When your pregnant do you spot
Bleeding and spotting from the vagina during pregnancy
Bleeding and spotting from the vagina during pregnancy are common
If you bleed or spot during pregnancy, it doesn’t always mean there’s a problem but in some cases they may be signs of a problem for you or your baby’s health
If you have heavy bleeding, call your health care provider right away
Tell your provider about any bleeding or spotting you have during pregnancy
Bleeding and spotting from the vagina during pregnancy are common. Up to 1 out of 4 (up to 25%) of all pregnant women have some bleeding or spotting during their pregnancy.
Bleeding and spotting in pregnancy don’t always mean there’s a problem, but they can be a sign of miscarriage or other serious complications. Miscarriage is when a baby dies in the womb before 20 weeks of pregnancy.
Call your health care provider if you have any bleeding or spotting, even if it stops. It may not be caused by anything serious, but your provider needs to find out what’s causing it.
What’s the difference between bleeding and spotting?
Bleeding or spotting can happen anytime, from the time you get pregnant to right before you give birth. Spotting is light bleeding. It happens when you have a few drops of blood on your underwear. Spotting is so light that the blood wouldn’t cover a panty liner. Bleeding is when the blood flow is heavier, enough that you need a panty liner or pad to keep the blood from soaking your underwear and clothes.
What should you do if you have bleeding or spotting during pregnancy?
Call your health care provider if you have any kind of bleeding during pregnancy and do these things:
- Keep track of how heavy your bleeding is, if it gets heavier or lighter, and how many pads you are using.
- Check the color of the blood. Your provider may want to know. It can be different colors, like brown, dark or bright red.
- Don’t use a tampon, douche or have sex when you’re bleeding.

Call your health care provider right away at any time during pregnancy or go to the emergency room if you have:
- Heavy bleeding
- Bleeding with pain or cramping
- Dizziness and bleeding
- Pain in your belly or pelvis
What causes bleeding or spotting early in pregnancy?
It’s normal to have some spotting or bleeding early in pregnancy. Bleeding or spotting in the first trimester may not be a problem. It can be caused by:
- Having sex
- An infection
- Implantation. When a fertilized egg (embryo) attaches to the lining of the uterus (womb) and begins to grow.
- Hormone changes. Hormones are chemicals made by the body.
- Changes in your cervix. The cervix is opening to the uterus that sits at the top of the vagina.
- Certain types of testing during pregnancy like an amniocentesis or Chorionic villus sampling (CVS). These are tests that are done to check for genetic abnormalities in your baby.
 Genetic abnormalities are changes in the genes that are passed down to a baby from mom or dad. These genetic changes can cause health problems for a baby.
Genetic abnormalities are changes in the genes that are passed down to a baby from mom or dad. These genetic changes can cause health problems for a baby. - Problems related to smoking. If you smoke, it’s best to stop before pregnancy or as soon as you know you’re pregnant.
Sometimes bleeding or spotting in the first trimester is a sign of a serious problem, like:
- Miscarriage. Almost all women who miscarry have bleeding or spotting before the miscarriage.
- Ectopic pregnancy. This is when a fertilized egg implants itself outside of the uterus and begins to grow. An ectopic pregnancy cannot result in the birth of a baby. It can cause serious, dangerous problems for the pregnant woman.
- Molar pregnancy. This is when a mass of tissue forms inside the womb, instead of a baby. Molar pregnancy is rare.
What causes bleeding or spotting later in pregnancy?
Bleeding or spotting later in pregnancy may be caused by:
- Labor
- Having sex
- An internal exam by your health care provider
- Problems with the cervix, like an infection, growths, inflammation or cervical insufficiency.
 This is when a woman’s cervix opens too early. Inflammation of the cervix is when it may be painful, swollen, red or irritated.
This is when a woman’s cervix opens too early. Inflammation of the cervix is when it may be painful, swollen, red or irritated.
Bleeding or spotting later in pregnancy may be a sign of a serious problem, like:
- Preterm labor. This is labor that happens too early, before 37 weeks of pregnancy.
- Placenta previa. This is when the placenta lies very low in the uterus and covers all or part of the cervix.
- Placenta accreta. This is when the placenta grows into the wall of the uterus too deeply.
- Placental abruption. This is when the placenta separates from the wall of the uterus before birth.
- Uterine rupture. This is when the uterus tears during labor. This happens very rarely. It can happen if you have a scar in the uterus from a prior cesarean birth (also called c-section) or another kind of surgery on the uterus.
 A c-section is surgery in which your baby is born through a cut that your doctor makes in your belly and uterus.
A c-section is surgery in which your baby is born through a cut that your doctor makes in your belly and uterus.
How are bleeding and spotting treated?
Your treatment depends on what caused your bleeding. You may need a medical exam and tests.
Most of the time, treatment for bleeding or spotting is rest. Your provider may also suggest treatments like:
- Take time off from work and stay off your feet for a little while
- You may need medicine to help protect your baby from Rh disease. Rh disease is when your blood and baby’s blood are incompatible (can’t be together). This disease can cause serious problems — even death — for your baby.
- Don’t have sex, douche or use tampons
- If you have heavy bleeding, you may need a hospital stay or surgery
Last reviewed April 2020
10 Early Signs That You Might Be Pregnant
Written by Joseph Saling
In this Article
- Do All Women Get Early Symptoms of Pregnancy?
- Spotting and Cramping
- Breast Changes
- Fatigue
- Nausea (Morning Sickness)
- Missed Period
- Other Early Symptoms of Pregnancy
Are you wondering if you might be pregnant? The only way to know for sure is by taking a pregnancy test.
But there are early symptoms of pregnancy that may point to the possibility. Here's what to look for.
Do All Women Get Early Symptoms of Pregnancy?
Every woman is different. So are their experiences of pregnancy. Not every woman has the same symptoms or even the same symptoms from one pregnancy to the next.
Also, because the early symptoms of pregnancy often mimic the symptoms you might experience right before and during menstruation, you may not realize you're pregnant.
What follows is a description of some of the most common early symptoms of pregnancy. You should know that these symptoms may be caused by other things besides being pregnant. So the fact that you notice some of these symptoms does not necessarily mean you are pregnant. The only way to tell for sure is with a pregnancy test.
Spotting and Cramping
After conception, the fertilized egg attaches itself to wall of the uterus. This can cause one of the earliest signs of pregnancy -- spotting and, sometimes, cramping.
That's called implantation bleeding. It occurs anywhere from six to 12 days after the egg is fertilized.
The cramps resemble menstrual cramps, so some women mistake them and the bleeding for the start of their period. The bleeding and cramps, however, are slight.
Besides bleeding, a woman may notice a white, milky discharge from their vagina. That's related to the thickening of the vagina's walls, which starts almost immediately after conception. The increased growth of cells lining the vagina causes the discharge.
This discharge, which can continue throughout pregnancy, is typically harmless and doesn't require treatment. But if there is a bad smell related to the discharge or a burning and itching sensation, tell your doctor so they can check on whether you have a yeast or bacterial infection or STD.
Breast Changes
Breast changes are another very early sign of pregnancy. A woman's hormone levels rapidly change after conception. Because of the changes, their breasts may become swollen, sore, or tingly a week or two later. Or they may feel heavier or fuller or feel tender to the touch. The area around the nipples, called the areola, may also darken.
Or they may feel heavier or fuller or feel tender to the touch. The area around the nipples, called the areola, may also darken.
Other things could cause breast changes. But if the changes are an early symptom of pregnancy, keep in mind that it is going to take several weeks to get used to the new levels of hormones. But when it does, breast pain should ease up.
Fatigue
Feeling very tired is normal in pregnancy, starting early on.
A woman can start feeling unusually fatigued as soon as one week after conceiving.
Why? It's often related to a high level of a hormone called progesterone, although other things -- such as lower levels of blood sugar, lower blood pressure, and a boost in blood production -- can all contribute.
If fatigue is related to pregnancy, it's important to get plenty of rest. Eating foods that are rich in protein and iron can help offset it.
Nausea (Morning Sickness)
Morning sickness is a famous symptom of pregnancy.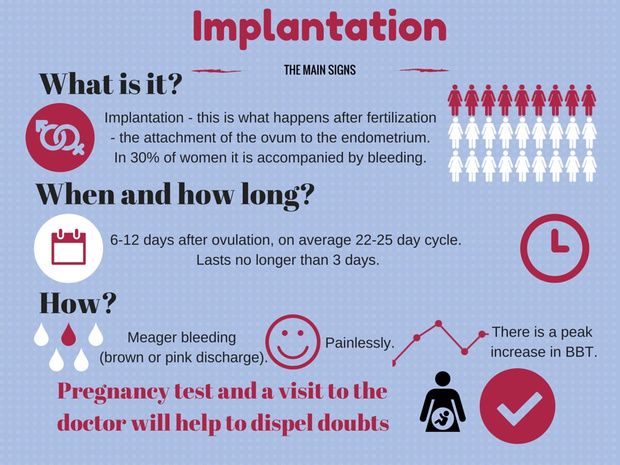 But not every pregnant woman gets it.
But not every pregnant woman gets it.
The exact cause of morning sickness is not known but pregnancy hormones likely contribute to this symptom. Nausea during pregnancy may occur at any time of the day but most commonly in the morning.
Also, some women crave, or can't stand, certain foods when they become pregnant. That's also related to hormonal changes. The effect can be so strong that even the thought of what used to be a favorite food can turn a pregnant woman's stomach.
It's possible that the nausea, cravings, and food aversions can last for the entire pregnancy. Fortunately, the symptoms lessen for many women at about the 13th or 14th week of their pregnancy.
In the meantime, be sure to eat a healthy diet so that you and your developing baby get essential nutrients. You can talk to your doctor for advice on that.
Missed Period
The most obvious early symptom of pregnancy -- and the one that prompts most women to get a pregnancy test -- is a missed period. But not all missed or delayed periods are caused by pregnancy.
But not all missed or delayed periods are caused by pregnancy.
Also, women can experience some bleeding during pregnancy. If you are pregnant, ask your doctor what you should be aware of with bleeding. For example, when is bleeding normal and when is it a sign of an emergency?
There are reasons, besides pregnancy, for missing a period. it might be that you gained or lost too much weight. Hormonal problems, fatigue, or stress are other possibilities. Some women miss their period when they stop taking birth control pills. But if a period is late and pregnancy is a possibility, you may want to get a pregnancy test.
Other Early Symptoms of Pregnancy
Pregnancy brings changes in your hormonal balance. And that can cause other symptoms that include:
- Frequent urination. For many women, this starts around the sixth or eighth week after conception. Although this could be caused by a urinary tract infection, diabetes, or using diuretics, if you're pregnant, it's most likely due to hormonal levels.
- Constipation. During pregnancy, higher levels of the hormone progesterone can make you constipated. Progesterone causes food to pass more slowly through your intestines. To ease the problem, drink plenty of water, exercise, and eat plenty of high-fiber foods.
- Mood swings. These are common, especially during the first trimester. These are also related to changes in hormones.
- Headaches and back pain. Many pregnant women report frequent mild headaches, and others experience back pain.
- Dizziness and fainting. These may be related to dilating blood vessels, lower blood pressure, and lower blood sugar.
A pregnant woman could have all of these symptoms, or maybe have only one or two. If any of these symptoms become bothersome, talk with your doctor about them so you can make a plan to offset them.
Health & Pregnancy Guide
- Getting Pregnant
- First Trimester
- Second Trimester
- Third Trimester
- Labor and Delivery
- Pregnancy Complications
- All Guide Topics
Why is it possible not to notice pregnancy until the very birth?
Article author: Yudina Elena Alexandrovna , obstetrician-gynecologist
The first type of is a hidden pregnancy, when the body does not show signs of conception, or when its symptoms can be interpreted differently.
The second type of is when a woman does not let the thought that she will soon become a mother. Such pregnancies are more often associated with mental disorders or young age. There are not many such cases, but they do occur.
Consider the first type
As a rule, a woman with normal weight monitors her menstrual cycle and regularly visits a gynecologist. The probability of not noticing pregnancy is higher in overweight women. If the menstrual cycle is disturbed, toxicosis may not be noted, and the only sign of pregnancy is only the growth of the abdomen. At the same time, obese women with an irregular menstrual cycle due to hormonal failure believe that they are insured against pregnancy and, thereby, miss the fact of conception. In addition, it is quite possible not to notice pregnancy in the case of a small child and the fullness of the expectant mother. Also, polycystic ovary syndrome, combined with overweight and an increase in subcutaneous fat on the abdomen, can mislead the fair sex.
The probability of not noticing pregnancy is higher in overweight women. If the menstrual cycle is disturbed, toxicosis may not be noted, and the only sign of pregnancy is only the growth of the abdomen. At the same time, obese women with an irregular menstrual cycle due to hormonal failure believe that they are insured against pregnancy and, thereby, miss the fact of conception. In addition, it is quite possible not to notice pregnancy in the case of a small child and the fullness of the expectant mother. Also, polycystic ovary syndrome, combined with overweight and an increase in subcutaneous fat on the abdomen, can mislead the fair sex.
Along with this, there are anatomical reasons not to notice the “interesting position”. If the fetus is located too high and there is no growth of the abdomen (especially in overweight women with an irregular cycle), which should prompt a woman to think about pregnancy, then the state when the child begins to move is mistaken for flatulence, and poor health and toxicosis are associated with food poisoning. In athletic women, on the contrary, trained abdominal muscles can hide the child and his movements well. In addition, due to anatomical features, such as the bending of the uterus, the abdomen may grow very little.
In athletic women, on the contrary, trained abdominal muscles can hide the child and his movements well. In addition, due to anatomical features, such as the bending of the uterus, the abdomen may grow very little.
There are women with false signs of pregnancy, in which all the clinical symptoms of a traditional pregnancy (weight gain, lactation, abdominal growth and toxicosis) appear, but there is no baby in the stomach.
There is a category of women (as a rule, they take pill forms of contraceptives, or have a diagnosis of infertility, or who have had a displacement of the intrauterine device), who do not notice the fact of the onset of pregnancy due to the fact that in the early stages it is accompanied by signs of interruption (bloody discharge pain in the lower abdomen). A woman perceives these symptoms as painful menstruation with a violation of the menstrual cycle. At the same time, they assure the doctor that menstruation was every month, but more abundant and painful.
Some women who have already conceived have bleeding, which they may confuse with the so-called "menstruation". For example, in the case when the placenta is located in the lower part of the uterus and covers its internal pharynx (this should be interpreted as a threat of abortion). Such patients require closer attention and careful monitoring.
After childbirth, women forget that ovulation can occur before the first menstruation even in the presence of active lactation, therefore, fertilization is possible. In addition, if the fair sex did not start taking birth control pills in the first 5 days of the cycle, missed taking them, or had vomiting and diarrhea, then the pill could not be absorbed. As a result, follicle growth and ovulation are triggered. In such cases, additional contraception is needed.
During menopause, ovulation can occur at any time. During this period, a woman feels mood swings, dizziness, nausea and a regular weight gain. At this time, it is necessary to visit a gynecologist more often and use contraception, since the fact of an unplanned pregnancy is not excluded.
The second type is characterized by the following
Many young girls may show a symptom of physiological denial of their pregnancy, because they do not want a child, are emotionally unprepared to cope with this situation and are afraid of their parents (girls are afraid of the publicity of their sexual contacts) and consequences of pregnancy. A married woman may experience the same problems because of infidelity to her husband. Fatigue they attribute to overwork or sleep problems. Mentally ill women who, in principle, do not know and do not understand what is happening to them, may also not know about their pregnancy.
If you experience any unusual symptoms such as weight gain, missing or unusual menstruation, we recommend that you contact your doctor.
Make an appointment with a gynecologist
For more details, consult a qualified specialist at the Semeynaya clinic.
To find out the prices for a gynecological appointment or other questions, follow the link below:
Pregnancy - from the first days
With the onset of pregnancy, a woman's body immediately begins to rebuild in work and prepare for bearing a baby. After all, a young mother has a journey of 40 weeks, when she will carry a baby in herself, and her body will create all the most favorable conditions for this, provide the baby not only with a small, cozy apartment, but also with nutrition and oxygen. A woman who has received a long-awaited pregnancy treats all changes in her body with special attention, listens to every new sensation!
After all, a young mother has a journey of 40 weeks, when she will carry a baby in herself, and her body will create all the most favorable conditions for this, provide the baby not only with a small, cozy apartment, but also with nutrition and oxygen. A woman who has received a long-awaited pregnancy treats all changes in her body with special attention, listens to every new sensation!
And how should a woman feel at the very beginning of pregnancy?
The first sign of an "interesting" situation, of course, menstruation that did not start on time . Already on the first day of delay, you can do a urinary pregnancy test, with a high probability it will show the true result. More informative and important for an obstetrician-gynecologist will be the value of Human Chorionic Gonadotropin, determined by the blood of a pregnant woman, this is a hormone that is produced by the future placenta, it appears in the woman's body from the first hours of pregnancy and actively increases in the future. By the amount of this hormone, the doctor will judge the gestational age, the absence of pathological conditions and the developmental norms of this pregnancy and will guide you on the most optimal terms for ultrasound examination.
By the amount of this hormone, the doctor will judge the gestational age, the absence of pathological conditions and the developmental norms of this pregnancy and will guide you on the most optimal terms for ultrasound examination.
Breast engorgement and enlargement. Gradually appearing symptom. If a woman has examined her breasts during the last year, was examined by a mammologist, underwent an ultrasound examination of the mammary glands, and received a conclusion from the doctor - she is healthy, there is nothing to worry about! The mammary glands enter a new phase of development and prepare for the upcoming feeding of the child. If the mammary glands have not been examined for more than a year, it is recommended to undergo an ultrasound scan to exclude possible pathology, especially since the obstetrician-gynecologist will need this examination to register for pregnancy.
Drawing pains in the lower abdomen. May be normal only if they occur no more than 1-2 times a day, and go away on their own after a few minutes. In other cases, pain in the lower abdomen, of course, is not an indicator of a pathological or complicated course of pregnancy, but it is still necessary to consult a doctor. The gynecologist will determine the cause of the pain and give recommendations on the regimen, permissible loads and, if necessary, prescribe treatment.
In other cases, pain in the lower abdomen, of course, is not an indicator of a pathological or complicated course of pregnancy, but it is still necessary to consult a doctor. The gynecologist will determine the cause of the pain and give recommendations on the regimen, permissible loads and, if necessary, prescribe treatment.
Nausea and vomiting. Not the most pleasant, but almost inevitable signs of pregnancy. If nausea occurs predominantly in the morning, try to fight it with food. Before going to bed, prepare for yourself a piece of an apple or a banana, you can have a cracker or a biscuit cookie, even a cracker will do. In the morning after waking up, without getting out of bed, enjoy the "piece" waiting for you, very often this is what saves you from an attack of morning sickness. A small spoonful of honey helps. Drink more liquids, mineral water, juices, tea. Ginger tea fights toxicosis well. Eat small meals. At least 5-7 times a day. Food should not be fatty or spicy. Avoid stuffy rooms. Walk outdoors more. Daytime naps are recommended. If vomiting occurs, especially more than 1-2 times a day, you should consult a doctor. Additional examination and more serious treatment may be required.
Avoid stuffy rooms. Walk outdoors more. Daytime naps are recommended. If vomiting occurs, especially more than 1-2 times a day, you should consult a doctor. Additional examination and more serious treatment may be required.
Discharge from the genital tract becomes more profuse during pregnancy. Normally, this is a clear, odorless mucous discharge. If there is “something wrong” in the discharge, it is better to consult a doctor. They will take a swab from you to determine the degree of purity of the vagina, see why the discharge has changed its character, and whether it needs treatment. Since during pregnancy the woman's body is in an immunosuppressive state, that is, the mother's immunity is reduced, inflammatory changes in the vagina may occur, which during pregnancy is very important to treat in a timely manner.
If you are concerned about bloody or brown discharge from the genital tract, you should not panic, but you must definitely consult a doctor on the same day.