What is chloasma in pregnancy
Chloasma--the mask of pregnancy - PubMed
Review
. 2008 Oct;32 Suppl 2:139-41.
Ivan Bolanca 1 , Zeljana Bolanca, Krunoslav Kuna, Ante Vuković, Neven Tuckar, Radoslav Herman, Goran Grubisić
Affiliations
Affiliation
- 1 University Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, University Hospital Sestre milosrdnice, Zagreb, Croatia. [email protected]
- PMID: 19140277
Review
Ivan Bolanca et al. Coll Antropol. 2008 Oct.
. 2008 Oct;32 Suppl 2:139-41.
Authors
Ivan Bolanca 1 , Zeljana Bolanca, Krunoslav Kuna, Ante Vuković, Neven Tuckar, Radoslav Herman, Goran Grubisić
Affiliation
- 1 University Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, University Hospital Sestre milosrdnice, Zagreb, Croatia.
[email protected]
- PMID: 19140277
Abstract
Chloasma is a required hypermelanosis of sun-exposed areas occurred during pregnancy and it can affect 50-70% of pregnant women. It presents as symmetric hyperpigmented macules, which can confluent or punctuate. The most common locations are the cheeks, the upper lip, the chin and the forehead. The exact mechanism by which pregnancy affects the process of melanogenesis is unknown. Estrogen, progesterone, and melanocyte-stimulating hormone (MSH) levels are normally increased during the third trimester of pregnancy. However, nulliparous patients with chloasma have no increased levels of estrogen or MSH. In addition, the occurrence of melasma with estrogen- and progesterone-containing oral contraceptive pills has been reported. The observation that postmenopausal woman who are given progesterone develop melasma, while those who are given only estrogen do not, implicates progesterone as playing a critical role in the development of melasma. UV-B, UV-A, and visible light are all capable of stimulating melanogenesis. The condition is self-limited; however spontaneous resolution is time-consuming and may take months to resolve normal pigmentation. Therefore, it is worthwhile to prevent the onset of chloasma, by strict photoprotection. Prudent measures to avoid sun exposure include hats and other forms of shade combined with the application of a broad-spectrum sunscreen at least daily. Sunscreens containing physical blockers, such as titanium dioxide and zinc oxide, are preferred over chemical blockers because of their broader protection. Chloasma can be difficult to treat. Quick fixes with destructive modalities (eg, cryotherapy, medium-depth chemical peels, lasers) yield unpredictable results and are associated with a number of potential adverse effects.
The observation that postmenopausal woman who are given progesterone develop melasma, while those who are given only estrogen do not, implicates progesterone as playing a critical role in the development of melasma. UV-B, UV-A, and visible light are all capable of stimulating melanogenesis. The condition is self-limited; however spontaneous resolution is time-consuming and may take months to resolve normal pigmentation. Therefore, it is worthwhile to prevent the onset of chloasma, by strict photoprotection. Prudent measures to avoid sun exposure include hats and other forms of shade combined with the application of a broad-spectrum sunscreen at least daily. Sunscreens containing physical blockers, such as titanium dioxide and zinc oxide, are preferred over chemical blockers because of their broader protection. Chloasma can be difficult to treat. Quick fixes with destructive modalities (eg, cryotherapy, medium-depth chemical peels, lasers) yield unpredictable results and are associated with a number of potential adverse effects. The mainstay of treatment remains topical depigmenting agents. Hydroquinone (HQ) is most commonly used.
The mainstay of treatment remains topical depigmenting agents. Hydroquinone (HQ) is most commonly used.
Similar articles
-
Evaluation of the effectiveness of a broad-spectrum sunscreen in the prevention of chloasma in pregnant women.
Lakhdar H, Zouhair K, Khadir K, Essari A, Richard A, Seité S, Rougier A. Lakhdar H, et al. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2007 Jul;21(6):738-42. doi: 10.1111/j.1468-3083.2007.02185.x. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2007. PMID: 17567299 Clinical Trial.
-
[Facial melanosis (melasma)].
Witkiewicz IM, Neering H. Witkiewicz IM, et al. Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd. 1981 Apr 18;125(16):609-11. Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd. 1981. PMID: 7242709 Dutch.
-
Near-visible light and UV photoprotection in the treatment of melasma: a double-blind randomized trial.
Castanedo-Cazares JP, Hernandez-Blanco D, Carlos-Ortega B, Fuentes-Ahumada C, Torres-Álvarez B. Castanedo-Cazares JP, et al. Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed. 2014 Feb;30(1):35-42. doi: 10.1111/phpp.12086. Epub 2013 Dec 3. Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed. 2014. PMID: 24313385 Clinical Trial.
-
Advances in the treatment of melasma: a review of the recent literature.
Ball Arefiev KL, Hantash BM. Ball Arefiev KL, et al. Dermatol Surg. 2012 Jul;38(7 Pt 1):971-84. doi: 10.1111/j.1524-4725.2012.02435.x. Epub 2012 May 14. Dermatol Surg. 2012. PMID: 22583339 Review.
-
Melasma--updated treatments.
Situm M, Kolić M, Bolanca Z, Ljubicić I, Misanović B. Situm M, et al. Coll Antropol. 2011 Sep;35 Suppl 2:315-8. Coll Antropol. 2011. PMID: 22220462 Review.
See all similar articles
Cited by
-
Loss of EMP2 Inhibits Melanogenesis of MNT1 Melanoma Cells via Regulation of TRP-2.
Enkhtaivan E, Kim HJ, Kim B, Byun HJ, Yu L, Nguyen TM, Nguyen TH, Do PA, Kim EJ, Kim KS, Huy HP, Rahman M, Jang JY, Rho SB, Lee H, Kang GJ, Park MK, Kim NH, Choi CI, Lee K, Han HK, Cho J, Lee AY, Lee CH. Enkhtaivan E, et al. Biomol Ther (Seoul). 2022 Mar 1;30(2):203-211. doi: 10.4062/biomolther.2022.001. Biomol Ther (Seoul).
 2022. PMID: 35221300 Free PMC article.
2022. PMID: 35221300 Free PMC article. -
Sex Hormones and Optic Nerve Disorders: A Review.
Nuzzi R, Scalabrin S, Becco A, Panzica G. Nuzzi R, et al. Front Neurosci. 2019 Feb 11;13:57. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2019.00057. eCollection 2019. Front Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 30804741 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ocular changes during pregnancy.
Naderan M. Naderan M. J Curr Ophthalmol. 2018 Jan 3;30(3):202-210. doi: 10.1016/j.joco.2017.11.012. eCollection 2018 Sep. J Curr Ophthalmol. 2018. PMID: 30197948 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lack of pregnancy warnings on over-the-counter dermatologic products containing potentially harmful hydroquinone.
Bio LL, Cies JJ. Bio LL, et al. J Perinatol. 2017 Jul;37(7):778-781. doi: 10.1038/jp.2017.35. Epub 2017 Mar 30. J Perinatol. 2017. PMID: 28358386
-
Melasma: a clinical and epidemiological review.
Handel AC, Miot LD, Miot HA. Handel AC, et al. An Bras Dermatol. 2014 Sep-Oct;89(5):771-82. doi: 10.1590/abd1806-4841.20143063. An Bras Dermatol. 2014. PMID: 25184917 Free PMC article. Review.
See all "Cited by" articles
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Changes to your skin during pregnancy
beginning of content3-minute read
Listen
As your pregnancy develops, you may find that you experience changes to your skin and hair. Some women can develop dark patches on their face and hormonal changes can make your skin a little darker.
Some women can develop dark patches on their face and hormonal changes can make your skin a little darker.
You may also develop stretch marks on your body, particularly around your stomach where your skin is stretching to accommodate your growing baby.
Chloasma - dark patches on the face
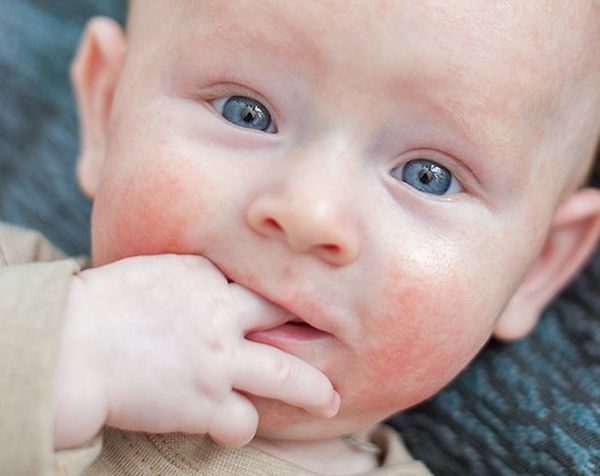
Some pregnant women develop dark irregular patches on their face most commonly on the upper cheek, nose, lips, and forehead. This is called 'chloasma'. It is also sometimes known as 'melasma' or the 'mask of pregnancy'.
Chloasma is thought to be due to stimulation of pigment-producing cells by female sex hormones so that they produce more melanin pigments (dark coloured pigments) when the skin is exposed to sun. Some women develop these patches when they take oral contraceptives (the pill).
Women with a light brown skin type who are living in regions with intense sun exposure are more likely to develop these patches. The patches usually fade over a period of several months after giving birth, though they may last for several years for some women.
Careful protection of the skin using broad spectrum sunscreens every day during pregnancy and while taking the pill may make it less likely that chloasma will develop. It is necessary to continue to use sunscreen after pregnancy as sun exposure may cause the patches to reappear. Some creams that need to be prescribed by doctors may help to fade the patches.
Skin and hair changes
Hormonal changes taking place in pregnancy will make your nipples and the area around them go darker. Your skin colour may also darken a little, either in patches or all over. Birthmarks, moles and freckles may also darken. Some women develop a dark line down the middle of their stomach, called 'linea nigra'. These changes will gradually fade after the baby is born, although your nipples may remain a little darker.
If you sunbathe while you are pregnant, you may burn more easily. Protect your skin with a good high-factor sunscreen and don't stay in the sun for a long time.
Hair growth can also increase in pregnancy, and your hair may be greasier. After the baby is born, it may seem as if you are losing a lot of hair but you are simply losing the extra hair.
After the baby is born, it may seem as if you are losing a lot of hair but you are simply losing the extra hair.
Stretch marks
Many women develop stretch marks during their pregnancy, usually in the last 3 months.
They usually appear on your stomach or sometimes on your upper thighs or breasts. Stretch marks are not harmful and over time, your skin will shrink and the stretch marks will fade into white-coloured scars.
Find out more on stretch marks.
Sources:
Royal Women's Hospital Victoria (Common concerns in early pregnancy - itching and skin), The Australasian College of Dermatologists (Striae), The Australasian College of Dermatologists (Melasma)Learn more here about the development and quality assurance of healthdirect content.
Last reviewed: January 2020
Back To Top
Related pages
- Common discomforts during pregnancy
- Stretch marks
Healthdirect Australia acknowledges the Traditional Owners of Country throughout Australia and their continuing connection to land, sea and community. We pay our respects to the Traditional Owners and to Elders both past and present.
We pay our respects to the Traditional Owners and to Elders both past and present.
This information is for your general information and use only and is not intended to be used as medical advice and should not be used to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any medical condition, nor should it be used for therapeutic purposes.
The information is not a substitute for independent professional advice and should not be used as an alternative to professional health care. If you have a particular medical problem, please consult a healthcare professional.
Except as permitted under the Copyright Act 1968, this publication or any part of it may not be reproduced, altered, adapted, stored and/or distributed in any form or by any means without the prior written permission of Healthdirect Australia.
Support this browser is being discontinued for Pregnancy, Birth and Baby
Support for this browser is being discontinued for this site
- Internet Explorer 11 and lower
We currently support Microsoft Edge, Chrome, Firefox and Safari. For more information, please visit the links below:
For more information, please visit the links below:
- Chrome by Google
- Firefox by Mozilla
- Microsoft Edge
- Safari by Apple
You are welcome to continue browsing this site with this browser. Some features, tools or interaction may not work correctly.
Pregnancy mask, or postpartum pigmentation - PURE
Inevitably, after the birth of a child, a woman's body undergoes significant changes. And if changes in the figure or size of the breast are quite expected, then the appearance of extensive age spots is unlikely to leave anyone indifferent. Pigmentation that occurs during or after pregnancy is often referred to as “mask of pregnancy”.
What is a “pregnancy mask”?
This kind of pigmentation appears in the center of the forehead, on the back of the nose, above the upper lip, on the chin (centrofascial chloasma), on the cheeks, temples, wings of the nose (molar), on the corners of the lower jaw.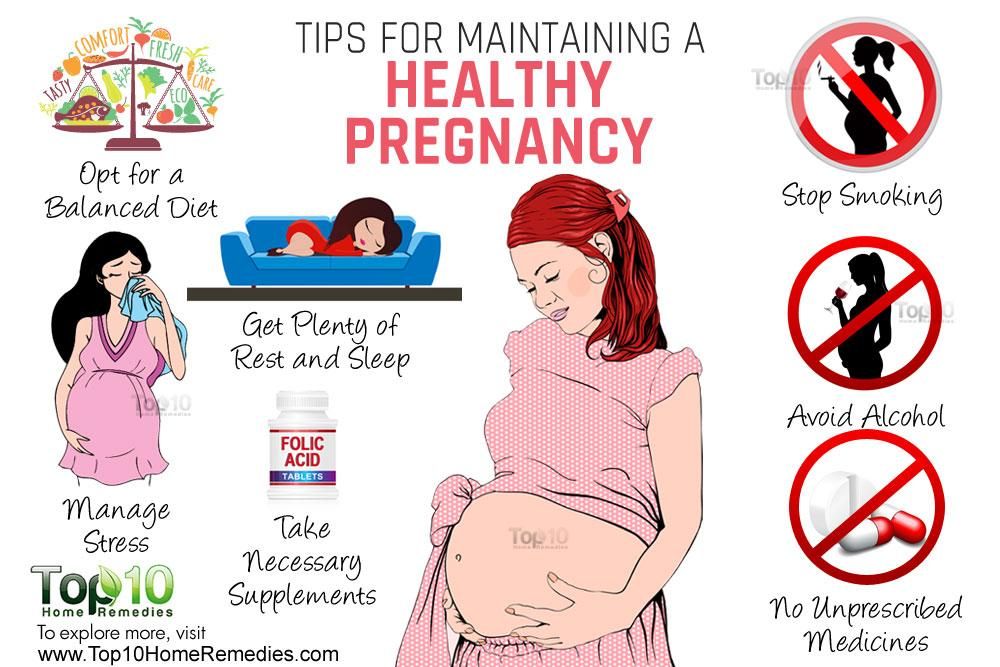 Term “mask” appeared due to the peculiarity of the spots to quickly merge into one, forming a kind of “mask”.
Term “mask” appeared due to the peculiarity of the spots to quickly merge into one, forming a kind of “mask”.
In fact, not only the face, but also the body is affected by such pigmentation. So, for example, the “white line of the abdomen” darkens - a strip from the pubis to the navel, armpits and elbows.
Causes
Such age spots appear in the third trimester of pregnancy. Despite the fact that absolutely all women are at risk, the “mask of pregnant women” most often appears in owners of II-III phototypes.
The main cause of pigmentation is hormonal changes in a woman's body. Melanocyte cells, which synthesize melanin, are responsible for the appearance of any pigment on the skin, as well as hair color and the pigment layer of the retina. The hormones estrogen and progesterone activate the melanocytes, and in response, they begin to produce more melanin. During pregnancy, progesterone levels are higher. As a result, the risk of pigmentation increases.
It is important to understand that such a process does not indicate a failure in the body. Melanocytes perform the protective function of the body from ultraviolet radiation. By increasing progesterone, the body puts melanocytes on alert to protect the baby and mother from the harmful effects of ultraviolet radiation.
The statement about the hormonal trace in the occurrence of pigmentation is also confirmed by the fact that pigmentation appears in women taking hormonal drugs that increase progesterone. So, doctors often warn patients taking oral contraceptives not to sunbathe.
Another possible cause of pigmentation in pregnant women is the hormone melanotropin. Its content in the blood of pregnant women is also increased. Most of the studies say that the increase in melanotropin is due to the fact that expectant mothers have increased production of adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH), which stimulates the production of melanotropin.
Methods for preventing and lightening the “pregnancy mask”
Trying to specifically lower progesterone levels during pregnancy is a senseless and unsafe undertaking. In addition, postpartum pigmentation tends to “disappear” in some cases within six months after childbirth. If you notice that pigmentation does not go away on its own, it makes sense to contact an endocrinologist to check the necessary hormones.
In addition, postpartum pigmentation tends to “disappear” in some cases within six months after childbirth. If you notice that pigmentation does not go away on its own, it makes sense to contact an endocrinologist to check the necessary hormones.
Now more and more doctors are paying attention to the fact that pigmentation during pregnancy is rare in women taking folic acid - it is prescribed to almost all women planning a pregnancy for the healthy development of the baby. Studies explain this effect by the ability of folic acid to normalize the exchange of melanin in the skin. However, we strongly advise against taking anything without a doctor's prescription.
Properly selected home care can both reduce the likelihood of pigmentation and help lighten existing ones. When planning your pregnancy care regimen, focus on reliable sunscreen and antioxidants. It is important to choose sunscreens with stable filters. In order not to run around cosmetic stores with a list of SPF filters and be sure of the safety of the sunscreen used, choose Japanese manufacturers.
Antioxidants are more difficult.
Photosomes are now the most powerful antioxidant, a unique component from blue-green algae that restores intracellular DNA and the immune system of cells suppressed by ultraviolet radiation.
Photosomes can be found in Bemetic GR Elixir Toner. In addition to photosomes that protect DNA, tranexamic acid is present in the composition, which has a powerful lightening effect. When creating a means for lightening pigmentation, the manufacturer did not bypass gluconolactone, which, according to in vitro studies, provides up to 50% protection against ultraviolet radiation, reducing the likelihood of sunburn and pigmentation.
Important! The product is safe to use during pregnancy.
To solve the problem of already existing pigmentation, it is worth paying attention to the components that inhibit the activity of the enzyme responsible for pigment production. These ingredients include:
- Vitamin C. Vitamin C serums help lighten light pigmentation by inhibiting tyrosinase activity. In addition, vitamin C stimulates the production of collagen and gives the skin a radiance.
Vitamin C serums help lighten light pigmentation by inhibiting tyrosinase activity. In addition, vitamin C stimulates the production of collagen and gives the skin a radiance.
Among the vitamin C products, the 20% vitamin C serum from the American brand Timeless stands out. The product is suitable for use on both the face and body, and is also safe to use during pregnancy.
- Alpha Lipoic Acid. It is valued for its ability to repair damaged cells after exposure to ultraviolet radiation. In addition to the brightening effect, it has a powerful lifting effect due to the suppression of the photoaging process. Alpha-lipoic acid is present in the Bemetic G toner-elixir. In addition to brightening, the product provides gentle exfoliation, tightens pores and provides a noticeable lifting effect.
- Kojic acid and alpha arbutin. These two ingredients are often found together in formulas. The brightening effect is due to the ability to inhibit tyrosinase activity and gently exfoliate the stratum corneum. Both ingredients can be found in Sesderma Hidroquin Depigmentation Gel brightening cream. In addition to kojic acid and alpha-arbutin, the composition contains ferulic acid and retinol. Due to the presence of the latter, the product is not suitable for use during pregnancy.
Both ingredients can be found in Sesderma Hidroquin Depigmentation Gel brightening cream. In addition to kojic acid and alpha-arbutin, the composition contains ferulic acid and retinol. Due to the presence of the latter, the product is not suitable for use during pregnancy.
- Tranexamic acid. A study comparing the effect of 4% hydroquinone and 3% tranexamic acid leaves no doubt about the effectiveness of the latter in lightening pigmentation. According to the study, 3% tranexamic acid had the same brightening effect as 4% hydroquinone. A nice bonus is that tranexamic acid is safe to use during pregnancy.
Tranexamic acid is present in the Bemetic GR toner-elixir.
- Azelaic acid. It has both brightening and anti-inflammatory effects. This feature of the component allows the agent to have a beneficial effect both on the course of acne and on lightening pigmentation.
Azelaic acid is found in the Paula's Choice 10% Azelaic Acid booster. The product is safe to use during pregnancy.
The most important advice we can give is not to panic if pigmentation occurs. It may resolve on its own. Moreover, the cosmetic market and cosmetology can offer a solution to the problem.
Author of the article: Safiyat Akhmatova
Pigmentation during pregnancy is not a disease
Waiting for a little baby is the most magical and unique period in a woman's life. The expectant mother becomes mysterious, sensitive, caring and unhurried.
The body of a pregnant woman changes every day, and this is natural - after all, a small defenseless little man grows under her heart, whose life and health largely depends on her mother.
A woman already from the first weeks of pregnancy notices changes in her body: the shape is rounded, the breast becomes one size larger and more sensitive than before.
Pigmentation is a fairly common phenomenon during an interesting situation. The appearance of pigmentation on the face and body excites many women.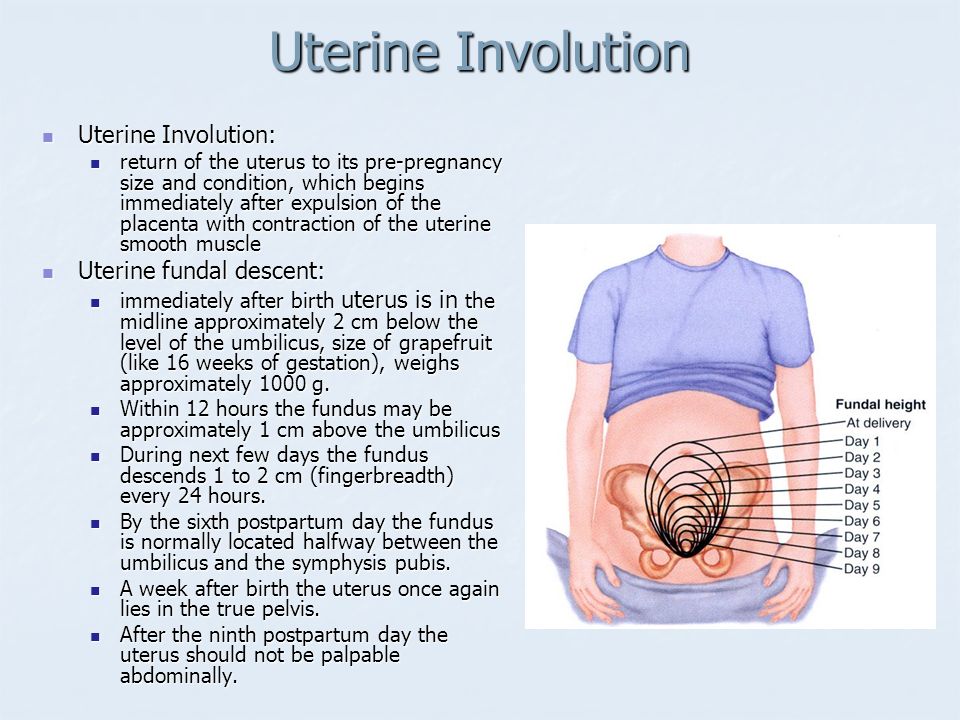
Some of them are interested in the causes of pigmentation on the skin, while others are trying to find ways to get rid of it. Pigment is a brown coloring matter. Pigmentation is more common in brunettes and dark-skinned women.
There is a popular belief that if a woman's skin deteriorates during pregnancy and age spots become noticeable, she will be a girl! But it is hardly possible to believe in it one hundred percent. Skin pigmentation is a temporary phenomenon, like pregnancy itself, and age spots also happen with boys in the tummy.
Brown spots in pregnant women are called differently: chloasma, mask, hyperpigmentation of the skin. Pigmentation most often appears on a woman's forehead, cheeks, chin, and also happens above the upper lip. A woman can also notice pigmented areas of skin with sharply defined edges on the neck, chest and tummy in the form of a thin strip. If earlier, with the beginning of spring, you had freckles on your face, then most likely their appearance will intensify during pregnancy as a kind of manifestation of pigmentation.
What causes pigmentation during pregnancy? Of course, this is a hormonal restructuring of the body of the woman herself, changes in the work of all organs, primarily the adrenal cortex and pituitary gland. There are opinions that pigmentation is a genetic phenomenon, and also takes place in case of a lack of folic acid in a woman's body.
In order to prevent and prevent the appearance of pigmented skin areas, pregnant women are advised to take quite affordable preventive measures:
- reduce the amount of time you spend in the sun. Bright sunlight has beneficial properties, thanks to which vitamin D is constantly produced in the body, but even a short stay in the open sun can provoke pigmentation. If possible, wear light clothing that covers the body, as well as use sunscreen for children with a sufficiently high degree of protection;
- carefully monitor your own health, avoid hypothermia and colds;
- limit the use of cosmetics as much as possible in the summer to avoid the appearance of pigmentation and allergies;
- take complex vitamins specially formulated for pregnant women, especially folic acid;
- eat right, include more vegetables, fruits, cereals and dairy products in your menu;
- avoid stressful situations, do not get nervous and do not "wind" yourself over trifles.

Experts believe that when pigmentation appears while expecting a baby, a woman should not take measures to remove them and especially worry about this, she should try to calmly accept these changes in the body, because the spots disappear, as a rule, on their own within two months after childbirth. But for a woman in an interesting position, even such harmless spots can ruin her mood and bring her to tears.
You always want to be beautiful and well-groomed!
If during pregnancy you were “lucky” to become a carrier of specific age spots, then here are some tips to make them less noticeable:
- You can prepare a mask of kefir and lemon juice. Apply such a mask to the skin, hold for about 15-20 minutes, then rinse thoroughly with warm water;
- gentle curd mask is a reliable helper in the fight against age spots: mix cottage cheese with curdled milk, apply this mixture on your face for 15 minutes, then rinse thoroughly with boiled water;
- cucumber mask is good for whitening age spots.