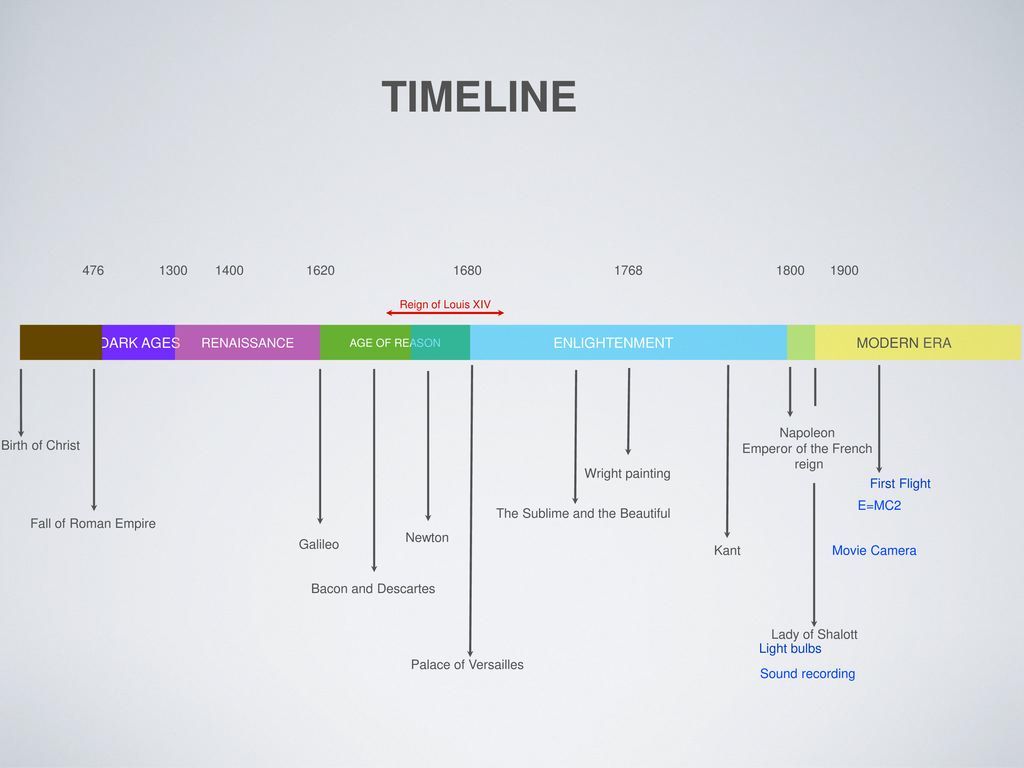
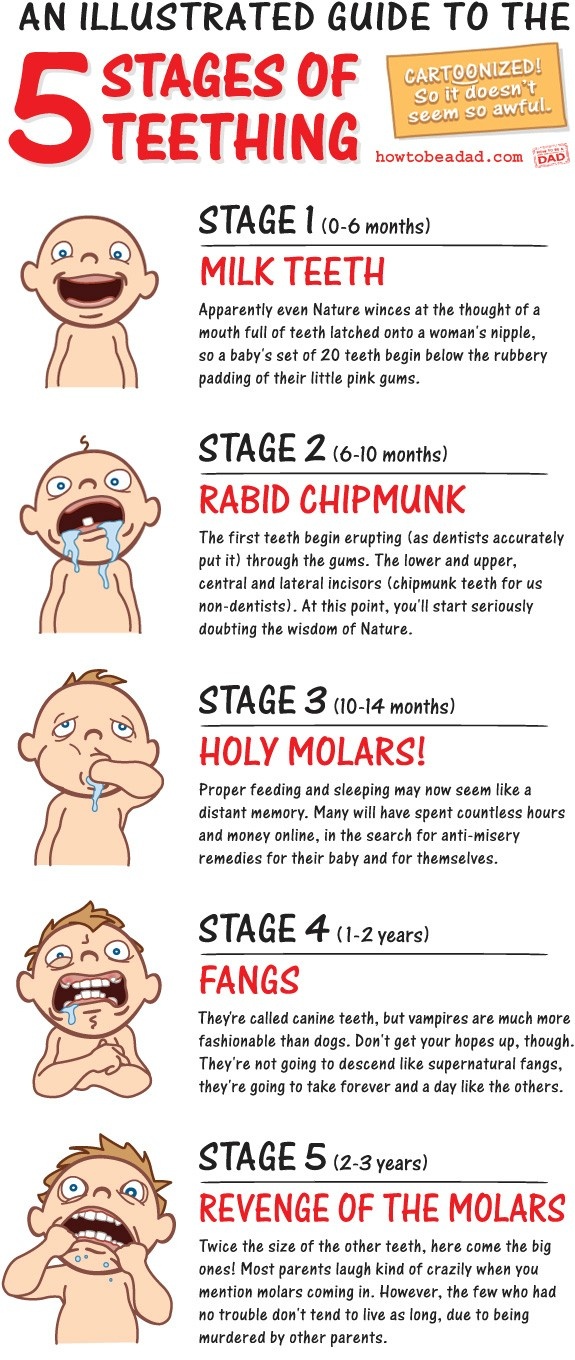
When are you out of the first trimester
Everything you need to know about the first trimester (weeks 1 to 12)
Tommy's PregnancyHub
You’re pregnant: congratulations! The first weeks of your pregnancy are a vital time as your body gets busy building a baby. How exciting!
First trimester: key stages
The first trimester begins on the first day of your last period and lasts until the end of week 12. This means that by the time you know for sure you're pregnant, you might already be five or six weeks pregnant!
A lot happens during these first three months. The fertilised egg rapidly divides into layers of cells and implants in the wall of your womb where it carries on growing. These layers of cells become an embryo, which is what the baby is called at this stage.
During this trimester, your baby grows faster than at any other time. By six weeks, a heartbeat can usually be heard and by the end of week 12, your baby's bones, muscles and all the organs of the body have formed. At this point, your baby looks like a tiny human being and is now called a fetus. He or she will even be practising swallowing!
Try our Healthy Pregnancy Tool to find out everything you need to know about your pregnancy
When am I due?
Find out your due date using our due date calculator!
When will I see a midwife?
Your first midwife appointment (also known as antenatal appointment) is the 'booking' appointment. This usually happens between week 8 and 10 of your pregnancy. Find out how to register with a midwife and when your appointments will be here.
Keeping your baby safe
There are some things that you can do during pregnancy that have an effect on your baby. Find out about them by clicking the link below.
Find the complete list of pregnancy dos and don'ts (and reasons why) here
Not sure whether you are pregnant?
Find out about the symptoms that mean you may be pregnant here.
Your physical and mental health in pregnancy
We also have lots of useful tips for coping with everyday pregnancy niggles. It’s common for women to experience symptoms such as morning sickness, cramp and indigestion during the first trimester.
It’s common for women to experience symptoms such as morning sickness, cramp and indigestion during the first trimester.
Don't forget that your mental health is just as important as your physical health. It's normal to feel some anxiety and stress but it shouldn't be ongoing. If what you’re feeling isn’t normal for you, talk to your GP or midwife about it. They are there to help.
Exercise, such as yoga, has been shown to reduce anxiety and is a great way to stay active during your pregnancy, too.
Read more about mental wellbeing in pregnancy
Read more about diabetes and pregnancy
Read more about pregnancy with a high BMI
Read more about exercise and pregnancy
Read about the symptoms to look out for in pregnancy
Track your baby's development
Sign up to a free pregnancy email from our midwives to track your baby's development and give you reminders of all you need to know through the 9 months of pregnancy. Click here to sign up.
Review dates
Reviewed: 28 June 2018 | Next review: 28 June 2021
This content is currently being reviewed by our team. Updated information will be coming soon.
Updated information will be coming soon.
Back to top
First Trimester Of Pregnancy: What To Expect
What is the first trimester of pregnancy?
Pregnancy has three trimesters or stages. Each trimester is about 13 weeks or three months long. A full-term pregnancy lasts 40 weeks or between nine and 10 months. Your healthcare provider will talk to you about fetal development in terms of weeks. Your first trimester of pregnancy lasts until the 13th week of pregnancy.
It may seem strange, but your pregnancy actually begins on the first day of your last menstrual period. This is called the gestational age of the pregnancy. A pregnancy care provider calculates your due date by adding 40 weeks to the first day of your last menstrual period. So this means, by the time you know you’re pregnant, you’re already about four weeks along. This can be very confusing!
Understanding weeks of pregnancy
The first two weeks of pregnancy are part of your normal menstrual cycle — the first week is your period and the second week is ovulation. Once you ovulate, your egg travels through your fallopian tube to your uterus. If it meets up with sperm, they combine and conception occurs (fertilization).
Once you ovulate, your egg travels through your fallopian tube to your uterus. If it meets up with sperm, they combine and conception occurs (fertilization).
During the third week of pregnancy, the fertilized egg travels to your uterus. On its way down to your uterus, it divides into more cells. Once it reaches your uterus, it implants into your uterine lining. This triggers your body to recognize that you’re pregnant and a series of changes begin to happen. Most people miss their period and then get a positive pregnancy test.
How long is the first trimester?
The first trimester begins before you’re pregnant. It starts on the first day of your last menstrual period and goes until the 13th week of pregnancy.
What can I expect in my first trimester?
Your first trimester of pregnancy is full of many physical and emotional changes. It can be a very overwhelming time, and your mind may be racing with questions. Plus, your hormones are in overdrive. In fact, your body produces more estrogen during one pregnancy than it does during your entire life when you’re not pregnant. This surge in hormones can cause some unpleasant pregnancy symptoms. You may find yourself feeling moody, bloated and tired. While you may not see a prominent baby bump yet, your uterus is expanding and your blood volume is increasing.
This surge in hormones can cause some unpleasant pregnancy symptoms. You may find yourself feeling moody, bloated and tired. While you may not see a prominent baby bump yet, your uterus is expanding and your blood volume is increasing.
It’s OK to feel both excited and nervous. Talking to your friends, partner or a healthcare provider may help you feel better as you navigate your pregnancy journey.
What should I do in my first trimester?
Your first trimester is very important. You might not look or feel pregnant, but lots of changes are happening.
If you don’t have a healthcare provider or a pregnancy care provider, you should find one as soon as possible. Getting early pregnancy care can help you avoid any potential complications. Make a list of questions or concerns you have so you’re ready for your first appointment. Check with your health insurance about pregnancy coverage so you know what to expect and where you can get care. If you don’t have health insurance, there are programs and agencies to help you get prenatal care.
There are different types of pregnancy care providers that take care of you during pregnancy, labor, delivery and postpartum. These include obstetricians, midwives, and sometimes, primary care physicians. In addition to selecting a pregnancy care provider, you may also consider places to deliver your baby. While most people choose to give birth in a hospital, some people prefer birthing centers or home births.
Now is a great time to think about your overall health and what lifestyle changes you may need to make now that you’re pregnant. For example, think about how pregnancy affects your work, finances, habits and daily activities.
How does the fetus develop in the first trimester of pregnancy?
Several developments occur in the first trimester. Although you can’t see it happening, there’s a lot going on inside your body after sperm fertilizes an egg.
Weeks one to four of pregnancy
During the first month of pregnancy, several important structures form. These structures are a tiny clump of cells, but will grow to become the amniotic sac, placenta and umbilical cord. A tube that becomes the fetus’s brain and spinal cord forms, as well as its circulatory system. A face, circles for eyes and the beginning of a mouth take shape.
These structures are a tiny clump of cells, but will grow to become the amniotic sac, placenta and umbilical cord. A tube that becomes the fetus’s brain and spinal cord forms, as well as its circulatory system. A face, circles for eyes and the beginning of a mouth take shape.
The embryo is about a quarter-inch inch long — smaller than a grain of rice.
Weeks five to eight of pregnancy
Several major organs begin to develop during the sixth week of pregnancy including the fetal lungs, heart, ears, arms and legs. Bones begin to replace tissue. Its head is large in proportion to the rest of its body, but it look more human now. The fetus has a distinct mouth, nose and face. Some providers do an early ultrasound to confirm a heartbeat during this time.
By the end of the eighth week of pregnancy, the embryo becomes a fetus. It’s about 1 inch long or the size of a raspberry.
Weeks nine to 12 of pregnancy
Towards the end of your first trimester, the fetus will have toes, fingers and nails. It will start to move by opening and closings its hands and mouth. The fetus’s urinary and digestive systems are also fully functioning. At around 12 weeks of pregnancy, your provider can listen to the fetal heart using a Doppler ultrasound. It also has either a vagina or a penis at this point (though your provider can’t see it on an ultrasound).
It will start to move by opening and closings its hands and mouth. The fetus’s urinary and digestive systems are also fully functioning. At around 12 weeks of pregnancy, your provider can listen to the fetal heart using a Doppler ultrasound. It also has either a vagina or a penis at this point (though your provider can’t see it on an ultrasound).
By the end of the 12th week of pregnancy, the fetus is between 3 and 4 inches long — about the size of a plum. It weighs about 1 ounce.
Why is the first trimester of pregnancy so critical?
The first trimester is so important because most of the fetus’s major organs and body systems are developing. Toxins, harmful substances and infection can severely damage a fetus’s growth and development during this time. It could increase your baby’s risk of being born with a congenital disorder.
What are the most common symptoms during the first trimester?
Every person and every pregnancy is unique. An increase in hormones cause most pregnancy symptoms. Some of the most common are:
Some of the most common are:
- Sore breasts: Hormones may make your breasts feel tender and large. It’s common to need bigger bras before the end of your first trimester. The veins in your breasts may become noticeable because they’re carrying more blood. Other changes to your breasts may include darkened areolas or changes to your nipples.
- Nausea: Morning sickness is one of the telltale signs of early pregnancy. Despite its name, it can last all day and all night. Try eating smaller meals or bland, low-fat foods. Some people find relief by eating foods containing ginger.
- Mood swings: The sudden rush of hormones may put you on a rollercoaster of emotions. You may alternate between feeling anxious or scared to excited or weepy within a span of 30 minutes. It may be helpful to talk through your feelings with a friend or your partner.
- Feeling tired: Your body is hard at work during the first trimester of pregnancy.
 This may leave you feeling exceptionally tired. Be sure to get plenty of rest. Most people get some energy back in the second trimester.
This may leave you feeling exceptionally tired. Be sure to get plenty of rest. Most people get some energy back in the second trimester. - Needing to pee: Your uterus begins to grow to support the pregnancy. It may begin pressing on your bladder, causing you to need to pee more often.
- Acne or other skin changes: Hormones cause your skin to create more oil during pregnancy. This can lead to clogged pores and acne in some people. There are other skin conditions that appear during pregnancy, but most appear in the second or third trimesters.
- Mild shortness of breath: You may feel short of breath with light physical activity.
Your heart is pumping more blood during pregnancy. This means your pulse may be quicker and you may find yourself losing energy more easily. Be mindful of how much demand pregnancy puts on your body and take rests when you feel tired or out of breath.
What tests will I have in the first trimester of pregnancy?
Checkups, screenings and other tests during pregnancy help keep you and the fetus healthy. Care during pregnancy is commonly referred to as prenatal care. Prenatal care appointments are important because your pregnancy care provider discusses what you can expect during pregnancy and delivery, performs checkups and screenings and answers any questions you have.
Care during pregnancy is commonly referred to as prenatal care. Prenatal care appointments are important because your pregnancy care provider discusses what you can expect during pregnancy and delivery, performs checkups and screenings and answers any questions you have.
Your first prenatal visit
You’ll have between two and three prenatal visits during your first trimester. This can vary depending on your provider or if you’re a high-risk pregnancy. You can expect to discuss your personal medical history, gynecological and obstetrical history (prior pregnancies and births), as well any family medical history that may affect your pregnancy. This visit is very thorough to make sure you and the growing fetus are healthy.
At your first prenatal visit your provider will calculate your due date. You can also expect them to perform the following:
- A physical exam, including checking your weight and blood pressure.
- A pelvic exam.
- A Pap test (if you’re due for one).

- Tests to check for certain sexually transmitted infections (STIs).
- Check your pee for bacteria, protein and glucose (sugar).
- Order blood tests to check hormone levels, Rh factor, iron levels and certain diseases.
- Check the fetal heart rate.
Some providers use transvaginal ultrasound at your first appointment to confirm pregnancy and measure the fetal heart rate and size. This ultrasound also shows if you’re expecting multiples. A transvaginal ultrasound involves your provider placing a wand inside your vagina. Most pregnant people are offered at least one ultrasound in their first trimester, but the exact timing varies depending on your provider. If you’re expecting multiples, you may be offered additional ultrasounds in your first trimester.
Your provider may suggest other screening tests during pregnancy. Screening tests identify if you or the fetus are at risk for certain health conditions. Based on the results of your screening, you may need diagnostic tests. Diagnostic tests confirm or rule out health problems. In the first trimester, your provider may suggest a screening to detect a higher risk of chromosomal disorders like Down syndrome. Talk to your provider about the screenings they recommend.
Diagnostic tests confirm or rule out health problems. In the first trimester, your provider may suggest a screening to detect a higher risk of chromosomal disorders like Down syndrome. Talk to your provider about the screenings they recommend.
What should I not do in the first trimester of pregnancy?
Once you find out you’re pregnant, it’s normal to have to make some lifestyle changes. These changes help ensure that everyone is healthy. You should avoid the following things during your first trimester of pregnancy:
- Alcohol.
- Cigarettes and tobacco.
- Recreational drugs like opioids.
- Contact sports like football or activities that put pressure on your abdomen.
- Foods like raw fish (sushi), fish high in mercury, uncooked or undercooked meats, lunchmeat and unpasteurized milk, cheese or juice.
- Hot tubs and saunas.
How do I take care of myself in the first trimester of pregnancy?
Staying healthy is important throughout all three trimesters of pregnancy. Here are some helpful tips on staying healthy during the first 13 weeks of pregnancy:
Here are some helpful tips on staying healthy during the first 13 weeks of pregnancy:
- Stay active as much as you can. Listen to your body and stop for rest if you feel any discomfort while exercising. You may need to modify your exercise routine during pregnancy.
- Take a prenatal vitamin containing folic acid.
- Eat a variety of healthy foods including fruits, vegetables, meat, eggs and whole grains.
- Get plenty of rest.
- Drink plenty of water.
- Attend all of your prenatal appointments.
Is it normal to bleed during the first trimester of pregnancy?
Light bleeding or spotting during pregnancy is usually OK in the first few weeks of pregnancy. Some people experience implantation bleeding (when a fertilized egg burrows unto your uterine lining). Call your pregnancy care provider if you’re bleeding heavily or the bleeding lasts more than one day.
What prenatal vitamin should I take?
The vitamins and minerals in your food (or in prenatal vitamins) help support the fetus as it grows and develops.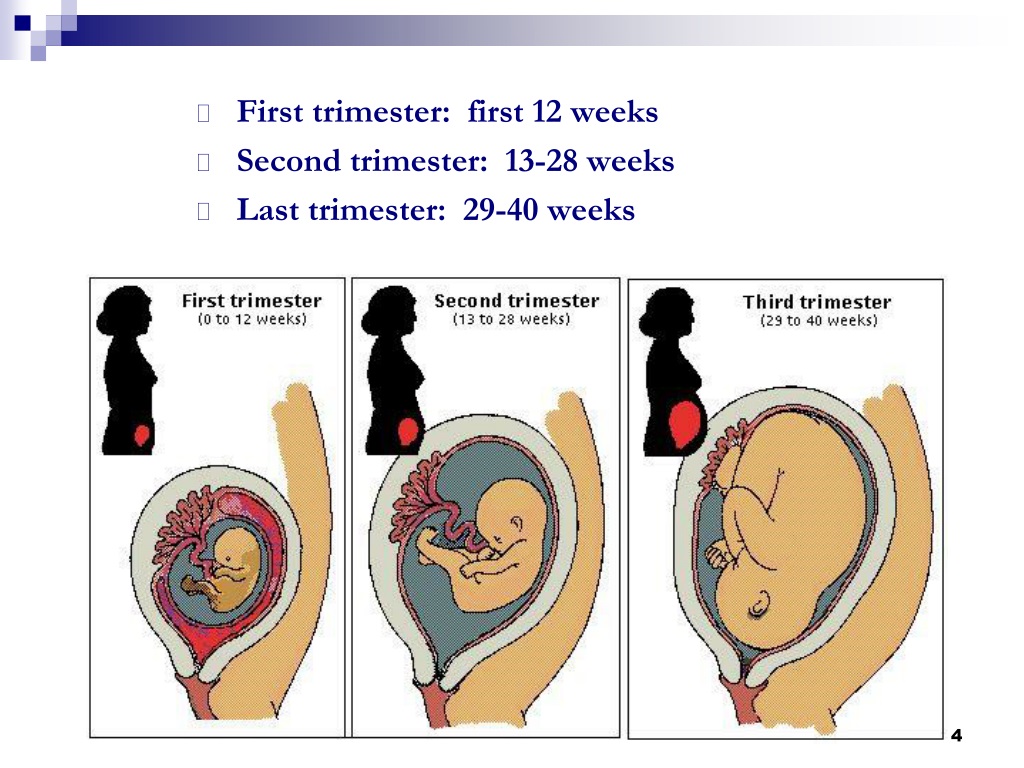 Most providers recommend taking a prenatal vitamin as soon as you begin trying to get pregnant. Vitamins containing folic acid, iron and calcium help support a healthy pregnancy. Talk to your provider if you’re unsure about which prenatal vitamin to take.
Most providers recommend taking a prenatal vitamin as soon as you begin trying to get pregnant. Vitamins containing folic acid, iron and calcium help support a healthy pregnancy. Talk to your provider if you’re unsure about which prenatal vitamin to take.
Can I drink caffeine during pregnancy?
Most healthcare providers recommend limiting caffeine consumption to under 200 milligrams per day during pregnancy. That’s about 12 ounces of coffee or three cans of Mtn Dew®. This is because a fetus can’t metabolize caffeine so it can build up in their body and cause complications.
When should I call my pregnancy care provider during the first trimester?
Call your provider right away if you have:
- A fever higher than 100.4 degrees Fahrenheit.
- Heavy bleeding or unusual vaginal discharge.
- Severe cramping in your belly, arms or legs or abdominal pain.
- Persistent vomiting and/or diarrhea.
- Fainting spells or dizziness.
- Swelling in your hands, fingers or face.
- Blurred vision or spots before your eyes.
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Pregnancy is an exciting, and sometimes scary, time in your life. You may feel overwhelmed with information and have lots of questions. During the first trimester of pregnancy, your body is growing and changing rapidly. The fetus is growing and developing, too. In fact, by the end of the first trimester, the fetus is the size of a lemon. You may begin having symptoms of pregnancy like nausea, sore breasts or needing to pee more often. Schedule an appointment with a pregnancy care provider as soon as you know you’re pregnant. Regular prenatal care is important so you and the fetus stay healthy and strong during pregnancy.
Doctors about pregnancy | Art-Med
Popular medical publications of doctors about pregnancy - planning, first signs, tests, diseases during pregnancy, medication, etc. A reminder for a future mother.
Thyroid gland and pregnancy
Iodine is an essential component of thyroid hormones. Normally, the body of pregnant women should receive 200 mcg of iodine daily. A decrease in iodine intake during pregnancy leads to chronic stimulation of the thyroid gland, a relative decrease in the level of thyroxine in the blood, and the formation of goiter in both the mother and the fetus.
Normally, the body of pregnant women should receive 200 mcg of iodine daily. A decrease in iodine intake during pregnancy leads to chronic stimulation of the thyroid gland, a relative decrease in the level of thyroxine in the blood, and the formation of goiter in both the mother and the fetus.
Placenta and its role in the development of pregnancy - Makarov I.O.
The mature placenta is a disc-shaped structure 15-20 cm in diameter and 2.5-3.5 cm thick. Its mass reaches 500-600 g. The maternal surface of the placenta, which faces the wall of the uterus, has a rough surface formed by the structures of the basal part of the decidua. The fruiting surface of the placenta, which faces the fetus, is covered with an amniotic membrane. Under it are visible vessels that go from the place of attachment of the umbilical cord to the edge of the placenta.
Feto-placental insufficiency (FPI) - Makarov I.O.
Changes in the respiratory function of the placenta are mainly evidenced by symptoms of fetal hypoxia. In this case, at first, the pregnant woman pays attention to the increased (erratic) motor activity of the fetus, then to its decrease or complete absence. The most characteristic sign of chronic feto-placental insufficiency is intrauterine growth retardation.
In this case, at first, the pregnant woman pays attention to the increased (erratic) motor activity of the fetus, then to its decrease or complete absence. The most characteristic sign of chronic feto-placental insufficiency is intrauterine growth retardation.
Pregnancy calendar - Nesyaeva E.V.
Pregnancy is one of the most wonderful periods in a woman's life. What happens inside the uterus, how does your child grow and what changes are typical for the female body? Let's start in order. First of all, I want to remind you that they distinguish between the true gestational age - from the day of conception and obstetric, which is counted from the first day of the last menstruation.
How to behave during pregnancy? - Burkov S.G.
Most women go to the doctor only when they are sick, when the main thing is to cure them, and personal hygiene issues remain in the background. Therefore, I will try to give some reasonable advice regarding the details of personal hygiene.
Physiological pregnancy and related changes in the body - Burkov S.G.
Physiological pregnancy lasts an average of 10 lunar months (1 lunar month - 28 days), i.e. 40 weeks or 280 days. The entire period of pregnancy is usually divided into trimesters. The 1st trimester begins with fertilization and ends at 12-13 weeks, the second - ends at 28 weeks, from the same period the third trimester of pregnancy begins, ending with childbirth.
Iron deficiency anemia in pregnant women - Burkov S.G.
Iron deficiency anemia is a very common disease characterized by a decrease in the iron content in the blood serum and bone marrow, resulting in impaired formation of hemoglobin. Statistics show that at the end of the gestational period, 1/3 of pregnant women develop severe anemia. In recent years, due to a drop in living standards, primarily a deterioration in the quality of nutrition, in our country the number of women with anemia, which is a nutritionally dependent disease, has increased significantly.
First signs of pregnancy
How can you tell if you are pregnant or not? Suppose you have a delay in the next menstruation. A day, two, a week passes - there is no menstrual bleeding. And you feel nausea in the morning, the mammary glands seem heavy. Or there is excessive drowsiness, the usual actions of others cause irritation, and some smells are simply unbearable. It is possible that your appetite has increased, and food disappears from the refrigerator with unusual speed and in strange combinations. At the same time, drooling also flows, night trips to the toilet have become more frequent, and even during the day, long walks are problematic because of the frequent urge to urinate.
Arterial hypertension and pregnancy - Burkov S.G.
Doctors define arterial hypertension (hypertension) as a disease, the leading symptom of which is a persistent increase in blood pressure (BP), caused by neuro-functional disorders of vascular tone.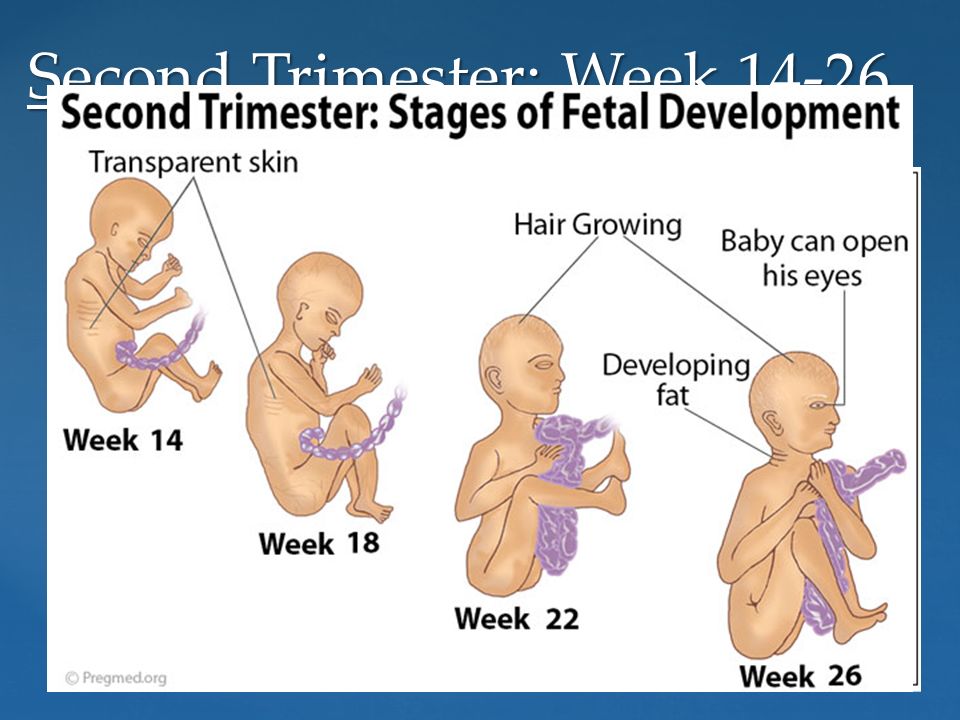 It is always necessary to limit the disease from the so-called symptomatic hypertension, in which an increase in blood pressure is a symptom of the disease and, moreover, far from being the main one.
It is always necessary to limit the disease from the so-called symptomatic hypertension, in which an increase in blood pressure is a symptom of the disease and, moreover, far from being the main one.
Varicose disease and pregnancy - Burkov S.G.
20-50% of pregnant women have varicose veins in the lower extremities. Sometimes it is combined with varicose veins of the external and internal genital organs, less often - the mammary glands. To a large extent, hormonal changes occurring in the body of a pregnant woman are predisposing ...
Arterial hypotension and pregnancy - Burkov S.G.
Often during pregnancy, especially at its beginning, there is a decrease in blood pressure. This condition is called arterial hypotension.
Boy or girl? Who do we want - sex or a child?
It is not uncommon for a married couple to give preference - sometimes quite categorical - to a certain gender of the expected baby. It happens that the mood for one or another gender of the child is especially pronounced in one of the spouses, the eldest child, or the future grandmother (or future grandfather). This is a very dramatic situation for the whole family and especially for the unborn child, as he comes into this world as an outcast and lives with this feeling.
It happens that the mood for one or another gender of the child is especially pronounced in one of the spouses, the eldest child, or the future grandmother (or future grandfather). This is a very dramatic situation for the whole family and especially for the unborn child, as he comes into this world as an outcast and lives with this feeling.
Uterine fibroids and pregnancy
The classic manifestations of uterine fibroids are prolonged cyclic (i.e., regular, corresponding to the menstrual cycle) bleeding (menorrhagia), which is often accompanied by acyclic (irregular) uterine bleeding (metrorrhagia). When these symptoms appear, you should go to the gynecologist. Difficulties in conception caused by fibroids are explained by a variety of factors, including compression of the fallopian tubes, which impedes the movement of spermatozoa, and impaired ovulation.
Pyelonephritis and pregnancy
Pyelonephritis is an infection of the upper urinary tract, i. e. kidneys and renal pelvis. Acute pyelonephritis occurs in 12% of pregnant women, more often during the first pregnancy, as a rule, in the second half of it (in most cases on the 20-26th week). The disease begins with fever up to 38-40 degrees, chills, headache, general malaise, pain in the limbs. Nausea and vomiting may occur. Usually there is frequent painful urination, pain when urinating, there is pain in the lower back and costovertebral angle.
e. kidneys and renal pelvis. Acute pyelonephritis occurs in 12% of pregnant women, more often during the first pregnancy, as a rule, in the second half of it (in most cases on the 20-26th week). The disease begins with fever up to 38-40 degrees, chills, headache, general malaise, pain in the limbs. Nausea and vomiting may occur. Usually there is frequent painful urination, pain when urinating, there is pain in the lower back and costovertebral angle.
Narrow pelvis - features of pregnancy and childbirth - Makarov I.O.
With an anatomically narrow pelvis in nulliparous women, the fetal head, due to a discrepancy with the size of the pelvis, remains mobile over the entrance to the pelvis in the last weeks of pregnancy. In this regard, the bottom of the uterus rises higher than usual, which makes it difficult for the heart and lungs to work. In the presence of a narrow pelvis, prerequisites are created for the formation of a transverse and oblique position of the fetus, for incorrect insertion of the head or its extensor presentation.
Illegal pregnancy - Makarov I.O.
A miscarriage, also called a missed pregnancy, results in the death of the embryo/fetus, but there are no clinical signs of spontaneous miscarriage. What you need to know about a missed pregnancy and how to reduce the likelihood of miscarriage.
Urinary tract infection during pregnancy - Makarov I.O.
During pregnancy, conditions are created for stagnation of urine and disturbance of its outflow due to a significant expansion of the renal pelvis, elongation of the ureters, a decrease in the tone and contractility of the muscles of various parts of the urinary system, and displacement of the kidneys. In addition, the outflow of urine from the kidneys worsens due to the mechanical pressure of the pregnant uterus on the ureters. In this regard, in 1/3 of pregnant women there is a reverse reflux of urine from the bladder into the ureters, which contributes to the spread of infectious agents to the upper urinary system.
Antiphospholipid syndrome and pregnancy - Makarov I.O.
One of the main and most dangerous clinical manifestations of antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) is recurrent thrombosis. Most often, venous thrombosis occurs, localized in the deep veins of the legs, which is associated with the risk of developing thromboembolism of the branches of the pulmonary artery. Clinical manifestations of arterial thrombosis are peripheral gangrene, aortic arch syndrome, blindness, cerebral circulation disorders, etc. The risk of thrombotic complications increases with the course of pregnancy and in the postpartum period.
The role of the therapist in planning and managing pregnancy - Zosimova Yu.M.
It is known that the planning and management of pregnancy is mainly the prerogative of obstetrician-gynecologists. And yet, why is it that the general practitioner or family doctor is given such a big role all over the world? In order to understand why the timely diagnosis and treatment of extragenital (not related to the reproductive system) diseases are so extremely important for choosing the right tactics for managing pregnancy and delivery, let's consider some forms of diseases that accompany pregnancy.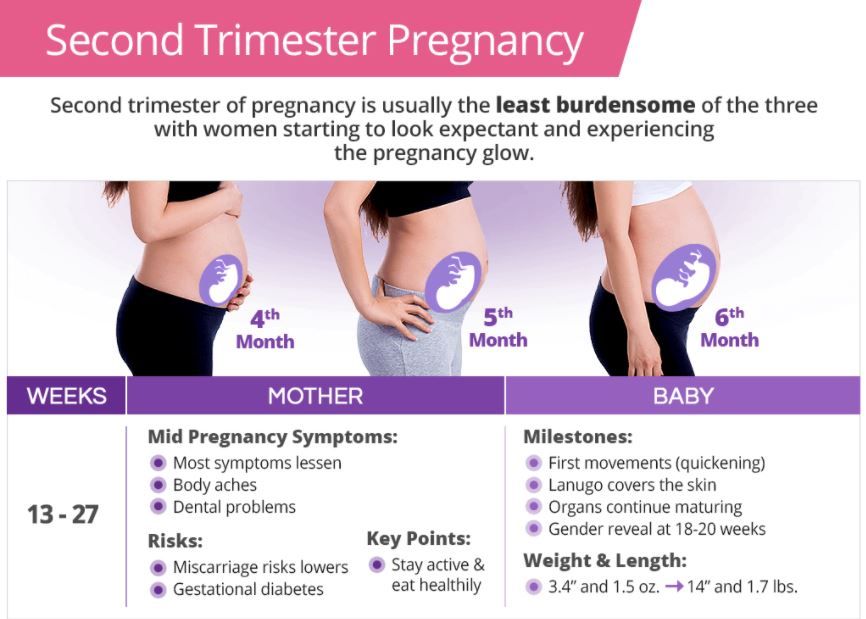
Early toxicosis - Makarov I.O.
Vomiting in pregnant women in the first trimester is one of the most common manifestations of early toxicosis. With a normal pregnancy, the presence of nausea and vomiting is acceptable no more than 2-3 times a day in the morning on an empty stomach, which does not violate the general condition of the patient and does not require treatment. As a rule, by 12-13 weeks, nausea and vomiting stop. Vomiting is pathological, which is observed several times during the day, regardless of food intake, accompanied by a decrease in appetite, a change in taste and olfactory sensations, a feeling of weakness, and a decrease in body weight.
Preeclampsia - Makarov I.O.
Preeclampsia or late toxicosis of pregnant women is a complication of pregnancy that occurs in the second half and is characterized by dysfunction of vital organs and systems. Preeclampsia is divided into dropsy of pregnancy, nephropathy of pregnancy, preeclampsia and eclampsia.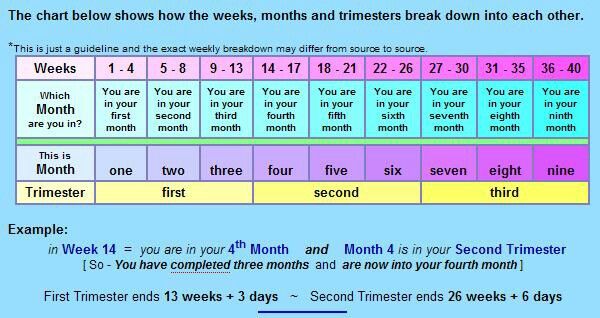 Dropsy of pregnant women, due to fluid retention in the body, is characterized by persistent edema and is one of the early symptoms of preeclampsia. Latent edema is evidenced by pathological (more than 300 g per week) or uneven weekly weight gain.
Dropsy of pregnant women, due to fluid retention in the body, is characterized by persistent edema and is one of the early symptoms of preeclampsia. Latent edema is evidenced by pathological (more than 300 g per week) or uneven weekly weight gain.
How to plan the sex of the unborn child? Conception of a boy or girl - Komova O.A.
The expectation and birth of a baby is one of the most significant events in a family's life. The question of who will be born - a son or a daughter - is also one of the main ones, especially if the family already has children. Often, future parents, even at the stage of pregnancy planning, begin to study popular literature, listen to the advice of friends, follow the numerous recommendations of healers - and all with one goal: to give birth to a child of the desired gender ...
Bacterial infections during pregnancy - Makarov I.O.
Among the inflammatory diseases of bacterial origin that occur during pregnancy, a significant place is occupied by conditions caused by disturbances in the normal microflora of the genitourinary tract. Bacterial vaginosis occurs in 15 - 20% of pregnant women, and is a serious risk factor for the development of infectious complications. In the first trimester of pregnancy, for the treatment of bacterial vaginosis, it is possible to prescribe clindamycin 2% in the form of a vaginal cream of 5.0 g for 3-7 days or povidone-iodine 1 vaginal suppository per day for 14 days or from the 10th week Terzhinan 1 vaginal tablet 10 days.
Bacterial vaginosis occurs in 15 - 20% of pregnant women, and is a serious risk factor for the development of infectious complications. In the first trimester of pregnancy, for the treatment of bacterial vaginosis, it is possible to prescribe clindamycin 2% in the form of a vaginal cream of 5.0 g for 3-7 days or povidone-iodine 1 vaginal suppository per day for 14 days or from the 10th week Terzhinan 1 vaginal tablet 10 days.
Changes in the digestive, endocrine and urinary systems during pregnancy - Makarov I.O.
Due to the hypotonic effect of progesterone on the smooth muscles of the intestines, constipation is often noted in pregnant women. The absorption in the intestine of microelements, water, nutrients increases. In the first months of pregnancy, there is an increase in appetite, which later becomes common. Often there are various changes in taste sensations, certain taste whims or intolerance to certain products appear, which is associated with hormonal changes, as well as with a decrease in the secretory function of the gastrointestinal tract.
Changes in the respiratory and immune systems during pregnancy - Makarov I.O.
Changes in the immune system in a woman during pregnancy are aimed at ensuring the development of the fetus, which is an antigen-foreign body for the mother's body. Changes that occur before 16 weeks of pregnancy are aimed at creating a favorable immune background for implantation of the fetal egg, growth and development of the fetus and placenta. Immunocompetent cells of the reproductive system and regional lymph nodes, reacting to the embryo, provide local immunity of the uterus during pregnancy.
Changes in the cardiovascular system, blood and metabolism during pregnancy - Makarov I.O.
The changes in the cardiovascular system that occur during pregnancy are aimed at ensuring the vital activity of the pregnant woman's body, as well as delivering sufficient oxygen and nutrients to the fetus and removing its metabolic products.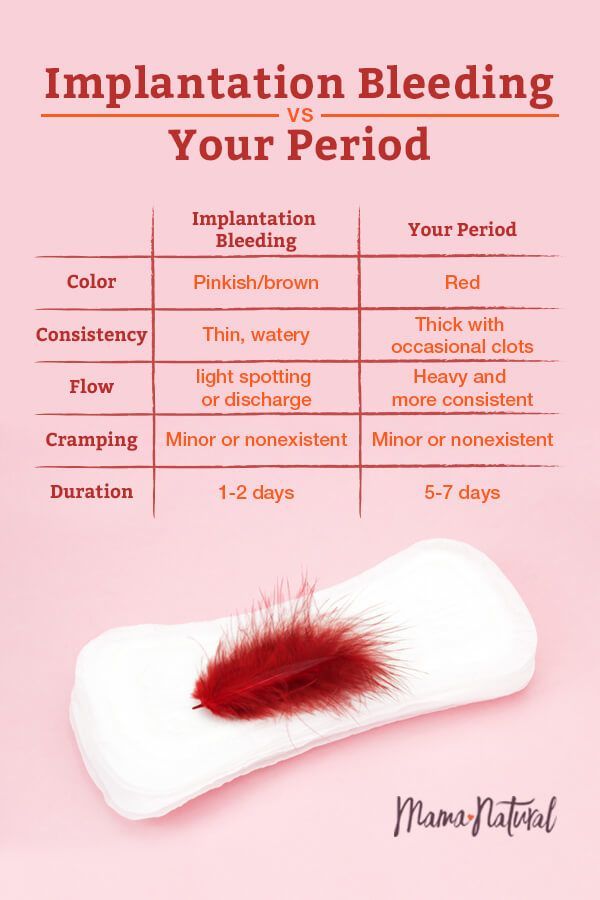 An increase in the volume of circulating blood is noted from the first trimester of pregnancy, reaching maximum values by 36 weeks. Starting from the middle of pregnancy, in the supine position, the enlarged uterus can compress the inferior vena cava and aorta.
An increase in the volume of circulating blood is noted from the first trimester of pregnancy, reaching maximum values by 36 weeks. Starting from the middle of pregnancy, in the supine position, the enlarged uterus can compress the inferior vena cava and aorta.
Multiple pregnancy - twins and twins - Nesyaeva E.V.
A woman's ovaries normally produce one egg each cycle. In this case, the ovaries work alternately. Under the influence of a wide variety of factors, the maturation of several eggs can occur - in one or both ovaries. If a woman has several sexual partners, it is possible for the eggs to be fertilized by the sperm of different men, respectively, in this situation, the twins can have different fathers.
Changes in the genital organs and mammary glands during pregnancy - Makarov I.O.
Under the influence of hormones (progesterone and estrogens), adaptive changes occur in the body of a pregnant woman, the vaginal epithelium thickens under the influence of estrogen, and the process of its desquamation is activated, which leads to an increase in the amount of discharge from the vagina. The fallopian tubes become thicker during pregnancy, their blood supply increases, and cyclic processes in the ovaries stop. Bifidobacteria, located on the surface of the epithelial cells of the vagina, are able to produce a number of biologically active substances, which ensures the creation of a biological barrier.
The fallopian tubes become thicker during pregnancy, their blood supply increases, and cyclic processes in the ovaries stop. Bifidobacteria, located on the surface of the epithelial cells of the vagina, are able to produce a number of biologically active substances, which ensures the creation of a biological barrier.
Prenatal viral infection - Makarov I.O.
In the diagnosis of intrauterine infection, immunological tests are used to detect specific antibodies to pathogens, the cultural method (inoculation), as well as the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) method. For the study, blood and material taken from the vagina and from the cervical canal are used. In some cases, amniotic fluid obtained by amniocentesis is used for research. Let us dwell on the most typical viral diseases of the embryo and fetus.
Spontaneous abortion or miscarriage - Makarov I.O.
Spontaneous termination of pregnancy before 22 weeks from the first day of the last menstrual period is classified as spontaneous abortion or miscarriage. The frequency of this complication of pregnancy reaches 15% -20%. For the abortion that has begun, an increase in the contractile activity of the uterus is characteristic. Cramping pains become more pronounced. Blood discharge from the vagina is due to partial detachment of the fetal egg from the uterine wall. The cervical canal may be closed or slightly open.
The frequency of this complication of pregnancy reaches 15% -20%. For the abortion that has begun, an increase in the contractile activity of the uterus is characteristic. Cramping pains become more pronounced. Blood discharge from the vagina is due to partial detachment of the fetal egg from the uterine wall. The cervical canal may be closed or slightly open.
Diseases of the liver and biliary tract during pregnancy - Makarov I.O.
During pregnancy, the load on the liver increases significantly due to changes in carbohydrate, fat and protein metabolism. In the liver, inactivation of steroid hormones increases. Its detoxification function is somewhat reduced. Correct and timely identification of the causes of liver and biliary tract disease is important for resolving questions about the tactics of pregnancy and predicting its outcome.
Pregnancy and appendicitis - Makarov I.O.
The main prerequisite for the development of appendicitis during pregnancy is the displacement of the caecum along with the appendix upward and outward due to an increase in the pregnant uterus. In this case, the vermiform appendix is bent, stretched, blood supply deteriorated and emptying is disturbed. Often occurring during pregnancy, the tendency to constipation contributes to the stagnation of intestinal contents and an increase in the activity of the intestinal microflora.
In this case, the vermiform appendix is bent, stretched, blood supply deteriorated and emptying is disturbed. Often occurring during pregnancy, the tendency to constipation contributes to the stagnation of intestinal contents and an increase in the activity of the intestinal microflora.
Tuberculosis and pregnancy - Makarov I.O.
If active pulmonary tuberculosis is suspected, x-rays are required, regardless of gestational age. The fear of using this method in pregnant women can lead to a belated diagnosis of an advanced tuberculous process. During chest x-rays in pregnant women, special techniques and protective equipment are used to minimize the possibility of x-ray damage to the fetus.
Diseases of the nervous system and pregnancy - Makarov I.O.
With neuralgia of the lateral femoral cutaneous nerve, due to its compression under the inguinal ligament, paresthesia, burning, numbness and decreased sensitivity along the outer surface of the thigh occur. These sensations increase in the standing position and decrease with hip flexion. This complication usually occurs in the third trimester of pregnancy and disappears within a few weeks after delivery.
These sensations increase in the standing position and decrease with hip flexion. This complication usually occurs in the third trimester of pregnancy and disappears within a few weeks after delivery.
Respiratory diseases and pregnancy - Makarov I.O.
Treatment of bronchitis in pregnant women is to combat intoxication and restore impaired bronchial function. In this case, patients are prescribed a drink: hot tea with honey and lemon, milk with soda or alkaline mineral water, linden tea, decoctions of thyme, thermopsis, coltsfoot. It is possible to use expectorants and mucolytics (bromhexine, bisolvon), as well as antitussives (libexin, glauvent).
Arterial hypotension and pregnancy - Makarov I.O.
The development of hypotension in pregnant women is explained by the inhibition of ovarian function, the influence of the placenta, the action of prostaglandins, the immune response to placental and fetal antigens, resulting in a reduced or increased release of a number of biological substances that affect vascular tone. Among the many causes of arterial hypotension in pregnant women are adrenal dysfunction, neurological disorders, vegetative pathology, disruption of the central mechanisms of blood circulation regulation, prolonged physical inactivity, malnutrition, and much more.
Among the many causes of arterial hypotension in pregnant women are adrenal dysfunction, neurological disorders, vegetative pathology, disruption of the central mechanisms of blood circulation regulation, prolonged physical inactivity, malnutrition, and much more.
Diabetes mellitus and pregnancy - Makarov I.O.
During pregnancy, the course of diabetes changes significantly. Three stages of these changes can be distinguished. In the first trimester of pregnancy, the course of the disease improves. The level of glucose in the blood decreases, the sensitivity of tissues to insulin increases, which can lead to the development of hypoglycemia. From 13 weeks of pregnancy, there is a deterioration in the course of the disease, an increase in hyperglycemia, which can lead to ketoacidosis and precoma.
Diseases of the urinary system during pregnancy - Makarov I.O.
Acute cystitis (inflammation of the bladder mucosa) is the most common type of inflammatory disease of the urinary system in women. Among pregnant women, acute cystitis develops in 1-3% of women, more often in the first trimester, when the uterus is still in the small pelvis and puts pressure on the bladder.
Among pregnant women, acute cystitis develops in 1-3% of women, more often in the first trimester, when the uterus is still in the small pelvis and puts pressure on the bladder.
Miscarriage - Odareeva E.V.
The main causes of miscarriage and spontaneous abortion include genetic factors, STDs, endocrine disorders, immune factors, uterine diseases (myoma, developmental anomalies, etc.). Let us consider in more detail the influence of the main factors leading to miscarriage and the features of therapeutic and diagnostic measures in these situations.
Trophoblastic disease - Makarov I.O.
Taking medication during pregnancy - Makarov I.O.
There is no doubt that various drugs can have a negative effect on the fetus. However, the degree of this influence is very diverse and depends on many factors, which will be presented in more detail below. Even medications that are widely used and approved during pregnancy can cause various complications in the fetus and newborn.
Diseases of the adrenal cortex and pregnancy - Makarov I.O.
The causes of dysfunction of the adrenal cortex are the inferiority of enzymatic processes, congenital hyperplasia of the adrenal cortex as a result of a genetic defect in one or more enzyme systems. Changes in enzyme systems in the adrenal cortex can be the cause of primary hyper- and hypoaldosteronism, occurring with symptoms of insufficient or excessive adrenal function.
Pregnancy (memo for the expectant mother) - Makarov I.O.
When planning a pregnancy, no matter what the number, you should remember that in general, pregnancy should occur against a favorable background. If the previous pregnancy ended unsuccessfully for some reason, it is not at all necessary that the same complications may arise again.
Immunological incompatibility of maternal and fetal blood - Makarov I.O.
Sometimes during pregnancy there is an immunological incompatibility of the blood of the mother and fetus (Rhesus conflict), which can subsequently develop into hemolytic disease of the fetus and newborn. For this reason, anti-Rhesus immunoglobulin is administered to pregnant women with Rh-negative blood at week 28; after childbirth, the administration of immunoglobulin is repeated in the first 48-72 hours.
For this reason, anti-Rhesus immunoglobulin is administered to pregnant women with Rh-negative blood at week 28; after childbirth, the administration of immunoglobulin is repeated in the first 48-72 hours.
Intrauterine infection - Makarov I.O.
Due to the high level of infection in pregnant women at the present time, as well as the risk of impaired fetal development and the birth of a sick child, the problem of intrauterine infection of the fetus is one of the most urgent in obstetric practice. Although the presence of infection in the mother is a risk factor for intrauterine infection of the fetus, this does not always lead to his disease.
Post-term pregnancy - Makarov I.O.
Postponement of pregnancy is one of the important problems due to the higher rate of complications in childbirth, more frequent operative delivery and poorer birth outcomes. It is known that the duration of a normal pregnancy is an average of 280 days. If the duration of pregnancy increases by 10-14 days or more, i.e. is over 294 days, then pregnancy is possible.
If the duration of pregnancy increases by 10-14 days or more, i.e. is over 294 days, then pregnancy is possible.
Superstitions related to pregnancy and childbirth - Komova O.A.
Any woman who is expecting a child knows that in her position she is doomed to listen to numerous advice from relatives and friends, and sometimes even from complete strangers. Among such advice, most of all are prohibitions. Don't do it, don't walk, don't look, don't eat... How can you figure out which of these instructions are justified "from a medical point of view", and which ones are just a tribute to the beliefs of our great-great-great-grandmothers. But you can still figure it out.
Pregnancy - traffic rules - Komova O.A.
When it comes to pregnancy, many people imagine the image of a clumsy, overweight woman with a big belly. Most expectant mothers fearfully expect that their growing belly is about to make it difficult for them to move around. However, it is most likely that these sensations will never become familiar to you. After all, the stomach grows gradually, and you can easily adapt to this. However, from the very beginning of pregnancy, changes begin in a woman's body, which must be taken into account when you walk, sit, lie down, and do housework.
However, it is most likely that these sensations will never become familiar to you. After all, the stomach grows gradually, and you can easily adapt to this. However, from the very beginning of pregnancy, changes begin in a woman's body, which must be taken into account when you walk, sit, lie down, and do housework.
Non-developing pregnancy - Nesyaeva E.V.
Unfortunately, situations are not uncommon when the onset of pregnancy at some stage stops its development and is interrupted. Intrauterine death of an embryo in the early stages of development (up to 28 weeks) is called a non-developing pregnancy. Most often this occurs in the first trimester - up to 12 weeks. Of course, it is difficult for a woman "attuned" to motherhood to survive the loss of a child - even at a very early stage of pregnancy. However, realizing all the drama of this situation, we will not touch on its psychological aspects for the time being and will focus on the medical aspects - first of all, so that those who have suffered such a misfortune have the opportunity to objectively assess their condition, learn about its causes and, if possible, make sure it doesn't happen again.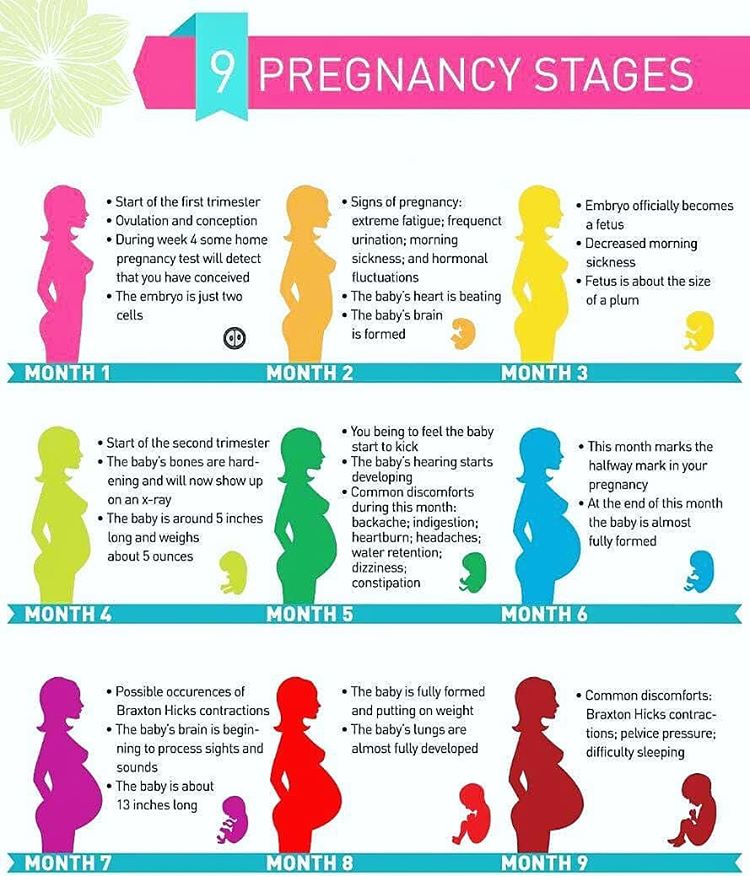
Unable to get pregnant? - Nesyaeva E.V.
Every married couple sooner or later plans to conceive and give birth to a child. Unfortunately, not everyone succeeds. The absence of pregnancy with regular unprotected intercourse for 1 year is called infertility.
What is CTG? - Makarov I.O.
CTG (cardiotocography) is a method of functional assessment of the state of the fetus during pregnancy and childbirth based on the registration of its heart rate and its changes depending on uterine contractions, the action of external stimuli or the activity of the fetus itself.
How to determine ovulation? - Makarov I.O.
For correct pregnancy planning, identification of various disorders of the reproductive system, selection of the optimal method of contraception, it is necessary to have a clear idea of the nature of a woman's menstrual function, one of the key elements of which is ovulation.
Complications during pregnancy - Makarov I.O.
Early toxicosis, bleeding, pain in the lower abdomen and lower back, increased uterine tone - how to avoid complications during pregnancy? The entire period of pregnancy is usually divided into three parts - trimesters. The first trimester is the early fetal period, which lasts up to 12 weeks. In the first trimester of pregnancy, 1 week after fertilization, the implantation of the fetal egg occurs, the formation of the future placenta and the development of the embryo begin.
Caesarean section - Makarov I.O.
Pregnancy and TORCH infections - Komova O.A.
Here is the pregnancy card. Now your position as a future mother is fixed not only by subjective feelings, but also by an official document. But there are some points that can somewhat overshadow your good mood. This is an analysis. And not only the usual ones - urine or blood, but also some mysterious tests "for infections.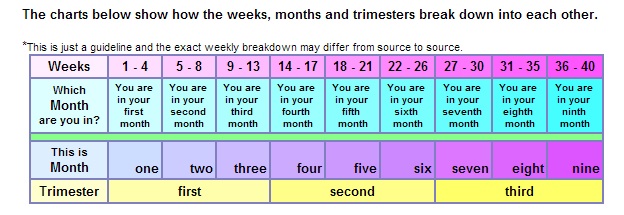 " You may wonder: "I'm not sick, why is all this necessary?"
" You may wonder: "I'm not sick, why is all this necessary?"
Urine and blood tests for hormones during pregnancy - Komova O.A.
During pregnancy, the hormonal background of a woman changes - such a phrase can often be heard when explaining many processes occurring in the body of a future mother. What is the hormonal background and how does it affect the course of pregnancy and the development of the baby? Hormones are produced by special glands or individual cells, released into the blood and carried throughout the body normally causing a certain biological effect. So, for example, progesterone ensures the preservation of pregnancy, it is "responsible" for the normal attachment of the fetal egg to the uterus and for its development.
Late pregnancy
Do you remember the wife of Taras Bulba, who accompanied her adult sons to the Zaporozhian Sich? "Poor old woman" - this is how Gogol calls this woman, who was at most forty years old. Unloved, aged early, turned ugly, covered with premature wrinkles, "she was pitiful, like any woman of that remote century" ... Five centuries have passed - and how our life has changed. Now it would hardly occur to anyone to call a forty-year-old woman an old woman. Few people will be surprised to meet her on the street with a stroller. And it will be almost impossible to guess who it is - a young grandmother or a young mother.
Unloved, aged early, turned ugly, covered with premature wrinkles, "she was pitiful, like any woman of that remote century" ... Five centuries have passed - and how our life has changed. Now it would hardly occur to anyone to call a forty-year-old woman an old woman. Few people will be surprised to meet her on the street with a stroller. And it will be almost impossible to guess who it is - a young grandmother or a young mother.
Multiple pregnancy - Makarov I.O.
A multiple pregnancy is a pregnancy in which two or more fetuses develop simultaneously (twins, triplets, etc.). Children born in multiple pregnancies are twins. Multiple pregnancy occurs in 0.4 - 1.6% of cases. Currently, there is a tendency to increase the frequency of its occurrence due to the more active use of assisted reproduction technologies, including in vitro fertilization.
Laboratory screening during pregnancy - Makarov I.O.
The main purpose of laboratory screening is to identify patients at risk for possible fetal abnormalities.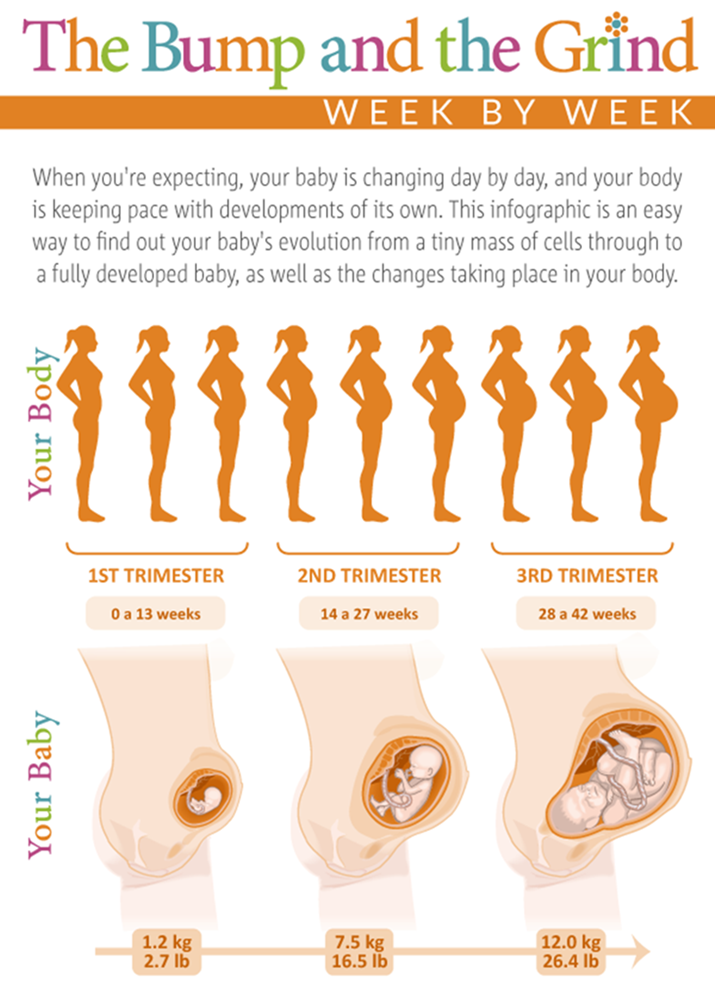 In addition to malformations, deviations from the norm of the studied parameters may indicate a possible risk of various complications during the course of pregnancy.
In addition to malformations, deviations from the norm of the studied parameters may indicate a possible risk of various complications during the course of pregnancy.
Miscarriage - Nesyaeva E.V.
Unfortunately, situations are not uncommon when the onset of pregnancy at some stage stops its development and is interrupted. Miscarriage is considered to be spontaneous interruption of pregnancy from the beginning of the development of the embryo to 37 weeks of pregnancy. Depending on the period of interruption, spontaneous miscarriage is distinguished (up to 16 weeks - early, from 17 to 28 weeks - late) and premature birth (from 29up to 37 weeks of pregnancy).
3rd trimester of pregnancy
So, the seventh month of pregnancy has begun. Many women breathe a sigh of relief: there is not so long left. In addition, you have already got used to your situation and have learned to cope with the difficulties that arise. What complications await the expectant mother at the "finish line"?
2nd trimester of pregnancy
By the fourth month of pregnancy, the risk of complications decreases significantly. Of all cases of spontaneous abortion, this period accounts for less than 25% - these are the so-called late miscarriages. Although the development of an ectopic pregnancy may still continue in the second trimester, in the vast majority of cases it is still detected in the first three months.
ARI during pregnancy - Nesyaeva E.V.
Pregnancy is a special state in a woman's life when, while taking care of her health, she also takes care of the health of her baby. It must not be forgotten that the fetus is formed from the mother's egg and the father's sperm, so it is half a foreign organism for a woman. And the immune system, in order not to reject this "foreign" half, is in a state of immunosuppression...
Popular about medical genetic counseling in obstetrics
What is the main concern of a pregnant woman? Of course, whether the child will be born full and healthy. The patient receives answers to this question, mainly from her obstetrician, leading the pregnancy. But there are situations when the obstetrician may also be in a difficult position and will not be able to correctly explain the problem that has arisen and give the right advice to the pregnant woman.
The patient receives answers to this question, mainly from her obstetrician, leading the pregnancy. But there are situations when the obstetrician may also be in a difficult position and will not be able to correctly explain the problem that has arisen and give the right advice to the pregnant woman.
1st trimester of pregnancy
The first trimester of pregnancy is a great time, but be prepared for the fact that it is at this stage that a woman will face most of the difficulties and problems that she is destined to face throughout her pregnancy.
The question is asked by Natalia, - a question-answer from the specialists of the clinic "Mother and Child"
Natalia:
10/23/2014
Hello! I really need your help. I am 10 weeks pregnant. (Last period July 26) This is my third pregnancy. The first one went well without complications and in 2001 I gave birth to a healthy boy. True, she gave birth with ruptures and there was a divergence of the sutures in the vagina, but after childbirth this did not bother in any way. The second time the pregnancy ended at 9weeks of abortion, because the doctors said that the pregnancy stopped ... After that, I once again passed all the tests - they all gave a negative. the result, except for ureaplasmosis () but I had it in my first pregnancy and I did not treat it with anything. In March last year, my husband and I were completely treated and here is a new pregnancy. But since the 4th week, my lower abdomen has been constantly hurting. Was at the reception: at 6 weeks they did an ultrasound scan, everything is fine with the child, the development is acc. term, but the uterus is in good shape. I took a course of duphaston for 10 days, 1 tab. 2 times a day, suppositories with papaverine-2r / d, and intramuscularly 5 injections of hCG (1 time / d every other day). There were no discharges and there are none, but the stomach still hurts. I passed hormonal tests: DHA-1, 5 (at a rate of up to 1, 3), all tests for infections (there is immunity to rubella, cytomegalovirus, the rest are negative), TSH, hCG, testosterone, progesterone are normal.
The second time the pregnancy ended at 9weeks of abortion, because the doctors said that the pregnancy stopped ... After that, I once again passed all the tests - they all gave a negative. the result, except for ureaplasmosis () but I had it in my first pregnancy and I did not treat it with anything. In March last year, my husband and I were completely treated and here is a new pregnancy. But since the 4th week, my lower abdomen has been constantly hurting. Was at the reception: at 6 weeks they did an ultrasound scan, everything is fine with the child, the development is acc. term, but the uterus is in good shape. I took a course of duphaston for 10 days, 1 tab. 2 times a day, suppositories with papaverine-2r / d, and intramuscularly 5 injections of hCG (1 time / d every other day). There were no discharges and there are none, but the stomach still hurts. I passed hormonal tests: DHA-1, 5 (at a rate of up to 1, 3), all tests for infections (there is immunity to rubella, cytomegalovirus, the rest are negative), TSH, hCG, testosterone, progesterone are normal. The doctor prescribed dexamethasone 1r / d for 1/4, but in the annotation I read that in the first trimester it is possible only for health reasons. Even at 6 weeks for 3 days there was a severe runny nose with lacrimation, it was very hard to endure. Could this have affected the child? Please, I know you have a lot of questions, but I really need your answer. Why can the stomach hurt and is it dangerous for the child - we really want a healthy child! And is it necessary to take dexamethasone, maybe you can get by with less dangerous means, please advise?! Thank you in advance, good health to you and your loved ones.
The doctor prescribed dexamethasone 1r / d for 1/4, but in the annotation I read that in the first trimester it is possible only for health reasons. Even at 6 weeks for 3 days there was a severe runny nose with lacrimation, it was very hard to endure. Could this have affected the child? Please, I know you have a lot of questions, but I really need your answer. Why can the stomach hurt and is it dangerous for the child - we really want a healthy child! And is it necessary to take dexamethasone, maybe you can get by with less dangerous means, please advise?! Thank you in advance, good health to you and your loved ones.
Clinic "Mother and Child" Kuntsevo:
01/26/2021
Dear Natalia, Drawing pains in the lower abdomen is a fairly common symptom in the first 12-14 weeks of pregnancy. If all the data (tests, ultrasound) are within the normal range, this indicates a normal pregnancy. Pregnancy develops in the uterus, the uterus is a muscular organ, the property of the muscle is sometimes reduced and this is the norm.