Pregnancy risks over 40
Pregnancy After 40: What to Expect
Written by Alexandra Benisek
In this Article
- What Are the Risks of Pregnancy After 40?
- What Are the Benefits of Pregnancy After 40?
- How Can You Prepare for a New Baby After 40?
While 1 in 4 people in their 20s and 30s will get pregnant for any one menstrual cycle, only 1 out of every 10 people will become pregnant for any one menstrual cycle by age 40. At this age, you have a 44% chance of pregnancy within 1 year. This is because as you get older, the number of eggs in your ovaries decline. With age, you’re also at a higher risk for disorders that affect your fertility.
If you get pregnant at 40 to 45 years old, experts consider this a “late” pregnancy. But it’s still possible to get pregnant and deliver a healthy baby in your 40s. Childbirth at older ages has become more common too. Since the 1990s, birth rates in people aged 40-44 have gone up. To prepare for a baby at 40, it’s important to consider the risks and benefits.
What Are the Risks of Pregnancy After 40?
In people who can get pregnant, the peak reproductive years span the time between your late teens and late 20s. Your fertility will begin to go down around age 30. This process continues more quickly starting in your mid-30s. Once you reach 45, your fertility will usually be so low that a natural pregnancy is unlikely for most people.
But some women may still have a “menopause baby.” This refers to a pregnancy and delivery that happens when you’re in perimenopause, the transition into menopause (which is when your ovaries have stopped releasing eggs).
The sperm-producing parent may also have a decline in fertility with age. While this isn’t as predictable, it could still affect your chances of pregnancy at 40.
Other risks of pregnancy at 40 include complications that are more common at this age. Older women tend to have more health issues than younger women, such as high blood pressure.
This condition can put you at a higher risk for preeclampsia, which is when you suddenly develop high blood pressure and signs of organ damage while pregnant. If doctors don’t treat this, it can lead to serious or fatal problems for you and your baby.
If doctors don’t treat this, it can lead to serious or fatal problems for you and your baby.
But later-in-life pregnancies can also affect the health of your baby, even if you don’t have any health conditions. If you get pregnant at 40, you’ll have a higher risk of:
A higher birth weight of your baby. One study found that the risk of macrosomia (or a higher birth weight of your baby) goes up with age.
Placenta previa. This happens when your baby’s placenta either partly or completely covers your cervix, which is the exit area of your uterus. With this condition, you may bleed more while pregnant and during your delivery.
Gestational diabetes. This is when you get diabetes for the first time while you’re pregnant. It causes high blood sugar that can affect your baby’s health and your pregnancy.
Gestational hypertension. This is high blood pressure that develops during pregnancy. It’s different from preeclampsia, which is a blood pressure complication during pregnancy.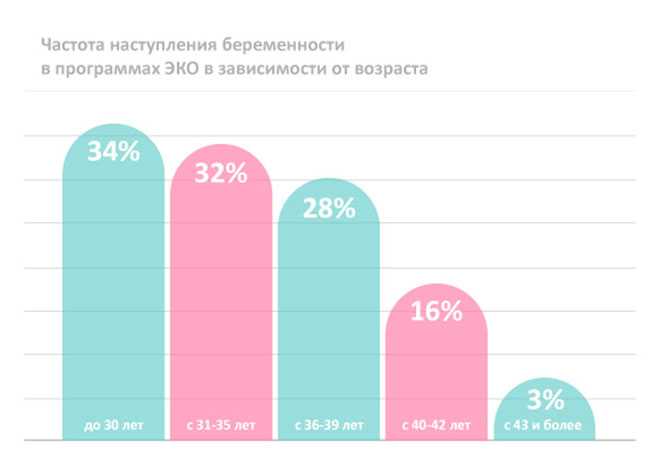
Miscarriage or stillbirth. You’re more likely to have a miscarriage if you’re older. At age 40, 27% of pregnancies end in a miscarriage compared to 16% for those 30 or younger.
C-section. If you’re 40 or older, you’re more likely to have a C-section delivery than a vaginal delivery.
Down syndrome. The risk of having a child with Down syndrome goes up as you age. At the age of 20, 1 in 1,480 children will be born with the condition. But at age 40, this risk goes up to 1 in 85. At age 45, your child’s risk is 1 in 35.
Need for ablood transfusion. This can help save your life in an emergency blood loss situation during pregnancy. But it comes with the risk of complications as well.
What Are the Benefits of Pregnancy After 40?
While there are more health risks with pregnancy at 40, there are also some upsides to later births. You may:
- Have a more established career that allows you to have more time to raise a child
- Have a better financial status at an older age
- Want to have a child with a partner you met later in life
- Find that you’re more mature and ready to handle the responsibility of a child
Studies have also shown that a child later in life may lower your mental decline, lengthen your life, and lead your child to have better educational results (like higher graduation rates and test scores).
How Can You Prepare for a New Baby After 40?
To prepare to have a child, it’s important to create a reproductive life plan. With this, you and your doctor can prepare for you to have children at your desired age.
If you want to get pregnant now, make sure you’re as healthy as possible. Stop alcohol, marijuana, and tobacco use. Talk to your doctor about prenatal vitamins with folic acid.
Visit your doctor to chat about your diet and lifestyle, sexually transmitted infection (STI) screening, a healthy prepregnancy weight, and any other concerns before you get pregnant. Everyone should make an appointment before they try to get pregnant, but this is especially crucial if you’re 40 and older.
If you don’t want to get pregnant now but may want to have a baby at an older age, talk to your doctor about:
In vitro fertilization (IVF). With this method, experts combine a sperm and egg in a laboratory to grow an embryo. Your doctor can then freeze the embryo for later use.
Oocyte cryopreservation. This is when your doctor freezes your eggs. They’ll take some of your eggs from your ovaries and freeze them so you can use them later in IVF.
You can still get pregnant naturally at 40, but these methods may heighten your chances of having a baby at a later age.
Benefits, Risks, and What to Expect
Having a baby after the age of 40 has become an increasingly common occurrence. In fact, the Centers for Disease Control and Preventiom (CDC) (CDC) explains that the rate has increased since the 1970s, with the number of first-time births among women ages 40 to 44 more than doubling between 1990 and 2012.Mathews TJ, et al. (2014). First births to older women continue to rise. https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/products/databriefs/db152.htm
While women are often told it’s best to have children before the age of 35, data suggests otherwise.
There are multiple reasons why women are waiting to have children, including fertility treatments, early careers, and settling down later in life. If you’re curious about what it’s like to have a baby at 40, consider all the range of benefits, risks, and other facts you need to know.
If you’re curious about what it’s like to have a baby at 40, consider all the range of benefits, risks, and other facts you need to know.
Sometimes the benefits of having a baby later in life can outweigh those of having children when you’re in your 20s or 30s.
For one, you might have already established your career and can dedicate more time to raising children. Or your financial situation could be more favorable.
You may have also had a change in your relationship status and you want to have a baby with your partner.
These are among some of the most common benefits of having a child at age 40. However, some research suggests potential other benefits, including:
- reduced cognitive declineKarim R, et al. (2016). Effect of reproductive history and exogenous hormone use on cognitive function in mid‐ and late life. DOI: 10.1111/jgs.14658
- longer life spanSun F, et al. (2015). Extended maternal age at birth of last child and women’s longevity in the long life family study.
 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4270889/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4270889/ - better educational outcomes in children, such as higher test scores and graduation ratesBarclay K, et al. (2016). Advanced maternal age and offspring outcomes: Reproductive aging and counterbalancing period trends. DOI: 10.1111/j.1728-4457.2016.00105.x
Due to advances in technology surrounding fertility, pregnancy, and delivery, it’s possible to safely have a baby at age 40. However, any pregnancy after age 40 is considered high risk. Your doctor will monitor you and the baby closely for the following:
- high blood pressure — this may increase your risk of a pregnancy complication called preeclampsia
- gestational diabetes
- birth defects, such as Down syndrome
- miscarriage
- low birth weight
- ectopic pregnancy, which sometimes happens with in vitro fertilization (IVF)
Advancements in fertility technological have been a driving force in the increase in women waiting to have children. Some options available to women include:
Some options available to women include:
- infertility treatments, such as IVF
- freezing eggs when you’re younger so that you can have them available when you’re older
- sperm banks
- surrogacy
Even with all of these options available, a woman’s fertility rate does decrease significantly after 35 years of age. According to the Office on Women’s Health, one-third of couples after the age of 35 experience fertility issues.Infertility. (2018). https://www.womenshealth.gov/a-z-topics/infertility This may be attributed to the following risk factors that increase with age:
- fewer number of eggs left to fertilize
- unhealthy eggs
- ovaries can’t release eggs properly
- increased risk of miscarriage
- higher chances of health conditions that can impede fertility
The number of egg cells (oocytes) you have also decreases significantly after the age of 35. According to the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG), the number drops from 25,000 at age 37 to just 1,000 at age 51. Female age-related fertility decline. (2014). https://www.acog.org/Clinical-Guidance-and-Publications/Committee-Opinions/Committee-on-Gynecologic-Practice/Female-Age-Related-Fertility-Decline During puberty, you have between 300,000 and 500,000 oocytes.
Female age-related fertility decline. (2014). https://www.acog.org/Clinical-Guidance-and-Publications/Committee-Opinions/Committee-on-Gynecologic-Practice/Female-Age-Related-Fertility-Decline During puberty, you have between 300,000 and 500,000 oocytes.
It can take some time to get pregnant, regardless of age. But if you’re over 40 years old and you’ve been trying unsuccessfully to have a baby naturally for six months, it may be time to see a fertility specialist.
A fertility specialist will run tests to see if there are factors that are affecting your ability to get pregnant. These may include ultrasounds to look at your uterus and ovaries, or blood tests to check your ovarian reserve.
According to ACOG, most women after age 45 can’t get pregnant naturally.Having a baby after age 35: How aging affects fertility and pregnancy. (2018). https://www.acog.org/Patients/FAQs/Having-a-Baby-After-Age-35-How-Aging-Affects-Fertility-and-Pregnancy
If you are experiencing infertility, talk to your doctor about the following options to help determine if one is right for you:
- Fertility drugs.
 These help with hormones that can assist with successful ovulation.
These help with hormones that can assist with successful ovulation. - Assisted reproductive technology (ART). This works by removing eggs and fertilizing them in a lab before inserting them back into the uterus. ART may work for women with ovulation issues, and it can also work for surrogates. There’s an estimated 11 percent success rate in women ages 41 to 42.Infertility. (2018). https://www.womenshealth.gov/a-z-topics/infertility One of the most common types of ART is IVF.
- Intrauterine insemination (IUI). Also called artificial insemination, this process works by injecting sperm into the uterus. IUI may be especially helpful if male infertility is suspected.
Just as it’s statistically more difficult to conceive after the age of 40, pregnancy itself can also be more challenging as you age.
You may have more aches and pains due to joints and bones that are already starting to lose mass with age. You might also be more susceptible to high blood pressure and gestational diabetes. Pregnancy-related fatigue may be more pronounced as you get older, too.
Pregnancy-related fatigue may be more pronounced as you get older, too.
It’s important to talk to your OB-GYN about what else you can expect during your pregnancy based on your age and overall health.
Vaginal delivery may be less likely after the age of 40. This is primarily due to fertility treatments that can increase risk for premature birth. You may also be at an increased risk of preeclampsia, which may necessitate a cesarean delivery to save both mother and baby.
If your baby is delivered vaginally, the process may be more challenging as you get older. There’s also an increased risk of stillbirth.
Many women do successfully deliver healthy babies at or over the age of 40. Talk to your doctor about what to expect, and come up with a backup plan. For example, if you’re planning a vaginal delivery, talk to your partner and support group about what help you’ll need if you require a cesarean delivery instead.
Age in and of itself does not increase your risk for multiples. However, women who use fertility drugs or IVF for conception are at a higher risk of twins or multiples.Infertility. (2018). https://www.womenshealth.gov/a-z-topics/infertility This is because of the way the medications increase ovulation.
However, women who use fertility drugs or IVF for conception are at a higher risk of twins or multiples.Infertility. (2018). https://www.womenshealth.gov/a-z-topics/infertility This is because of the way the medications increase ovulation.
Having twins also increases the risk that your babies will be more prematurely.
Getting pregnant after age 40 can take longer for some women than others. Still, your fertility specialist will need to work with you quickly since your fertility rate drops dramatically in your 40s.
If you’re unable to conceive naturally, you’ll want to consider whether you’re up for potentially multiple tries with fertility treatments and if you have the means to cover the treatments.
Having a baby at 40 is much more common than it used to be, so if you’ve waited to have children until now, you’ll have a lot of company.
Despite the challenges it can take to conceive, having children in your 40s is definitely a possibility.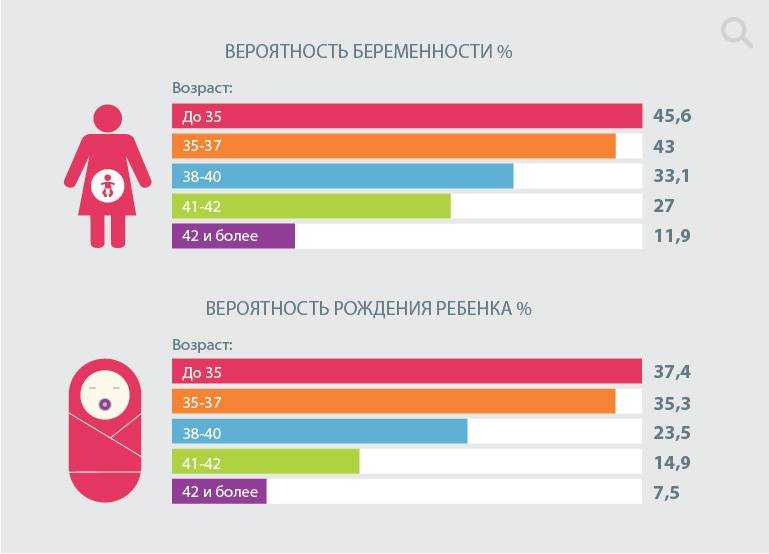 You’ll want to talk to your doctor about all your individual risk factors before starting a family at this stage in your life.
You’ll want to talk to your doctor about all your individual risk factors before starting a family at this stage in your life.
Pregnancy after 40: how to prepare and give birth to a healthy baby
Is there an ideal age for pregnancy and childbirth? "Yes!" — experts of the department of assisted reproductive technologies (ART) of the Veresaev hospital are sure.
“The most favorable age for conceiving, bearing and giving birth to a baby is 20-35 years old, but theoretically, if a woman is in good health, she can become a mother even at 60 years old, but here you need to understand that getting pregnant at this age is possible only with the help of assisted reproductive technologies using donor or previously frozen eggs. The most “adult” pregnant woman after IVF was 52 years old,” says Karina Grigoryan, head of the ART department, obstetrician-gynecologist, doctor of the highest category, candidate of medical sciences.
What changes in a woman's body after 40 years and how it can affect conception, pregnancy and child?
The probability that women of the older reproductive group have various chronic diseases, including hypertension and diabetes, is high. Such pathologies tend to worsen during pregnancy, which means they can become a formidable complication for the mother and fetus.
Such pathologies tend to worsen during pregnancy, which means they can become a formidable complication for the mother and fetus.
In principle, the chances of conception decrease with age. This is due to changes in the reproductive system - the uterus, ovaries. The regular "aging" of germ cells increases the number of complications during pregnancy and can lead to fetal malformations:
- Genetic and non-genetic
- Preeclampsia, which in turn leads to increased blood pressure, disruption of the kidneys, edema, impaired blood flow in the vessels of the uterus, placenta and umbilical cord of the fetus
Of course, the capabilities of modern medicine, in particular, prenatal screenings allow timely diagnosis of pathological conditions on the part of the fetus and the pregnant woman, which means making the right decision on the further medical support of the woman in a timely manner.
Does pregnancy rejuvenate the body?
So says the popular rumor and partly we can agree with it.
It is known that the placenta, which is formed by the 12th week of pregnancy, has a powerful hormonal secretion. A high concentration of the female sex hormone estrogen has a beneficial effect on the appearance of the expectant mother.
What are the features of the course of pregnancy in a future mother 40+?
The main feature is an increase in the frequency of complications during pregnancy. Unfortunately, the risk of genetic diseases in a child increases several times - Down syndrome, Edwards, Patau, etc., heart defects and the central nervous system of the fetus. Therefore, the course of pregnancy at this age should always be under the close supervision of obstetricians and doctors of prenatal diagnosis.
Are there any diseases that are considered a contraindication to pregnancy 40+?
Contraindication to pregnancy is not age, but first of all the presence of severe chronic diseases, and they can be observed both in women over 40 years old and in very young patients. We are talking about such pathologies as multiple sclerosis, uncompensated and not treatable hypertension, severe heart disease, genitourinary system, mental, oncological diseases, etc.
We are talking about such pathologies as multiple sclerosis, uncompensated and not treatable hypertension, severe heart disease, genitourinary system, mental, oncological diseases, etc.
How to prepare for pregnancy after 40?
If we are talking about a planned pregnancy, then in the pregravid period, the expectant mother is recommended to undergo a thorough examination: laboratory tests, a visit to a gynecologist, a therapist, ultrasound of the abdominal organs, kidneys, thyroid gland, vessels of the lower extremities and mammography.
If it's a second or third pregnancy after 40, does it carry the same risks as the first?
In a multiparous woman after 40 years, the body is “adapted” to pregnancy, the frequency of complications may be lower in general, but in this case we are not talking about fetal malformations, the risk of which does not depend on the number of previous births.
"Late" delivery is an indication for caesarean section?
The woman's age is not an indication for operative delivery. Many of our patients of the older reproductive group, including those who became pregnant with the help of IVF, gave birth themselves, naturally, and the birth went smoothly.
Many of our patients of the older reproductive group, including those who became pregnant with the help of IVF, gave birth themselves, naturally, and the birth went smoothly.
What are some of the postpartum issues that a 40+ mother may encounter?
If a woman was planning a pregnancy, had a complete examination, correction of pathological conditions, then the recovery postpartum period will run smoothly for her. Maybe not as fast as in 20-25 years, but quite successfully.
If we talk about women entering pregnancy with many chronic diseases, not examined, then we can expect various "surprises" in the postpartum period.
In any case, all mothers need care, support and help.
Pros and cons of pregnancy after 40?
Of course "for" with both hands. All women have successful pregnancies and healthy babies.
To learn more about assisted reproductive technologies available at the ART department of the Veresaev hospital, please call the single contact center: 8 (499) 450-55-81 (ext. 8).
8).
Childbirth at 40+: doctor about late childbirth
Obstetrician-gynecologist of the highest category Pilipenko Lyudmila Nikolaevna spoke about the risks of late motherhood and modern methods of preventing them
Childbirth at 40+ is trending today . Why, forty are enough examples of successful childbirth even after fifty years. The reasons for this reproductive behavior are many and usually complex. It can be economic, psychological, and any other reasons. But - most importantly - the level of modern medicine and new reproductive technologies make later motherhood physically possible.
And indeed, in recent years, childbirth at the age of 40 is no longer surprising, it has become quite commonplace.
Moreover, in many developed countries of the world, in particular in Great Britain and the USA, the number of women who gave birth after 40 already exceeds the number of those who became a mother before the age of 20.
The development of reproductive technologies and advances in medicine are shifting the female age of childbearing further and further. Bridget Nielsen gave birth at 54, Janet Jackson at 50, Halle Berry at 47, Rachel Weisz at 48.
Bridget Nielsen gave birth at 54, Janet Jackson at 50, Halle Berry at 47, Rachel Weisz at 48.
Since pregnancy and childbirth place an enormous burden on all organs and systems of the mother's body, the question arises: how safe is very late motherhood for the woman and for the child?
Women over 40 have significantly higher rates of complications during pregnancy and childbirth than those who give birth at a younger age.
If you decide to postpone motherhood until after 40, be prepared for the fact that pregnancy and childbirth can be associated with high risks.
The decision to give birth after 40 certainly needs to be approached with even more awareness than a pregnancy at a young age.
On one side of the scale - a new page in life and a lot of positive emotions, and on the other - a high risk of chromosomal abnormalities in a child.
From the point of view of nature, everything is quite clear: it is better to give birth to children from 23 to 35 years.
Because young women have better egg quality, the probability of chromosomal pathology in the fetus is less, they themselves still have a lot of strength and health not only to successfully carry and give birth to a baby, but also to get up at night in the first years. Starting from the age of thirty-five, it can be said that the countdown begins, and the woman's fertility is slowly falling, and the risks are becoming more and more.
A woman who decides to give birth after the age of forty should understand the peculiarities of such a pregnancy and try to reduce these risks in every possible way.
The risk of pathologies in the fetus increases
Starting from the age of 35, and especially after 40, the likelihood of a chromosomal abnormality in a child increases. These can be both relatively common pathologies such as Down syndrome, Patau or Edwards, and more rare ones. Let's take Down's syndrome as the most common and compatible with life. So, if a 30-year-old mother has a chance of having a baby with Down syndrome is about one in 800, then by the age of 40 we are already talking about a ratio of one to a hundred, and at 44 years old - one to 25.
So, if a 30-year-old mother has a chance of having a baby with Down syndrome is about one in 800, then by the age of 40 we are already talking about a ratio of one to a hundred, and at 44 years old - one to 25.
That's why all these categorical statements “Did you get pregnant at 40? You're having a baby with Down's Syndrome!" far from the truth. Yes, the risk increases, but the probability is still not critical.
In addition, there are modern, highly accurate and safe methods for testing the fetus for genetic abnormalities. For example, a non-invasive prenatal test is performed, that is, a test on the mother's blood, starting from 10-11 weeks of pregnancy. Fetal DNA is isolated from the mother's blood and they look for genetic abnormalities - both frequent and quite rare.
Of course, there are more traditional and also quite accurate research methods, but they are associated with a risk to the fetus, because tissues are tested that are previously removed from the uterine cavity.
There are also screenings that are carried out in the first and second trimester in antenatal clinics for blood and ultrasound. Their accuracy is quite low, and if it is important for you to know about the presence or absence of a chromosomal abnormality in the fetus, then it is advisable to use more accurate methods.
50% of late pregnancies are terminated before 12 weeks
Also, in parallel with the increase in the likelihood of pathologies, the frequency of abortions in the early stages is also growing, that is, these are interconnected things. Half of all late pregnancies are terminated before twelve weeks. Accordingly, it will be either a frozen pregnancy or a miscarriage.
Caesarean section will help avoid intrauterine death of the fetus
In addition to genetic defects in the embryo and early termination of pregnancy, women of the older age group may experience a number of other problems associated specifically with age and health. It can be a whole baggage of gynecological diseases, some operations, uterine fibroids that occurred at the age of 38-40 years. And all this can have an impact on the course of pregnancy, on the risks of bleeding during childbirth, even on the birth itself.
It can be a whole baggage of gynecological diseases, some operations, uterine fibroids that occurred at the age of 38-40 years. And all this can have an impact on the course of pregnancy, on the risks of bleeding during childbirth, even on the birth itself.
It is authentically known that in pregnant women older than 39 it is advisable not to wait for forty weeks, but to give birth earlier.
Because, starting from the thirty-ninth week, the percentage of intrauterine death of the fetus increases: the placenta works under heavy load, the body has practically spent all its strength on pregnancy. In a normal situation, the body understands that its resources are not enough, and childbirth begins.
In patients of the older age group, the “time to go” mechanism may not start, and the fetus simply dies in utero. And this is a normal child, with a normal set of chromosomes, just the placenta in the last stages no longer copes with its function, and the “lever” for the onset of labor does not work. Therefore, doctors recommend such women to have a caesarean section at a period of 38-39weeks.
Therefore, doctors recommend such women to have a caesarean section at a period of 38-39weeks.
The main thing is a healthy lifestyle
In general, the outcome of pregnancy and childbirth depends on how healthy the woman is. At forty years old, different people's body can be preserved in different ways. The place of residence of the family plays a significant role: it is one thing when a woman lives in nature, eats natural products, moves enough, and quite another when she lives in a metropolis, eats food from the nearest supermarket, is little in the fresh air, but sits a lot at the monitor and nervous.
But this does not mean that if your health is not very good, you should not dream of a child. Even in the most difficult cases, healthy children are obtained, although such pregnancies are, of course, more difficult. This is done in our medical center by several specialists at once: an endocrinologist, a therapist, a gynecologist. We live in an iodine-deficient area, and the longer we live in it, the more likely it is that thyroid disorders will accumulate, such as hypothyroidism.
Preventive medical examinations should be carried out regularly.
Do not think that when you are 40 years old, that's it, you can't give birth.
When deciding to give birth at a later age, a woman needs to undergo a complete examination. That is, not only to look at the reproductive system, but also to check the heart, blood vessels, hormones, and so on. It is equally important to start (at least start!) Leading a healthy lifestyle: quit bad habits, start eating right and love physical activity.
Our Avicenna Medical Center has been successfully specializing in the treatment of infertility and miscarriage for more than 11 years, as well as in preparing women for pregnancy and further management of pregnancy.
Obstetricians - gynecologists together with a urologist - andrologist and narrow specialists solve numerous problems of future parents so that a healthy long-awaited baby is born.
To prepare for pregnancy, an integrated approach and highly effective methods are used, which are not available in most other centers: lymphocytotherapy, SCL.