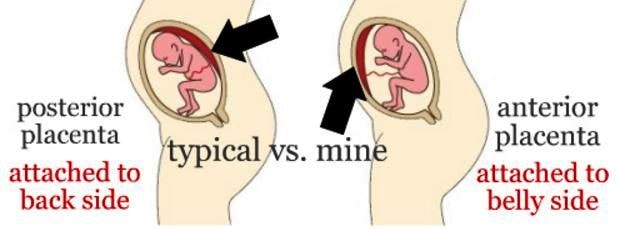
What does posterior placenta mean
Anterior Placenta and Gender: Predicting Baby’s Sex
For many expecting parents, after finding out that they’re pregnant, the question they want answered as soon as possible is: Is it a boy or a girl?
The good news is that you don’t have to wait until delivery to find out if you don’t want to. In most cases, an ultrasound can determine your baby’s sex as early as 16 weeks, and optional first trimester testing can tell you even earlier.
But since an ultrasound isn’t 100 percent reliable, and not everyone opts for early screening tests, you might use the position of your placenta to predict what you’re having.
According to some, having an anterior placenta means you’re having a girl, whereas a posterior placenta means you’re having a boy. But is this an accurate way to predict biological sex? Let’s take a look.
There are two types of cells that make up an embryo. There are the cells that develop into the baby, and the cells that develop into the placenta. The placenta is an organ that gives your baby oxygen and nutrients, and it also removes waste.
The placenta attaches to the wall of your uterus, and its position can be anywhere — front, back, right, or left. If the placenta attaches to the back of the uterus, it’s known as a posterior placenta. If it attaches to the front of the uterus, it’s called an anterior placenta.
Both types are common. One theory is that sleep position after conception might influence the location of the placenta, but that hasn’t been verified by research.
The idea of using the placement of the placenta to identify sex isn’t new. The idea that an anterior placenta means you’re having a girl may have come out of a different theory related to left-right placement.
In 2011, a paper attributed to Dr. Saad Ramzi Ismail claimed that when the placenta attaches to the right of the uterus, women were more likely to have a boy. And when the placenta attaches to the left, they were more likely to have a girl. (The study, titled “The Relationship Between Placental Location and Fetal Gender [Ramzi’s Method],” is not available online in a credible, peer-reviewed journal.)
(The study, titled “The Relationship Between Placental Location and Fetal Gender [Ramzi’s Method],” is not available online in a credible, peer-reviewed journal.)
This became known as Ramzi’s theory. But interestingly, his research only evaluated the right and left position of the placenta. It didn’t evaluate front (anterior) and back (posterior) positions.
The precise origin of the belief that an anterior placenta means a girl baby is unknown. Yet, the question comes up numerous times on online forums and discussion boards, with many women claiming that they had an anterior placenta with their girl pregnancies.
Truthfully, there isn’t enough concrete research or evidence to back up the theory linking an anterior placenta with having a girl.
One 2014 study on the topic, though, evaluated 200 placentas — with 103 anterior and 97 posterior. According to the results, 72.8 percent of pregnancies with girls did have an anterior placenta, compared to only 27.2 percent of pregnancies with boys.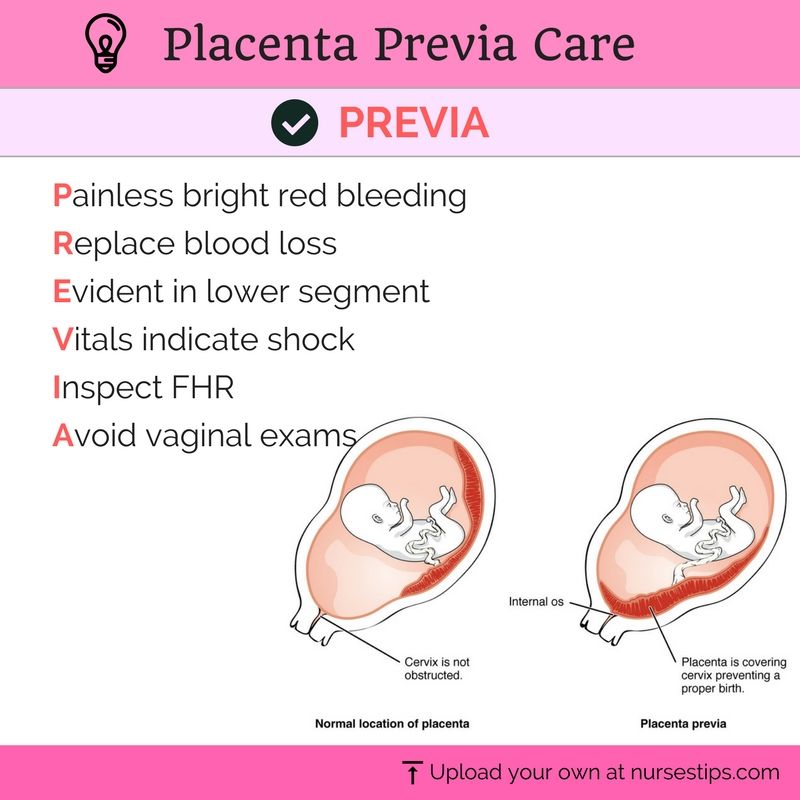
The study concluded that while the location of the placenta had “significant relation with fetal gender,” more research is needed. So having an anterior placenta doesn’t indicate with certainty that you’re having a girl.
Using the location of your placenta to predict your baby’s sex is a fun game to play. But when it comes down to truly identifying biological sex, using the location of your placenta isn’t an accurate way.
There are a few ways to determine the sex of a baby. One is to have an ultrasound and locate your baby’s genitals. Additionally, tests that look for chromosome abnormalities can detect a baby’s sex. These include noninvasive prenatal testing, amniocentesis, and chorionic villus sampling.
Even though the placenta usually attaches to the back of the uterus, it’s perfectly fine to have an anterior placenta. However, this may or may not indicate that you’re having a girl. So before making any big announcements, you may want to confirm your theory with an ultrasound or blood test.
Posterior Placenta: 5 Myths (and Facts) You Need to Know
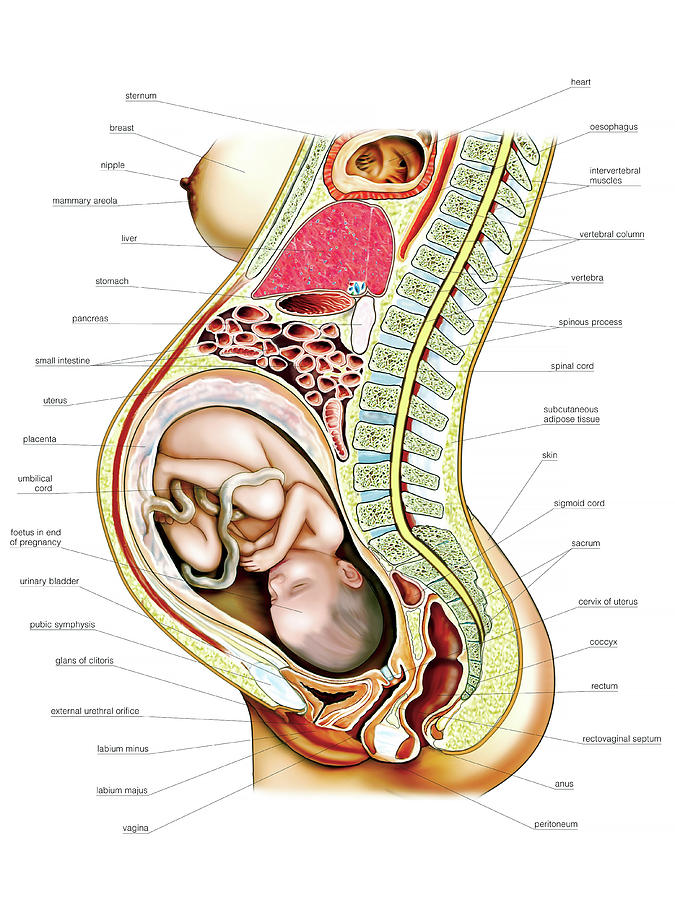
The placenta is an organ that supplies oxygen and nutrients via the umbilical cord to the baby and plays an important role in pregnancy.
“Ultrasound reports sometimes mention a posterior or an anterior placenta but these are not significant findings,” says Dr. Anita Sabherwal Anand, Senior Obstetrician-Gynecologist at Sitaram Bhartia Hospital in South Delhi.
Where is the placenta located?The placenta can be positioned in any of these ways:
Anterior placenta: This means that the placenta is located toward the front wall of the uterus.
Posterior placenta: The placenta is attached to the back wall of the uterus. The term ‘fundal posterior’ means that the placenta is toward the top and back of the uterine wall as ‘fundal’ means the top of the fundus/uterus.
Low Lying Placenta: The placenta is often positioned in the lower segment of the uterus in the early weeks of pregnancy.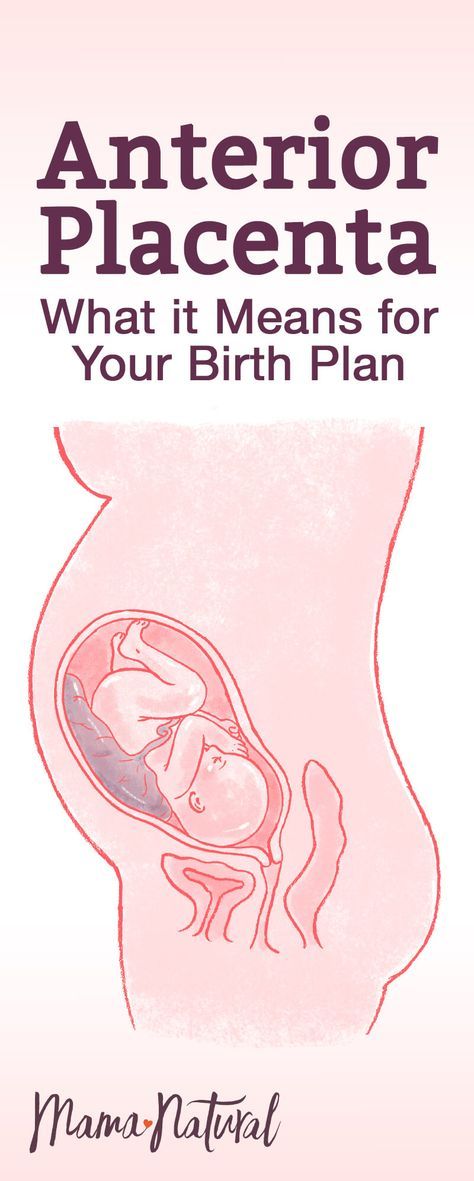 After 20 weeks as the uterus grows bigger, the placenta shifts away from the lower segment.
After 20 weeks as the uterus grows bigger, the placenta shifts away from the lower segment.
Most positions of the placenta, whether it is located at the back or the front do not signify anything in particular.
5 Myths to know about Posterior PlacentaExpecting parents often have queries around placenta position and the baby’s gender, the best position for a normal delivery and so on.
The doctor clarifies these concerns so that expecting couples can be more informed and less stressed about pregnancy.
- Posterior placenta linked to gender of fetus: There is no scientific evidence that proves that a posterior placenta means a boy or a girl. The same holds true for a fundal posterior placenta and an anterior placenta.“A few studies may have indicated a relation between the placental position and gender but there are no references to this theory in medical literature.
 ”
” - Posterior placenta heightens fetal movement: “A few anecdotal reports suggest that mothers feel stronger kicks early in pregnancy when the placenta is positioned at the back or subtle kicks due to an anterior placenta as it cushions the kicks, but there is no solid study that validates these claims. “
- Posterior placenta increases risk of preterm labour: None of the national or international obstetrics guidelines substantiate the findings that a posterior placenta increases the risk of preterm delivery and an anterior placenta increases the risk of pregnancy induced hypertension, gestational diabetes or intrauterine growth restriction.
- Posterior placenta is the best position: It is believed that this is the most ideal position as it allows the baby to move into the correct position.
- Posterior placenta impacts chances of normal delivery: “You can have a vaginal birth as long as the placenta does not cover the cervix, as this prevents the baby from descending down the birth canal and causes painless bleeding.
 ”
”
“In such a situation, a cesarean becomes the best method to deliver the baby safely.”
The position of the placenta can vary from woman to woman and each of her pregnancies.
“It can be exciting to discuss every detail of an ultrasound report with friends and family but you needn’t become unnecessarily anxious about unscientific assertions. Enjoy your pregnancy – eat right, practice breathing exercises and yoga – and believe that all will be well!”
This blog post has been written with editorial inputs from Dr. Anita Sabherwal Anand, who has over 24 years of experience, and is known for the time and attention she gives to pregnant couples.
Please call us on +919871001458 to book an Appointment.
Medically Reviewed by Dr. Anita Sabherwal Anand
MBBS, MD, DNB Secondary (Obstetrics & Gynecology)
More Resources:
- 5 Easy Tips You Need to Know for a Normal Delivery
- Ask Your Gynaecologist for her C-Section Rate
- C-Section Delivery: 9 Indications Where It May Be Avoidable
What does posterior placenta mean | mother today
Are you pregnant and diagnosed? posterior placenta? What does posterior placenta mean? placenta This is the organ that nourishes the fetus during pregnancy.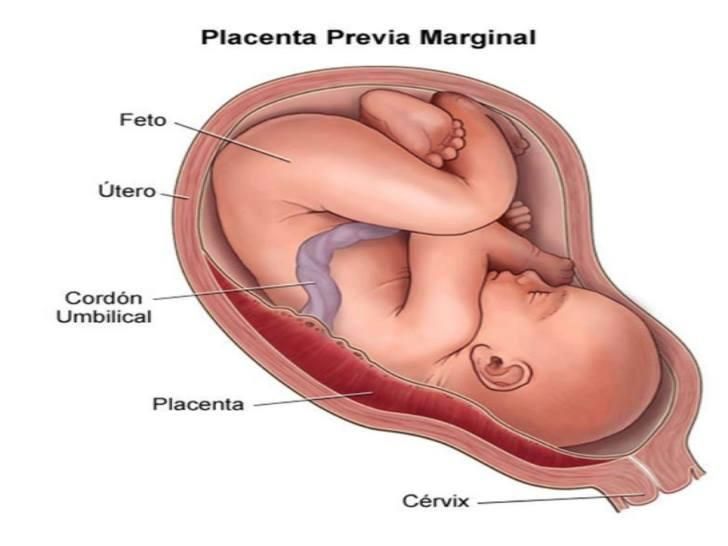 and that doesn't necessarily mean there's a problem. In our other article, we have already talked about the types of placenta and all the consequences that they carry. depending on your location.
and that doesn't necessarily mean there's a problem. In our other article, we have already talked about the types of placenta and all the consequences that they carry. depending on your location.
Anterior placenta It is named so because of the way it is located inside the mother's body. To learn more about its functions, you can read Everything You Can Do for Your Baby This is a vital organ for its development. Provides oxygen and nutrients for proper growth. That they develop this or that position is a special way, and for this we are going to analyze what its consequences are.
Index
- 1 What is the posterior placenta? nine0022
- 2 How large should the placenta be to ensure a normal pregnancy?
- 3 Interesting fact about the posterior placenta
What is the posterior placenta?
The placenta develops during pregnancy as a vital organ for the development of the baby. Inside the uterus, it can take various positions, can be placed in front or behind , On the side right or left , en Lower part or Lower area or area upper part of the uterus (fundamental).
Inside the uterus, it can take various positions, can be placed in front or behind , On the side right or left , en Lower part or Lower area or area upper part of the uterus (fundamental).
La posterior placenta means that the placenta is located in the posterior wall of the uterus . It is located in the nearest part of the spine, in the back region. anterior placenta is located antagonistically, it is located in front of or in the area closest to the mother's navel. So during gestation, the baby's kicks can be felt more noticeably.
Any of the three positions of the placenta during pregnancy ( anterior, posterior, or fundus ) do not report any complications. This also does not entail any special check . The presence of an anterior placenta does not mean that the mother will suffer from any injury or that she will suffer from severe back pain.
There is a curious fact, the anterior placenta, located in the posterior region, can cause fetal movements to become noticeable much later . The placenta functions as a region, softens the impacts and movements of the child, and thus they will not be perceived until they become much more intense.
How big should the placenta be to ensure a normal pregnancy?
Both an anterior and posterior placenta are considered normal pregnancies. Anterior placenta means that it is located in the surface of the uterus closest to the navel and the posterior placenta is located in the area closest to the back.
The problem occurs when the placenta is located in the lower region (previous placenta) , near the opening of the cervix or at the exit of the baby during labour. This arrangement does not appear to be a normal pregnancy and, given the potential consequences, should be monitored continuously.
Placenta previa can be represented as marginal or total prior. This is a marginal disease as it can occur near the skin of the uterus in early pregnancy. But as the pregnancy progresses and the uterus grows in size, the placenta can move out of place and thus not interfere with childbirth. If this does not happen at the end of pregnancy and if delivery is impossible, perform a caesarean section.
An interesting fact about the back of the placenta
It was predicted that when the placenta is behind People say that the sex of the baby will be a boy. If, on the contrary, is the previous one, it will be a girl . This is an interesting fact, but it does not have a scientific basis that confirms this theory 100%.
Yes, it was shown Ramsey Method where depending where the placenta is located and chorionic villi . If the ultrasound shows that the placenta is on the right side next to the placenta, all the probabilities point to the birth of a boy. If the placenta and chorionic villi are located on the left, then the embryo can be born as a girl. If you want to know more details, you can read everything the placenta does for your baby.
If the ultrasound shows that the placenta is on the right side next to the placenta, all the probabilities point to the birth of a boy. If the placenta and chorionic villi are located on the left, then the embryo can be born as a girl. If you want to know more details, you can read everything the placenta does for your baby.
The content of the article complies with our principles of editorial ethics. To report a bug, click here. nine0003
You may be interested
Makarov I.O. • Placenta previa
Ultrasound scanner WS80
The ideal instrument for prenatal examinations. Unique image quality and a full range of diagnostic programs for an expert assessment of a woman's health.
In the normal course of pregnancy, the placenta is usually located in the fundus or body of the uterus, along the back wall, with the transition to the side walls, i.e. in those areas where the walls of the uterus are best supplied with blood.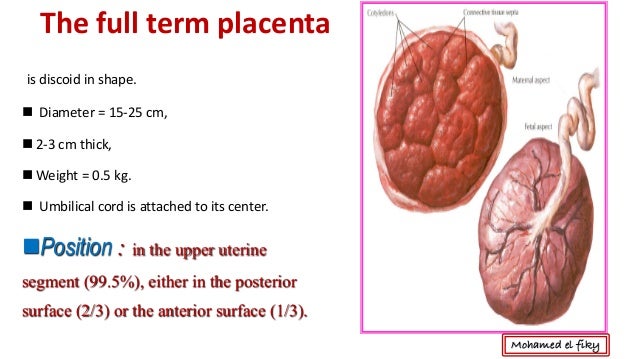 On the anterior wall, the placenta is located somewhat less frequently, since the anterior wall of the uterus undergoes significantly more changes than the posterior one. In addition, the location of the placenta on the back wall protects it from accidental injury. nine0003
On the anterior wall, the placenta is located somewhat less frequently, since the anterior wall of the uterus undergoes significantly more changes than the posterior one. In addition, the location of the placenta on the back wall protects it from accidental injury. nine0003
Placenta previa is a pathology in which the placenta is located in the lower parts of the uterus along any wall, partially or completely blocking the area of the internal os. The incidence of placenta previa averages from 0.1% to 1% of the total number of births.
If the placenta only partially covers the area of the internal pharynx, then it is an incomplete presentation, which occurs with a frequency of 70-80% of the total number of presentations. If the placenta completely covers the area of the internal os, then this is a complete placenta previa. This option occurs with a frequency of 20-30%. nine0003
There is also a low location of the placenta, when its edge is at a lower level than it should be in the norm, but does not cover the area of the internal os.
Causes of low or low placenta
There are several causes of low or low placenta. The most common causes are pathological changes in the inner layer of the uterus (endometrium) due to inflammation, surgical interventions (curettage, caesarean section, removal of myomatous nodes, etc.), multiple complicated births. In addition, violations of the attachment of the placenta can be caused by uterine fibroids, endometriosis, underdevelopment of the uterus, isthmicocervical insufficiency, inflammation of the cervix, multiple pregnancy. It should be noted that placenta previa is more common in re-pregnant women than in primiparas. Due to these factors, the fetal egg that enters the uterine cavity after fertilization cannot be implanted in the upper sections of the uterus in a timely manner, and this process is carried out only when the fetal egg has already descended into its lower sections. nine0003
The most common manifestation in placenta previa is recurrent bleeding from the genital tract. Bleeding can occur during various periods of pregnancy, starting from its earliest terms. However, most often they are observed already in the second half of pregnancy due to the formation of the lower segment of the uterus. In the last weeks of pregnancy, when uterine contractions become more intense, bleeding may increase.
Bleeding can occur during various periods of pregnancy, starting from its earliest terms. However, most often they are observed already in the second half of pregnancy due to the formation of the lower segment of the uterus. In the last weeks of pregnancy, when uterine contractions become more intense, bleeding may increase.
Bleeding is caused by repeated abruption of the placenta, which is unable to stretch following the stretching of the uterine wall as pregnancy progresses or labor starts. In this case, the placenta partially exfoliates, and bleeding occurs from the vessels of the uterus. The fetus does not shed blood. However, he is threatened by oxygen starvation, since the exfoliated part of the placenta is not involved in gas exchange. nine0003
Provoking factors for bleeding during pregnancy can be: physical activity, sudden coughing, vaginal examination, sexual intercourse, increased intra-abdominal pressure with constipation, thermal procedures (hot bath, sauna).
With complete placenta previa, bleeding often occurs suddenly, without pain, and can be very heavy.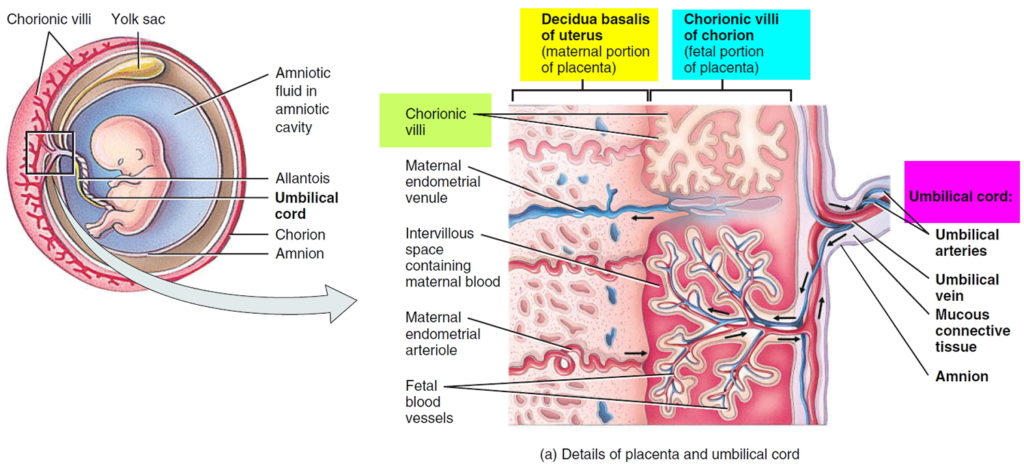 Bleeding may stop, but reappear after some time, or may continue in the form of scanty discharge. In the last weeks of pregnancy, bleeding resumes and / or increases. nine0003
Bleeding may stop, but reappear after some time, or may continue in the form of scanty discharge. In the last weeks of pregnancy, bleeding resumes and / or increases. nine0003
With incomplete placenta previa, bleeding may begin at the very end of pregnancy. However, more often it occurs at the beginning of labor. The amount of bleeding depends on the size of the placenta previa. The more placental tissue is present, the earlier and more bleeding begins.
Recurrent bleeding during pregnancy complicated by placenta previa in most cases leads to the development of anemia.
Pregnancy with placenta previa is often complicated by the threat of miscarriage, which is due to the same reasons as the occurrence of an incorrect location of the placenta. Preterm labor most often occurs in patients with complete placenta previa. nine0003
Pregnant women with placenta previa are characterized by low blood pressure, which occurs in 25%-34% of cases.
Preeclampsia (nephropathy, late toxicosis) is also no exception for pregnant women with placenta previa.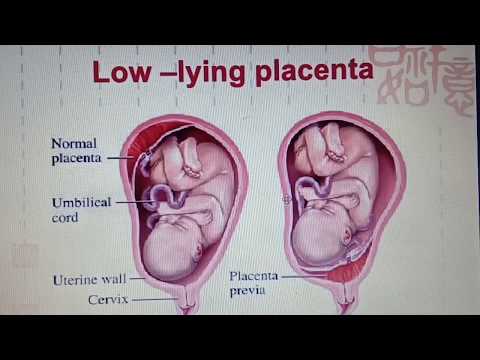 This complication, which occurs against the background of dysfunction of a number of organs and systems, as well as with symptoms of blood clotting disorders, significantly worsens the nature of recurrent bleeding.
This complication, which occurs against the background of dysfunction of a number of organs and systems, as well as with symptoms of blood clotting disorders, significantly worsens the nature of recurrent bleeding.
Placenta previa is often accompanied by fetal placental insufficiency, lack of oxygen for the fetus and delayed development. The exfoliated part of the placenta is switched off from the general system of the uteroplacental circulation and does not participate in gas exchange. With placenta previa, an incorrect position of the fetus (oblique, transverse) or breech presentation is often formed, which in turn are accompanied by certain complications. nine0003
In obstetric practice, the term "migration of the placenta" is widely rooted, which, in fact, does not reflect the real essence of what is happening. The change in the location of the placenta is carried out due to a change in the structure of the lower segment of the uterus during pregnancy and the direction of growth of the placenta towards a better blood supply to the sections of the uterine wall (towards the bottom of the uterus) compared to its lower sections. A more favorable prognosis in terms of placental migration is noted when it is located on the anterior wall of the uterus. Usually the process of "migration of the placenta occurs within 6-10 weeks and is completed by the middle of 33-34 weeks of pregnancy.
A more favorable prognosis in terms of placental migration is noted when it is located on the anterior wall of the uterus. Usually the process of "migration of the placenta occurs within 6-10 weeks and is completed by the middle of 33-34 weeks of pregnancy.
Diagnosis of placenta previa
Placenta previa is not difficult to detect. The presence of placenta previa may be indicated by complaints of a pregnant woman about bleeding. In this case, recurrent bleeding from the second half of pregnancy, as a rule, is associated with complete placenta previa. Bleeding at the end of pregnancy or at the beginning of labor is more often associated with incomplete placenta previa.
In the presence of bleeding, carefully examine the walls of the vagina and cervix using speculums to exclude trauma or pathology of the cervix, which may also be accompanied by the presence of bloody discharge. nine0003
A vaginal examination of a pregnant woman also easily reveals clear diagnostic signs indicating an abnormal location of the placenta. However, such a study must be performed as carefully as possible, in compliance with all the necessary rules to prevent possible bleeding.
However, such a study must be performed as carefully as possible, in compliance with all the necessary rules to prevent possible bleeding.
Currently, the most objective and safest method for diagnosing placenta previa is ultrasound, which allows you to establish the fact of placenta previa and the variant of placenta previa (complete, incomplete), determine the size, structure and area of the placenta, assess the degree of detachment, as well as get an accurate picture of the migration of the placenta. nine0003
If the ultrasound revealed a complete placenta previa, then a vaginal examination should not be performed at all. The criterion for the low location of the placenta in the III trimester of pregnancy (28 - 40 weeks) is the distance from the edge of the placenta to the area of the internal os 5 cm or less. Placenta previa is indicated by the presence of placental tissue in the area of the internal os.
The nature of the localization of the placenta in the II and III trimesters of pregnancy (up to 27 weeks) is judged by the ratio of the distance from the edge of the placenta to the area of the internal os, with the diameter value (BDP) of the fetal head.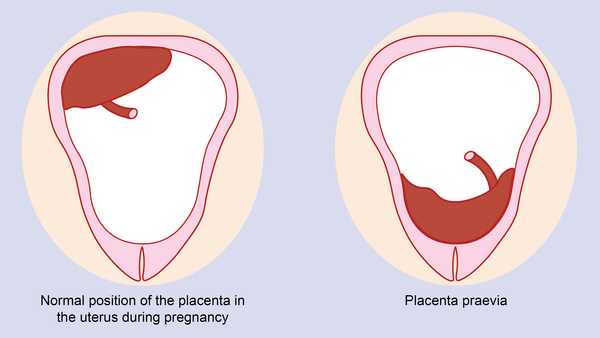 nine0003
nine0003
If an abnormal location of the placenta is detected, a dynamic study should be carried out to monitor its "migration". For these purposes, it is advisable to perform at least three echographic controls during pregnancy at 16, 24-26 and 34-36 weeks.
Ultrasound should be done when the bladder is moderately full. With the help of ultrasound, it is also possible to determine the presence of an accumulation of blood (hematoma) between the placenta and the wall of the uterus during placental abruption (in the event that there was no outflow of blood from the uterine cavity). If the site of placental abruption occupies no more than 1/4 of the area of the placenta, then the prognosis for the fetus is relatively favorable. In the event that the hematoma occupies more than 1/3 of the area of the placenta, then most often this leads to the death of the fetus. nine0003
Medical support for pregnant women with placenta previa
The nature of management and treatment of pregnant women with placenta previa depends on the severity of bleeding and the amount of blood loss.
In the first half of pregnancy, if there are no blood discharges, then the pregnant woman can be at home under outpatient control in compliance with the regime that excludes the action of provoking factors that can cause bleeding (restriction of physical activity, sexual activity, stressful situations, etc.)
Observation and treatment for more than 24 weeks of pregnancy is carried out only in an obstetric hospital.
Treatment aimed at continuing the pregnancy up to 37-38 weeks is possible if the bleeding is not heavy, and the general condition of the pregnant woman and the fetus is satisfactory. Even despite the cessation of bloody discharge from the genital tract, pregnant women with placenta previa can under no circumstances be discharged from the hospital before delivery.
Management of pregnant women in an obstetric hospital provides for: observance of strict bed rest; the use of drugs that ensure the optimization of the normalization of contractile activity; treatment of anemia and fetal placental insufficiency. nine0003
nine0003
Emergency caesarean section, regardless of gestational age, is indicated for: recurrent bleeding; a combination of small blood loss with anemia and a decrease in blood pressure; simultaneous profuse blood loss; complete placenta previa and bleeding.
The operation is performed according to vital indications on the part of the mother, regardless of the duration of pregnancy and the condition of the fetus.
In the event that the pregnancy has been carried to 37-38 weeks and placenta previa persists, depending on the situation, the most optimal method of delivery is chosen on an individual basis. nine0003
The absolute indication for elective caesarean section is placenta previa. Childbirth through the natural birth canal in this situation is impossible, since the placenta that covers the internal os does not allow the presenting part of the fetus (fetal head or pelvic end) to be inserted into the pelvic inlet. In addition, in the process of increasing uterine contractions, the placenta will exfoliate more and more, and the bleeding will increase significantly.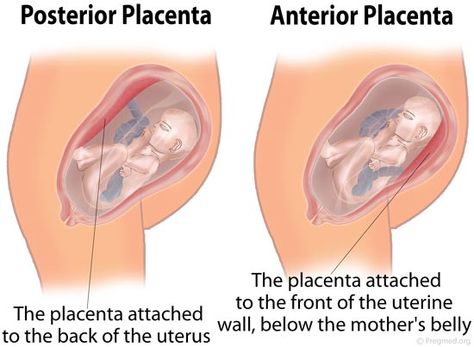
In case of incomplete placenta previa and in the presence of concomitant complications (breech presentation, incorrect position of the fetus, scar on the uterus, multiple pregnancy, severe polyhydramnios, narrow pelvis, age of the primiparous over 30 years, etc.), a caesarean section should also be performed in a planned manner. nine0003
If the above associated complications are absent and there is no blood discharge, then you can wait until the onset of spontaneous labor activity, followed by early opening of the fetal bladder. In the event that after opening the fetal bladder, bleeding nevertheless began, then it is necessary to resolve the issue of performing a caesarean section.
If, with incomplete placenta previa, bleeding occurs before the onset of labor, then the fetal bladder is opened. The necessity and expediency of this procedure is due to the fact that when the membranes are opened, the fetal head is inserted into the entrance to the pelvis and presses the exfoliated part of the placenta against the wall of the uterus and pelvis, which helps to stop further placental abruption and stop bleeding. If bleeding after opening the fetal bladder continues and / or the cervix is immature, then a caesarean section is performed. In the case of stopping bleeding, it is possible to conduct labor through the natural birth canal (with a favorable obstetric situation). nine0003
If bleeding after opening the fetal bladder continues and / or the cervix is immature, then a caesarean section is performed. In the case of stopping bleeding, it is possible to conduct labor through the natural birth canal (with a favorable obstetric situation). nine0003
Bleeding can also begin in the early stages of labor, from the moment of the first contractions. In this case, early opening of the fetal bladder is also shown.
Thus, the management of childbirth with incomplete placenta previa through the natural birth canal is possible if: the bleeding stopped after opening the fetal bladder; mature cervix; labor activity is good; there is a cephalic presentation of the fetus.
However, caesarean section is one of the most frequently chosen methods of delivery by obstetricians in placenta previa and is performed with a frequency of 70% -80% in this pathology. nine0003
Other typical complications in childbirth with incomplete placenta previa are weakness of labor and insufficient oxygen supply to the fetus (fetal hypoxia).