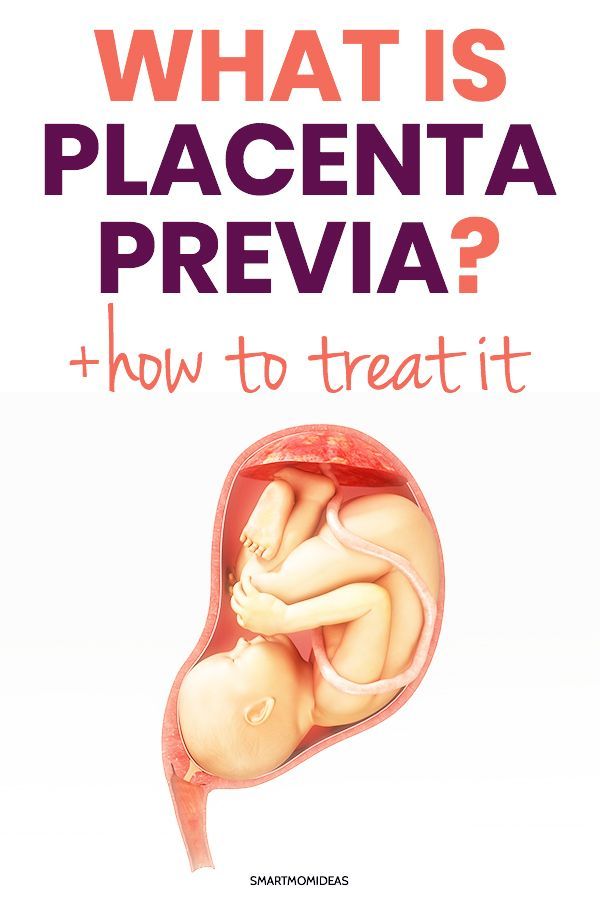
What does it mean if placenta is low
What complications can affect the placenta?
Complications that can affect the placenta during pregnancy or childbirth include:
- low-lying placenta and placenta praevia
- retained placenta – when part of the placenta remains in the womb after giving birth
- placental abruption – when the placenta starts to come away from the wall of the womb
These complications aren't common.
Low-lying placenta and placenta praevia
As your pregnancy progresses, your womb expands and this affects the placenta's position. The area where the placenta is attached usually stretches upwards, away from your cervix.
If the placenta stays low in your womb, near to or covering your cervix, it may block the baby's way out.
This is called low-lying placenta if the placenta is less than 2cm from the cervix, or placenta praevia if the placenta is completely covering the cervix.
Placenta praevia, where the cervix is completely covered at the end of pregnancy, affects about 1 in every 200 births.
The position of your placenta will be recorded at your 18- to 21-week ultrasound scan.
If your placenta is significantly low, you'll be offered an extra ultrasound scan later in your pregnancy (usually at about 32 weeks) to check its position again.
For 9 in every 10 women, the placenta will have moved into the upper part of the womb by this point.
If the placenta is still low in your womb, there's a higher chance that you could bleed during your pregnancy or during your baby's birth. This bleeding can be very heavy and put you and your baby at risk.
You may be advised to come into hospital at the end of your pregnancy so emergency treatment (such as a blood transfusion) can be given very quickly if you bleed.
If the placenta is near or covering the cervix, your baby can't be delivered through the vagina, so a caesarean section will be recommended.
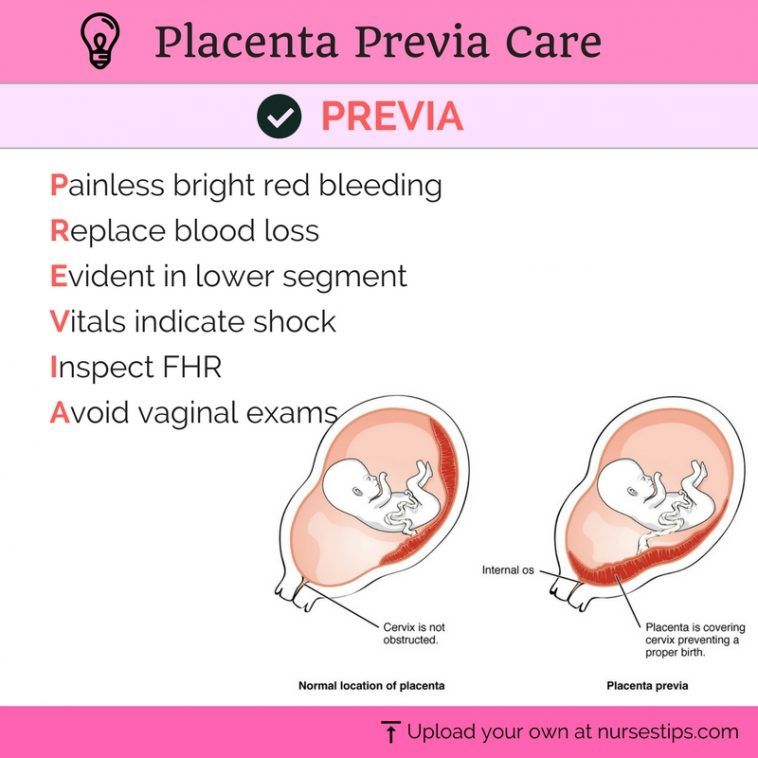
A low-lying placenta can be associated with painless, bright red bleeding from the vagina during the last 3 months of pregnancy. If this happens to you, contact your midwife or GP immediately.
Retained placenta
After your baby's born, part of the placenta or membranes can remain in the womb. This is known as retained placenta. If untreated, a retained placenta can cause life-threatening bleeding.
Breastfeeding your baby as soon as possible after the birth can help your womb contract and push the placenta out.
Your midwife may also ask you to change your position (for example, by moving to a sitting or squatting position). In some cases, you may be given an injection of a medicine to help your womb contract.
If these methods don't work, a doctor may need to remove the placenta by hand. This can be painful, so you'll be given an anaesthetic.
Placental abruption
Placental abruption is a serious condition in which the placenta starts to come away from the inside of the womb wall.
It can cause stomach pain, bleeding from the vagina and frequent contractions.
It can also affect the baby, increasing the risk of premature birth, growth problems and stillbirth.
It's not clear what causes placental abruption, but factors that increase the risk include injury to the abdominal area, smoking, cocaine use and high blood pressure.
If you're near your due date, the baby will need to be born straight away and a caesarean section may be recommended.
But if the baby's very premature and the abruption is minor, you may be kept in hospital for close observation.
Always speak to your midwife or GP if you're concerned about any aspect of your health when you're pregnant. You can also call NHS 111.
Further information
- Vaginal bleeding in pregnancy
- Antenatal care
Page last reviewed: 22 August 2022
Next review due: 22 August 2025
Low-lying placenta (placenta praevia) | Tommy's
Is a low-lying placenta common?
The position of your placenta will be checked at your mid-trimester ultrasound scan, at around 18-21 weeks of pregnancy. If your placenta is low-lying, you have another scan later in your pregnancy (usually about 32 weeks).
Because the lower part of the womb stretches more as the baby grows, the placenta usually moves into the upper part of the womb by this point. 90% of women who have a low-lying placenta at 20 weeks will not go on to have a low-lying placenta later in the pregnancy.
If you have had a baby by caesarean section before, the placenta is less likely to move upwards.
Only 1 in every 200 women have placenta praevia at the end of their pregnancy.
Am I likely to have placenta praevia?
Placenta praevia is more likely if you:
- smoke cigarettes
- have had fertility treatment to get pregnant, such as in vitro fertilisation (IVF)
- have had 1 or more caesarean sections
- are aged 40 or older
- are having more than 1 baby
- have had surgery on the womb
- are a cocaine user
- are expecting a boy
- have endometriosis.
Is there anything I can do to help the placenta move up?
Unfortunately not. The best thing you can do is concentrate on staying as healthy as you can. You may need extra scans, so make sure you go to all your antenatal appointments and follow your healthcare professional’s advice.
How can placenta praevia affect me and my baby?
There is a risk that you may have vaginal bleeding, particularly towards the end of your pregnancy.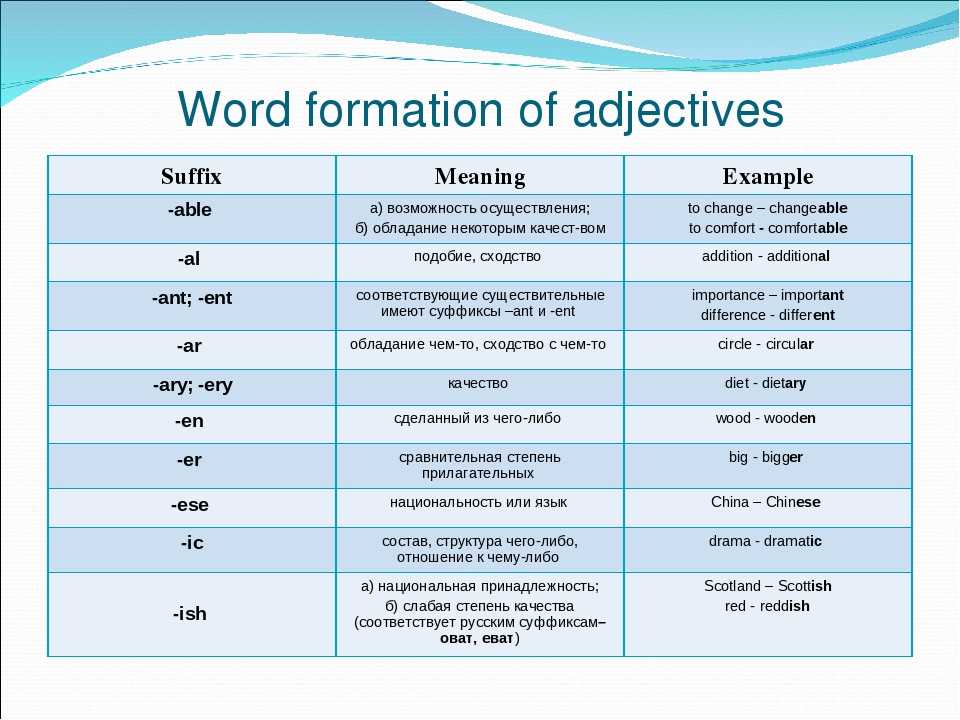 Bleeding from placenta praevia may be very heavy and can sometimes put mum and baby at risk.
Bleeding from placenta praevia may be very heavy and can sometimes put mum and baby at risk.
How is a low-lying placenta diagnosed?
Your midwife or doctor will look at your placenta’s position at your 18 to 21 week ultrasound scan.
If your placenta is low, you'll be offered an extra ultrasound scan later in your pregnancy (usually at about 32 weeks) to check its position again.
In 90% of cases, the placenta is no longer low-lying by this point.
Your midwife or doctor may think you have placenta praevia if:
- you have bleeding during the second or third trimester – this is usually painless and may happen after sex
- if the baby is lying in an unusual position, for example bottom first (breech) or lying across the womb (transverse)
If you have any bleeding during pregnancy, with or without pain, you should always get checked out straight away. If you’re in your first trimester, contact your doctor, midwife or Early Pregnancy Unit. If you are more than 12 weeks pregnant, go to your local A&E or contact your hospital maternity unit immediately.
If you are more than 12 weeks pregnant, go to your local A&E or contact your hospital maternity unit immediately.
You may be advised to avoid having sex (including the use of penetrative sex toys) for the rest of your pregnancy.
What treatment will I have?
Extra scans
If your placenta is low-lying at your 20-week scan, you’ll be offered another ultrasound scan at around 32 weeks. This may include a transvaginal ultrasound scan, which is when a probe is gently placed inside the vagina to check exactly where your placenta is lying. Don’t worry, this is safe for you and your baby.
The length of your cervix may also be measured at your 32-week scan to predict whether you may go into labour early and whether you are at increased risk of bleeding.
If the placenta hasn’t moved up, you should be offered another ultrasound scan at 36 weeks. The results of this scan will help you and your doctor plan the safest way for you to give birth.
Medication
If you have placental praevia, there is a risk you may give birth prematurely. So you may be offered a course of steroid injections between 34 and 36 weeks of pregnancy to help your baby’s lungs to become more mature.
So you may be offered a course of steroid injections between 34 and 36 weeks of pregnancy to help your baby’s lungs to become more mature.
If you do go into labour early, you may be offered medication to try to stop your contractions. This will give you time to have a course of steroid injections. If you have severe bleeding or progressing labour your baby may need to be delivered.
If you have vaginal bleeding, you may need to be admitted to hospital. This is because there is a small risk that you could bleed suddenly and heavily. If this happens, you may need an emergency caesarean section.
What do I need to do if I have a low-lying placenta?
If you know you have a low-lying placenta, you should contact the hospital immediately if you have:
- vaginal bleeding, including spotting
- contractions
- pain, including any vague, period-like aches.
If you have any bleeding, your doctor may need to do an internal examination to check where it’s coming from. This is safe and they will ask for your permission before they start.
This is safe and they will ask for your permission before they start.
Anaemia
Anaemia is a blood condition that develops when you don’t have enough red blood cells. Red blood cells contain haemoglobin, a protein that carries oxygen around your body and to your baby.
If you have a low-lying placenta, it’s important to try to avoid developing anaemia, which can be common in pregnancy. Eating a healthy, balanced diet will help you either prevent or manage anaemia. Iron supplements may also help, if your healthcare team recommends them.
How will my baby be born?
Your healthcare team will talk to you about what your options are for giving birth.
You may be advised to give birth early if you have any heavy bleeding before your due date.
If the edge of your placenta is very close (less than 20mm) to your cervix (entrance to the womb), the Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists state that the safest way to give birth is by caesarean section. This will usually be between 36 and 37 weeks. Your doctor will discuss your options with you, but how you give birth is ultimately your decision. But if you have had vaginal bleeding during your pregnancy, you may be advised to have your caesarean earlier than this.
This will usually be between 36 and 37 weeks. Your doctor will discuss your options with you, but how you give birth is ultimately your decision. But if you have had vaginal bleeding during your pregnancy, you may be advised to have your caesarean earlier than this.
If the placenta is further than 20mm from your cervix, you may be able to have a vaginal birth if you want one.
If you are having a caesarean section, a senior obstetrician (a doctor who specialises in pregnancy) will be there. This is because you may have heavy bleeding during the surgery. If this happens, you may need a blood transfusion. This is more likely if you have placenta praevia.
Talk to your doctor before your surgery if, for any reason, you do not want a blood transfusion.
Unfortunately, complications are more common in caesarean sections if you have a low-lying placenta. Your doctor should talk to you about the risks of major bleeding and hysterectomy (removal of the womb) before your caesarean.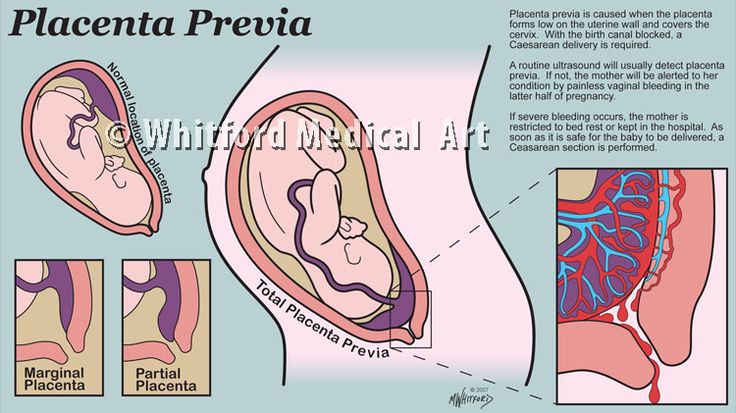 For most women, the risk of hysterectomy is low and will only occur as a last resort if other measures to control bleeding are not effective.
For most women, the risk of hysterectomy is low and will only occur as a last resort if other measures to control bleeding are not effective.
If you have placenta praevia:
- you are at higher risk of having your baby early (less than 37 weeks).
- your baby will need to be born by caesarean section because the placenta is blocking the birth canal.
Your mental health
Being diagnosed with complications in pregnancy can be hard. And being asked to look out for certain symptoms, such as bleeding, and needing extra appointments and check-ups can cause anxiety and stress. It may also be a lonely experience when those around you don’t understand what it’s like.
Remember that you can tell your midwife or doctor how you feel. They will do their best to reassure you and answer any questions you may have.
You can also call our pregnancy line on 0800 014 7800 (Monday to Friday, 9am to 5pm), or email us at [email protected]
If you are struggling to cope, there is professional support available.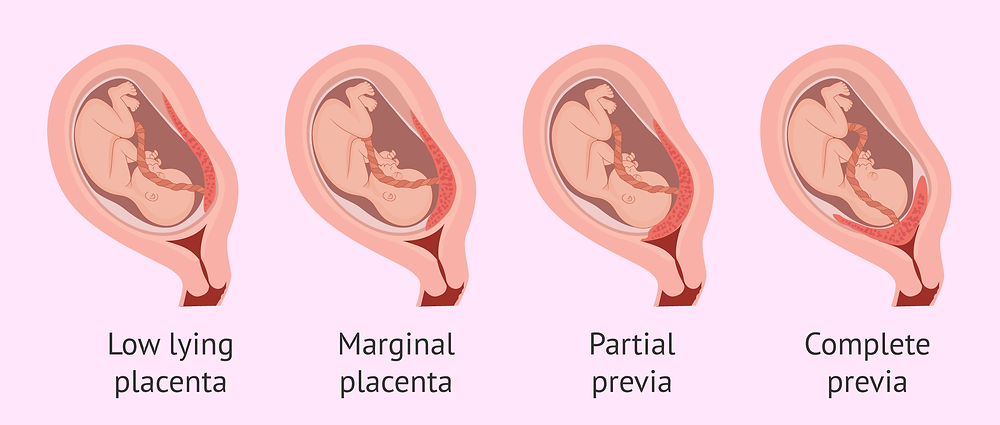 Don’t suffer in silence. Tell your midwife or GP how you feel. They will help you access the support you need.
Don’t suffer in silence. Tell your midwife or GP how you feel. They will help you access the support you need.
Find out more about looking after our mental health in pregnancy.
Low placenta
Home / Gynecologist / Low placenta
Placenta is a temporary organ that is formed in the body of a pregnant woman in order to maintain a connection between her body and the fetus. She filters the blood , which the unborn baby feeds on, cleansing it of toxins and other harmful substances.
This pathology can be very dangerous in some cases, while in others it goes away without any treatment and does not bring problems.
Types of location of the placenta
Usually the placenta is attached to the posterior wall of the uterus closer to its bottom . It is worth noting that the uterus is an inverted vessel, and its bottom is located on top. This is the best option for the location of the placenta. However, this does not always work out. In some cases, the placenta is attached to the anterior wall. Which is also not a pathology.
However, this does not always work out. In some cases, the placenta is attached to the anterior wall. Which is also not a pathology.
The low position of the placenta during pregnancy is much more dangerous. If the placenta is located low, it is subjected to stronger pressure from the fetus, and even with any external influence, the risk is damage to the placenta or its detachment increases. In addition, in the later stages, an actively moving baby can also damage the placenta, or squeeze the umbilical cord.
A placenta is said to be low when there is less than 6 cm between its lower edge and the os of the uterus. The anterior wall has a greater tendency to stretch, and migration is also characteristic of it, however, the direction of migration is opposite: usually the placenta moves in the opposite direction, down to the cervix.
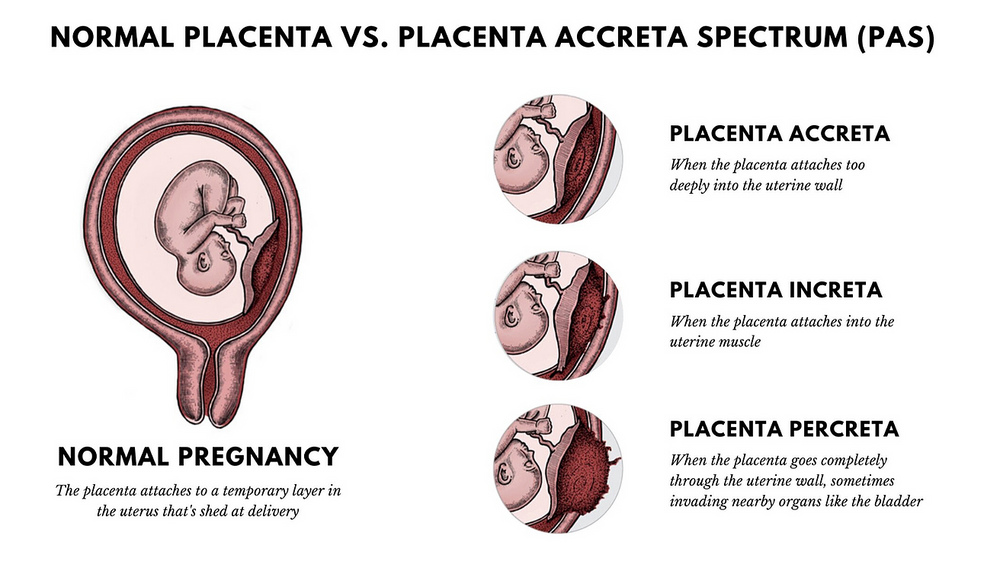
An even more complex and dangerous pathology of the location of the placenta is its partial or complete presentation .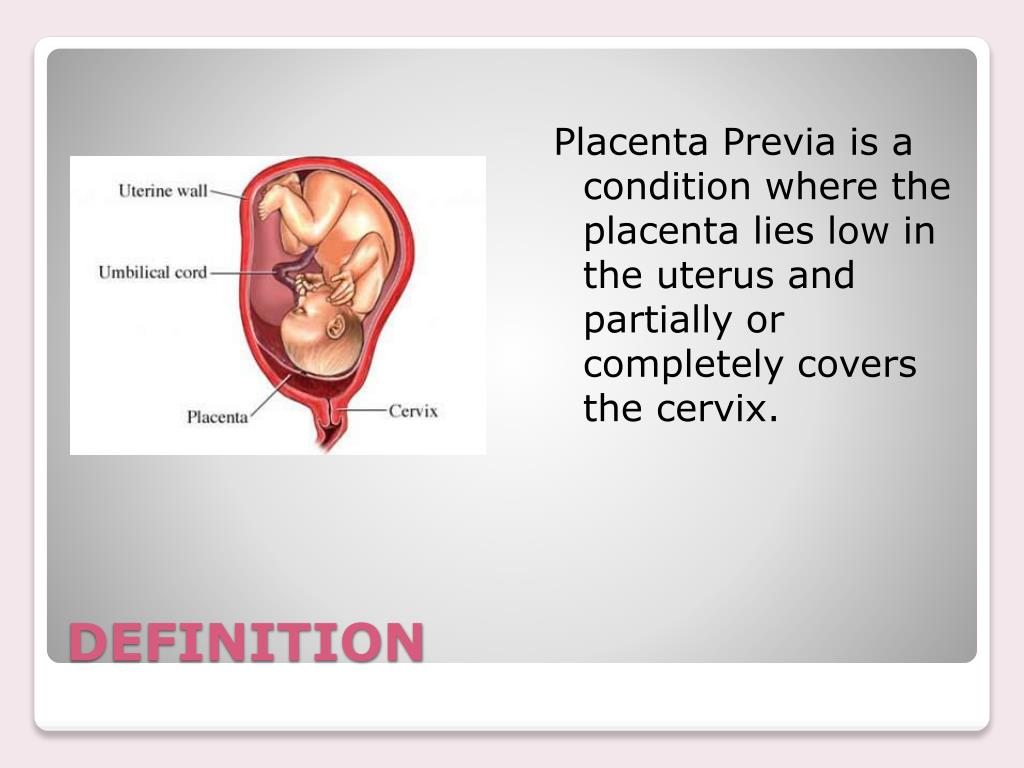 Previa is a condition when the placenta partially or completely obscures the cervix of the uterus.
Previa is a condition when the placenta partially or completely obscures the cervix of the uterus.
Causes of low placenta
Many causes of low placenta are due to internal factors - diseases during pregnancy and the condition of the female genital organs . They can be:
- damage to the mucous membrane of the uterus;
- inflammatory processes;
- infections;
- previous abortions;
- miscarriages in the past;
- cesarean section;
- various gynecological operations;
- pathology of the structure, development, functioning of the uterus;
- multiple pregnancy;
- unhealthy lifestyle: active smoking, excessive alcohol consumption;
- previous diseases of the uterus: endometritis, fibroids;
- parity - many births in the past;
- the woman's age is over 35 years.
Curettage of the uterus in the past is the main cause of this pathology.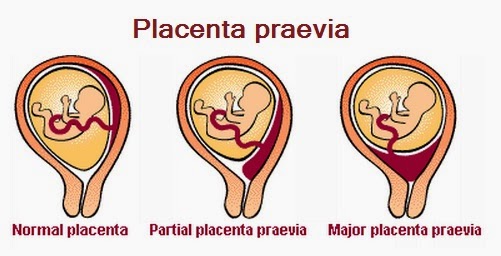 Damage to the mucosa prevents the fetal egg from gaining a foothold in the upper segment of this organ, and it remains below, at the neck.
Damage to the mucosa prevents the fetal egg from gaining a foothold in the upper segment of this organ, and it remains below, at the neck.
Symptoms of low placenta
The danger of this pathology is that it practically does not manifest itself. Usually, signs that not everything is in order with the placenta are the result of already running and irreversible processes - for example, its detachment. It can be:
- drawing pains, feeling of heaviness in the abdomen;
- bloody discharge with a low location of the placenta is an alarm signal that it is necessary to call an ambulance;
- freezing of the fetus in the womb for a long time, or, conversely, its too violent activity - this is caused by hypoxia;
- on ultrasound with such a pathology in 50% of cases is the wrong presentation of the fetus;
- in 30% of cases, women suffer from severe toxicosis.
A pregnant woman herself cannot suspect that she has a low placenta.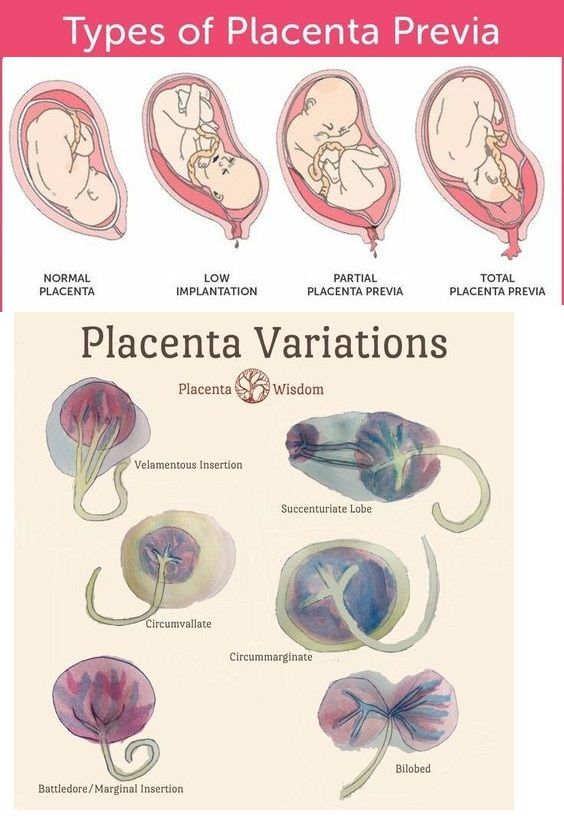 This can only be seen on planned ultrasounds, which must be passed by everyone. After an ultrasound examination, they can not only clarify or refute the diagnosis, but also determine the type of pathology.
This can only be seen on planned ultrasounds, which must be passed by everyone. After an ultrasound examination, they can not only clarify or refute the diagnosis, but also determine the type of pathology.
Treatment and prevention of low placentation
Management of pregnancy with low placentation is always very careful. A woman will have to undergo ultrasound many times, limit physical activity and stop sexual activity. For a long time, increased uterine tone can provoke detachment of an improperly located placenta, from there bleeding, and possible death of the fetus as a result of acute hypoxia, if placental abruption is large. Bleeding can even provoke a gynecological examination of the cervix, therefore, for no particular reason, doctors try not to conduct examinations on the chair.
Listen to the doctors and hope for the best. Many women give birth on their own or by caesarean section of healthy babies with low placenta previa.
If you need help from an experienced gynecologist, sign up for a consultation by calling 8 (49244) 9-32-49, 8 (910) 174-77-72.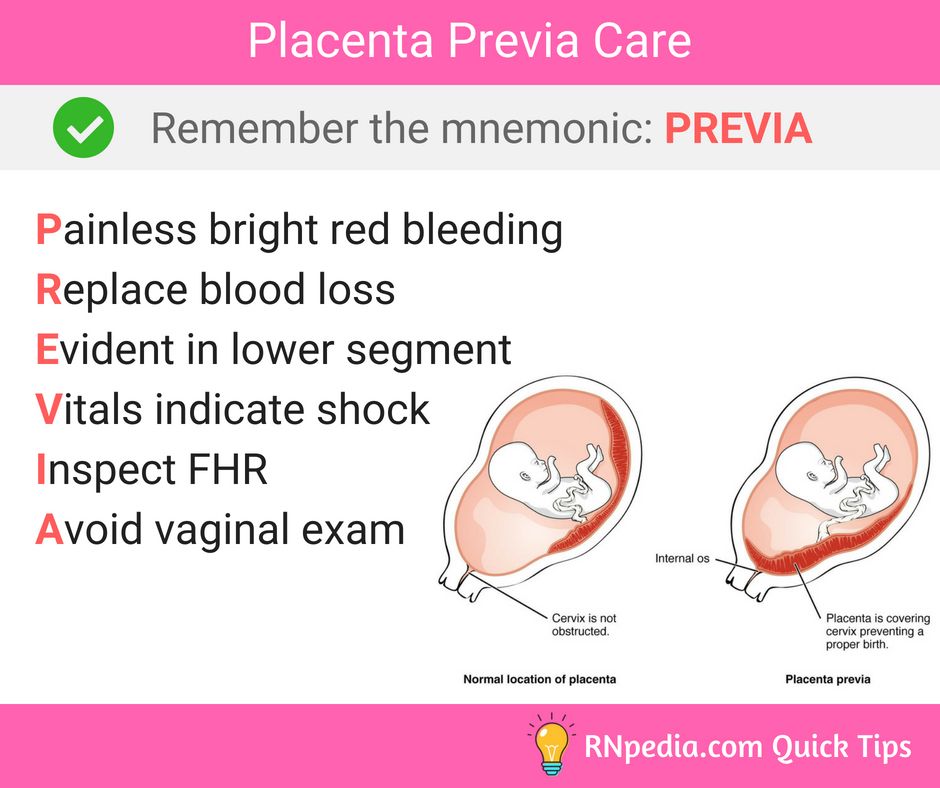
News All
NEW YEAR, FIREWORKS, FIREWORKS… How to protect your eyes? Councils of doctors of the medical center "Sever", Alexandrov
Read more...
"Touchy skin" - how not to get aggravated during the New Year holidays? Let's talk with the dermatologist of the medical center "Sever" - Karaeva Elmira Zulfigarovna.
Read more...
Poll
What other doctors would you like to see in our center
Ask a doctor online
Guaranteed answer within an hour
Ask a question
- one
Placenta: structure, functions, location.
- 2
What is low placentation.
- 3
Migration of the placenta.
- four
Causes of low placentation.
- 5
What is dangerous low placentation during pregnancy.
- 6
Symptoms of low placentation.
- 7
Recommendations for low placentation.
- eight
Methods of treatment.
- 9
Features of childbirth with low placentation.
- ten
Prevention.
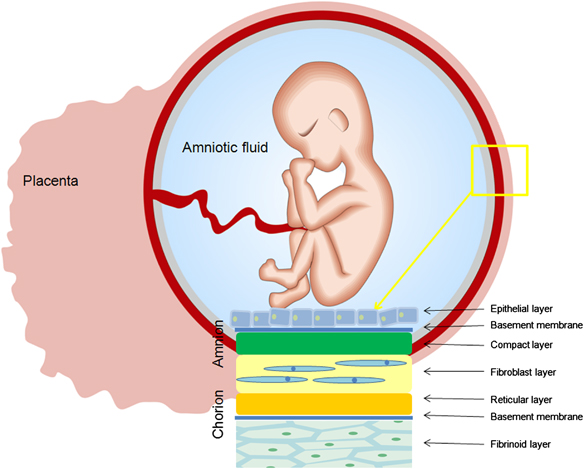
The placenta is an organ that develops in the uterine cavity during pregnancy and provides a link between the mother's body and the fetus. The main part of the placenta are special villi that branch out in it and form from the beginning of pregnancy. Inside the villi, the baby's blood circulates, and outside the villi are actively washed by the blood coming from the mother. That is, the placenta combines two circulatory systems at once - maternal from the side of the uterus and fetal from the side of the amniotic membranes and the baby, but does not allow the blood of the mother and the unborn child to mix.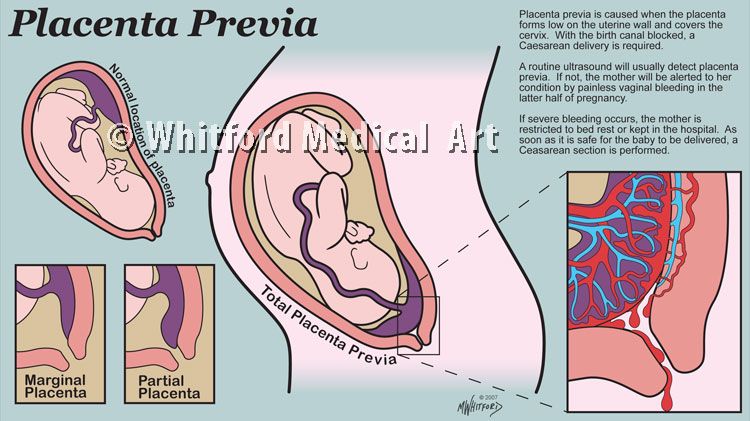
Functions of the placenta:
- Gas exchange: oxygen from the mother's blood enters the fetus's blood, and carbon dioxide is transported in the opposite direction.
- Trophic and excretory: through the placenta the fetus receives water, electrolytes, nutrients and minerals, vitamins, and the placenta also participates in the removal of metabolites.
- Hormonal: The placenta works as an endocrine gland, it produces hormones that are important for childbearing and lactation. It forms chorionic gonadotropin, placental lactogen, prolactin, progesterone, estrogens, and the placenta is also able to secrete testosterone, serotonin, relaxin and other hormones.
- Protective: the placenta has immune properties, plays a role in the regulation and development of the immune system of the mother and fetus. At the same time, it prevents the emergence of an immune conflict between the organisms of the mother and child.
 The placenta does not protect the fetus from certain drugs, drugs, alcohol, nicotine, and viruses.
The placenta does not protect the fetus from certain drugs, drugs, alcohol, nicotine, and viruses.
Normally, the placenta is attached to the front or back wall of the uterus closer to its bottom (the bottom of the uterus is at the top) - there are many blood vessels in this place, therefore, the most favorable conditions are created for attaching the placenta and establishing uteroplacental blood flow. There are a number of factors that prevent the normal location of the placenta in the uterine cavity, these can be uterine fibroids, tumors of the uterine wall, malformations, many pregnancies in the past, inflammatory processes in the uterus, abortions. In these cases, low attachment of the placenta may occur.
Low placentation is the location of the placenta closer than 5.5 - 6 cm from the internal os of the uterus. This is far from a rare condition, but you should not panic, because if this diagnosis is made before 30 - 34 weeks of pregnancy, it is not final. The placenta can move, migrate, the walls of the uterus stretch unevenly, and there is a very high probability that by 34 weeks the placenta will be higher than 5 - 6 cm from the internal os of the uterus. But it is worth remembering that if the diagnosis was made even in the early stages, a pregnant woman must follow certain lifestyle recommendations and be examined regularly.
The placenta can move, migrate, the walls of the uterus stretch unevenly, and there is a very high probability that by 34 weeks the placenta will be higher than 5 - 6 cm from the internal os of the uterus. But it is worth remembering that if the diagnosis was made even in the early stages, a pregnant woman must follow certain lifestyle recommendations and be examined regularly.
Migration of the placenta
During pregnancy, the placenta slightly changes its thickness and total volume, which leads to a change in its appearance and localization. The low location of the placenta is often detected early, but as the fetus grows and the size of the uterus increases, it grows, rising closer to the bottom of the uterus. As a rule, closer to the time of childbirth, the child's place occupies the correct position. Most often this happens when the placenta is attached to the back wall.
When the placenta is located along the anterior wall, the placenta may migrate down.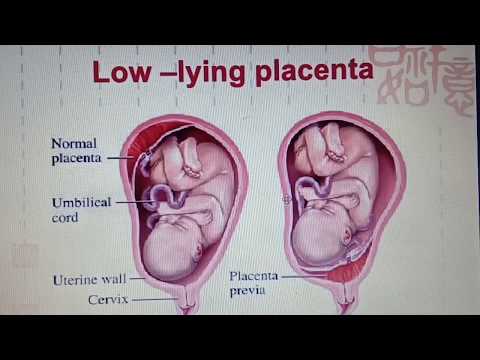 This is due to the fact that the anterior wall is more extensible, and if the posterior wall stretches in the direction from the cervix up to the bottom, then the anterior wall stretches from the center, and to the sides, and to the bottom and to the cervix. That is why it is possible that the placenta will remain close to the cervix, while the formation of both low placentation and placenta previa is not excluded.
This is due to the fact that the anterior wall is more extensible, and if the posterior wall stretches in the direction from the cervix up to the bottom, then the anterior wall stretches from the center, and to the sides, and to the bottom and to the cervix. That is why it is possible that the placenta will remain close to the cervix, while the formation of both low placentation and placenta previa is not excluded.
Causes of low placentation:
- inflammatory processes of the walls of the uterus;
- infectious lesions of the walls of the uterus;
- consequences of miscarriages and abortions;
- curettage of the uterus;
- scars after caesarean section;
- stitches after operations;
- uterine fibroids;
- underdevelopment of the uterus, bicornuate, saddle uterus, infantile uterus;
- multiple pregnancy;
- mother's age is over 30 - 35 years.
Why is low placentation dangerous during pregnancy
First of all, it is necessary to understand in which cases there is no reason for concern
- If the placenta is low at the first ultrasound at 12-16 weeks, then there is no reason to worry.
 Most likely, as the uterus grows, the placenta will change its position and rise up. At the same time, the process of bearing the fetus is not disturbed, childbirth takes place independently without complications.
Most likely, as the uterus grows, the placenta will change its position and rise up. At the same time, the process of bearing the fetus is not disturbed, childbirth takes place independently without complications. - If low placentation is detected in terms of more than 20 weeks, you should also not worry, it is from this period that the active growth of the fetus will begin and the process of placental migration upward will go more actively.
- If low placentation is detected after 30 weeks, additional monitoring is needed, but also do not worry too much, since the placenta can migrate up to 34 - 36 weeks inclusive, and with low placentation, natural childbirth is possible without complications.
But, unfortunately, starting from the second trimester of pregnancy, the development of complications is not excluded, which is associated with an increase in the weight of the fetus and an increase in pressure on the embryonic organ. These complications include:
- anemia in a pregnant woman, which can lead to frequent bleeding;
- when the vessels are squeezed, blood flow deteriorates, which threatens with hypoxia and fetal growth retardation;
- insufficient space for the fetus in the uterus leads to malpresentation of the fetus;
- placental abruption can lead to impaired blood circulation in the fetus;
- a low-lying placental organ prevents the baby's head from lowering into the small pelvis, which will lead to difficulty in natural childbirth;
- during contractions, the placenta can move and block the birth canal, which will make natural childbirth impossible and an urgent caesarean section will have to be performed;
- if a caesarean section is necessary, low placentation along the anterior wall of the uterus makes the operation difficult and leads to large blood loss.
But in any case, even when making this diagnosis in the late stages of pregnancy, you should not panic, since in 90% of cases such a pregnancy ends successfully with the birth of a healthy baby, in 60% it is possible to give birth on their own, in 40% - by caesarean section.
Symptoms of low placentation
As a rule, in the early stages of pregnancy, low placentation is asymptomatic, pathology can only be detected at 12-13 weeks with ultrasound. The lower the placenta is located towards the exit from the uterus, the stronger the signs of low placentation will appear:
- pain in the lower abdomen, having a pulling character;
- small spotting after strong physical exertion;
- pain in the lower back and lower abdomen with detachment.
20% of pregnant women with low placentation may also experience:
- headache or dizziness;
- low pressure;
- nausea and vomiting;
- swelling.
The earlier low placentation is diagnosed, the lower the risk of developing dangerous complications, which is why you should definitely visit a gynecologist at an early stage. Low placentation in early pregnancy is diagnosed in almost 80% of women, but after 30 weeks, in most pregnant women, the embryonic organ rises.
Recommendations for low placentation
Strongly contraindicated:
- abrupt movements;
- excessive physical activity;
- vaginal procedures;
- weight lifting;
- stress and overwork.
Recommended:
- in a sitting and lying position, give the legs an elevated position, this improves blood circulation in the area of \u200b\u200bthe placenta and contributes to its rise;
- do not sit cross-legged, as such a posture interferes with normal blood circulation.
- lie down and get up gently, without jerking;
- when the first signs of blood smearing appear, you should consult a doctor, if bleeding occurs, call an ambulance.
Sex with low placentation is possible only in the absence of obvious symptoms and contraindications (detachment of the placental organ, pain, bleeding).
When having sex with a partner, it is important to take basic precautions:
- hygiene, be sure to visit the bathroom before starting intimacy;
- do not make sudden movements, strong shocks can harm, so the friction must be done gently, the penetration is shallow.
- the choice of position is also important, the pressure on the uterus will be less if the woman is lying on her side.
- if there is a threat of abortion, sexual intercourse is contraindicated, during this period even masturbation and anal sex can cause serious complications due to uterine contraction during orgasm, which will lead to placental abruption.
Treatment methods for low placentation
There is no medical treatment for this disease. According to statistics, 8 - 9 out of 10 cases, the placental organ independently takes the correct position, as the uterus grows.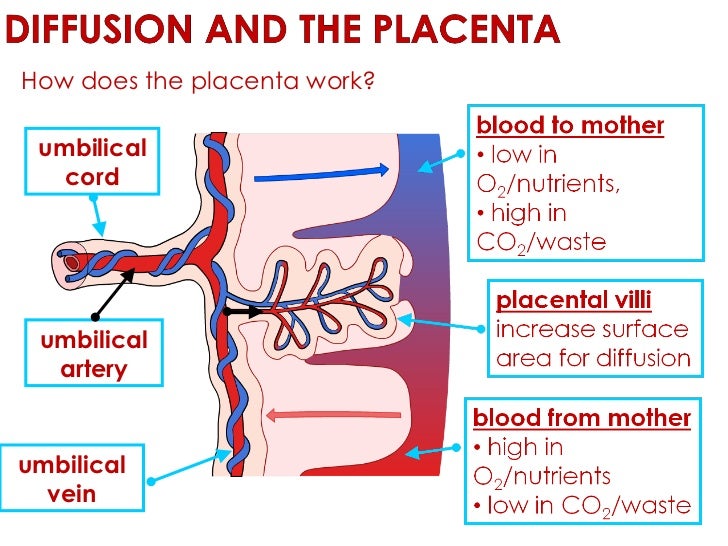 Therefore, a diagnosis made at 20 - 22 weeks or 32 weeks of pregnancy should not be considered critical. Until the 34th - 36th week, the position of the placenta changes, which means that there is a possibility of the complete disappearance of the pathology, it is only necessary to follow all the doctor's recommendations. Throughout pregnancy, with a low location of the placenta, it is important to be observed by a specialist and undergo regular ultrasound examinations. With bleeding and severe pain, it is urgent to call an ambulance.
Therefore, a diagnosis made at 20 - 22 weeks or 32 weeks of pregnancy should not be considered critical. Until the 34th - 36th week, the position of the placenta changes, which means that there is a possibility of the complete disappearance of the pathology, it is only necessary to follow all the doctor's recommendations. Throughout pregnancy, with a low location of the placenta, it is important to be observed by a specialist and undergo regular ultrasound examinations. With bleeding and severe pain, it is urgent to call an ambulance.
Features of childbirth with low placentation
If, with low placentation, the pregnancy took place under the supervision of doctors and all recommendations were followed, then, as a rule, natural delivery takes place without complications and ends happily.
Several factors influence the course of labor:
- place of attachment of the placenta;
- the nature of the course of pregnancy;
- the occurrence of complications during the gestation period;
- associated pathologies.