What is a high pulse rate during pregnancy
Physical Changes During Pregnancy - Women's Health Issues
Pregnancy causes many changes in a woman’s body. Most of them disappear after delivery. These changes cause some symptoms, which are normal. However, certain disorders, such as gestational diabetes Gestational diabetes For women who have diabetes before they become pregnant, the risks of complications during pregnancy depend on how long diabetes has been present and whether complications of diabetes, such... Common.TooltipReadMore , can develop during pregnancy, and some symptoms may indicate such a disorder.
Symptoms that should be immediately reported to a doctor if they occur during pregnancy include the following:
Persistent or unusual headaches
Persistent nausea and vomiting Nausea and Vomiting During Early Pregnancy Up to 80% of pregnant women have nausea and vomiting to some extent. Nausea and vomiting are most common and most severe during the 1st trimester.
Although commonly called morning sickness,... Common.TooltipReadMore
Light-headedness
Disturbances of eyesight
Pain or cramps in the lower abdomen Pelvic Pain During Early Pregnancy Early in pregnancy, many women have pelvic pain. Pelvic pain refers to pain in the lowest part of the torso, in the area below the abdomen and between the hipbones (pelvis). The pain may be... Common.TooltipReadMore
Contractions
Vaginal bleeding Vaginal Bleeding During Early Pregnancy During the first 20 weeks of pregnancy, 20 to 30% of women have vaginal bleeding. In about half of these women, the pregnancy ends in a miscarriage. If miscarriage does not occur immediately... Common.TooltipReadMore
Leakage of amniotic fluid (described as "the water breaks")
Swelling Swelling During Late Pregnancy As pregnancy progresses, fluid may accumulate in tissues, usually in the feet, ankles, and legs, causing them to swell and appear puffy.
 This condition is called edema. Occasionally, the face... Common.TooltipReadMore of the hands or feet
This condition is called edema. Occasionally, the face... Common.TooltipReadMore of the hands or feetDecreased urine production
Any illness or infection
Tremor (shaking of the hands, feet, or both)
Seizures
Rapid heart rate
Decreased movement of the fetus
If labor was quick in previous pregnancies, women should notify their doctor as soon as they have any indication that labor is starting.
Fatigue is common, especially in the first 12 weeks and again in late pregnancy. The woman may need to get more rest than usual.
By 12 weeks of pregnancy, the enlarging uterus may cause the woman’s abdomen to protrude slightly. The uterus continues to enlarge throughout pregnancy. The enlarging uterus extends to the level of the navel by 20 weeks and to the lower edge of the rib cage by 36 weeks.
The amount of normal vaginal discharge, which is clear or whitish, commonly increases. This increase is usually normal. However, if the discharge has an unusual color or smell or is accompanied by vaginal itching and burning, a woman should see her doctor. Such symptoms may indicate a vaginal infection. Some vaginal infections, such as trichomoniasis Trichomonas Vaginitis Trichomonas vaginitis is a vaginal infection due to the protozoa Trichomonas vaginalis. Trichomonas vaginitis is usually sexually transmitted. It can cause a green or yellow... Common.TooltipReadMore (a protozoan infection) and candidiasis Vaginal Yeast Infection (Candidiasis) The vagina is infected by a yeast called Candida, usually Candida albicans, resulting in a yeast infection called candidiasis. Being pregnant or having diabetes or a weakened immune... Common.TooltipReadMore (a yeast infection), are common during pregnancy and can be treated.
This increase is usually normal. However, if the discharge has an unusual color or smell or is accompanied by vaginal itching and burning, a woman should see her doctor. Such symptoms may indicate a vaginal infection. Some vaginal infections, such as trichomoniasis Trichomonas Vaginitis Trichomonas vaginitis is a vaginal infection due to the protozoa Trichomonas vaginalis. Trichomonas vaginitis is usually sexually transmitted. It can cause a green or yellow... Common.TooltipReadMore (a protozoan infection) and candidiasis Vaginal Yeast Infection (Candidiasis) The vagina is infected by a yeast called Candida, usually Candida albicans, resulting in a yeast infection called candidiasis. Being pregnant or having diabetes or a weakened immune... Common.TooltipReadMore (a yeast infection), are common during pregnancy and can be treated.
The breasts tend to enlarge because hormones (mainly estrogen) are preparing the breasts for milk production. The glands that produce milk gradually increase in number and become able to produce milk. The breasts may feel firm and tender. Wearing a bra that fits properly and provides support may help.
The glands that produce milk gradually increase in number and become able to produce milk. The breasts may feel firm and tender. Wearing a bra that fits properly and provides support may help.
During the last weeks of pregnancy, the breasts may produce a thin, yellowish or milky discharge (colostrum). Colostrum is also produced during the first few days after delivery, before breast milk is produced. This fluid, which is rich in minerals and antibodies, is the breastfed baby's first food.
During pregnancy, the woman’s heart must work harder because as the fetus grows, the heart must pump more blood to the uterus. By the end of pregnancy, the uterus is receiving one fifth of the woman’s prepregnancy blood supply. During pregnancy, the amount of blood pumped by the heart (cardiac output) increases by 30 to 50%. As cardiac output increases, the heart rate at rest speeds up from a normal prepregnancy rate of about 70 beats per minute to as high as 90 beats per minute. During exercise, cardiac output and heart rate increase more when a woman is pregnant than when she is not. At about 30 weeks of pregnancy, cardiac output decreases slightly. Then during labor, it increases by an additional 30%. After delivery, cardiac output decreases rapidly at first, then more slowly. It returns to the prepregnancy level about 6 weeks after delivery.
At about 30 weeks of pregnancy, cardiac output decreases slightly. Then during labor, it increases by an additional 30%. After delivery, cardiac output decreases rapidly at first, then more slowly. It returns to the prepregnancy level about 6 weeks after delivery.
Certain heart murmurs and irregularities in heart rhythm Overview of Abnormal Heart Rhythms Abnormal heart rhythms (arrhythmias) are sequences of heartbeats that are irregular, too fast, too slow, or conducted via an abnormal electrical pathway through the heart. Heart disorders are... Common.TooltipReadMore may appear because the heart is working harder. Sometimes a pregnant woman may feel these irregularities. Such changes are normal during pregnancy. However, other abnormal heart sounds and rhythms (for example, diastolic murmurs and a rapid, irregular heart rate), which occur more often in pregnant women, may require treatment. (Diastolic heart murmurs are murmurs that occur just before the heart contracts. )
)
Blood pressure usually decreases during the 2nd trimester but may return to a normal prepregnancy level in the 3rd trimester.
The volume of blood increases by almost 50% during pregnancy. The amount of fluid in the blood increases more than the number of red blood cells (which carry oxygen). Thus, even though there are more red blood cells, blood tests indicate mild anemia, which is normal. For reasons not clearly understood, the number of white blood cells (which fight infection) increases slightly during pregnancy and increases markedly during labor and the first few days after delivery.
Did You Know...
The enlarging uterus interferes with the return of blood from the legs and the pelvic area to the heart. As a result, swelling Swelling During Late Pregnancy As pregnancy progresses, fluid may accumulate in tissues, usually in the feet, ankles, and legs, causing them to swell and appear puffy. This condition is called edema. Occasionally, the face... Common. TooltipReadMore (edema) is common, especially in the legs. Varicose veins Varicose Veins Varicose veins are abnormally enlarged superficial veins in the legs. Varicose veins may cause your legs to ache, itch, and feel tired. Doctors can detect varicose veins by examining the skin... Common.TooltipReadMore commonly develop in the legs and in the area around the vaginal opening (vulva). They sometimes cause discomfort. Clothing that is loose around the waist and legs is more comfortable and does not restrict blood flow. Some measures not only ease the discomfort but may also reduce leg swelling and make varicose veins more likely to disappear after delivery:
TooltipReadMore (edema) is common, especially in the legs. Varicose veins Varicose Veins Varicose veins are abnormally enlarged superficial veins in the legs. Varicose veins may cause your legs to ache, itch, and feel tired. Doctors can detect varicose veins by examining the skin... Common.TooltipReadMore commonly develop in the legs and in the area around the vaginal opening (vulva). They sometimes cause discomfort. Clothing that is loose around the waist and legs is more comfortable and does not restrict blood flow. Some measures not only ease the discomfort but may also reduce leg swelling and make varicose veins more likely to disappear after delivery:
Wearing elastic support hose
Resting frequently with the legs elevated
Lying on the left side
Like the heart, the kidneys work harder throughout pregnancy. They filter the increasing volume of blood. The volume of blood filtered by the kidneys reaches a maximum between 16 and 24 weeks and remains at the maximum until just before the baby is due. Then, pressure from the enlarging uterus may slightly decrease the blood supply to the kidneys.
Then, pressure from the enlarging uterus may slightly decrease the blood supply to the kidneys.
Activity of the kidneys normally increases when a person lies down and decreases when a person stands. This difference is amplified during pregnancy—one reason a pregnant woman needs to urinate frequently while trying to sleep. Late in pregnancy, lying on the side, particularly the left side, increases kidney activity more than lying on the back. Lying on the left side relieves the pressure that the enlarged uterus puts on the main vein that carries blood from the legs. As a result, blood flow improves and kidney activity increases.
The uterus presses on the bladder, reducing its size so that it fills with urine more quickly than usual. This pressure also makes a pregnant woman need to urinate more often and more urgently.
The high level of progesterone, a hormone produced continuously during pregnancy, signals the body to breath faster and deeper. As a result, a pregnant woman exhales more carbon dioxide to keep the level of carbon dioxide low. (Carbon dioxide is a waste product given off during respiration.) The woman may breathe faster also because the enlarging uterus limits how much the lungs can expand when she breathes in. The circumference of the woman’s chest enlarges slightly.
(Carbon dioxide is a waste product given off during respiration.) The woman may breathe faster also because the enlarging uterus limits how much the lungs can expand when she breathes in. The circumference of the woman’s chest enlarges slightly.
Virtually every pregnant woman becomes somewhat more out of breath when she exerts herself, especially toward the end of pregnancy. During exercise, the breathing rate increases more when a woman is pregnant than when she is not.
Because more blood is being pumped, the lining of the airways receives more blood and swells somewhat, narrowing the airways. As a result, the nose occasionally feels stuffy, and the eustachian tubes (which connect the middle ear and back of the nose) may become blocked. These effects can slightly change the tone and quality of the woman’s voice.
Nausea and vomiting Nausea and Vomiting During Early Pregnancy Up to 80% of pregnant women have nausea and vomiting to some extent. Nausea and vomiting are most common and most severe during the 1st trimester. Although commonly called morning sickness,... Common.TooltipReadMore , particularly in the mornings (morning sickness), are common. They may be caused by the high levels of estrogen and human chorionic gonadotropin, two hormones that help maintain the pregnancy.
Although commonly called morning sickness,... Common.TooltipReadMore , particularly in the mornings (morning sickness), are common. They may be caused by the high levels of estrogen and human chorionic gonadotropin, two hormones that help maintain the pregnancy.
Nausea and vomiting may be relieved by changing the diet or patterns of eating—for example, by doing the following:
Drinking and eating small portions frequently
Eating before getting hungry
Eating bland foods (such as bouillon, consommé, rice, and pasta)
Eating plain soda crackers and sipping a carbonated drink
Keeping crackers by the bed and eating one or two before getting up to relieve morning sickness
No drugs specifically designed to treat morning sickness are currently available. Sometimes nausea and vomiting are so intense or persistent that dehydration, weight loss, or other problems develop—a disorder called hyperemesis gravidarum Hyperemesis Gravidarum Hyperemesis gravidarum is extremely severe nausea and excessive vomiting during pregnancy. Women with hyperemesis gravidarum, unlike women with ordinary morning sickness, lose weight and become... Common.TooltipReadMore . Women with this disorder may need to be treated with drugs that relieve nausea (antiemetic drugs) or to be hospitalized temporarily and given fluids intravenously.
Women with hyperemesis gravidarum, unlike women with ordinary morning sickness, lose weight and become... Common.TooltipReadMore . Women with this disorder may need to be treated with drugs that relieve nausea (antiemetic drugs) or to be hospitalized temporarily and given fluids intravenously.
Heartburn and belching are common, possibly because food remains in the stomach longer and because the ringlike muscle (sphincter) at the lower end of the esophagus tends to relax, allowing the stomach’s contents to flow backward into the esophagus. Several measures can help relieve heartburn:
Eating smaller meals
Not bending or lying flat for several hours after eating
Avoiding caffeine, tobacco, alcohol, and aspirin and related drugs (salicylates)
Taking liquid antacids, but not antacids that contain sodium bicarbonate because they contain so much salt (sodium)
Heartburn during the night can be relieved by the following:
The stomach produces less acid during pregnancy. Consequently, stomach ulcers rarely develop during pregnancy, and those that already exist often start to heal.
Consequently, stomach ulcers rarely develop during pregnancy, and those that already exist often start to heal.
As pregnancy progresses, pressure from the enlarging uterus on the rectum and the lower part of the intestine may cause constipation. Constipation may be worsened because the high level of progesterone during pregnancy slows the automatic waves of muscular contractions in the intestine, which normally move food along. Eating a high-fiber diet, drinking plenty of fluids, and exercising regularly can help prevent constipation.
Hemorrhoids, a common problem, may result from pressure of the enlarging uterus or from constipation. Stool softeners, an anesthetic gel, or warm soaks can be used if hemorrhoids hurt.
Pica, a craving for strange foods or nonfoods (such as starch or clay), may develop.
Occasionally, pregnant women, usually those who also have morning sickness, have excess saliva. This symptom may be distressing but is harmless.
Gallstones Gallstones Gallstones are collections of solid material (predominantly crystals of cholesterol) in the gallbladder. The liver can secrete too much cholesterol, which is carried with bile to the gallbladder... Common.TooltipReadMore appear to be more common during pregnancy.
The liver can secrete too much cholesterol, which is carried with bile to the gallbladder... Common.TooltipReadMore appear to be more common during pregnancy.
Mask of pregnancy (melasma) is a blotchy, brownish pigment that may appear on the skin of the forehead and cheeks. The skin surrounding the nipples (areolae) may also darken. A dark line (called linea nigra) commonly appears down the middle of the abdomen. These changes may occur because the placenta produces a hormone that stimulates melanocytes, the cells that make a dark brown skin pigment (melanin).
Pink stretch marks sometimes appear on the abdomen. This change probably results from rapid growth of the uterus and an increase in levels of adrenal hormones.
Small blood vessels may form a red spiderlike pattern on the skin, usually above the waist. These formations are called spider angiomas.
Thin-walled, dilated capillaries may become visible, especially in the lower legs.
Two intensely itchy rashes occur only during pregnancy:
Pruritic urticarial papules and plaques of pregnancy Polymorphic Eruption of Pregnancy Polymorphic eruption of pregnancy is intensely itchy rashes that occur only during pregnancy.
 Pregnancy complications, such as polymorphic eruption of pregnancy, are problems that occur only... Common.TooltipReadMore (urticaria of pregnancy) typically appears during the last 2 to 3 weeks of pregnancy but may appear any time after the 24th week. Occasionally, they appear after delivery. The cause is unknown.
Pregnancy complications, such as polymorphic eruption of pregnancy, are problems that occur only... Common.TooltipReadMore (urticaria of pregnancy) typically appears during the last 2 to 3 weeks of pregnancy but may appear any time after the 24th week. Occasionally, they appear after delivery. The cause is unknown.Pemphigoid (herpes) gestationis Pemphigoid Gestationis Pemphigoid gestationis is a rare, intensely itchy rash that occurs during or just after pregnancy. Typically, the rash starts around the navel, appears during the 2nd or 3rd trimester, and disappears... Common.TooltipReadMore can appear any time after the 12th week of pregnancy or immediately after delivery. The cause is thought to be abnormal antibodies that attack the body’s own tissues—an autoimmune reaction Causes An autoimmune disorder is a malfunction of the body's immune system that causes the body to attack its own tissues. What triggers an autoimmune disorder is not known.
 Symptoms vary depending... Common.TooltipReadMore .
Symptoms vary depending... Common.TooltipReadMore .
Pregnancy affects virtually all hormones in the body, mostly because of the effects of hormones produced by the placenta. For example, the placenta produces a hormone that stimulates the woman’s thyroid gland to become more active and produce larger amounts of thyroid hormones. When the thyroid gland becomes more active (as it does in hyperthyroidism Thyroid Disorders During Pregnancy Thyroid disorders may be present before women become pregnant, or they may develop during pregnancy. Being pregnant does not change the symptoms of thyroid disorders. How the fetus is affected... Common.TooltipReadMore ), the heart may beat faster, causing the woman to become aware of her heartbeat (have palpitations). Perspiration may increase, mood swings may occur, and the thyroid gland may enlarge. However, the disorder hyperthyroidism, in which the thyroid gland malfunctions and is overactive, develops in fewer than 0. 1% of pregnancies.
1% of pregnancies.
Levels of estrogen and progesterone increase early during pregnancy because human chorionic gonadotropin, the main hormone the placenta produces, stimulates the ovaries to continuously produce them. After 9 to 10 weeks of pregnancy, the placenta itself produces large amounts of estrogen and progesterone. Estrogen and progesterone help maintain the pregnancy.
The placenta stimulates the adrenal glands to produce more aldosterone and cortisol (which help regulate how much fluid the kidneys excrete). As a result, more fluids are retained.
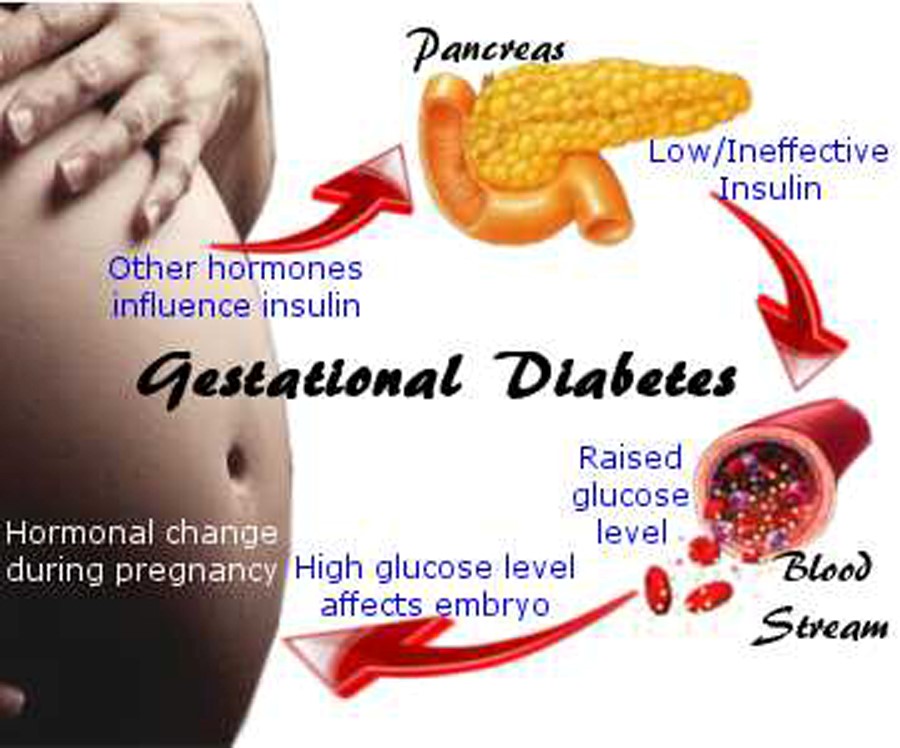
During pregnancy, changes in hormone levels affect how the body handles sugar. Later during pregnancy, the body does not respond as well to insulin as it normally does. Consequently, the sugar level increases. More insulin (a hormone that controls the sugar level in the blood) is needed during pregnancy. Consequently, diabetes Diabetes Mellitus (DM) Diabetes mellitus is a disorder in which the body does not produce enough or respond normally to insulin, causing blood sugar (glucose) levels to be abnormally high. Urination and thirst are... Common.TooltipReadMore , if already present, may worsen during pregnancy. Diabetes can also begin during pregnancy. This disorder is called gestational diabetes Gestational diabetes For women who have diabetes before they become pregnant, the risks of complications during pregnancy depend on how long diabetes has been present and whether complications of diabetes, such... Common.TooltipReadMore .
Urination and thirst are... Common.TooltipReadMore , if already present, may worsen during pregnancy. Diabetes can also begin during pregnancy. This disorder is called gestational diabetes Gestational diabetes For women who have diabetes before they become pregnant, the risks of complications during pregnancy depend on how long diabetes has been present and whether complications of diabetes, such... Common.TooltipReadMore .
The joints and ligaments (fibrous cords and cartilage that connect bones) in the woman’s pelvis loosen and become more flexible. This change helps make room for the enlarging uterus and prepare the woman for delivery of the baby. As a result, the woman’s posture changes somewhat.
Backache in varying degrees is common because the spine curves more to balance the weight of the enlarging uterus. Avoiding heavy lifting, bending the knees (not the waist) to pick things up, and maintaining good posture can help. Wearing flat shoes with good support or a lightweight maternity girdle may reduce strain on the back.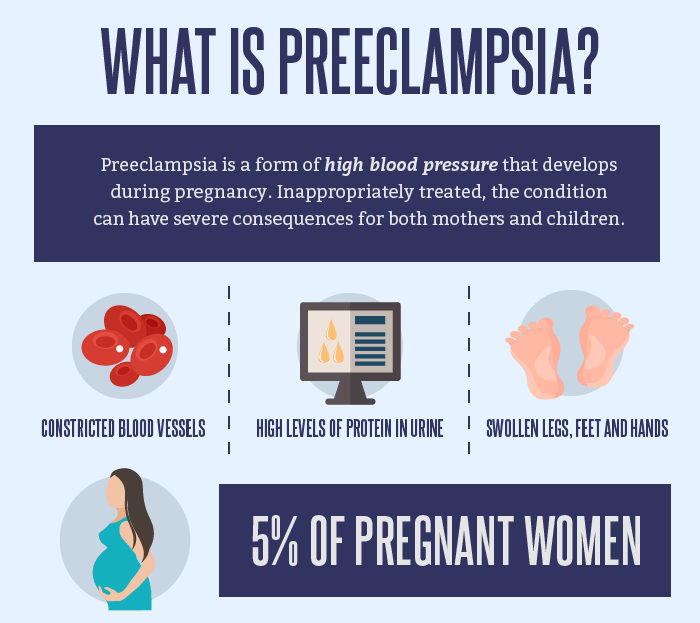
| Generic Name | Select Brand Names |
|---|---|
caffeine |
Cafcit, NoDoz, Stay Awake, Vivarin |
aspirin |
Anacin Adult Low Strength, Aspergum, Aspir-Low, Aspirtab , Aspir-Trin , Bayer Advanced Aspirin, Bayer Aspirin, Bayer Aspirin Extra Strength, Bayer Aspirin Plus, Bayer Aspirin Regimen, Bayer Children's Aspirin, Bayer Extra Strength, Bayer Extra Strength Plus, Bayer Genuine Aspirin, Bayer Low Dose Aspirin Regimen, Bayer Womens Aspirin , BeneHealth Aspirin, Bufferin, Bufferin Extra Strength, Bufferin Low Dose, DURLAZA, Easprin , Ecotrin, Ecotrin Low Strength, Genacote, Halfprin, MiniPrin, St. Joseph Adult Low Strength, St. Joseph Aspirin, VAZALORE, Zero Order Release Aspirin, ZORprin |
sodium bicarbonate |
Alka-Seltzer Heartburn Relief, Baros, Neut |
insulin |
Afrezza, Exubera |
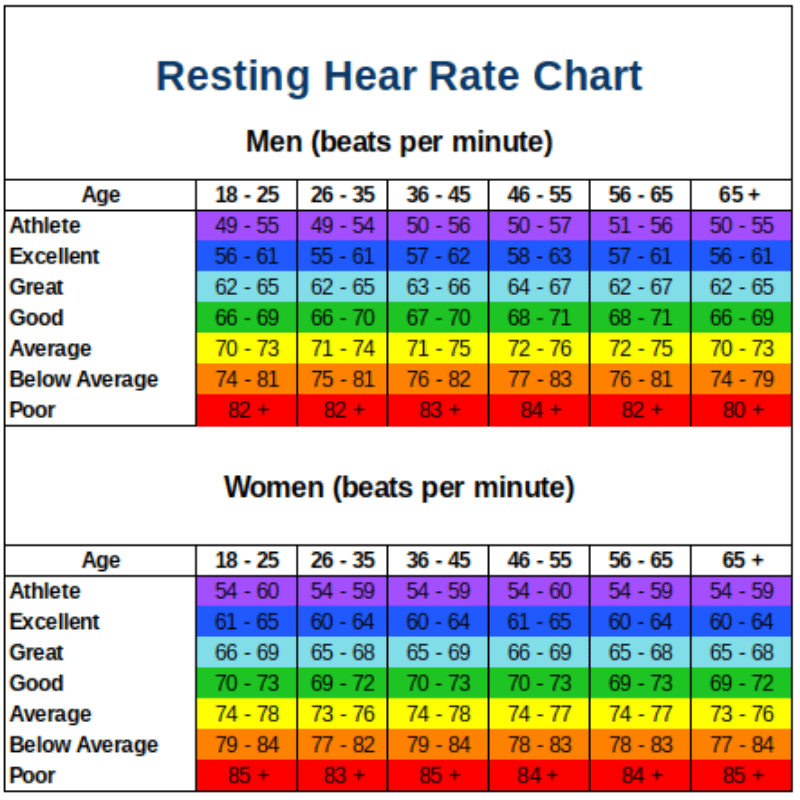
Heart rate during pregnancy: What is normal
Heart rate normally increases during pregnancy, as the body works to pump blood to the organs and placenta.
Many pregnant people also experience a drop in blood pressure, especially in early pregnancy.
There is a wide range of normal heart rates in pregnancy. Knowing a person’s prepregnancy heart rate may help predict their typical pregnancy heart rate.
There is no standard definition of a pregnancy heart rate that is too high or too low. Instead, doctors look at a person’s baseline heart rate and how their heart rate changes over time.
A 2019 meta-analysis looked at heart rate increases in 36,239 pregnant people. The authors found the average heart rate increase was around 10%, or 7–8 beats per minute (BPM).
The study also found that the average heart rate rises steadily through pregnancy. At 10 weeks, the average heart rate was 79.3 BPM. By 40 weeks, the average rate was 86.9 BPM.
A person’s heart rate during pregnancy may be higher or lower than these figures if their prepregnancy heart rate is higher or lower.
Brief heart palpitations and slight changes in pregnancy heart rate are common.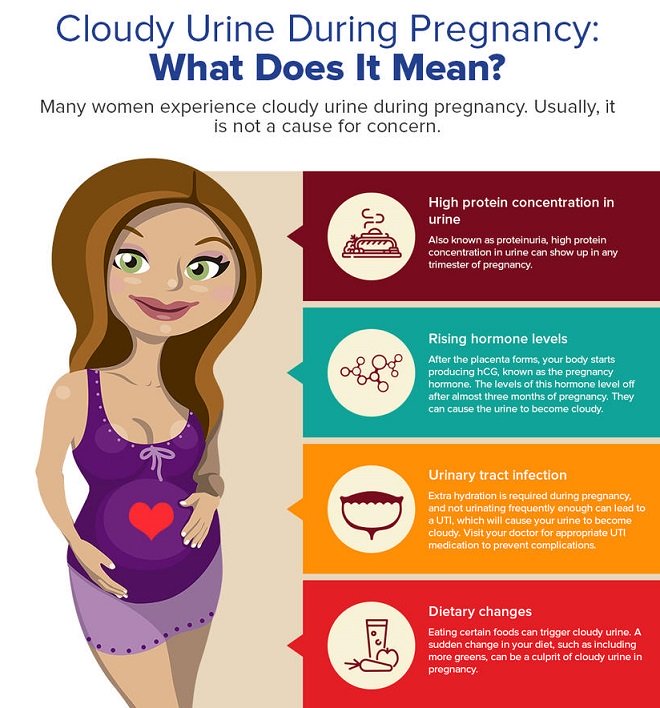 A 2007 study emphasizes that while these changes in heart rate can signal a heart problem in rare cases, most are harmless.
A 2007 study emphasizes that while these changes in heart rate can signal a heart problem in rare cases, most are harmless.
A person’s heart rate might not fall into the average range during pregnancy for a few reasons.
Abnormal starting heart rate
People with low or high resting heart rates may experience pregnancy heart rates that are also outside of the normal range.
Heart disease
Sometimes, changes in heart rate signal a problem with the heart’s electrical system, a blocked artery, or other heart health problems.
Heart health issues are more common during pregnancy. Heart disease is a leading cause of pregnancy-related death.
Preexisting arrhythmias
Arrhythmias are heart palpitations or other disturbances of the heart rate. People with a history of arrhythmias may find that pregnancy worsens their condition.
Exercise
People who are physically active may have lower resting heart rates. This can extend to pregnancy.
Anxiety
Anxiety makes a person’s heart beat faster. Some people also become anxious when they notice their heart is beating quickly, which can lead to more anxiety.
People whose heart rate falls outside their normal range should focus on why this happens, rather than trying to reach a particular number of BPM. Talk to a doctor before trying to change the heart rate.
In general, a healthful lifestyle may help a person remain healthy during pregnancy and can support a normal heart rate.
Exercise
Moderate exercise is usually safe during pregnancy, but talk to a doctor before trying a new or difficult routine.
Most pregnant people need at least 150 minutes of aerobic exercise per week.
Try walking, swimming, and other low-impact options. Yoga or stretching may help support healthy muscles and reduce pregnancy aches and pains.
Eat a healthful diet
Talk to a doctor about how best to nourish the body during pregnancy.
Most pregnant people need 2,200–2,900 calories per day.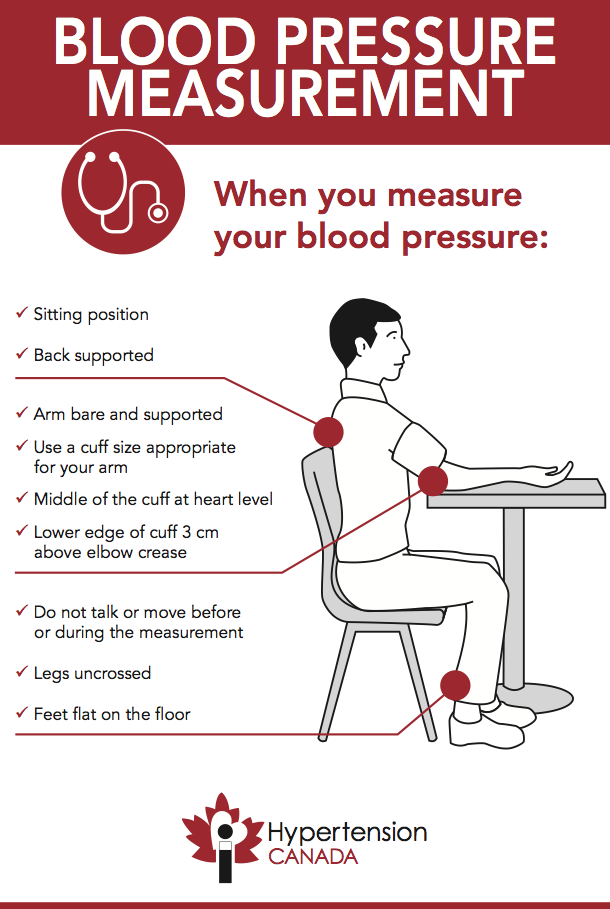 This varies with age, body size, activity level, and other factors.
This varies with age, body size, activity level, and other factors.
Proteins, fruits, vegetables, and other nourishing foods can help protect the heart.
Get proper prenatal care
See a doctor or midwife at least once during the first trimester, then schedule appointments regularly according to the healthcare provider’s recommendations.
Regular prenatal care involves monitoring heart health and can reduce the risk of developing an untreated heart issue.
Manage anxiety and mental health
Anxiety can make the heart beat faster and make pregnancy more difficult.
People experiencing anxiety should talk to a doctor, practice slow and deep breathing, and speak with a mental health counselor specializing in prenatal mental health.
It is important to have regular prenatal visits with a doctor or midwife during pregnancy. Discuss any changes in heart rate, and make sure the healthcare provider takes heart rate and blood pressure readings.
A person should call 911 or their nearest emergency department immediately if they experience:
- chest pain or pressure
- trouble breathing
- an intense headache, stomach pain, or sudden swelling in one or both feet or legs
- sudden high blood pressure
Heart rate changes during pregnancy are normal. The body has to pump more blood and compensates by lowering blood pressure and pumping faster.
The body has to pump more blood and compensates by lowering blood pressure and pumping faster.
Some people do not notice these changes, but others could find them alarming or uncomfortable.
If a pregnant person has any symptoms that seem abnormal, they should speak to a healthcare provider.
reasons and whether you need to see a doctor In the second and third trimesters, heart palpitations occur due to the need for the heart to pump more and more blood.
Also read
Often in the last weeks expectant mothers complain not only of tachycardia, but also of shortness of breath, weakness and dizziness. It is important here not to ignore such symptoms and to clearly determine with the doctor whether they develop against the background of an ongoing pregnancy or are still the result of cardiac problems or thyroid diseases.
Tachycardia - acceleration of the heart rate (pulse) over 90 beats per minute. Tachycardia is not always a symptom of the disease. Most often, the heart beat is accelerated due to the action of catecholamines resulting from emotions or physical exertion (sinus tachycardia).
Most often, the heart beat is accelerated due to the action of catecholamines resulting from emotions or physical exertion (sinus tachycardia).
Causes of palpitations in 1-2-3 trimesters
Pregnant health
During pregnancy, a woman's body undergoes many changes that affect the functioning of the cardiovascular system. At the beginning of pregnancy, some time after fertilization, progesterone begins to rise actively, which causes vasodilation and a slight decrease in blood pressure. This can lead to symptoms such as palpitations or tachycardia.
As the pregnancy progresses and the end of the second trimester approaches, the heart begins to work 30-50% more intensively. During this period, there is a change in the work of the cardiovascular system, which transports blood, which is so important for the mother and fetus. At the same time, blood transport occurs at a fairly active pace, as a result, an increase in heart rate and even shortness of breath can develop.
It is quite obvious that in order to meet the needs of the body of both a pregnant woman and a baby, the activity of the cardiovascular system must undergo certain changes. During pregnancy, the volume of circulating blood increases, along with this, cardiac output and, accordingly, the heart rate increase. That is why before pregnancy a woman's pulse can range from 60 to 70 beats per minute, and in the last trimester it increases to 9.0.
High heart rate during pregnancy is usually a physiological phenomenon.
Other causes of rapid heartbeat:
- increased emotional stress;
- anemia, fatigue;
- thyroid disease;
- manifestation of congenital heart defects.
Be sure to see a cardiologist if tachycardia is accompanied by other alarming symptoms: shortness of breath, sweating, chest pain, fever.
Tachycardia with chest pain
Also read
Pregnant women with complaints of heart palpitations and chest pain should definitely be examined and diagnosed by a cardiologist. Naturally, not every feeling of chest pain indicates the presence of a pathology of the heart. A similar symptom can develop against the background of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. So, often discomfort and soreness in the chest are the causes of heartburn - gastroesophageal reflux disease. Sometimes such pain is associated with respiratory infections, for example, it is often noted with pneumonia.
Naturally, not every feeling of chest pain indicates the presence of a pathology of the heart. A similar symptom can develop against the background of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. So, often discomfort and soreness in the chest are the causes of heartburn - gastroesophageal reflux disease. Sometimes such pain is associated with respiratory infections, for example, it is often noted with pneumonia.
Another cause of chest pain may be the banal activity of the baby. So, in the second trimester, the child can show whole "acrobatic stunts" in the mother's stomach. Because of this, various unpleasant symptoms and discomfort may appear.
Tachycardia, shortness of breath and fatigue during pregnancy - when to run to the hospital?
Increased levels of progesterone circulating in the blood stimulate the respiratory center in the brain, which in turn stimulates the frequency and depth of the pregnant woman's breathing. In the third trimester, the enlarged uterus puts pressure on the diaphragm, making it difficult to take deep breaths and force a woman to breathe faster with smaller volumes. So, often there is a feeling that shortness of breath has appeared and there is not enough air.
So, often there is a feeling that shortness of breath has appeared and there is not enough air.
Also read
Indeed, high heart rate, shortness of breath, fatigue during pregnancy most often act as a physiological phenomenon. But doctors note that sometimes such signs should still cause concern and make you see a doctor, especially if they are accompanied by dizziness and loss of consciousness.
There are quite a few possible diseases in which a pregnant woman develops tachycardia. Such a problem can occur with anemia, hyperthyroidism, as well as with various infections or acute cardiac pathologies. It is for this reason that if the expectant mother has other symptoms besides a high pulse, you should consult a doctor. It may turn out that an increase in heart rate is a symptom of a certain disease, the existence of which will require treatment.
We were consulted by family medicine doctor Christina Shevchenko.
Read also: What are we complaining about: 5 most common problems of pregnant women
Pulse during pregnancy - tips in the pregnancy calendar on Babyblog.
 ru example to ensure the development and functioning of the child. The baby receives oxygen and all nutrients from the mother's blood, respectively, the heart of a pregnant woman works in an enhanced mode. By the second trimester of pregnancy, the volume of work at the heart increases significantly. This is due to the fact that during this period all the vital organs of the crumbs are formed. Accordingly, the volume of circulating blood increases, and the child requires a full supply of nutrients and oxygen.
ru example to ensure the development and functioning of the child. The baby receives oxygen and all nutrients from the mother's blood, respectively, the heart of a pregnant woman works in an enhanced mode. By the second trimester of pregnancy, the volume of work at the heart increases significantly. This is due to the fact that during this period all the vital organs of the crumbs are formed. Accordingly, the volume of circulating blood increases, and the child requires a full supply of nutrients and oxygen. That is why the pulse quickens during pregnancy, it becomes especially noticeable from the second trimester. Most women during this period begin to feel shortness of breath, palpitations, tachycardia and difficulty breathing. This cannot but worry the expectant mother, so let's talk further about what pulse during pregnancy is considered normal and does not threaten the baby's health.
Normal pulse during pregnancy
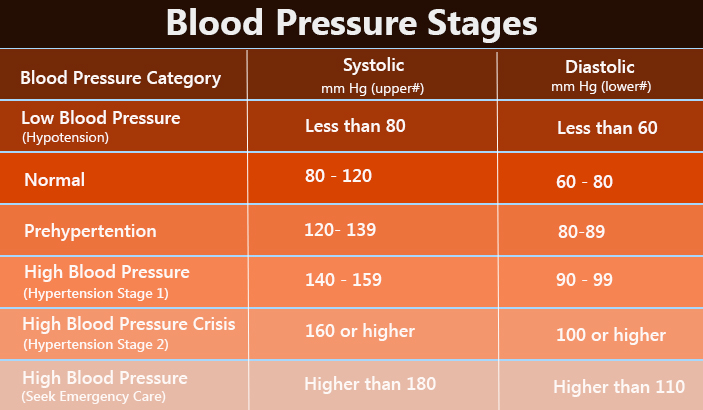
During pregnancy, an increased pulse is considered normal, the main thing is to know what value is the limit and make sure that the pulse does not exceed the bar.
Every pregnant woman has her own pulse rate. Usually, during the period of bearing a baby, the pulse increases by 10-15 units. For example, if before pregnancy a woman's pulse was 85 units, then a pulse of 95–100 units is normal. Experts believe that for 100-110 beats per minute, this is the highest bar in terms of the pulse rate. Exceeding these values is a "bell" for a woman. It is necessary to undergo an examination to identify the cause of the malfunction of the cardiovascular system.
In the third trimester of pregnancy, a woman's pulse can rise noticeably and remain quite high until the end of pregnancy, about 120 beats per minute.
Causes of increased heart rate during pregnancy
The pulse during pregnancy can increase for various reasons. For example, an increase in heart rate can be provoked by physical activity, lying on your back, large weight gain, poor diet, and other reasons. To prevent such jumps in the pulse, it is very important to monitor your diet, lead a proper lifestyle and not overstrain the body.
Low heart rate
Some women experience a decrease in heart rate during pregnancy, this is called bradycardia. Expectant mothers do not experience any unpleasant sensations when the pulse drops, although some may experience dizziness and even fainting. Often, against the background of a low pulse, the pressure also decreases significantly.
In general, bradycardia is not very common, but still you need to keep in mind that if you have a decrease in heart rate, then you need to consult a specialist, as this can lead to heart disease.
It is worth saying that a slightly slow pulse does not have a negative impact on both the condition of the pregnant woman and the development of the baby.
Treat or not?
Usually, in order for the expectant mother's pulse to return to normal, she just needs to lie down and rest. There is no need to worry about the baby, it is reliably protected from various dangers from the outside. Even if the mother's pulse rises sharply to 140 beats per minute, the baby's heart will beat in a normal rhythm.