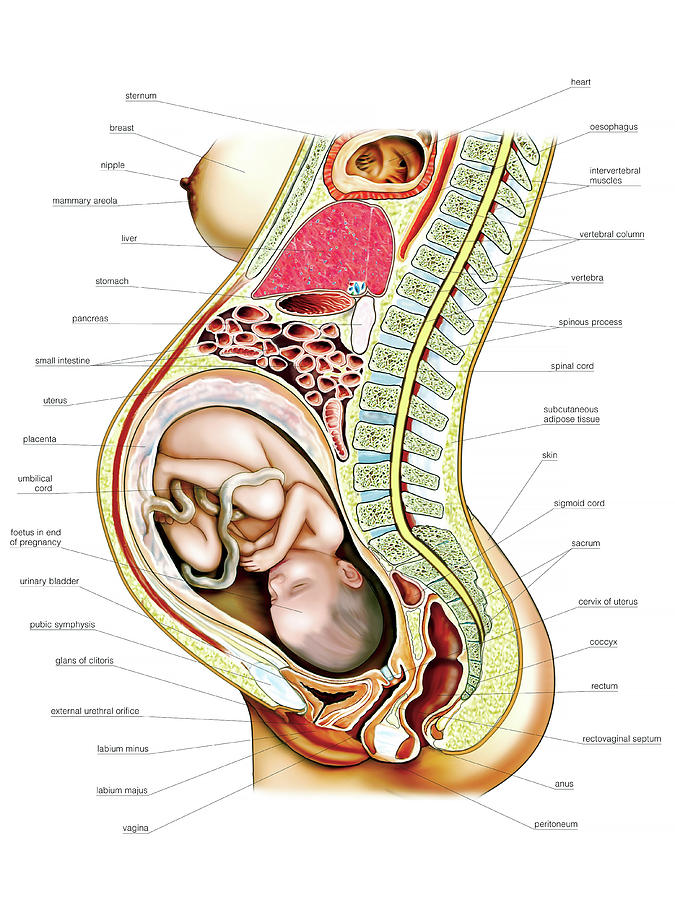
Bowel movement pain during pregnancy
Abdominal Pain During Pregnancy: Causes and Treatment
Abdominal Pain During Pregnancy: Causes and Treatment- Health Conditions
- Featured
- Breast Cancer
- IBD
- Migraine
- Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
- Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Type 2 Diabetes
- Articles
- Acid Reflux
- ADHD
- Allergies
- Alzheimer's & Dementia
- Bipolar Disorder
- Cancer
- Crohn's Disease
- Chronic Pain
- Cold & Flu
- COPD
- Depression
- Fibromyalgia
- Heart Disease
- High Cholesterol
- HIV
- Hypertension
- IPF
- Osteoarthritis
- Psoriasis
- Skin Disorders and Care
- STDs
- Featured
- Discover
- Wellness Topics
- Nutrition
- Fitness
- Skin Care
- Sexual Health
- Women's Health
- Mental Well-Being
- Sleep
- Product Reviews
- Vitamins & Supplements
- Sleep
- Mental Health
- Nutrition
- At-Home Testing
- CBD
- Men’s Health
- Original Series
- Fresh Food Fast
- Diagnosis Diaries
- You’re Not Alone
- Present Tense
- Video Series
- Youth in Focus
- Healthy Harvest
- No More Silence
- Future of Health
- Wellness Topics
- Plan
- Health Challenges
- Mindful Eating
- Sugar Savvy
- Move Your Body
- Gut Health
- Mood Foods
- Align Your Spine
- Find Care
- Primary Care
- Mental Health
- OB-GYN
- Dermatologists
- Neurologists
- Cardiologists
- Orthopedists
- Lifestyle Quizzes
- Weight Management
- Am I Depressed? A Quiz for Teens
- Are You a Workaholic?
- How Well Do You Sleep?
- Tools & Resources
- Health News
- Find a Diet
- Find Healthy Snacks
- Drugs A-Z
- Health A-Z
- Health Challenges
- Connect
- Breast Cancer
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease
- Psoriatic Arthritis
- Migraine
- Multiple Sclerosis
- Psoriasis
Medically reviewed by Debra Rose Wilson, Ph. D., MSN, R.N., IBCLC, AHN-BC, CHT — By Annette McDermott on June 18, 2015
Pregnancy abdominal pain
Abdominal pain during pregnancy isn’t unusual, but it can be scary. The pain may be sharp and stabbing, or dull and achy.
It can be challenging to determine if your pain is serious or mild. It’s important to know what’s normal and when to call your doctor.
Pregnancy gas pain
Gas can cause excruciating abdominal pain. It may stay in one area or travel throughout your belly, back, and chest.
According to the Mayo Clinic, women experience more gas during pregnancy due to increased progesterone. Progesterone causes intestinal muscles to relax and extends the time it takes food to get through the intestines. Food remains in the colon longer, which allows more gas to develop.
As your pregnancy progresses, your enlarging uterus puts extra pressure on your organs, which can slow digestion further and allow gas to build up.
Treatment
If abdominal pain is caused by gas, it should respond to lifestyle changes. Try eating several small meals throughout the day and drink lots of water.
Try eating several small meals throughout the day and drink lots of water.
Exercise may also help aid digestion. Identify foods that trigger gas and avoid them. Fried and greasy foods, as well as beans and cabbage, are common culprits. Avoid all carbonated beverages, too.
Many women write off abdominal pain during pregnancy as gas, but there are other benign reasons for pain to occur.
Round ligament pain
There are two large round ligaments that run from the uterus through the groin. These ligaments support the uterus. As the uterus stretches to accommodate your growing baby, so do the ligaments.
This may cause sharp or dull pain in the abdomen, hips, or groin. Shifting your position, sneezing, or coughing can trigger round ligament pain. This usually occurs in the last half of the pregnancy.
Treatment
To reduce or eliminate round ligament pain, practice getting up slowly if you’re sitting or lying down. If you feel a sneeze or cough coming on, bend and flex your hips.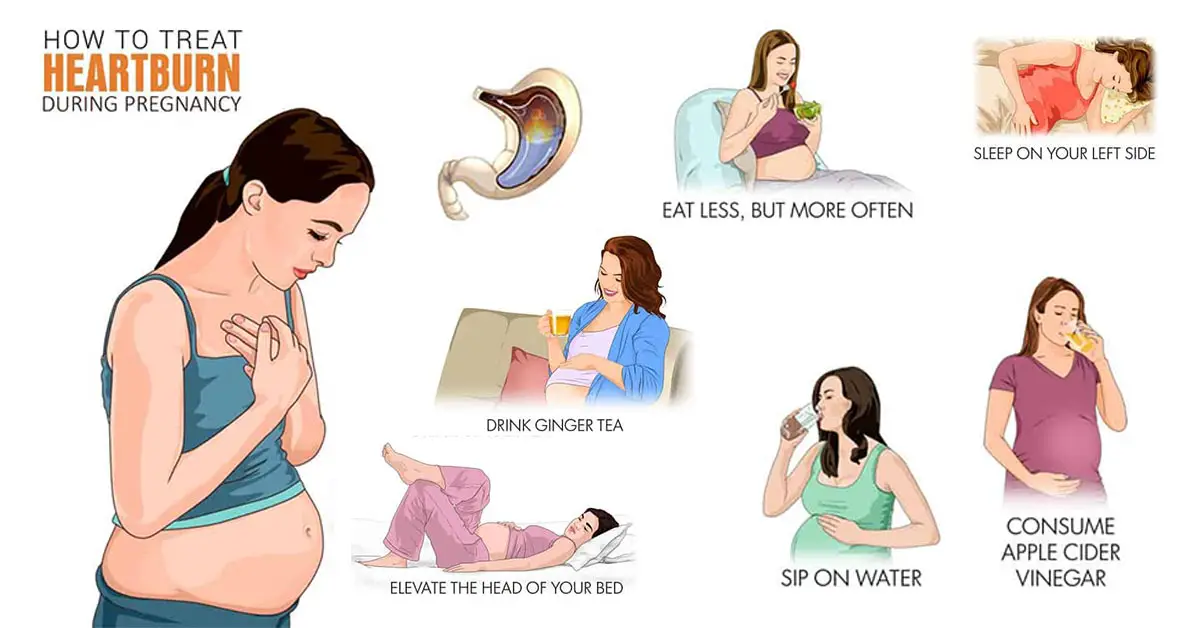 This can help to reduce the pressure on the ligaments.
This can help to reduce the pressure on the ligaments.
Daily stretching is also an effective method for reducing round ligament pain.
Constipation
Constipation is a common complaint among pregnant women. Fluctuating hormones, diet that’s short on fluids or fiber, lack of exercise, iron pills, or general anxiety can all lead to constipation. Constipation may cause severe pain. It’s often described as cramping or sharp and stabbing pain.
Treatment
Try increasing the amount of fiber in your diet. Increasing fluids may also help. Pregnant women should drink at least 8 to 10 glasses of water each day. Talk to your doctor before taking a stool softener. Some stool softeners aren’t recommended during pregnancy.
Braxton-Hicks contractions
These “practice” or “false” contractions occur when the uterine muscles contract for up to two minutes. The contractions aren’t labor and are irregular and unpredictable. They may cause pain and uncomfortable pressure, but they’re a normal part of pregnancy.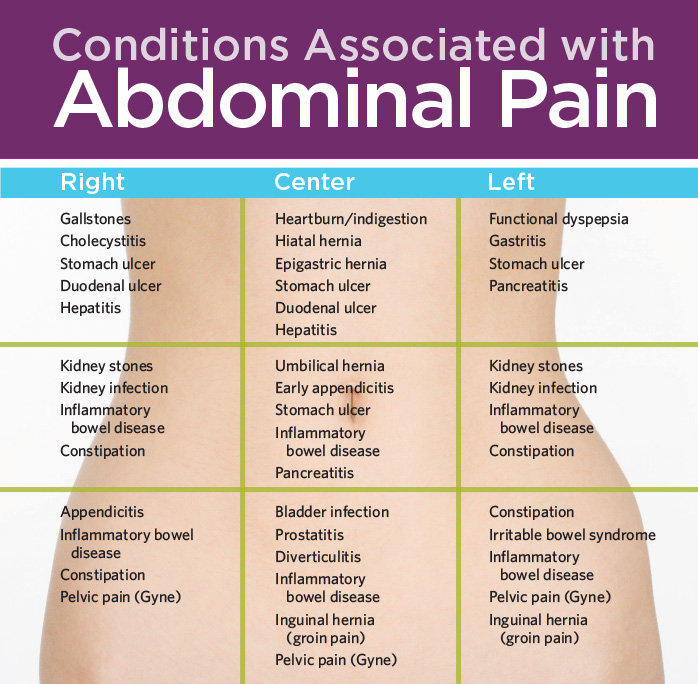
Braxton-Hicks contractions often occur in the third trimester of pregnancy. Unlike labor contractions, these contractions don’t get progressively more painful or more frequent over time.
HELLP syndrome
HELLP syndrome is an acronym for its three main parts: hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes, and low platelets. It’s a life-threatening complication of pregnancy.
It’s unclear what causes HELLP, but some women develop the condition after receiving a preeclampsia diagnosis. According to the Preeclampsia Foundation, of the 5 to 8 percent of women in the United States who develop preeclampsia, it’s estimated that 15 percent will develop HELLP.
Women without preeclampsia may also acquire this syndrome. HELLP is more common in first-time pregnancies.
Right upper-quadrant abdominal pain is a symptom of HELLP. Other symptoms include:
- headache
- fatigue and malaise
- nausea and vomiting
- blurry vision
- high blood pressure
- edema (swelling)
- bleeding
If you have abdominal pain accompanied by any of these additional HELLP symptoms, seek medical advice right away.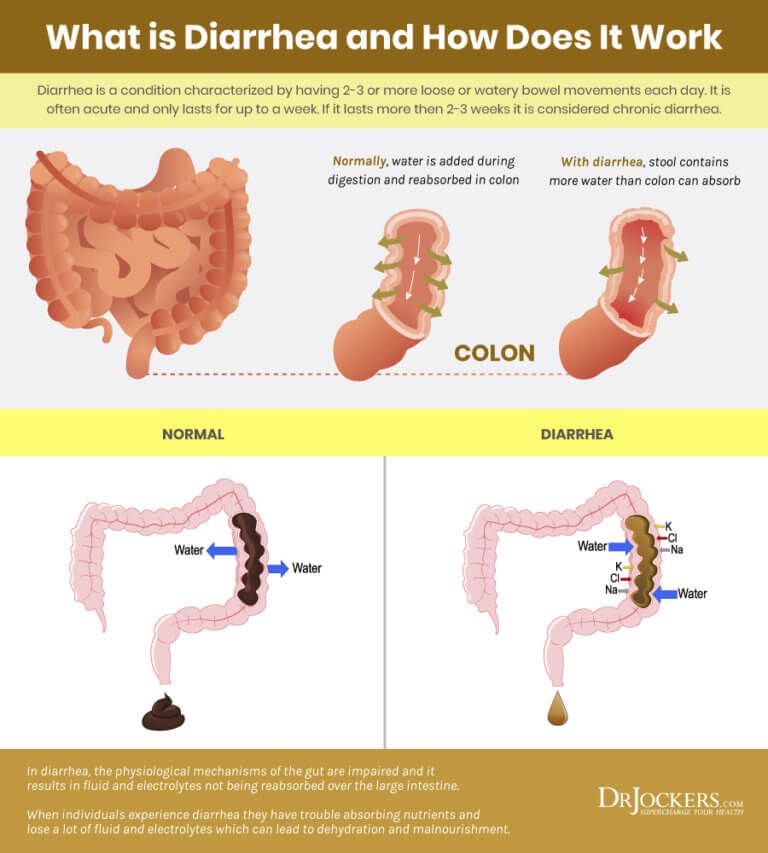 Dangerous complications or even death can result if HELLP isn’t treated immediately.
Dangerous complications or even death can result if HELLP isn’t treated immediately.
Other reasons for concern
Abdominal pain during pregnancy may also be a sign of other, more serious conditions. These include:
- miscarriage
- ectopic pregnancy
- placental abruption
- preeclampsia
These conditions require immediate medical attention.
Conditions not directly related to pregnancy may also cause abdominal pain. These include:
- kidney stones
- urinary tract infections (UTIs)
- gallstones
- pancreatitis
- appendicitis
- bowel obstruction
- food allergies or sensitivities
- peptic ulcer disease
- a stomach virus
Call your doctor immediately if your pain is accompanied by any of the following:
- fever or chills
- vaginal bleeding or spotting
- vaginal discharge
- repetitive contractions
- nausea or vomiting
- lightheadedness
- pain or burning during or after urination
When considering if abdominal pain is gas or something more serious, keep all of this information in mind.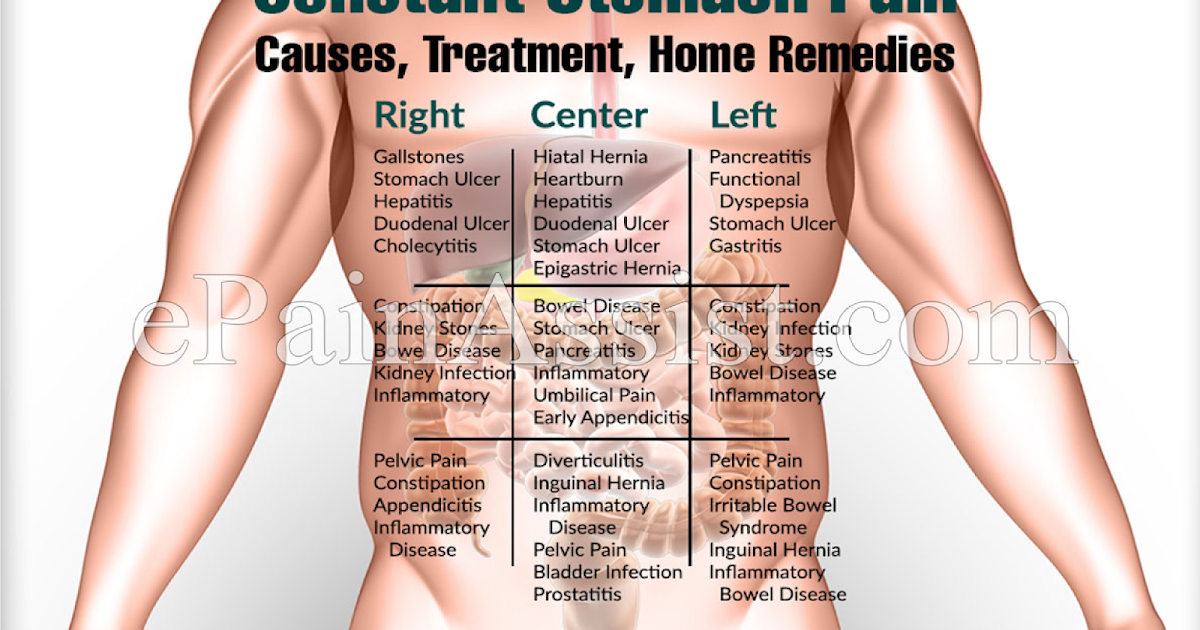 Though at times severe, gas pain usually resolves itself within a short period of time. It’s often relieved when you burp or pass gas.
Though at times severe, gas pain usually resolves itself within a short period of time. It’s often relieved when you burp or pass gas.
You may be able to connect an episode to something you ate or a period of stress. Gas isn’t accompanied by fever, vomiting, bleeding, or other serious symptoms. Gas pains don’t get longer, stronger, and closer together over time. That’s likely early labor.
Whenever in doubt, call your doctor or go in and seek treatment at your birthing center. It’s always better to err on the side of caution.
Last medically reviewed on August 18, 2017
- Parenthood
- Pregnancy
How we reviewed this article:
Healthline has strict sourcing guidelines and relies on peer-reviewed studies, academic research institutions, and medical associations. We avoid using tertiary references. You can learn more about how we ensure our content is accurate and current by reading our editorial policy.
- Gas. (2016).
marchofdimes.org/pregnancy/gas.aspx - HELLP syndrome. (2015).
preeclampsia.org/health-information/hellp-syndrome - Murry MM. (2013). Pregnancy week by week: Pregnancy and you blog: Gas in pregnancy: Why it happens, what to do.
mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/pregnancy-week-by-week/expert-blog/gas-in-pregnancy/bgp-20055810 - Murry MM. (2014). Pregnancy week by week: Pregnancy and you blog: Round ligament pain: Understanding this pregnancy complaint.
mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/pregnancy-week-by-week/expert-blog/round-ligament-pain/bgp-20111536 - Pregnancy: Body changes and discomforts: Constipation.
womenshealth.gov/pregnancy/youre-pregnant-now-what/body-changes-and-discomforts - Pregnancy: Staying healthy and safe: When to call the doctor. (2017).
womenshealth.gov/pregnancy/youre-pregnant-now-what/staying-healthy-and-safe - Tobah YB.
 (2017). Pregnancy week by week: Pregnancy and you blog: Is it safe to take stool softeners to treat pregnancy constipation?
(2017). Pregnancy week by week: Pregnancy and you blog: Is it safe to take stool softeners to treat pregnancy constipation?
mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/pregnancy-week-by-week/expert-answers/pregnancy-constipation/faq-20058550 - True vs false labor. (2016).
my.clevelandclinic.org/health/articles/true-vs-false-labor
Our experts continually monitor the health and wellness space, and we update our articles when new information becomes available.
Current Version
Aug 18, 2017
Medically Reviewed By
Debra Rose Wilson, PhD, MSN, RN, IBCLC, AHN-BC, CHT
Jun 18, 2015
Written By
Annette McDermott
Edited By
Frank Crooks
Share this article
Medically reviewed by Debra Rose Wilson, Ph.D., MSN, R.N., IBCLC, AHN-BC, CHT — By Annette McDermott on June 18, 2015
Read this next
How Constipation Feels
Medically reviewed by Saurabh Sethi, M.
 D., MPH
D., MPHConstipation can make you feel constantly bloated, uncomfortable, or even achy. Read about signs of constipation, including while you’re pregnant or…
READ MORE
5 Safe Remedies for Constipation in Pregnancy
Medically reviewed by Lynn Starr, RNC-OB
Feeling constipated during pregnancy is common, but uncomfortable. Here are some safe remedies that offer relief.
READ MORE
What to Know About Pregnancy Hemorrhoids
Hemorrhoids are common during pregnancy. They're often caused by increased blood volume and extra pressure from your growing baby.
READ MORE
Should I Take Unisom During Pregnancy?
Medically reviewed by Alan Carter, Pharm.D.
Here’s what you need to know about taking Unisom and other sleep aids during pregnancy.
READ MORE
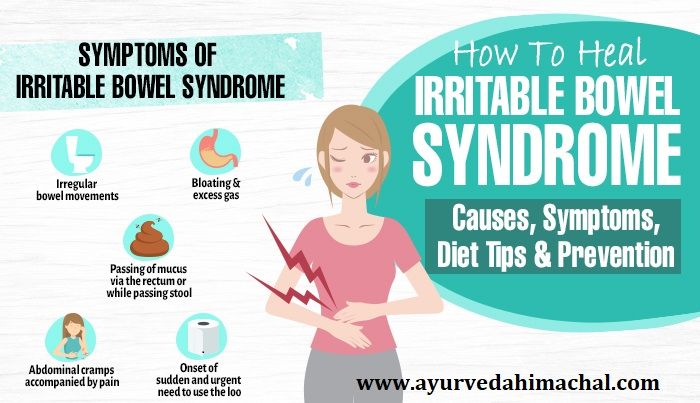
9 Signs and Symptoms of Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
By Matthew Thorpe, MD, PhD
Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) causes abdominal pain accompanied by diarrhea, constipation, or periods of both. Here are 9 signs and symptoms of IBS.
READ MORE
13 Foods That Cause Bloating (and What to Eat Instead)
By Adda Bjarnadottir, MS, RDN (Ice)
Bloating is often caused by certain foods. This article lists 13 foods that are known to cause bloating, and shows you what to replace them with.
READ MORE
Is Overlying Bowel Gas Something to Worry About?
Overlying bowel gas isn't serious, but it can cause pain or an unclear ultrasound. We'll go over the common symptoms and when you should talk with…
READ MORE
Why Do My Farts Smell So Bad? Smelly Farts Explained
Medically reviewed by Cynthia Taylor Chavoustie, MPAS, PA-C
Passing gas occurs naturally, but if your farts smell rotten, something could be wrong.
Learn about common causes and how to get rid of smelly farts.
READ MORE
Why Protein Makes Your Farts Stink and How to Treat Flatulence
Eating an excessive amount of protein may cause flatulence. If excessive farting becomes a problem, you can correct this issue with these dietary…
READ MORE
Why TUMS Won’t Help Get Rid of Gas
Medically reviewed by Femi Aremu, PharmD
Standard TUMS do not help with gas. Learn more about what treatments do help fight gas, as well as how to prevent it in the first place.
READ MORE
4 common pregnancy-related GI issues, and when to call the doctor | Your Pregnancy Matters
Mild gastrointestinal issues are common during pregnancy, but if you’re concerned, call your doctor.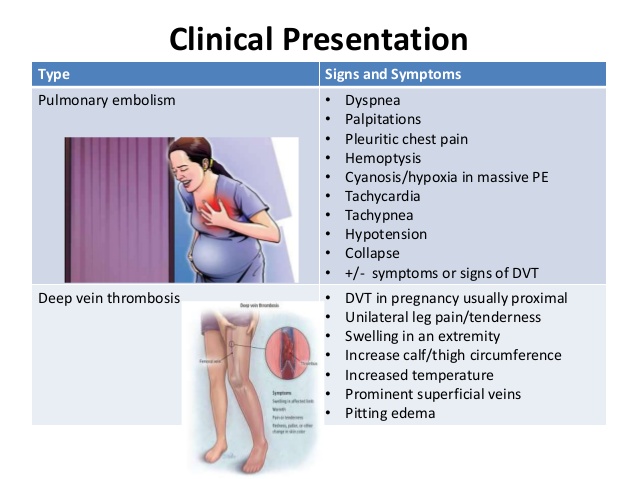
Gastrointestinal (GI) issues are common during pregnancy. As your baby grows, you’ll have less available real estate in your abdomen for your intestines, stomach, and esophagus to function. Additionally, hormonal changes can affect digestion and other GI functions.
Most GI symptoms pass relatively quickly during pregnancy and can be treated with over-the-counter remedies at home. However, to avoid potential complications, women should be aware of what’s normal and when to call the doctor when it comes to GI health during pregnancy.
1. Nausea and vomiting
During the first 16 weeks of pregnancy, we expect some mild to moderate nausea and vomiting – the infamous period of morning sickness. In fact, for many women, nausea is one of the earliest symptoms of pregnancy.
If you have severe symptoms, a doctor can recommend medication to reduce dehydration and discomfort. For mild symptoms, or if you prefer not to take medication, you can usually manage symptoms with dietary changes or vitamin therapy under the care of your doctor.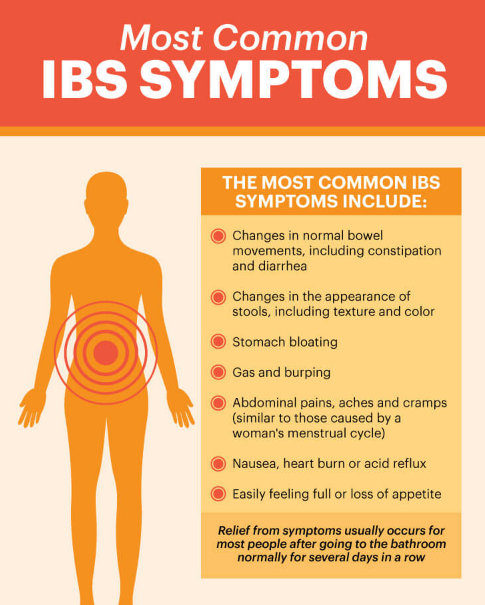
After 16 weeks of pregnancy, vomiting typically is not pregnancy-related and might be due to a bug or infection. In rare cases, vomiting can be caused by more serious medical concerns, such as hepatitis, pancreatitis, or ulcers. If you experience nausea or vomiting past the first trimester of pregnancy, don’t assume it’s pregnancy-related, and don’t let your doctor assume so, either, without checking for underlying causes.
2. Heartburn
Heartburn, or gastroesophageal reflux, affects three of five people in the general population. By the time women reach the third trimester, as many as half will experience heartburn at one point or another. During pregnancy, the muscle between the esophagus and stomach relaxes due to hormonal changes related to pregnancy. At the same time, the growing uterus puts increased pressure on the stomach. The combination is a perfect storm for heartburn.
Eating smaller, more frequent meals can help stave off heartburn. Standard treatments – antacids, proton pump inhibitors (Prevacid), or h3 blockers (Tagamet or Pepcid) – are generally safe during pregnancy.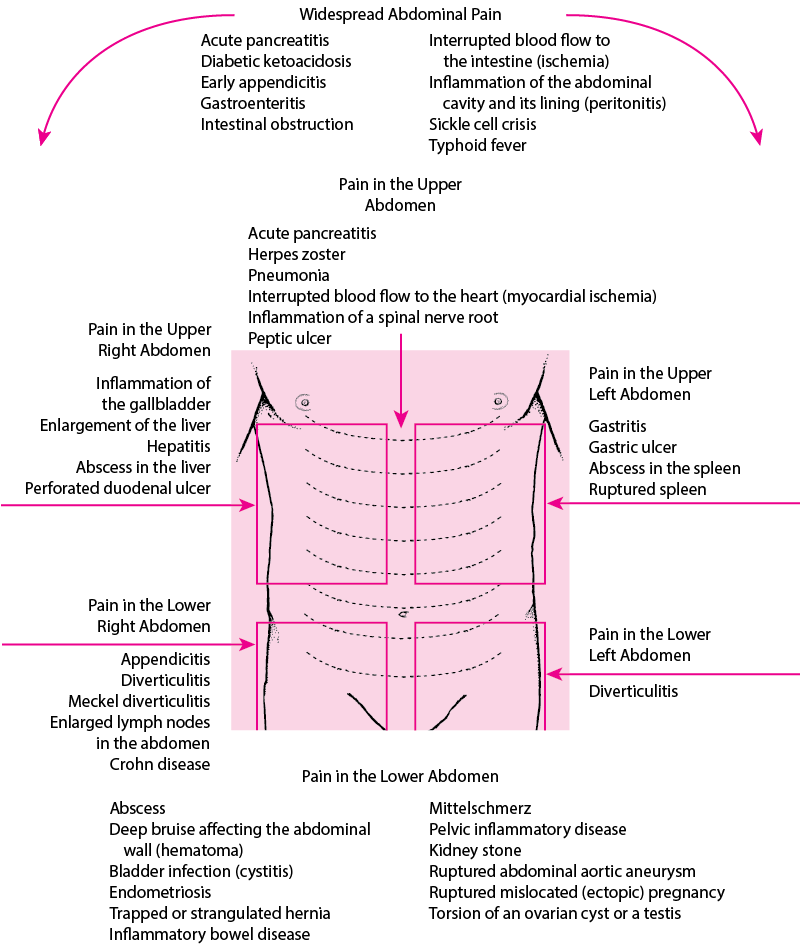
However, if you experience pain below the ribs in your upper abdomen, call your doctor. Although rare, epigastric pain can be a sign of fatty liver disease or preeclampsia, a serious blood pressure disease that can arise suddenly during pregnancy.
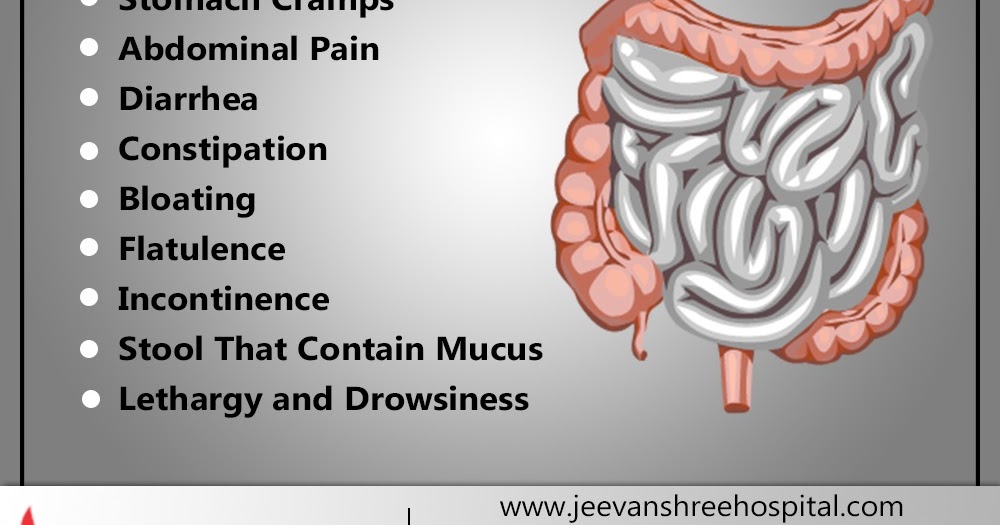
3. Diarrhea
Let’s face it – diarrhea is the worst. When it lasts just a few days, diarrhea typically is related to an infection (usually gastroenteritis) or eating something that upsets your stomach. Check in with your doctor to determine the best treatment option to reduce dehydration and duration of illness.
Diarrhea that develops without an identifiable trigger or in combination with low back pain and increased vaginal discharge or mucus can be symptoms of preterm labor. Call your doctor immediately if you experience this combination of symptoms.
4. Constipation
Pregnancy hormones affect the lower GI tract, effectively slowing down the transit of stool through the bowels. This slow-motion process allows more water to be absorbed in the stools, which makes them hard to pass. Certain prenatal vitamins and iron therapy also can contribute to constipation. Later in pregnancy, pressure from the growing uterus can also make it harder to pass stools, which increases the risk of hemorrhoids.
Certain prenatal vitamins and iron therapy also can contribute to constipation. Later in pregnancy, pressure from the growing uterus can also make it harder to pass stools, which increases the risk of hemorrhoids.
Drinking more fluids and eating more fiber is effective in reducing and preventing constipation. Stool softeners are safe to use as well, and some iron supplements actually contain them. More severe constipation might require a mild laxative. Talk to your doctor about additional treatments if you experience abdominal pain, bloody stools, or painful hemorrhoids.
Most women will experience GI concerns at some point during pregnancy. If your symptoms are serious or if you are concerned, talk to your doctor. It’s better to be safe, and we’re here to help your pregnancy – and GI tract – flow smoothly.
Stay on top of health care news. Subscribe to our blog today.
Signs, symptoms and causes of hemorrhoids in pregnant women - NEARMEDIC network of clinics
The main causes of hemorrhoids in pregnant women can be as follows:
- Chronic constipation.
 In this case, the stretching and tension of the walls of the rectum increases during defecation, which leads to the formation of hemorrhoids. In pregnant women, constipation occurs much more often due to a decrease in intestinal tone.
In this case, the stretching and tension of the walls of the rectum increases during defecation, which leads to the formation of hemorrhoids. In pregnant women, constipation occurs much more often due to a decrease in intestinal tone. - Inactive lifestyle. With hypodynamia, blood stagnation occurs in the venous plexus of the rectum, which eventually leads to vein thrombosis and the formation of hemorrhoids. Features of the condition do not always allow pregnant women to be mobile, therefore they have a high risk of developing this disease. nine0006
- Disturbance of blood circulation in the lower half of the body. During pregnancy, the uterus grows and compresses the inferior vena cava. This leads to stagnation of blood in the veins of the legs and rectum. During childbirth, a woman's intra-abdominal pressure rises greatly - this can cause hemorrhoids after pregnancy.
Signs of hemorrhoids in pregnant women
The longer the period, the higher the likelihood of developing the disease.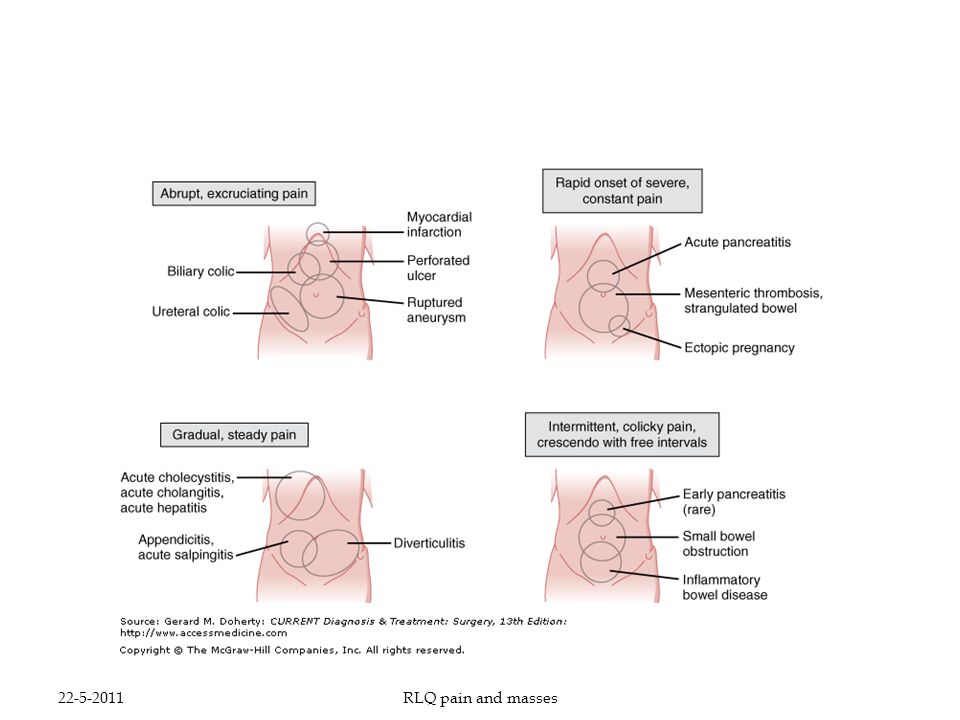 Most often, hemorrhoids appear in the 3rd trimester or after childbirth. nine0003
Most often, hemorrhoids appear in the 3rd trimester or after childbirth. nine0003
The blood vessels of the hemorrhoidal plexus of the rectum gradually dilate. Over longer periods, the stretching of the veins becomes even stronger. With the expansion of the walls of the veins of the rectum, they lose their elasticity. This provokes protrusion of the veins under the mucous membrane.
If hemorrhoids protrude only into the lumen of the rectum and do not come out of the anus, then we are talking about the treatment of hemorrhoids of the 1st stage. The farther, the larger the knots become and the more they sag from the anus. In the second stage of hemorrhoids, the nodes sag from the anus, but are easily set back on their own. The third stage occurs when the nodes can no longer cope back. nine0003
The symptoms of the disease depend on its stage.
- Internal hemorrhoids. Symptoms are mild, there is no sagging of hemorrhoids from the anus. At this stage, women may experience pain during bowel movements, slight bleeding or fresh blood on the stool, and itching and discomfort in the anus.

- External hemorrhoids. The main symptom is the sagging of one or more purple-red nodes from the anus. This manifestation is the main sign of what is required, and not of another disease, such as anal fissure. Walking, sitting and defecation in this case become extremely painful. nine0006
Urgent medical attention is required in case of infringement of the hemorrhoid - a pregnant woman experiences very severe pain in the anus with fever.
Treatment of hemorrhoids during pregnancy
If a woman already has any symptoms of hemorrhoids - itching, pain in the anus, bleeding from the anus, etc. - professional treatment is required.
At NEARMEDIC, the first stage of treatment is the preventive measures described above, which stop the progression of the disease. Then the woman is prescribed drugs, both local and systemic. But due to pregnancy, local therapy is preferable, as this reduces the risk of side effects, increases the effectiveness of treatment and reduces the negative effects of drugs on the child. In any case, the medicine is prescribed only by the attending physician who observes the woman during pregnancy. nine0003
In any case, the medicine is prescribed only by the attending physician who observes the woman during pregnancy. nine0003
In the case when a woman already has prolapsed nodes that cannot be set, an operation is prescribed. Other indications for surgical intervention are infringement or necrosis of the hemorrhoid, as well as acute inflammation. Most often, in NEARMEDIC surgery is postponed until the postpartum period, and during pregnancy they are limited to conservative treatment.
Prevention of hemorrhoids during pregnancy
Due to the fact that all pregnant women are at high risk of developing hemorrhoids, NEARMEDIC clinic doctors strongly recommend that preventive measures be taken throughout pregnancy, without waiting for symptoms to appear. nine0003
- Relief of constipation. To do this, you need to adjust your diet: eat more foods that contain coarse vegetable fiber - vegetables, fruits, cereals, cereals, prunes. Dairy products also have a beneficial effect on digestion.
On the contrary, it is better to refuse meat and other foods rich in protein. As well as from an excess of fat, coffee and hot spices.
- Hygiene. It is recommended to wash the perineum and anus after each act of defecation. In addition, once a day you can take sitz baths with antiseptics: chamomile infusion, a weak solution of potassium permanganate, etc. nine0006
Doctors
Who treat hemorrhoids during pregnancy
More doctorsClinics in Moscow
For all questions, you can contact the single contact center: +7 (495) 6-171-171
Hemorrhoids during pregnancy. Features of occurrence and treatment
HEALTH Be healthy and happy together with ONLY CLINIC!
September 28, 2015 16:00
During pregnancy, a disease such as hemorrhoids can often worsen. It is very important to start treatment in time - at the stage of occurrence
Treatment of hemorrhoids during pregnancy should take into account the physical health of the woman and the condition of her child.
Causes of occurrence
The risk of hemorrhoids during pregnancy is associated with the process of uterine enlargement, which impairs blood circulation in the pelvis and reduces vascular tone. Hemorrhoids from the very beginning of the occurrence contributes to the occurrence of constipation, and hypodynamia of the vessels during pregnancy further contributes to the deterioration of this process. nine0003
In addition, during the birth process (during attempts), intra-abdominal pressure sharply increases, and when a child is born, a large number of vessels are injured. All this contributes to the development of hemorrhoids.
Therefore, it is very important to treat hemorrhoids when they occur, already during pregnancy.
Symptoms
At the first appearance, hemorrhoids may not manifest themselves in any way and there may be no symptoms. In the process of the development of the disease, pain in the anus begins to appear, which greatly intensifies during defecation. Also, constipation increases the pain of a woman during pregnancy. At the moment of emptying the intestines, a woman can feel the hemorrhoids crawling out of the rectum. These are internal nodes that can go outside. Quite often, hemorrhoids are accompanied by burning and itching of the anus, as well as the release of blood during bowel movements. nine0003
Hemorrhoids can cause complications. With the advanced course of the disease, hemorrhoids turn into thrombosis of the nodes. This can increase pain and increase body temperature. Then comes the acute stage, when these nodes fall out or are pinched. In this case, the only way to get rid of the disease may be surgery.
Treatment
Hemorrhoids in pregnant women require careful and complex treatment. The most important measures are:
1. Diet. A woman should eliminate foods that can cause constipation from her diet. It is recommended to consume more fruits, vegetables, cereals, dairy products and other products that have a laxative effect.