When does uterus move up
Your Body throughout Pregnancy
Your Body Before Pregnancy
Next Image
Your Body Before Pregnancy
Before pregnancy, most of the space in your abdomen is taken up by the large and small intestines. There is no real separation between the areas of your pelvis and abdomen.
In the picture here, you can see that the vagina is behind the bladder (sac that collects urine) and urethra (tube for moving urine out of bladder and body). In its normal position, your uterus is above and behind the bladder, with the cervix protruding into the vagina. The pelvic colon, rectum and anal canal are behind the vagina and uterus.
Previous | Next
Your Body at 6-7 Weeks of Pregnancy
Next Image
Your Body at 6-7 Weeks of Pregnancy
When you are between 6 and 7 weeks pregnant, you may be experiencing the early signs of pregnancy: your period has stopped and you may have nausea, breast tenderness and swelling, frequent urination and fatigue.
At this point, your uterus has begun to grow and become more egg-shaped. The pressure of the growing uterus on the bladder causes frequent urge to urinate.
In this image, you can see the beginnings of the placenta in the uterus. The embryo is about 1/4 inch to 1/2 inch long and weighs 1/1,000th of an ounce.
The embryo’s head is large in proportion to the rest of the body. The internal organs are forming and the heart has been beating since the end of the 4th week.
The embryo is floating in the amniotic sac. Buds for the arms and legs emerge in the 5th week and, by the 7th week, buds for fingers and toes also appear. The umbilical cord is lengthening and will continue to grow, allowing the fetus freedom to move. The 7th week represents a milestone in development: the embryo is now considered a fetus.
Previous | Next
Your Body at 12 Weeks of Pregnancy
Next Image
Your Body at 12 Weeks of Pregnancy
At the 12th week of pregnancy, the placenta is much larger.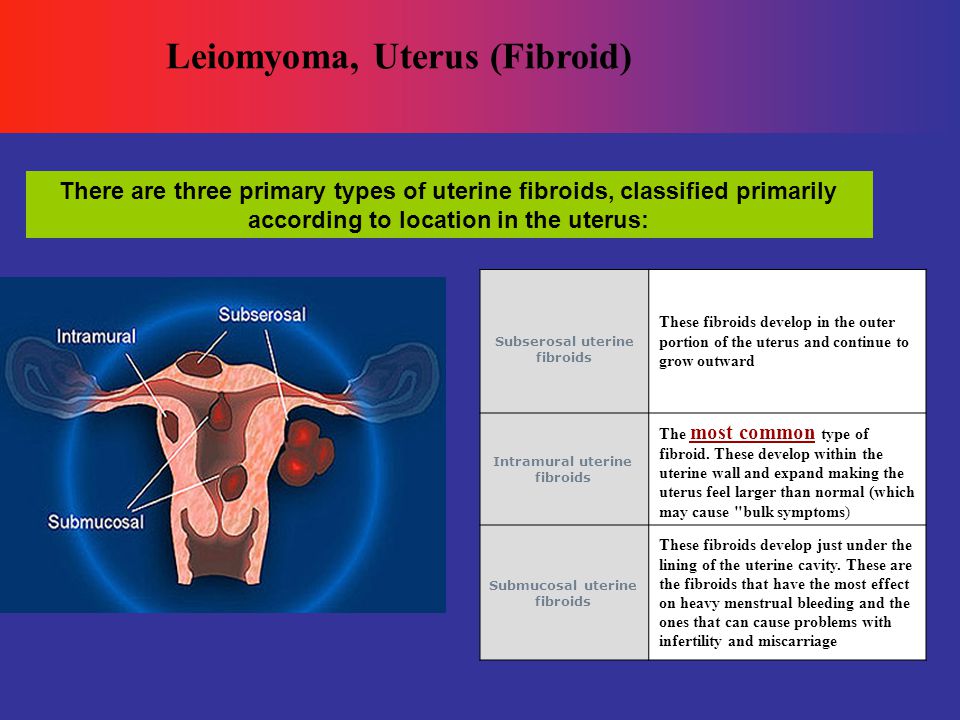 It now produces the hormones needed to sustain the pregnancy. Your uterus is the size of a grapefruit and completely fills the pelvis. It rises up into the area of the abdomen, as shown in the image. The fundus, the upper end of the uterus, is just above the top of the symphysis where the pubic bones join together. This upward growth of the uterus takes pressure off the bladder and decreases the need for frequent urination. The mucus plug, a barrier to protect the growing fetus, fills your cervical canal.
It now produces the hormones needed to sustain the pregnancy. Your uterus is the size of a grapefruit and completely fills the pelvis. It rises up into the area of the abdomen, as shown in the image. The fundus, the upper end of the uterus, is just above the top of the symphysis where the pubic bones join together. This upward growth of the uterus takes pressure off the bladder and decreases the need for frequent urination. The mucus plug, a barrier to protect the growing fetus, fills your cervical canal.
The fetus is now about 3 inches long and weighs about 1 ounce. By this week, the fetus has fingernails and toenails and can open and close the fingers. The fetus will start to move, but you will not feel it yet.
Previous | Next
Your Body at 20 Weeks of Pregnancy
Next Image
Your Body at 20 Weeks of Pregnancy
By the 20th week of pregnancy, your uterus can be felt at the level of your belly button (umbilicus).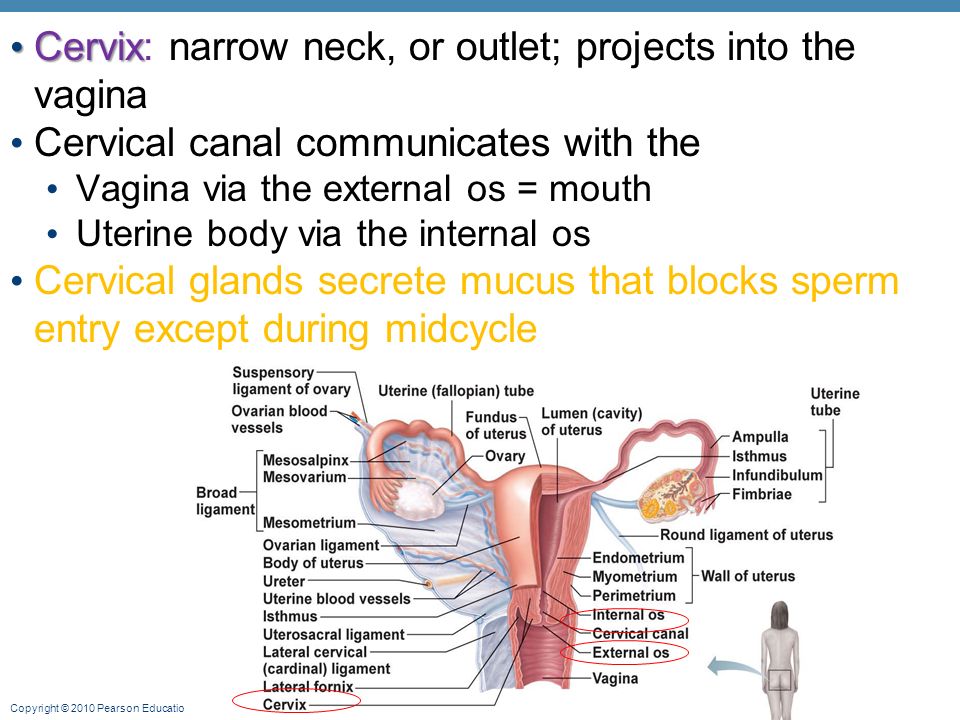 The pelvic colon and small intestines are crowded upward and backward. The ascending and descending colon maintain their usual positions.
The pelvic colon and small intestines are crowded upward and backward. The ascending and descending colon maintain their usual positions.
At this point, your uterus is especially enlarged where the placenta attaches to it (usually on the front or back wall). This gives the uterus an uneven bulge. The wall of the uterus, which lengthens and thickens early in pregnancy, stretches as the fetus grows, and becomes thinner now – just 3 to 5 millimeters thick. Your bladder moves up but not as much as your uterus, which straightens as it moves up.
As your uterus moves up, it rests against the lower portion of the front of your abdominal wall, causing it to bulge forward noticeably by your 20th week. The size of the bulge depends on how strong your abdominal muscles are. If they are firm, the uterus may be pressed against the spinal column, and there will be no noticeable bulge; if they are weak, the pressure of the uterus against the inside wall makes a sizeable bulge.
At this point, you should be able to feel light movements of the fetus. This is called “quickening.” You may recognize this earlier if you have been pregnant before. The fetus sleeps and wakes at regular intervals, is more active, is about 9 inches long and weighs between a half-pound and a pound.
This is called “quickening.” You may recognize this earlier if you have been pregnant before. The fetus sleeps and wakes at regular intervals, is more active, is about 9 inches long and weighs between a half-pound and a pound.
Previous | Next
Next Image
At this point in pregnancy, the top of your uterus is about one-third of the distance between the bellybutton and the xiphoid cartilage at the lower end of your breastbone. Constipation is common because your uterus is pressing on your lower colon and hormones slow down your body’s excretion process. Between the growth of your uterus and general weight gain, you may be feeling fatigued. Some women also experience heartburn as your uterus presses against your stomach.
Your breasts are also changing to get ready for breastfeeding. First colostrum and then milk are produced by the grape-like clusters of tiny sacs (alveoli) deep within the breast tissue. Clusters of alveoli form lobules, which come together to form 15 to 20 lobes. Each lobe connects to a lactiferous duct for conveying milk. As the ducts extend toward the nipple and areola (darker area around the nipple), they widen into the lactiferous sinuses. These sinuses (or milk pools) release the milk through 15 to 20 tiny nipple openings in each breast when the baby nurses.
At week 28, the fetus is about 16 inches long and weighs two to three pounds. The skin is wrinkled but will become less so as more fat builds up under the skin in the next few weeks. Fine, downy hair called lanugo, and a waxy white protective substance covering the skin called vernix, are on the fetus’ body. Its eyes are open, and eyebrows and eyelashes were formed in the fourth month. The fetus sucks its thumb and its taste buds have developed. It kicks, stretches and moves frequently in your uterus—you’ll feel it moving around and others might even be able to see these movements!
It kicks, stretches and moves frequently in your uterus—you’ll feel it moving around and others might even be able to see these movements!
Fetal organs and systems are quite well developed by the 28th week of pregnancy, but the final two months of gestation are important for further maturation of all body systems and organs.
Previous | Next
Your Body at 36 Weeks of Pregnancy
Next Image
Your Body at 36 Weeks of Pregnancy
By the end of the 36th week of pregnancy, your enlarged uterus almost fills the space within your abdomen. The fetus is inside the membrane sac within the uterus and high within the abdomen. The muscles of your abdomen support much of its weight.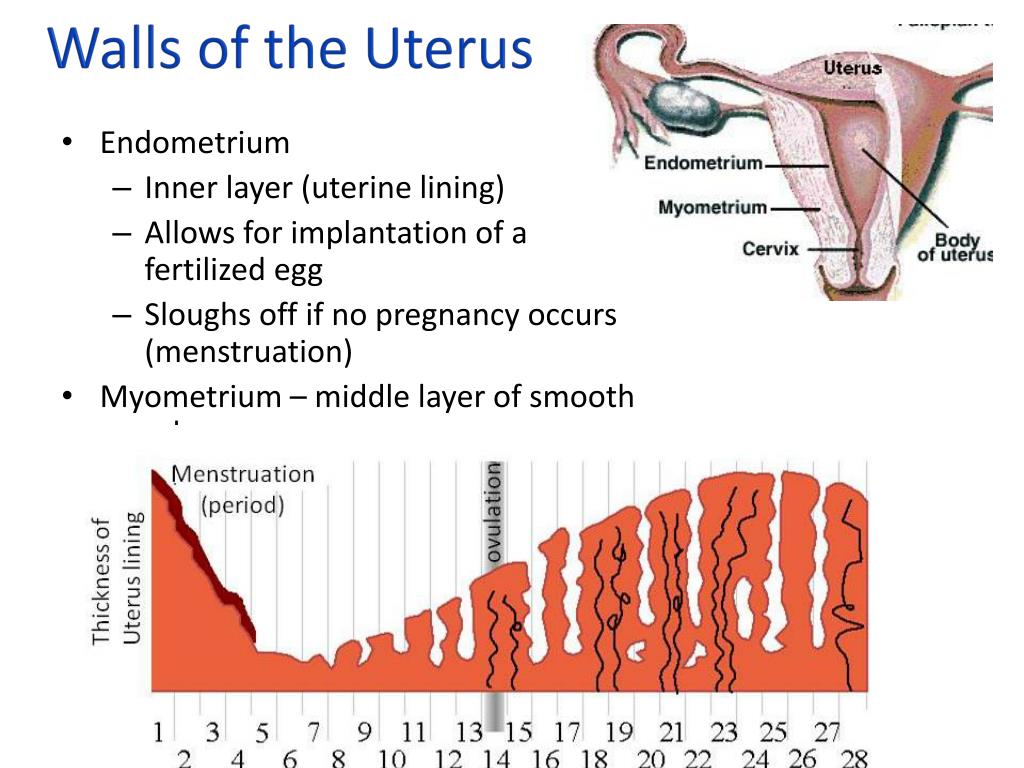
During this week, the top of the uterus is at the tip of the xiphoid cartilage at the lower end of the breastbone, which is pushed forward.
The change in the position of the heart and the upward pressure of the diaphragm may make it hard to breathe at this point. The crowding of your stomach and intestines may contribute to discomfort after eating.
Your cervix is long, thick and filled with the mucous plug. By the 36th week, your vagina and urethra are elongated and all the tissues in the perineum (area between vaginal and anal openings) are enlarged. The swollen perineum projects outward in the last weeks of pregnancy and readily expands during labor.
The brain of the fetus is growing rapidly, but bones in the skull are soft so that he or she will fit through your vagina at birth. The lungs are still forming. You will likely feel the fetus kicking and may be aware of rhythmic movements, which could be hiccups or thumb sucking. Another possible sensation, sudden movement, may be a startle response.
Previous | Next
Your Body at 40 Weeks of Pregnancy (Internal)
Next Image
Your Body at 40 Weeks of Pregnancy (Internal)
At full term, or 40 weeks of pregnancy, the fetus’ head has generally lowered into your pelvis, where it takes up most of the space. This is called “lightening.” In first pregnancies, this may happen a few weeks before labor. In repeat pregnancies, this can happen at the time of labor. The canal of the broad, enlarged cervix is still filled with the plug of mucous. If this is your first pregnancy, the small opening at the bottom of your cervix is usually not dilated, whereas if you have given birth before, it will often be open as wide as two fingers some time before labor begins.
At this point, you may be experiencing frequent urination, increased constipation, edema (water retention) and aching legs or vulva. Varicose veins in the vulva, rectum and legs are also possible. This is because of the position of the uterus, the pressure of the baby's head and a loss of muscle tone as the hormone relaxin loosens your tissues in preparation for birth. Other changes at this time include increased development of blood vessels and increased amount of blood.
Previous | Next
Your Body at 40 Weeks of Pregnancy (External)
Next Image
Your Body at 40 Weeks of Pregnancy (External)
You can see that the round ligament is long and enlarged. It is also farther forward because of the twisting of the uterus. The enlarged uterosacral ligament is shown stretched taut by the enlarged uterus. Backaches in late pregnancy may be due to the stress of the weight of your uterus on the ligaments that connect it to your spine.
It is also farther forward because of the twisting of the uterus. The enlarged uterosacral ligament is shown stretched taut by the enlarged uterus. Backaches in late pregnancy may be due to the stress of the weight of your uterus on the ligaments that connect it to your spine.
Because your uterus dropped a bit, you may be able to breathe and eat more comfortably near the end of your pregnancy.
At this time, the lungs of the fetus are likely fully mature and ready to begin breathing. The fetus gains about a half pound every week at the end of pregnancy, for a birth weight of roughly 7 pounds, and is growing longer for a birth length of about 18 to 21 inches.
Labor starting on its own around week 40 is a sign that your body is ready to give birth and your baby is ready to be born.
Previous | Next
Is my baby growing? — Maternity-Matters
Well, here is something I never thought I’d be suggesting: DIY checking of the growth of your baby!
This is one of the key assessments midwives and doctors make during pregnancy and it is an important one
Because we are working on keeping you safe (which also keeps baby safe) and preventing Covid-19 for you and for everyone, many sites have switched to providing antenatal care by phone or video/FaceTime. This means we don’t have as many visits where we will be placing our hands on your tummy to see how baby is growing
This means we don’t have as many visits where we will be placing our hands on your tummy to see how baby is growing
So, here is an idea I have
It’s just an idea
I don’t know if it will work
I think it will help and I don’t think it will harm
I don’t want you to get stressed about this
Check with your midwife and/or doctor to see what they recommend for you — they may have a much better idea!
Step 1: Understanding how the womb (uterus) grows during pregnancy
For the first 12 weeks, it is in the pelvis, behind your pubic bone, competing for space with your bladder
After 12 weeks, as it is growing, it moves out of the pelvis and into the abdomen (the tummy)
By 20 weeks, the womb should have reached your belly button
By 38 weeks in the first pregnancy, it has reached the top of the tummy and is right up under the ribs
By 40 weeks, it is usually dropping a bit and somewhere in this time the pressure on your bladder is increasing again
Step 2: Finding the fundus (aka, the top of the womb)
The best time to start feeling is about 20 weeks
Start with the flat of your hand on your tummy, above the belly button
Move your fingers up and down, feeling for an edge
You are feeling for a firmness/a change in how soft or hard your tummy feels and it should change around about the belly button once you are 20 weeks pregnant
This is when I would like you to try to find it
You can feel for it yourself or get your partner/a friend to help you
It took me lots of practice to get good at this
Don’t worry if you don’t get it straight away
Sometimes it is not so obvious that baby is growing when you feel the tummy, but it is really obvious when you take a side-on photograph
Step 3: Mark with a pen
Once you have found the place where it feels firmer, take a pen and mark it off
Step 4: Take a photograph and send it to to your midwife/doctor before each telehealth visit
If you can’t find the spot where it feels firmer, don’t worry.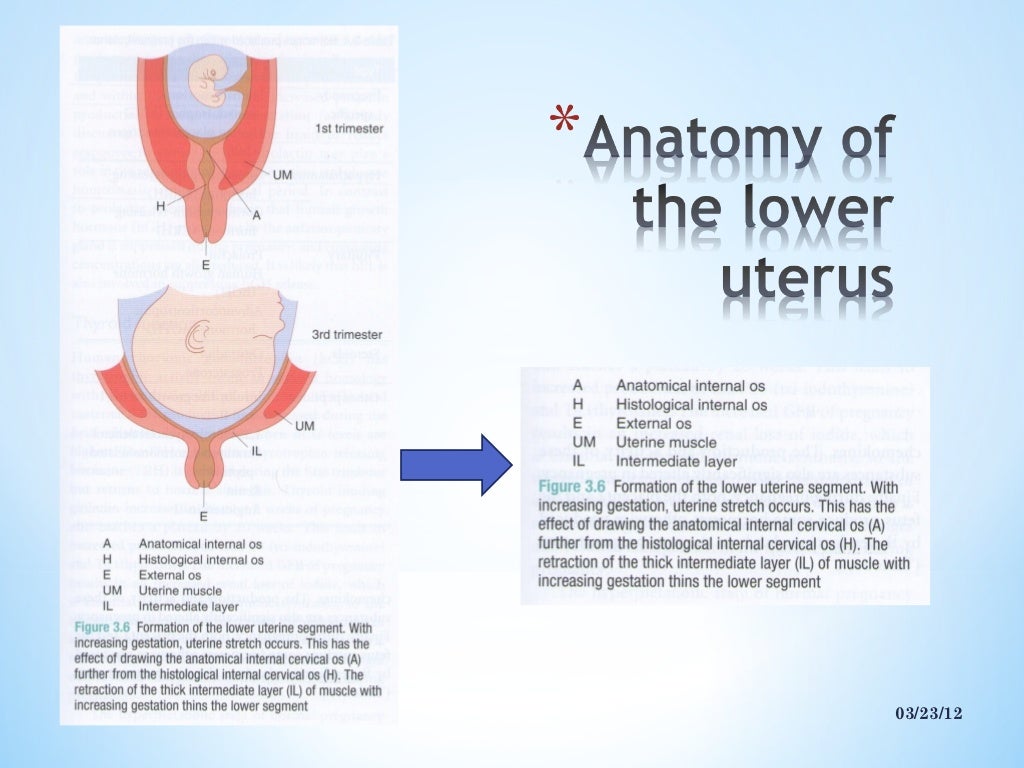 Let us know if your clothes are getting tighter, you look bigger and/or take a side-on selfie (or have someone take your photo side on) and send that through instead
Let us know if your clothes are getting tighter, you look bigger and/or take a side-on selfie (or have someone take your photo side on) and send that through instead
Following on from the first video, here we show a self examination 4 weeks later.
COVID19, First trimester, Second trimester, Third trimesterWendy Burtonabdominal palpation, is my baby growing, how to check for baby's growth, antenatal care covid 19
0 LikesHow the belly grows - articles from the specialists of the clinic "Mother and Child"
Bagriy Alexander Tarasovich
Anesthesiologist-resuscitator
Clinical hospital "AVICENNA" GC "Mother and Child"
Let's say right away that how the belly looks and grows during pregnancy depends on many reasons: the physique of a woman, the structure of the pelvis, the state of the muscles, height uterus and baby, the amount of amniotic fluid. Therefore, for some, the belly grows faster, for some it is slower, for some mothers it is large, for others it can be almost invisible. But still, there are some general patterns of growth and size of the abdomen during pregnancy.
Therefore, for some, the belly grows faster, for some it is slower, for some mothers it is large, for others it can be almost invisible. But still, there are some general patterns of growth and size of the abdomen during pregnancy.
Growth rate
1st trimester
As a rule, in the early stages of pregnancy, the belly does not increase in size or increases very slightly. This is due to the fact that the uterus is still very small and takes up little space in the pelvis. So, for example, by the end of 4th week the uterus reaches only the size of a chicken egg, by the 8th week increases to the size of a goose, but most importantly, at this time it still does not reach the pubic articulation (located in the lower abdomen ). That is why in the early stages no increase in the abdomen is visible. And only after 12th week (end of the first trimester of pregnancy) the fundus of the uterus begins to rise above the womb.
II trimester
At this time, the child is rapidly gaining height and weight, and the uterus is also growing rapidly. That is why, at a period of 12-16 weeks, an attentive mother will see that the stomach has already become noticeable. True, others will pay attention to the woman’s new position at about 20-q weeks, especially if she wears tight-fitting things.
III trimester
By the beginning of the third trimester, no one doubts pregnancy. The abdomen is clearly visible even if the woman is wearing loose clothing.
Sharp, round, various
Approximately from the second trimester of pregnancy, during each examination, the obstetrician-gynecologist determines the height of the uterine fundus and measures the circumference of the abdomen at the level of the navel. Why does the doctor so carefully monitor the increase in mother's tummy? The fact is that this is the easiest way to control the growth and development of the unborn baby.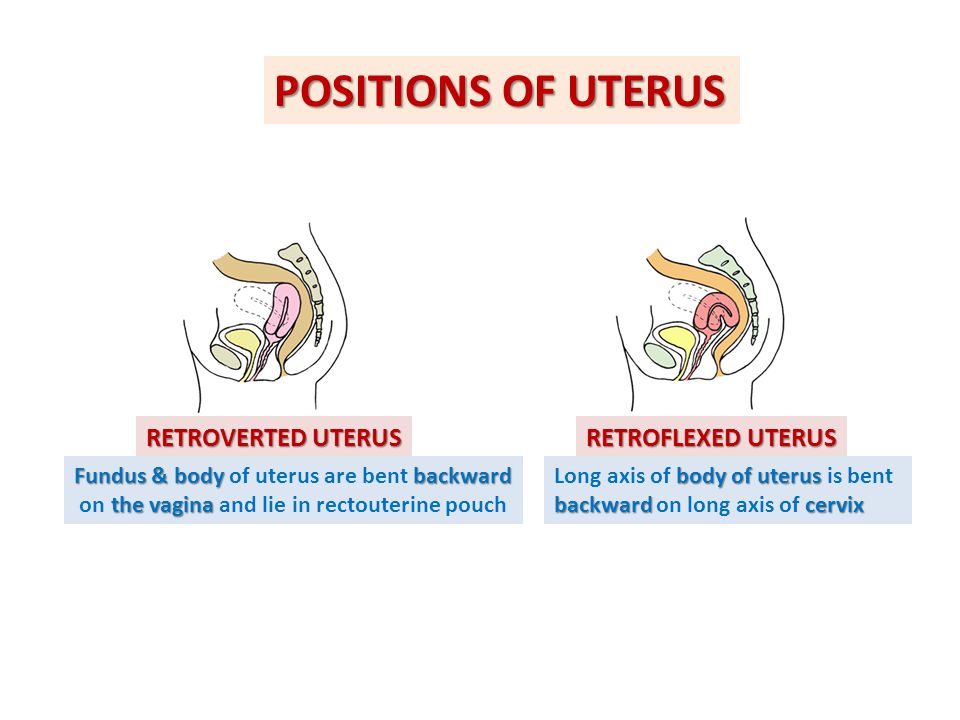
One of the formulas for estimating fetal weight by fundal height (FHH): the shape of the abdomen often tried to determine the sex of the child. It was believed that a round belly portends a girl, and an elongated, oblong, “sharp” one portends a boy. However, these predictions did not always come true, since the shape and size of the abdomen do not depend at all on the sex of the child.
- In large, tall women, the belly may be small and not very noticeable until advanced pregnancy, and in thin, petite women (especially with a narrow pelvis or large baby), the belly seems very large.
- Significant influence on the shape of the abdomen has a state of muscle tone of the anterior abdominal wall and uterus. During the first pregnancy and good muscle tone, the abdomen may look more "tight" than in subsequent pregnancies. In addition, with repeated pregnancies as a result of reduced muscle tone of the anterior abdominal wall, the child does not take the final position until the last month of pregnancy.
 Because of this, the shape of the abdomen can also be "stretched".
Because of this, the shape of the abdomen can also be "stretched". - If a woman is expecting twins, her belly will be larger than with a single pregnancy.
- And often the belly can be large simply because a woman ceases to limit herself in nutrition, eats "for two."
- If the baby grows quickly or is large, then the mother's belly can grow faster and be larger.
- Babies are located in the uterus in different ways. With some types of presentation, the stomach will be less noticeable, with others it will begin to grow earlier and will appear larger.
Feeling the belly
The belly of the expectant mother changes not only externally. From the 20th week of pregnancy, the mother begins to feel movements of the baby . At first, they look like light flutters, over time, the movements become more intense, because by the end of pregnancy, the mass and size of the child increase, and now it is not as spacious in the uterus as before. The number of movements gradually decreases, but their strength grows.
The number of movements gradually decreases, but their strength grows.
The movements of the crumbs, especially intense ones, can cause unpleasant sensations in a woman, especially in the right or left hypochondrium .
This is explained by the fact that during cephalic presentation (the baby is located in the uterus head down), the blows of the baby's legs are projected into the region of the mother's internal organs: the liver, stomach, intestines and spleen. Such sensations and even pains are natural and do not require treatment.
And sometimes pains appear in the lateral sections of the abdomen.
They occur due to the fact that during pregnancy the ligaments that support the uterus and ovaries are stretched.
In addition, changes occur in the fallopian tubes (they thicken, blood circulation increases in them), in the ovaries (they increase slightly in size, cyclic processes stop in them, and the position of the ovaries changes due to an increase in the size of the uterus). Slight pain in the lower abdomen may occur several times during the day, but, as a rule, they quickly disappear if the woman takes a position that is comfortable for her. Sometimes periodic discomfort in the lower lateral parts of the abdomen appear with constipation, which is also common in pregnant women: during pregnancy, hormones are produced that relax the uterus, they have a similar effect on the intestines: its peristalsis is disturbed, resulting in constipation.
Slight pain in the lower abdomen may occur several times during the day, but, as a rule, they quickly disappear if the woman takes a position that is comfortable for her. Sometimes periodic discomfort in the lower lateral parts of the abdomen appear with constipation, which is also common in pregnant women: during pregnancy, hormones are produced that relax the uterus, they have a similar effect on the intestines: its peristalsis is disturbed, resulting in constipation.
The belly can be large or small, bulging forward or as if swollen, low or high - everything will depend on the individual characteristics of the pregnancy.
How the belly grows and looks during pregnancy depends on many factors: the physique of the woman, the structure of the pelvis, the condition of the muscles, the growth of the uterus and the baby, the amount of amniotic fluid.
Most often, the belly begins to grow after the 12th week of pregnancy, and others will be able to notice the woman's interesting position only from the 20th week. However, everything is strictly individual, there is absolutely no exact definition of the timing of the appearance of the abdomen, it is simply impossible to predict.
However, everything is strictly individual, there is absolutely no exact definition of the timing of the appearance of the abdomen, it is simply impossible to predict.
Don't be upset if the shape or size of your belly does not match the average, because everyone is different. Focus on your constitution, the work of your body and the development of the baby.
REFERENCE
At 4 weeks, the uterus reaches the size of a hen's egg.
Goose egg at 8 weeks.
At 12 weeks, the uterus reaches the upper edge of the pubic bone. The belly is not visible yet.
At 16 weeks, the abdomen is rounded, the uterus is in the middle of the distance between the pubis and the navel.
At 20 weeks, the abdomen is visible to others, the fundus of the uterus is 4 cm below the navel.
At 24 weeks, the fundus of the uterus is at the level of the navel.
At 28 weeks, the uterus is already above the navel.
At 32 weeks, the navel begins to smooth out. Abdominal circumference - 80-85 cm.
Abdominal circumference - 80-85 cm.
At 40 weeks, the navel protrudes noticeably. Abdominal circumference 96-98 cm
Make an appointment
to the doctor - Bagriy Alexander Tarasovich
Clinical Hospital "AVICENNA" Group of Companies "Mother and Child"
Anesthesiology and resuscitation
By clicking on the send button, I consent to the processing of personal data
Attention! Prices for services in different clinics may vary. To clarify the current cost, select the clinic
The administration of the clinic takes all measures to update the prices for programs in a timely manner, however, in order to avoid possible misunderstandings, we recommend that you check the cost of services by phone / with the managers of the clinic
Clinical Hospital "AVICENNA" GK "Mother and Child" Novosibirsk Center for Reproductive Medicine
All directionsGynecological proceduresSpecialist consultations (adults)Specialist consultations (children)Laboratory of molecular geneticsGeneral clinical examinationsProcedural roomTherapeutic examinationsUltrasound examinations of adults
01.
Gynecological procedures
02.
Consultations of specialists (adults)
03.
Consultations of specialists (children's)
04.
Laboratory of molecular genetics
05.
General studies
06. 9000
Therapeutic research
08.
Adult ultrasound
Nothing found
The administration of the clinic takes all measures to timely update the price list posted on the website, however, in order to avoid possible misunderstandings, we advise you to clarify the cost of services and the timing of the tests by calling
How does the belly actually grow week by week during pregnancy
The growth of the abdomen in pregnant women directly depends on the rate of uterine enlargement, the rate of which, in turn, is influenced by several factors. This is the number of fetuses, the volume of amniotic fluid, as well as the weight of the children themselves and the placenta. How the belly grows during pregnancy by weeks, what is the difference in size in obese and thin women, primiparous and multiparous, we will write in this article.
How the belly grows during pregnancy by weeks, what is the difference in size in obese and thin women, primiparous and multiparous, we will write in this article.
When the belly appears during pregnancy
It is impossible to predict exactly when it will begin to grow, but in the early stages, the waist circumference practically does not change. However, each new gram of the embryo stretches the uterus, as a result, both it and the tummy increase.
After the test showed 2 strips, the volume of the uterus does not exceed 5 ml with a mass of 50-60 g. But at about the 5th week of pregnancy, it begins to grow, and a gradual but systematic development of new muscle fibers occurs. After all, the uterus will have to stretch almost 500 times in relation to its original size.
At 9 weeks gestation, the uterus becomes the size of a goose egg. As long as it fits within the boundaries of the small pelvis, the stomach does not grow. Further, the uterus grows even more and rises above the level of the small pelvis, heading into the abdominal cavity.
At this time, the waist also begins to slowly expand, and after 14-15 weeks, you can measure the height of the fundus of the uterine uterus. It is its wide part - the bottom - that rises into the abdominal cavity and determines the circumference of the abdomen during pregnancy by weeks.
After 16 weeks, the abdomen increases significantly and becomes noticeable in most women. The growth rate of the tummy by weeks depends on the physique, dimensions of the small pelvis, the number and weight of the fetuses.
Attention! The circumference of the abdomen (CO) of a pregnant woman is a purely individual indicator, since initially the waist circumference of each woman is different. The height of the uterine fundus more accurately reflects the size of the fetus by week of pregnancy, so the doctor measures both parameters.
How the belly grows by week of pregnancy
| Pregnancy period, weeks | WDM, cm | coolant, see | Peculiarities |
| 12 | 2-6 | The uterus reaches the upper border of the pubic bone, the abdomen is not yet visible at this time | |
| 16 | 10-18 | The anterior abdominal wall is rounded, the uterus is located at the midpoint between the pubis and the navel | |
| 20 | 18-24 | 70-75 | Pregnancy is already noticeable to others, the bottom of the uterus is 4 cm below the navel |
| 22 | 20-26 | 72-78 | |
| 24 | 22-27 | 75-80 | The fundus of the uterus reaches the navel |
| 26 | 24-28 | 77-82 | |
| 28 | 26-32 | 80-85 | The uterus rises above the navel |
| thirty | 28-33 | 82-87 | |
| 32 | 30-33 | 85-90 | The navel is flattened |
| 34 | 32-35 | 87-92 | |
| 36 | 33-38 | 90-95 | |
| 38 | 36-40 | 92-98 | |
| 40 | 34-38 | 95-100 | The navel protrudes |
How the belly grows during 1, 2, 3 pregnancies by months
During the first pregnancy, the abdomen increases most slowly, due to the peculiarities of the stretching of the musculoskeletal apparatus and the divergence of the bones. In nulliparous women, he begins to act only at 23-24 weeks.
In nulliparous women, he begins to act only at 23-24 weeks.
If the pregnancy is repeated, the "growth" at the waist level appears already at 12-20 weeks, although most women notice it after 15-16. However, in some women, the belly during pregnancy is rounded as early as 4 months, while in others it is not visible until almost the very birth.
This is due to the different elasticity of the anterior abdominal wall. In those who give birth not for the first time, it is more stretched, therefore the stomach appears earlier than in primiparas. After the birth of 2 babies, the muscles and ligaments weaken significantly, therefore, during the third pregnancy, the stomach increases even faster by weeks.
The belly grows very quickly during pregnancy with twins: expectant mothers look pregnant already at 14-15 weeks. From this time on, the rapid growth of babies begins, the sizes of which will increasingly differ from a singleton pregnancy.
Waist circumference is mainly of interest to a woman, and for a doctor, an important indicator is the height of the uterine fundus. It is she who shows how the fetus develops by weeks, and whether there are any prerequisites for high or low water. Our doctors at a remote consultation will answer all your questions and give the necessary recommendations.
It is she who shows how the fetus develops by weeks, and whether there are any prerequisites for high or low water. Our doctors at a remote consultation will answer all your questions and give the necessary recommendations.
Fetal growth by week
Fetal growth by week of pregnancy can be seen in the following table.
| Term | Embryo size by week of pregnancy | |
| Length, mm | Weight, g | |
| 1-3 | The stage of transformation of the zygote into a blastocyst | |
| 4 | The blastocyst transforms into an embryo less than 1 mm long | 0.5 |
| 5 | 1.5 | Up to 1 |
| 6 | 3. | 1.5 |
| 7 | 5-7 | 1.5 |
| 8 | 25 | |
| 9 | 55 | 5 |
| 10 | 60-70 | 10 |
| eleven | 80 | 15 |
| 12 | 90-100 | 20 |
| 13 | 110 | thirty |
| 14 | 120-140 | 50 |
| 15 | 160 | 100 |
| 16 | 170 | 130 |
| 17 | 190-200 | 160 |
| 18 | 220 | 220 |
| 19 | 300 | 240 |
| 20 | 260 | 350 |
| 21 | 280 | 400 |
| 22 | 300 | 500 |
| 23 | 300-305 | 570 |
| 24 | 310 | 600 |
| 25 | 340 | 750 |
| 26 | 350 | 830 |
| 3rd trimester | ||
| 27 | 365 | 1000 |
| 28 | 375 | 1300 |
| 29 | 380 | 1500 |
| thirty | 410 | 1600 |
| 31 | 415 | 1850 |
| 32 | 430 | 1700-2000 |
| 33 | 445 | 2000 |
| 34 | 450 | 2200-2500 |
| 35 | 460 | 2400-2900 |
| 36 | 460-480 | 2700-3000 |
| 37 | 490-520 | 3100 |
| 38 | 500-520 | 3300-3600 |
| 39 | 530 and more | 2900-4000 |
| 40 | All organs are formed, growth is complete, cartilage and bones are hardened. | |
The time when the stomach begins to protrude forward depends not only on the size of the uterus by week of pregnancy. It matters which side the placenta is attached to: if it is located at the back wall, the stomach enlarges later, since the uterus with the baby is quite comfortably placed among the internal organs.
Attached to the anterior wall of the uterus, the placenta provokes an earlier increase in the waist. In both cases, the uterus grows at the same rate, but with an anterior location, it puts more pressure on the muscles of the peritoneum and stretches them.
Case study:
A 25-year-old pregnant woman came to the maternity hospital in the direction of a gynecologist from a antenatal clinic. In the emergency room, the patient was asked why the abdomen was not visible if the period was already long. The reason is a slight deficit in body weight before pregnancy, so the “interesting position” is not particularly noticeable. The birth was successful, a girl was born in 3650.
The reason is a slight deficit in body weight before pregnancy, so the “interesting position” is not particularly noticeable. The birth was successful, a girl was born in 3650.
FAQ
Is it true that in overweight women, pregnancy becomes noticeable later, compared with thin and slender women?
+
Yes, in women who are prone to fullness, the figure often changes only in the last months. In slender women, changes become apparent much earlier.
I heard that with a narrow pelvis, the stomach visually seems larger. Why?
+
Because the baby's head is raised too high. This is a variant of the norm, and the size of the child does not matter.
What if the belly is too big, and its size exceeds the norm?
+
Inflated figures may indicate polyhydramnios or a large fetus. However, rather large deviations are allowed, in one direction or another, therefore, without additional examination, they are not particularly informative.
Expert opinion
The belly during pregnancy grows week by week for everyone at different rates. Most often, the state of a woman “in position” becomes noticeable only after the 20th week, but the pregnant woman herself can see that the picture has changed around the 12th week.
But everything is very individual, because the size of the increase depends on many factors, and there are no absolutely exact guidelines, just as there are no strictly defined terms for increasing the uterus. If your dimensions "do not pass" according to the average norms, this is not yet an indicator of pathology. The main thing is the normal well-being and health of the unborn baby.
We publish only verified information
Article author
Menshikova Maria Viktorovna obstetrician-gynecologist
Experience 38 years
Consultations 1816
Art.
 5-4
5-4  Only the cranial bones remain mobile, which is required to pass through the birth canal without damage.
Only the cranial bones remain mobile, which is required to pass through the birth canal without damage.