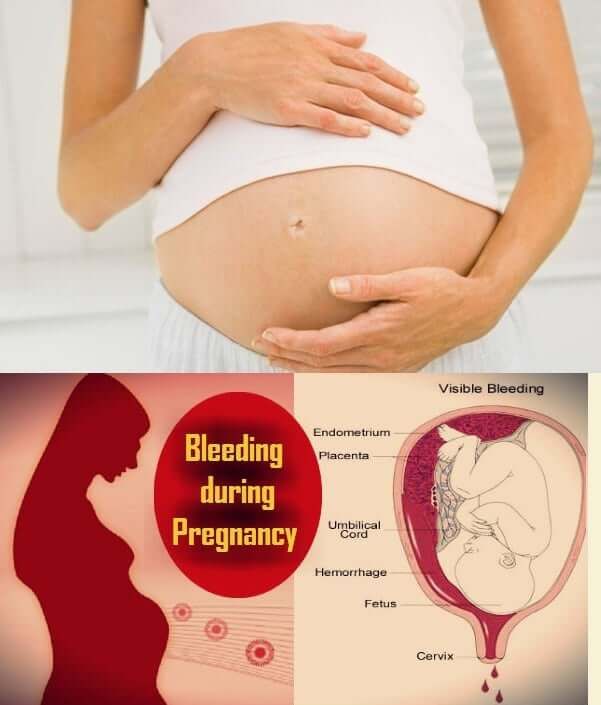
Bleeding from breast during pregnancy
Bloody nipple discharge during pregnancy: a rationale for conservative treatment
. 1990 Apr;43(4):228-30.
doi: 10.1002/jso.2930430408.
R Lafreniere 1
Affiliations
Affiliation
- 1 Department of Surgery, University of Calgary, Alberta, Canada.
- PMID: 2325421
- DOI: 10.1002/jso.2930430408
R Lafreniere. J Surg Oncol. 1990 Apr.
. 1990 Apr;43(4):228-30.
doi: 10.1002/jso.2930430408.
Author
R Lafreniere 1
Affiliation
- 1 Department of Surgery, University of Calgary, Alberta, Canada.
- PMID: 2325421
- DOI: 10.1002/jso.2930430408
Abstract
Five cases of bloody nipple discharge during pregnancy without associated breast masses were seen over the past 3 years by the author. Because of the reported association of breast cancer with bloody nipple discharge, close follow-up of these women at monthly intervals during pregnancy and trimonthly during the postpartum period was carried out. In all instances, the discharge appeared late during the second trimester or during the third trimester of pregnancy. It was unilateral and spontaneous and arose from multiple ducts, and it was associated with an increase in breast size and always with the larger breast of the two. The discharge cytologic study done on all cases was negative for neoplastic cells and the discharges resolved spontaneously within 2 months of onset. Postpartum follow-up ranging from 6 months to 3 years has revealed no evidence of neoplastic changes thus far. Mammograms ordered before these patients were referred were not helpful due to the increase in density of the breast tissue secondary to the pregnancy. Because a few cases of breast cancer during pregnancy have presented solely with a bloody nipple discharge, I recommend extremely close follow-up of these women and no surgical intervention unless a mass is discovered or the nipple discharge cytology is either suspicious or positive at the initial visit or during follow-up.
In all instances, the discharge appeared late during the second trimester or during the third trimester of pregnancy. It was unilateral and spontaneous and arose from multiple ducts, and it was associated with an increase in breast size and always with the larger breast of the two. The discharge cytologic study done on all cases was negative for neoplastic cells and the discharges resolved spontaneously within 2 months of onset. Postpartum follow-up ranging from 6 months to 3 years has revealed no evidence of neoplastic changes thus far. Mammograms ordered before these patients were referred were not helpful due to the increase in density of the breast tissue secondary to the pregnancy. Because a few cases of breast cancer during pregnancy have presented solely with a bloody nipple discharge, I recommend extremely close follow-up of these women and no surgical intervention unless a mass is discovered or the nipple discharge cytology is either suspicious or positive at the initial visit or during follow-up.
Similar articles
-
Significance of nipple discharge clinical patterns in the selection of cases for cytologic examination.
Ciatto S, Bravetti P, Cariaggi P. Ciatto S, et al. Acta Cytol. 1986 Jan-Feb;30(1):17-20. Acta Cytol. 1986. PMID: 3456180
-
Management of nipple discharge.
Leis HP Jr. Leis HP Jr. World J Surg. 1989 Nov-Dec;13(6):736-42. World J Surg. 1989. PMID: 2696228 Review.
-
Surgical management of nipple discharge.
Markopoulos C, Mantas D, Kouskos E, Antonopoulou Z, Lambadariou K, Revenas K, Papachristodoulou A. Markopoulos C, et al. Eur J Gynaecol Oncol.
 2006;27(3):275-8. Eur J Gynaecol Oncol. 2006. PMID: 16800258
2006;27(3):275-8. Eur J Gynaecol Oncol. 2006. PMID: 16800258 -
Nonpuerperal nipple discharge in Nigerian women.
Chiedozi LC. Chiedozi LC. Trop Geogr Med. 1986 Dec;38(4):398-403. Trop Geogr Med. 1986. PMID: 3810844
-
Management of Nipple Discharge.
Vavolizza RD, Dengel LT. Vavolizza RD, et al. Surg Clin North Am. 2022 Dec;102(6):1077-1087. doi: 10.1016/j.suc.2022.06.006. Surg Clin North Am. 2022. PMID: 36335926 Review.
See all similar articles
Cited by
-
Rusty pipe syndrome: a case report and review of the literature.
Tang H, Zhu W, Chen J, Zhang D.
 Tang H, et al. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2022 Oct 13;22(1):770. doi: 10.1186/s12884-022-05048-5. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2022. PMID: 36229800 Free PMC article. Review.
Tang H, et al. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2022 Oct 13;22(1):770. doi: 10.1186/s12884-022-05048-5. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2022. PMID: 36229800 Free PMC article. Review. -
Blood-Stained Colostrum: A Rare Phenomenon at an Early Lactation Stage.
Katarzyna W, Małgorzata P, Agata WP, Wioletta M, Jan M, Katarzyna R, Maciej W. Katarzyna W, et al. Children (Basel). 2022 Feb 6;9(2):213. doi: 10.3390/children9020213. Children (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35204933 Free PMC article.
-
Pregnancy related breast diseases in a developing African country: Initial Sonographic Evaluation.
Adeniji-Sofoluwe AT, Obajimi GO, Obajimi MO. Adeniji-Sofoluwe AT, et al. Pan Afr Med J. 2015 Mar 13;20:239. doi: 10.11604/pamj.
 2015.20.239.4830. eCollection 2015. Pan Afr Med J. 2015. PMID: 27386035 Free PMC article.
2015.20.239.4830. eCollection 2015. Pan Afr Med J. 2015. PMID: 27386035 Free PMC article. -
Breast diseases during pregnancy and lactation.
Yu JH, Kim MJ, Cho H, Liu HJ, Han SJ, Ahn TG. Yu JH, et al. Obstet Gynecol Sci. 2013 May;56(3):143-59. doi: 10.5468/ogs.2013.56.3.143. Epub 2013 May 16. Obstet Gynecol Sci. 2013. PMID: 24327995 Free PMC article. Review.
MeSH terms
Is bloody nipple discharge during pregnancy normal?
Bloody discharge sounds scary, find out if it is a matter of concern or your body's way to trick you during pregnancy.
The thought itself is scary, isn t it? Imagine if you suddenly notice blood oozing out of your nipples for no rhyme and reason. Sure it is going to freak you out, no matter whether you are pregnant or not. But during pregnancy a lot of changes happen to your breast they grow in size, start to produce milk, prepare for the lactation phase, get sore and tender, etc. But still bleeding through your nipple is not something you will expect during pregnancy. At worst, nipple discharge or even bloody discharge from breast could be indicative of an untoward incident like breast cancer, but bloody discharge during pregnancy is usually unheard of. Here are symptoms of breast cancer that you should never ignore.
But during pregnancy a lot of changes happen to your breast they grow in size, start to produce milk, prepare for the lactation phase, get sore and tender, etc. But still bleeding through your nipple is not something you will expect during pregnancy. At worst, nipple discharge or even bloody discharge from breast could be indicative of an untoward incident like breast cancer, but bloody discharge during pregnancy is usually unheard of. Here are symptoms of breast cancer that you should never ignore.
But if you are pregnant and see some blood oozing out of your breasts, don t fret. Though rare, bloody discharge during pregnancy can be absolutely normal. A study trying to explore the various changes happening in the body during pregnancy pointed out that a marginal section of women can suffer from bloody discharge during pregnancy. As the blood flow in the breasts increases rapidly during pregnancy it can change the dynamics of the epithelial cells of the breasts and lead to bloody discharge through the nipple.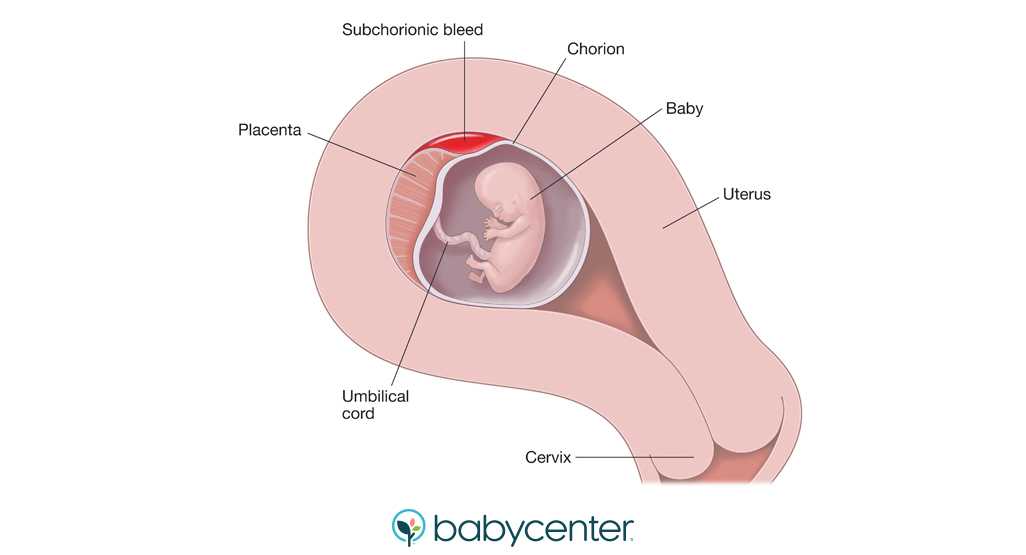 The chance of experiencing this kind of discharge is more at the end of the second trimester or during the third trimester. Here are changes that happen to your breast during pregnancy.
The chance of experiencing this kind of discharge is more at the end of the second trimester or during the third trimester. Here are changes that happen to your breast during pregnancy.
Slight bloody nipple discharge accounts to approximately 20 percent of nipple discharge during pregnancy and 15 percent during lactation. This phenomenon mostly stops as the mother starts breastfeeding. But in very rare cases can persist throughout the whole lactation period. Diagnostic cytology tests must be performed for the wounds of nipples by feeding. If the result, physical examination and ultrasound are normal, the follow-up test should be recommended in a timely manner.
Even though studies might suggest that it is harmless if you notice any such unusual symptom report it to your doctor. Another study was done in the year 1990 stated that blood discharge from nipple during pregnancy is usually harmless and was associated with an increase in breast size, usually the larger of the two. But close medical examination is indeed necessary as the symptom mimics those of breast cancer. This study also noticed that the incidence disappeared after two months of its onset. Even a close follow-up after three years have shown that there was no evidence of developed carcinoma in the breasts. But the study also warned that one should not ignore the symptom solely thinking that it is harmless as few cases of breast cancer during pregnancy have presented solely with a bloody nipple discharge. So, a close follow-up and check-up with the gynaecologist become necessary.
But close medical examination is indeed necessary as the symptom mimics those of breast cancer. This study also noticed that the incidence disappeared after two months of its onset. Even a close follow-up after three years have shown that there was no evidence of developed carcinoma in the breasts. But the study also warned that one should not ignore the symptom solely thinking that it is harmless as few cases of breast cancer during pregnancy have presented solely with a bloody nipple discharge. So, a close follow-up and check-up with the gynaecologist become necessary.
References:
Yu, J. H., Kim, M. J., Cho, H., Liu, H. J., Han, S.-J., & Ahn, T.-G. (2013). Breast diseases during pregnancy and lactation. Obstetrics & Gynecology Science, 56(3), 143 159. https://doi.org/10.5468/ogs.2013.56.3.143
1: Lafreniere R. Bloody nipple discharge during pregnancy: a rationale for conservative treatment. J Surg Oncol. 1990 Apr;43(4):228-30. PubMed PMID: 2325421.
PubMed PMID: 2325421.
Image source: Shutterstock
Total Wellness is now just a click away.
Follow us on
Breast cancer in pregnant women. What is Breast Cancer in Pregnancy?
IMPORTANT
The information in this section should not be used for self-diagnosis or self-treatment. In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, only the attending physician should prescribe diagnostic tests. For diagnosis and proper treatment, you should contact your doctor.
Breast cancer in pregnant women is a malignant neoplasia of the breast detected during gestation, lactation, or within 12 months after childbirth. It is manifested by nodular or diffuse compaction of the mammary glands, their heaviness and soreness, discomfort, pain in the areola, discharge from the nipple, local skin changes, and an increase in axillary lymph nodes. Diagnosed by ultrasound, trepanobiopsy, MRI of the mammary glands. During the gestation period, surgical methods of treatment are used (usually modified versions of radical mastectomy), chemotherapy according to the AC scheme. After childbirth, therapy is supplemented with hormonal drugs and radiation techniques.
Diagnosed by ultrasound, trepanobiopsy, MRI of the mammary glands. During the gestation period, surgical methods of treatment are used (usually modified versions of radical mastectomy), chemotherapy according to the AC scheme. After childbirth, therapy is supplemented with hormonal drugs and radiation techniques.
ICD-10
C50 Malignant neoplasm of breast
- Causes
- Pathogenesis
- Classification
- Breast cancer symptoms in pregnant women
- Complications
- Diagnostics
- Treatment of breast cancer in pregnant women
- Prognosis and prevention
- Prices for treatment
General
Malignant tumors of the mammary glands are the second most common type of neoplasia diagnosed in pregnant women. Their occurrence is 1:3,000 - 1:10,000 gestations. The median age of women diagnosed with pregnancy-associated breast cancer is 33 years. Up to 82% of patients detect a neoplasm on their own in the first trimester, while in almost 3/4 of cases late stages of neoplasia are diagnosed with tumor sizes from 6 to 15 cm, and metastases in internal organs are found in every fifth pregnant woman. Due to untimely diagnosis of the disease, the delay in starting treatment is on average 2-3.5 months.
Up to 82% of patients detect a neoplasm on their own in the first trimester, while in almost 3/4 of cases late stages of neoplasia are diagnosed with tumor sizes from 6 to 15 cm, and metastases in internal organs are found in every fifth pregnant woman. Due to untimely diagnosis of the disease, the delay in starting treatment is on average 2-3.5 months.
Breast cancer in pregnant women
Causes
The etiology of malignant neoplasia in gestation is the same as in non-pregnant women. In 5-10% of cases, the development of cancer is due to an inherited mutation of the BRCA1/BRCA2 genes. In the rest of the patients, the neoplasm occurs against the background of dyshormonal conditions, the effects of adverse environmental factors (mutagenic chemicals, radiation, etc.), and immunity deficiency. As a rule, tumors detected in the mammary glands of pregnant women occur before conception, but their growth can accelerate against the background of physiological gestational changes. According to experts in the field of oncology and obstetrics, specific provoking factors for rapid oncogenesis during pregnancy are:
According to experts in the field of oncology and obstetrics, specific provoking factors for rapid oncogenesis during pregnancy are:
- Hormonal changes. More than 70% of breast cancer in pregnant women is estrogen-dependent (ER+). During gestation, the level of estrogen in the blood increases by almost 30 times. Under the influence of hormones, the mammary glands are prepared for lactation: the breast swells, the number of alveoli and milk ducts increases in it. Hyperestrogen stimulation may promote faster development of cancer cells.
- Reduced immunity. Since the fetus is genetically alien to the mother's body, physiological changes in the immune system of pregnant women are aimed at reducing the overall reactivity. Due to an increase in the number of T-suppressors, a decrease in the level of T-helpers, the appearance of blocking antibodies, the effector link of immunity is suppressed. As a result, the immune system is less able to detect and destroy its own degenerating cells.

Pathogenesis
A probable mechanism for the development of breast cancer in pregnant women is based on the stimulation of the growth of transformed cells by estrogens and progesterone. Enhanced estrogenic action induces the synthesis of growth factors, under the influence of which the epithelial cells of the mammary glands, including malignant tumors, proliferate. At the same time, cell apoptosis is inhibited, and pathological neovascularization begins due to the induced transcription of the growth factor of the vascular endothelium.
Since estrogens are able to neutralize the effect of inhibitory growth factors, a negative feedback is activated that stimulates cellular hyperplasia. One of the estrogenic effects is a rapid increase in the number of micrometastases caused by stimulation of the so-called dormant metastatic formations. The role of progesterone in the oncogenesis of mammary neoplasia is still being clarified. Its effects may be related to the maintenance of cyclical proliferation of glandular cells during gestation and growth promotion with the potential to modify the response of normal and degenerate glandular epithelium.
Its effects may be related to the maintenance of cyclical proliferation of glandular cells during gestation and growth promotion with the potential to modify the response of normal and degenerate glandular epithelium.
Classification
The systematization of breast cancer forms during pregnancy is based on the same criteria as outside the gestational period - the anatomical location of the neoplasia, its size, the characteristics of metastasis to the lymph nodes and distant organs, the histological structure, the level of cell differentiation, the type of expressed receptors of malignant cells. The most significant role in the development of optimal pregnancy support tactics is played by the classification of the tumor by stages of development. Oncomammologists distinguish:
- Non-invasive cancer (carcinoma in situ). Neoplasia is localized in the milk duct or lobule. Lymph nodes are intact. The clinic is missing. Cancer becomes an accidental finding during a routine examination.
 most favorable form. It is possible to continue gestation after surgical treatment.
most favorable form. It is possible to continue gestation after surgical treatment. - Stage I cancer. The maximum diameter of the neoplasm does not exceed 2 cm. Neoplasia grows into the surrounding breast tissue, but does not metastasize. It can be determined clinically as a nodular compaction. Surgical intervention allows you to save the pregnancy.
- Stage II cancer. In stage IIA, the tumor is up to 2 cm in size with metastasis to the axillary lymph nodes on the affected side or up to 5 cm without metastases. In stage IIB cancer, the size of neoplasia is 2-5 cm in the presence of metastases in the lymph nodes, or from 5 cm or more - in their absence. To preserve gestation, a radical mastectomy is indicated.
- Stage III cancer. The tumor grows up to 5 or more centimeters, or there are conglomerates of soldered axillary lymph nodes, germination of cancer in the skin of the breast, chest tissue, damage to the subclavian and supraclavicular lymph nodes. Distant metastases are possible.

- Stage IV cancer. There is a massive lesion of the mammary gland with germination of surrounding tissues, dissemination into the skin, ulcerations. Perhaps the involvement in the process of the second breast, axillary lymph nodes on the opposite side. Multiple distant metastases are characteristic.
At III-IV stages of the oncological process, at the request of the patient and her relatives, it is permissible to maintain gestation with early delivery within the period of sufficient viability of the child. In such cases, the implementation of radical surgery allows you to stop the spread of the tumor and start active therapy in the postpartum period. The appointment of some chemotherapy drugs is possible from the 15th week of gestation.
Breast cancer symptoms in pregnant women
Although gestational physiological changes in tissues complicate the detection of a malignant mass, there are markers that increase cancer alertness.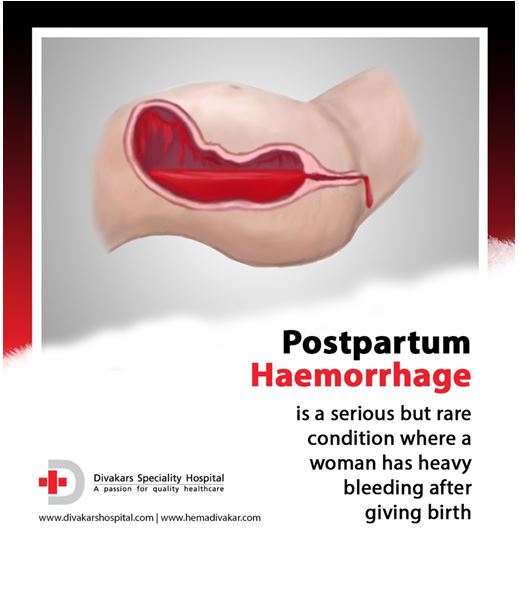 The development of cancer may be indicated by the appearance in one of the mammary glands of a node or unformed compaction, pain and severity. In some patients, against the background of general engorgement, the shape of the affected mammary gland changes asymmetrically, irregularities, areas of retractions or local swelling appear on the skin.
The development of cancer may be indicated by the appearance in one of the mammary glands of a node or unformed compaction, pain and severity. In some patients, against the background of general engorgement, the shape of the affected mammary gland changes asymmetrically, irregularities, areas of retractions or local swelling appear on the skin.
Often there is tingling, pain in the nipple-areolar region, the nipple may be retracted, and sanious discharge appears. In the presence of regional metastases in the armpit on the affected side, enlarged lymph nodes are determined, in more severe cases, the lymph nodes are palpated above and below the clavicle, in the opposite axillary cavity. Signs of general intoxication in the form of loss of appetite, weight loss, increasing weakness and fatigue are typical only for the terminal stages of the disease.
Complications
Breast cancer that occurs in pregnant women can progress rapidly and be complicated by metastasis. Common forms of the disease are detected in 72-85% of patients, in 20% of women the internal organs are affected by metastases. In some cases, inflammation of the tissues surrounding the tumor develops. According to most obstetrician-gynecologists, breast cancer does not have a negative impact on the child, however, in the later stages of the disease, in the presence of tumor intoxication, fetal hypoxia is possible. The use of chemotherapy drugs in the II-III trimesters can provoke premature birth, myelosuppression in a woman and a child, fetal growth retardation, stillbirth, massive postpartum hemorrhage, infectious complications (endometritis, chorioamnionitis, etc.).
Common forms of the disease are detected in 72-85% of patients, in 20% of women the internal organs are affected by metastases. In some cases, inflammation of the tissues surrounding the tumor develops. According to most obstetrician-gynecologists, breast cancer does not have a negative impact on the child, however, in the later stages of the disease, in the presence of tumor intoxication, fetal hypoxia is possible. The use of chemotherapy drugs in the II-III trimesters can provoke premature birth, myelosuppression in a woman and a child, fetal growth retardation, stillbirth, massive postpartum hemorrhage, infectious complications (endometritis, chorioamnionitis, etc.).
Diagnostics
Because pregnant women often perceive the initial signs of a tumor as specific changes in the mammary glands before lactation, breast cancer during gestation is usually diagnosed at a later stage. Diagnostically significant radiological research methods during pregnancy are used to a limited extent due to the possible negative impact on the fetus, however, other modern methods can detect a tumor and correctly assess the stage of the oncological process. The most informative when detecting malignant neoplasia of the breast are:
The most informative when detecting malignant neoplasia of the breast are:
- Mammography. Ultrasound of the mammary glands is the best method for screening the diagnosis of malignant tumors in pregnant and lactating women. The information content of ultrasonography, supplemented by color and power Doppler, reaches 97%. Usually, on ultrasound, the cancer looks like a hypervascular hypoechoic mass of irregular shape and inhomogeneous structure. With the help of ultrasound, it is convenient to examine regional lymph nodes.
- Trepanobiopsy of the breast. The material obtained with a biopsy gun is used to determine the morphological structure of the neoplasm and its immunohistochemical profile (receptor status, Her2-neu gene amplification, Ki-67 proliferative index, etc.). Trepanobiopsy is more informative than puncture biopsy, it allows to verify the diagnosis in 99.0-99.8% of cases.
- Tomography. Breast MRI is performed when sonography results are inconclusive.
 Layered visualization makes it possible to accurately assess the size and prevalence of neoplasia. Whole-body MRI is recommended to detect metastases. In the first trimester, scanning is carried out with caution due to possible cavitation and overheating of the embryo. Contrasting is allowed in exceptional cases.
Layered visualization makes it possible to accurately assess the size and prevalence of neoplasia. Whole-body MRI is recommended to detect metastases. In the first trimester, scanning is carried out with caution due to possible cavitation and overheating of the embryo. Contrasting is allowed in exceptional cases.
Mammography is rarely prescribed for pregnant women with suspected breast cancer, which is associated with possible damaging effects on the fetus and obtaining false-negative results in 25% of cases. As additional methods of examination, it is recommended to determine the tumor marker CA 15-3, cytology of a smear obtained from the nipple of the affected mammary gland, risk assessment for the development of BRCA-associated cancer, ductoscopy, breast radiothermometry, electrical impedance mammography. The disease is differentiated from mastitis, benign neoplasia (cysts, adenomas, fibroadenomas, lipomas, leaf-shaped tumors), galactocele, hamartomas, lymphomas, sarcomas, tuberculosis. In addition to the oncomammologist, the patient is consulted by an oncologist, a chemotherapist, a surgeon, a phthisiatrician, an infectious disease specialist, according to indications.
In addition to the oncomammologist, the patient is consulted by an oncologist, a chemotherapist, a surgeon, a phthisiatrician, an infectious disease specialist, according to indications.
Treatment of breast cancer in pregnant women
If earlier detection of a malignant neoplasm of the breast served as a sufficient reason for terminating a pregnancy, in recent decades, strategies have been used that involve early initiation of therapy and preservation of gestation. The choice of medical tactics in each specific case of cancer is carried out individually, taking into account the stage of the process, the gestational age and the decision of the pregnant woman. In the 1st trimester, if invasive forms of the tumor are detected, it is recommended to terminate the pregnancy with a medical abortion, in the 2nd-3rd trimester, if the patient wants to extend it to the minimum possible term for the birth of a viable fetus. After artificial interruption of gestation, treatment is carried out according to standard protocols for oncological care. When deciding to keep a child, the following options may be used:
When deciding to keep a child, the following options may be used:
- Surgical treatment. The most justified intervention in the early stages of cancer is radical mastectomy, if necessary, supplemented by axillary dissection without subsequent radiation therapy. Lumpectomy, quadrantectomy, sectoral resection of the breast are performed less frequently. Oncoplastic surgery is not recommended. The volume and duration of the intervention in the late stages of the disease are determined individually.
- Prescribing chemotherapy drugs. Antineoplastic agents can be used after 14 weeks of gestational age. The later drug treatment is started, the less likely it is that fetal malformations will occur. The drugs of choice are alkylating cytostatics and anthracycline antibiotics. In advanced forms of cancer, neoadjuvant polychemotherapy is used as a preparatory step before radical surgery.
Hormone therapy, which is most effective in receptor-positive forms of cancer, is not carried out by pregnant women due to the teratogenic effect of estrogen antagonists. The appointment of radiation therapy is possible only after the completion of gestation. The recommended method of delivery is natural childbirth. Caesarean section is carried out only in the presence of obstetric indications or severe extragenital pathology incompatible with labor loads.
The appointment of radiation therapy is possible only after the completion of gestation. The recommended method of delivery is natural childbirth. Caesarean section is carried out only in the presence of obstetric indications or severe extragenital pathology incompatible with labor loads.
Prognosis and prevention
Survival rates for patients diagnosed with breast cancer during pregnancy do not differ from those for non-pregnant women. Interruption of gestation does not affect the outcome of the disease. However, in general, the prognosis is more serious, since pregnant women often have advanced forms of cancer. The minimum safe interval from the end of treatment to the next pregnancy, according to different authors, ranges from 6 months to 5 years. The main task of breast cancer prevention is to detect a tumor at an early stage using screening methods (ultrasound, mammography).
You can share your medical history, what helped you in the treatment of breast cancer in pregnant women.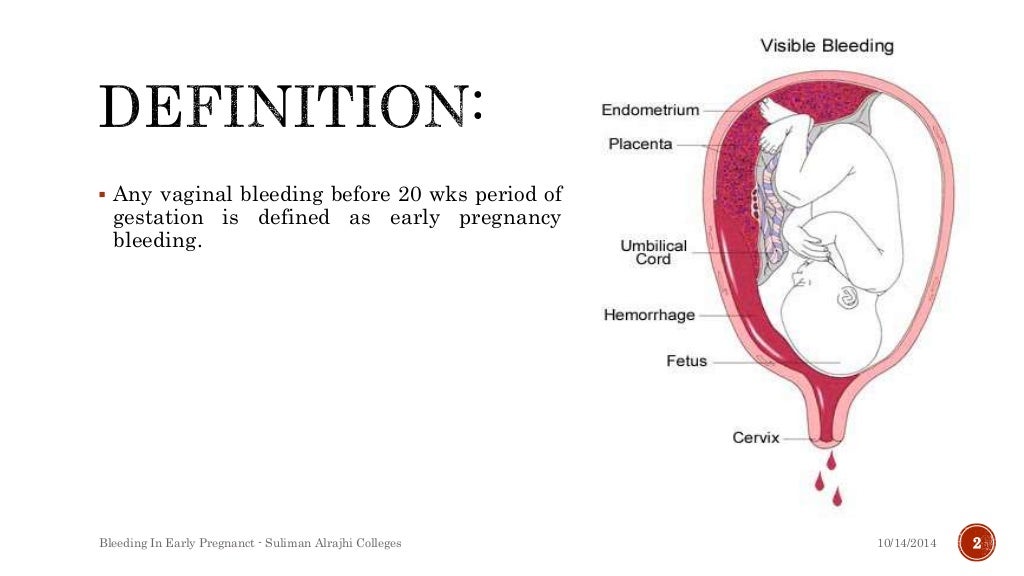
Sources
- Breast cancer and pregnancy / Lud LN, Lud NG// Bulletin of the Vitebsk State Medical University. – 2008.
- Pregnancy-associated breast cancer/ Nikulina LR, Kuzmichev DE, Skrebov RV, Chekashina DV// Public Health of Yugra: experience and innovations. - 2016 - No. 3.
- Breast cancer and pregnancy: features of diagnosis and treatment/ Ivanova OA, Zhiltsova EK, Ivanov VG, Popova RT, Ermochenkova AM// Malignant tumors. – 2014.
- Breast cancer and pregnancy. Current state of the problem/ Parokonnaya A.A.// Practical oncology. - 2009 - Vol. 10, No. 4.
- This article was prepared based on the materials of the site: https://www.krasotaimedicina.ru/
IMPORTANT
Information from this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment. In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, only the attending physician should prescribe diagnostic tests. For diagnosis and proper treatment, you should contact your doctor.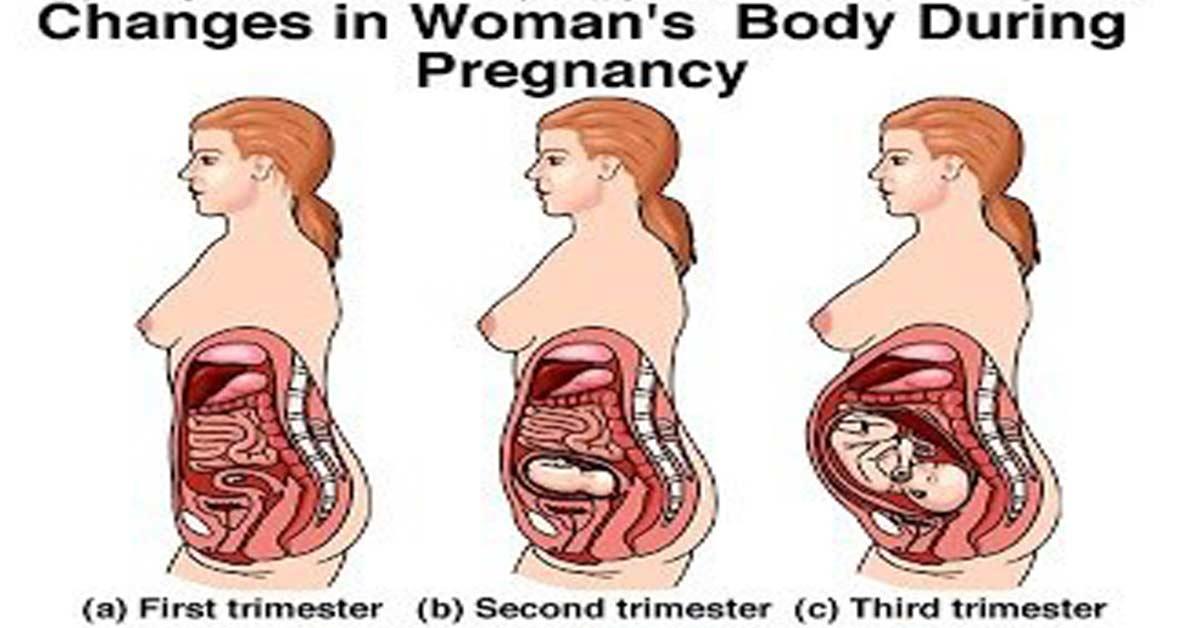
Bloody discharge during pregnancy ᐈ Blood during early pregnancy
Seeing bloody discharge, a pregnant woman is always frightened. They are considered a symptom of miscarriage and other equally serious pathologies. At the same time, in some cases, the appearance of a small amount of blood is considered the norm and does not pose a threat to the life and health of the fetus or the expectant mother.
In early pregnancy, bloody discharge occurs in 25% of women. In most cases, they are associated with the implantation of the fetal egg to the wall of the uterus. Also, scanty spotting may appear on the dates of the expected menstruation. If they end quickly, are not accompanied by pain, and the woman has not had miscarriages or pregnancy complications before, most likely she has nothing to worry about. However, it is necessary to consult an obstetrician-gynecologist and undergo an examination.
Why bloody discharge can appear and when it is dangerous, said Elena Petrovna Domnich, obstetrician-gynecologist of the highest category, gynecologist-endocrinologist, ultrasound specialist of the ADONIS medical center.
Elena Nikolaevna, tell me, can a woman have periods during pregnancy?
- Sometimes during pregnancy, a woman may experience spotting, but this should not be interpreted as menstruation. Menstruation occurs at the end of the menstrual cycle, during which the endometrium changes, first proliferative, then secretory. During the cycle, the endometrium prepares for pregnancy, and if it does not occur, then menstruation begins.
In the event of pregnancy, menstruation is not possible, although bleeding may occur at the expected time. Because of this, some women do not immediately know that they are pregnant. However, when the obstetrician-gynecologist at the reception asks them about the nature of the discharge, it always turns out that they are different from menstrual. As a rule, they are more scarce, pass faster and are not accompanied by other symptoms. Sometimes a woman says that her period was very recent, but at the time of examination and examination, we find that she is already 8 or 12 weeks pregnant.
How often does this happen? Is spotting during pregnancy an exception or a fairly common occurrence?
- Bloody discharge is rare in pregnant women, but still it cannot be said that these are exceptional cases.
Tell me, if a woman is planning to conceive a child, and during the expected period she has unusual discharge, should she take a pregnancy test?
– Yes, but it is better to visit an obstetrician-gynecologist. There are cases when a woman is pregnant, but the test strip shows a negative result. To accurately determine whether there is a pregnancy, allows a blood test for the level of hCG.
So bleeding during pregnancy is not menstruation, but bleeding? Why can it appear and why is it dangerous?
- Yes, that's right. This is bleeding, not menstruation. It can be a symptom of a miscarriage, ectopic pregnancy, or other pathology. For diagnosis, you must consult a doctor.
For diagnosis, you must consult a doctor.
Tell me more, if a woman has a discharge and thinks she is menstruating, but a previous pregnancy test came back positive, could it be wrong?
- A pregnancy test is sometimes positive even if it is not. This happens if a woman has formed luteal cysts or developed a thyroid disease.
Bloody discharge during pregnancy requires contacting the antenatal clinic or the medical center where the woman was registered for pregnancy management. Sometimes they may not be dangerous, but without diagnosis, it cannot be ruled out that this is a symptom of a serious disorder.
Bleeding may occur with:
- threatened miscarriage;
- ectopic pregnancy;
- infectious diseases of the reproductive system;
- cysts;
- myomas;
- cervical erosion;
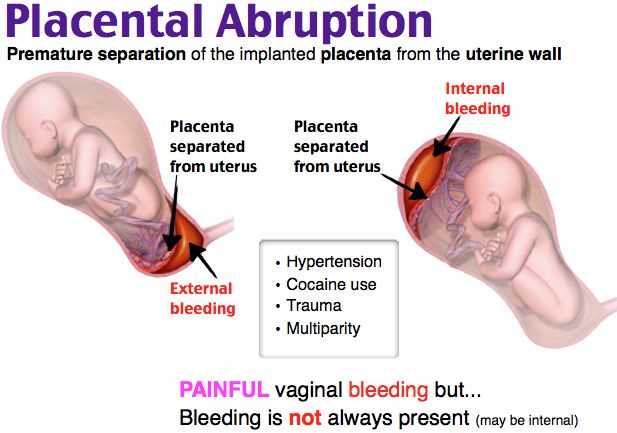
- placental abruption;
- threatened preterm birth.
You can watch the video version of Elena Petrovna Domnich's interview here.