Frequent braxton hicks 35 weeks
Baby and You at 35 Weeks Pregnant: Symptoms and Development
In this article:
Key takeaways at week 35
Baby's development at week 35
3D anatomy views
Pregnancy symptoms this week
Your body at 35 weeks
Signs of labor at 35 weeks
Tips for week 35
Checklist for week 35
Key Takeaways at 35 Weeks Pregnant
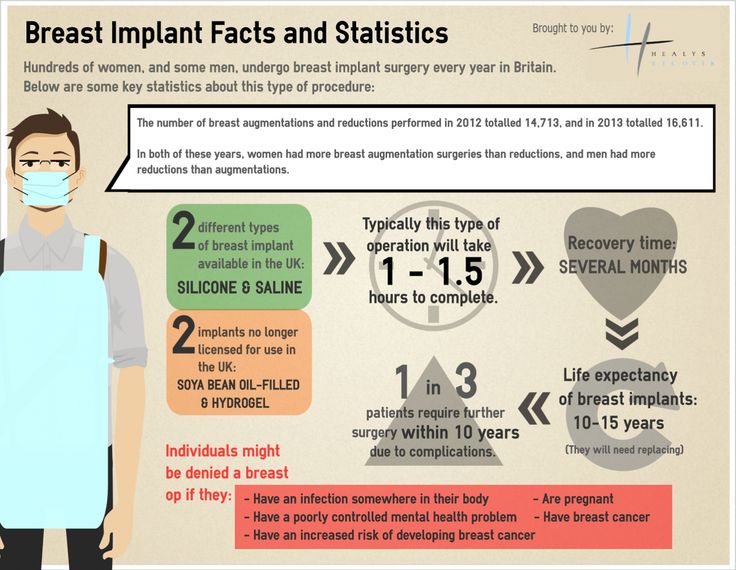
- At this stage, it might feel like you’re all belly—and with good reason. Believe it or not, your uterus has grown to about 500 to 1,000 times its original size.
- Make sure you know the signs of labor. Braxton Hicks contractions will feel intense at this point; make sure they’re not getting stronger and more frequent. If they are, call your doctor.
- The Group B strep test will be happening in the next week or two. Your doctor will swab your vaginal area and rectum and have it tested for bacteria called Group B Strep. It’s common, but can be harmful to baby. Don’t worry, if you’re positive, you’ll just be given antibiotics during labor to protect baby.
At 35 weeks, some moms-to-be feel like they have a ton of stuff left to do before baby’s arrival. Others can barely wait for baby to make their debut. Either way, try not to stress; baby will show up when they’re ready and won’t care if you haven’t checked every little detail off your list. As long as you’ve got a safe place for baby to sleep, some diapers and an infant car seat for the ride home, you’ve already got a bunch of baby’s basic needs taken care of.
Watch Week 35 Highlights
Baby at Week 35
Baby’s hearing is now fully developed, and your 35-week fetus responds best to high-pitched noises. If you’re pregnant with a boy, you would see on a 35 weeks pregnant ultrasound that his testes have probably fully descended. (Bet you hadn’t thought about that one!)
How big is baby at 35 weeks?
At 35 weeks pregnant, baby is as big as a pineapple. Baby measures about 18.2 inches from head to heel. From here on out, they won't get much longer but will keep plumping up. Your 35-week fetus now weighs about 5.3 pounds, and will put on a pound or more of baby fat before you meet them.
Your 35-week fetus now weighs about 5.3 pounds, and will put on a pound or more of baby fat before you meet them.
35 weeks pregnant is how many months?
Thirty-five weeks pregnant is eight months pregnant, although doctors refer to your stage in pregnancy by week, not month. Just about five more weeks left!
35 week ultrasound
Wondering if you’ll get an ultrasound this week? Probably not—unless you’re considered high risk. This week or next, you may have a Group B strep test. For it, your doctor will take a swab of your vaginal area and rectum and have it tested for bacteria called Group B Strep. This bacteria is common and isn’t going to make you sick, but it could be harmful to baby if they’re exposed to it at birth, so knowing whether you have it is important. If you do, you’ll be given antibiotics during the birth to prevent exposure, and that’s that. Easy peasy.
3D Views: My Baby, My Body
See their progress for yourself with our 3D interactive tool.
See My Baby in 3D
See My Body in 3D
ADVERTISEMENT
Pregnancy Symptoms at Week 35
As you wrap up your eighth month, you’re probably feeling some of these 35 weeks pregnant symptoms:
Frequent urge to pee
Yup, your bladder is being pressed on by baby (or babies, if you’re 35 weeks pregnant with twins), who’s likely sitting pretty low in your pelvis, getting ready for birth. Don’t let the extra trips to the bathroom deter you from drinking lots of water, though—dehydration puts you at risk for preterm labor, so drink up.
Constipation
We’ve said it before and we’ll say it again: Make sure to get plenty of fiber in your diet. If you’ve tried everything and are still struggling with constipation, ask your doctor if it’s okay for you to take a fiber supplement or a stool softener.
Aches and pains in the hips and pelvis
These ouchies are continuing—and you may even be feeling a few new ones. While you’re dealing with discomfort, look on the bright side: It’s a sign your body is getting ready to deliver your baby. Yep, all of this pain actually has a purpose! Your ligaments are loosening so that baby can make their way out of your uterus and into the world.
While you’re dealing with discomfort, look on the bright side: It’s a sign your body is getting ready to deliver your baby. Yep, all of this pain actually has a purpose! Your ligaments are loosening so that baby can make their way out of your uterus and into the world.
Braxton Hicks contractions
At 35 weeks pregnant, you may have noticed an increase in the number of contractions you're having. It’s kind of crazy how hard your belly can get! Just keep an eye on those contractions; rest when you get them and drink lots of water.
Is it normal to be really tired at 35 weeks pregnant?
You are definitely not alone in feeling fatigued at 35 weeks! Your body’s aches and pains, your bursting bladder and your very active baby all make insomnia a very real possibility at this stage of your pregnancy. You may also be experiencing symptoms such as leg cramps or heartburn that can prevent you from sleeping soundly. Just try to get all the rest you can now—in a few weeks, it will be much harder to sleep with a new baby to love and care for!
Your Pregnant Belly at 35 Weeks
Growing, growing, growing. Yup, baby and you. Now that you’ve reached 35 weeks pregnant, your uterus has grown to about 500 to 1,000 times its original size, a number that might sound exaggerated to everyone else—but to you, it probably feels more like a million. You can expect to gain about a half-pound each week until you give birth.
Yup, baby and you. Now that you’ve reached 35 weeks pregnant, your uterus has grown to about 500 to 1,000 times its original size, a number that might sound exaggerated to everyone else—but to you, it probably feels more like a million. You can expect to gain about a half-pound each week until you give birth.
When you’re 35 weeks pregnant, it’s a good idea to review the signs of labor. You may think this is early, but about 11 percent of singleton moms give birth prematurely, while moms who are 35 weeks pregnant with twins are close to being considered full term at this point.
Signs of Labor at 35 Weeks
This is not a drill! Here are signs of actual, call-the-OB-and-grab-your-hospital-bag labor:
Water breaking.
You’ll know your water has broken if you experience something that’s less like discharge and more like a flow of water. It can happen in a big gush (like in the movies) or in a slow trickle that just keeps coming.
Painful contractions
Those Braxton Hicks have nothing on real contractions. If you’re suddenly feeling pain in your 35 weeks pregnant belly or back instead of some mild tightness, it could be time.
If you’re suddenly feeling pain in your 35 weeks pregnant belly or back instead of some mild tightness, it could be time.
Regular contractions
True contractions happen regularly and don’t stop—they get more frequent, and more painful. Your doctor will probably tell you at what point to call and let them know about your contractions. A good rule of thumb is to call when contractions are about five minutes apart for a first pregnancy. If it’s not your first, call earlier—more like when they’re 10 to 15 minutes apart—because those labors tend to be much shorter.
Unsure if any 35 weeks pregnant symptom could be a sign of labor? Always call the doctor just to be safe.
Can baby be born at 35 weeks and be healthy?
Yes! While it’s still a couple more weeks until baby reaches “early term” at 37 weeks, they can still be born now and be just as healthy in the long run as one born later. Don’t be surprised if your doctor wants to extend baby’s hospital stay a bit just to make sure all is well.
It's not too early to start organizing the pile of goods needed for your hospital (or birth center) stay!… Cluttering your labor and postpartum space will bring unnecessary stress, not to mention tripping hazards in darkened rooms. Think comfort, familiarity and necessities: your bed pillow, personal toiletries, stretchy clothes, special objects for labor focal points, phones/chargers, snacks, baby outfit, car seat. Channel your inner minimalist!
Julie Lamppa
APRN, CNM, certified nurse midwife at the Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minnesota, and the co-author of Obstetricks: Mayo Clinic Tips and Tricks for Pregnancy, Birth and More
Tips for 35 Weeks Pregnant
Feeling over it? We hear you. Don’t worry, your pregnancy journey will be over soon enough—and the reward will be worth it! In the meantime, here are some ways to stay busy this week.
Pack your hospital bag
If you haven’t done so already, it’s time to prepare for delivery. There are things you’ll need (insurance information, photo ID) and there are things that you’ll want (socks, comfortable clothes for the trip home). Here’s a checklist if you need ideas for what to pack.
Here’s a checklist if you need ideas for what to pack.
Use your pregnancy pillow
At the 35-week mark, this pillow has probably been a lifesaver for you. It helps you maintain that ideal left-side sleeping position, and it also relieves pressure on your hips while you’re lying in bed.
Watch your water intake before bed
There’s not a whole lot you can do about your frequent trips to the bathroom—it’s just part of being 35 weeks pregnant. Up all night? Limit how much water you drink in the hour or two before you go to bed to reduce the number of middle-of-the-night wake ups.
Eat more salads
They’re a great way to get more fiber in your diet to prevent constipation. Start with spinach or kale, add some lentils or roasted chickpeas (or go fruit-forward with pears, berries or apples) and top with sesame seeds or chopped almonds—they’re all tasty fiber-rich foods.
I thought I'd miss beer the most while pregnant, and while that was true, nothing compared to how much I missed sleeping on my stomach! I've been a stomach sleeper my whole life, and that first postpartum sleep on my belly in my own bed was heaven
Kate T. , mom of one
, mom of one
ADVERTISEMENT
Braxton Hicks contractions | Pregnancy Birth and Baby
Braxton Hicks contractions | Pregnancy Birth and Baby beginning of content6-minute read
Listen
Key facts
- Braxton Hicks contractions are a normal part of pregnancy.
- Braxton Hicks contractions feel like the muscles across your belly are tightening.
- Braxton Hicks contractions are irregular, usually lasting for about 30 seconds — while they can be uncomfortable, they aren’t usually painful.
- Braxton Hicks contractions don’t mean that you’re going into labour.
- If you’re not sure if you are having Braxton Hicks or labour contractions, contact your doctor or midwife.
What are Braxton Hicks contractions?
If you feel tightening or pressure in your abdomen (tummy) during your pregnancy, you may be having Braxton Hicks contractions. Braxton Hicks are sometimes called ‘false’ or ‘practice’ contractions. They’re a normal part of pregnancy that can come and go.
Braxton Hicks are sometimes called ‘false’ or ‘practice’ contractions. They’re a normal part of pregnancy that can come and go.
Braxton Hicks contractions prepare your body for giving birth by toning the muscles in your uterus.
Braxton Hicks contractions don’t cause labour and aren’t a sign that labour is beginning.
If you’re not sure whether you’re experiencing Braxton Hicks contractions or actual labour, contact your doctor or midwife.
What do Braxton Hicks contractions feel like?
Braxton Hicks contractions feel like the muscles across your belly are tightening.
Braxton Hicks contractions come irregularly and usually last for about 30 seconds. However, they can last for up to 2 minutes. While they can be uncomfortable, they usually aren’t painful.
When do you get Braxton Hicks contractions?
Braxton Hicks contractions can occur from early in your pregnancy, but you may not feel them until the second trimester. They are most often felt in the third trimester.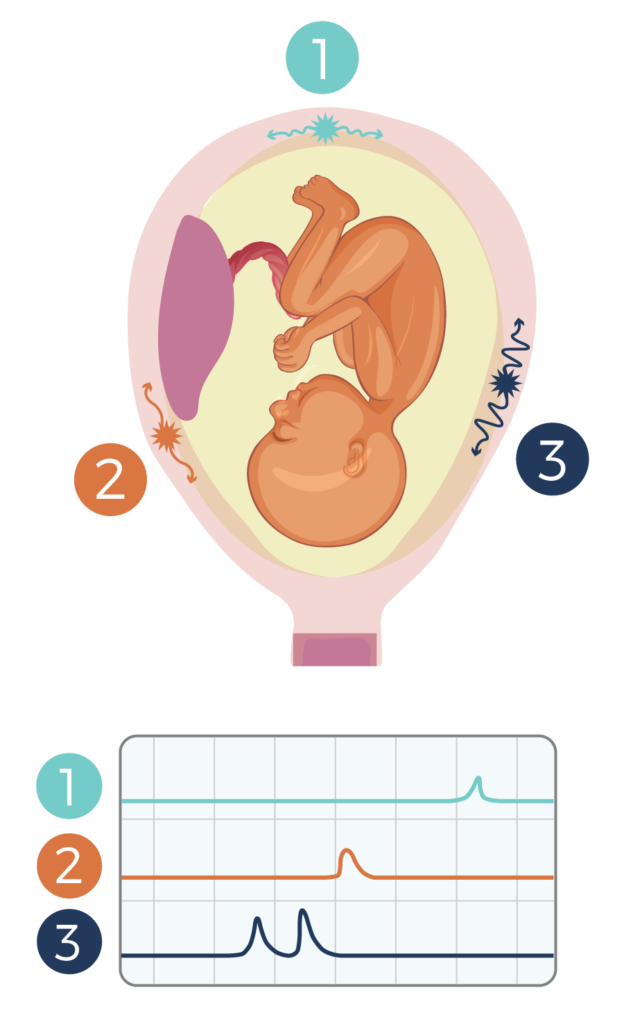
In late pregnancy, you may experience Braxton Hicks contractions more often.
How are Braxton Hicks contractions different from labour pain?
There are some differences between Braxton Hicks contractions and true labour contractions. Your doctor or midwife will consider these differences when deciding whether you’re in labour.
Braxton Hicks contractions:
- don’t open or dilate your cervix
- usually last for about 30 seconds
- can be uncomfortable, but usually aren’t painful
- come and go at irregular times
- usually occur no more than once or twice an hour, a few times a day — until late in your pregnancy
- usually stop if you change position or activity or go for a walk
- usually stop if you have a warm bath or shower
Real labour contractions:
- open or dilate your cervix
- last 30 to 70 seconds
- are painful or require all of your attention
- become very regular, and get closer together as time passes
- last longer as time passes
- get stronger or come more often when you walk
- get stronger over time
Should I call my doctor or midwife?
Call your doctor or midwife or go to the hospital if:
- your waters break
- you have contractions that are getting stronger, closer together and more regular
If you’re less than 37 weeks pregnant, contractions can be a sign of premature labour. Contact your doctor or midwife immediately if you feel pain, pressure or discomfort in your:
Contact your doctor or midwife immediately if you feel pain, pressure or discomfort in your:
- pelvis
- abdomen (tummy)
- lower back
You should also contact your doctor or midwife immediately if you have any signs of labour.
At any stage of pregnancy, you should contact your doctor or midwife immediately if you:
- have persistent pain in your abdomen (tummy)
- have vaginal bleeding
- are concerned about your baby’s movements
- feel very unwell
If you’re in doubt, don’t hesitate to call your doctor or midwife for advice.
How can I ease the discomfort?
Braxton Hicks contractions are normal and don’t need treatment. But if you feel uncomfortable, you can try:
- lying down or changing position
- taking a walk
- relaxing in a warm bath
- having a massage
- staying hydrated
- urinating (weeing)
It may help to practise your breathing exercises during your Braxton Hicks contractions.
Resources and support
For more information about Braxton Hicks contractions speak to your doctor or midwife.
Speak to a maternal child health nurse
Call Pregnancy, Birth and Baby to speak to a maternal child health nurse on 1800 882 436 or video call. Available 7am to midnight (AET), 7 days a week.
Sources:
Mater Mothers' Hospital (Labour and birth information), QLD Health (Journey of labour), Tasmanian Government Dept of Health (Your health during pregnancy), RANZCOG (Labour and birth), Western Sydney Local health district (How will I know I’m in labour? Fact Sheet), Queensland Government (Preterm labour and birth)Learn more here about the development and quality assurance of healthdirect content.
Last reviewed: December 2022
Back To Top
Related pages
- Health professionals involved in your pregnancy
- Giving birth - stages of labour
- Premature baby
Need more information?
Pregnancy at week 22
By week 22, some parts of your baby’s body are fully formed, while some women experience Braxton Hicks contractions about now.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Pregnancy at week 35
You'll probably be having lots of Braxton Hicks contractions by now. It's your body's way of preparing for the birth. They should stop if you move position.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Giving birth - contractions
Contractions are when the muscles in your uterus tighten and then relax. They occur throughout the later stages of your pregnancy.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
What happens to your body in childbirth
During childbirth, your body's hormones, ligaments and muscles, as well as the shape of your pelvis, all work together to bring your baby safely into the world.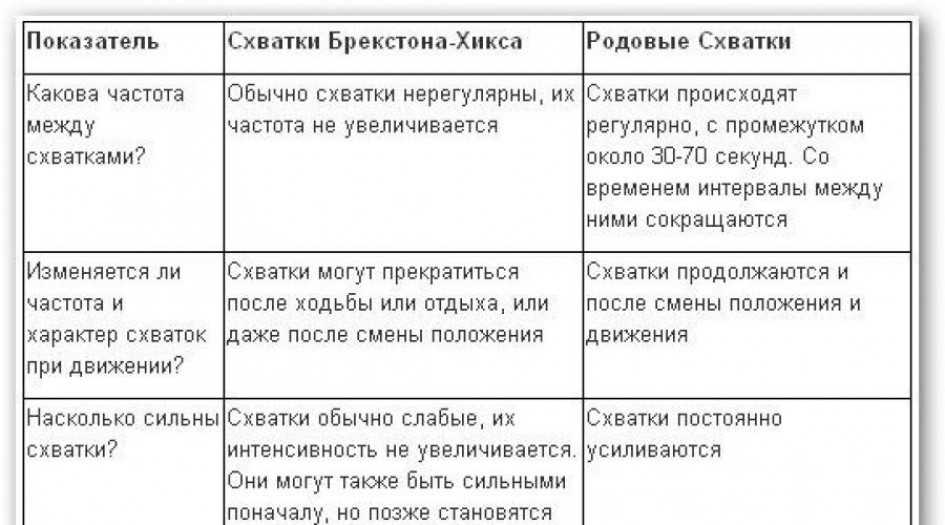
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Anatomy of pregnancy and birth - uterus
The uterus is your growing baby’s home during pregnancy. Learn how the uterus works, nurtures your baby and how it changes while you are pregnant.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Preterm labour - MyDr.com.au
Going into labour before your 37th week of pregnancy is called preterm labour, or premature labour. Find out what it means for you and your baby.
Read more on myDr website
38 weeks pregnant | Raising Children Network
38 weeks pregnant? In this pregnancy week by week guide, find out how your baby is growing, how your body is changing and how to look after yourself.
Read more on raisingchildren.net.au website
26 weeks pregnant | Raising Children Network
26 weeks pregnant? In this pregnancy week by week guide, find out how your baby is growing, how your body is changing and how to look after yourself.
Read more on raisingchildren.net.au website
Giving birth - early signs of labour
You can know the early signs of labour, even if you cannot predict when your labour will begin. Find out also what to do if something appears to be wrong.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Anatomy of pregnancy and birth
From conception to giving birth, a woman's body goes through many physical changes. Learn what happens to your body during pregnancy and labour.
Learn what happens to your body during pregnancy and labour.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Disclaimer
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is not responsible for the content and advertising on the external website you are now entering.
OKNeed further advice or guidance from our maternal child health nurses?
1800 882 436
Video call
- Contact us
- About us
- A-Z topics
- Symptom Checker
- Service Finder
- Subscribe to newsletters
- Linking to us
- Information partners
- Terms of use
- Privacy
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is funded by the Australian Government and operated by Healthdirect Australia.
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby’s information and advice are developed and managed within a rigorous clinical governance framework.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
Healthdirect Australia acknowledges the Traditional Owners of Country throughout Australia and their continuing connection to land, sea and community. We pay our respects to the Traditional Owners and to Elders both past and present.
This information is for your general information and use only and is not intended to be used as medical advice and should not be used to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any medical condition, nor should it be used for therapeutic purposes.
The information is not a substitute for independent professional advice and should not be used as an alternative to professional health care. If you have a particular medical problem, please consult a healthcare professional.
If you have a particular medical problem, please consult a healthcare professional.
Except as permitted under the Copyright Act 1968, this publication or any part of it may not be reproduced, altered, adapted, stored and/or distributed in any form or by any means without the prior written permission of Healthdirect Australia.
Support this browser is being discontinued for Pregnancy, Birth and Baby
Support for this browser is being discontinued for this site
- Internet Explorer 11 and lower
We currently support Microsoft Edge, Chrome, Firefox and Safari. For more information, please visit the links below:
- Chrome by Google
- Firefox by Mozilla
- Microsoft Edge
- Safari by Apple
You are welcome to continue browsing this site with this browser. Some features, tools or interaction may not work correctly.
Pregnancy: the beginning of the end - October 28, 2015
All news A dancer tattooed with images of Putin performed with the Rasputin show in Chelyabinsk. Photo and video
Photo and video
Mobilized were sentenced to three years in prison for refusing to participate in a special operation: news from the Northern Military District for April 6
In the Chelyabinsk region, four fishermen died after falling through the ice Red-eared turtle of the Miass River
Chelyabinsk police officers found a teenager who shot at the windows on Pionerskaya
A Chelyabinsk school was sued under contracts with the Ural Food Plant
The head of the district, accused of fraud for 4 million, was placed under house arrest
They sound noble! How nobles and aristocrats called their children - 12 beautiful names
In Russia, the incidence of HIV has risen sharply. Let's talk about the situation in the Southern Urals
Demolish - period. The Federal Property Management Agency responded to the claims of doctors who are being expelled from the house on Kisegach
The OMK Trubodetal plant became a laureate of the 2022 Sovetsky District Man of the Year contest
The ski-roller track will be shortened in order to build an interuniversity campus in Chelyabinsk
He took away an apartment, beat and dunked a child in the toilet. A mother of two children accuses her ex-military husband of fraud and bullying
A mother of two children accuses her ex-military husband of fraud and bullying
Chelyabinsk residents are alarmed by the shallowing of the Shershnevsky reservoir after winter
We are waiting for an Arctic cyclone: it will become sharply cold in the Chelyabinsk region
Even a 5th grader can do it: try to solve these 10 math problems without a calculator
“You died. Well, they died, and that’s it”: how officials buried a 64-year-old artist, depriving him of his pension and stood in line: what kind of miracle elixirs for all diseases are sold to old people all over the country
“Please don’t worry”: the Ministry of Emergency Situations warned the residents of Chelyabinsk about sounds similar to explosions
The police arrived at the courtyard in the North-West of Chelyabinsk in response to a call about shooting at windows
You will be blown up by this: 8 products belly grows
Survive on 16,000 and not hate the world. How a journalist lived on the minimum wage and why she couldn't complete the experiment
A modern grocery discounter has arrived in the city. Why are goods cheaper there?0003
Why are goods cheaper there?0003
“The house can collapse at any moment”: residents of a high-rise building accused the ex-ombudsman Sevastyanov of dangerous repairs to the basement
They want to give money to utility debtors to pay off their debts. Who will pay for the idea of deputies?
“My wife visited me for a year, then that was all. I’m not offended”: who and why is imprisoned in the only prison in the South Urals
“We’ll have to close”: alternative pension providers in Chelyabinsk will lose their jobs
A trawl with a bulldozer rammed a bridge in Chelyabinsk
Comedians parodied the terrorist attack in St. Petersburg — the UK started checking: news from the NWO for April 5
One of the buildings of the Ministry of Defense is on fire in Moscow
The sign forbidding entry to the parking lot near the Manhattan residential complex was removed
Itching in the nose: 3 popular notes in perfumes that scare everyone away - check your perfume
"In clubs in an embrace with models": the wife left the football player Pavel Pogrebnyak due to numerous betrayals - the couple has three children
"When I squeezed in, I almost crushed": residents suburbs cannot go to Chelyabinsk due to lack of minibuses
“I was in shock”: doctors discovered that a mother is allergic to her own son – this happens to one in 50,000 pregnant women he's smiling. " The doctor debunks the myths about the most popular mental disorder
" The doctor debunks the myths about the most popular mental disorder
All news
Pregnancy is associated with continuous expectation. First, a woman hopefully waits for the results of the tests, then she waits for the toxicosis to disappear, then she waits for the first opportunity to see the baby on the screen of the ultrasound scanner, then she waits for the start of maternity leave in order to fully devote herself to preparing for the birth of a son or daughter. But after the 30th week, all the thoughts of a pregnant woman revolve around one event - the immediate upcoming birth.
If a woman has already gone through this stage, then her expectations in the last weeks of her term are rather of an observational nature: she would not miss it. But in the first pregnancy, the anticipation of the onset of labor is scary. Women now and then turn to their girlfriends who have given birth with the same questions: how to understand that childbirth has begun?
The female body is designed in such a way that for such an important event as the birth of a child, it begins to prepare in advance. Of course, under the influence of negative factors such as stress, unusual physical activity, change of time and climate zones (if a woman travels in the last weeks of pregnancy), childbirth can begin prematurely, but in most cases it is still worth talking about the systematic preparation of the body.
Of course, under the influence of negative factors such as stress, unusual physical activity, change of time and climate zones (if a woman travels in the last weeks of pregnancy), childbirth can begin prematurely, but in most cases it is still worth talking about the systematic preparation of the body.
30-35 weeks
Around week 30, the expectant mother begins to experience rare, irregular and initially painless uterine contractions. This usually happens when the body is in a horizontal position. The abdomen hardens for a few seconds, some women feel a decrease in the sensitivity of its skin. These are Braxton Hicks contractions - training contractions of the uterus, which is preparing for more serious stress. No treatment is required in this case. You can relieve discomfort by taking a warm shower and “breathing” with your stomach for a couple of minutes. Usually, doctors advise putting your hand at the level of the navel and breathing so that the hand rises during inhalation and falls as you exhale.
Approximately at 32-34 weeks, the musculoskeletal system begins to prepare for childbirth. Usually women feel a pulling pain in the sacrum and thighs, the gait turns into a duck, that is, the woman walks, waddling from side to side. During this period, breathing exercises and stretching exercises will be very helpful. “I advise women to do butterfly or cat exercises,” says fitness trainer Marina Efanova . - For the first, you need to sit on the floor and bend your legs so that the feet are connected to each other, the heels are pressed to the crotch, and the knees look in different directions. You need to lightly press your hands on your knees, as if trying to press them to the floor, in order to feel how the inner surface of the thigh is stretched. If you perform this exercise daily, the muscles will become more elastic due to increased blood supply.
The cat exercise is performed on all fours. It is necessary to alternately round the back and bend it as low as possible. At the same time, you should try to arch your back up in the waist area, and bend in the area of the shoulder blades. Massage and swimming will also help prepare the muscles for labor. By the way, small physical activity will help get rid of another unpleasant sensation - pulling pains in the lower abdomen.
At the same time, you should try to arch your back up in the waist area, and bend in the area of the shoulder blades. Massage and swimming will also help prepare the muscles for labor. By the way, small physical activity will help get rid of another unpleasant sensation - pulling pains in the lower abdomen.
At this time, the baby turns its head towards the exit, so the pregnant woman's stomach drops, it becomes easier to breathe, heartburn and heaviness in the stomach disappear, but, on the other hand, pressure on the bladder increases. Microlosses of urine when coughing and sneezing become unpleasant companions of the expectant mother. At the same time, mucous discharge from the vagina increases - partly due to changes in the hormonal background, partly due to the increasing pressure of the fetus on the pelvic organs. In the same period, the swelling of the lower extremities also increases.
Another indicator of the approaching "moment X" is the nesting instinct. About three to four weeks before giving birth, a woman suddenly has an irresistible desire to make repairs, clean the apartment, rearrange the furniture or even change it. Psychologists advise the relatives of a pregnant woman to let her throw out her surging desires, naturally, within reason. Let him sort out the trash in the pantry or rub grandmother’s silverware to a shine, but it’s better to protect the expectant mother from hard work and unnecessary worries.
Psychologists advise the relatives of a pregnant woman to let her throw out her surging desires, naturally, within reason. Let him sort out the trash in the pantry or rub grandmother’s silverware to a shine, but it’s better to protect the expectant mother from hard work and unnecessary worries.
This is the finish line, where any day can become a holiday for the family. During this period, a woman should listen carefully to her condition and observe the changes taking place in the body. First of all, you should pay attention to the mucous secretions. If they look like a piece of melted jelly with small streaks of blood or brown color and their volume is about a tablespoon, then this is a mucous plug. She is a clear harbinger of the onset of childbirth. In some women, the mucus plug leaves a few days before labor, in others - just before it begins, so from this moment you need to be on the alert.
The second sign of the imminent appearance of the baby is true contractions. With the first pregnancy, they can last from eight to twelve hours, with the second or more - from five to eight hours.
With the first pregnancy, they can last from eight to twelve hours, with the second or more - from five to eight hours.
How to distinguish false contractions from true ones
- False contractions are irregular, while true ones have a clear periodicity, getting stronger every hour. If within an hour a woman experiences six or more bouts of contractions, which gradually increase, then with a high probability we can talk about the onset of labor.
- False contractions last 10-20 seconds and disappear without a trace if you take a warm shower. True ones last 30 seconds or more and do not go away even after a shower.
- If between contractions a woman feels well and can fall asleep, then most likely these are false contractions. When true, the body begins to work hard, pressure rises, appetite drops, dizziness, headaches and muscle pains (in the back, hips) may appear, so the woman feels discomfort.
- During false contractions there is no mucous discharge from the vagina, while true ones are often accompanied by discharge mixed with blood
As mentioned earlier, training contractions begin as early as the 30th week of pregnancy, gradually they become more frequent.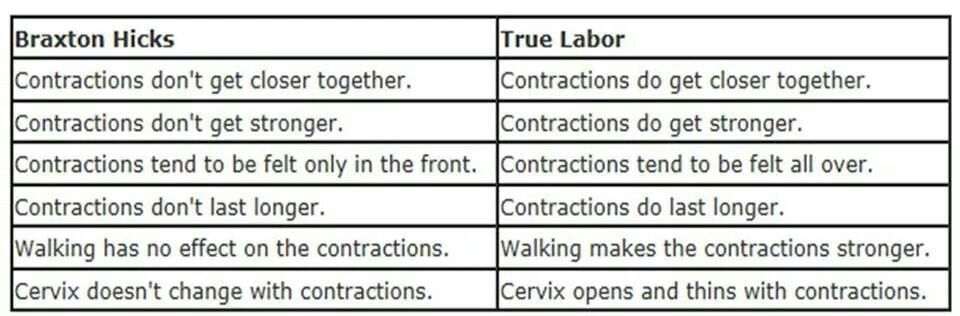 How to determine how training (otherwise they are also called false) contractions differ from real, generic ones?
How to determine how training (otherwise they are also called false) contractions differ from real, generic ones?
There are several clear indicators for this:
- Regularity. False contractions are irregular, true contractions gradually become stronger, longer and more frequent. However, sometimes in the evenings there are periods of regular contractions (for two or four hours), which then go away on their own. It is better to write down the time and duration of contractions in a special notebook - it will help you cope with the excitement, and it will be useful for the doctor to assess your condition.
- Duration. False contractions last 15-20 seconds, true contractions gradually become longer. If the expectant mother managed to fall asleep peacefully between contractions, then they were false.
- You can take a warm shower or bath. False contractions will disappear, true contractions will continue.
- Well-known American pediatricians William and Martha Cerza suggest the following method: if a woman doubts whether she has begun labor or not, you need to follow the nature of the contractions for an hour.
 Labor (true) contractions last an average of 10-12 hours for the first birth and 6-8 hours for repeated ones.
Labor (true) contractions last an average of 10-12 hours for the first birth and 6-8 hours for repeated ones.
Normally, amniotic fluid drains at the end of the first stage of labor, when the cervix is dilated to seven centimeters or more. But sometimes it happens even earlier, sometimes even before the start of contractions. What is important to pay attention to if a woman's water has broken?
- Color: normal water should be light and transparent, white flakes are also acceptable - this is a cheese-like lubricant. Dark, greenish-brown water is a warning sign of fetal hypoxia
- Odour: Normal amniotic fluid is odorless. An unpleasant smell may indicate that the baby is passing meconium - the original feces.
- Quantity of water: there are usually about 1-1.5 liters. 500-700 ml - insufficient volume, often occurs with a post-term pregnancy. However, do not rush to diagnose yourself. Sometimes only the so-called anterior waters leave at first, while the fetal bladder itself may still remain intact.
 In this case, the amount of amniotic fluid can be quite small - about 200-300 ml.
In this case, the amount of amniotic fluid can be quite small - about 200-300 ml.
In any case, if a pregnant woman's water has broken, then labor should begin within 24 hours, so it's better not to delay the preparations. After the waters break, the nature of the contractions changes, they become stronger and more painful.
So, when is the time to go to the hospital?
- If within an hour a woman feels about ten contractions with a break of 5-7 minutes.
- If the duration of each contraction is 30-60 seconds.
- If the amniotic fluid broke - especially if it happened at one moment - the water rushed in a stream.
Serious symptoms for which you need to go to the hospital urgently:
- Unexpected bleeding (more than during normal menstruation).
- Sudden pain in the uterine region - not at all the same as pain during contractions.
- Constant dizziness.
Each woman in labor begins and proceeds differently. For some, it’s like a textbook, when contractions develop gradually, the intervals between them gradually decrease, for others everything is rapid, their contractions are immediately painful, and the intervals between them are short. For the third, the first period, on the contrary, is delayed. A woman needs to be guided by her condition and constantly keep her doctor, if any, up to date.
For some, it’s like a textbook, when contractions develop gradually, the intervals between them gradually decrease, for others everything is rapid, their contractions are immediately painful, and the intervals between them are short. For the third, the first period, on the contrary, is delayed. A woman needs to be guided by her condition and constantly keep her doctor, if any, up to date.
When I first got pregnant, nine months seemed like a very long time. But, as you know, no pregnancy can last forever, so this term is coming to an end. For any woman in labor, the doctor will certainly set the expected date of birth. But, despite this, the real birthday of the baby may differ significantly from the planned date. The thing is, every pregnancy is different. A period of 37 and 42 weeks is considered normal. Moreover, such a pattern was noticed: if the menstrual cycle of the expectant mother was short - 21 days, then, most likely, the pregnancy will end at 38-39weeks. And in women with a long cycle (up to 36 days), pregnancy continues until 41-42 weeks.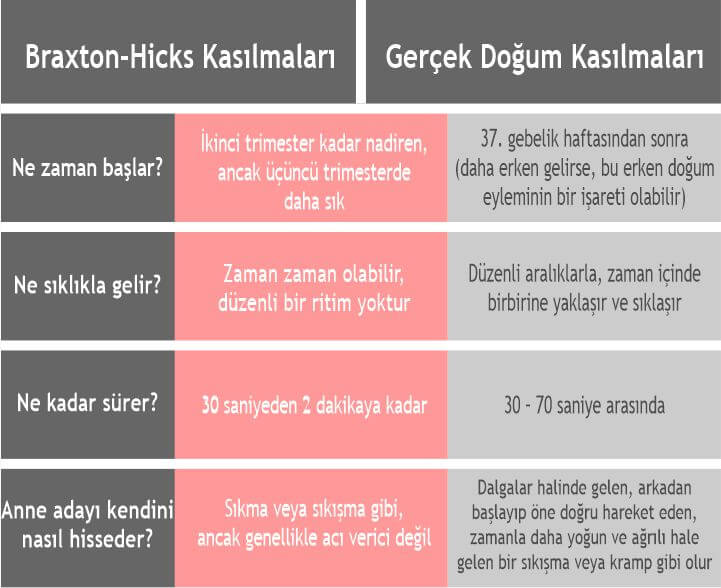 However, experts remind you that if, nevertheless, the gestation period approaches 40 weeks, and the baby is in no hurry to be born, you need to regularly visit a doctor who will monitor the child's condition using cardiotocography, ultrasound and Doppler.
However, experts remind you that if, nevertheless, the gestation period approaches 40 weeks, and the baby is in no hurry to be born, you need to regularly visit a doctor who will monitor the child's condition using cardiotocography, ultrasound and Doppler.
Photo: Photo from Shutterstock.com
Inna Miller
Pregnancy Maternity Hospital Childbirth
- LIKE14
- LAUGHTER0
- SURPRISE1
- ANGER0
- SAD0
See the typo? Select fragment and press Ctrl+Enter
COMMENTS55
Read all comments
Guest
Log in
Media news2
Media news2
what happens, development of pregnancy and fetus
week33 - 36 weeks of pregnancy
Elena Gevorkova
Obstetrician-gynecologist, Moscow
33rd week
BABY
At the 33rd week, the weight of the fetus is 1800-1900 g, and the body length is 43-44 cm. The amount of subcutaneous fat increases, due to which the folds and wrinkles on the baby's body are smoothed out, the skin turns pink. The fluffy hairs that cover the body of the fetus, which are called lanugo, become smaller, and the hair on the head darkens and thickens. The baby's skin is covered with a thin layer of cheese-like lubricant, its largest amount accumulates in the folds - axillary, cervical, inguinal - as well as on the back of the body and face. Grease is a viscous mass of white color, it is a secret of the sebaceous glands, mixed with skin scales. Its function is to protect the baby's skin from damage and facilitate its passage through the birth canal.
The amount of subcutaneous fat increases, due to which the folds and wrinkles on the baby's body are smoothed out, the skin turns pink. The fluffy hairs that cover the body of the fetus, which are called lanugo, become smaller, and the hair on the head darkens and thickens. The baby's skin is covered with a thin layer of cheese-like lubricant, its largest amount accumulates in the folds - axillary, cervical, inguinal - as well as on the back of the body and face. Grease is a viscous mass of white color, it is a secret of the sebaceous glands, mixed with skin scales. Its function is to protect the baby's skin from damage and facilitate its passage through the birth canal.
By this time, fetal movements gradually change their habitual character - they become more and more limited and less pronounced in amplitude due to insufficient space. However, the strength of the movements increases, since by this time the muscular system of the fetus is already sufficiently strengthened. Sharp and strong tremors of the fetus can be sensitive to the internal organs of a pregnant woman. Depending on the position of the baby, the liver, stomach, bladder, ribs, etc. may “suffer”. By 33 weeks, the movements of the fetus are already quite coordinated.
Depending on the position of the baby, the liver, stomach, bladder, ribs, etc. may “suffer”. By 33 weeks, the movements of the fetus are already quite coordinated.
FUTURE MOTHER
The height of the fundus of the uterus from the level of the pubis at this time is 34 cm. The volume of the abdomen is increased due to the weight of the baby, placenta, amniotic fluid. The increase in uterine pressure and strong tremors of the fetus can cause some discomfort in the pregnant woman. Many movements previously available to the expectant mother, such as squats, become limited. Moderate physical activity - walking, fitness, etc. - Requires frequent respite.
A change in the center of gravity increases the load on the spine, which can manifest itself as pain in the lower back, sacrum, and pelvic region. The pressure of the uterus on the stomach can cause or increase nausea, heartburn, and a feeling of heaviness. An increase of almost 1 liter of the volume of circulating blood in the body of a pregnant woman increases the load on the kidneys, and the growing uterus puts pressure on the bladder. All this can be manifested by frequent urination.
All this can be manifested by frequent urination.
These ailments are usually associated with the mechanical pressure of the uterus on the surrounding organs; they are not symptoms of the disease and are temporary. And to relieve nausea, heartburn and a feeling of heaviness in the stomach, frequent meals in small portions are recommended.
34th week
BABY
By this time, the weight of the fetus is approximately 2100 g, and the height is 45 cm. From this period, the cheeks are very pronounced, because, developing a sucking reflex, the fetus often sucks its thumb. This leads to the fact that the baby strengthens the facial muscles, in particular the buccal. The total muscle mass of the fetus increases, the bones become denser.
There is an intensive functioning of the baby's internal organs. During the day, he repeatedly swallows portions of amniotic fluid. Passing through the gastrointestinal tract, the amniotic fluid stimulates the work of the muscular wall. The dense part of the amniotic fluid, which is a suspension of skin flakes, lubricant, vellus hair, is processed by the enzymes of the liver and pancreas, and the liquid part is intensively excreted by the kidneys of the fetus.
The dense part of the amniotic fluid, which is a suspension of skin flakes, lubricant, vellus hair, is processed by the enzymes of the liver and pancreas, and the liquid part is intensively excreted by the kidneys of the fetus.
Approximately 500 ml of amniotic fluid is treated in this way per day. The production of bile continues, which accumulates in the gallbladder and, as the stomach fills with a suspension of amniotic water, enters the lumen of the small intestine. The functional development of the liver and pancreas during the prenatal period does not play a significant role, since the fetus does not have digestion; processes for the production of bile and enzymes: lipase, which breaks down fats; trypsin, which breaks down proteins; amylase, which breaks down carbohydrates, etc. - are preparatory in nature.
FUTURE MOTHER
Most pregnant women begin to feel rather intense false contractions at this time. Strictly speaking, false or training contractions, which are also called Braxton-Hicks contractions, can occur after the 20th week of pregnancy: the longer the period, the more frequent and pronounced the contractions. They are episodic contractions of the muscles of the uterus, lasting from a few seconds to 3-5 minutes. Braxton-Hicks contractions are not pathological - this is a completely normal process of preparing the muscles of the uterus for the difficult process of childbirth. This phenomenon with varying degrees of intensity is observed in almost all pregnant women.
Many primiparas are concerned about the difference between preparatory contractions and labor.
Here are some differences:
- Frequency of contractions. Training bouts do not become more frequent, the intervals between them may be different. Labor pains are regular, the interval between them is reduced.
- Duration of contractions. Training bouts have different durations, from a few seconds to minutes, their duration does not increase over time. Labor pains tend to lengthen.
- Soreness. Preparatory contractions may not be accompanied by pain at all, or they may be quite noticeable, up to a feeling of sharp pain.
However, their intensity weakens over time and the pain disappears. Labor pains are painful and constantly intensify.
- Localization. Braxton-Hicks contractions can be felt in various places - in the lower part of the uterus, in the region of its bottom, along the side walls, covering the entire abdomen. Labor pains begin with a contraction of the lower abdomen, spreading to the front. Often in childbirth, pain in the lower back is felt, while the nature of the pain resembles menstrual pain.
- Relationship with body position. Preparatory contractions may disappear after walking or, on the contrary, rest. A change in body position can relieve the tension in some muscles, which also causes a decrease in the appearance of training contractions. Labor pains may be somewhat relieved in a certain position - when leaning forward, in the knee-elbow position, etc. - but their frequency and duration will still increase.
- Reaction to medication. The use of antispasmodic drugs - NO-ShPY, BUSCOPAN, PAPAVERIN, etc.
- approved by the attending physician, can weaken or completely stop false contractions. The effect of antispasmodics on labor pains is minimal.
Any pain or discomfort should be reported to the gynecologist: this will help the expectant mother to resolve doubts and cope with anxiety. Feeling safe is the best companion of pregnancy.
35th week
BABY
The length of the body of the fetus is 46--47 cm, weight - 2200-2300 g. These figures in the last weeks of pregnancy can vary greatly. The growth and weight of the fetus largely depend on heredity, individual parameters. Starting from 35 weeks, the baby will gain 200-250 g weekly. The fetus occupies almost the entire uterine cavity, its back is rounded, arms and legs are bent, brought to the body. The layer of subcutaneous fat increases significantly, which significantly “rounds” the body of the fetus. The closing of the eyelids and the contraction of facial muscles change the baby's facial expression quite often. The skin of the body becomes pink, smooth, the amount of cheese-like lubricant begins to decrease. Vellus hair covers separate small areas of the body - shoulders, back. The nails protrude beyond the tips of the fingers.
FUTURE MOTHER
The fundus of the uterus is 35 cm higher from the pubis and 15 cm higher from the navel. particularly light. The growing uterus does not allow the lungs to expand, respiratory movements are limited, which is manifested by shortness of breath. Almost all pregnant women to one degree or another experience a feeling of shortness of breath - a feeling of lack of air, frequent and shallow breathing, a desire to take a deep breath. As a rule, these sensations occur for a period of 28 weeks and reach their peak at the 35-36th week. After 37 weeks of pregnancy, the abdomen droops, which greatly facilitates breathing.
Shortness of breath during pregnancy is associated not only with the mechanical pressure of the uterus on the diaphragm, but also with the relaxing effect of hormones on the muscles of the bronchi and lungs. Most often, it is provoked by physical activity - climbing stairs, a long walk, etc. However, it is not uncommon for shortness of breath to occur at rest, especially when lying down. Both prolonged lying in a horizontal position and excessive exercise can contribute to increased shortness of breath. To alleviate her condition, the expectant mother needs to be rational about the daily routine - it is reasonable to alternate rest and physical activity. It is important to monitor your posture, as slouching exacerbates shortness of breath, reducing the already insufficient lung capacity. If shortness of breath is accompanied by blue lips or nails, sensations of pain behind the sternum, darkening before the eyes, nausea or vomiting, fainting, then an urgent need to consult a doctor.
36th week
BABY
The growth of the fetus by this term is approximately 47-48 cm, and the weight is about 2300-2500 g. The fetus enters a period of intensive preparation for childbirth. Each of the organs is already functionally mature enough to ensure the viability of the fetus. 36 weeks is the beginning of the preparatory journey, and the upcoming weeks of pregnancy are designed to finally form the baby's readiness for extrauterine life.
By 36 weeks, the fetus is in its final position in the uterus. As a rule, this is a longitudinal position, occipital presentation - in this case, the fetus is located head down, facing the mother's back. This is the most comfortable position that ensures the greatest safety of the baby during childbirth. More rarely, breech presentation is a condition in which the buttocks and legs of the fetus are located at the bottom of the uterus. This is a relative indication for operative delivery. The final decision on caesarean section or independent childbirth is made by doctors in each case individually.
A change in the position of the fetus in the uterus is possible, but this happens infrequently, since at this time the fetus occupies almost all the free space in the uterus, which significantly limits its motor activity. As a rule, if a change in the position of the fetus occurs, then only from the pelvic to the head. The reverse cases - the transition of the baby from the head position to the pelvic position - are practically impossible, since the head of the fetus is heavier than the buttocks and occupies the longitudinal position completely, by analogy with a float in water, the heavy part of which always outweighs.
FUTURE MOTHER
The height of the uterus is 36 cm, the volume of the abdomen is maximally increased, the bottom reaches the costal arches. At this time, the pregnant woman's body also begins its journey of preparing for the upcoming birth. Changes begin with hormonal changes: the level of special hormones, oxytocin and prostaglandins, increases slightly in a woman. These active substances play a crucial role in the process of preparing for childbirth and directly during them. A slight increase in their level from the period of 36-37 weeks of pregnancy leads to an increase in Braxton-Hicks training contractions, an increase in urination and defecation, and the appearance of more abundant mucous discharge from the vagina.