What to expect in a twin pregnancy
Pregnant with Twins: What to Expect
Learning you’re pregnant with twins likely causes a rush of emotions. Some women are excited about the prospect of twins — double the cuteness and baby snuggles! Others may feel a little uncertain or even overwhelmed. After all, there are two babies rather than just one. Not to mention, twin pregnancies come with added risk compared to a typical single-baby pregnancy (or “singleton” pregnancy).
Let’s look at how twin pregnancies differ from single-baby pregnancies, from conception to birth.
Signs You Might Be Having Twins
There are some early signs to watch for that could indicate you’re pregnant with twins, but every pregnancy will be a unique and different experience for each woman.
Faster Weight Gain and Severe Morning Sickness
Some women who have twin pregnancies will have more severe morning sickness and faster weight gain. Does that indicate twins? Maybe, maybe not. These symptoms can happen in any pregnancy, so they are not definitive signs of twins.
Blood Test
Blood tests can also reveal the likelihood of twins within the first few weeks after your missed period. Higher than expected beta results could indicate twins.
Ultrasounds
But the only definitive answer to whether you’re having twins is an ultrasound. You’ll most likely find out if you are pregnant with twins when you have your first-trimester ultrasound, which is scheduled for around 7 or 8 weeks gestation.
Differences Between Twin Pregnancies vs. Singleton Pregnancies
Mothers expecting multiples can expect to have a bit more on their plate. You should plan on finding support through friends, family, and local support groups. Your doctor may have some insight into resources available in your area.
Even uncomplicated pregnancies with twins can cause women to feel more tired than they would if they were only carrying one baby. Ensure you eat enough nutrient-dense foods during pregnancy to meet your body’s nutritional needs, too. Pay close attention to your iron intake. You may want to supplement iron through prenatal vitamins and eat plenty of iron-rich foods.
Pay close attention to your iron intake. You may want to supplement iron through prenatal vitamins and eat plenty of iron-rich foods.
Women expecting twins can also plan on delivering their babies before the 40-week mark of pregnancy. Even in twin pregnancies considered lower risk, delivery may be recommended by 36 to 38 weeks.
Breastfeeding twins has unique challenges but is still possible. Connect with a lactation consultant to help overcome challenges associated with nursing twins so you can continue breastfeeding for as long as possible.
Typical Weight Gain with Twins
Weight gain during pregnancy is expected — and healthy. Your body will be growing two tiny humans! That means you can expect to gain, on average, about 45 pounds during a twin pregnancy. This is about 10 pounds more than a singleton pregnancy.
| Body Mass Index (BMI) Pre-pregnancy | Recommended Weight Gain |
18. 5-24.9 5-24.9 | 37-54 lb |
| 25-29.9 | 31-50 lb |
| >/= 30 | 25-42 lb |
Keep in mind pregnancy weight includes:
- increased fluids, such as amniotic fluid and blood supply,
- increased fat stores so your body can sustain the pregnancies,
- and of course the weight of the babies themselves.
Types of Twin Pregnancies
Fraternal vs. Identical Twin Pregnancies
Many people are already familiar with the differences between fraternal and identical twins. Fraternal twins occur when two eggs are released, fertilized, and implanted. They are the more common type of twins. Identical twins occur when a single egg is split into multiple identical embryos.
But there is another way multiple pregnancies are classified, which affects how closely they are monitored.
Mono/Di vs Di/Di vs Mono/Mono Twin Pregnancies
There are three main types of twin pregnancies:
- Mono-chorionic, di-amniotic (Mono/Di): they share one placenta and have their own amniotic sacs; these twins are identical.

- Di-chorionic, di-amniotic (Di/Di): they each have their own placenta and amniotic sacs; they could be identical or fraternal.
- Mono-chorionic, mono-amniotic (Mono/Mono): they share both a placenta and an amniotic sac; these twins are identical.
Di/Di twin pregnancies carry the lowest risk of the three types because both babies have their own placenta and amniotic sac. When both babies share one placenta, there is the risk of one baby getting the majority of the blood flow. Twin transfusion syndrome occurs in 10 to 15 percent of Mono/Di twin pregnancies.
Prenatal Care for Twin Pregnancy: Week by Week
Prenatal appointments for multiples will be very similar to singleton pregnancies for the first two trimesters unless the pregnancy is high risk.
Prenatal appointments for singletons typically include:
- Checking your weight
- Checking your blood pressure
- Performing a fundal measurement — your OBGYN will measure the distance from your pubic bone to the top of your uterus to determine the baby’s size and growth rate
- Monitoring fetal heart rate — your OBGYN will listen to and monitor your baby’s heartbeat
- Ultrasounds, according to schedule
Because fundal measurements are not an accurate way to estimate the babies’ growth during a twin pregnancy, as they are in typical pregnancies, you can expect to get regular ultrasounds after the 20-week mark.
For low-risk twin pregnancies, expect to get ultrasounds at 24, 28, 32, and 36 weeks. Higher-risk pregnancies, such as mono-chorionic twins, may have ultrasounds every two weeks starting as early as 16 weeks gestation.
You can also expect regular non-stress tests every two weeks in the third trimester, during which your doctor will listen to the babies’ heartbeats for 20 to 30 minutes. This helps to assess how well the babies are tolerating pregnancy.
What Are the Chances of Having Twins?
The Odds of Twins
Everyone wants to know what their chances of having twins are. It turns out, older women are more likely to get pregnant with twins. At the age of 20, a woman has a 1% chance of getting pregnant with twins, but at age 40, that likelihood jumps to a 7% chance.
Genetic Factors of Having Twins
There is also some genetic tendency with twins. If someone in your immediate family had twins or if you are a twin, then you may be more likely to get pregnant with twins.
How to Get Pregnant with Twins
Women who are taking fertility prescriptions to induce ovulation may have a greater likelihood of having twins.
If a woman is using IVF to get pregnant, she can request a twin pregnancy. However, it is important to note that twin pregnancies carry more risk than single-baby pregnancies.
But there are no known herbs, supplements, foods or sex positions that are proven to increase the odds of having twins.
Risks of Twin Pregnancies
Although some women may think a twin pregnancy is more desirable, given that one pregnancy results in two babies, most practitioners would caution them about the increased risk of complications.
Common risks of being pregnant with twins include:
- Higher likelihood of developing gestational diabetes
- High blood pressure
- Increased risk of preterm delivery
- Higher likelihood of needing a C-section
- Risk of twin-twin transfusion syndrome in mono-chorionic pregnancies
What to Expect During Labor and Delivery of Twins
Recommended delivery timing varies depending on the type of twin pregnancy and is as follows:
- Di/Di: delivery by 36-38 weeks is recommended due to an increased risk of stillbirth at 40 weeks
- Mono/Di: delivery recommended at 36 weeks
- Mono/Mono: delivery at 32 weeks
If you are pregnant with twins, it isn’t certain that you’ll have to have a C-section, but it is fairly likely. The capability of a woman to deliver twins vaginally depends on the position and sizes of the babies. If the first baby is head down and the babies are the same size or baby one is larger, then a vaginal delivery for both babies can be attempted.
The capability of a woman to deliver twins vaginally depends on the position and sizes of the babies. If the first baby is head down and the babies are the same size or baby one is larger, then a vaginal delivery for both babies can be attempted.
At Madison Women’s Health, we often encourage women to have an epidural when delivering twins. Having an epidural in place can save time if an emergency C-section is needed. It can also make the experience more tolerable if the second baby is breech (positioned feet first) and needs assistance.
If a woman wants to deliver twins vaginally, the delivery will begin in a normal labor room where the baby and mother will be monitored closely. When the mother begins to push, she will be moved to the Operating Room (OR) in case an emergency C-section is needed. There will likely be a pediatrician, anesthesiologist, surgical tech, and an ultrasound technician present to monitor the vital signs of the mother and baby.
The healthcare team knows that twin deliveries carry more risk, so these measures should be taken to keep the mother and baby safe.
Talk with your provider about making the experience as relaxing as possible by incorporating calming music and having a support person present. (Want some ideas for making your birthing experience as calm as possible? Read this blog post.) Assuming your babies don’t need medical support when they are born, you should still be able to do skin-to-skin contact immediately after delivery.
Community Support for Twin Pregnancies
When you learn you’re having twins, you will probably have many questions. At Madison Women’s Health, we’ve delivered many twins. Some of us have even had twins ourselves! But we know some of the best advice, tips, and tricks for how to cope when you’re outnumbered by babies comes from other parents who have been there, done that!
We encourage you to get involved in a community support group for parents of multiples. In Madison, we recommend “Moms of Multiples.” You’ll also want to speak with a lactation consultant.
Finally, if you have supportive friends and family nearby, remember to ask them for help. Chances are they would love a few extra moments to snuggle your little ones so you can get some much-needed rest. If you have any questions or concerns about having twins, please speak with your OBGYN. We’re here for you every step of the way.
Chances are they would love a few extra moments to snuggle your little ones so you can get some much-needed rest. If you have any questions or concerns about having twins, please speak with your OBGYN. We’re here for you every step of the way.
Dr. Dickmeyer has been providing healthcare for women in the Madison area since 1998 and is a founding member of Madison Women’s Health. Her specialties include minimally invasive surgical techniques, high and low risk obstetrics, pelvic floor disorders and postmenopausal medicine.
Expecting Twins? Here Are 11 Things You Should Know About Twin Pregnancies
Experts share their advice if you are pregnant with twins.
Written by Denise Mann
If you are expecting twins and wonder what it will be like, many people can relate. That moment when you find out you've got two babies on the way often comes from out of the blue. Although you probably can't fully imagine what it will mean for your day to day life, you can learn a lot before the twins arrive.
A twin pregnancy is a double blessing, but it can also carry greater risks than singleton pregnancies.
Get to know these things about twin pregnancies from conception through delivery.
No. 1: You are more likely to become pregnant with twins naturally when you are in your 30s and 40s.
We all hear that the older we get, the harder it is to conceive. But it may actually make a twin pregnancy more likely, says Abdulla Al-Khan, MD, the director and chief of maternal and fetal medicine and surgery at Hackensack University Medical Center in New Jersey. "Once you are 25 or into your 30s and 40s, ovulatory cycles are not regular anymore. If you are not regular and do ovulate, you could be ovulating two follicles at the same time." Voila! A twin pregnancy -- without assisted reproductive technologies.
No. 2: If you have two buns in the oven, you may need extra folic acid.
When you're pregnant with twins, you may need more folic acid to help stave off birth defects, says Manju Monga, MD, the Berel Held Professor and the division director of maternal-fetal medicine at the University of Texas Health Sciences Center in Houston.
"We recommend 1 milligram of folic acid per day for twin pregnancies and 0.4 milligrams for singleton pregnancies," says Monga, who has twins. Folic acid is known to reduce risk of neural tube birth defects such as spina bifida.
No.3: Being pregnant with twins means more doctor visits.
Twin pregnancies need more monitoring than single pregnancies, Monga says. "We tend to do more frequent ultrasounds for growth in twin pregnancies, compared with one anatomy scan and one growth scan in a singleton pregnancy."
Twins may also have to have twice weekly fetal testing as you get closer to your due date. That may involve more ultrasounds or being placed on the fetal heart rate monitor for the testing.
No. 4: Morning sickness may be worse with twin pregnancies.
"One of the things that is postulated as causing morning sickness is high levels of human chorionic gonadotropin, and we know that levels of this hormone are higher in twin pregnancies, so women carrying twins have a higher incidence of nausea and vomiting in the first trimester," says Al-Khan. The good news? Most morning sickness abates within 12 to 14 weeks of pregnancy -- even in twin pregnancies.
The good news? Most morning sickness abates within 12 to 14 weeks of pregnancy -- even in twin pregnancies.
That's not all, Monga says. Women pregnant with twins complain of more back pain, sleeping difficulties, and heartburn than those who are carrying one child. Being pregnant with twins also carries a higher rate of maternal anemia and a higher rate of postpartum hemorrhage (bleeding) after delivery.
No. 5: Spotting may be more common during twin pregnancies.
"When you spot in the first trimester, you could be undergoing a miscarriage, and miscarriages are more common in mothers of twins, triplets, and quadruplets -- so we see more spotting in first trimester with multiples," Al-Khan says.
If you do have spotting, don't panic. "A little spotting in the absence of cramps is reassuring,but when you are cramping, passing clots, and actively bleeding, that is a sign that's something is happening and you should seek medical advice."
No. 6: You don't feel the babies kicking any earlier with twin pregnancies.

"Generally when you are pregnant with twins, fetal movements become more noticeable at weeks 18 through 20 of pregnancy, and the same is true in singleton pregnancies," Al-Khan says.
When you begin to feel fetal movements actually depends on whether this is your first pregnancy. "If you have been pregnant before, you know what fetal movement is, but if you are pregnant for the first time, you really can't distinguish the movement from gastrointestinal activity."
No. 7: If you're pregnant with twins, you may gain more weight than if you're carrying one child.
"With twins, mothers gain more weight as there are two babies, two placentas, and more amniotic fluid," says Al-Khan. "You also need more calories for twin pregnancies."
Still, there is not a well-established formula for weight gain during twin pregnancies, says Monga. "The average weight gain is 25 pounds for singleton pregnancy and 30-35 pounds for twins. We don't want moms pregnant with twins to gain more than 40 [pounds] or less than 15 pounds. "
"
The Institute of Medicine's provisional guidelines for weight gain in women expecting twins say:
- Women of normal weight should aim to gain 37-54 pounds
- Overweight women should aim to gain 31-50 pounds
- Obese women should aim to gain 25-42 pounds
Exactly how much weight should you gain? The IOM recommends that you talk to your health care provider about that, because every pregnancy is unique.
No. 8: Risk of developing gestational diabetes is higher in twin pregnancies.
"The gestational diabetes risk is higher in twin pregnancy," says Monga. She notes that gestational diabetes can mean having larger babies and needing a C-section delivery -- but twins tend not to be big babies. Still, developing gestational diabetes during pregnancy also makes you more likely to develop type 2 diabetes later in life, she says.
No. 9: Risk of preeclampsia during pregnancy is higher in twin pregnancies.
"People really don't know what causes preeclampsia to start, but we know it occurs more frequently in twin pregnancies," Monga says. Preeclampsia is marked by high blood pressure, protein in the urine, and sometimes swelling in the feet, legs, and hands. It is the precursor to the more serious, potentially fatal eclampsia.
Preeclampsia is marked by high blood pressure, protein in the urine, and sometimes swelling in the feet, legs, and hands. It is the precursor to the more serious, potentially fatal eclampsia.
No. 10: Labor (and delivery) may come early with twin pregnancies.
Most women carrying twins go into labor at 36 to 37 weeks, as opposed to 40 in a single pregnancy, Al-Khan says, and some may go even earlier. "Generally, if the twins are born after 34 weeks, there should not be a major concern, but a premature baby is still a premature baby," Al-Khan says. "Twins are at higher risk of preterm labor and delivery and have higher degree of respiratory issues."
As a result of being born too early, twins may be born at low birth weights, and such babies tend to have more health problems than babies born weighing more than 5.5 pounds.
Unfortunately, there is no evidence that bed rest alone prevents preterm labor or delivery in twin pregnancies, and the use of agents to stop preterm labor have not been proven to be effective either, he says. "Stopping premature labor is challenging in multiple gestations."
"Stopping premature labor is challenging in multiple gestations."
No. 11: Cesarean section deliveries may be more common in twin pregnancies.
"The likelihood of having a C-section is absolutely higher in twin pregnancies," Al-Khan says. "There is also a higher incidence of the baby being in breech position among twins than singletons." When the baby is in a breech position, a C-section delivery is usually required.
articles from the specialists of the clinic "Mother and Child"
Arifullina Claudia Viktorovna
Gastroenterologist
Clinical Hospital "AVICENNA" GC "Mother and Child"
There is data on the frequency of twins in case of anomalies in the development of the uterus, characterized by its bifurcation (bicornuate uterus, having a septum in the cavity, etc.). The cause of polyembryony may be the separation of blastomeres (in the early stages of crushing), resulting from hypoxia, cooling, acidity and ionic composition of the medium, exposure to toxic and other factors.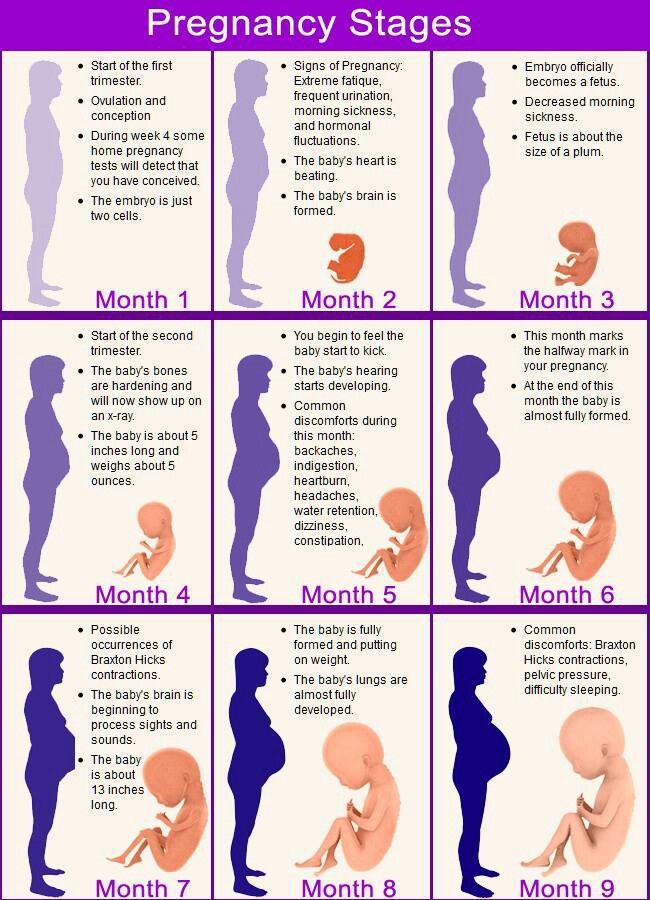 Multiple pregnancy can occur: as a result of the fertilization of two or more simultaneously mature eggs, as well as the development of two or more embryos from one fertilized egg. nine0003
Multiple pregnancy can occur: as a result of the fertilization of two or more simultaneously mature eggs, as well as the development of two or more embryos from one fertilized egg. nine0003
Twins formed from two (three, etc.) eggs are called dizygotic (polyzygotic), those arising from one are called identical. The origin of fraternal twins (polyzygotic twins): the simultaneous maturation (and ovulation) of two or more follicles in one ovary is possible. There may be maturation of two or more follicles and ovulation in both ovaries.
A third way of the origin of fraternal (multi-ovular) twins is possible - the fertilization of two or more eggs that have matured in one follicle. The origin of identical twins: most often, the occurrence of identical twins is associated with the fertilization of an egg that has two or more nuclei. a single embryonic germ in the stage of crushing is divided into two parts; from each part an embryo (fruit) is formed. Twin twin. Fertilized eggs develop on their own.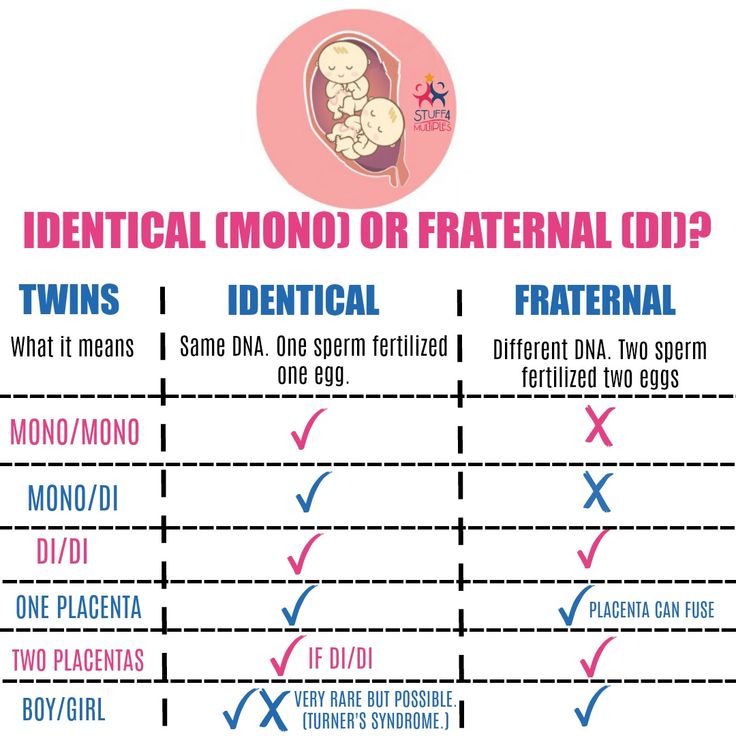 After penetration into the mucous membrane, each embryo develops its own aqueous and fleecy membranes; in the future, each twin forms its own placenta with an independent network of vessels, each fetal egg, except for the chorion and amnion, has an independent capsular membrane (decidua capsularis). In some cases, anastomoses are formed between the vessels of independent placentas. Twins can be same-sex (both boys or both girls) or different-sex (boy and girl). Their blood type can be the same or different. Identical twin. Identical twins have a common capsular and fleecy membrane and a common placenta; the vessels (both arterial and venous) of both twins in the placenta communicate with the help of numerous anastomoses. The water membrane of each twin is separate, the septum between the fetal sacs consists of two water membranes (biamniotic twins). nine0003
After penetration into the mucous membrane, each embryo develops its own aqueous and fleecy membranes; in the future, each twin forms its own placenta with an independent network of vessels, each fetal egg, except for the chorion and amnion, has an independent capsular membrane (decidua capsularis). In some cases, anastomoses are formed between the vessels of independent placentas. Twins can be same-sex (both boys or both girls) or different-sex (boy and girl). Their blood type can be the same or different. Identical twin. Identical twins have a common capsular and fleecy membrane and a common placenta; the vessels (both arterial and venous) of both twins in the placenta communicate with the help of numerous anastomoses. The water membrane of each twin is separate, the septum between the fetal sacs consists of two water membranes (biamniotic twins). nine0003
Identical twins always belong to the same sex (both boys or both girls), look alike, have the same blood type.
In fraternal twins, the membranes in the septum are arranged as follows: amnion - chorion, chorion - amnion; with monozygotic amnion-amnion.
Important signs for the diagnosis are: blood type (and other blood factors), eye color, hair color, skin texture of the fingertips, shape and location of teeth. In identical twins, these signs are completely the same. Fraternal twins share the same similarities as normal siblings. nine0017
MULTIPLE PREGNANCY
With multiple pregnancy, increased demands are made on the woman's body: the cardiovascular system, lungs, liver, nights and other organs function with great stress. In this regard, multiple pregnancies are more difficult than single pregnancies.
- Pregnant women often complain of fatigue and shortness of breath, which increases towards the end of pregnancy. The cause of shortness of breath is a difficulty in the activity of the heart due to a significant displacement of the diaphragm by the bottom of the uterus, the size of which is larger in multiple pregnancy than in singleton. nine0031
- Often there is a dilation of the veins of the lower extremities.
 By the end of pregnancy, there is often an increase in the urge to urinate due to the pressure of a large fetus on the bladder.
By the end of pregnancy, there is often an increase in the urge to urinate due to the pressure of a large fetus on the bladder. - Pregnant women often complain of heartburn and constipation.
- In multiple pregnancies, toxicosis occurs more often than in singleton pregnancies: vomiting, salivation, edema, nephropathy, eclampsia.
- With twins, polyhydramnios of one of the fetuses is often found, which leads to a sharp increase and hyperextension of the uterus, shortness of breath, tachycardia and other disorders. Polyhydramnios is more common in one of the identical twins. In some cases, the polyhydramnios of one twin is accompanied by an oligohydramnios of the other fetus. nine0031
- Premature termination of multiple pregnancies often occurs.
- With twins, preterm birth occurs in at least 25% of women.
- Prematurity is more common in triplets than in twins. The greater the number of gestated fetuses, the more often preterm births are observed.

- Development of term twins is normal in most cases. However, their body weight is usually less than that of single fetuses. Often there is a difference in body weight of twins by 200-300 g, and sometimes more. nine0031
- Uneven development of twins is associated with unequal intake of nutrients from a single placental circulation.
- Often there is a difference not only in weight, but also in the length of the body of the twins. In connection with this, the theory of supergenesis (superfoetatio) was put forward. Proponents of this hypothesis believe that fertilization of eggs of different ovulation periods is possible, i.e., the onset of a new pregnancy in the presence of an already existing, previously occurring, pregnancy. nine0031
- Due to the uneven delivery of nutrients and oxygen, a significant developmental disorder and even death of one of the twins can occur. This is more commonly seen in identical twins. The dead fetus is squeezed by the second, well-growing fetus, the amniotic fluid is absorbed, the placenta undergoes regression.
 The compressed mummified fetus ("paper fetus") is released from the uterus along with the placenta after the birth of a live twin. Polyhydramnios of one fetus, which occurs during multiple pregnancies, often also prevents the other twin from developing correctly. With pronounced polyhydramnios, certain anomalies in the development of the fetus, which grows with an excess of amniotic fluid, are often observed. Rarely, fused twins are born (fusion can be in the head, chest, abdomen, pelvis) and twins with other malformations. nine0031
The compressed mummified fetus ("paper fetus") is released from the uterus along with the placenta after the birth of a live twin. Polyhydramnios of one fetus, which occurs during multiple pregnancies, often also prevents the other twin from developing correctly. With pronounced polyhydramnios, certain anomalies in the development of the fetus, which grows with an excess of amniotic fluid, are often observed. Rarely, fused twins are born (fusion can be in the head, chest, abdomen, pelvis) and twins with other malformations. nine0031 - The position of the fetus in the uterine cavity in most cases (about 90%) is normal. In the longitudinal position, different presentation options are observed: both fetuses are presented with the head, both with the pelvic end, one with the head, and the other with the pelvic end. With longitudinal presentation, one fetus may be behind the other, which makes diagnosis difficult. Less commonly observed is the longitudinal position of one fetus and the transverse position of the other.
 The most rare is the transverse position of both twins. nine0031
The most rare is the transverse position of both twins. nine0031 - Position of the twins in the uterus, both fetuses are presented with the head, one fetus is presented with the head, the second - with the pelvic end, both fetuses are in the transverse position
- In case of multiple pregnancies, women are taken to a special account and carefully monitored. When the earliest signs of complications appear, the pregnant woman is sent to the pregnancy pathology department of the maternity hospital. Given the frequent occurrence of preterm birth, it is recommended that a pregnant woman with twins be sent to the maternity hospital 2 to 3 weeks before delivery, even in the absence of complications. nine0031
RECOGNITION OF MULTIPLE PREGNANCY
Diagnosis of multiple pregnancy often presents significant difficulties, especially in its first half. In the second half, towards the end of pregnancy, the recognition of twins (triplets) is facilitated.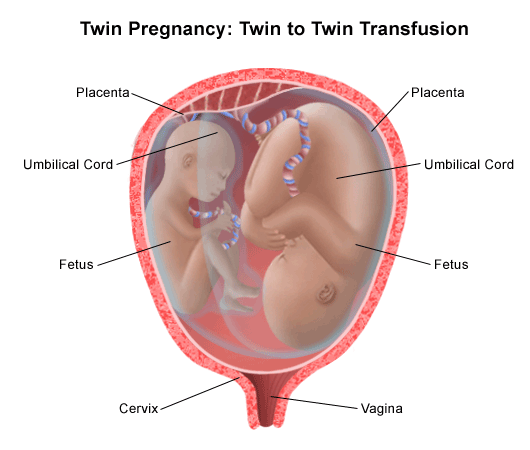 However, diagnostic errors occur during the study at the end of pregnancy and even during childbirth.
However, diagnostic errors occur during the study at the end of pregnancy and even during childbirth.
When recognizing a multiple pregnancy, the following signs are taken into account: nine0017
- The enlargement of the uterus in multiple pregnancy occurs faster than in pregnancy with one fetus, so the size of the uterus does not correspond to the gestational age. The bottom of the uterus is usually high, especially at the end of pregnancy, the circumference of the abdomen during this period reaches 100-110 cm or more.
- The following signs are unstable and not sufficiently reliable: a) deepening of the uterine fundus (saddle uterus), the formation of which is associated with protrusion of the corners of the uterus with large parts of the fetus; b) the presence of a longitudinal depression on the anterior wall of the uterus, which is formed as a result of the fruits that are in a longitudinal position adjacent to each other; c) the presence of a horizontal groove on the anterior wall of the uterus with the transverse position of the fetus.
 nine0031
nine0031 - The small size of the presenting head with a significant volume of the pregnant uterus and the high standing of its bottom also make it possible to suspect a multiple pregnancy. The presence of this sign is explained by the fact that the study determines the head of one and the pelvic end (in the bottom of the uterus) of another fetus, which lies slightly higher.
- Feeling the movement of the fetus in different places and probing parts of the fetus in different parts of the abdomen (both on the right and on the left) also indicate multiple pregnancies. nine0031
Make an appointment
to the doctor - Arifullina Claudia Viktorovna
Clinical Hospital "AVICENNA" GC "Mother and Child"
GastroenterologyPediatric Gastroenterology
By clicking on the send button, I consent to the processing of personal data
Attention! Prices for services in different clinics may vary. To clarify the current cost, select the clinic
The administration of the clinic takes all measures to update the prices for programs in a timely manner, however, in order to avoid possible misunderstandings, we recommend that you check the cost of services by phone / with the managers of the clinic
Clinical Hospital "AVICENNA" Group of Companies "Mother and Child" Novosibirsk Center for Reproductive Medicine
All directionsGynecological proceduresSpecialist consultations (adults)Specialist consultations (children)Laboratory of molecular geneticsGeneral clinical examinationsProcedural roomTherapeutic examinationsUltrasound examinations for adults
nine0002 01.
Gynecological procedures
02.
Consultations of specialists (adults)
03.
Consultations of specialists (children's)
04.
Laboratory of molecular genetics
05.
General clinical studies
06 06.
Treatment Room
07.
Therapeutic Research
08.
Adult Ultrasound
Nothing found
The administration of the clinic takes all measures to update the price list posted on the website in a timely manner, however, in order to avoid possible misunderstandings, we advise you to clarify the cost of services and the timing of the tests by calling
Development of twins by weeks of pregnancy
Pregnancy
Article
0 reviews
According to various estimates, there are 70-80 million pairs of twins in the world today. At the same time, multiple pregnancy is becoming more common. Researchers name different reasons for multiple pregnancy: heredity, modern methods of infertility treatment, in particular IVF, the increased average age of women in labor. One way or another, pregnancy with twins is a very exciting and wonderful period that requires special attention. nine0003
At the same time, multiple pregnancy is becoming more common. Researchers name different reasons for multiple pregnancy: heredity, modern methods of infertility treatment, in particular IVF, the increased average age of women in labor. One way or another, pregnancy with twins is a very exciting and wonderful period that requires special attention. nine0003
6 min. for reading Feb. 17, 2022
Pregnancy with twins: signs and features of the course
The signs of twins are not much different from the symptoms of a singleton pregnancy. The essence of the differences is in the intensity and earlier period of these manifestations.
- Early toxicosis is one of the most common signs of multiple pregnancy. Nausea, vomiting, odor intolerance, drowsiness and dizziness can disturb the expectant mother from the first days of the birth of babies.
 Symptoms stop at 12-15 weeks. nine0031 Accelerated weight gain and belly growth — during pregnancy with twins, a woman rapidly gains from 15 to 15 kg, and only 8 kg with one fetus.
Symptoms stop at 12-15 weeks. nine0031 Accelerated weight gain and belly growth — during pregnancy with twins, a woman rapidly gains from 15 to 15 kg, and only 8 kg with one fetus. - Frequent urination - the uterus grows faster and already in the early stages presses on the bladder, provoking frequent urination. In addition, filling the abdominal cavity, the enlarged uterus makes it difficult for the outflow of bile and raises the diaphragm. This causes bitterness in the mouth and shortness of breath, two more signs of twin pregnancy. nine0031
- Movements of two babies are much more intense and grow faster.
Read also: Multiple pregnancy: 7 signs
Multiple pregnancy requires great care from future parents and doctors. With the development of two babies, the risk of miscarriage and premature birth increases, and the load on the mother's body also increases significantly.
Rapid and strong weight gain often adversely affects the condition of blood vessels, spine and joints. As a result - back pain, swelling of the legs and varicose veins. nine0003
An enlarged uterus puts more pressure on the internal organs in the abdominal cavity. Therefore, mothers of twins are more often annoyed by constipation and heartburn. Also, a large amount of fluid in the body increases the risk of anemia.
See also: Anemia during pregnancy
Childbirth in multiple pregnancies occurs several weeks earlier: most often at 36-38 weeks, but the probability of even earlier births must be taken into account. In addition, most twins are born by caesarean section, as there is an increased risk of complications during vaginal delivery. nine0003
Interesting
Twins have a special advantage: babies quickly adapt to a new environment, grow and gain weight at an accelerated pace, so they easily catch up with their peers.
Types of multiple pregnancy
There are two main types of twins:
- Identical, or identical - appear when the ovum divides into several cells, most often two. As a rule, identical twins are of the same sex, have the same set of genes, blood type and Rh factor, and are almost indistinguishable in appearance. nine0031
- Fraternal twins develop from two fertilized eggs. They have separate fetal sacs and different placentas. They can be of different sexes and resemble each other no more than ordinary brothers and sisters. This type of multiple pregnancy is much more common.
Interesting
Colloquially, fraternal twins are called twins. But from a scientific point of view, this is not true, because such a term does not exist. nine0157
Pregnancy with twins by weeks
First trimester
- 5-6 weeks. It is already possible with a high probability to identify twins, but only through ultrasound.

See also: 1st trimester screening: what is it and how is it done?
- 8 weeks. A multiple pregnancy can be diagnosed by a gynecologist during examination. But this method of definition is not very accurate. This week, the placenta is strengthening, the fetuses already have the rudiments of all organs and the neural tube. On an ultrasound of twins, you can see how the hearts contract. nine0031
- 10 weeks. The size of both babies reaches 4.5 cm, all organs and systems are actively formed.
- 11 weeks. The expectant mother has a tummy and the symptoms of toxicosis gradually subside.
- 12 weeks. The twins have grown to 6 cm and fixed on the wall of the uterus, so the likelihood of a miscarriage has decreased significantly.
II trimester
- 13 weeks. The weight of the twins is growing more and more actively every week, now it is about 14 g. At the same time, the uterus increases dramatically, sometimes causing pain in the lumbar region.
 nine0031
nine0031 - 14 weeks. The uterus is growing rapidly and is already much taller than in a singleton pregnancy.
- 15 weeks. The twins have already gained about 60 g and have grown to 10 cm. They train breathing movements and suck their fingers.
- 16 weeks. The belly of the mother of twins looks like she is at 18 weeks of a singleton pregnancy. The crumbs are already moving, but the tremors are still weak and not felt.
- 17 weeks. The stomach has become large, it interferes with sleep. Now is the time to take intensive care of your skin to avoid stretch marks. nine0031
- 18 weeks. The abdomen is enlarged. To reduce stress on your back, wear a brace. If the pregnancy is the second, the first movements are already noticeable. It is possible to increase the tone of the uterus.
- 19 weeks. Babies grow “by leaps and bounds”: they have stretched up to 25 cm and have already gained almost 300 g each. The nervous system and lungs are actively forming, a reaction to bright light appears, the crumbs begin to feel the presence of each other.

- 20 weeks. The mother-to-be feels the twins for the first time, and their bond grows stronger. Children form their own schedule of periods of sleep and activity. Kidneys worked. nine0031
- 21 weeks. Babies are great at hearing and recognizing sounds. They have learned to open their eyes, but their eyesight is still very weak. The bones have become stronger, the coordination of movements has improved.
- 22 weeks. The time of the planned ultrasound, during which it may turn out that the children differ in height and weight. If the difference is insignificant, there is nothing to worry about.
Read also: 2nd trimester screening: when to do it?
- 23 weeks. Babies are actively gaining weight and have already “ate” 500 g. During this period, it is important for mom to monitor nutrition and seriously take care of her health. nine0031
- 24 weeks. The weight has increased even more. Be attentive to your feelings: the risk of pyelonephritis, preeclampsia or placenta previa has increased.

- 25 weeks. The belly and the twins inside grow equally fast. It's time to focus on the health of the kids and think about maternity leave.
- 26 weeks. The uterus filled the abdominal cavity, squeezing the intestines, causing labored breathing and frequent urination.
- 27 weeks. The weight of the twins is approaching 1 kg. Increased risk of amniotic fluid leakage and preterm birth. nine0031
- 28 weeks. Babies weigh more than 1 kg and are quite viable. It's time to go on maternity leave.
III trimester
- 29 weeks. The twins stock up on fat and prepare to face the outside world. Weight reaches 1100–1300 g.
- 30 weeks. Growth stops a little, but weight gain is becoming more and more active. Babies take their final position in the uterus. If they are positioned incorrectly, this may be an indication for a caesarean section. The twins can already breathe on their own, regulate their body temperature, and the intestines are quite ready for eating.
 nine0031
nine0031 - 31 weeks. The abdomen has grown to its maximum size. The movements of the twins became intense, up to pain. During this period, it is desirable to be more outdoors.
See also: How much weight can I put on?
- 32 weeks. Vital organs and systems are formed, the kids just have to gain the right weight. Surfactant is actively produced - a special substance that helps the lungs of a newborn to straighten out. nine0031
- 33 weeks. Strong men already weigh almost 2 kg and are more than 40 cm tall. From now on, the expectant mother needs to visit the doctor weekly.
- 34 weeks. Twins become crowded in the mother's tummy, the kids move less. The uterus descends lower, allowing you to breathe fully.
- 35 weeks. The twins are quite ready to meet their parents.
- 36-37 weeks. Since earlier births are the norm for multiple pregnancies, most babies are born at this time. With twin pregnancy, 38 weeks is quite rare.