White dots on bottom of foot
Lumps and Bumps on your Feet?
Skip to contentQuite often, patients come to our clinic with bumps on their tissue and ask us what they are. Usually, these findings are incidental, normal, not painful and not sinister. As with any condition that walks through our doors, the diagnosis is very important so consulting with a suitable practitioner who can accurately diagnose your condition is vital. Two lesser-known conditions that occur in the foot are plantar fibromatosis and piezogenic pedal papules.
Plantar Fibromatosis
Plantar fibromatosis is a relatively rare condition in which fibrotic tissue gathers in the bottom of the foot. Also referred to as ledderhose disease, the cause for these lumps in the bottom of the foot are generally unknown. Plantar fibromatosis is benign and it occurs in the aponeurosis of the plantar fascia. It occurs more frequently in men between the ages of 30-50. People with other soft tissue contractures (such as Dupuytren’s), diabetes, epilepsy, alcoholics people with liver disease and keloids are thought to be at a greater risk for developing plantar fibromatosis. Although the fibromatosis is not painful, pain may occur in the bottom of the foot because of the lesion taking up space. Logically, prolonged standing, running, and stretching can be uncomfortable.
The diagnosis of plantar fibromatosis can usually be done clinically. Soft tissue imaging (such as ultrasound or MRI) can clarify the nature of the lesion but usually isn’t necessary. Conservative treatment of plantar fibromatosis can include manual therapy, graston, active release technique, stretching, strengthening, footwear modification and orthotics. For more symptomatic and larger lesions, consultation with a medical foot specialist may be warranted. In some cases, topical medication or cortisone injections might be helpful. For very large lesions surgical excision can be considered.
Piezogenic Pedal Papules
Piezogenic pedal papules are small, yellow to white bumps that occur on the bottom and sides of the foot when weight bearing, and they disappear when non-weightbearing.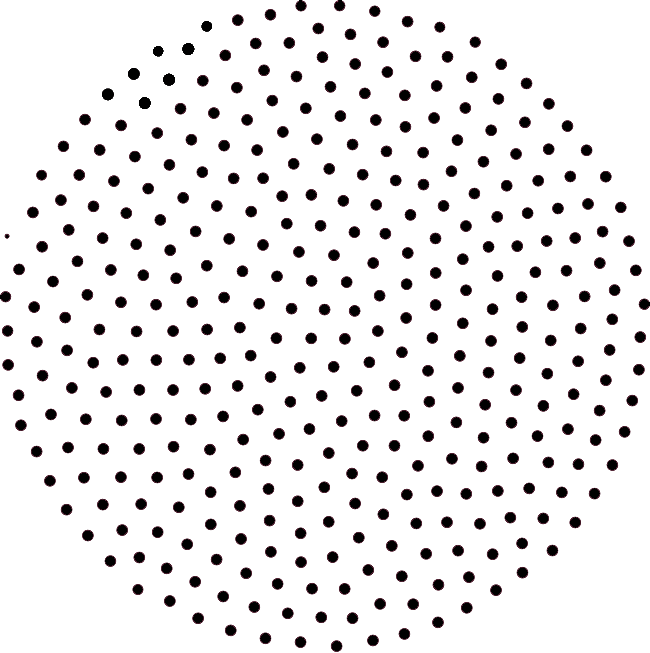 They can also present when pressure is applied to the foot. They are generally considered as normal variants and are not usually painful. They are small herniations of subcutaneous tissue. As an example, imagine a sausage with pencil-sized holes in the skin of the sausage and the meat bulging through those holes when pressure is applied. Piezogenic pedal papules have a relation to weak collagen which is why the tissue extrudes through the weakened tissue wall. Given the relationship to weak collagen, piezogenic pedal papules have been linked to various connective tissue disorders such as Ehlers-Danlos and Prader-Willi. Although the research hasn’t given us a specific cause and there still is much to be learned about this condition, we do know that certain populations are more at risk for piezogenic pedal papules. Those who are obese, those with flat feet and people who stand a lot are more likely to experience these papules. Logically, figure skaters, long distance runners and those who participate in high-impact sports with lots of jumping often present with these papules.
They can also present when pressure is applied to the foot. They are generally considered as normal variants and are not usually painful. They are small herniations of subcutaneous tissue. As an example, imagine a sausage with pencil-sized holes in the skin of the sausage and the meat bulging through those holes when pressure is applied. Piezogenic pedal papules have a relation to weak collagen which is why the tissue extrudes through the weakened tissue wall. Given the relationship to weak collagen, piezogenic pedal papules have been linked to various connective tissue disorders such as Ehlers-Danlos and Prader-Willi. Although the research hasn’t given us a specific cause and there still is much to be learned about this condition, we do know that certain populations are more at risk for piezogenic pedal papules. Those who are obese, those with flat feet and people who stand a lot are more likely to experience these papules. Logically, figure skaters, long distance runners and those who participate in high-impact sports with lots of jumping often present with these papules.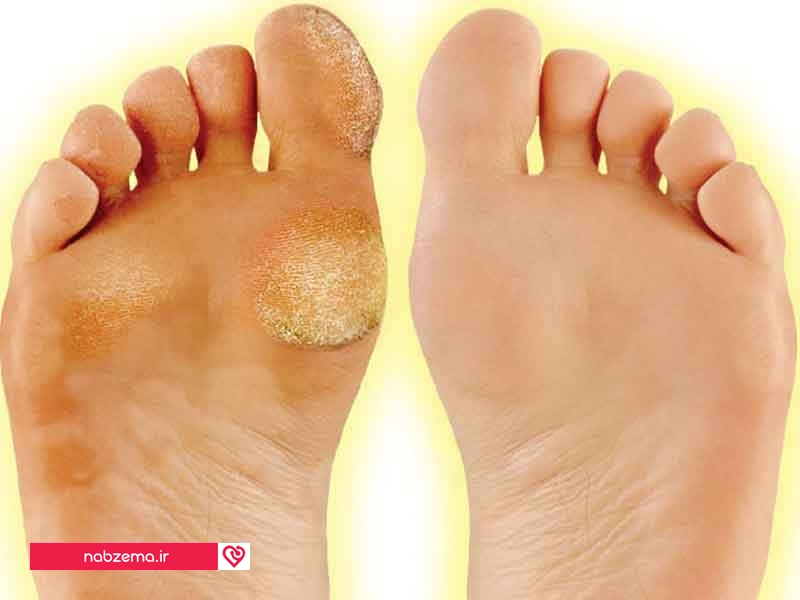
In most cases of piezogenic pedal papules there is no pain. As such, we don’t really know much about this phenomenon, and we don’t know the incidence because most cases likely go undiagnosed or unnoticed. At a clinic like Burlington Sports Therapy, we don’t really treat symptomatic piezogenic pedal papules. If there is suspicion of these lesions being a pain generator we would recommend those patients consult with their medical doctor and discuss referral to a suitable medical specialist with experience in this rare situation. That being said, we would recommend the patient strengthen the intrinsic muscles of the foot and we would counsel these patients on avoiding aggravating factors and modifying their activities as such.
By: Dr. Kevin McIntyre B.Kin., DC
References
Young JR, Sternback S, Willinger M et al. Orthop Res Rev 2018.
Shelley WB, Rawnsley HM. Painful feet due to herniation of fat. JAMA. 1968 Jul 29;205(5):308-9.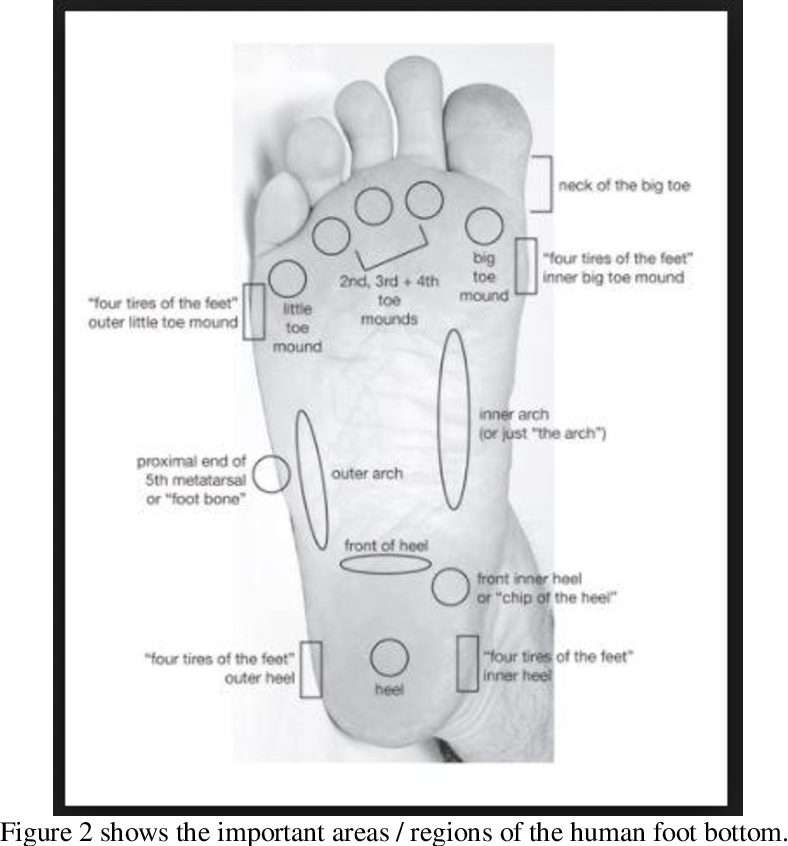
Laing VB, Fleischer AB. Piezogenic wrist papules: a common and asymptomatic finding. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1991 Mar;24(3):415-7.
Mai Y, Nishie W, Sugai T, Imafuku K, Arita K, Shimizu H. Disappearing subcutaneous papules and nodules: Characteristic features of muscle herniation and piezogenic pedal papules. J Dermatol. 2017 Dec;44(12):e361-e362.
Share This Story, Choose Your Platform!
Contact us today to book an appointment
First Name*
Last Name*
Email Address*
Phone Number
Subject*
Message*
Recent Posts
- Iliotibial Band Pain | Pain on the Outside of the Knee
- The Importance of Mental and Physical Health on Recovery from Physical Injuries
- Whiplash Treatment (Lessons Learned from my Recent Fall)
- The Importance of Balance
- What are Bunions (Hallux Valgus)?
Categories
- Chiropractic
- Massage Therapy
- News
- Physiotherapy
- Research
- Special Techniques
- Uncategorized
Common Fungal Skin Infections
- Home
- A-Z
Superficial skin fungus infections such as “white spot”, ringworm and athlete’s foot are common. Find out how to cure a fungal skin infection.
Find out how to cure a fungal skin infection.
The most common types of superficial fungal infections include "white spot", ringworm, athlete's foot and candidiasis (or moniliasis).
What is “White Spot”?
“White spot” or “panau” (in Malay) is a superficial fungal skin infection. The medical term is pityriasis versicolor or tinea versicolor. It usually affects adults and causes an itchy, scaly rash that appears as white, pink or brown patches on the face, neck, chest, back, shoulders and limbs. The condition is often aggravated by excessive sweating.
What is Ringworm?
Ringworm is a common term for a superficial fungal infection of the skin, which appears as scaly, red, round patches with a tendency to form rings. It is known as tinea corporis when it affects the body and tinea cruris when it affects the groin. Tinea capitis, or ringworm of the scalp, affects mainly children and can cause hair loss. However, this condition is relatively uncommon in Singapore. Healing may result in pigmentation of the skin.
Healing may result in pigmentation of the skin.
What is Athlete’s Foot?
Athlete’s foot is otherwise known as tinea pedis and is one of the most common fungal skin infections. The skin on the soles and toe webs typically becomes very scaly and peels. It is itchy, and occasionally small blisters may appear. The infection can also affect the toenails.
What is Moniliasis/Candidiasis?
This is a yeast infection that often affects moist areas like the skin folds, armpits and groin. It also occurs commonly on the genitalia and can cause a vaginal discharge in women. It is more common in people with diabetes mellitus and appears as itchy red spots or patches.
How to Prevent Superficial Fungal Skin Infections
Fungi grow where the skin is warm and sweaty. Keep the space between your toes, the skin folds in the groin area and the armpits dry to prevent such fungal infections. The use of powder may also help. Here are some other steps you can take to prevent superficial fungal skin infections:
- Wear slippers and avoid walking around barefoot in areas where the floor is wet as fungi may be present; such areas may include common showers, gyms, public toilets and swimming pools.
- Avoid sharing personal napkins, towels, combs and hair brushes as they may be infected, and these fungal skin infections are contagious.
- Nylon socks and covered shoes make your feet sweat. Instead, wear cotton socks to absorb the sweat or open-toe sandals if your feet sweat profusely. Always change your socks daily.
- Avoid wearing damp shoes. Try to alternate between two pairs of shoes.
How to Treat Superficial Fungal Skin Infections
Apply antifungal cream to the affected areas two to three times a day for four weeks. Do not stop using the medication even when the rash has cleared. Continue using it for at least seven days after the infection appears to have cleared. In the case of white spots, the white colour remains even after the fungal skin infection has been successfully treated. However, this will gradually improve over time as the skin recovers its normal colour.
Oral antifungal medications are needed for fungal skin infections affecting large areas. Your doctor may prescribe them.
Your doctor may prescribe them.
For prevention of white spots, use an antifungal shampoo and body wash once a month on your scalp and body. Leave it on for 10 minutes before washing it off. In the event of an infection, use this daily for seven to 14 days consecutively. Seek medical attention if the condition does not improve. Do not attempt to further self-medicate.
Fungal nail infections can be treated but often require prolonged treatment. It is important to realise that eradication of the fungi does not guarantee that the nails will return to a normal appearance.
Download the HealthHub app on Google Play or Apple Store to access more health and wellness advice at your fingertips.
Read these next:
- Q&A: Athlete's Foot
- Common Skin Conditions Linked to Housework
This article was last reviewed on Monday, October 11, 2021
755
Common Fungal Skin Infections
Catalog-Item Reuse
risk factors and possible complications
Human skin anomalies, their causes and classification have a wide range of definitions. This factor complicates the diagnosis of the disease and treatment procedures. White spots on the heels are a defect that can turn out to be a disease.
This factor complicates the diagnosis of the disease and treatment procedures. White spots on the heels are a defect that can turn out to be a disease.
Contents
- What white spots may indicate
- Causes and symptoms of appearance
- Features of localization
- Methods of treatment
- Risk factors and complications
- Hygiene rules and prevention
What white spots may indicate
The appearance of white spots on the feet indicates the occurrence of disorders in the human body. Outwardly, they can have various forms.
A) Large flat spots or corns:
- from wearing uncomfortable shoes;
- due to flat feet and excessive pressure on the foot;
- due to dryness of the skin of the feet and its lack of elasticity.
B) A corn-like stain - from uncomfortable shoes.
C) Formations in the form of tubercles on the heel of the foot, which are usually white:
- may protrude above the skin;
- be flat and not protrude;
- in the form of small knots;
- gray or brown flat plaques - "senile".
D) White plaque on the feet as a change in skin pigmentation.
E) White spots with holes or dots - another subtype of skin disease.
E) Cracks in the heel or other part of the sole.
All of them are related to cosmetic phenomena, but the causes of their occurrence should be sought with the help of a dermatologist.
The presence of external manifestations on the skin often indicates the papilloma virus, it is unpleasant and painful to move around. The virus is transmitted through the contact of carrier objects with damaged areas on the skin (cracks). Activation of activity occurs against the background of a general weakening of the immune system or as a result of an experienced nervous shock.
Spots called white may have other colors. They are divided into vascular - their appearance is caused by various inflammatory processes, and pigmentary - due to the reaction to ultraviolet rays. Or due to changes that have occurred within the body.
We advise you to read
The list of possible diseases is extensive:
- evidence of incipient varicose veins in the lower extremities are hemorrhagic spots;
- indistinct reddened areas that itch, may itch - this is erythema;
- causeless hematomas, blue dots indicate the presence of vascular pathologies and a lack of vitamin C;
- small scaly sheets, and the skin under them becomes denser - this is roseola;
- The appearance of areas of skin that are paler in color (whitish bloom) than the rest of the skin may be one of the signs of infection with syphilis.
If the leg, foot or heel is "stained" with white spots, buying medicines from a pharmacy can help with the treatment. But it is more correct to start therapy with a diagnosis made by a doctor.
Causes and symptoms of appearance
The absence of pain due to the appearance of white spots on the feet in the form of a small spot or large area has a cosmetic etiology. A qualified specialist will tell you about it.
A qualified specialist will tell you about it.
One of the most common diseases that cause such manifestations is vitiligo. It is also the cause of the appearance of white spots on the skin of a child, as well as pitiriasis.
The condition of the skin depends on the functional health of the human liver, which synthesizes melanin. The work of the gallbladder and biliary tract affects the pigmented appearance. Ultrasound examination will give an answer about the condition in this part of the body.
A blood test for thyroid hormones will help to identify the cause of the disease associated with the state of the thyroid gland.
Past intoxication of the body, changes in the immune status and the formation of parasites (helminthic invasions) in the body that block the absorption of copper provoke skin anomalies.
In addition to disease conditions, spots can also occur from excessive exposure to ultraviolet rays (in solariums), due to hormonal changes during pregnancy in women.
Given the diversity of depigmented areas that have a common name, but different nature, it is impossible to indicate the symptoms of the disease. They are united by one thing - the external manifestation on the skin, in most cases white and the absence of pain.
Among the features of the course of vitiligo in children, two are worth highlighting:
- Age from three years.
- The appearance of white spots of type B, in which, after a year of rapid spread, the process stops. Vitiligo type A disease does not have such a time division into periods, it is less common among children.
Spots caused by pityriasis (a mild form of dermatitis) do not form on the child's feet, but appear on most of the body.
Features of localization
White spots appear on different parts of the skin of the body, but in most cases they affect the lower limbs and heels. This statement will be especially true in relation to corns, cracks, corns and warts. The heel localization of the above types is explained by the fact that the main reasons for their appearance are problems associated with walking and the load on this part of the foot.
The heel localization of the above types is explained by the fact that the main reasons for their appearance are problems associated with walking and the load on this part of the foot.
Methods of treatment
When diagnosing the occurrence of vitiligo (diseases of internal organs, etc.), the initial cause should be eliminated in order to normalize the functioning of these organs and the endocrine system. Apply special procedures to get rid of parasites, sedatives to stabilize the patient's nervous activity.
The remedies offered by traditional healers are either difficult to prepare (according to one recipe, 21 types of plants plus lemon peel and 2 liters of vodka are needed for an infusion of medicinal herbs), or inconvenient to use (treatment of stains with one's own urine). Medical therapy appears to be more effective and practical.
Childhood vitiligo is treated with steroid creams or medications (Psoralen (P) in combination with ultraviolet light sessions.
For white wart-like spots, use:
- freezing techniques (liquid nitrogen) to kill the tissues and then peel them off;
- treatment of the affected area with cantharidin;
- stimulation of the immune system;
- drug Amiquinod for the production of antibodies by the patient's body to fight the papillomavirus;
- cutting tubercles with a scalpel, electric needle or cauterization with a laser device - treatment is operative, but leaves scars.
Treatment of white spots such as corns and calluses in many cases is a complex of preventive measures.
Risk factors and complications
The range of risk of white spots in their variety of forms and types is wide. The health of the legs and feet depends on careful attitude to this part of the body. The main, most reliable means of protection against the disease is a healthy lifestyle, in which the work of internal organs and the nervous system is not exposed to negative external influences. This remedy will best protect the body from the introduction of disease from the outside.
This remedy will best protect the body from the introduction of disease from the outside.
From the list of complications arising as a result of an illness, it is worth highlighting the danger of developing flat feet and the appearance of a disease of the spine (with corns). No less serious is the development of hyperkeratosis (from excess keratin). There may be core calluses in the space between the fingers, which lead to the appearance of fungal infections and to a similar disease of the nails on the toes. Holes may appear in the keratinized tissues of the heels (holes like ulcerative lesions).
The causes of hyperkeratosis are similar to the causes of the appearance of white spots in the form of corns or calluses, cracks. If a white coating appears on the heels, this may be the cause of the disease. It causes inconvenience to a person, and treatment requires considerable effort.
Rules of hygiene and prevention
Treatment of age spots on the heels caused by excessive physical impact on these parts of the body is carried out by making changes in foot care (massage, therapeutic baths, medicated ointments, timely pedicure).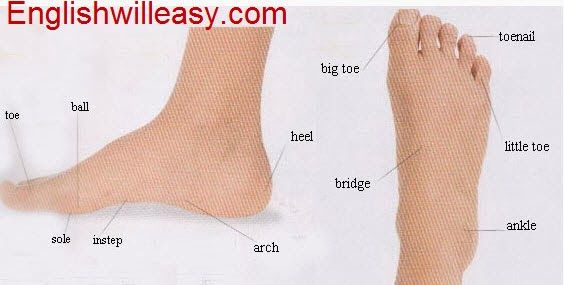 It will help to change shoes for comfortable walking, regular gymnastic exercises for the feet, daily hygiene procedures. Maintaining a comfortable neuropsychological state and dietary restraint to maintain a physiologically normal body weight will be important proactive actions.
It will help to change shoes for comfortable walking, regular gymnastic exercises for the feet, daily hygiene procedures. Maintaining a comfortable neuropsychological state and dietary restraint to maintain a physiologically normal body weight will be important proactive actions.
White spots on the feet require careful diagnosis and examination of the body. If for no reason it became painful to attack, formations appeared on the skin, consult a doctor to rule out the presence of pathologies.
Article verified by the editors
Not Found (#404)
Paracelsus Medical Center
Page not found.
The above error occurred while the Web server was processing your request.
Please contact us if you think this is a server error. thank you.
Leave feedback Write to management Jobs
Please wait, download may take time
Loading. ..
..
Do you know which doctor you want to see
You know the service you want to sign up for
Service selection
A second consultation is considered to be a consultation of one specialist within 30 days from the date of the previous appointment. On the 31st day from the previous visit to a specialist of this profile, the consultation will be primary.
The choice of a specialist
Service selected:
Choosing a specialist service
A second consultation is considered to be a consultation of one specialist within 30 days from the date of the previous appointment. On the 31st day from the previous visit to a specialist of this profile, the consultation will be primary.
On the 31st day from the previous visit to a specialist of this profile, the consultation will be primary.
Address selection:
st. Vikulova, 33, building 2 st. Bolshakova, d. 68
Date selection:
Time of receipt:
Password
Password
Register Can't login? account activation
To gain access to your personal account, enter the e-mail that was specified during registration, we will send instructions for password recovery
To gain access to your personal account, enter the e-mail that was specified during registration, we will send instructions for reactivating your account
Your application has been accepted, our specialists will answer your question as soon as possible!
Telephone
Commentary
By clicking on the confirmation button, I agree with personal data processing policy
Dear patients!
Multidisciplinary Clinic and Maternity Hospital "Paracelsus" informs you, according to the Letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation to the Federal Tax Service dated March 25, 2022. N BS-4-11 / 3605, that subparagraph 3 of paragraph 1 of Article 219 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation provides for the taxpayer's right to receive a social tax deduction in the amount paid by him in the tax period for medical services provided by medical organizations engaged in medical activities , him, his spouse, parents, children (including adopted children) under the age of 18, wards under the age of 18 (in accordance with the list of medical services approved by the Government of the Russian Federation).
N BS-4-11 / 3605, that subparagraph 3 of paragraph 1 of Article 219 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation provides for the taxpayer's right to receive a social tax deduction in the amount paid by him in the tax period for medical services provided by medical organizations engaged in medical activities , him, his spouse, parents, children (including adopted children) under the age of 18, wards under the age of 18 (in accordance with the list of medical services approved by the Government of the Russian Federation).
Joint order of the Ministry of Taxation of Russia and the Ministry of Health of Russia of July 25, 2001 N 289 / BG-3-04 / 256 (hereinafter - the order of July 25, 2001) approved the form of the Certificate of payment for medical services for submission to the tax authorities of the Russian Federation (hereinafter - the Certificate payment for medical services).
This certificate certifies the fact of receiving a medical service and its payment through the cash desk of a healthcare institution at the expense of the taxpayer.