Can throwing up be a sign of pregnancy
Pregnancy - signs and symptoms
Significant hormonal changes take place during pregnancy. These trigger a variety of symptoms. Some women experience many of the symptoms of pregnancy, while others may have only a few.
Symptoms of early pregnancy include missed periods, breast changes, tiredness, frequent urination, and nausea and vomiting (morning sickness). However, these symptoms may be caused by other factors and do not necessarily mean that you are pregnant, so if you suspect you are pregnant take a home pregnancy test and see your GP.
A wide range of changes can occur in your body in the later stages of pregnancy, including backache, headache, leg cramps or varicose veins, itch or tingling, constipation, haemorrhoids or indigestion, vaginitis or vaginal discharge, or mood changes or depression.
If you have any concerns don’t hesitate to talk to your GP. See your GP right away if you experience symptoms like vaginal bleeding or breaking waters, chronic pain, high temperature, severe headaches or vision loss.
The signs of early pregnancy can include:
- missed period
- nausea and vomiting (often called ‘morning’ sickness, but it can occur at any time)
- breast tenderness and enlargement
- fatigue
- passing urine more frequently than usual, particularly at night
- cravings for some foods, distaste for foods you usually like, and a sour or metallic taste that persists even when you’re not eating (dysgeusia).
Many of the signs of pregnancy, such as a missed period (amenorrhoea), nausea (morning sickness) or tiredness can also be caused by stress or illness, so if you think you are pregnant take a home pregnancy test (urine test) or see your GP, who will administer a urine test, blood test or ultrasound scan.
Missed period
Missing a period is often the first sign of possible pregnancy. However, some women experience light bleeding around the time of their expected period.
Nausea and vomiting
‘Morning’ sickness is a condition that affects more than half of all pregnant women. The symptoms include nausea and vomiting, and loss of appetite. Many women with morning sickness don’t just get symptoms in the morning but experience them throughout the whole day.
The symptoms include nausea and vomiting, and loss of appetite. Many women with morning sickness don’t just get symptoms in the morning but experience them throughout the whole day.
Morning sickness usually begins around the fourth to sixth week of pregnancy and may settle by week 12, although it can continue for longer or return at around 32 weeks.
Breast changes
During pregnancy, the breasts become fuller, swollen and tender. These changes are similar to those you may have noticed in the few days before your period. During pregnancy, the skin around the nipple becomes darker and the veins in the breast become more obvious.
Fatigue
Overwhelming tiredness is common in early pregnancy. This is most likely caused by the massive increase in the sex hormone progesterone. Progesterone is needed to maintain the pregnancy and help the baby to grow, but it also slows your metabolism.
Try to get some more sleep or rest when you can during this early stage. Your energy levels will probably rise again by around the fourth month of pregnancy when the placenta is well established.
Your energy levels will probably rise again by around the fourth month of pregnancy when the placenta is well established.
Tiredness during pregnancy can also be caused by anaemia, which is most commonly caused by iron deficiency. Eating iron-rich foods is important in the prevention of iron deficiency anaemia during pregnancy. Medical treatment of anaemia in pregnancy usually involves taking iron tablets. Sometimes an iron infusion (iron medicine given by a drip) is needed. This needs a hospital admission but only takes a few hours. Some iron infusions can be given by your GP.
Frequent urination
Pregnancy causes an increase in levels of body fluids and greater kidney efficiency. The swelling uterus also presses against the bladder. As a result, most women start experiencing more frequent urination within the first few weeks of becoming pregnant.
Food cravings
Cravings for certain foods are very common in pregnancy, especially for foods that provide energy and calcium, such as milk and other dairy products. You may also notice a sudden distaste for foods you previously liked.
You may also notice a sudden distaste for foods you previously liked.
Some women even develop an unusual taste for non-food items such as soil or paper. This is called ‘pica’ and may indicate a nutrient deficiency. Please speak to your GP or midwife if this develops.
Other symptoms of pregnancy
Many of these symptoms may also be indicative of other conditions. If in doubt, see your GP.
- backache
- breathlessness
- constipation
- haemorrhoids (piles)
- headaches
- heartburn and indigestion
- itchy skin
- leg cramps
- mood changes (such as unexplained crying)
- tingling and numbness in your hands
- vaginal discharge
- vaginitis
- varicose veins and leg oedema (swelling).
Backache
Back pain during pregnancy can affect more than 1 in 3 women. This is usually due to loosening of ligaments and change in posture due to the growing pregnancy.
You can help reduce back pain during pregnancy by wearing flat heeled shoes, using chairs with good back support, avoiding lifting heavy objects, and doing gentle exercise. Exercising in water can reduce back pain in pregnancy, and physiotherapy and acupuncture may also help.
Exercising in water can reduce back pain in pregnancy, and physiotherapy and acupuncture may also help.
Breathlessness
At the onset of pregnancy the hormone progesterone increases your lung capacity. This enables you to carry more oxygen to your baby and get rid of waste products such as the carbon dioxide that you both produce. At each breath you breathe more deeply and the amount of air you inhale (and exhale) increases significantly. This can make you feel short of breath.
In addition, as pregnancy approaches term, the pressure of the enlarging uterus and baby on your diaphragm can make your breathing feel more laboured.
Contact your doctor or midwife if you experience sudden onset of breathlessness associated with any of the following:
- pain
- palpitations (heart pounding)
- extreme tiredness
- exercise.
Constipation
Constipation refers to infrequent, hard bowel movements that are difficult to pass. Constipation is a common problem in pregnancy that may be caused by pregnancy hormones slowing your gastrointestinal movement, or by the pressure of your growing uterus on your rectum.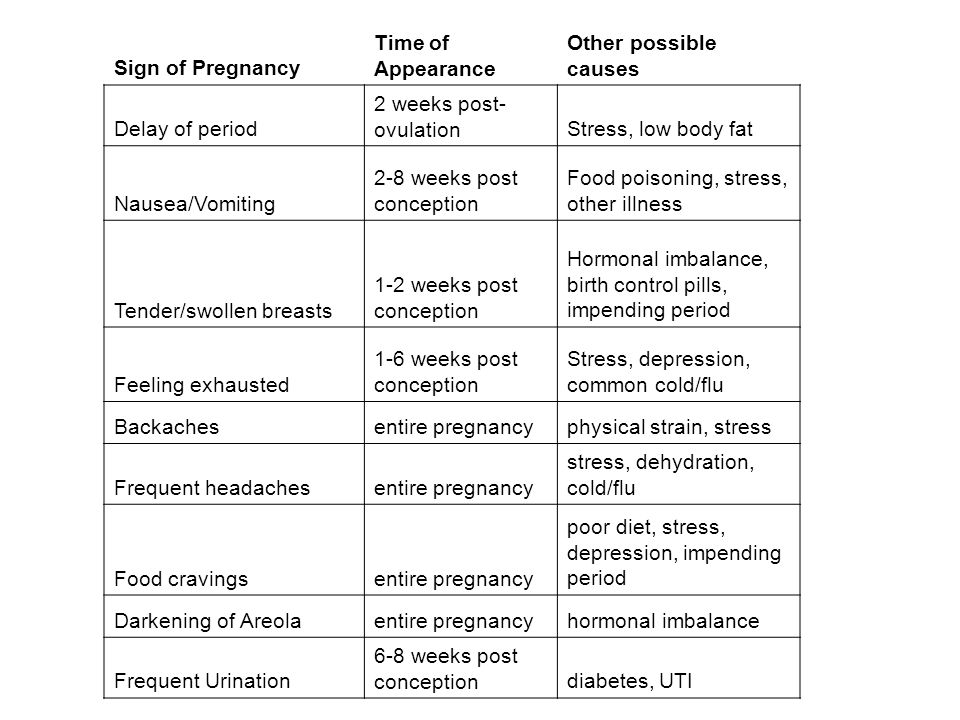
If you experience constipation during pregnancy, you are advised to:
- drink plenty of water every day.
- increase your dietary fibre (such as bran, wheat and fresh fruit and vegetables).
- do gentle, low impact exercise such as swimming, walking or yoga.
Don't take over-the-counter laxatives without first consulting your midwife or GP. If changes to your diet and lifestyle don't make a difference then your GP or midwife can prescribe a laxative that is safe to use in pregnancy.
Haemorrhoids (piles)
You may develop haemorrhoids (also known as piles) as a result of straining from constipation or the pressure of your baby’s head. Be reassured, symptoms usually resolve on their own soon after birth.
If you have bleeding from haemorrhoids, itching, discomfort or pain it is recommended that you:
- Alleviate or prevent constipation by increasing your daily water and fibre intake.
- Sit in warm salty water for about 15 minutes, especially after a bowel motion.

- Apply haemorrhoid cream.
If the bleeding or pain continues, talk with your GP (doctor) or midwife.
Headaches
Contact your GP or midwife if you have a headache during pregnancy that is not relieved by paracetamol (such as Panadol), especially in the second half of pregnancy.
A persistent headache can be associated with pre-eclampsia – a condition that can affect your kidneys and thus increase blood pressure and decrease blood flow to your baby.
Heartburn and indigestion
Heartburn, reflux or indigestion is the pain and discomfort associated with acid from the stomach entering and ‘burning’ the oesophagus.
Indigestion is more common during pregnancy due to the pressure of the enlarging uterus on the organs of the abdomen and the action of the hormone progesterone that relaxes the muscle between the oesophagus and stomach.
If you are experiencing heartburn, reflux or indigestion, it is recommended that you:
- Eat small and more frequent meals.

- Avoid eating just before going to bed.
- Sleep with extra pillows so your head is raised.
- Wear loose-fitting clothing.
- Avoid any food or fluid that aggravates symptoms – such as fatty foods (including fried foods, fatty meats and pastry), spicy foods (including curry and chilli), alcohol and caffeine (including tea, coffee, chocolate and cola).
- Consult your doctor before taking antacids.
If these strategies do not relieve your symptoms, please consult your GP, who may prescribe a medication that will safely reduce the secretion of acid.
Itchy skin
Widespread itching over the body is not common in pregnancy but it can be very distressing, interfering with sleep and enjoyment of pregnancy. Dry skin and eczema are the most common causes but sometimes there may be no apparent cause for the itching. In rare cases, where the palms of the hands and soles of the feet are itchy, it may be due to serious liver disease – a blood test can be done to check for this.
An itchy rash in the later part of pregnancy is thought to be caused by the body’s reaction to the stretching of the skin. This is called PUPPS. Itching can be controlled by using moisturisers and antihistamines. Ask your doctor or midwife what antihistamines are safe in pregnancy.
Leg cramps
Leg cramps occur due to a build-up of acids that cause involuntary contractions of the affected muscles. They are experienced by up to half of pregnant women, usually at night. Leg cramps are more likely in the second and third trimesters.
If you experience leg cramps, it is recommended that during an episode you:
- Walk around.
- Stretch and massage the affected muscle(s) to disperse the build-up of acids.
- Apply a warm pack to the affected muscle(s).
If you find cramps troublesome, discuss with your GP or midwife the option of taking magnesium lactate or citrate morning and evening.
Mood changes
Some newly pregnant women experience mood changes such as irritability. Other pregnant women experience feelings of elation. It is thought that the pregnancy hormones influence chemicals in the brain, causing mood changes.
Other pregnant women experience feelings of elation. It is thought that the pregnancy hormones influence chemicals in the brain, causing mood changes.
During pregnancy, 1 in 10 women experience depression. Depression is treatable, so if you are feeling depressed or ‘down’ during pregnancy it is extremely important to get help early. Please contact your GP (doctor), midwife or maternal and child health nurse as soon as possible.
Tingling and numbness in your hands (carpal tunnel syndrome)
Carpal tunnel syndrome – tingling and numbness in your hands – affects up to 60 per cent of women during pregnancy. It is caused by compression of the median nerve due to an increase in the tissue fluids during pregnancy.
Carpal tunnel syndrome may be mild, intermittently painful, or severe, which may cause partial paralysis of the thumb or loss of sensation. Symptoms usually resolve on their own soon after birth.
If you are experiencing tingling and numbness in your hands, inform your doctor or midwife.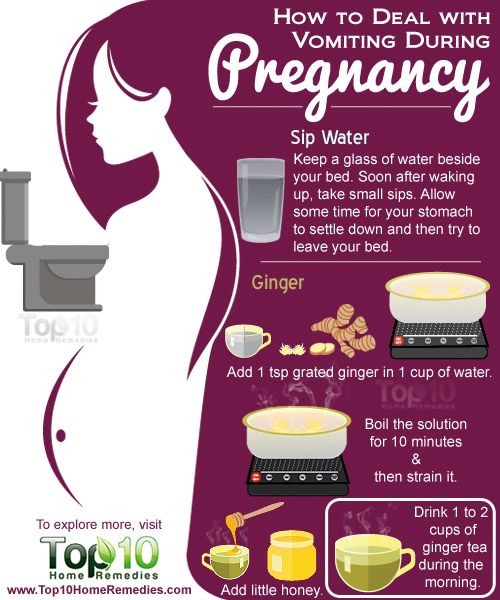 In very severe cases, your doctor may recommend corticosteroid injections or surgical treatment.
In very severe cases, your doctor may recommend corticosteroid injections or surgical treatment.
Vaginal discharge
An increase in vaginal discharge is a common change during pregnancy. If it is associated with itchiness, pain, a bad odour or pain on passing urine then it may be due to an infection. Seek treatment from your GP.
Vaginitis
Vaginitis is inflammation of the vagina, and is a distressing complaint for many women. It is more frequent during pregnancy. Some causes of vaginitis include vaginal thrush, bacterial vaginosis, trichomoniasis and chlamydia. See your GP for diagnosis and treatment
Varicose veins and leg oedema (swelling)
Varicose veins of the legs are very common in pregnancy due to a combination of factors, including increased volume of circulating blood during pregnancy, and pressure of the pregnant uterus on the larger veins. This increased pressure on the veins can also result in swelling of the legs (oedema) that can cause pain, feelings of heaviness, cramps (especially at night) and other unusual sensations.
If you have varicose veins, it is recommended that you:
- Wear support stockings.
- Avoid standing for long periods.
- Exercise gently and regularly (walking or swimming).
- Lie down to rest with feet elevated, when you can.
- Try massaging your legs.
- Tell your doctor or midwife at your next pregnancy visit.
It is recommended that you contact your hospital or carer if you are worried or if you have any of the following during pregnancy:
- vaginal bleeding
- less movement of your baby than usual
- severe stomach pain
- pain that doesn’t go away
- leaking amniotic fluid (that is, if your waters break)
- a high temperature
- vomiting that will not stop
- a headache that will not go away
- vision loss or blurred vision
- widespread itching of the skin
- sudden swelling of face, hands and feet.
Read more about problems that can occur during pregnancy.
Where to get help
- In an emergency, call 000 for an ambulance
- Your GP (doctor)
- Midwife
- Obstetrician
- Your maternity hospital
- Your maternal and child health nurse
- Pharmacist
- Sexual Health VictoriaExternal Link Tel. 1800 013 952
- Sexual Health Victoria - Our ClinicsExternal Link
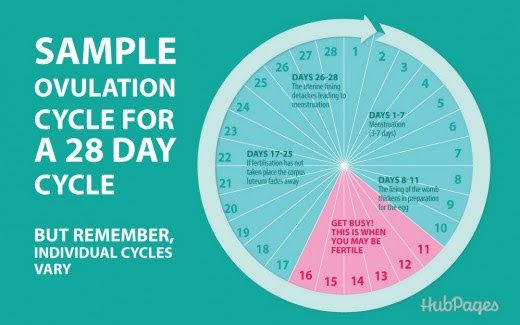
When does morning sickness start?
Nausea is a well-known symptom of pregnancy, affecting at least 70% of expecting mothers. Also called morning sickness, nausea usually begins at around six weeks, peaks between weeks 8-11, and typically fades near the end of the first trimester. However, some women experience nausea as both a second trimester and third trimester symptom.
The early weeks of pregnancy can be an exciting and confusing time. You’re beginning a journey that involves many physical and emotional changes,, and you don’t always know how you’ll feel from one day to the next. But we’re here to help you understand the changes you’re going through, and morning sickness can be one of the most noticeable.
Below, we cover what to expect and what you can do to find some relief from this common pregnancy symptom.
What is morning sickness and what are the symptoms?
Morning sickness is a feeling of nausea, sometimes also accompanied by vomiting. It can be one of the earliest signs of pregnancy for many women, appearing a couple weeks after a positive pregnancy test.
Despite being called morning sickness, nausea in pregnancy can happen at any time of day. Women often feel the most nauseous on an empty stomach, which is most apparent when you wake up after not eating all night, hence how it got its name.
Symptoms of morning sickness frequently occur on their own, but can also be triggered by certain foods, smells, heat, stress and other factors. The feeling can range from slight queasiness, like being a little carsick, to more intense nausea and vomiting.
Can you be pregnant and not have morning sickness?
Morning sickness is made out to be very common in movies and television, and it is.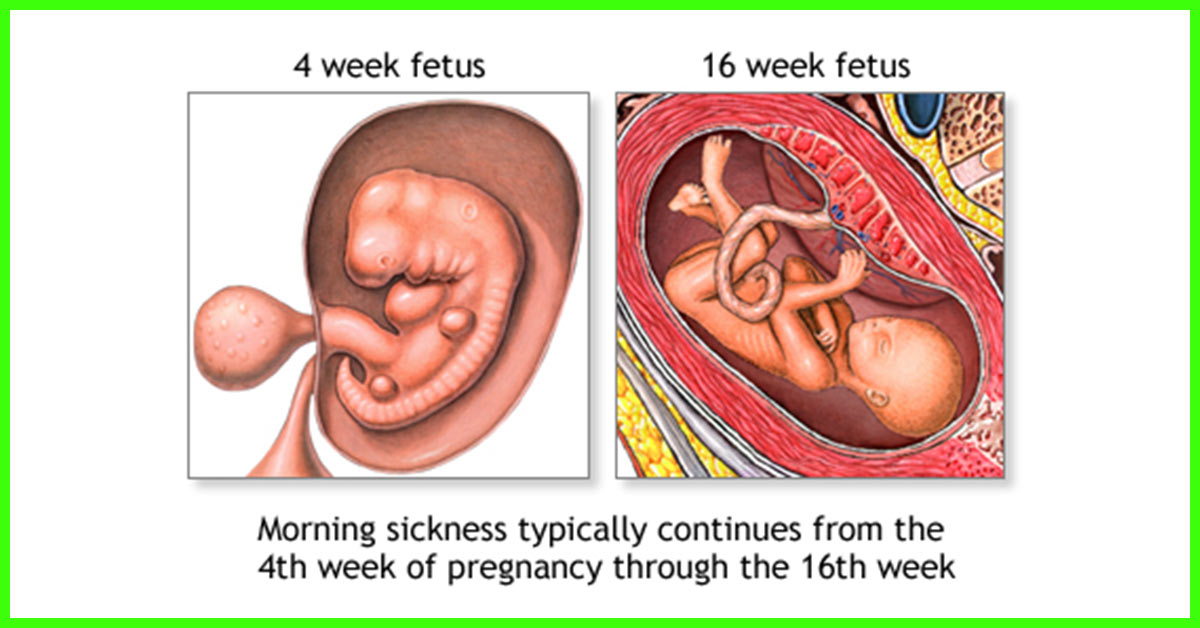 But it’s also possible to be pregnant without experiencing it. Three out of 10 pregnant women don’t experience morning sickness, so it’s not rare or concerning if that’s the case.
But it’s also possible to be pregnant without experiencing it. Three out of 10 pregnant women don’t experience morning sickness, so it’s not rare or concerning if that’s the case.
The same goes for aversions to certain foods or smells. Every pregnancy is unique, so not every pregnant woman will experience the same symptoms. If you think you could be pregnant but aren’t experiencing morning sickness or other symptoms, taking a pregnancy test is the only way to find out for sure.
What causes morning sickness?
While the exact cause isn't well understood, many doctors believe morning sickness happens because of hormones. The pregnancy hormone human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) reaches its highest level around the same time morning sickness is most severe. And, increases in the hormones estrogen and progesterone can make it harder for your body to digest food, adding to stomach discomfort.
When does morning sickness start?
If you’re one of the many pregnant women who experience morning sickness, you may start feeling nauseous somewhere around the sixth week of your pregnancy, typically two weeks after your first missed period. Symptoms may appear gradually or seem to happen overnight.
Symptoms may appear gradually or seem to happen overnight.
Is it normal to be nauseous all day when pregnant?
Don’t be fooled by the name. Morning sickness doesn’t only happen in the morning, and it’s very normal for it to last all day. No two women experience it in the same way. Also, some women who had morning sickness in their first pregnancy may not have any nausea at all in their second, and vice-versa.
When does morning sickness end?
Morning nausea usually peaks between weeks 8-11, and typically fades by the end of the first trimester. However, some women can experience nausea in their second trimester, and some even notice nausea near the end of pregnancy.
If your morning sickness lasts beyond your first trimester, you may be more sensitive to the effects of hormonal changes during pregnancy. Or you may just have a more delicate stomach. But it’s a good idea to bring up your morning sickness with your doctor or midwife to learn about your options for relief.
Hyperemesis gravidarum (HG)
If you’re throwing up more than two to three times a day and aren’t able to keep anything down, you may have hyperemesis gravidarum (HG), a form of severe morning sickness. Some cases can be treated with pressure-point wristbands, like those worn to prevent motion sickness. In other cases, you might need medication, bed rest or intravenous (IV) fluids to help reduce or eliminate symptoms.
Many women tolerate morning sickness because they know that nausea in pregnancy is very common, however they may not realize that severe vomiting is not as normal and requires attention. That’s why it’s important to know the signs of HG. Talk to your care provider right away if you are vomiting so much that you:
- Become persistently dehydrated
- Can’t keep any foods or liquids down for 24 hours
- Feel weak, dizzy or faint and/or lightheaded
- Lose three or more pounds in a week
It’s important to know what’s normal and what’s not. If you have any concerns about your morning sickness, our experienced team of OB-GYNs and midwives can help you get personalized care that’s right for you.
If you have any concerns about your morning sickness, our experienced team of OB-GYNs and midwives can help you get personalized care that’s right for you.
Is morning sickness bad for the baby?
It’s natural to wonder about whether your nausea and loss of appetite could be harmful to your baby. But rest assured, if you’re still able to eat and stay hydrated, your baby will still get all their needed nutrients. In rare and severe cases of morning sickness, your doctor or midwife will work to ensure that you and baby are getting the necessary nutrition and hydration to stay healthy.
What can I do to find relief from pregnancy nausea?
You don’t have to tough it out and wait for the day your morning sickness subsides. There are plenty of simple, safe and effective strategies you can try to combat nausea.
Eat smaller meals throughout the day
Having an empty stomach for too long can make anyone feel sick. Eating small snacks throughout the day in between larger meals can keep you from feeling queasy. But remember, eating too much can make you feel just as nauseous. It’s all about finding a balance that will keep you feeling good.
But remember, eating too much can make you feel just as nauseous. It’s all about finding a balance that will keep you feeling good.
Avoid trigger foods
Some food and drinks are difficult to digest and may make you feel sicker. Try to stay away from caffeine, acidic foods such as tomatoes, and greasy or spicy foods.
Iron supplements can also contribute to nausea and constipation, so talk to your doctor or midwife if you’re taking one.
Try the B.R.A.T. diet
If you can’t seem to find anything that agrees with you, try these foods that are bland and easy to digest: bananas, rice, applesauce and toast.
Stay hydrated
Drink a lot of fluids. In addition to water, sports hydration drinks, broth and juice can help replace nutrients that you may lose from vomiting.
Consume ginger
Eating and drinking foods with ginger can help calm the feelings of nausea. Easy options include ginger ale, ginger hard candy, ginger lollipops or ginger tea.
Take a vitamin B6 supplement
Though it may already be present in your prenatal vitamin, taking additional vitamin B6 has shown to be effective in reducing nausea during pregnancy. You can take up 25 to 50 mg of vitamin B6 per day, but it’s best to talk to your care provider before taking additional supplements.
Wear a wristband
As mentioned above, there are a variety of wristbands available over the counter that are designed to prevent motion sickness. They work by applying pressure to specific pressure points that can help ease nausea.
Experiment with different temperatures
You may have an easier time eating or drinking cold foods and beverages, or your stomach may feel calmer after a hot meal. Room temperature or warm food and drinks can sometimes cause nausea.
Keep a morning sickness record
What time of day does nausea strike? What are you doing when it does? By tracking your symptoms, you just might identify triggers that make you queasy – like certain foods or smells – so you can avoid them going forward.
Pack the essentials
If morning sickness does end up causing you to vomit, you can make it easier by carrying a few supplies with you. Feeling prepared by bringing a toothbrush and toothpaste, mouthwash, a backup shirt and even a plastic bag can give you peace of mind and make morning sickness feel more manageable.
Ask your doctor or midwife about finding relief from pregnancy nausea
These remedies may not work for everyone, and there are other solutions for more persistent symptoms. Talk to your care provider about anti-nausea medications that are safe to take while pregnant.
While morning sickness can be a challenging part of any pregnancy, it’s also a sign that your body is doing what it needs to support your growing baby. That said, you shouldn’t have to suffer through pregnancy nausea that interferes with your daily life and your ability to be present at work or with family.
Fortunately, there’s help available to make your pregnancy a bit smoother and more comfortable. If you’d like to explore your options for improving symptoms of pregnancy nausea, our women's health experts are here to help.
Signs of pregnancy - Health Clinic 365 Yekaterinburg
Gynecology, pregnancy
Pregnancy management
Gynecologist
Pregnancy symptoms - what is it?
Symptoms of pregnancy or signs of pregnancy are, as a rule, a combination of certain physiological changes in the body that a woman notices in herself already in the early stages of pregnancy.
Sometimes we hear that it is wrong to say “pregnancy symptoms”, because if there are symptoms, then there is a disease, and pregnancy is not a disease. But if we dig into dictionaries, we find that the word “symptom” comes from the Greek sýmptoma, i.e. "sign", "case", "coincidence". Thus, "pregnancy symptoms" is just a synonym for the phrase "signs of pregnancy", which is absolutely correct. The symptoms of early pregnancy or the first symptoms of pregnancy are different from the symptoms that occur in the later stages.
Knowing the signs of pregnancy allows a woman in the early stages to show increased attention to her health, and, consequently, to the health of the unborn baby, a pregnant woman will be able to determine pregnancy in the earliest possible time and, accordingly, resolve the issue for herself in time about its prolongation (preservation, continuation).
Every woman is remarkably different, so the symptoms a woman may experience during pregnancy may vary. Some women feel pregnant even before the test is positive. Below are nine symptoms of pregnancy.
The first symptom of pregnancy is implantation bleeding.
This is one of the earliest symptoms. On the sixth - twelfth day after conception, the introduction (attachment, implantation) of the embryo into the wall of the uterus occurs. Some women notice a small amount of red discharge (spots), which may be pink or reddish brown. If you have pain along with spotting or bleeding, see your doctor immediately as this could be a sign of an ectopic pregnancy.
The second symptom of pregnancy, also the main one, is the delay in menstruation
This symptom must be present during a normal pregnancy. You should be aware that sometimes bleeding occurs during pregnancy. The main thing is not to confuse them with menstruation, especially on those days when you should have started your period, that is, at 4, 8, 12 weeks of pregnancy. Bleeding during pregnancy is a sign of a threatened abortion. Therefore, if you notice this symptom in yourself, then immediately contact a specialized medical institution. With timely treatment, there is every chance to save the desired pregnancy. Menstruation does not occur throughout pregnancy and, as a rule, during breastfeeding.
The third symptom of pregnancy is increased basal body temperature.
Basal body temperature rises above 37 degrees during pregnancy. If you notice some symptoms of pregnancy in yourself or even confirmed it with a doctor and at the same time observe a decrease in basal temperature, consult a doctor. A decrease in basal temperature may be due to the threat of miscarriage. For the result to be reliable, measure the temperature correctly. It should be measured in the rectum, immediately after waking up, in the morning.
A decrease in basal temperature may be due to the threat of miscarriage. For the result to be reliable, measure the temperature correctly. It should be measured in the rectum, immediately after waking up, in the morning.
The fourth symptom of pregnancy is profuse discharge.
In this case, we do not mean bleeding. Women know that normal vaginal discharge is odorless and almost colorless. Their number increases during ovulation and, as you now know, during pregnancy. On 9/10, you are pregnant if you have a missed period, heavy discharge, and an elevated basal body temperature.
The fifth symptom of pregnancy - swelling and (or) increased sensitivity of the mammary glands.
Many women say that the sensitivity of the mammary glands changes. This symptom may appear 1 to 2 weeks after conception. Swelling and increased sensitivity of the breast may appear not only as a result of pregnancy. Other causes are: premenstrual syndrome (PMS), birth control pills, or hormonal imbalances.
Other causes are: premenstrual syndrome (PMS), birth control pills, or hormonal imbalances.
The sixth symptom of pregnancy is toxicosis.
Nausea or vomiting in the morning usually does not occur early in pregnancy, but some women experience nausea as early as the third week. Many women believe that toxicosis is morning sickness and vomiting. But it is not so. In addition to nausea and vomiting, signs of toxicosis include a heightened sense of smell and aversion to certain foods. Many pregnant women cannot tolerate certain smells during early pregnancy. A heightened sense of smell is a side effect of a rapidly rising level of estrogen in your blood. Aversion to certain foods is even more common than cravings for certain foods during pregnancy. You may suddenly find that certain foods, even your favorites, disgust you.
The feeling of fatigue, which will be discussed below, is also referred to by some obstetricians as manifestations of toxicosis. Toxicosis, most often, goes away on its own by 12-14 weeks of pregnancy.
Toxicosis, most often, goes away on its own by 12-14 weeks of pregnancy.
The seventh symptom of pregnancy is feeling tired.
Fatigue can be as pronounced as if you had run a marathon. Fatigue is caused by increased levels of progesterone and other hormones necessary for the development of the child.
The eighth symptom of pregnancy is frequent urination and constipation.
You may suddenly become aware that you are going to the bathroom with alarming frequency.
The ninth symptom of pregnancy is headache and migraine.
Usually headaches are caused by hormonal changes in the body. If headaches occur, you should not self-medicate, since most known painkillers are contraindicated during pregnancy, especially in the early stages.
Related articles:
Birth certificate
Exchange card. Sick leave. Decree
Decree
Federal Pregnancy Standard
Ultrasound during pregnancy
Below below the abdomen
menstrual pain
Signs of pregnancy
Hysteroscopy
Kolposcopy
hysterosalpingography
9000 Uzi of low tanksmography 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000
003
Prolapse of internal organs
Premature birth
Removal of uterus
Intimate plastic surgery
First signs of pregnancy | Kotex®
Although pregnancy tests and ultrasound are the only ways to accurately determine pregnancy, there are a number of signs and symptoms to watch out for. The first signs of pregnancy include not only the absence of a period, but may also include fatigue, sensitivity to smells, and morning sickness. It is worth remembering that these are POSSIBLE signs of pregnancy, they can appear in both pregnant and non-pregnant women and are associated with ovulation and menstruation.
When do symptoms appear?
Oddly enough, the first week of pregnancy is determined by the date of the last menstruation.
Your last period counts as the first week of pregnancy, even if you haven't actually been pregnant yet. The estimated due date is calculated from the first day of your last period.
Taking a home pregnancy test is the cheapest and easiest way to find out if you're pregnant. Remember that home pregnancy tests measure the level of a hormone called human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) in the urine, and there is usually less of it in urine than in blood.
The test gives the most accurate results from the moment of missed menstruation.
The menstrual cycle is considered delayed if the menstruation did not begin within 5 or more days after the day of their expected start.
However, it is worth remembering that even the day after the expected delay, more than a third of women will give a negative result from such home tests, and if you test too early, the result can be negative, even if you are already pregnant. You can do another test at home after a couple of days to get a more accurate result.
You can do another test at home after a couple of days to get a more accurate result.
Signs and symptoms of pregnancy
If you are pregnant for the first time, then you may not notice these first signs of pregnancy or confuse them with symptoms of impending menstruation.
It is not worth spending long hours looking for answers on the forums in experiences, in any case, your research will not change what has already happened or has not happened, but mood and sleep can thoroughly spoil.
Slight lower abdominal pain and spotting
Absence of menstruation
Fatigue
Nausea
Breast swelling
Frequent urination
Constipation
Vertigo on motion
Mood swings
Temperature changes
High blood pressure
Pain and slight bleeding
From weeks 1 to 4, changes in a woman's body are still happening at the cellular level.:strip_icc():format(jpeg)/kly-media-production/medias/2785562/original/028627600_1556001360-shutterstock_1019963743.jpg) A fertilized egg creates a group of cells filled with fluid, which is called a blastocyst, which, after pregnancy, will have to turn into organs and body parts of the fetus.
A fertilized egg creates a group of cells filled with fluid, which is called a blastocyst, which, after pregnancy, will have to turn into organs and body parts of the fetus.
Approximately 10-14 days after conception (4 weeks), the blastocyst attaches itself to the endometrium lining the uterine wall. This process can cause some bleeding, which can be confused with light menstruation.
Here are some signs of such bleeding:
-
color can be red, pink or brown
-
bleeding: usually comparable to normal menstruation, usually lighter
-
painful sensations
-
usually lasts about three days
No period
After the blastocyst attaches to the walls of the uterus, the body begins to produce a hormone called human chorionic gonadotropin, which tells the body that it is time to stop releasing eggs from the ovaries every month. Most often, after conception, menstruation disappears at 4 weeks of pregnancy.
Most often, after conception, menstruation disappears at 4 weeks of pregnancy.
If you're late, it's worth taking a home pregnancy test, especially if you have irregular periods.
Fatigue
Fatigue may appear at any time during pregnancy. During pregnancy, progesterone levels rise, and this hormone can make you feel sleepy. If you feel tired, then make sure you get enough sleep.
Morning sickness and vomiting
Nausea and morning vomiting usually develop between 4 and 6 weeks of gestation. In fact, such symptoms can occur not only in the morning, but in general at any time of the day. This symptom is typical for the first 12 weeks of pregnancy. If you often feel sick, then you need to make sure that you drink enough water to avoid dehydration.
Breast swelling and tenderness
Breast changes may begin at 4-6 weeks of gestation. They are also associated with changes in hormone levels. Most often, the breast swells somewhat and becomes more sensitive than usual. Usually these symptoms disappear in the future, when the body gets used to the changed hormonal background.
They are also associated with changes in hormone levels. Most often, the breast swells somewhat and becomes more sensitive than usual. Usually these symptoms disappear in the future, when the body gets used to the changed hormonal background.
Frequent urination
During pregnancy, blood flow increases and this causes the kidneys to process more fluid than usual, which can cause frequent urination even in the early stages of pregnancy.
Constipation and bloating
This symptom is similar to the typical menstrual symptom and is also caused by hormonal changes, which can slow down the digestive processes, which causes bloating and constipation.
High blood pressure and dizziness during pregnancy
Most often in the early stages of pregnancy in women, blood pressure drops, which can cause a feeling of dizziness due to vasodilation of the brain. High blood pressure in the first 20 weeks of pregnancy usually means that there are some health problems that occur along with pregnancy. Such a symptom may have been present unnoticed prior to pregnancy, or it may have developed during the process. In such cases, it is especially important to monitor your blood pressure and consult your doctor.
High blood pressure in the first 20 weeks of pregnancy usually means that there are some health problems that occur along with pregnancy. Such a symptom may have been present unnoticed prior to pregnancy, or it may have developed during the process. In such cases, it is especially important to monitor your blood pressure and consult your doctor.
Mood swings
Since estrogen and progesterone levels are elevated during pregnancy, this can cause changes in your emotional background and you may become more sensitive than usual. They can cause such strong feelings as depression, irritability, euphoria and anxiety.
Increase in basal body temperature
Basal body temperature is the lowest body temperature it reaches during rest or sleep. It is determined by measuring the temperature in the early morning by inserting a thermometer into the rectum. Normal body temperature may also rise, especially during heat or physical activity.