What is a nt ultrasound
NT Scan: What You’ll Find Out
If you recently found out you’re pregnant, you’ll have several doctor appointments and screenings from now until the birth of your baby. Prenatal screenings can identify problems with your health, such as anemia or gestational diabetes. Screenings also can monitor your baby-to-be’s health, and help identify chromosomal abnormalities.
Pregnancy screenings take place during the first, second, and third trimesters. The first trimester screening is a type of prenatal testing that provides your doctor with early information about your baby’s health — namely your baby’s risk for chromosome abnormalities.
A nuchal translucency (NT) scan screens your baby for these abnormalities. This test is typically scheduled between weeks 11 and 13 of pregnancy.
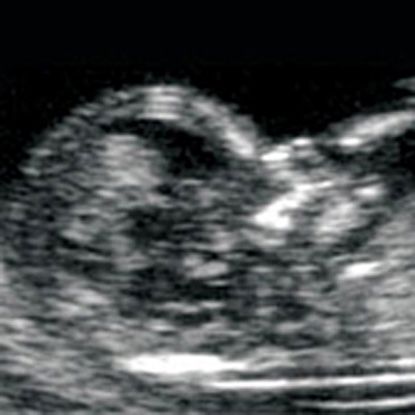
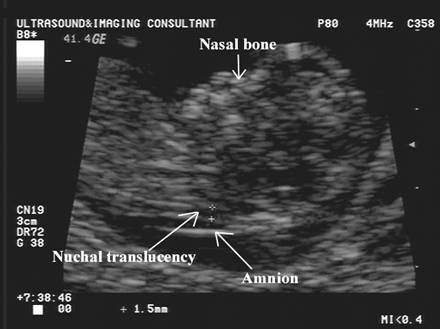
An NT scan is a common screening test that occurs during the first trimester of pregnancy. This test measures the size of the clear tissue, called the nuchal translucency, at the back of your baby’s neck.
It’s not unusual for a fetus to have fluid or clear space at the back of their neck. But too much clear space can indicate Down syndrome, or might show another chromosome abnormality like Patau syndrome or Edwards syndrome.
Our body cells have many parts, including a nucleus. The nucleus holds our genetic material. In most cases, the nucleus has 23 pairs of chromosomes, which are equally inherited from both parents.
Individuals born with Down syndrome have an extra copy of chromosome 21. Down syndrome, which can’t be cured, causes developmental delays and distinct physical characteristics.
These include:
- a small stature
- eyes with an upward slant
- low muscle tone
This condition affects 1 in every 700 babies born in the United States. It’s one of the most common genetic conditions.
Patau syndrome and Edwards syndrome are rare and often fatal chromosome abnormalities. Unfortunately, most babies born with these abnormalities die within the first year of life.
The clear space in the back of a developing baby’s neck can disappear by week 15, so an NT scan should be completed in the first trimester.
This test can also include blood work to measure your levels of plasma protein and human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG), a maternal hormone. Abnormal levels of either may indicate a chromosome problem.
During the screening, your doctor or a technician will take an abdominal ultrasound. You could alternatively have a transvaginal test, where an ultrasound probe is inserted through your vagina.
An ultrasound uses high frequency sound waves to create an image from inside your body. From this image, your doctor or technician measures the translucency, or clear space, at the back of your baby’s neck. They can then enter your age or date of birth in a computer program to calculate the risk of your baby having an abnormality.
An NT scan cannot diagnose Down syndrome or any other chromosome abnormality. The test only predicts the risk. Talk to your doctor about available blood tests. They also can help assess your baby’s risk.
Talk to your doctor about available blood tests. They also can help assess your baby’s risk.
As with any prediction, the accuracy rate varies. If you combine an NT scan with blood testing, the screening is about 85 percent accurate for predicting the risk of Down syndrome. If you don’t combine blood testing with the scan, the accuracy rate drops to 75 percent.
No special preparation is required for an NT scan. In most cases, testing is completed in about 30 minutes. During the scan, you’ll lie down on an exam table as the technician moves an ultrasound wand over your stomach.
The ultrasound pictures may be easier to read if you have a full bladder, so your doctor may recommend drinking water about one hour before your appointment. The ultrasound tech needs access to your lower abdomen, so make sure you wear comfortable clothing that makes it accessible.
Results from the scan may be available on the same day of testing, and your doctor may discuss the findings with you before you leave.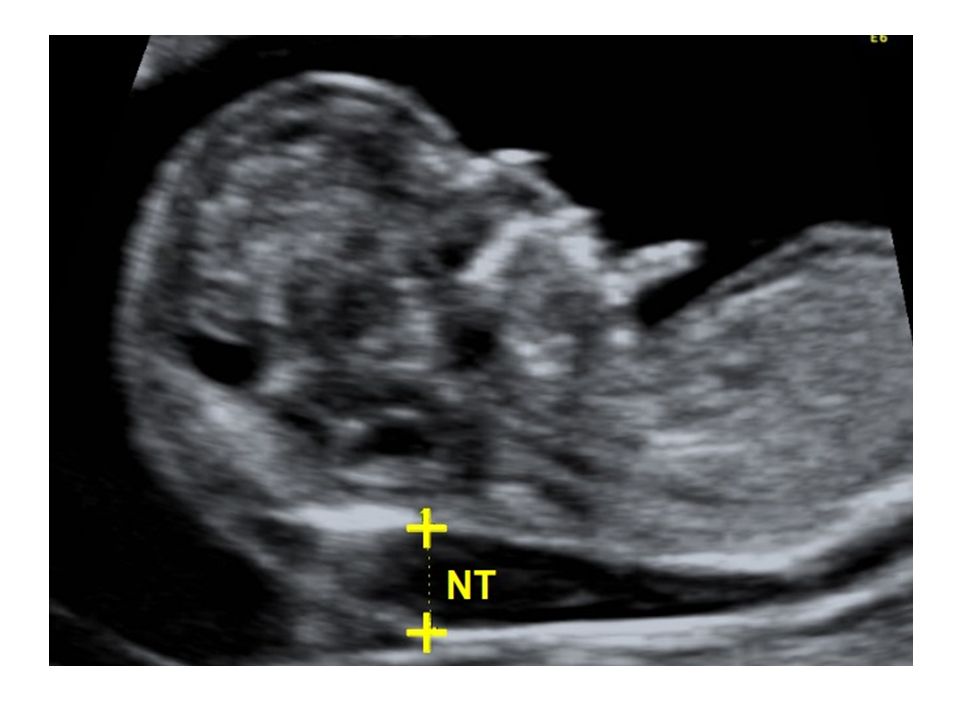 It’s important to remember that receiving an abnormal result from an NT scan doesn’t necessarily mean that your baby has a chromosome problem. Similarly, normal test results can’t guarantee that your baby won’t be born with Down syndrome.
It’s important to remember that receiving an abnormal result from an NT scan doesn’t necessarily mean that your baby has a chromosome problem. Similarly, normal test results can’t guarantee that your baby won’t be born with Down syndrome.
This test isn’t perfect. There’s a 5 percent false-positive rate. In other words, 5 percent of women tested receive positive results, but the baby is fine. After a positive result, your doctor may suggest another blood test called prenatal cell-free DNA screening. This test examines fetal DNA in your bloodstream to assess your baby’s risk for Down syndrome and other chromosome abnormalities.
It can be frightening to receive inconclusive or positive results from an NT scan. Keep in mind that an NT scan can only predict your baby’s risk: It doesn’t offer a definitive answer about chromosomal abnormalities. An NT scan is a screening test, not a diagnostic test.
There are differences between screening and diagnostic testing. The purpose of a screening test is to identify risk factors for a particular disease or condition. Diagnostic testing, on the other hand, confirms the presence of a disease or condition.
Diagnostic testing, on the other hand, confirms the presence of a disease or condition.
To diagnosis a chromosome abnormality, ask your doctor about diagnostic testing. Options include an amniocentesis, which is when a needle is inserted through your stomach into the amniotic sac to retrieve a fluid sample. Amniotic fluid contains cells that provide genetic information about your baby.
Another option is chorionic villus sampling. A sample of your placental tissue is removed and tested for chromosome abnormalities and genetic problems. There’s a small risk of miscarriage with both tests.
An NT scan is a safe, noninvasive test that doesn’t cause any harm to you or your baby. Keep in mind that this first trimester screening is recommended, but it’s optional. Some women skip this particular test because they don’t want to know their risk. Talk to your doctor if you experience anxiety, or are worried about how the results might affect you.
Nuchal translucency test Information | Mount Sinai
Nuchal translucency screening; NT; Nuchal fold test; Nuchal fold scan; Prenatal genetic screening; Down syndrome - nuchal translucency
The nuchal translucency test measures the nuchal fold thickness. This is an area of tissue at the back of an unborn baby's neck. Measuring this thickness helps assess the risk for Down syndrome and other genetic problems in the baby.
This is an area of tissue at the back of an unborn baby's neck. Measuring this thickness helps assess the risk for Down syndrome and other genetic problems in the baby.
How the Test is Performed
Your health care provider uses abdominal ultrasound (not vaginal) to measure the nuchal fold.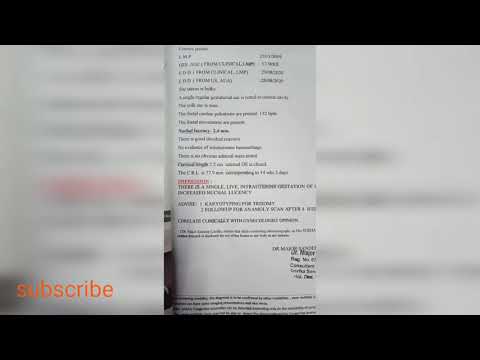 All unborn babies have some fluid at the back of their neck. In a baby with Down syndrome or other genetic disorders, there is more fluid than normal. This makes the space look thicker.
All unborn babies have some fluid at the back of their neck. In a baby with Down syndrome or other genetic disorders, there is more fluid than normal. This makes the space look thicker.
A blood test of the mother is also done. Together, these two tests will tell if the baby could have Down syndrome or another genetic disorder.
How to Prepare for the Test
Having a full bladder will give the best ultrasound picture. You may be asked to drink 2 to 3 glasses of liquid an hour before the test. DO NOT urinate before your ultrasound.
How the Test will Feel
You may have some discomfort from pressure on your bladder during the ultrasound.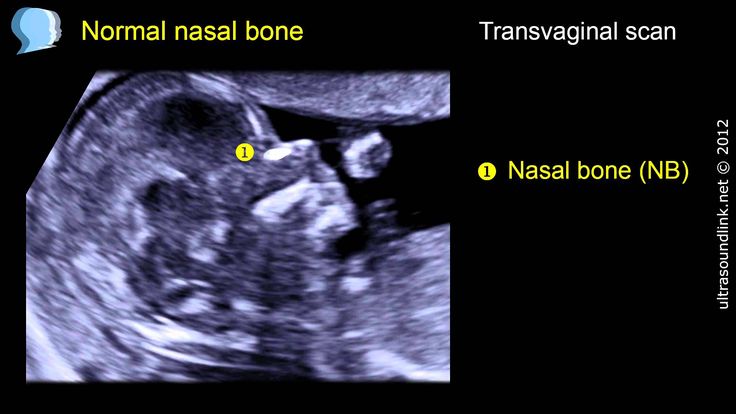 The gel used during the test may feel slightly cold and wet. You will not feel the ultrasound waves.
The gel used during the test may feel slightly cold and wet. You will not feel the ultrasound waves.
Why the Test is Performed
Your provider may advise this test to screen your baby for Down syndrome. Many pregnant women decide to have this test.
Nuchal translucency is usually done between the 11th and 14th week of pregnancy. It can be done earlier in pregnancy than amniocentesis. This is another test that checks for birth defects.
Normal Results
A normal amount of fluid in the back of the neck during ultrasound means it is very unlikely your baby has Down syndrome or another genetic disorder.
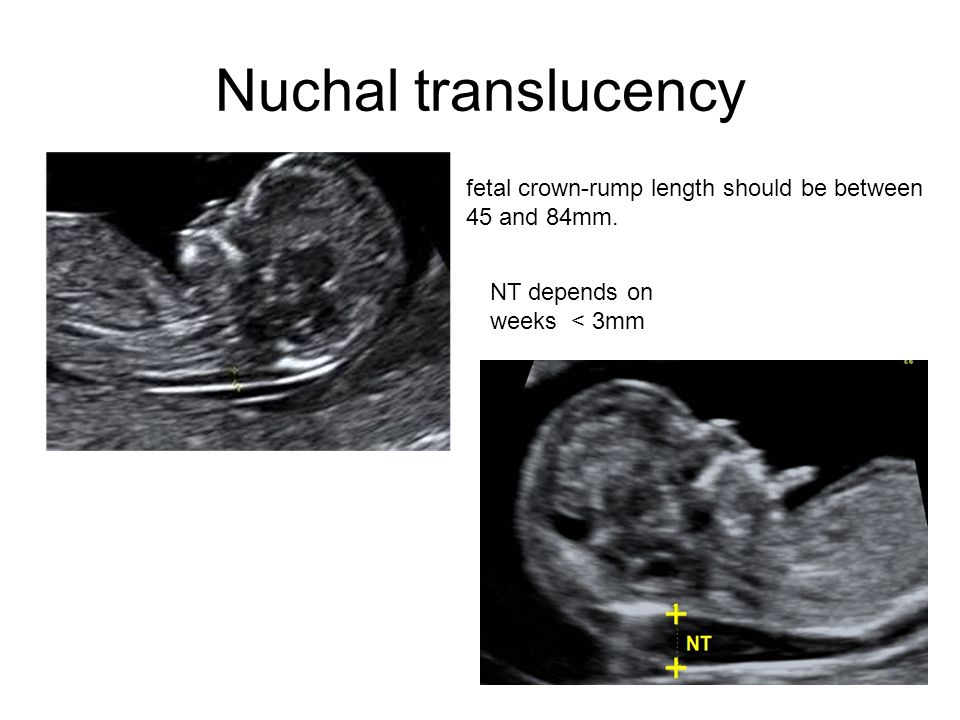
Nuchal translucency measurement increases with gestational age. This is the period between conception and birth. The higher the measurement compared to babies the same gestational age, the higher the risk is for certain genetic disorders.
The measurements below are considered low risk for genetic disorders:
- At 11 weeks -- up to 2 mm
- At 13 weeks, 6 days -- up to 2.8 mm
What Abnormal Results Mean
More fluid than normal in the back of the neck means there is a higher risk for Down syndrome, trisomy 18, trisomy 13, Turner syndrome, or congenital heart disease. But it does not tell for certain that the baby has Down syndrome or another genetic disorder.
If the result is abnormal, other tests can be done. Most of the time, the other test done is amniocentesis.
Risks
There are no known risks from ultrasound.
Driscoll DA, Simpson JL. Genetic screening and diagnosis. In: Landon MB, Galan HL, Jauniaux ERM, et al, eds. Gabbe's Obstetrics: Normal and Problem Pregnancies. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2021:chap 10.
Walsh JM, D'Alton ME. Nuchal translucency. In: Copel JA, D'Alton ME, Feltovich H, et al, eds. Obstetric Imaging: Fetal Diagnosis and Care. 2nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2018:chap 45.
2nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2018:chap 45.
Last reviewed on: 3/31/2020
Reviewed by: John D. Jacobson, MD, Professor of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Loma Linda University School of Medicine, Loma Linda Center for Fertility, Loma Linda, CA. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.
Ant-Med Medical Center | some visitor reviews, prices for services, address and phone number
Ultrasound of the heart (ECHO KG) from 1500
Comprehensive examination for children under 1 year old (ultrasound of TB, NSG, ultrasound of OB) 3500
Comprehensive examination for children up to 1 year 3800
Neurosonography 1200
Hip ultrasound 1000
Ultrasound of the thymus 1200
Ultrasound of the scrotum 1000
PCR test for COVID19 qual. 24 hours 2500
24 hours 2500
PCR test for COVID19 qual. with results in English (24h) 2500
PCR test for COVID19 qual. URGENT 12 noon 3000
Anti-COVID19 IgG assay, neutralizing anti-RDB, S1 protein (blood, quant.) 2000
COVID19 antibody test IgG anti-nucleocapsid protein antibody (blood) 1450
Anti-COVID19 IgM antibody test (blood) 1450
Detection of IgG antibodies to antigens of the vaccine "EpiVacCoron" 1250
PCR test for COVID19 (smear) n. 24h. 2500
PCR test for COVID19 (smear) n.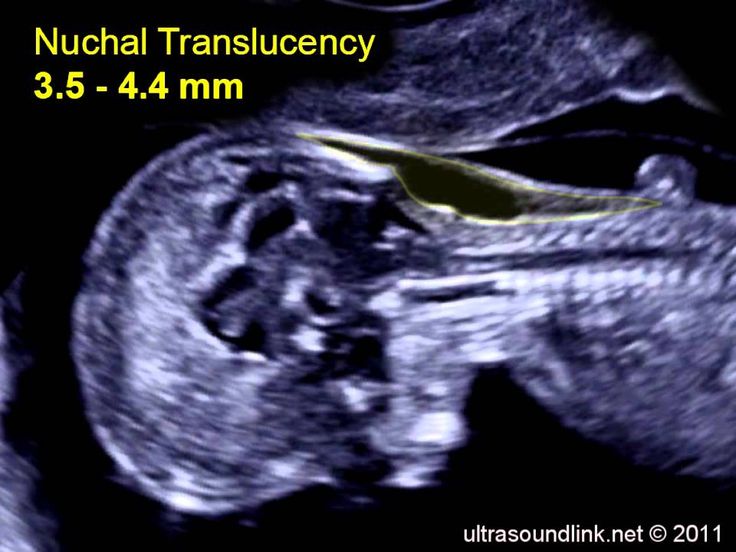 24h. with result in English 2500
24h. with result in English 2500
PCR test for COVID19 qual. URGENT 12 hrs. with results in English. language 4100
PCR test for COVID19 URGENT in 5 hours. by NAA in English 4500
USG of neck vessels from 1700
USDG of head and neck vessels 3200 - 3800
Ultrasound of the veins of the lower extremities (CDS of the veins of the lower extremities) from 1600
Ultrasound of the arteries of the lower extremities from 1600
Ultrasound of limb vessels (veins and arteries) 3200 — 3800
Ultrasound of the veins (arteries) of the upper extremities from 1600
24-hour Holter ECG monitoring (Holter ECG) 3-channel 24 hours 2500
Holter monitoring (ECG Holter) 12 channels 24 hours 2800
Ambulatory blood pressure monitoring (ABPM) 2000
ECG with interpretation 1000
ECG without interpretation 800
Electroencephalogram 2000
Medical Center Ant-Med on Prospekt Mira in Fryazino - reviews, photos, prices, telephone, address and how to get there - Medical centers - Moscow
/ 16 reviews
Opens in 11 hours 31 minutes
- Description
-
The ANT-Med Medical Center in Fryazino focuses its activities on disease prevention.
 The specialists of the center believe that it is necessary to visit medical facilities not only when something gets sick, but also for preventive examinations. The center offers a complete diagnostic examination: ultrasound and laboratory tests. Excellent service conditions, high professionalism of employees and availability of modern equipment are waiting for you.
The specialists of the center believe that it is necessary to visit medical facilities not only when something gets sick, but also for preventive examinations. The center offers a complete diagnostic examination: ultrasound and laboratory tests. Excellent service conditions, high professionalism of employees and availability of modern equipment are waiting for you.
Telephone
+7 (496) 255-73-... - show +7 (985) 387-73-... - show +7 (939) 111-75-... - show
Get directions
By car, on foot or by public transport… show directions
- Opening hours
-
Mon-Thu: 08:00-20:00; Fri: 08:00-19:00; Sat: 08:00-18:00
- Company on the web
-
ant-med.obiz.ru
- Are you the owner?
-
- Get access
- Get widget
- Report a bug
48 photos medical center Ant-Med on Prospekt Mira in Fryazino
Specialists of the Ant-Med Medical Center on Mira Avenue in Fryazino
-
Vyacheslav Feliksovich Ordynsky
Experience 41 years • Ultrasound doctor, functional diagnostics doctor
No reviews yet
Long experience
-
Lyubov Sergeevna Orlova
Experience 39 years • Obstetrician, ultrasound doctor, gynecologist, gynecologist-endocrinologist
No reviews yet
Long experience
show more
- Search:
-
Speciality
- Experience AnyOver 5 yearsOver 15 years
-
Children's
Similar medical centers
All reviews in a row 16
Sort by: by date at the rate by popularity From photo
Frequently asked Questions about Ant-Med Medical Center
- 📍 What is the address of Ant-Med Medical Center?
Organization address: Russia, Moscow region, Fryazino, Prospekt Mira, 31.
- ☎️ How can I contact Ant-Med Medical Center?
Phone number to receive calls: +7 (496) 255-73-37.
- 🕖 What schedule does he work in this organization?
The schedule for receiving visitors is as follows: Mon-Thurs: 08:00 - 20:00; Fri: 08:00 - 19:00; Sat: 08:00 - 18:00.
- ⭐ How Zoon.ru users rate is this establishment?
The average rating of the establishment from Zoon.ru users is 3.1. You can visit the page with reviews of Ant-Med Medical Center , to leave your feedback!
- 🧾 Is it possible to see with a list of services at this establishment?
Such information is in the section where the services and prices of the Ant-Med Medical Center are indicated.
- 📷 How many photos are there in the profile of Ant-Med Medical Center on Zoon.ru?
There are 48 images on the page of Ant-Med Medical Center.
- 👩⚕️👨⚕️ What doctors work at Ant-Med Medical Center?
On Zoon.ru you can find a list of 13 specialists working at Ant-Med Medical Center and detailed information: age, grades, availability of reviews, etc.
- ✔️ Can I trust the information posted on this page?
Zoon.ru tries to post as much as possible Accurate and up-to-date information about establishments. If you see an inaccuracy and/or are the owner this institution, you can use feedback form.
Information is for informational purposes only and does not replace qualified medical care.