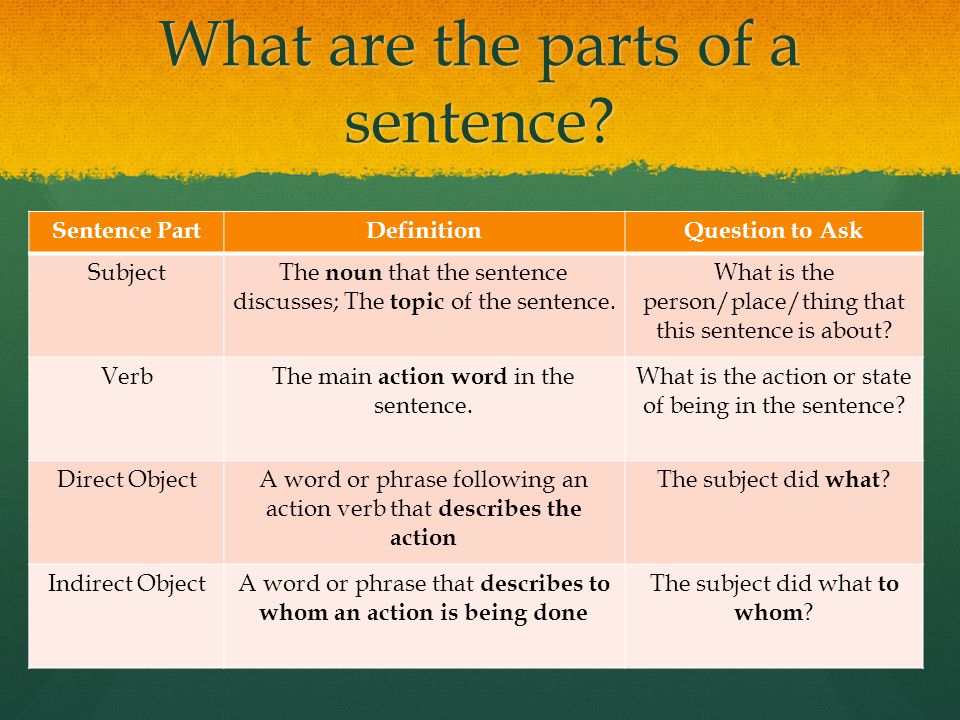
How can i help my child gain weight
Underweight children aged 6 to 12
Children aged 6 to 12 are still growing, which means they need the energy (calories) and nutrients that come from a varied and balanced diet. If your child is underweight, they may not be getting enough calories.
If you're concerned that your child is underweight or not growing normally, see a GP. Low weight can occur for a number of reasons.
How can I tell if my child is underweight?
As a parent, it can be difficult to tell if your child is underweight.
If you already know your child's height and weight, and want to know if they're a healthy weight, you can check using our healthy weight calculator.
If your child is in Year 6 (ages 10 and 11), they may have already been weighed and their height measured as part of the National Child Measurement Programme.
In some areas you may be sent the results for your child. In other areas you will have to contact your local authority to find out your child's measurements.
If results show that your child is underweight, consult a GP, who can talk to you about the possible causes.
If there is a problem with your child's diet, the GP can give advice that will help bring your child up to a healthy weight, or refer them to a dietitian.
Your child's diet
All children need the energy (calories) and nutrients that come from a varied and balanced diet.
If your child is underweight, it may be tempting to fill them up with high-calorie but unhealthy foods, such as sweets, cake, chocolate and sugary and fatty foods and drinks. However, it's important that your child gains weight in a healthy way, and this means eating a balanced diet.
Once your child is 5, they should be eating a healthy, low-fat diet like the one recommended for adults. Find out more in What to feed young children.
What is a balanced diet?
The government advises that children aged 5 and over follow the Eatwell Guide. This guide shows the proportions in which different types of foods are needed to have a balanced diet:
- Eat at least 5 portions of a variety of fruit and vegetables every day.
- Base meals on potatoes, bread, rice, pasta or other starchy carbohydrates. Choose wholegrain where possible.
- Have some dairy or dairy alternatives (such as soya drinks and yoghurts). Choose lower-fat and lower-sugar options.
- Eat some beans and pulses, fish, eggs, meat and other protein. Aim for 2 portions of fish every week – 1 of which should be oily, such as salmon or mackerel.

- Choose unsaturated oils and spreads and eat in small amounts.
- Drink plenty of fluids – the government recommends 6 to 8 glasses a day.
Try to choose a variety of different foods from the 5 main food groups.
Consume foods and drinks that are high in fat, salt and sugar less often and in small amounts.
Most people in the UK eat and drink too many calories, too much fat, sugar and salt, and not enough fruit, vegetables, oily fish or fibre.
Learn more about the different food groups and how they form part of a healthy, balanced diet.
Children's meals at home
Do you find it difficult to make time to prepare healthy balanced meals for the whole family? If so, that might be part of the reason your child is not consuming enough calories.
Try to make time for breakfast and dinner, and eat together as a family. Make mealtime a fun part of the day.
Make mealtime a fun part of the day.
Children's lunches
During the week, your child will eat lunch at school. It's impossible to monitor exactly what your child eats away from home, but you can help your child make healthy choices.
- Talk to your child about the importance of a healthy and balanced diet.
- Give your child prepaid school lunches, or a healthy packed lunch, instead of giving money that your child can spend on food.
- Find out what the school's healthy eating policy is.
These days, school lunches are more likely to meet a child's nutritional requirements compared with the average packed lunch.
If you would prefer to make your child a packed lunch, make sure it is nutritionally balanced.
A healthier packed lunch should:
- be based on starchy carbohydrates (bread, potatoes, rice, pasta)
- include fresh fruit and vegetables/salad
- include protein such as beans and pulses, eggs, fish, meat, cheese (or dairy alternative)
- include a side dish, such as a low-fat and lower-sugar yoghurt (or dairy alternative), tea cake, fruit bread, plain rice/corn cakes, homemade plain popcorn, sugar-free jelly
- include a drink, such as water, skimmed or semi-skimmed milk, sugar-free or no-added sugar drink
Get ideas from Change4Life for what to put in your child's school packed lunch.
How to increase your child's calorie intake
To help your child gain weight, try increasing their portion sizes at mealtimes, especially for starchy foods such as bread, rice, pasta and potatoes.
Alternatively, if your child finds it hard to eat larger portions, try increasing the energy density of your child's meals, until they have reached a healthy weight.
Energy density is the amount of energy (calories) per gram of food. Higher energy density foods tend to be higher in fat, such as cheese, nuts, whole milk and nut butters.
Try:
- a jacket potato with baked beans topped with grated cheese
- tuna pasta bake
- mashed avocado topped with chopped hardboiled egg on wholemeal toast
You can also boost your child's daily calorie intake by providing healthier snacks.
Great snack ideas include:
- small sandwiches with a protein filling, such as cheese or eggs
- cheese and crackers or cheese on wholemeal or brown bread
- yoghurt, which contains protein and calcium
- breadsticks and vegetable dips such as hummus
Keep your child active
Even if your child is underweight, it's still important that they're physically active.
Physical activity helps them develop strong, healthy bones and muscles. It's an important part of how they learn about themselves and the world. And, best of all, it's great fun.
Children over 5 should do a minimum of 60 minutes of activity each day. But the amount of physical activity your child should do may be different if they're underweight. A GP, practice nurse or school nurse can advise you on this.
Find ideas on how to get active with your child.
Monitor your child's progress
If you provide a healthy diet using these guidelines, you should see your child's weight and growth improve.
Keep regular records of your child's height and weight, and take your child back to the GP to check that their weight gain is happening as it should.
Once your child has reached a healthy weight, their diet may need adjusting so that they do not become overweight.
A Dietitian's Best Advice If Your Child Is Underweight – Cleveland Clinic – Cleveland Clinic
As a parent, of course you’re trying to keep your child happy and healthy. You’re focused on providing the right amount of nutrients to help them grow and be strong.
But despite your best efforts, some children still may not achieve the recommended weight. This leaves you asking “is my child underweight for their age or size?”
This leaves you asking “is my child underweight for their age or size?”
So what makes a child underweight? How can you get an underweight child to gain weight they need to grow? You may also wonder “when should I worry about my child’s weight?” if the things you do as a parent don’t seem to be helping.
Pediatric registered dietitian, Jennifer Hyland, RD, answers some common questions about weight, and how healthcare providers can help families get on track and help their underweight child gain in a healthy way.
Q: What qualifies as ‘underweight’ for a child?
A: A child is underweight if they’re in the bottom 5th percentile for weight compared to their height. Underweight is not only classified compared to other children their age, but to their height as we clinically look for a child to be proportionate.
The way pediatricians and dietitians monitor children is on a weight-to-length measurement for children from birth to age 2.
After age 2, we use the Centers for Disease Control growth charts to look at weight, height and BMI (body mass index) for age. BMI for this age range compares a child’s weight to their height. A BMI for age less than the 5th percentile indicates a child is underweight.
BMI for this age range compares a child’s weight to their height. A BMI for age less than the 5th percentile indicates a child is underweight.
Advertising Policy
Q: How can I tell if my child is underweight?
A: There are several signs that parents should watch for:
- Every kid has their own optimal weight. But if your child’s weight percentile declines on the growth charts at annual pediatrician visits, that’s cause for concern.
- At home keep an eye on how clothes fit your child. If a younger child doesn’t begin to outgrow her clothes each season, you should meet with your pediatrician.
- At bath time or at the swimming pool or beach during warm months, watch to see whether you can see your child’s ribs. Ribs that stick out or are prominently visible are a sign that your child may be underweight.
Q: Are there medical issues that cause this problem?
A: Children born prematurely are often underweight because their growth needs to catch up with peers. But a common reason older children are underweight is inadequate food intake.
But a common reason older children are underweight is inadequate food intake.
This may or may not be a result of picky eating. There are also several medical issues that can suppress appetite or block nutrient absorption. These include:
- Medications: Those used in attention deficit-hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), which can suppress appetite.
- Food allergies: These can make getting enough calories a challenge. The more food allergies, the greater the challenge.
- Hormonal or digestive problems: These or other issues of inadequate nutrient absorption can sometimes keep children from gaining weight as they grow.
Q: Are there daily situations that might keep my child from maintaining a healthy diet?
A: When a pediatrician finds that your child is underweight, they may schedule a one-day consultation with a dietitian. The goal is to rule out poor food intake as the issue, and if so, the dietitian can offer recommendations.
You’ll usually be asked to keep a food record that examines your child’s eating habits. The dietitian will also look at other possibilities:
- For daycare-aged kids: Some centers are better than others at documenting that your child is consuming enough calories during the day.
- For older kids: Sports and other school activities often create a hectic schedule where kids just don’t eat enough. If active, they may also have a higher caloric need but may not be making up for it.
- For children who stay with multiple households: When parents are separated or divorced, that could cause kids to miss meals without either parent communicating or knowing.
Q: What eating habits should children avoid?
A: There are some common trends that many parents should focus on preventing or avoiding to help their child gain weight properly.
Advertising Policy
- “Grazing” or excessive snacking: This is one of the most common pitfalls.
 Families should set meal and snack times so that the child has time to get hungry before sitting down to a nutritionally balanced dinner. “Grazing” will fill the child up on foods with low energy density. They’ll actually get more calories if they wait for meals.
Families should set meal and snack times so that the child has time to get hungry before sitting down to a nutritionally balanced dinner. “Grazing” will fill the child up on foods with low energy density. They’ll actually get more calories if they wait for meals. - Use of electronics: Where to eat is just as important as what to eat. Healthy snacks are encouraged but children should eat them at the table — not mindlessly in front of the television, phone or computer screen.
- Avoid fruit juices: Especially those with added sugar. Juices and other sugary beverages will fill kids up without providing them with any energy, fat or protein.
- Protein powders: These aren’t recommended since even underweight kids still seem to get enough protein in their diet (and these powders don’t provide a balance of nutrients needed for weight gain).
Q: How can families help children gain weight in a healthy way?
A: Believe it or not, the goal is to incorporate more fats into the child’s diet — not just any fats like saturated fats from fried foods, but healthy fats like those from oils and nut butters. Here are some suggestions:
Here are some suggestions:
- Add nut butters. For example, encourage kids who like raw fruits and vegetables to eat celery sticks or apple slices with peanut butter.
- Sneak in healthy oils. It is also beneficial to sneak in some olive oil or other heart healthy oils by adding it to foods, which can help even the pickiest eaters.
- Try oral supplements. Ask to speak with a registered dietitian about if an oral supplement is right for your child.
The overall goal is to instill sustainable, healthy eating habits. That’s why it’s important to meet with a dietitian who will also help monitor your child’s progress and offer tips and recipes.
Q: What if my family has special dietary needs or beliefs?
A: Dietitians work closely with parents and families to aid their understanding of why food intake is inadequate and make a plan that fits each families goals and beliefs.
“Dietitians focus on working one-on-one with families to help children gain weight in a way that is consistent with the family’s dietary preferences,” Hyland says. “They can work with all sorts of preferences and varieties of food, including organic foods, whole foods, vegan diets, or diets influenced by religious or cultural beliefs.”
“They can work with all sorts of preferences and varieties of food, including organic foods, whole foods, vegan diets, or diets influenced by religious or cultural beliefs.”
The birth of a small child is not uncommon today. Often, such babies are born on time or a little earlier, but due to a lack of weight, they can significantly lag behind their peers in development. Pediatricians and neuropathologists closely monitor the child's condition, because a child's body weight deficiency is a risk factor for changes in the neurological status, functional disorders of the cardiovascular and autonomic nervous systems. But because of their weakness, underweight children do not eat well, and the rate of weight gain in children born with low body weight determines their further physical and psychomotor development and the formation of the immune system.
How much should a newborn gain in weight?
To assess the development of your child and the compliance with the norm of the main indicators (height, weight), you can contact a pediatrician or independently - according to existing tables. In the first months, the child is actively growing, adding up to 25-60 grams per day. Small children with adequate nutrition can increase body weight more intensively than their peers. For the first month of life, children should gain up to 1.3-1.7 kg. After 5-6 months of life, the intensity of weight gain decreases somewhat - in 30 days, the increase can be only 400-700 grams.
In the first months, the child is actively growing, adding up to 25-60 grams per day. Small children with adequate nutrition can increase body weight more intensively than their peers. For the first month of life, children should gain up to 1.3-1.7 kg. After 5-6 months of life, the intensity of weight gain decreases somewhat - in 30 days, the increase can be only 400-700 grams.
The length of the child's body during the first month increases by 4-7 cm, and after 5-6 months of life, growth is added less intensively - by 2-3 cm. But parents should understand that these figures are approximate. Each child is individual. Its weight and height depend on many factors: heredity, the quality of the mother's nutrition, the state of health of the newborn, the severity of childbirth.
Why is the child not gaining weight well?
The main cause of underweight in the neonatal period is the baby's refusal to breastfeed. Small children have poor appetite and spend most of the day sleeping. Often, parents have to wake up the child for a long time, and after a few minutes of sucking on the breast or a bottle of formula, the newborn falls asleep again. Children are especially sleepy, in whom pronounced physiological jaundice was observed in the first days of life.
Often, parents have to wake up the child for a long time, and after a few minutes of sucking on the breast or a bottle of formula, the newborn falls asleep again. Children are especially sleepy, in whom pronounced physiological jaundice was observed in the first days of life.
As a result, after the next weighing, the doctor can tell the mother that the newborn has not gained weight at all or the increase is insignificant. If the situation does not improve for several months, the mother and baby may be hospitalized for a comprehensive examination and tube feeding in a hospital setting.
Sometimes the cause of low weight gain lies in non-compliance with breastfeeding tactics. Pediatricians recommend applying the baby to only one breast during feeding so that it sucks out the "hind" milk, which is of particular energy value and rich in nutrients. Due to their inexperience, mothers offer both breasts to newborns. In this case, the child sucks the upper milk without making any effort and quickly falls asleep, slightly satisfying his hunger.
If the baby has had an infectious disease, has been ill for a long time, suffered from a high temperature or an intestinal disorder, then the monthly weight gain may be significantly less than usual. In this case, the timing of the introduction of complementary foods is also shifted, and during the period of illness, in general, many children practically refuse to eat, which is reflected in their weight. Parents should actively communicate with the pediatrician, if necessary, ask him questions of interest and adhere to all recommendations.
How to help a child gain weight and catch up with his peers in his development?
If you are breastfeeding, pay special attention to your diet. Drink as much liquid as possible: low-fat milk, compotes, hypoallergenic juices. Your diet must include boiled or baked meat. Take extra vitamins (as advised by the doctor). Breastfeed your baby immediately after waking up, when he is active, in a good mood and does not want to sleep.
But sometimes women's milk is produced in insufficient quantities or the baby does not have enough strength to suck it out. In this case, it is necessary to start supplementing with special infant formula as soon as possible. For children prone to allergic reactions, special hypoallergenic products are intended, which can be bought at a pharmacy, having previously discussed the mixture option with a pediatric nutritionist or pediatrician. Small babies are not adapted to intensive sucking, so the nipple on the bottle must be soft and pliable so that the child can fill up without problems.
In addition, in order to increase the rate of weight gain and, accordingly, for the proper growth and development of the child, it is recommended to give courses of preparations containing L-carnitine (levorcarnitine), an essential vitamin-like substance that has anabolic properties and has proven itself to normalize body weight in case of its deficiency. In addition, by increasing the secretory and enzymatic activity of gastric and intestinal juices, appetite and digestion improve. One of these drugs is Elkar, containing an aqueous solution of L-carnitine. Elkar is included in the "National program for optimizing the feeding of children in the first year of life" as a means of correcting malnutrition of the II degree.
One of these drugs is Elkar, containing an aqueous solution of L-carnitine. Elkar is included in the "National program for optimizing the feeding of children in the first year of life" as a means of correcting malnutrition of the II degree.
In children, in contrast to the adult body, where levocarnitine is among the substances produced, the synthesis of this compound covers only 1% of the required amount. Of course, the required amount of L-carnitine is found in breast milk, but if natural feeding is impaired or impossible, the drug must be added to the diet.
In underweight children, psychomotor development is often retarded, which can subsequently manifest itself in the form of speech defects, instability of the nervous system. Elcar improves the energy supply of brain activity, which will help to avoid or reduce the degree of development of functional failure in various areas of the child's neuropsychic response (motor, emotional-motivational, vegetative, cognitive spheres).
Another very important point: levocarnitine improves immunity, which is vital for small children, since almost all of them are predisposed to the development of infectious diseases.
The rate of weight gain is influenced by many external and internal factors. The task of parents is to help the crumbs get stronger as soon as possible. Walk more with your child in the fresh air so that his body receives the necessary amount of oxygen. And don't forget to visit your pediatrician. Small children need professional medical supervision and the attention of loved ones.
Baby is underweight. What to do with low weight?
0-6 months
Article
5/5 1 reviews
Every mother worries about her baby growing up healthy, that's why she is so happy about chubby cheeks and new kilograms. But there are children who slowly gain weight, and then their parents begin to care about the low weight of the child. When is it worth starting to worry and what to do so that the little one develops correctly?
But there are children who slowly gain weight, and then their parents begin to care about the low weight of the child. When is it worth starting to worry and what to do so that the little one develops correctly?
3 min. for reading Feb. 17, 2022
Let's figure out how much a baby should weigh. By the time one year is reached, the baby's norm is about 10 kg, but this is also affected by his growth and heredity. It is important to consider not only indicators of height and weight, but also their ratio. The next year, the mass is gaining more slowly - about 2.5-4 kg in 12 months. Remember that weight gain happens gradually, not evenly every month.
For boys , the norm is considered if he weighs:
- 10-13 kg at 1.5 years;
- 11-14.5 kg at 2 years;
- 13-17 kg at 3 years;
- 16-22 kg at 5 years.
Girls may gain weight more slowly:
- 9.
 5-12 kg at 1.5 years;
5-12 kg at 1.5 years; - 10.5-13.5 kg at 2 years;
- 12.5-16.5 kg at 3 years;
- 15.5-21.5 kg at 5 years.
Low birth weight: what affects
The weight and further development of the baby is affected by the following factors :
- Mother's nutrition during pregnancy. A woman should watch her diet and take in all the nutrients her baby needs.
- Mom's emotional state. A possible cause of low birth weight in a child is constant anxious thoughts and depression during pregnancy.
- Bad habits. Smoking and drinking can also delay a child's weight gain.
- Heredity, the constitution of the body of mom and dad. Big parents are more likely to have a big baby.
- Childbirth . A premature baby always weighs less than a baby who was born at term.
Why the child is not gaining weight
If the child has a good appetite but is not gaining weight, see a specialist. The pediatrician will conduct the necessary studies to exclude possible diseases. An underweight baby can be the result of problems with the intestines, in which food is poorly absorbed, and the body loses a lot of fluid. Also, the "culprit" may be diabetes, neurological diseases, thyroid dysfunction, low hemoglobin levels.
The pediatrician will conduct the necessary studies to exclude possible diseases. An underweight baby can be the result of problems with the intestines, in which food is poorly absorbed, and the body loses a lot of fluid. Also, the "culprit" may be diabetes, neurological diseases, thyroid dysfunction, low hemoglobin levels.
Other causes of underweight in children include:
- worms, in which a good appetite may be maintained, but weight does not increase;
- unbalanced and monotonous diet, when the baby does not receive enough vitamins and nutrients;
- If we are talking about a baby, then the reason for the lack of weight may be the incorrect introduction of complementary foods.
Weight gain: how to promote it
Review the child's menu, but before that it is better to consult a specialist. Doctors recommend not feeding your baby “empty” calories: if the baby is not gaining weight well, try increasing the calorie content of food, but do it gradually. Food should be fractional.
Food should be fractional.
It is also important not only to increase the amount of food consumed, but also to add vitamins, because very often hypovitaminosis is found in children with low weight. The physical growth of the child is normalized if the baby has a vitamin deficiency, so the pediatrician may advise taking a vitamin-mineral complex so that the baby can develop correctly and in a timely manner. Try to offer 3-5 different types of fruits and vegetables daily to complete your meal plan. We must not forget about meat products, fish, milk, cereals, because the children's diet should have enough proteins and easily digestible carbohydrates.
Read also: What you need to know about meat
If you are concerned about the low weight of the child, it is worth noting that this does not affect his future height and weight. Often such children catch up with their peers in the first year of life, but large babies gain weight more slowly.