How effective is a membrane sweep at 40 weeks
The effectiveness of sweeping membranes at term: a randomized trial
Save citation to file
Format: Summary (text)PubMedPMIDAbstract (text)CSV
Add to Collections
- Create a new collection
- Add to an existing collection
Name your collection:
Name must be less than 100 characters
Choose a collection:
Unable to load your collection due to an error
Please try again
Add to My Bibliography
- My Bibliography
Unable to load your delegates due to an error
Please try again
Your saved search
Name of saved search:
Search terms:
Test search terms
Email: (change)
Which day? The first SundayThe first MondayThe first TuesdayThe first WednesdayThe first ThursdayThe first FridayThe first SaturdayThe first dayThe first weekday
Which day? SundayMondayTuesdayWednesdayThursdayFridaySaturday
Report format: SummarySummary (text)AbstractAbstract (text)PubMed
Send at most: 1 item5 items10 items20 items50 items100 items200 items
Send even when there aren't any new results
Optional text in email:
Create a file for external citation management software
Full text links
Wolters Kluwer
Full text links
Clinical Trial
. 1997 Apr;89(4):586-90.
doi: 10.1016/S0029-7844(97)00004-5.
J Crane 1 , K Bennett, D Young, R Windrim, H Kravitz
Affiliations
Affiliation
- 1 Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Memorial University of Newfoundland, St. John's, Canada.
- PMID: 9083317
- DOI: 10.1016/S0029-7844(97)00004-5
Clinical Trial
J Crane et al. Obstet Gynecol. 1997 Apr.
. 1997 Apr;89(4):586-90.
doi: 10.1016/S0029-7844(97)00004-5.
Authors
J Crane 1 , K Bennett, D Young, R Windrim, H Kravitz
Affiliation
- 1 Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Memorial University of Newfoundland, St. John's, Canada.
- PMID: 9083317
- DOI: 10.1016/S0029-7844(97)00004-5
Abstract
Objective: To determine whether sweeping or stripping membranes at 38-40 weeks' gestation leads to spontaneous labor within 7 days.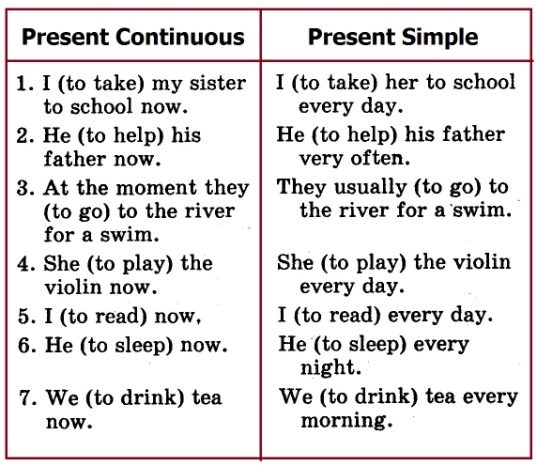
Methods: One hundred fifty antenatal low-risk patients at 38-40 weeks' gestation were assigned randomly to sweeping or control (ie, Bishop score only) groups and stratified based on the ability to pass a finger through the internal os. The primary outcome was the rate of spontaneous labor within 7 days. Major secondary outcomes included the spontaneous labor rate before 41 weeks and the overall spontaneous labor rate. Other outcomes included maternal and neonatal morbidity. The sample size was calculated based on doubling of the spontaneous labor rate within 7 days from 28% to 56% (alpha = 0.05, beta = 0.10).
Results: The subjects were demographically similar between the groups. There were no differences between the groups in the primary outcome of spontaneous labor within 7 days (33% sweeping, 38% control; P = .39) or in the secondary outcomes of spontaneous labor before 41 weeks (P = .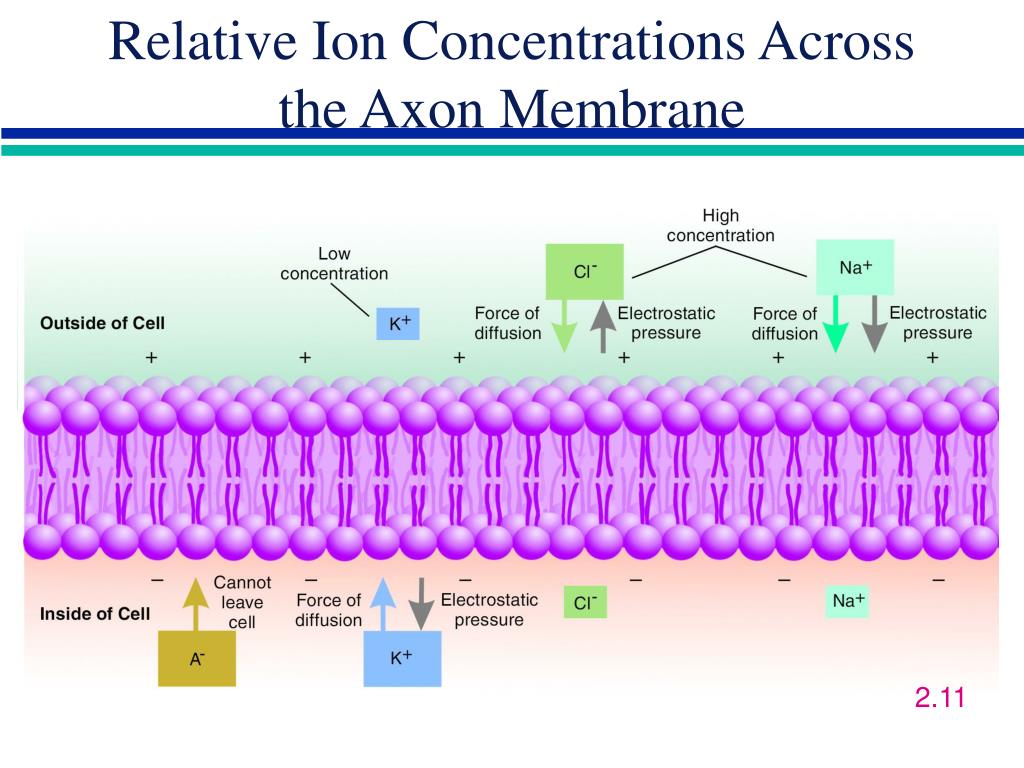 66) or the overall spontaneous labor rate (P = .09). The Bishop score predicted spontaneous labor within 7 days (P = .003), and gestational age at enrollment predicted spontaneous labor before 41 weeks (P = .008) and the overall spontaneous labor rate (P = .008), using logistic regression to control for potential confounders.
66) or the overall spontaneous labor rate (P = .09). The Bishop score predicted spontaneous labor within 7 days (P = .003), and gestational age at enrollment predicted spontaneous labor before 41 weeks (P = .008) and the overall spontaneous labor rate (P = .008), using logistic regression to control for potential confounders.
Conclusions: Sweeping membranes once at 38-40 weeks' gestation does not significantly increase the proportion of women who begin spontaneous labor within 7 days.
Similar articles
-
Effect of membrane sweeping at term pregnancy on duration of pregnancy and labor induction: a randomized trial.
Kashanian M, Akbarian A, Baradaran H, Samiee MM. Kashanian M, et al. Gynecol Obstet Invest. 2006;62(1):41-4. doi: 10.1159/000091842. Epub 2006 Mar 3.
 Gynecol Obstet Invest. 2006. PMID: 16534210 Clinical Trial.
Gynecol Obstet Invest. 2006. PMID: 16534210 Clinical Trial. -
The effect of membrane sweeping on prelabor rupture of membranes: a randomized controlled trial.
Hill MJ, McWilliams GD, Garcia-Sur D, Chen B, Munroe M, Hoeldtke NJ. Hill MJ, et al. Obstet Gynecol. 2008 Jun;111(6):1313-9. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0b013e31816fdcf3. Obstet Gynecol. 2008. PMID: 18515514 Clinical Trial.
-
Membrane sweeping and prevention of post-term pregnancy in low-risk pregnancies: a randomised controlled trial.
de Miranda E, van der Bom JG, Bonsel GJ, Bleker OP, Rosendaal FR. de Miranda E, et al. BJOG. 2006 Apr;113(4):402-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.2006.00870.x. Epub 2006 Feb 20.
 BJOG. 2006. PMID: 16489935 Clinical Trial.
BJOG. 2006. PMID: 16489935 Clinical Trial. -
[From the Cochrane Library: routine membrane sweeping ('stripping') for induction of labor in full-term pregnancies effective, but not always useful].
Hamerlynck JV, Middeldorp S. Hamerlynck JV, et al. Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd. 2005 Nov 5;149(45):2508-10. Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd. 2005. PMID: 16304888 Review. Dutch.
-
Amniotic membrane sweeping.
Heilman E, Sushereba E. Heilman E, et al. Semin Perinatol. 2015 Oct;39(6):466-70. doi: 10.1053/j.semperi.2015.07.010. Epub 2015 Sep 11. Semin Perinatol. 2015. PMID: 26365011 Review.
See all similar articles
Cited by
-
Membrane sweeping for induction of labour.

Finucane EM, Murphy DJ, Biesty LM, Gyte GM, Cotter AM, Ryan EM, Boulvain M, Devane D. Finucane EM, et al. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Feb 27;2(2):CD000451. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD000451.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 32103497 Free PMC article.
-
Use of labour induction and risk of cesarean delivery: a systematic review and meta-analysis.
Mishanina E, Rogozinska E, Thatthi T, Uddin-Khan R, Khan KS, Meads C. Mishanina E, et al. CMAJ. 2014 Jun 10;186(9):665-73. doi: 10.1503/cmaj.130925. Epub 2014 Apr 28. CMAJ. 2014. PMID: 24778358 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Randomized clinical trial evaluating the frequency of membrane sweeping with an unfavorable cervix at 39 weeks.
Putnam K, Magann EF, Doherty DA, Poole AT, Magann MI, Warner WB, Chauhan SP. Putnam K, et al. Int J Womens Health. 2011;3:287-94. doi: 10.2147/IJWH.S23436. Epub 2011 Aug 19. Int J Womens Health. 2011. PMID: 21892340 Free PMC article.
-
Membrane sweeping for induction of labour.
Boulvain M, Stan C, Irion O. Boulvain M, et al. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005 Jan 25;2005(1):CD000451. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD000451.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005. PMID: 15674873 Free PMC article. Updated. Review.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Full text links
Wolters Kluwer
Cite
Format: AMA APA MLA NLM
Send To
Sweeping of the membranes at 39 weeks in nulliparous women: a randomised controlled trial
Save citation to file
Format: Summary (text)PubMedPMIDAbstract (text)CSV
Add to Collections
- Create a new collection
- Add to an existing collection
Name your collection:
Name must be less than 100 characters
Choose a collection:
Unable to load your collection due to an error
Please try again
Add to My Bibliography
- My Bibliography
Unable to load your delegates due to an error
Please try again
Your saved search
Name of saved search:
Search terms:
Test search terms
Email: (change)
Which day? The first SundayThe first MondayThe first TuesdayThe first WednesdayThe first ThursdayThe first FridayThe first SaturdayThe first dayThe first weekday
Which day? SundayMondayTuesdayWednesdayThursdayFridaySaturday
Report format: SummarySummary (text)AbstractAbstract (text)PubMed
Send at most: 1 item5 items10 items20 items50 items100 items200 items
Send even when there aren't any new results
Optional text in email:
Create a file for external citation management software
Clinical Trial
. 1998 Jan;105(1):41-4.
1998 Jan;105(1):41-4.
doi: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.1998.tb09348.x.
H Cammu 1 , V Haitsma
Affiliations
Affiliation
- 1 Department of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, A.Z.V.U.B., Brussels, Belgium.
- PMID: 9442160
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.1998.tb09348.x
Clinical Trial
H Cammu et al. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1998 Jan.
. 1998 Jan;105(1):41-4.
doi: 10. 1111/j.1471-0528.1998.tb09348.x.
1111/j.1471-0528.1998.tb09348.x.
Authors
H Cammu 1 , V Haitsma
Affiliation
- 1 Department of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, A.Z.V.U.B., Brussels, Belgium.
- PMID: 9442160
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.1998.tb09348.x
Abstract
Objective: To determine whether weekly sweeping of the membranes from 39 weeks of gestation results in a reduction in the number of women reaching 41 completed weeks and subsequently in a reduction of the number of women who will need induction of labour.
Design: Randomised controlled trial.
Participants: Two hundred and seventy-eight nulliparous women, who were seen at the antenatal clinic of a university teaching hospital, were randomly allocated at 39 weeks of gestation to receive on a weekly basis either sweeping of the membranes (n = 140) or a routine pelvic examination (n = 138).
Main outcome measures: The time interval between randomisation and delivery, the incidence of prolonged pregnancy (i.e. > 41 completed weeks), and the incidence of induction of labour.
Results: In 24 women (17%) sweeping of the membranes was not possible. Fifty-three women (38%) in the sweeping group and 50 women (36%) in the control group were delivered within one week after randomisation. Women allocated to sweeping showed a trend towards having a shorter randomisation-delivery interval: 9.4 days versus 10.6 days in the controls (P = 0.087). Sweeping had no statistically significant effect on the mean duration of pregnancy (282.8 days in the sweeping group versus 283.8 days in the control group, P = 0.127). The need for induction of labour was significantly reduced in those women who underwent sweeping (11% versus 26%, P = 0.004), merely as a result of a decrease in the number of women that exceeded 41 weeks (19% versus 33%, P = 0.016).
Women allocated to sweeping showed a trend towards having a shorter randomisation-delivery interval: 9.4 days versus 10.6 days in the controls (P = 0.087). Sweeping had no statistically significant effect on the mean duration of pregnancy (282.8 days in the sweeping group versus 283.8 days in the control group, P = 0.127). The need for induction of labour was significantly reduced in those women who underwent sweeping (11% versus 26%, P = 0.004), merely as a result of a decrease in the number of women that exceeded 41 weeks (19% versus 33%, P = 0.016).
Conclusion: Sweeping of the membranes weekly from 39 weeks does not increase the number of women who will deliver within the first week but significantly decreases the number that will reach 41 weeks. Induction of labour then becomes less necessary.
Similar articles
-
Does sweeping of membranes beyond 40 weeks reduce the need for formal induction of labour?
Wong SF, Hui SK, Choi H, Ho LC.
 Wong SF, et al. BJOG. 2002 Jun;109(6):632-6. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.2002.01193.x. BJOG. 2002. PMID: 12118640 Clinical Trial.
Wong SF, et al. BJOG. 2002 Jun;109(6):632-6. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.2002.01193.x. BJOG. 2002. PMID: 12118640 Clinical Trial. -
Effect of membrane sweeping at term pregnancy on duration of pregnancy and labor induction: a randomized trial.
Kashanian M, Akbarian A, Baradaran H, Samiee MM. Kashanian M, et al. Gynecol Obstet Invest. 2006;62(1):41-4. doi: 10.1159/000091842. Epub 2006 Mar 3. Gynecol Obstet Invest. 2006. PMID: 16534210 Clinical Trial.
-
Membrane sweeping for induction of labour.
Boulvain M, Stan C, Irion O. Boulvain M, et al. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2001;(2):CD000451. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD000451. Cochrane Database Syst Rev.
 2001. PMID: 11405964 Updated. Review.
2001. PMID: 11405964 Updated. Review. -
Does sweeping of the membranes reduce the need for formal induction of labour? A randomised controlled trial.
Boulvain M, Fraser WD, Marcoux S, Fontaine JY, Bazin S, Pinault JJ, Blouin D. Boulvain M, et al. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1998 Jan;105(1):34-40. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.1998.tb09347.x. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1998. PMID: 9442159 Clinical Trial.
-
Sweeping of the membranes to prevent post-term pregnancy and to induce labour: a systematic review.
Boulvain M, Irion O, Marcoux S, Fraser W. Boulvain M, et al. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1999 May;106(5):481-5. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.1999.tb08302.x. Br J Obstet Gynaecol.
 1999. PMID: 10430199 Review.
1999. PMID: 10430199 Review.
See all similar articles
Cited by
-
Membrane sweeping for induction of labour.
Finucane EM, Murphy DJ, Biesty LM, Gyte GM, Cotter AM, Ryan EM, Boulvain M, Devane D. Finucane EM, et al. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Feb 27;2(2):CD000451. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD000451.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 32103497 Free PMC article.
-
Randomized clinical trial evaluating the frequency of membrane sweeping with an unfavorable cervix at 39 weeks.
Putnam K, Magann EF, Doherty DA, Poole AT, Magann MI, Warner WB, Chauhan SP. Putnam K, et al. Int J Womens Health. 2011;3:287-94.
 doi: 10.2147/IJWH.S23436. Epub 2011 Aug 19. Int J Womens Health. 2011. PMID: 21892340 Free PMC article.
doi: 10.2147/IJWH.S23436. Epub 2011 Aug 19. Int J Womens Health. 2011. PMID: 21892340 Free PMC article. -
Membrane sweeping for induction of labour.
Boulvain M, Stan C, Irion O. Boulvain M, et al. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005 Jan 25;2005(1):CD000451. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD000451.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005. PMID: 15674873 Free PMC article. Updated. Review.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Cite
Format: AMA APA MLA NLM
Send To
Amniotomy (rupture of the amniotic sac) | Articles by EMC doctors about diseases, diagnosis and treatment
Write to WhatsApp
July 11, 2018
Many pregnant women are afraid of amniotomy. Such fear is associated to a greater extent with a lack of knowledge about this procedure. In fact, amniotomy is a standard medical procedure that is performed in the delivery room without the presence of anesthesiologists.
Such fear is associated to a greater extent with a lack of knowledge about this procedure. In fact, amniotomy is a standard medical procedure that is performed in the delivery room without the presence of anesthesiologists.
What is an amniotomy?
In the womb, the fetus is in the amniotic sac, a membrane that is filled with a fluid called amniotic fluid. During childbirth, the amniotic sac helps open the uterus, which is necessary for the birth of the baby.
Amniotomy is an artificial opening of the amniotic sac.
How is an amniotomy performed?
Everything is done on an outpatient basis. In advance, a woman does not need to prepare for the procedure. The amniotomy is performed by an obstetrician-gynecologist, without the participation of a surgeon and an anesthesiologist. There is no pain during or after the procedure. This is due to the fact that the opened shell is devoid of pain receptors.
The doctor opens the bladder with a special disposable instrument - an amniotome. With further dilution of the membranes, amniotic fluid comes out. And in some cases, to determine the amount of remaining water, manipulation can be carried out under ultrasound control.
With further dilution of the membranes, amniotic fluid comes out. And in some cases, to determine the amount of remaining water, manipulation can be carried out under ultrasound control.
Usually, 5-10 minutes after the end of the amniotomy, the woman can move independently.
Indications for amniotomy
Although the procedure is simple, it is carried out only when indicated:
-
Weak labor activity. In this case, the procedure is performed to enhance contractions and the speedy onset of childbirth. If the uterus is well prepared for childbirth, delivery usually occurs within a few hours after the amniotomy.
-
Flat shape of the amniotic sac. With such a problem, there is a poor content of water, which leads to a delay in childbirth and the absence of contractions.
-
Very tough sheath. In this case, self-opening of the bubble is impossible. The birth of a baby in a bubble is extremely dangerous: due to lack of oxygen, the child can suffocate.
-
Postterm pregnancy. After 41 weeks of pregnancy, the child begins oxygen starvation. Therefore, as in the case of weak labor activity, the procedure is performed for the speedy onset of childbirth.
-
High water. A large amount of water stretches the uterus. This leads to complications in childbirth.
-
Rhesus conflict. This problem can lead to fetal death. To save the baby, doctors can cause an urgent birth.
-
Toxicosis. Long-lasting toxicosis, up to the 3rd trimester, leads to an increase in blood pressure in a woman, an increased protein content in the tests, and edema. These factors complicate pregnancy and threaten not only the health of the pregnant woman, but also the baby.
-
Low-lying placenta.
Contraindications for amniotomy
-
Cord presentation.
-
Incorrect presentation of the fetus.
-
Disproportionate size of the fetus to the size of the pelvis of the pregnant woman.

-
Multiple pregnancy.
-
Placental presentation.
Risks of amniotomy
Risks are practically reduced to zero. If many decades ago, cases of fetal infection were often recorded, now this is a rarity, since amniotomy is performed under sterile conditions using disposable equipment. Very rarely, bleeding can begin - in such cases, specialists decide to perform a CS.
Doctors do not perform an amniotomy if the woman is against the procedure on principle. This usually happens if the pregnant woman does not know enough about the procedure and thinks that it will entail serious consequences. The main task of the doctor in this matter is to tell in detail why in a particular situation it is very important to perform an amniotomy and why refusing it can be dangerous. Only after detailed explanations should a woman make a decision.
Since the procedure is performed manually, its results largely depend on the doctor. Therefore, you need to contact only specialized clinics, where doctors with extensive experience in amniotomy, management of complicated pregnancy and childbirth work.
Therefore, you need to contact only specialized clinics, where doctors with extensive experience in amniotomy, management of complicated pregnancy and childbirth work.
Types of amniotomy
-
Antenatal amniotomy. It is carried out to accelerate the onset of childbirth, when the period has come up, but childbirth has not begun.
-
Early amniotomy. It is usually carried out during childbirth, with a dense shell of the bladder or incomplete opening of the cervix (up to 4-5 cm).
-
Timely opening of the bladder. It is carried out during childbirth, with the opening of the cervix by 6-9see for accelerating full uterine dilation.
-
Late process. Such an amniotomy is performed in the second stage of labor if the bubble has not burst on its own and there is a possibility that the baby will be born in the shell.
Benefits of contacting EMC
-
Specialists of the EMC maternity hospital trained in the best European clinics.
-
Doctors specialize in the management of complex pregnancies and various cases of complicated childbirth.
-
The latest operating and resuscitation equipment.
-
Department of Neonatology.
-
Constant monitoring of patients by medical personnel.
Rate
Average: 3.44 (16 ratings)
Write to whatsapp
Birth History: Placenta Increta
If you are told that terminating your pregnancy is the best decision, seek a second opinion. Sometimes it helps to save a whole life - the life of an unborn baby. This was the case with our patient.
09 April 2023
All stories
Childbirth №3.
 Stimulation after caesarean in an attempt to give birth vaginally. — 6 answers
Stimulation after caesarean in an attempt to give birth vaginally. — 6 answers December 2019.
it took me 1.5 years to voice how everything was. I really wanted to give birth naturally, but due to the risk of developing HELP syndrome, it was decided to give stimulation at 37+2 weeks. I wrote in between contractions))) and the second part was 6 hours after the birth. I will publish it in my diary, otherwise the story will be very long.
Progress notes:
18:00 My husband called the hospital and was told to come at 19:30. They came to the junction to the generic, as far as I knew the information, they had to check the opening. If so, let him go home. If not, put a balloon (Folley catheter) and put it in the hospital under supervision for the night. But apparently I came across the liveliest of the medical staff on duty😅 she checked and immediately shoved the catheter into me. He says 2 cm opening, but this is not enough. Let's be sure 😂Last year, studies were conducted that proved the effectiveness of stimulation at 37 weeks with the risks of preeclampsia and AD. Well, okay... where can I go))) Inspection and installation of the device is painless. Certainly not pleasant, but no more.
Well, okay... where can I go))) Inspection and installation of the device is painless. Certainly not pleasant, but no more.
20:15 I'm under CTG. I hope for contractions, but something is dull like in a tank... you need to ask about the wireless CTG and go wag your back, maybe it will help😂 Complained that I forgot to have dinner, I was worried. Eiii... I will be fed deliciously!!! Hooray!!!
20:34 my husband brought me a "family suitcase" since I'm staying, I'll need my clothes 😅 2
1:00 the first and hopefully the last unsuccessful attempt to install an infusion (catheter) in the arm. Why don't they believe me that my veins escape when a needle pierces the skin ...
The doctor came and quickly inserted the catheter. I am happy)) bombarded her with questions. We joked and laughed. Just in case, I asked for a pill to sleep well.
They fed me:
21:30 sent my husband home, let him rest and sleep. Tomorrow he will arrive in the morning) 22:00 changing the bed😂 I'm lucky. I came across the one where the butt is high and it didn’t work out in any way. They brought a new, fresh one)) you can drink your pill and go to sleep.
I came across the one where the butt is high and it didn’t work out in any way. They brought a new, fresh one)) you can drink your pill and go to sleep.
3:30 while walking or standing, something else was catching. But I wanted to sleep more than play the hero and walk around these sweet sensations))) so everything quickly faded away in the prone position. The mephisipam pill was strange ... I dreamed of the nurse who gave it, the hospital, some adventures and .. Hello, insomnia. I'm rested and ready to fight. But nothing happens 😂 my wrist hurts where the catheter is. Also with my right hand, I’ll type with my nose😅
6:35 so I didn’t fall asleep anymore ... Chatting with the girls in the chat, spinning from side to side, drinking and peeing. At some point, a little mucus came out with blood. "Cork"!!! I thought I was delighted. As a result, the nurse came and kindly offered me to take a shower, they say, or get ready for an examination and we’ll start doing something with you😄
7:15 A nice man doctor came (I didn’t make up my eyelashes for nothing) explained everything in the 3rd circle and checked how things were with the balcony and the opening. Things are wonderful, the balloon fell out and the opening is good, more than 4 cm. But! The son’s head is very high, and pricking the bubble is risky for the prolapse of the umbilical cord. We decided to wait for the day shift, then the issue will be resolved. Options 2 or ignite the membranes and push the child externally. Or make contractions with medicine and he will go down by himself. But in any case, there is a risk. The risk of what I would like ... After 40 minutes, the midwife and two nurses came. Without going into details: nothing happened again😒 As soon as the midwife touched the head, the son simply moved it to another corner. Very high and mobile. This can be dangerous prolapse of the umbilical cord. What to do? Try to lower the son into the pelvis with his head so that he does not move. Most likely, they will administer a medicine for regular contractions, but with my history of CS, this is also fraught ... Although, no matter how you approach the risk, there is and will be in any case.
Things are wonderful, the balloon fell out and the opening is good, more than 4 cm. But! The son’s head is very high, and pricking the bubble is risky for the prolapse of the umbilical cord. We decided to wait for the day shift, then the issue will be resolved. Options 2 or ignite the membranes and push the child externally. Or make contractions with medicine and he will go down by himself. But in any case, there is a risk. The risk of what I would like ... After 40 minutes, the midwife and two nurses came. Without going into details: nothing happened again😒 As soon as the midwife touched the head, the son simply moved it to another corner. Very high and mobile. This can be dangerous prolapse of the umbilical cord. What to do? Try to lower the son into the pelvis with his head so that he does not move. Most likely, they will administer a medicine for regular contractions, but with my history of CS, this is also fraught ... Although, no matter how you approach the risk, there is and will be in any case.