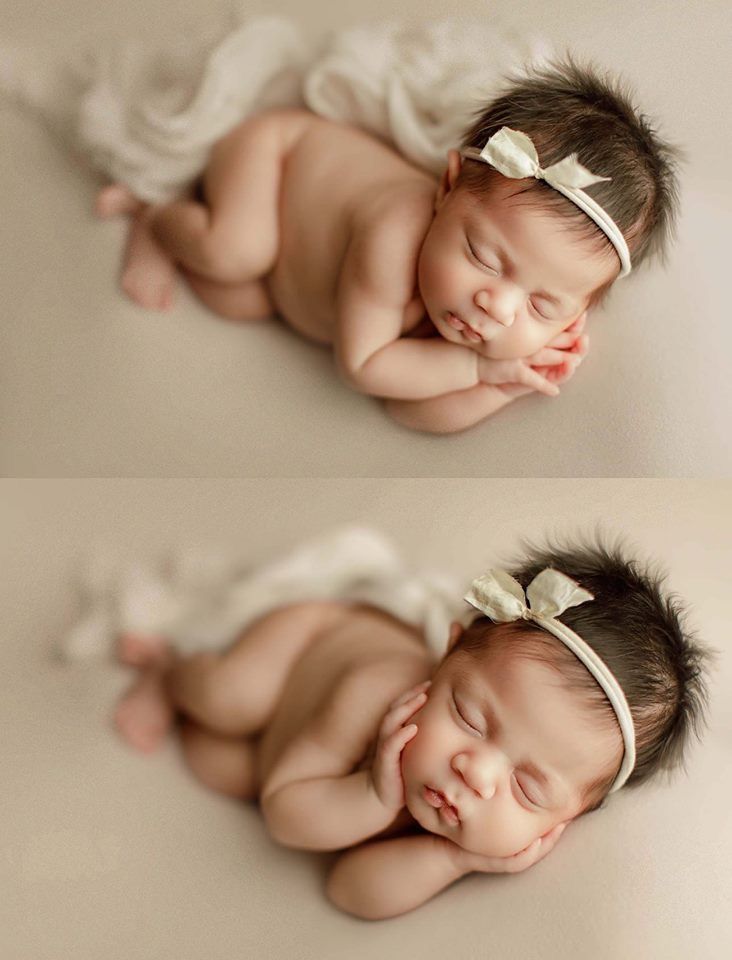
5 reasons why a baby can be born with teeth
HealthBaby
- Photo
- Thanasis Zovoilis / The Image Bank / Getty Images
The rudiments of milk teeth are formed in a child in the womb - at 6 weeks of gestation. But the process of teething normally begins at 3-7 months of life. One can understand the surprise of the parents, and sometimes the medical staff, when a newborn is born with one or even several teeth at once. What is this pathology, a joke of nature, a cause for concern? And in general, does this really happen? We deal with a specialist.
But the process of teething normally begins at 3-7 months of life. One can understand the surprise of the parents, and sometimes the medical staff, when a newborn is born with one or even several teeth at once. What is this pathology, a joke of nature, a cause for concern? And in general, does this really happen? We deal with a specialist.
orthodontist, DR MINKO DENTAL CLINIC
One in a thousand
Cases when a baby is born with teeth already erupted - as a rule, these are incisors - do occur in medical practice, although quite rarely. They are found mainly in girls.
Such teeth are called natal. They may not yet be fully erupted and only palpable, or appear completely. Most of them do not have a root or it is poorly developed, very fragile, unstable. They can occupy a normal position or be displaced - cross the gum, form an additional dentition, which interferes with the formation of milk and permanent teeth. It can also affect the development of the jaw apparatus and facial bones.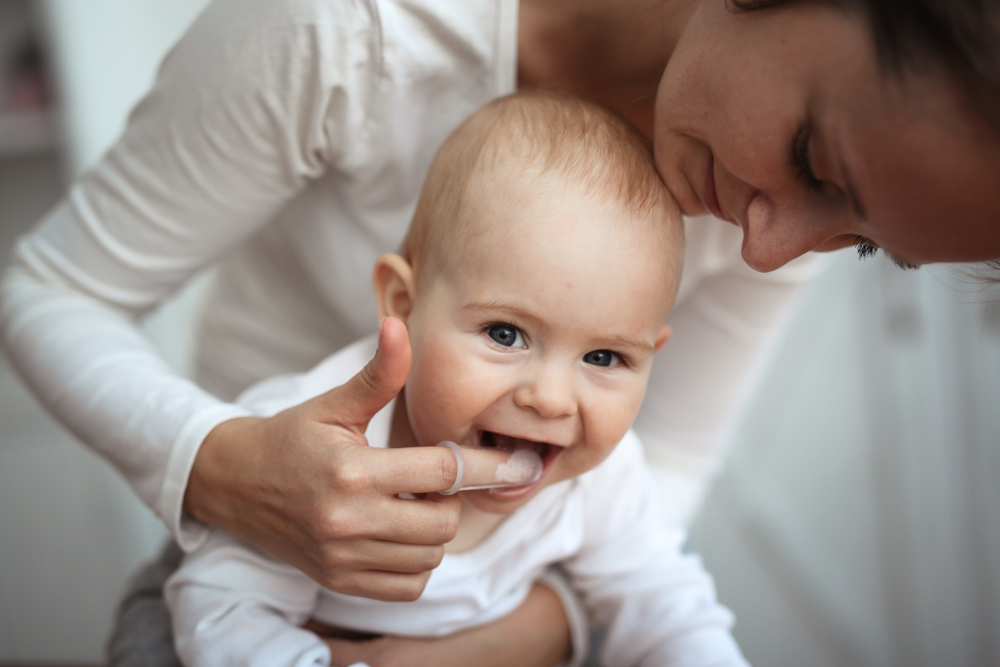 Natal teeth can cause discomfort to both the baby and the mother, in particular during feeding.
Natal teeth can cause discomfort to both the baby and the mother, in particular during feeding.
Sometimes natal teeth can be associated with developmental anomalies, but these are extremely rare cases.
Why a baby is born with teeth
As a rule, the reason is that the buds of the teeth were located too close to the gums - the so-called superficial location, due to which eruption occurs prematurely.
Since the phenomenon is not particularly common, its nature has not yet been fully studied. Most often, 4 more reasons are considered:
-
genetic predisposition;
-
complications during pregnancy;
- Photo
- Getty Images
Should natal teeth be extracted
What should parents do? First of all, you need to show the baby to the dentist. It is not at all necessary that a child born with teeth will have some problems in the future. But this is still a pathology, so it is better to keep the situation under control.
But this is still a pathology, so it is better to keep the situation under control.
Is it necessary to remove such teeth - the question is decided on an individual basis.
If possible, the tooth should be saved, the extraction process is a trauma for the child, and the operation is rather painful. Now there are silicone breast pads that prevent tissue damage during feeding. Please note that this tooth also needs to be cleaned. This will help special fingertips.
Most likely, removal will be indispensable if:
-
they are abnormally located - for example, form the second row. This can affect the formation of milk, and in the future, permanent teeth, leading to bite problems.
-
teeth can damage, injure the mouth or cause pain to the child - have sharp edges, are too brittle and can crumble, have not fully erupted.
In addition to natal teeth, the doctor must examine the entire cavity and make sure that there are no jaw deformities, palate pathology. In some cases, x-rays and consultation with a specialized specialist may be required.
In some cases, x-rays and consultation with a specialized specialist may be required.
It is important to visit the dentist periodically - if you still have problems with your bite, for example, you can take timely action.
Anna Gerasimenko
Reading today
“My mother-in-law constantly makes sharp remarks about my appearance. What should she answer?
Vivid images and a lot of emotions: the most memorable exits of the Welsh in 2022 - 25 photos13 photos
All tips
It is not uncommon for a child to get injured during active play. And everything would be fine if it is not a tooth injury. Many parents panic in search of a solution, and many simply do not know how to do the right thing so that this trauma does not affect the future of the child. Especially for this case, we have prepared an action plan for parents, in case the child gets a tooth injury...
Child knocked out a milk tooth
- Usually milk teeth are not subject to re-engraftment.

- See a doctor to monitor surrounding teeth and tissues.
The child hit the milk tooth
- Make sure the tooth is in its original position.
- Is it normal for a child to close their teeth?
- Orally displaced teeth must be replaced immediately.
- Reposition the tooth using a damp cloth or gauze.
- Impacted deciduous teeth are left under observation until they come out on their own.
- The most important thing is time. Call our pediatric dentistry immediately.
- Locate tooth if possible
- Many permanent teeth can be replanted into place, but! Take the tooth only by the crown - not by the root.
- Store the tooth in saliva or milk.
- If you can, insert the tooth into place in the socket.
- Contact our clinic immediately if the child is concerned about pain or increased sensitivity of the teeth to the air, then a child's prosthesis will be required.

- If possible, save the tooth fragment, put it in water or milk.
- It is sometimes possible to bond the chip to the tooth using a composite material.
- Contact our clinic immediately for an appointment with a doctor.
- Thoroughly brush your child's teeth.
- Floss all teeth.
- Give your child Paracetamol or Ibuprofen pain tablets.
- Contact our clinic immediately.
- An appointment must be made immediately so as not to interrupt the process of correcting the child's bite.
- We will do our best to accommodate you as soon as possible.
- If possible, remove loose parts of the structure from the oral cavity.
- Isolate all protruding parts with wax to avoid injury.
- Do not try to remove the stuck wire from your cheek, tongue, or gums.