When should i worry if im pregnant
Warning signs during pregnancy | Pregnancy Birth and Baby
Warning signs during pregnancy | Pregnancy Birth and Baby beginning of content4-minute read
Listen
Pregnancy is a time of great change for your body, and in your life, as you get ready for your baby to arrive. It also can be a time when you may be worried about some of the changes you are experiencing, and you want to know when you should seek help.
Most changes in your body are likely to be a normal part of pregnancy. Most pregnancy health issues are mild and common. However, some signs can indicate that things may not be going well, and could point to a more serious pregnancy complication.
Some of these symptoms may appear at different stages of your pregnancy; others might occur at any time. Even if you are not sure about your symptoms but think that something just doesn't feel right with your own or your baby's health, it's important to get it checked out.
Contact your doctor, midwife or hospital immediately if you have any of the following symptoms:
Any time during pregnancy
While some signs may only appear at certain times during your pregnancy, many can occur at any stage, including:
- prolonged or severe vomiting
- bleeding from your vagina
- a discharge from your vagina that is unusual, or a lot more than usual
- severe or long-lasting headaches
- dizziness
- continuing weight loss
- fever or chills
- urgency, pain or a burning feeling when urinating (weeing)
- feeling constantly out of breath, dizzy or weak or having a racing heart
- you have had a blow to your stomach (such as from a fall, crash or a family violence incident)
- you are experiencing problems with your emotional health that last longer than 2 weeks, such as feeling depressed, anxious or being unable to do your usual, everyday tasks
Early pregnancy (before 20 weeks)
Certain types of pain in the early stages of pregnancy could be a sign of miscarriage or an ectopic pregnancy:
- persistent or severe pain on one side of your abdomen or pain in the tip of one shoulder
- severe pain or cramping in your lower abdomen (tummy)
Later pregnancy (after 20 weeks)
Although some discomfort is common during the later stages of pregnancy, some signs need to be checked by a doctor immediately, including:
- changes to your vision, flashing lights or blurry eyesight, which are signs of pre-eclampsia
- sudden, severe swelling in your hands, feet or face
- an extreme itchiness of your skin, including hands and feet
- a large amount of swelling in your legs (which is also painful)
- if your baby has stopped moving or is moving differently
What happens next?
When you see your healthcare professional, they may perform some tests to check or maintain the health of you and your baby. These tests may include:
These tests may include:
- a health assessment and investigation
- an ultrasound or blood test
You may also receive a referral to another doctor or specialist, and you can also get emotional support.
How can I avoid pregnancy complications?
It's often not possible to avoid a complication in pregnancy. You may have a higher chance of developing one if you have a health problem before conception, or had one during a previous pregnancy. There may also be a higher chance if you have a family history of pregnancy complications.
It may be possible to lessen the chance of developing a problem, or reduce the chance of a complication becoming worse, by making sure you go to all of your antenatal appointments. If a potential health issue is found, you may need additional antenatal appointments to more closely monitor the health of you and your baby.
Where to get help
- Phone your doctor, midwife or maternity hospital urgently if you have any concerns.

- Visit your hospital or call triple zero (000) and ask for an ambulance.
Other sources of advice
- Call Pregnancy, Birth and Baby on 1800 882 436 to speak to a maternal child health nurse.
- Consider visiting healthdirect's Symptom Checker for pregnancy if you are experiencing discomfort in pregnancy or are worried about any symptoms.
Sources:
NSW Health (Early pregnancy – when things go wrong), BabyCenter (Pregnancy symptoms you should never ignore), Raising Children Network (Health problems in pregnancy)Learn more here about the development and quality assurance of healthdirect content.
Last reviewed: April 2021
Back To Top
Need more information?
Early pregnancy: when things go wrong - Maternal, child and family health
Early pregnancy – when things go wrong is a resource that offers expert advice and support to women experiencing complications in early pregnancy.
Read more on NSW Health website
What is a stillbirth?
The cause of a stillbirth is often unknown, but you can help to lower the risk. Learn about prevention, warning signs and giving birth to a stillborn baby here.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Pregnancy: premature labour & birth | Raising Children Network
Are you likely to be having a premature birth? Here’s all you need to know about preparing for and recovering from premature labour and birth.
Read more on raisingchildren.net.au website
Premature babies and birth | Raising Children Network
Premature babies are born before 37 weeks of pregnancy. Our essential guide covers premature birth, babies, development, NICU and more.
Our essential guide covers premature birth, babies, development, NICU and more.
Read more on raisingchildren.net.au website
Pregnancy: miscarriage & stillbirth | Raising Children Network
Have you experienced a miscarriage or stillbirth? Find articles and videos about coping with the grief of losing a pregnancy or having a stillbirth.
Read more on raisingchildren.net.au website
Bleeding or pain in early pregnancy
One in 4 women will experience bleeding and/or pain during their first 12 weeks of pregnancy. Unfortunately half of these pregnancies may also end in miscarriage, which cannot be prevented.
Read more on WA Health website
What really happens during a miscarriage
Understand what actually happens during a miscarriage and what you might see and feel. Please be warned that this article contains some graphic descriptions.
Please be warned that this article contains some graphic descriptions.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Stillbirth and neonatal death | Raising Children Network
Information about pregnancy loss, stillbirth and neonatal death, including grief and getting support.
Read more on raisingchildren.net.au website
Pregnancy - preeclampsia - Better Health Channel
There is no evidence that preeclampsia is caused by emotional stress, working too hard or not getting enough rest.
Read more on Better Health Channel website
Keeping your baby's remains for testing - Miscarriage Australia
If you miscarry at home, your doctor or specialist may have asked you to collect your pregnancy tissue for testing.
Read more on Miscarriage Australia website
Disclaimer
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is not responsible for the content and advertising on the external website you are now entering.
OKNeed further advice or guidance from our maternal child health nurses?
1800 882 436
Video call
- Contact us
- About us
- A-Z topics
- Symptom Checker
- Service Finder
- Subscribe to newsletters
- Linking to us
- Information partners
- Terms of use
- Privacy
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is funded by the Australian Government and operated by Healthdirect Australia.
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby’s information and advice are developed and managed within a rigorous clinical governance framework.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
Healthdirect Australia acknowledges the Traditional Owners of Country throughout Australia and their continuing connection to land, sea and community. We pay our respects to the Traditional Owners and to Elders both past and present.
This information is for your general information and use only and is not intended to be used as medical advice and should not be used to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any medical condition, nor should it be used for therapeutic purposes.
The information is not a substitute for independent professional advice and should not be used as an alternative to professional health care. If you have a particular medical problem, please consult a healthcare professional.
If you have a particular medical problem, please consult a healthcare professional.
Except as permitted under the Copyright Act 1968, this publication or any part of it may not be reproduced, altered, adapted, stored and/or distributed in any form or by any means without the prior written permission of Healthdirect Australia.
Support this browser is being discontinued for Pregnancy, Birth and Baby
Support for this browser is being discontinued for this site
- Internet Explorer 11 and lower
We currently support Microsoft Edge, Chrome, Firefox and Safari. For more information, please visit the links below:
- Chrome by Google
- Firefox by Mozilla
- Microsoft Edge
- Safari by Apple
You are welcome to continue browsing this site with this browser. Some features, tools or interaction may not work correctly.
Yes, You’re Pregnant
Missed Period
If your menstrual period is fairly consistent, and you miss one period, this is usually the first sign that indicates you may be pregnant. To be certain, however, it is recommended that you buy a pregnancy test kit, as a missed menstrual period may also be due to other causes, such as high stress levels or anxiety, or even due to other illnesses.
To be certain, however, it is recommended that you buy a pregnancy test kit, as a missed menstrual period may also be due to other causes, such as high stress levels or anxiety, or even due to other illnesses.
Nausea and Vomiting
These can also be possible signs of pregnancy. Nausea and vomiting, a combination of symptoms commonly called “morning sickness”, typically begins to occur around one to two months after conception. However, nausea and vomiting are not always fail-safe symptoms of pregnancy and can be triggered by other conditions as well. Some people have no morning sickness at all, while there are those who experience intense morning sickness all throughout and up until the very last month of pregnancy. Generally speaking though, morning sickness usually lessens or disappears when the pregnancy enters the second trimester.
Heightened Sense of Smell
An increase in the estrogen hormone during pregnancy can cause extreme sensitivity to smells, making you feel like gagging or vomiting when you come across certain odors. In some cases, a pregnant woman can no longer stand the smell of her own perfume.
In some cases, a pregnant woman can no longer stand the smell of her own perfume.
Sore, Swollen Breasts
A woman may experience swelling of her breasts during the first trimester of pregnancy. Due to an increased blood flow to the chest area, this may cause the breasts to be engorged, as well as more sensitive to touch, or more tender or taut, similar to the symptoms experienced during a woman’s menstrual period.
Fatigue
You may feel incredibly tired even though you hardly did anything, or feel very drowsy and fatigued all throughout the day, which may be due to rapidly increasing levels of progesterone in the body. However, these symptoms will usually lessen by the time you reach the second trimester.
Spotting or Light Bleeding
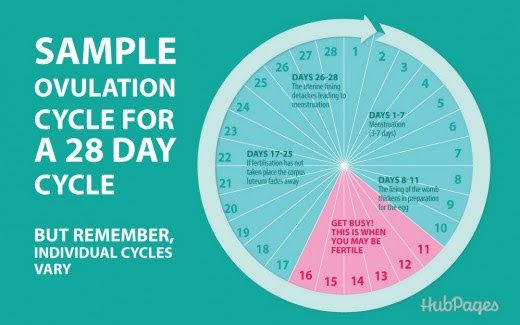
Some mothers may experience spotting or light vaginal bleeding around 11 or 12 days after conception when the embryo implants on the uterine wall, which also coincides with the missed menstrual period. This kind of spotting is usually a pale red or pinkish color and should stop on its own in 1-2 days. If, however, you are experiencing symptoms of vaginal bleeding along with abdominal pain, you should see a doctor as quickly as possible, as these could also be signs of an ectopic pregnancy or a miscarriage.
This kind of spotting is usually a pale red or pinkish color and should stop on its own in 1-2 days. If, however, you are experiencing symptoms of vaginal bleeding along with abdominal pain, you should see a doctor as quickly as possible, as these could also be signs of an ectopic pregnancy or a miscarriage.
Frequent Urination
About 1-2 weeks after a missed menstrual period, a pregnant mother will need to urinate much more frequently. This is because during pregnancy the body increases the amount of blood it pumps to various parts of the body. This causes the kidneys to process more fluid waste than usual and thus leads to more fluid in the bladder as well.
Constipation
When you get pregnant, changing hormonal levels in the body slow down digestion. The uterus also grows and expands, causing increased pressure on the bowels. Because of this, many mothers may experience constipation during pregnancy. To help relieve constipation, you should eat foods that are high in fiber, drink plenty of water, and get in some light exercise on a regular basis.
Irritability and Mood Swings
Pregnant women often find that they are more moody, irritable, and easily angered or offended. This is because the mother’s body is trying to adjust itself to new hormonal imbalances. Taking the time to understand these changes can help mothers to have a more positive experience, and help moods to normalize more quickly.
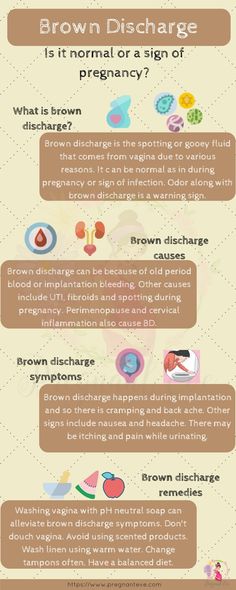
Slight Vaginal Discharge
When estrogen levels increase, and there is greater blood flow to the vaginal area, this may cause blood to build up at the cervix. This causes the cervical glands to work harder, and secrete more cervical fluid through the vagina. Normal bacteria and dead cells in the vaginal area are carried away with this fluid or vaginal discharge. This kind of discharge is not dangerous.
Although most pregnant mothers will experience similar symptoms, some women will experience a variety of different symptoms while others will have almost no symptoms at all. If you find that you are definitely pregnant, you should take extra care of your health during the early stages of pregnancy by eating healthy, nutritious food, drinking plenty of water, exercising appropriately and properly, and going for antenatal care and checkups in order to receive good medical advice and recommendations from your doctor.![]()
Psycho-emotional disorders during pregnancy. The need for their correction | Tyutyunnik V.L., Mikhailova O.I., Chukhareva N.A.
Currently, more and more attention is paid to the influence of a woman's psycho-emotional state on reproductive function, pregnancy and perinatal outcomes [2,4,14]. In recent years, in developed countries, there has been an increase in the frequency of various mental disorders in women of reproductive age, the proportion of patients taking psychotropic drugs has increased, including among women who are planning a pregnancy and pregnant women [3,6,9].
Almost all pregnant women are subject to sharp emotional swings, since the expectation of a child is associated with changes - both physical and emotional. Hormonal changes during pregnancy lead to the fact that the mood of a pregnant woman changes dramatically almost every hour.
A future mother can get rid of such emotional swings and feel calm during pregnancy by observing the rules of emotional health. Emotional balance and physical fitness are equally important for a pregnant woman, they equally help her prepare for motherhood. Due to the lack of maternal experience, a pregnant woman may experience sudden emotional outbursts. The first pregnancy is a new experience that is quite difficult to comprehend. Ignoring the fact that the emotions of a woman who is expecting a child is much more complex and sharper than usual, can lead to a number of problems, including in relations with her spouse. Acceptance of this fact is the basis of emotional health during pregnancy [1,5,11].
Emotional balance and physical fitness are equally important for a pregnant woman, they equally help her prepare for motherhood. Due to the lack of maternal experience, a pregnant woman may experience sudden emotional outbursts. The first pregnancy is a new experience that is quite difficult to comprehend. Ignoring the fact that the emotions of a woman who is expecting a child is much more complex and sharper than usual, can lead to a number of problems, including in relations with her spouse. Acceptance of this fact is the basis of emotional health during pregnancy [1,5,11].
Also, if a woman is pregnant for the first time, she experiences many fears, which include fear of childbirth and untimely termination of pregnancy, concern about the health of the unborn child and her own health, fear of labor pains and inevitable pain, fear of partner / spouse disappointment due to changes occurring with body. Modern women have to worry about careers, financial problems, and many additional costs associated with the appearance and upbringing of a new family member.
All these fears can lead to many negative emotions, such as anxiety, depression, irritation, anxiety, stress, anger, feelings of loneliness, confusion. Most often, changes in the psycho-emotional background during pregnancy lead to the development of depressive and anxiety disorders. Until the end, the pathogenesis of these changes is unclear, several theories are discussed, it is believed that changes in the hormonal background during pregnancy, including a significant increase in estrogens, and especially progesterone, in the blood serum can exacerbate existing emotional disorders [5,7,15]. As a rule, minor manifestations in the form of irritability, tearfulness, resentment accompany manifestations of early toxicosis in the first trimester of pregnancy - nausea, vomiting, etc. [6,10]. After the disappearance of these symptoms, the neuropsychic state of pregnant women usually improves. At the same time, an important role in the development of anxiety states is played by certain physical discomfort and psychological factors, which include forced changes in lifestyle, communication in the family and with work colleagues, concern for the health of the unborn child, financial difficulties - all this contributes to the appearance or exacerbation of psycho-emotional disorders during pregnancy. For some women, the onset of pregnancy is unexpected and not always desirable, however, due to the circumstances, a decision is made to prolong this pregnancy, which can lead to a further increase in stress and anxiety [5,8,12]. It should be noted that additional psychotraumatic factors may appear during pregnancy, such as the occurrence of pregnancy complications requiring hospitalization, or the detection of congenital malformations in the fetus, which can cause negative images and feelings [1,10,12].
For some women, the onset of pregnancy is unexpected and not always desirable, however, due to the circumstances, a decision is made to prolong this pregnancy, which can lead to a further increase in stress and anxiety [5,8,12]. It should be noted that additional psychotraumatic factors may appear during pregnancy, such as the occurrence of pregnancy complications requiring hospitalization, or the detection of congenital malformations in the fetus, which can cause negative images and feelings [1,10,12].
The state of psycho-emotional stress with the presence of anxiety of various levels is observed in 40% of women with a normal pregnancy [2,7,11]. Borderline neuropsychiatric disorders can be presented in the form of hypochondriacal and hysterical syndromes. However, there are other forms of gestational borderline neuropsychiatric disorders, their features are the invariable inclusion in the clinical picture of certain psychopathological phenomena directly related to pregnancy: various fears for the successful course of pregnancy, obsessive fears for the fate of the fetus, expectation of childbirth, conditioned reflex fears associated with unfavorable past pregnancies and childbirth [5,6,8]. A study of pregnant women who do not have signs of borderline neuropsychiatric disorders showed that character accentuation was established only in a quarter of women. The first trimester of pregnancy is usually characterized to some extent by the sharpening of existing character traits. Soft, vulnerable, insecure women become even more impressionable, sometimes excessively tearful, and anxious (those women who have had miscarriages in the past or this pregnancy are not going well, in this case, the fear of another abortion can become simply obsessive) ). Powerful women with a sharp character can become even more aggressive, irritable and demanding. In the third trimester of pregnancy, emotional swings may begin again in connection with the expectation of childbirth, and with them fear - especially women who have to experience this event for the first time are susceptible to it [5,6,11].
A study of pregnant women who do not have signs of borderline neuropsychiatric disorders showed that character accentuation was established only in a quarter of women. The first trimester of pregnancy is usually characterized to some extent by the sharpening of existing character traits. Soft, vulnerable, insecure women become even more impressionable, sometimes excessively tearful, and anxious (those women who have had miscarriages in the past or this pregnancy are not going well, in this case, the fear of another abortion can become simply obsessive) ). Powerful women with a sharp character can become even more aggressive, irritable and demanding. In the third trimester of pregnancy, emotional swings may begin again in connection with the expectation of childbirth, and with them fear - especially women who have to experience this event for the first time are susceptible to it [5,6,11].
Anxiety disorders may first appear during pregnancy, there may be a change in the course of already existing disorders. In one retrospective study in women with panic attacks, 20% of cases showed a decrease in symptoms during pregnancy, 54% remained unchanged, and 26% worsened the course of the disease [12]. The detection of depression in pregnant women is difficult. Many symptoms, such as emotional lability, increased fatigue, changes in appetite and cognitive decline, are often found in physiologically normal pregnancy. Under stress, the hormones of the adrenal glands of the mother release catecholamines (stress hormones) into the blood, and during the experience of positive emotions (joy, calm, etc.), the hypothalamic structures produce endorphins, which, penetrating through the placental barrier, directly affect the fetus. Consequently, mother and child are a single neurohumoral organism, and each of them equally suffers from the adverse influence of the outside world, which is recorded in long-term memory, affecting the entire subsequent life of the child. Positive maternal emotions cause an increase in the growth of the fetus and an increase in the level of its sensory perception.
In one retrospective study in women with panic attacks, 20% of cases showed a decrease in symptoms during pregnancy, 54% remained unchanged, and 26% worsened the course of the disease [12]. The detection of depression in pregnant women is difficult. Many symptoms, such as emotional lability, increased fatigue, changes in appetite and cognitive decline, are often found in physiologically normal pregnancy. Under stress, the hormones of the adrenal glands of the mother release catecholamines (stress hormones) into the blood, and during the experience of positive emotions (joy, calm, etc.), the hypothalamic structures produce endorphins, which, penetrating through the placental barrier, directly affect the fetus. Consequently, mother and child are a single neurohumoral organism, and each of them equally suffers from the adverse influence of the outside world, which is recorded in long-term memory, affecting the entire subsequent life of the child. Positive maternal emotions cause an increase in the growth of the fetus and an increase in the level of its sensory perception.
According to the literature [2,5,11,15], a significant effect of anxiety disorders on the course of pregnancy and perinatal outcomes has been noted: the frequency of placental insufficiency, fetal growth retardation, premature birth, the birth of children with low body weight, which subsequently affects negatively on long-term forecast for them.
Thus, emotional swings are dangerous not only for the woman herself, but also for her unborn child. When a pregnant woman experiences stress, her body produces more of the hormone cortisol, the main “stress hormone”. Cortisol increases blood pressure and blood sugar levels, negatively affects the strength of the immune system - which, of course, adversely affects the health of the child.
Stress during pregnancy is dangerous for a variety of reasons. Chronic stress experienced for several weeks can slow down the development of the cells of the body of the embryo, the growth of the fetus. This increases the risk of miscarriage or spontaneous abortion or premature birth. Elevated levels of stress hormones can damage the brain of an unborn baby and lead to parenting problems later on.
Elevated levels of stress hormones can damage the brain of an unborn baby and lead to parenting problems later on.
Psychological stress in the perinatal period brings with it a whole range of problems that require serious attention to the psychological sphere of a pregnant woman in order to avoid obstetric and other complications. However, diagnostic criteria for the transition of the stress syndrome from the link of adaptation to the link of pathogenesis of various diseases have not yet been found [2,4,15].
Emotional control is necessary to maintain normal emotional balance during pregnancy. A pregnant woman who successfully manages her emotions is aware of the changing emotional balance and is ready to accept what is happening to her.
There are several basic rules that will help to cope with emotional imbalance:
• You must come to terms with the fact that physical and emotional changes are an inevitable part of the pregnancy period. You need to understand that this is a temporary stage that will last only a few months and end a maximum of 1-2 months after the birth of the child.
• Each trimester of pregnancy brings new changes, both in the body and in the emotional state. The main source of information about pregnancy is special literature and the experience of women who have recently given birth, who can share their feelings and experiences.
• A pregnant woman is responsible for the emergence of a new life. Taking care of yourself means taking care of your child. Proper nutrition, rest and self-indulgence are essential.
• A pregnant woman should be open to dialogue and not be afraid to discuss her problems with a gynecologist, partner or friends - anyone who can provide emotional support. You should not keep fears and worries in yourself - this will only aggravate internal tension.
• Changes associated with pregnancy can lead to low energy and, as a result, rapid fatigue. You need to slow down, re-prioritize your work, and give yourself a break.
• Emotional tension and negative emotions can be overcome by being distracted by pleasant activities or hobbies. When emotions overwhelm you, try to analyze what is bothering you, and then find an adequate solution.
When emotions overwhelm you, try to analyze what is bothering you, and then find an adequate solution.
• Engaging in certain physical activities designed specifically for expectant mothers will help improve both physical and emotional health.
• The main components of emotional health during pregnancy are rest and comfort.
However, unfortunately, during pregnancy, a woman cannot always cope with nervous tension, irritability, anxiety, excitement and other symptoms of stress on her own. Therefore, in some situations, she needs medical help.
The relative risk of using drugs during pregnancy makes it difficult to choose therapy, therefore, for the correction of psycho-emotional disorders that occur during pregnancy, herbal drugs that have practically no side effects can be considered as highly safe therapy.
The basis of anti-anxiety complex herbal remedies is valerian. It has been used in traditional medicine for many years for its hypnotic and sedative effects and remains a highly sought after remedy to this day. The mild hypnotic effect of valerian makes it possible to use it for the relief of shallow insomnia caused by anxiety. In addition, the vegetotropic effect of valerian is well known, its ability to have a uniform effect on both mental and somatic (vegetative) symptoms of anxiety. Valerian preparations also have anxiolytic and neuroprotective effects. The spectrum of side effects of valerian is very narrow and practically limited only to allergic reactions. Although valerian extract is metabolized by the cytochrome P450 system, it has virtually no effect on the metabolism of other drugs, and thus unwanted drug interactions are excluded.
The mild hypnotic effect of valerian makes it possible to use it for the relief of shallow insomnia caused by anxiety. In addition, the vegetotropic effect of valerian is well known, its ability to have a uniform effect on both mental and somatic (vegetative) symptoms of anxiety. Valerian preparations also have anxiolytic and neuroprotective effects. The spectrum of side effects of valerian is very narrow and practically limited only to allergic reactions. Although valerian extract is metabolized by the cytochrome P450 system, it has virtually no effect on the metabolism of other drugs, and thus unwanted drug interactions are excluded.
Among the phytopreparations used by clinicians for the treatment of psycho-emotional disorders, Persen, a modern combined sedative preparation of plant origin, is widely used to relieve stress symptoms (anxiety, irritability and emotional stress) without causing drowsiness. Along with valerian, the composition of the drug includes dry extracts of medicinal plants with pronounced anxiolytic activity - peppermint and lemon balm (Table 1). The additional antispasmodic effect of peppermint makes it possible to successfully use the drug in patients with a pronounced somatic component of the anxiety syndrome. In addition, lemon balm has a nootropic (increased concentration and speed of problem solving), antioxidant effect. Persen is administered orally to adults and adolescents over 12 years old, 2-3 coated tablets, 2-3 times / day, Persen forte - inside to adults and adolescents over 12 years old, 1-2 capsules 2-3 times / day.
The additional antispasmodic effect of peppermint makes it possible to successfully use the drug in patients with a pronounced somatic component of the anxiety syndrome. In addition, lemon balm has a nootropic (increased concentration and speed of problem solving), antioxidant effect. Persen is administered orally to adults and adolescents over 12 years old, 2-3 coated tablets, 2-3 times / day, Persen forte - inside to adults and adolescents over 12 years old, 1-2 capsules 2-3 times / day.
The advantages of Persen over other sedatives are:
• the preparation contains only natural ingredients;
• the effectiveness and safety of herbal ingredients Persena are well studied;
• does not contain alcohol and bromine;
• can be combined with any psychotropic drugs, including antidepressants;
• effective as a fast-acting symptomatic remedy when it is necessary to stop the symptoms of anxiety, agitation, and during a course of treatment for stress conditions, anxiety and phobic disorders.
Due to the natural components of plant origin that are part of Persen, this drug can be used during pregnancy. In each case, the doctor must evaluate the benefits and risks of taking Persen and other drugs, depending on the severity of the symptoms of the disease.
Thus, to prevent possible development, as well as to treat psycho-emotional disorders in pregnant women, it is advisable to use sedatives, the effect of which softens the damaging effects of psychogenic factors.
Literature
1. Abramchenko V.V., Kovalenko N.P. Perinatal psychology: Theory, methodology, experience. Petrozavodsk, 2004. 350s.
2. Avedisova A.S. Anxiety disorders // Alexandrovsky Yu.A. "Mental disorders in general medical practice and their treatment". M: GEOTAR-MED. 2004, pp. 66–73.
3. Voznesenskaya T.G., Fedotova A.V., Fokina N.M. Persen-forte in the treatment of anxiety disorders in patients with psychovegetative syndrome // Treatment of nervous diseases. 2002. No. 3 (8). pp. 38–41.
No. 3 (8). pp. 38–41.
4. Vorobieva O.V. Psychovegetative syndrome associated with anxiety (issues of diagnosis and therapy) // Russian Medical Journal. 2006. V.14. No. 23. S. 1696-1699.
5. Grandilevskaya I.V. Psychological features of women's response to the identified pathology of pregnancy: Abstract of the thesis. dis. ... cand. psychol. Sciences. SPb., 2004.
6. Kasyanova O.A. Socio-psychological factors in preparing women for pregnancy, childbirth and motherhood: Abstract of the thesis. dis. ... cand. psychol. Sciences. Yaroslavl, 2005.
7. Kovalenko N.P. Psychoprophylaxis and psychocorrection of women during pregnancy and childbirth: Abstract of the thesis. dis. … doc. psychol. Sciences. SPb., 2001.
8. Filippova G.G. Psychological readiness for motherhood // Reader on perinatal psychology: Psychology of pregnancy, childbirth and the postpartum period. M., Izd-vo URAO, 2005. 328 p.
9 Davidson J.R.T. Pharmacotherapy of generalized anxiety // J. Clin. Psychiatry. 2001 Vol. 62. P. 46–50.
Clin. Psychiatry. 2001 Vol. 62. P. 46–50.
10. Fricchione G. Generalized anxiety disorder. // New Engl. J. Med. 2004 Vol. 351. No. 7. P. 675–682.
11. Gavin N.I., Gaynes B.N., Lohr K.N. et al. Perinatal depression: a systematic review of prevalence and incidence // Obstet. Gynecol. 2005 Vol. 106. P. 1071-1082.
12. Ross L.E., McLean L.M. Anxiety disorders during pregnancy and the postpartum period: A systematic review // J. Clin. Psychiatry. 2006 Vol. 67. No. 8. P. 1285–1298.
13. Ross L.E., Murray B.J., Steiner M. Sleep and perinatal mood disorders: a critical review // J. Psychiatry Neurosci. 2005 Vol. 30. No. 4. R. 247–256.
14. Rouillon F. Long term therapy of generalized anxiety disorder // Eur. J. Psychiatry. 2004 Vol. 19. No. 2. P. 96–101.
15. Soares C.N., Steiner M. Perinatal depression: searching for specific tools for a closer look at this window // J. Clin. Psychiatry. 2009 Vol. 70. No. 9. P. 1317–1318.
Fears during pregnancy | Nutriclub
Most women experience fear and anxiety during pregnancy. What most often worries expectant mothers and how to relieve excessive anxiety - we analyze it by points
What most often worries expectant mothers and how to relieve excessive anxiety - we analyze it by points
During pregnancy, the expectant mother undergoes major changes in her body. The feeling of anxiety and fear during this period is experienced by 90% of women - this is a natural psychological reaction to changes in hormonal levels and adaptation of the body to new conditions.
Is there something wrong with my child?
It is important to know that nature has done everything to protect your baby in the womb. And modern medicine is able to detect and prevent many diseases and deviations. Do your best - see your doctor regularly and stay active and healthy - and you'll be fine. Timely diagnosis will help to identify diseases and infections at the initial stage that can threaten the baby, and cure them in a timely manner. The expectant mother is tested, she is given an ultrasound scan and screenings to detect fetal pathologies. All this will help you relieve anxiety and fear for the health of the baby. In order to stop worrying, it is worth thinking about the positive experience of your acquaintances and girlfriends, remember that most children are born healthy and that many developmental disorders are successfully corrected after birth. Read less horror forums, attend yoga and pregnancy fitness classes, and walk more.
In order to stop worrying, it is worth thinking about the positive experience of your acquaintances and girlfriends, remember that most children are born healthy and that many developmental disorders are successfully corrected after birth. Read less horror forums, attend yoga and pregnancy fitness classes, and walk more.
I am afraid of childbirth
Fear of childbirth is a natural fear of physical pain. In order to get rid of it, you can be like childbirth preparation courses, where you will be taught how to breathe and push properly. Such courses are also good because you will see how many women are in the same position as you. You can discuss your concerns with the obstetrician-gynecologist in advance, decide how you will give birth: alone or with a partner, which type of anesthesia is preferable for you, if such a need arises. Remember that today doctors have a lot of opportunities to make the process of childbirth painless. In addition, you can prepare your body for childbirth by walking more, moving more and attending classes for pregnant women.
What if I'm a bad mom?
What if I take care of the child incorrectly and this will harm him? I will not have time to do everything that is necessary, because the child requires increased attention? I will not be able to properly feed and educate him? These are common fears that almost all women who give birth for the first time visit. It is important to know that there is nothing more natural than motherhood. You will cope with any number of children that will be born thanks to you. As a rule, as soon as the baby is born, everything comes by itself, and no one but you will understand your child better. And all your fears will dissipate in the first days of the baby's life. Not a single woman has a ready-made program for care and upbringing - instincts and daily practice help.
What if I can't breastfeed?
Only 5% of women cannot breastfeed for medical or psychological reasons. As a rule, these are such serious diseases as kidney pathology, heart defects, blood diseases, tumors, HIV infections, etc. There are acute psycho-emotional disorders that also prevent breastfeeding. If you do not have such diseases, then there is nothing to worry about. After childbirth, milk appears in all women without exception, and feeding on demand will provide the right amount of milk for the baby. Today, in many maternity hospitals, you can consult a nurse or even a breastfeeding specialist who will show you how to properly latch on to your baby. If you are concerned about cracks, then there are various products that are applied to the nipples before and after feeding, a breastfeeding specialist can also talk about this. And of course, a positive attitude is needed for successful feeding: remember that with mother's breast milk, the child receives absolutely all the trace elements he needs.
There are acute psycho-emotional disorders that also prevent breastfeeding. If you do not have such diseases, then there is nothing to worry about. After childbirth, milk appears in all women without exception, and feeding on demand will provide the right amount of milk for the baby. Today, in many maternity hospitals, you can consult a nurse or even a breastfeeding specialist who will show you how to properly latch on to your baby. If you are concerned about cracks, then there are various products that are applied to the nipples before and after feeding, a breastfeeding specialist can also talk about this. And of course, a positive attitude is needed for successful feeding: remember that with mother's breast milk, the child receives absolutely all the trace elements he needs.
Will my life change?
Life will change, but definitely for the better. If before pregnancy your days were full of interesting people and things, then this will not disappear anywhere. Rather, on the contrary - after the birth of a child, new ideas and interests will appear. As many women note, a decree is a chance to learn new skills and abilities, and possibly change the field of activity if you have been thinking about it for a long time. The fact is that caring for a child can be combined with other activities, the main thing is to set yourself up correctly. Today there are great opportunities for distance learning and professional development. These are books, online courses, webinars, remote work.
Rather, on the contrary - after the birth of a child, new ideas and interests will appear. As many women note, a decree is a chance to learn new skills and abilities, and possibly change the field of activity if you have been thinking about it for a long time. The fact is that caring for a child can be combined with other activities, the main thing is to set yourself up correctly. Today there are great opportunities for distance learning and professional development. These are books, online courses, webinars, remote work.
There is a common myth that a child chains his mother to the house. It all depends on the desire of the woman: with the baby it is quite possible to go on a visit, to meet with friends or colleagues, to travel. Also, most babies sleep very soundly and won't be distracted if you invite guests.
The main way to get rid of fears during pregnancy is to fill your life with events and people that make you happy. The condition of the mother is passed on to her child, and to please and take care of yourself is the most important thing you can do for the baby during this period.