What helps increase breast milk production
Low Milk Supply | WIC Breastfeeding Support
Many moms worry about low milk supply, but most of the time your body makes exactly what your baby needs, even if you don't realize it. There are also ways to tell if your baby is getting enough milk. If you aren't making enough, there are ways you can build your supply. And your WIC breastfeeding staff is always there to help!
Am I Making Enough Milk?
First, look for these signs that your baby is getting enough milk. For example, pay attention to the number of wet and dirty diapers and your baby's weight gain.
Things you should NOT worry about:
- How your breasts feel. Your breasts will feel softer and less full as your milk supply adjusts to your baby's needs. This does not mean you have low supply.
- If your baby nurses for shorter periods of time, such as only 5 minutes on each breast.
- If your baby's feeds are bunched together. This is called cluster feeding and happens when your baby starts nursing more often and for longer.
This can happen in the evenings or because of growth spurts.
- Not getting much milk when you express. Your baby is much more effective than a pump or hand expression at getting out milk. Find tips to help you pump.
If you are still concerned, talk to your baby's doctor about their growth.
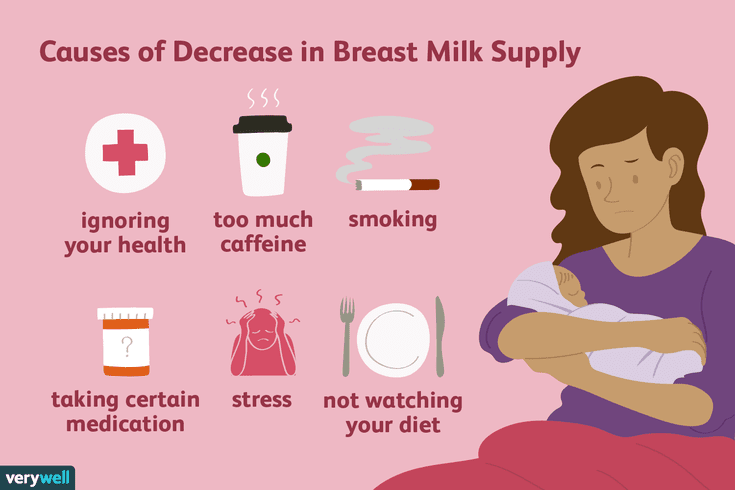
Causes of Low Milk Supply
While most moms make plenty of milk, some do have low milk supply. This might happen if you:
- Limit your baby's breastfeeding sessions. Remember, the more you feed on demand, the more milk you make.
- Give your baby infant formula instead of breastfeeding.
- Introduce solid foods before baby is 4-6 months old.
- Take certain birth control pills or other medicine.
- Don't get enough sleep.
- Drink alcohol or smoke.
- Have had breast surgery.
Talk to your doctor if you have hepatitis B or C, herpes, or diabetes. These conditions may also affect milk supply.
Increasing Your Milk Supply
Breastfeeding frequently—especially in the first hours, days, and weeks—is the main way to increase your milk supply. Your body will make milk to meet your baby's demand.
Try these tips to help you make more milk:
- Breastfeed every time your baby is hungry. In the early weeks, your baby will eat 8-12 times every 24 hours. It's best not to put your baby on a strict feeding schedule. Follow your baby's cues, and let your baby tell you when it's time to eat.
- Make sure your baby is latching well.
- Offer both breasts at each feeding. Let your baby finish the first side, then offer the other side.
- Empty your breasts at each feeding.
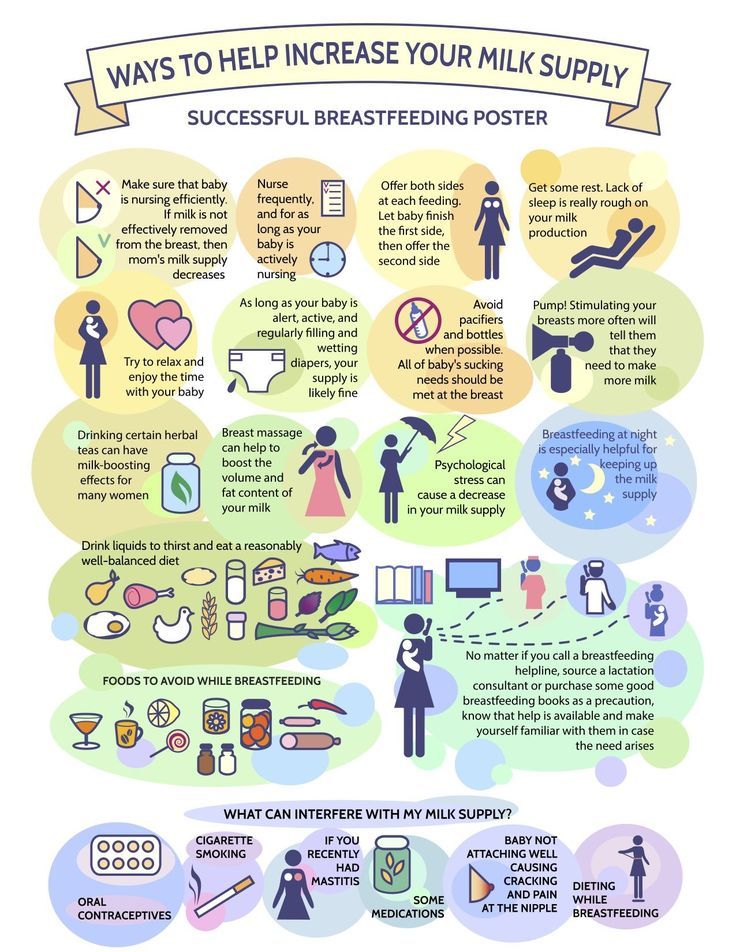 Hand express or pump after a feeding to draw out all the milk and signal your body to make more.
Hand express or pump after a feeding to draw out all the milk and signal your body to make more. - Avoid bottles and pacifiers in the early weeks. Feed your baby from your breast whenever you can.
- Get plenty of sleep, and eat a healthy diet.
- Pump or express your milk. Pumping or expressing milk frequently between nursing sessions, and consistently when you're away from your baby, can help build your milk supply.
- Relax and massage. Relax, hold your baby skin-to-skin, and massage your breasts before feeding to encourage your milk to let down.
- Take care of yourself. Get plenty of rest, eat well, drink enough fluids, and let others help you.
Consider Charting Your Progress
Record how often your baby is breastfeeding, for how long, and on which sides. If you are supplementing with infant formula, record how much your baby is getting and decrease the infant formula as your milk supply increases. WIC breastfeeding staff can help you determine how much infant formula your baby needs.
WIC breastfeeding staff can help you determine how much infant formula your baby needs.
Still Have Questions?
Contact your WIC breastfeeding expert. They can talk to you about supply concerns and give you tips to increase your supply to meet your baby's needs.
Breastfeeding: Tips to Increase Your Milk Supply l University Hospitals l Northeast Ohio
Signs That a Breastfed Baby Is Being Well Nourished
- Your baby nurses at least 8 to 16 times in 24 hours, or every 2 to 3 hours. Your baby may be fussy once or twice a day. At these times, he or she wants to nurse often for several hours before seeming full. This is called cluster feeding.
- Your baby wets at least 6 cloth or 5 disposable diapers and has at least 1 bowel movement in 24 hours. This occurs by 1 week of age.
- You can hear your baby swallow milk while nursing or you can feel your baby swallow when lightly touching his or her throat.
- Your breasts seem softer after nursing.
- Your baby gains 4 to 8 ounces a week after the first week. There is no need to weigh your baby at home. Your baby’s doctor will do this for you. You may notice that your baby has outgrown his or her clothing.
- Your baby has regained his/her birthweight by 10 to 14 days after birth.
Factors Which Can Cause Your Milk Supply to Decrease
- Your baby feeds fewer than 8 to 16 times in 24 hours. Milk production is affected by how well the breast is drained.
- Your baby has a very weak suck, or has an improper latch.
- Giving bottles of formula or water after nursing. Most babies will suck on a bottle after nursing. This just means they need to suck. It does not mean they are still hungry. Babies cry or fuss for many reasons, such as being tired, bored, wet, hot or cold.
- Giving solid foods too early and/or before you breastfeed. Most babies do not need solid foods for the first 6 months if they are breastfeeding 8 to 16 times a day.

- Smoking can cause a decreased milk supply and interfere with the letdown reflex. Here are some things you should do:
- Try to quit or cut down.
- Smoke after nursing, not before.
- Don’t smoke in the same room with your baby.
- Beginning birth control pills too soon can decrease your milk supply. Wait at least 6 weeks before taking birth control pills and then use only the mini-pill (Progestin). If you still notice a decrease in your milk supply, talk to your doctor about other birth control options. Other medications may also affect milk supply. Check with your doctor. (Refer to PI-682, Breastfeeding and Birth Control: You Have Options.)
- Mothers who are exhausted may notice a decrease in milk supply. To keep yourself from getting too tired:
- Sleep or relax when your baby sleeps.
- Eat balanced diet that includes high-protein food.
- Drink when you are thirsty so that your urine is pale yellow in color.
 Both under and excessive over hydration can decrease milk supply.
Both under and excessive over hydration can decrease milk supply. - Take an iron supplement if your healthcare provider says you are anemic.
- Talk with your doctor or nurse midwife about the need for vitamin supplement.
- Accept help when it is offered.
- Use nipple shields and pacifiers with caution.
- A breast flange that is too small or too large in size can hurt your milk supply.
- Pregnancy
- Breast reduction surgery may reduce milk supply.
If You Notice Your Milk Supply Is Low
You can increase your milk supply by:
- Nursing your baby often. Nurse every 2 hours during the day and every 3 to 4 hours at night (at least 8 to 16 times in 24 hours). If your baby will not nurse, use a good quality double electric breast pump to increase milk production. Pumping after breastfeeding signals your body to produce more milk.
- Nurse your baby at least 15 minutes at each breast.
 Do not limit nursing time. If your baby falls asleep after one breast, wake him or her and offer the second breast. A few babies may benefit from nursing at one breast per feeding to increase the fat content of the feeding. Switch nursing- switching breasts several times during a feeding has been shown to increase milk supply.
Do not limit nursing time. If your baby falls asleep after one breast, wake him or her and offer the second breast. A few babies may benefit from nursing at one breast per feeding to increase the fat content of the feeding. Switch nursing- switching breasts several times during a feeding has been shown to increase milk supply. - Gently massage breast before and during feedings.
- Use relaxation techniques to reduce stress and promote the flow of breast milk.
- Provide skin to skin time with your baby for about 20 minutes after feeds. This “kangaroo care” has been shown to increase milk supply.
- Be sure baby is positioned and latched correctly.
- Offer both breasts at each feeding.
- Try breast compression during the feeding to help drain the breast.
- Pump immediately after breastfeeding during the day. Rest at night. Some mothers find that they get more milk if they pump for 5 minutes, rest for 5 minutes, and pump for another 10 minutes.

Talk to your doctor about using medication or the herb fenugreek.
Works Cited
Wambach, Karen and Riordan, Jan “Breastfeeding and Human Lactation”, Fifth edition, Jones & Bartlett, 2016.
obstetrician-gynecologist Starostina Antonina Viktorovna.
For the normal development of lactation, first of all, it is necessary to organize the feeding of the child (feeding on demand, without a night break, the absence of nipples and pacifiers that suppress the suckling reflex of the baby), properly care for the breast, use a breast pump to stimulate and increase lactation, use according to indications other accessories for breastfeeding.
Sleep should be at least 10 hours a day - night and day. Outdoor walks for at least 2 hours. Frequent breastfeeding from birth (at least 10 times a day) with obligatory night feedings. Good nutrition and an increase in the amount of fluid consumed up to 1.5 - 2 liters per day (this is tea, soups, decoctions, milk, dairy products). Shower-massage: after feeding the baby and expressing milk, pour hot water (45 degrees) from the shower over the mammary gland that was fed, while massaging in circular motions from the nipple to the periphery and from top to bottom, while expressing milk. Duration 5-10 minutes.
Shower-massage: after feeding the baby and expressing milk, pour hot water (45 degrees) from the shower over the mammary gland that was fed, while massaging in circular motions from the nipple to the periphery and from top to bottom, while expressing milk. Duration 5-10 minutes.
Perform the procedure 2 times for the left and 2 times for the right breast during the day. Drink hot tea with milk 30 minutes before feeding.
Drink in small sips throughout the day.
- Steep 3 teaspoons of dry nettle with 2 cups of boiling water and infuse for 10-15 minutes (we only infuse fresh herb for 2 minutes). The resulting drink should be used during the day.
- A very effective remedy that stimulates the flow of milk and helps increase lactation is an infusion of walnuts, which is prepared as follows: brew 0.5 cups of peeled walnuts with 0.5 liters of boiling milk in a thermos and infuse for 3-4 hours. Infusion take 1/3 cup 20 minutes before each feeding, but not daily, but every other day.

- A mixture that promotes lactation is very good: 100 g dried apricots, 100 g raisins, 100 g figs, 1 glass of walnuts. Grind everything and mix with 100 g of honey and 100 g of butter. Use 1 tbsp. spoon 15-20 minutes before feeding. Watch your child's reaction! Allergy is possible.
- Useful green tea with dill seeds, raspberry leaves, linden, oregano, lemon balm.
Be sure to use special multivitamin complexes for pregnant and lactating women, which also help improve lactation. They will improve the quality of milk and increase its quantity:
- Hipp tea for nursing mothers.
- Apilac 0.01 under the tongue and dissolve. Take 2-3 times a day. Pay attention to the child's reaction! Allergy is possible.
- Vitamin E capsules 0.1-0.2 - 2 times a day.
- Ascorbic acid (vitamin C) up to 1 g per day.
- Brewer's yeast - liquid 60 g 3 times a day, dry 1 tsp. 4 times a day.
- Calcium pantothenate 1 tab. 3 times a day.

- Asparkam 1 tab. 3 times a day
In European countries, homeopathic remedies are widely used to stimulate lactation. Of the many homeopathic remedies to enhance lactation, the following remedies can be recommended: before each feeding of the child (20 minutes) \ Urtika urens 3 and Agnus castus 3 alternately and at night - Pulsatilla 6. Take 5 grains until the effect is obtained (from 3 days to 3 weeks). But in any case, you need to consult a doctor.
Lack of milk | How to increase the amount of milk
American Academy of Pediatrics and The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Breastfeeding Handbook for Physicians 2006). - American Academy of Pediatrics and American College of Obstetrics and Gynecology. Breastfeeding Medical Manual, 2006.
Donovan, T.J. & Buchanan, K. Medications for increasing milk supply in mothers expressing breastmilk for their preterm hospitalized infants. Cochrane . Database . Syst . Rev 3, CD 005544 (2012). - Donovan T.J. and Buchanan K., "Medicines for increasing the amount of milk in the accumulated mothers of premature babies during the hospitalization period", Cochrane Database Rev . 3 CD 005544(2012).
Cochrane . Database . Syst . Rev 3, CD 005544 (2012). - Donovan T.J. and Buchanan K., "Medicines for increasing the amount of milk in the accumulated mothers of premature babies during the hospitalization period", Cochrane Database Rev . 3 CD 005544(2012).
Hill, P.D., Aldag, J.C., Chatterton RT. Initiation and frequency of pumping and milk production in mothers of non-nursing preterm infants. J Hum Lact . 2001;17(1):9–13 - Hill P.D., Aldag J.S. and Chatterton, R.T., "Onset and frequency of expression and milk production in mothers who have given birth to premature babies and have not breastfed them." J Hum Lakt (Journal of the International Association of Lactation Consultants). 2001;17(1):9–13
Hill, P.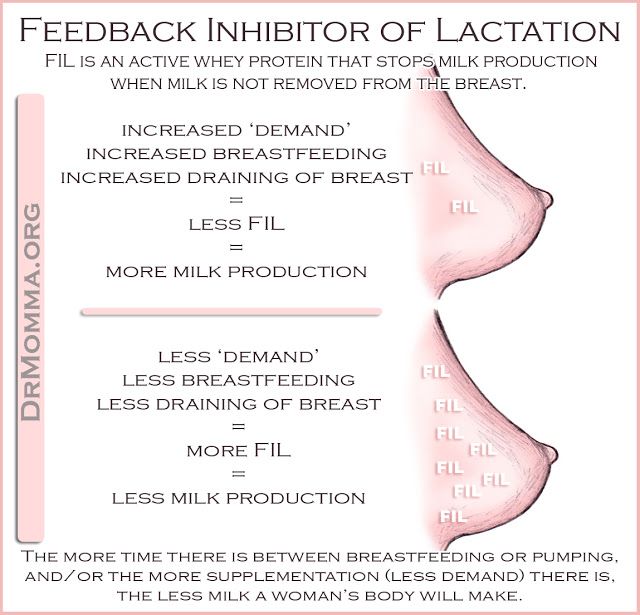 D., Aldag J.C., Chatterton RT, Zinaman M. Comparison of Milk Output Between Mothers of Preterm and Term Infants: The First 6 Weeks After Birth. J Hum Lact . 2005 February 1, 2005; 21(1):22–30. - Hill P.D., Aldag J.S., Chatterton R.T., Zinaman M., "Comparison of the amount of milk in mothers of full-term and premature babies in the first 6 weeks after birth." J Hum Lakt (Journal of the International Association of Lactation Consultants) 2005, 21(1): 22-30.
D., Aldag J.C., Chatterton RT, Zinaman M. Comparison of Milk Output Between Mothers of Preterm and Term Infants: The First 6 Weeks After Birth. J Hum Lact . 2005 February 1, 2005; 21(1):22–30. - Hill P.D., Aldag J.S., Chatterton R.T., Zinaman M., "Comparison of the amount of milk in mothers of full-term and premature babies in the first 6 weeks after birth." J Hum Lakt (Journal of the International Association of Lactation Consultants) 2005, 21(1): 22-30.
Kent, J.C. et al. Importance of vacuum for breastmilk expression. Breastfeed Med 3, 11-19 (2008). - Kent J.S. et al., "The Importance of Vacuum in Expression of Breast Milk". Brestfeed Med 3 (Breastfeeding Medicine). 3.11-19 (2008).
Kent, J.C. et al. Longitudinal changes in breastfeeding patterns from 1 to 6 months of lactation. Breastfeed Med 8, 401–407 (2013). - Kent J.S. et al., Longitudinal changes in breastfeeding patterns from 1 to 6 months of lactation. Brestfeed Med (Breastfeeding Medicine) 8, 401-407 (2013).
- Kent J.S. et al., Longitudinal changes in breastfeeding patterns from 1 to 6 months of lactation. Brestfeed Med (Breastfeeding Medicine) 8, 401-407 (2013).
Kent, J.C., Hepworth, A.R., Langton, D.B. & Hartmann, P.E. Impact of Measuring Milk Production by Test Weighing on Breastfeeding Confidence in Mothers of Term Infants. Breastfeed Med (2015). - "Measuring the amount of milk by weighing the baby and the impact of this process on the confidence of mothers of full-term babies." Brestfeed Med (Breastfeeding Medicine) 2015.
Morton, J., Hall, J.Y., Wong, R.J., Benitz, W.E. & Rhine, W.D. Combining hand techniques with electric pumping increases milk production in mothers of preterm infants. J Perinatol 29, 757–764 (2009). — Morton J., Hall J.I., Wong R.J., Benitz W.I. and Rhine, W.D., "Manual pumping combined with an electric breast pump increases breast milk production in mothers of preterm infants.![]() " J Perinatol (Journal of Perinatology) 29, 757-764 (2009)
" J Perinatol (Journal of Perinatology) 29, 757-764 (2009)
Parker, L.A., Sullivan, S., Krueger, C. & Mueller, M. Association of timing of initiation of breastmilk expression on milk volume and timing of lactogenesis stage II among mothers of very low-birth-weight infants. Breastfeed Med (2015). - Parker L.A., Sullivan C., Krueger S. and Muller M., "Association of the time of onset of pumping with the amount of milk and the timing of the onset of the second stage of lactogenesis in mothers of children who had extremely low birth weight." Brestfeed Med (Breastfeeding Medicine) (2015)
Prime, D.K., Garbin, C.P., Hartmann, P.E. & Kent, J.C. Simultaneous breast expression in breastfeeding women is more efficacious than sequential breast expression. Breastfeed Med 7, 442-447 (2012). - Prime D.K., Garbin S.P., Hartmann P.I. and Kent, J.S., "During the breastfeeding period, pumping both breasts at the same time is more productive than sequential pumping.