5 weeks pregnant and constipation
5 Weeks Pregnant: Symptoms, Tips, and More
At 5 weeks pregnant, your little one truly is little. At no larger than the size of a sesame seed, they’ll have just begun forming their first organs.
You might start to feel new things, too, both physically and emotionally. Let’s learn more about what you can expect in week 5 of your pregnancy.
5 weeks pregnant: What to expect
- You might have PMS-like symptoms such as fatigue, sore breasts, and morning sickness.
- Your baby is very tiny, only about 2 millimeters.
- Your baby’s heart might start beating now, though it may not be detected by ultrasound for another couple of weeks.
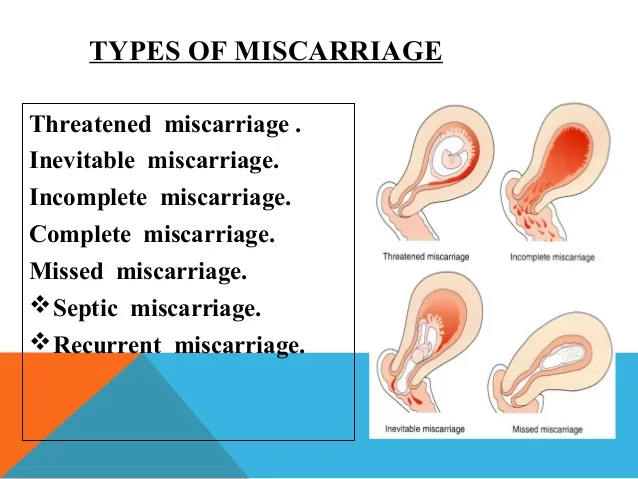
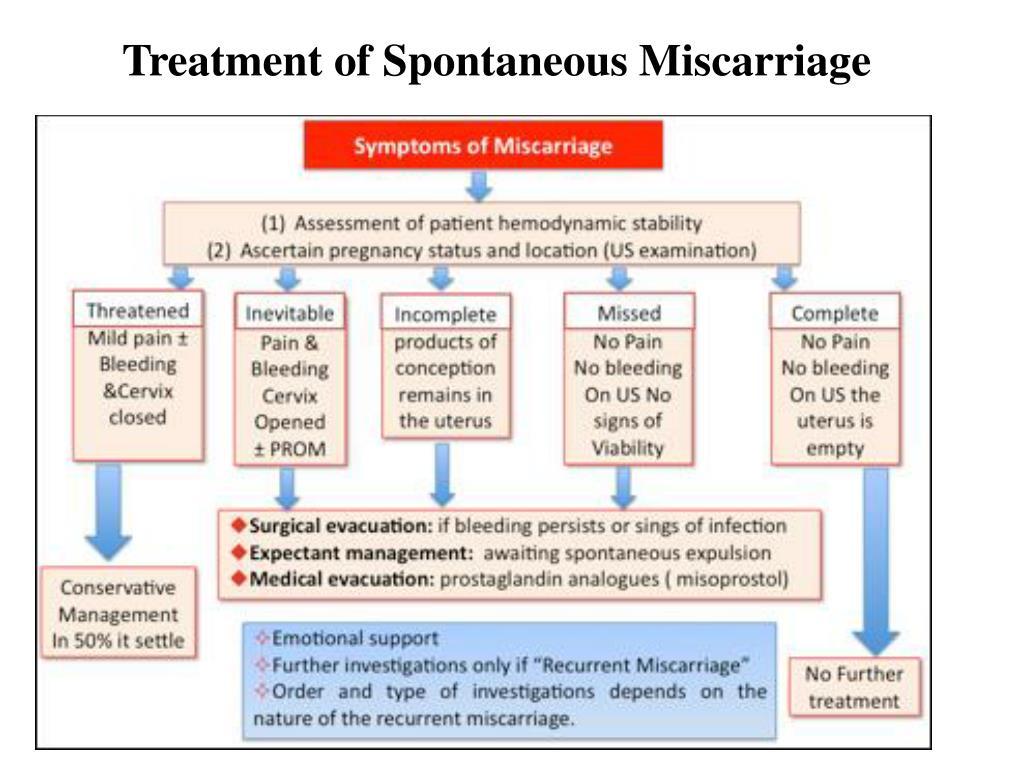
- You’ll want to learn about the signs of miscarriage and ectopic pregnancies.
Many people first learn that they’re expecting during the fifth week of pregnancy. By now you have missed your menstrual period, and a pregnancy test should have come back positive.
You may be dealing with lots of new emotions, feelings, and concerns. Not to worry, though — we’ve got you covered with all the details of this amazing time.
Share on PinterestIllustration by Alyssa Kiefer
The fifth week of pregnancy marks the start of the embryonic period. This is when baby’s body systems and structures begin to form, such as the heart, brain, and spinal cord.
Your baby’s heart beats at a steady rate now, though it may not be detected by ultrasound for another 1 or 2 weeks. The placenta is also starting to develop.
At this stage, your baby doesn’t look like a baby yet. The embryo is growing quickly, but it’s still very small, about the size of a pen tip or a sesame seed. Around this time, baby initially measures just 2 to 3 millimeters.
Your body is gearing up to go through big changes, too.
Pregnancy hormone levels are rapidly rising, and your uterus will begin to grow. You won’t look pregnant for a couple more months, but you may start to experience symptoms now.
If you’re carrying multiples, you may be able to detect your babies through an early ultrasound during week 5.
Your babies are measured in millimeters at this point, but you might see two gestational sacs or even a couple of tiny fetal poles as the week goes on.
Occasionally, you’ll detect two gestational sacs at this early stage, but only one baby at a later ultrasound. This is called vanishing twin syndrome. There’s often no clear reason for the loss, per 2021 research. You may have cramping and bleeding, or you may have no symptoms at all.
Pregnancy checklist at 5 weeks
- Choose a pregnancy professional. If you don’t already have an OBGYN to guide you through your pregnancy, start doing research now to find one you feel comfortable with.
- Start on a prenatal vitamin. If you’re not already taking a daily prenatal vitamin, now is a good time to start. Folic acid, a B vitamin essential for baby’s health, is usually higher in prenatals. You’ll want about 400 mcg per day.
- Limit caffeine. Even as little as half a cup of coffee a day may affect baby’s birth weight, experts say.
 This can increase their risk of complications as an infant.
This can increase their risk of complications as an infant. - Consider a pregnancy tracker app. There are lots of free apps available that can provide of information during your pregnancy — everything from baby’s size at each week to educational articles for your health and baby’s health.
Pregnancy symptoms are unique and unpredictable. Two people can each have healthy pregnancies without any of the same symptoms. Likewise, you may have bad nausea in your first pregnancy, but no morning sickness in a later pregnancy.
The swiftly rising levels of the hormones human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) and progesterone are responsible for many of the pregnancy symptoms you experience.
You can expect any of the following week 5 pregnancy symptoms:
- morning sickness
- lightheadedness
- frequent urination
- acute sense of smell
- abdominal cramps
- spotting
- fatigue
- breast changes
- food cravings and aversions
- constipation
- increased vaginal discharge
- mood swings
1.
 Morning sickness
Morning sicknessDon’t be fooled by the word “morning.” Nausea and vomiting can happen at any time during the day.
While morning sickness typically begins during week 6 of pregnancy, some people experience it earlier.
Eating several small meals throughout the day (instead of two or three big meals) may help to relieve these symptoms.
Call your doctor if you can’t keep any food or liquid down. This may be a sign of hyperemesis gravidarum, which is a rare disorder that involves continual nausea and vomiting during pregnancy. It sometimes requires in-patient treatment at a hospital.
2. Lightheadedness
Your blood pressure tends to run lower than usual during pregnancy. This can cause dizziness and even fainting.
If you feel dizzy, sit down if you’re standing or pull over if you’re driving.
3. Frequent urination
As your uterus expands, it can press against your bladder. This will likely cause you to need to urinate more frequently.
Go when you have the urge so that you avoid bladder infections. Drink plenty of water to avoid becoming dehydrated.
Drink plenty of water to avoid becoming dehydrated.
4. Abdominal cramps
You may experience mild cramping or bloating. This can be caused by the egg implanting or from your uterus stretching.
While mild cramping shouldn’t cause alarm, contact your doctor immediately if you experience severe pain that doesn’t go away.
5. Vaginal bleeding
Light bleeding, also known as spotting, around the time of your missed period is usually considered implantation bleeding.
While spotting can be caused by many factors, always let your doctor know if you notice any spotting or bleeding at any time during pregnancy.
6. Fatigue
As your progesterone levels increase, you may find yourself feeling sleepy and losing energy.
Fatigue is most common during the first trimester, but some people will experience fatigue throughout their pregnancy.
7. Breast changes
You may experience tender, sore, swollen, or fuller breasts as your hormone levels change. This is one of the earliest symptoms of pregnancy and may appear soon after conception.
This is one of the earliest symptoms of pregnancy and may appear soon after conception.
8. Food cravings and aversions
Your changing hormones can lead to a change in your appetite.
You may find yourself avoiding foods you used to enjoy, or you may start craving foods you don’t commonly eat. You can begin experiencing food cravings and aversions early on in your pregnancy.
9. Constipation
Your food will start moving more slowly through your digestive system to give nutrients more time to be absorbed into your bloodstream and reach your baby. This delayed transit can lead to constipation.
Eating more fiber and drinking lots of fluids can help relieve or eliminate constipation.
10. Increased vaginal discharge
Vaginal discharge during pregnancy may be expected. It should be thin, white, milky, and mild smelling.
If the discharge is green or yellowish, has a strong smell, or is accompanied by redness or itching, you should contact your doctor. This is likely a sign of a vaginal infection.
This is likely a sign of a vaginal infection.
11. Mood swings
Pregnancy can cause a lot of emotions. Not only can the idea of a new baby cause emotional stress, but the changes in your hormones can also affect your emotions.
It’s perfectly fine to feel a variety of emotions from day to day — such as elation, sadness, anxiety, fear, and exhaustion. If these feelings are extreme or last more than a few days, consult your doctor right away.
According to The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG), about 10 percent of pregnancies end in miscarriage.
Signs of a miscarriage include:
- vaginal bleeding (the most common sign, which tends to be heavier than spotting and may contain clots)
- abdominal or pelvic cramps
- back pain
Call your doctor if you experience any bleeding during pregnancy.
An ectopic or “tubal” pregnancy is a pregnancy that grows outside the uterus, most often in the fallopian tube. This type of pregnancy isn’t viable and can be life threatening to the birthing parent.
Symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy include:
- vaginal bleeding
- pelvic pain or cramping (possibly on one side)
- shoulder pain
- dizziness or fainting
Call your doctor right away if you feel as though you are having symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy.
According to the ACOG, individuals who have a supportive partner are more likely to engage in healthier behaviors, and their babies are more likely to be born with lower rates of preterm birth and growth issues.
A few ways you can support your pregnant partner include:
- Go with your partner to as many of their prenatal appointments as you can.
- Eat and prepare nutritious foods for both of you, so your partner is not doing it alone.
- Listen to your partner whenever they express their feelings regarding the pregnancy or birth, and know that mood shifts are a natural part of the process.
- Be open to discussing both the positive and negative aspects of pregnancy and birth.
Educating yourself on the changes during each trimester and well as the symptoms associated with those changes, and what your partner may need during delivery and after delivery, are great ways to support them.
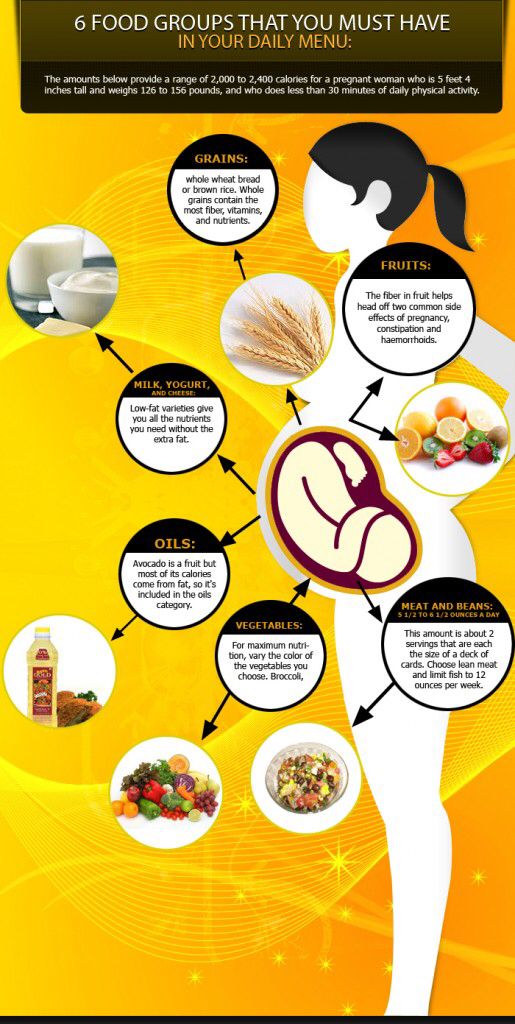
- Schedule your first prenatal doctor’s visit. This is important to do if you haven’t already done so. Going to checkups is a must for a healthy pregnancy. Your doctor will let you know what actions to take to keep your growing baby healthy for 9 months.
- Take a prenatal vitamin. Prenatal vitamins that contain high levels of folic acid may lower the risk of some birth defects. Many prenatal vitamins now provide omega-3 fatty acids DHA and EPA as well. These nutrients can be helpful for proper brain and eye development in baby, according to 2012 research. They can also help with the nutrition of breast milk.
- Add nutrient-dense foods to your diet. This includes fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, beans, nuts, and dairy.
 Maintaining a balanced, nutritious diet is important for your baby’s health.
Maintaining a balanced, nutritious diet is important for your baby’s health. - Practice food safety. Make sure your proteins are fully cooked and avoid high mercury seafood and unpasteurized dairy to prevent infection in your growing little one.
- Avoid substances that can harm baby. Don’t smoke cigarettes, drink alcohol or excessive caffeine, or use other substances like cannabis. There’s no safe amount of alcohol when pregnant. Some prescription and over-the-counter meds also aren’t safe during pregnancy. Let your doctor know about all medications, vitamins, supplements, and herbs you’re taking. Seek help if you need assistance with substance use.
Week 5 of your pregnancy is still early for the most dramatic changes and physical symptoms. But your teeny tiny baby is on their way to growing strong and healthy.
The decisions you make to take care of yourself and your little one this early on will directly impact all the factors later.
Make sure to see your doctor in order to understand the best choices to make for nutrition and lifestyle.
Constipation During Pregnancy | American Pregnancy Association
Constipation during pregnancy is a common problem and nearly half of all pregnant women get constipated at some point. Constipation occurs when there is abdominal pain or discomfort, difficult and infrequent bowel movements, and the passage of hard stools.
What causes constipation during pregnancy?
In general, worry, anxiety, minimal physical exercise, and a low-fiber diet may cause constipation. Constipation during pregnancy is due to the increase in progesterone hormones that relax the intestinal muscle causing food and waste to move slower through your system.
Sometimes iron tablets may contribute to constipation. Make sure you are drinking plenty of water if you are taking iron supplements. You may need to switch to a different type of iron tablet, but it is important to talk to your health care provider first.
How can I prevent or treat constipation during pregnancy?
Prevention and treatment of constipation involve many of the same steps.
Here are a few things that you can do to help prevent constipation from occurring or treat it if you are already experiencing it:
- Eat a high fiber diet: Ideally, you will consume 25 to 30 grams per day of dietary fiber from fruits, vegetables, breakfast cereals, whole-grain bread, prunes, and bran. This helps ensure bulkier stools that are easier to poop.
- Drink a lot of fluids: Drinking plenty of fluids is important, particularly when increasing fiber intake helps ensure softer stools. Drink 10 to 12 cups of fluids each day. It is the combination of a high fiber diet and plenty of liquids that best help you eliminate your waste. Sweat, hot/humid climates, and exercise may increase your need for additional fluids.
- Exercise routinely: If you are inactive, you have a greater chance of constipation.
 Walking, swimming and other moderate exercises will help the intestines work by stimulating your bowels. Schedule exercise three times a week for 20-30 minutes each.
Walking, swimming and other moderate exercises will help the intestines work by stimulating your bowels. Schedule exercise three times a week for 20-30 minutes each. - Over-the-counter remedies: There are over-the-counter products such as Metamucil (Category B) which may help soften your bowel movements and reduce constipation. Always speak to your health care provider before using over-the-counter medications.
- Reduce or eliminate iron supplements: Iron supplements may contribute to constipation. Good nutrition can often meet your iron needs during pregnancy. Taking smaller doses of iron throughout the day rather than taking it all at once can reduce constipation. Talk to your health care provider about checking your iron levels and recommendations to manage iron intake during pregnancy. Find natural ways to get iron here.
What remedies should not be used for constipation during pregnancy?
Laxative pills are NOT recommended for the treatment of constipation during pregnancy because they might stimulate uterine contractions and cause dehydration. Talk to your doctor about taking an over-the-counter fiber supplement or a laxative or stool softener.
Talk to your doctor about taking an over-the-counter fiber supplement or a laxative or stool softener.
Mineral oils should NOT be used during pregnancy because they reduce nutrient absorption.
Is constipation during pregnancy ever serious?
Usually not, but occasionally constipation during pregnancy can be a symptom of another problem. If you have severe constipation that’s accompanied by abdominal pain, alternates with diarrhea, or you pass mucus or blood, call your doctor or midwife immediately.
Also, straining during a bowel movement or passing a hard stool can lead to or worsen hemorrhoids, which are swollen veins in the rectal area. Hemorrhoids can be extremely uncomfortable, though they rarely cause serious problems. In most cases, they go away fairly soon after your baby is born. However, if the pain is severe, or if you have rectal bleeding, call your doctor.
Want to Know More?
- Nordic Naturals Probiotic Comfort – Supports regularity and alleviates bloating
- Laxatives During Pregnancy
- 7 Discomforts of Pregnancy
- Gas During Pregnancy
Compiled using information from the following sources:
Mayo Clinic Guide To A Healthy Pregnancy Harms, Roger W. , M.D., et al, Part 3.
, M.D., et al, Part 3.
William’s Obstetrics Twenty-Second Ed. Cunningham, F. Gary, et al, Ch. 8.
Manifestations of constipation in pregnant women - signs and symptoms
Co-author, editor and medical expert - Klimovich Elina Valerievna.
Number of views: 53 112
Last updated: 10/21/2022
Average read time: 4 minutes
Constipation is a common problem during pregnancy. About 75% of women complain of problems with bowel movements during pregnancy. At the same time, these difficulties remain in about a third of women after childbirth.
Contents:
Detailed description of the symptoms
What can cause constipation in a pregnant woman
Our bodies constantly produce substances that stimulate bowel movements. During pregnancy, the susceptibility of the intestinal muscles to various kinds of irritants is significantly reduced. The change in the intensity of intestinal reactions is due to the fact that it has a common innervation * with the uterus, because of this, any excessive activation of peristalsis can provoke contractile activity of the uterus. This can be a threat to the child. Unfortunately, this defensive reaction has unpleasant consequences - constipation. Often they occur between 17 and 36 weeks of pregnancy.
This can be a threat to the child. Unfortunately, this defensive reaction has unpleasant consequences - constipation. Often they occur between 17 and 36 weeks of pregnancy.
Clinically, constipation in pregnant women is manifested by several main symptoms:
- stool retention for more than 3 days and problems with passing gases, flatulence;
- unpleasant feeling of incomplete emptying of the bowels;
- the need to strain during bowel movements;
- painful stools;
- "sheep feces" (hard, dry, fragmented feces).
In the event of constipation, you should always seek medical advice, especially if you notice deterioration and pain.
Back to top
Detailed description of symptoms
Constipation is characterized by decreased stool frequency. It happens that a pregnant woman manages to empty her intestines only once a week or less. The consistency of feces changes, discomfort and pain in the abdomen (often in its left half), there is a feeling of dissatisfaction after the stool.
Atonic constipation is characterized by very painful defecation, which occurs with great difficulty. Due to microscopic tears of the mucous membrane of the anus, streaks of blood may appear on the surface of the feces. Spasmodic constipation is characterized by fragmented stools ("sheep feces"). This condition is often accompanied by flatulence, a feeling of pressure, expansion, spasmodic pains in the abdomen. With prolonged constipation, there may be a feeling of lethargy, fatigue, a significant decrease in efficiency.
Pain in a pregnant woman occurs for no apparent reason or may be the result of excitement or physical exertion. Attacks of acute pain or exacerbation of constant discomfort, as a rule, are associated with negative emotions. The pain can be of varying strength, for example, in some cases it radiates to the lower back, leg, anus, and even the genitals. In some pregnant women, along with abdominal pain, there is a burning sensation in the rectum and itching in the anus. Nausea, bitterness in the mouth are often noted; passing gases is difficult.
Nausea, bitterness in the mouth are often noted; passing gases is difficult.
Back to content
What constipation can cause in a pregnant woman
Feces in the rectum, which a pregnant woman cannot get rid of for a long time, bring her considerable discomfort. However, these are not the only consequences of constipation.
- The large intestine mucosa is characterized by absorptive capacity; in case of constipation, not only water is absorbed into the blood, but also various toxic metabolic products. Intoxication of the woman and the fetus can lead to negative consequences and disrupt the development of the child in the future.
- Due to overflowing with dense feces, the rectum presses on the uterus, which leads to irritation. Despite the fact that the sensitivity of the uterus during pregnancy is reduced, there is a certain risk of increased uterine tone and, as a result, premature birth.
- With constipation, the intestines press on the uterus and pelvic vessels, which disrupts the outflow of blood from them.
 For this reason, hemorrhoids can occur, which is manifested by the appearance of blood in the stool.
For this reason, hemorrhoids can occur, which is manifested by the appearance of blood in the stool.
Constipation in a pregnant woman is a serious problem. To solve it, contact your doctor.
*Innervation - the supply of organs and tissues with nerve fibers, which ensures their connection with the central nervous system (CNS).
Back to Contents
The information in this article is for reference only and does not replace professional medical advice. For diagnosis and treatment, contact a qualified specialist.
MICROLAX® during pregnancy - is it possible to use microclysters for pregnant women
Co-author, editor and medical expert - Klimovich Elina Valerievna.
Views: 116 584
Last update date: 21.10.2022 G.
Average Reading time: 7 minutes
The main symptoms of constipation during pregnancy
Causes during pregnancy
Why is it important to use laxatives in time during pregnancy?
Is MICROLAX ® suitable for pregnant women?
Benefits of using MICROLAX ® during pregnancy
How to use MICROLAX ® during pregnancy?
During pregnancy, many women have difficulty defecation. The constant discomfort associated with stool retention can seriously overshadow the happy waiting time for the baby. Often, the expectant mother does not attach much importance to recurrent constipation or considers them a natural phenomenon that you just need to endure. And some women are forced to put up with discomfort, because they are sure that there are no safe laxatives for pregnant women. However, this is fundamentally wrong. When constipation occurs, it is important to inform the doctor about this problem in a timely manner. The specialist will select a comprehensive treatment and prescribe modern preparations for bowel cleansing with an optimal safety profile, for example, MICROLAX ® .
The constant discomfort associated with stool retention can seriously overshadow the happy waiting time for the baby. Often, the expectant mother does not attach much importance to recurrent constipation or considers them a natural phenomenon that you just need to endure. And some women are forced to put up with discomfort, because they are sure that there are no safe laxatives for pregnant women. However, this is fundamentally wrong. When constipation occurs, it is important to inform the doctor about this problem in a timely manner. The specialist will select a comprehensive treatment and prescribe modern preparations for bowel cleansing with an optimal safety profile, for example, MICROLAX ® .
Up to contents
Main symptoms of constipation during pregnancy
Constipation in a pregnant woman is indicated by a decrease in the number of bowel movements: bowel cleansing occurs less than 3 times a week. A deviation from the norm is considered to be a delay in feces for more than 2 days. Violation of the frequency of bowel movements is often accompanied by other symptoms. The feces that accumulate in the intestines become hard and dry. Going to the toilet requires a lot of straining. Dense feces can injure the anus, then defecation will be accompanied by pain. In addition, with constipation, a pregnant woman may be disturbed by a feeling of fullness and blockage in the rectum. Often, even going to the toilet does not bring relief: after a bowel movement, there is a feeling that the intestines have not been completely cleansed. Often, constipation is accompanied by flatulence, bloating.
Violation of the frequency of bowel movements is often accompanied by other symptoms. The feces that accumulate in the intestines become hard and dry. Going to the toilet requires a lot of straining. Dense feces can injure the anus, then defecation will be accompanied by pain. In addition, with constipation, a pregnant woman may be disturbed by a feeling of fullness and blockage in the rectum. Often, even going to the toilet does not bring relief: after a bowel movement, there is a feeling that the intestines have not been completely cleansed. Often, constipation is accompanied by flatulence, bloating.
Up to content
Causes of constipation during pregnancy
Hormonal changes. In the early stages of pregnancy, the balance of hormones in a woman's body actively changes, in particular, the level of progesterone increases. It reduces the tone of the muscles of the small pelvis: this is important so that the fertilized egg can gain a foothold in the uterus. This action of progesterone also gives a side effect. The hormone slows down the digestive tract and reduces intestinal motility. Very often because of this, constipation occurs in the first trimester of pregnancy.
This action of progesterone also gives a side effect. The hormone slows down the digestive tract and reduces intestinal motility. Very often because of this, constipation occurs in the first trimester of pregnancy.
Decreased physical activity. Many women, having learned that they are expecting a child, give up an active lifestyle and sports. To a certain extent, this is justified, since serious physical exertion can be the cause of miscarriage. As the fetus develops, the outlines of the figure and body weight of the woman change, and for natural reasons it becomes difficult for her to actively move. Hypodynamia leads to a decrease in intestinal tone, which contributes to the development of constipation.
Taking certain drugs. For normal development, the fetus needs vitamins and microelements, so pregnant women are often prescribed medications containing these beneficial substances. Some of these drugs have a fixing property. First of all, these are products with a high content of calcium and iron.
Fluid deficiency in the body. In late pregnancy, many women experience swelling of the face, legs and arms. Because of this, expectant mothers try to drink less during the day and reduce the consumption of juicy fruits and vegetables. Lack of fluid and fiber leads to compaction of feces and difficulty in emptying the intestines.
Pressure from an enlarged uterus. During pregnancy, there is a displacement of the abdominal organs. The uterus takes up more and more space and compresses the surrounding tissues. This can lead to decreased sensitivity and intestinal motility. As a result, constipation occurs. In the later stages, shortly before childbirth, the lowered head of the fetus can also squeeze the intestines.
Back to Contents
Why is it so important to use laxatives during pregnancy?
Constipation can negatively affect the health of the expectant mother and her baby. Violation of the frequency of bowel movements in some cases can cause inflammatory diseases of the female genital organs and an imbalance in the intestinal microflora. The consequences of constipation in the later stages are especially undesirable. A rectum full of feces can increase the tone of the uterus. This, like too much straining during a bowel movement, can provoke premature birth. That is why it is important for a pregnant woman to cleanse the intestines in a timely manner, if necessary, using laxatives approved by the doctor for use.
The consequences of constipation in the later stages are especially undesirable. A rectum full of feces can increase the tone of the uterus. This, like too much straining during a bowel movement, can provoke premature birth. That is why it is important for a pregnant woman to cleanse the intestines in a timely manner, if necessary, using laxatives approved by the doctor for use.
Back to Contents
Is MICROLAX
® suitable for pregnant women? According to the instructions for medical use, it is allowed to use MICROLAX ® during pregnancy 1 . This modern laxative in the format of a disposable microclyster softens dense fecal masses in the rectum and does not affect other organs of the digestive system and small pelvis. The active components of the drug are practically not absorbed into the systemic circulation and do not cause uterine contractions. MICROLAX ® can be used in any trimester of pregnancy, after consulting a doctor.
Back to content
Benefits of using MICROLAX
® during pregnancyEffect of the drug. The effect of MICROLAX ® can begin as early as 5-15 minutes 2 after application, unlike oral medications, which can take effect at the most inopportune moment.
Hygienic packaging. Micro enema MICROLAX ® is intended for single use. It is completely ready for use and does not require preliminary antiseptic treatment.
Easy application. When using MICROLAX ® , a pregnant woman does not need to individually select the dosage. Microclyster contains the optimal amount of the drug for a single use. The flexible applicator tip allows you to safely and conveniently inject the laxative into the rectum.
Top of page
How to use MICROLAX
® during pregnancy?- Take the tube and break off the seal on the applicator tip.