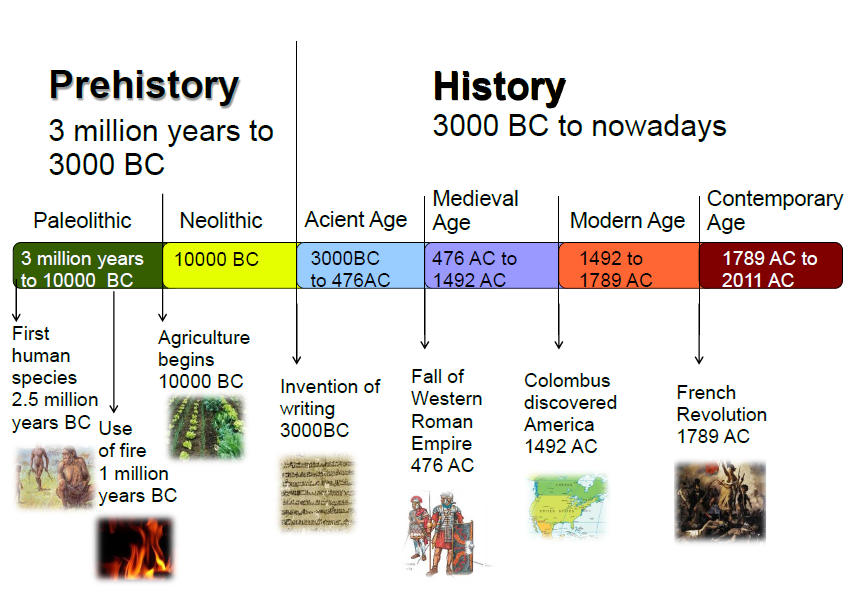
How to find the chronological age of a child
Chronological Age Calculator [Easy Calculate Person's Age]
Your chronological age represents how old you are. By definition, this is the number of years you’ve lived starting from the time of your birth. A person’s chronological age would determine his eligibility for school, for work, and for retirement. To find your chronological age, subtract your date of birth from the current date. When you subtract dates, it’s similar to when you subtract numbers. The only difference is that when you subtract months, you only use numbers 1-12 and for days, you only use numbers 1-29, 30 or 31. To get a more specific chronological age down to the number of seconds, you can use this chronological age calculator.
Loading Calculator…
Table of Contents
How to use the chronological age calculator?
Using an age calculator online is an easier and convenient way for you to get your exact chronological age. Unless you want to perform the calculation manually, this online tool can save you a lot of time and money. Here are some steps to use this calculator:
- First, enter your Date of Birth starting with the day, the month, then the year.
- The Age on this Date is already entered for you, but you can also change this date if you want.
- After entering the dates, the chronological age calculator will automatically generate your chronological age giving you the Years, Months, Weeks, Days, Hours, Minutes, and Seconds.
How to calculate chronological age
Before you use a Pearson age calculator or an age calculator online, it’s important to understand what your chronological age is first. Your chronological age refers to the exact amount of time you’ve lived. In other words, it’s how many days, months, and years you’ve lived no matter what type of lifestyle you have. Whether you follow a healthy diet and exercise regularly or you live a sedentary lifestyle, your chronological age will only change as time goes on.
The rate at which we age differs from one person to another. While some people age at a very rapid rate, the luckier ones age at a more gradual rate. That’s why some people look older than they are while others look really young even though they’re already chronologically old.
Most people confuse their chronological age with their biological age, but these are two very different things. Your chronological age refers to the amount of time you’ve lived from the time of your birth. But your biological age refers to how long it would be before you would start to suffer decline related to your age and your body would start to die. Let’s explain this by using an example.
For instance, we have two 45-year-old women. One of them is very lazy, doesn’t have any motivation to exercise, drinks a lot of alcohol, eats unhealthy foods, and smokes a lot. But the other one follows a healthy diet, exercises regularly, has a positive disposition, and looks after her overall health and wellbeing. The second woman may drink but only on occasion, and she doesn’t stress herself about things she cannot control. If these women had the same date of birth, that would mean that they have the same chronological age. However, they would have a very different biological age. Because of the way she lives her life, the first woman would have a very weak physique which means that she may already be about 57-years-old biologically.
The second woman may drink but only on occasion, and she doesn’t stress herself about things she cannot control. If these women had the same date of birth, that would mean that they have the same chronological age. However, they would have a very different biological age. Because of the way she lives her life, the first woman would have a very weak physique which means that she may already be about 57-years-old biologically.
For the second woman who takes better care of her body, her biological age could only be at 34-years-old or so. The first would be 12 years older than her chronological age while the second woman would be 11 years younger biologically.
This chronological age calculator will calculate your age all the way down to the second from your testing date. It does this by subtracting your date of birth from the test date. It’s a very convenient tool for you to use, especially when you need to get your chronological age in a pinch.
However, there may also be times when you won’t have access to a Pearson age calculator or any other type of online tool. In such a case, you can manually calculate your chronological age. To do this, let’s have another example.
In such a case, you can manually calculate your chronological age. To do this, let’s have another example.
For instance, a person wants to get his chronological age, and his date of birth was November 30, 1996. For this example, let’s say that he checked his chronological age on August 7, 2013. To get his chronological age, you should first create a subtraction problem by laying out all the information numerically.
For August 7, 2013, the numerical values would be 8, 7, and 2013
For November 30, 1996, the numerical values would be 11, 30, and 1996
First, start by subtracting the numerical values of the days. But in this case, the number for the test date is less than the number for the date of birth. Therefore, you need to borrow 30 days (1 whole month) from the numerical value of the month. This means that for the test day, the number of days would be 37 while the number of months would be 7. After borrowing, you can now get the value for the days:
After borrowing, you can now get the value for the days:
37 – 30 = 7 days
The next values to subtract are the months. Again, the number for the test date is less than the number for the date of birth. So you can borrow 12 months (1 whole year) from the numerical value of the years. Then the number of months would be 19 while the number of years would be 2012 for the test day. Now you can get the value for the months:
19 – 11 = 8 months
Finally, you can subtract the numerical values of the years without having to borrow any numbers:
2012 – 1996 = 16 years
After subtracting all of the numerical values, we now have the age of the person in our example which is 16 years, 8 months, and 7 days. Of course, if you compute manually, you won’t get your chronological age all the way down to the number of seconds. That’s why it’s a lot easier and more convenient to use our chronological age calculator to get the exact value you’re looking for.
That’s why it’s a lot easier and more convenient to use our chronological age calculator to get the exact value you’re looking for.
Chronological Age Calculator | Find Your Real Age
Created by Łucja Zaborowska, MD, PhD candidate
Reviewed by Bogna Szyk and Jack Bowater
Last updated: Nov 17, 2022
Table of contents:- How to calculate chronological age?
- How old was I on this date?
- This is your time!
- Average life expectancy
Chronological age calculator computes your age in years, months, weeks, days, hours, minutes, and seconds. If you've ever wondered "how old was I?" at a particular moment in your life, it's finally time to get the answer! Your exact age calculator just couldn't get any more precise (nanoseconds not included 😉).
How to calculate chronological age?
Calculating your chronological age might be quite a tremendous task if you intend to do it by yourself - subtracting years and months is the easy part. Then, you need to think about the weeks and days.
Then, you need to think about the weeks and days.
Remember that different months have a different number of days! February is the trickiest month when it comes to calculations. Every four years, it takes a value of 29 instead of 28 days. Each year that can be divided by four without a remainder (for example, 2020 /4 = 505), gives us precisely one more extra day (except for years that divide perfectly by 100, but not those that are also perfectly divisible by 400...).
The easiest way to calculate your time spent on Earth in days:
time = (years * 365) + (months * 31) + days
Explanation:
- Years - How old are you?
- Months - How many full months have passed since your last birthday?
- Days - How many days have already passed in the current month?
If you want to get the exact number of hours, minutes or second you've been alive, you need to multiply the number of days you've calculated by the following numbers:
- To get no.
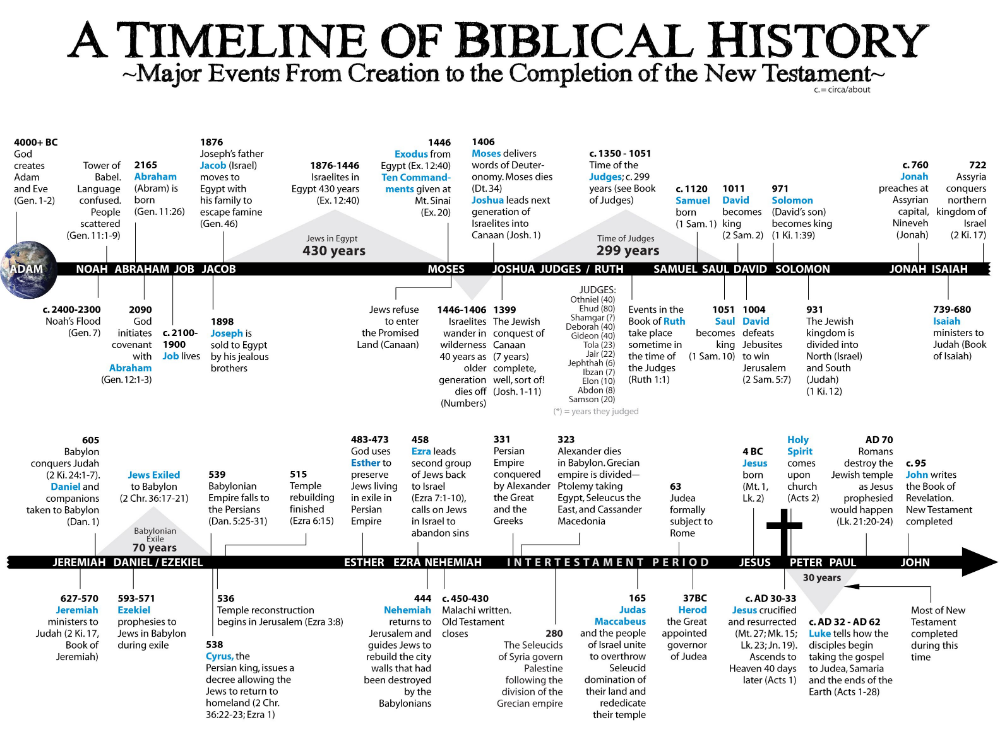 of hours:
of hours: Number of days * 24 - To get no. of minutes:
Number of days * 1440 - To get no. of seconds:
Number of days * 86 400
Why don't you check how long you have to wait until your next birthday with the [age calculator)(calc:3140)?
How old was I on this date?
Well... it depends. Did you know that people in Korea count their age differently than we in the West do? Try our Korean age calculator.
The way of calculating your age stays the same - the only variable that changes is the current date. You can enter any date you want into our chronological age calculator - as long as the event you intend to compute was after your birth date!
This is your time!
We calculated how many minutes and seconds you've been alive for. Have you been wondering what you spend it on? It is said that an average human being spends half of their lifetime... sleeping. The other major parts consist of work and school, where we spend another quarter of our lives.
What about all the other little parts of your day?
- Check how many weeks, months, or years will you spend writing emails during your entire lifetime with the email alternatives calculator, and what you could use this time for instead?
- Or what about finding out how long you spent in front of the TV and alternative activities with the TV alternatives calculator?
Average life expectancy
Our calculator, just like the Pearson chronological age calculator, is able to compute the minutes of your life up to this very moment. Now, let's have a look at statistics. What's the average life expectancy in your country?
- The life expectancy for the average American citizen is 79.11 years, with a significant difference between men (76.61 years) and women (81.65 years). These numbers have been rising consistently for the last 50 years or so.
- If you live in the European Union you might live a bit longer - it's 80.
 9 years for the general population, with 83.5 for women and 78.3 years for men. These numbers vary from country to country however.
9 years for the general population, with 83.5 for women and 78.3 years for men. These numbers vary from country to country however. - The average Australian will live even longer! Their average lifespan is equal to 82.5 years.
If you were ever wondering what can time do to your money, try our time value of money calculator!💰
Łucja Zaborowska, MD, PhD candidate
Date of birth
Current date
Your Age
Check out 29 similar time and date calculators ⏳
8-hour shiftAdd timeAge… 26 more
7. Chronological and biological age. Slow and accelerated types of individual development.
unevenness the rate of growth and development of an organism maturation stage is common regularity. However, during this period some individual peculiarities. For clarification (adjustment) the level of development of children use the concept biological and chronological age.
Chronological age - is the period that a child lives from birth until the moment of examination, having a clear age limit - day, month, year.
Biological age - set of morphofunctional characteristics of the body, depending on individual rate of growth and development.
Biological age to a large extent determined by chronological age. However, as studies have shown, difference between chronological and biological age can reach 5 years.
Pupils with delayed pace biological development less active on lessons. They have an increased distractibility and dysfunction. During the educational process, more pronounced eye strain analyzer, violations by musculoskeletal system and of cardio-vascular system.
Speedy pace biological development of the child leads ahead of biological age compared to chronological. Girls accelerated development is observed more often, than boys. For students with accelerated pace of biological development performance is lower than that of children, whose biological age corresponds to chronological. Among there are more children with hypertension and chronic tonsillitis, they have higher incidence rates, more frequent and sharper functional abnormalities appear.
Among there are more children with hypertension and chronic tonsillitis, they have higher incidence rates, more frequent and sharper functional abnormalities appear.
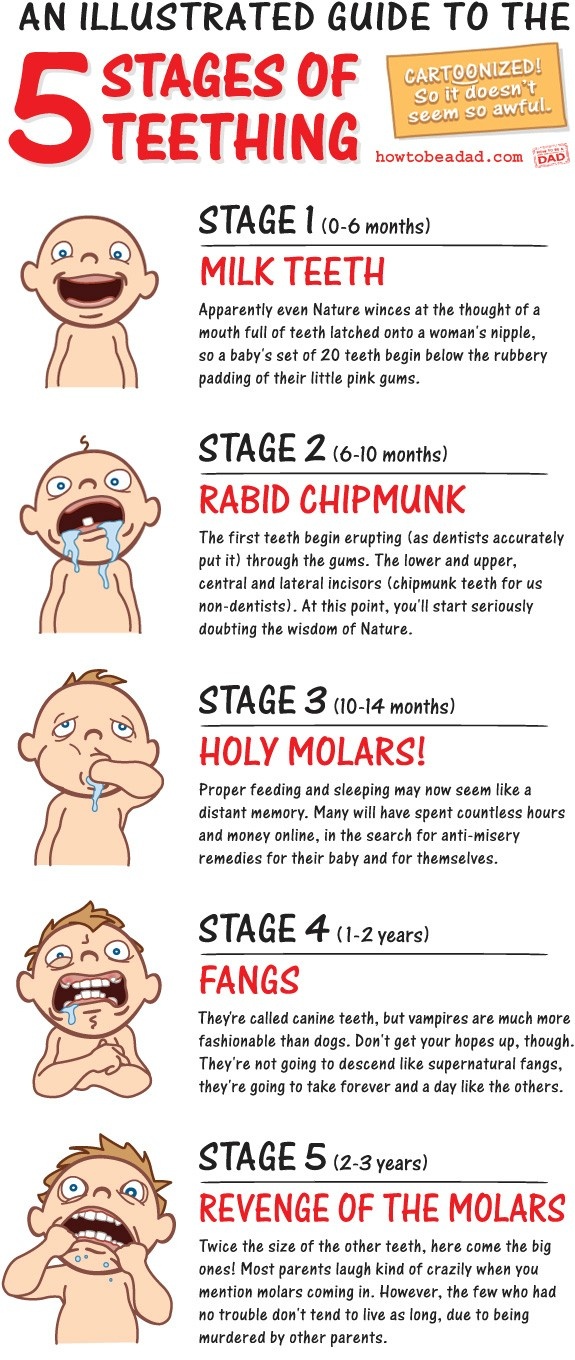
Most informative indicators of biological ages are the degree of ossification skeleton, eruption and shift time teeth, the appearance of secondary sexual signs in adolescents, the onset of menstruation in girls, as well as morphological indicators of physical development (length body and its annual increments).
Study physical development is carried out simultaneously with the study of the state health during in-depth medical examinations in children and adolescents institutions.
Doctrine about heterochrony was developed by A.P. Anokhin. They found that maturation different systems occurs unevenly, they are phased in, depending on from the needs of the body, providing the best adaptation to various periods of ontogeny. In the early years child's life primarily increased head and spinal mass brain, which cannot be considered random: there is an intensive formation functional systems of the body. Through nervous system is connected organism with the environment. IN the opposite is lymphatic tissue in the first years of life does not develop, its growth and formation take place in aged 10 - 12 years. Only after 12 years go intensive development of the genital organs and the development of childbearing function. Ability the child's body to specific types activity, its resistance to various environmental factors environments are determined by the level of maturation corresponding functional systems. So, the associative sections of the cerebral cortex brain, providing its integral function and readiness for schooling, mature gradually during individual development of the child by 6-7 years. Due with this forced education of children in early age may affect their subsequent development. System, transporting oxygen to tissues, also develops gradually and reaches maturity only by 16-17 years. Therefore, only in adolescence age at maturity cardiovascular and respiratory systems are allowed to run for a long time high physical activity and development endurance Knowledge this pattern helps teachers do your job right.
Through nervous system is connected organism with the environment. IN the opposite is lymphatic tissue in the first years of life does not develop, its growth and formation take place in aged 10 - 12 years. Only after 12 years go intensive development of the genital organs and the development of childbearing function. Ability the child's body to specific types activity, its resistance to various environmental factors environments are determined by the level of maturation corresponding functional systems. So, the associative sections of the cerebral cortex brain, providing its integral function and readiness for schooling, mature gradually during individual development of the child by 6-7 years. Due with this forced education of children in early age may affect their subsequent development. System, transporting oxygen to tissues, also develops gradually and reaches maturity only by 16-17 years. Therefore, only in adolescence age at maturity cardiovascular and respiratory systems are allowed to run for a long time high physical activity and development endurance Knowledge this pattern helps teachers do your job right. Yes, in period of speech motor formation functions the child needs speech communication, for the development of motor skills - physical activity.
Yes, in period of speech motor formation functions the child needs speech communication, for the development of motor skills - physical activity.
Considering sequence of development of one or another functional system in ontogeny, it is necessary to provide the same consistency in education child.
How to determine the biological age?
How to understand when old age comes? When the age approaches seventy or when "the pressure is naughty and the heart aches"?
There is no single way in which people grow old, which means that it is possible to determine when old age will come only very approximately. After all, someone at 80 will run a half marathon, and someone at 50 will not be able to overcome a couple of flights of stairs.
Why this happens is not exactly known. Many factors affect the rate of aging: lifestyle, genetics, chronic diseases.
In order to somehow measure it, scientists have introduced the concept of biological age. In the article we understand what it is and whether it can be slowed down.
In the article we understand what it is and whether it can be slowed down.
Contents
- Is biological age a scientific term or a fiction?
- How to measure your biological age
- Biomarkers of aging
- How genetics affects aging
- Is it possible to stop aging
What is biological age - a scientific term or a fiction?
There are two concepts in scientific articles: chronological and biological age. If with chronological age everything is more or less clear: it reflects the number of years since birth. Biological is a little more difficult.
Scientists have not yet given it an exact definition, but if we sum up their assumptions, it turns out that biological age is an indicator that reflects the degree of deterioration of the body.
But how to evaluate wear? After all, organs age differently and there can be a lot of parameters: clarity of vision, joint mobility, metabolic rate, cognitive functions.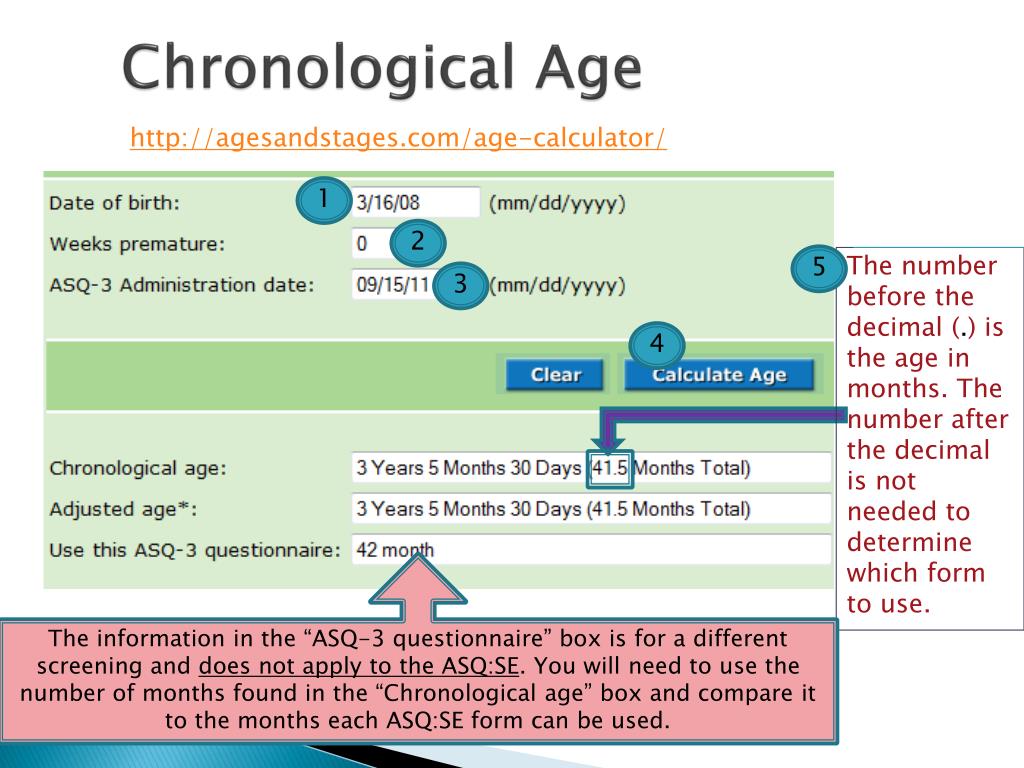 And for each of them, different people will have different readings.
And for each of them, different people will have different readings.
Someone will develop vision problems, but he will run 10 km daily and feel great, and someone will suffer from joint pain and have difficulty moving, but see perfectly.
How to measure biological age
There is no generally accepted calculation method yet. Scientists are still choosing suitable methods and formulas, and they are also continuing to search for common indicators or so-called aging biomarkers in order to assess the biological age of a person and understand how the body ages from the inside.
Such markers can be indicators of appearance, endurance, overweight, visual and hearing acuity, the state of blood vessels and the heart, cholesterol levels and changes in other blood parameters.
For example, scientists from the National Research Nizhny Novgorod State University. N. I. Lobachevsky launched an online calculator that analyzes the indicators of chronological age and blood to determine the biological age.
It is not known how accurate the result will be, but it may be interesting to see changes in dynamics.
Some medical services offer to calculate your “real age” by answering questions about your health and lifestyle in a questionnaire.
But such methods can hardly accurately predict possible age-related changes. Much more promising is the study of the mechanisms of cell aging.
Biomarkers of aging
The attention of many scientists studying the mechanisms of aging is directed to nine such indicators:
cell.com1) Shortening of telomeres
Telomeres are areas that protect the ends of chromosomes from destruction and fusion with neighboring chromosomes.
Scientists have found that the older a person is, the shorter the telomeres.
With each new cycle of cell division, telomeres shorten. And when they completely disappear, the limit of divisions (the Hayflick limit) sets in, and the mechanism of self-destruction is launched in the cell. She gets old and dies.
She gets old and dies.
By the age of eighty, telomeres become half as long.
Studies show that people with shorter telomeres have an increased risk of cancer, heart disease, and premature death.
2) Violation of proteostasis
Proteostasis - intracellular balance of proteins.
In order to function properly, proteins must have a certain structure and fold together in the right way.
If for some reason the protein structure changes, they can no longer connect with each other and perform the necessary functions. This can cause further cell damage and disease development.
3) Epigenetic changes
Epigenetic changes are changes that occur under the influence of external factors and can turn on or off some genes.
What is epigenetics and how does it work? Cells undergo a variety of epigenetic changes throughout life. The most studied of these are DNA methylation, chromatin remodeling, and histone modification.
The most studied of these are DNA methylation, chromatin remodeling, and histone modification.
It is known that aging is accompanied by accumulation of epigenetic changes. As a result of this, the life cycle of cells may be reduced or various diseases may develop.
Epigenetic changes, unlike genetic changes, are potentially reversible. That is why scientists are studying them in search of a way to combat age-related changes.
4) Altered nutrient sensitivity
Cells normally know how much and when they need nutrients, just as they know when to grow, divide or die.
But during life, by-products of metabolism accumulate in cells, as a result of which the mechanisms of intracellular regulation break down.
Because of this, cells can more actively signal that they lack nutrients. Although in reality it is not.
It is known that such activation of signaling pathways is associated with the aging of some cells and tissues.
5) Mitochondrial dysfunction
Each cell has structural elements that provide it with energy — mitochondria.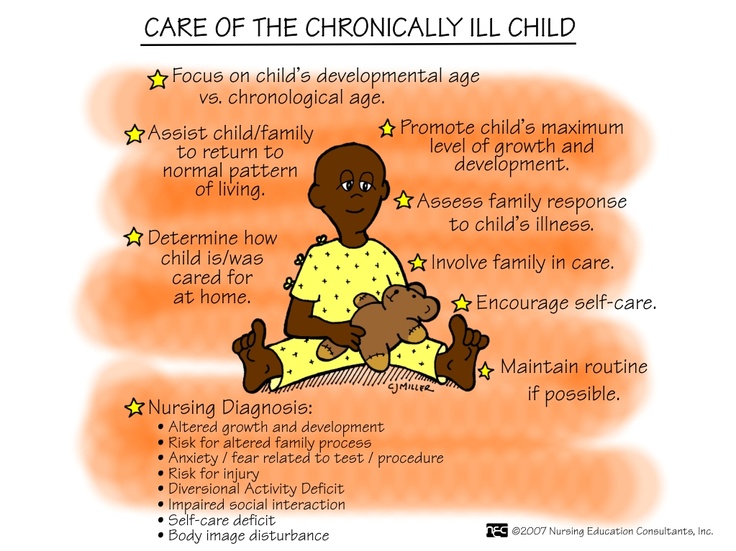 During life, the efficiency of mitochondria decreases, and by-products of mitochondrial activity, reactive oxygen species or so-called free radicals, accumulate in cells.
During life, the efficiency of mitochondria decreases, and by-products of mitochondrial activity, reactive oxygen species or so-called free radicals, accumulate in cells.
Free radicals damage healthy cells, accelerate their death, and therefore bring aging closer.
6) Cell aging
An aging cell is a cell whose division limit is approaching. Normally, a cell that can no longer divide should start the mechanism of self-destruction. But this is not always the case, over time, the body increasingly “misses” aging cells and they accumulate.
In addition, aging cells release free radicals and signal inflammation. Therefore, their accumulation negatively affects all cells of the body.
7) Reduced supply of stem cells
Stem cells are immature cells that have not yet “learned” to be, for example, blood cells or brain cells. But if necessary, they replace the dead cells. Thus they provide regeneration.
The largest stock of stem cells in newborns, with age, the number of cells decreases.

When the supply of stem cells is depleted, the cells age and die, and no new ones can take their place.
8) Violation of the transmission of intercellular signals
Normal cells constantly communicate with each other. If an injury occurs in one place or inflammation begins, they transmit a signal to the brain so that it sends a “rescue team” to the place of damage.
Once the signal is received, the cells stop telling others that something is wrong with them.
In senescent cells, this mechanism may not work and they do not stop giving SOS signals after the "incident" is over.
9) Instability of the genome
Genetic errors constantly accumulate in the body, which are normally eliminated by a special repair system. With age, this system does not work more often and errors accumulate. The best-known result of the accumulation of genetic mutations is malignant tumors.
How genetics affects aging
Genes can regulate the cell cycle, which means they can slow down or increase the rate of cell aging.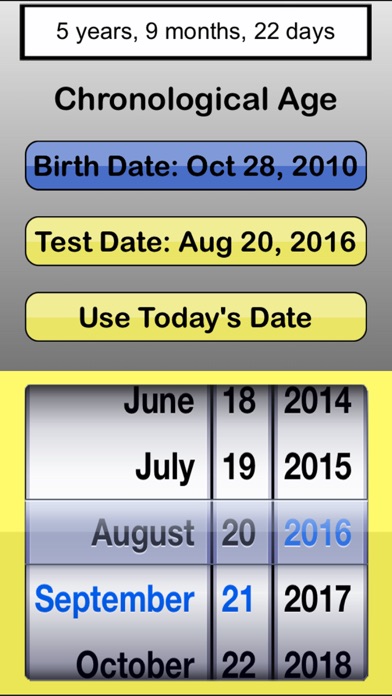
Scientists have already identified many candidate genes that can influence the rate of aging:
- Insulin-like growth factor (IGF-1)
Long-lived people have increased sensitivity to insulin while maintaining low plasma levels. And some mutations in IGF-1 lead to an increase in the lifespan of laboratory flies and mice.
- Fat metabolism genes
Fat metabolism slows down with age, which leads to the appearance of metabolic syndrome and atherosclerosis.
Fat imbalance is associated with changes in the activity of many genes.
An important role in the imbalance of fats and longevity is played by hormones-regulators of fat metabolism: adiponectin, leptin, ghrelin. And their work is controlled by specific genes.
- Regulatory genes for cell aging and apoptosis (p53, p21, p16, pRB)
These genes are involved in cancer prevention, cell cycle regulation and the death of unnecessary or harmful cells.
To learn more about genetic characteristics and understand how to preserve your health and youth, you can take the Atlas Genetic Test.
Is it possible to stop aging
So far, there are no proven ways to stop or reverse aging at the level of molecules and cells.
But there are things you can do to improve your overall health now, and thus slow down biological aging.
Recommendations are unlikely to surprise anyone. But this does not mean that they do not work:
- Get enough sleep
To stay healthy and wear out the body less, you need to sleep at least 7-8 hours a day.
- Eat a balanced diet
Diet should include different food groups: fruits, vegetables, whole grains, meat, fish. So you get all the necessary nutrients and energy supply.
- Give up cigarettes and try to reduce the amount of alcohol you drink
- Be physically active
Try to spend 30-40 minutes a day exercising. It doesn't matter what it will be: running, swimming, brisk walking or active games with children. Choose what you like and strengthen your muscles.
It doesn't matter what it will be: running, swimming, brisk walking or active games with children. Choose what you like and strengthen your muscles.
- Learn how to deal with stress Constant stress can be a powerful factor in damaging your health. Try to understand its causes and your reaction, learn the techniques of calming breathing. Youth largely depends on how you learn to relax.
More about staying young and healthy on the Atlas blog:
How to fix your biological clock so you can sleep well and get enough sleep
How to take care of your skin according to science? 7 universal rules
9 Ways to Reduce Cortisol and Prevent Stress
- National Institute on Aging. Biology of aging.
- Center for bioethics Harvard medical school. Does the distinction between biological and chronological age support legal age change?
- Clinical interventions in aging. Common methods of biological age estimation.