How much formula for 9 months
How Much Formula Does Your Baby Need
Read time: 4 minutes
What should I know about how much formula my baby needs?Understand how to estimate about how much formula your 0 to 6 month old needs per day
Learn about how formula needs change after 6 months of age
Know how hunger and fullness cues are an important part of how much formula your baby drinks
When it comes to feeding your baby, responding to your baby’s hunger cues and feeding on demand is best. But as parents we often want more specific guidance, especially when it comes to how many ounces of formula we should be feeding our baby each day. How much is enough? How much is too much? Let’s set the record straight.
How much formula for ages 0 to 6 months?During the first 6 months when solid foods are not yet in the picture, there’s a simple rule of thumb to figure out how much formula your baby needs:1) Offer 2. 5 ounces of formula per pound of body weight each day.1, 7 Remember that your baby may periodically take more or less than this amount depending on their hunger and growth spurts.Here is an example for a baby who weighs ten pounds: 10 pounds x 2.5 ounces = 25 ounces total per day2) To figure out the number of ounces per bottle, divide this number by the number of feedings your baby has in a day.If your baby feeds 8 times per day, you would divide 25 by 8, which comes out to a little over three ounces per feeding: 25 ounces total per day / 8 feeding times per day = 3.12 ounces per feeding
Read more: Everything You Need to Know About Preparing and Storing Infant Formula
Learn about: Preparing Formula: What Type of Water Should I Use?
How much formula for ages 6 to 12 months?Once your baby reaches six months of age, complimentary solid foods are introduced.2 You may find that they naturally take a little less formula as they get closer to 1 year. 3 This is normal!Just remember, formula and/or breastmilk should remain the primary source of nutrition, with solid foods secondary to that, up until your baby is one year old.4
3 This is normal!Just remember, formula and/or breastmilk should remain the primary source of nutrition, with solid foods secondary to that, up until your baby is one year old.4
Read more: Introducing Solids: First Foods and Textures
Want to make sure your baby is drinking the right amount of formula? Ask our Happy Baby Experts, who are registered dietitians and infant feeding experts, for free. Chat now!
Average formula amounts based on baby’s ageAge | Number of feedings per day | Amount of formula per feed |
Birth-1 week | 6-10 | 2-3 ounces |
1 week-1 month | 7-8 | 2-4 ounces |
1-3 months | 5-6 | 4-5 ounces |
3-6 months | 4-5 | 6-7 ounces |
6-9 months | 3-4 | 7-8 ounces |
9-12 months | 3 | 7-8 ounces |
Sources: 5, 6, 8
*Note that The American Academy of Pediatrics suggests babies should not be drinking more than 32 ounces of formula per day.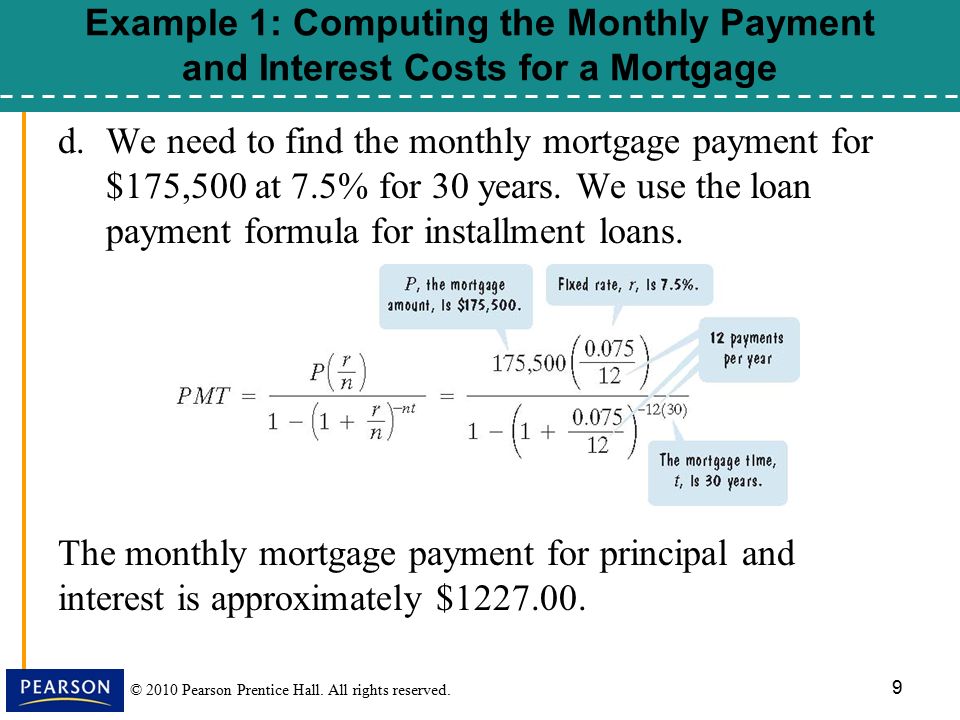 1 If you notice your little one is taking in more than this, reach out to your pediatrician to discuss.
1 If you notice your little one is taking in more than this, reach out to your pediatrician to discuss.
Keep in mind, each baby is different and the above formula amounts are just averages. Babies’ appetites may change, just as ours do! Your baby may eat more or less on any given day. By responding to your baby’s hunger cues (sucking on hands; opening and closing mouth; rooting) and fullness cues (starts and stops the feeding often; unlatching or spitting out the nipple; fidgets and is distracted; closes mouth), you will be giving your baby exactly what they need.9
Read more: Understanding Your Baby’s Hunger and Fullness Cues: Responsive Feeding
Try paced bottle feedingThis method of bottle-feeding helps prevent overfeeding by putting your little one in control and allowing them to eat exactly how much they need. 10 With a few simple steps, a slow-flow nipple, and a bit of practice, paced bottle feeding will come naturally to you and your little one. Read about how to do it here: What is Paced Bottle Feeding?
10 With a few simple steps, a slow-flow nipple, and a bit of practice, paced bottle feeding will come naturally to you and your little one. Read about how to do it here: What is Paced Bottle Feeding?
Your baby’s weight gain is the most important sign that your baby is getting enough formula. You’ll also want to look at diapers to know how your little one is doing.For a newborn, look for 5 or more wet diapers and at least 1 dirty diaper per day. An older baby may have 5 or more wet diapers per day along with 1 dirty diaper every day or even every 2 to 3 days.11 Remember that every baby has a different stooling pattern, so just watch your little one’s pattern and be aware when it changes.
Read more: Feeding Tips for Healthy Weight Gain in Babies and Toddlers
Learn about: Constipation in Babies and Toddlers
Let’s Chat!We know parenting often means sleepless nights, stressful days, and countless questions and confusion, and we want to support you in your feeding journey and beyond. Our Happy Baby Experts are a team of lactation consultants and registered dietitian nutritionists certified in infant and maternal nutrition – and they’re all moms, too! They’re here to offer personalized support on our free, one-on-one, live chat platform Monday through Friday, from 8am–6pm ET. No appointment needed, no email or sign-up required. Chat Now!
Our Happy Baby Experts are a team of lactation consultants and registered dietitian nutritionists certified in infant and maternal nutrition – and they’re all moms, too! They’re here to offer personalized support on our free, one-on-one, live chat platform Monday through Friday, from 8am–6pm ET. No appointment needed, no email or sign-up required. Chat Now!
Read more about the experts that help write our content!
For more information on this topic, check out the following articles:Should I Formula Feed On Demand or on a Schedule?
How do I Supplement my Breastfed Baby with Formula?
Choosing the Best Bottles and Nipples for my Baby
Should I Switch my Baby's Formula?
Amount and Schedule of Baby Formula Feedings
- In the first week after birth, babies should be eating no more than about 1 to 2 ounces (30 to 60 ml) per feed.
- During the first month, babies gradually eat more until they take 3 to 4 ounces (90 to 120 ml) per feed, amounting to 32 ounces per day.
 Formula-fed babies typically feed on a more regular schedule, such as every 3 or 4 hours. Breastfed babies usually take smaller, more frequent feedings than formula-fed infants.
Formula-fed babies typically feed on a more regular schedule, such as every 3 or 4 hours. Breastfed babies usually take smaller, more frequent feedings than formula-fed infants.
If your baby sleeps longer than 4 to 5 hours during the first few weeks after birth and starts missing feedings, wake them up and offer a bottle.
By the end of the first month: Your baby will be up to at least 3 to 4 ounces (120 mL) per feeding, with a fairly predictable schedule of feedings about every 3 to 4 hours.
By 6 months: Your baby will consume 6 to 8 ounces (180–240 mL) at each of 4 or 5 feedings in 24 hours.
Formula feeding based on body weight
On average, your baby should take in about 2½ ounces (75 mL) of infant formula a day for every pound (453 g) of body weight. But they probably will regulate their intake from day to day to meet their own specific needs, so let them tell you when they've had enough.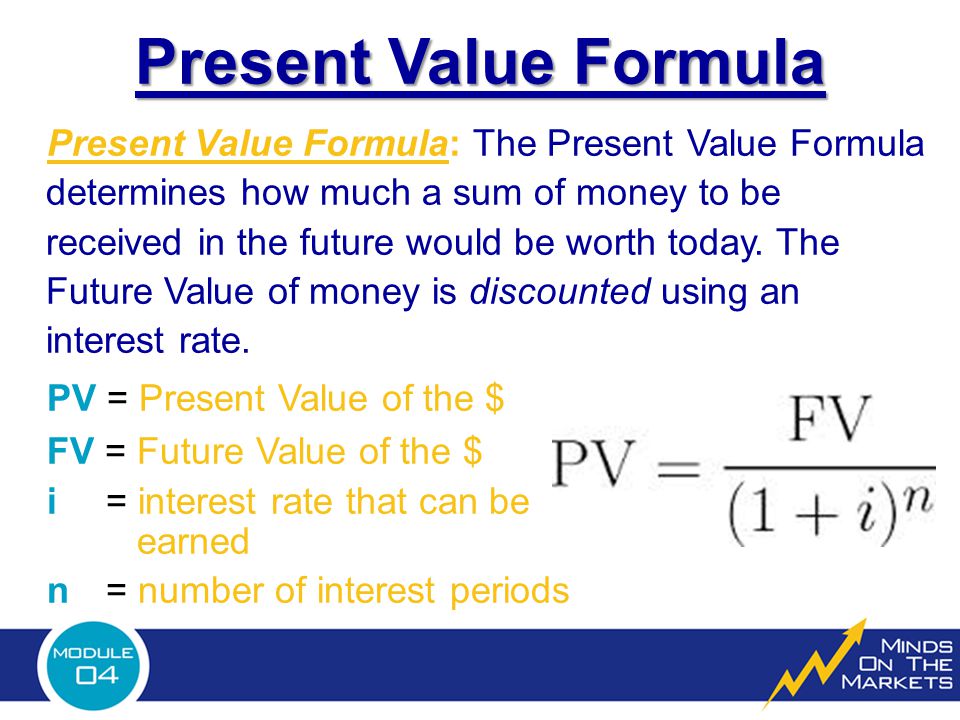 If they become fidgety or easily distracted during a feeding, they're probably finished. If they drain the bottle and continues smacking their lips, they might still be hungry.
If they become fidgety or easily distracted during a feeding, they're probably finished. If they drain the bottle and continues smacking their lips, they might still be hungry.
There are high and low limits, however. If your baby consistently seems to want more or less than this, discuss it with your pediatrician. Your baby should usually drink no more than an average of about 32 ounces (960 mL) of formula in 24 hours. Some babies have higher needs for sucking and may just want to suck on a pacifier after feeding.
On-demand feeding
Initially it is best to feed your formula-fed newborn a bottle on demand, or whenever they cry with hunger. As time passes, your baby will begin to develop a fairly regular timetable of their own. As you become familiar with their signals and needs, you'll be able to schedule their feedings around their routine.
Eating & sleeping patterns
Between 2 and 4 months of age (or when the baby weighs more than 12 lb. [5.4 kg]), most formula-fed babies no longer need a middle-of-the-night feedings.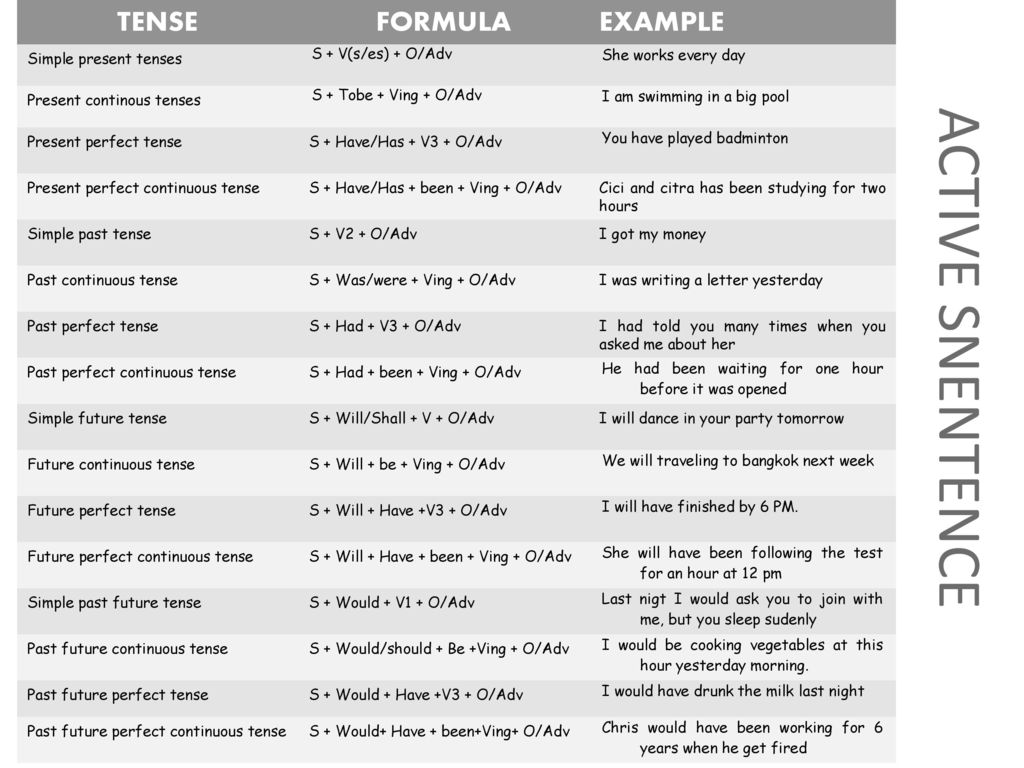 They're consuming more during the day, and their sleeping patterns have become more regular (although this varies considerably from baby to baby). Their stomach capacity has increased, too, which means they may go longer between daytime feedings—occasionally up to 4 or 5 hours at a time.
They're consuming more during the day, and their sleeping patterns have become more regular (although this varies considerably from baby to baby). Their stomach capacity has increased, too, which means they may go longer between daytime feedings—occasionally up to 4 or 5 hours at a time.
If your baby still seems to feed very frequently or consume larger amounts, try distracting them with play or with a pacifier. Sometimes patterns of obesity begin during infancy, so it is important not to overfeed your baby.
Getting to know your baby's feeding needs
The most important thing to remember, whether you breastfeed or bottlefeed, is that your baby's feeding needs are unique. No book―or website―can tell you precisely how much or how often they need to be fed or exactly how you should handle them during feedings. You will discover these things for yourself as you and your baby get to know each other.
More information
- How Often and How Much Should Your Baby Eat?
- Making Sure Your Baby is Getting Enough Milk
- Is Your Baby Hungry or Full? Responsive Feeding Explained (Video)
- Remedies for Spitty Babies
- Last Updated
- 5/16/2022
- Source
- Adapted from Caring for Your Baby and Young Child: Birth to Age 5 7th Edition (Copyright © 2019 American Academy of Pediatrics)
The information contained on this Web site should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your pediatrician. There may be variations in treatment that your pediatrician may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances.
There may be variations in treatment that your pediatrician may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances.
Feeding baby formula
All parents dream that their child grows and develops correctly and harmoniously. However, the formation of a child's body largely depends on balanced nutrition that the baby receives from the first days of life.
Dry milk drink "Baby milk" Valio Baby 3 NutriValio for feeding children over 12 months Read more
Of course, the best food for a baby is mother's milk, because it gives the child a lot of useful and necessary substances for growth and development. The quality of a child's nutrition in early childhood largely determines the state of his health in adulthood. In addition, nutrition is important in the development of the child's central nervous system and affects his intelligence and abilities.
If the child is artificially fed, it is all the more important to consciously approach the issue of his nutrition, carefully choosing the right mixture. Carefully monitor the feeding regime and introduce complementary foods in a timely manner. It is in the power of parents to provide the baby with health for many years.
Carefully monitor the feeding regime and introduce complementary foods in a timely manner. It is in the power of parents to provide the baby with health for many years.
#PROMO_BLOCK#
It is important to follow a few rules, always remembering that when choosing a diet, consultation with a doctor is required!
1. Give preference only to adapted mixtures, since in their composition they are as close as possible to the composition of breast milk.
2. Take into account the individual characteristics of the body and the state of health of the baby.
3. Take into account the age of the child and select mixtures of the appropriate stage - initial and subsequent. To make it easier for parents to navigate, the formulas are labeled with numbers: 1 (0–6 months), 2 (6–12 months), 3 (from 12 months). The initial (starter) mixture is indicated by the number 1 and is intended for children in the first six months of life. Subsequent formulas have the numbers 2 and 3 on the packaging.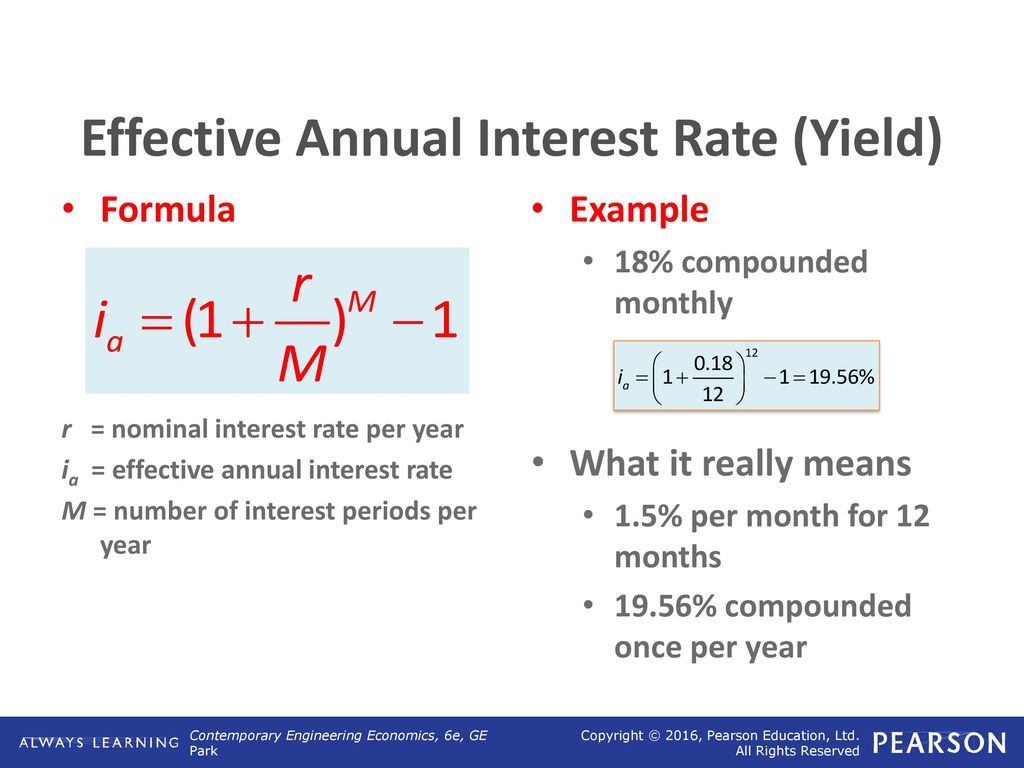 They are intended for older babies from 6 months. It is important to remember that in mixtures for each stage, the composition formula changes, taking into account the age-related characteristics of development and the needs of children.
They are intended for older babies from 6 months. It is important to remember that in mixtures for each stage, the composition formula changes, taking into account the age-related characteristics of development and the needs of children.
4. Observe the dosage in accordance with the instructions on the packaging. Deviation from these norms can adversely affect the well-being and health of the child. If you take too much dry matter, the mixture will come out with an increased content of nutrients, which can lead to more frequent regurgitation, unstable stools and excessive stress on the kidneys and intestines. If you take the powder less than the specified norm, then the mixture will turn out to be low-calorie and insufficiently nutritious - the baby will remain hungry.
5. Use specially prepared water to dilute the mixture. Only clean and boiled water should be used.
With artificial feeding, it is impossible to abruptly transfer the baby to a qualitatively new food and without the need to change the mixture. It is very important to properly control the amount of feeding. For each age, the daily volume is calculated, which is divided by the number of doses. This is done so that the actual volumes eaten by the baby do not exceed the calculated recommended norms. To calculate the amount of feeding for the baby yourself, you should rely on the following data.
It is very important to properly control the amount of feeding. For each age, the daily volume is calculated, which is divided by the number of doses. This is done so that the actual volumes eaten by the baby do not exceed the calculated recommended norms. To calculate the amount of feeding for the baby yourself, you should rely on the following data.
- For a child in the first days of life, the volume of feedings (day and night) per day should be 1/5 of the child's body weight. Approximately 600-900
- In the first 2 months, the volume of feeding per day should not exceed 1/5-1/6 of the child's body weight. For example, if a child weighs 4 kilograms, then he should eat no more than 800 g of the mixture per day.
- For a 2-4 month old baby, the daily formula is 1/6 of body weight (800-1000 g)
- For a 4-6 month old baby, the maximum daily amount of formula should be 1/7 of body weight (900-1000 g).
- After six months and up to 9 months, the baby should eat within the daily volume of the mixture not exceeding 1/8 of his body weight (1000-1100 g).
- At the age of 9–12 months, the daily volume of milk formula is already 1/9 of the child's body weight (1100–1200 g).
To calculate the volume of each feeding, it is necessary to divide the calculated daily volume of milk formula by the optimal number of feedings. With artificial feeding of children in the first months of life, as a rule, 6-7 meals a day are recommended after 3 or 3.5 hours with a 6.5 or 6-hour break.
0-2 months - 7-10 feedings per day
2-4 months - 6-7 feedings per day
4-6 months - 5-6 feedings per day
6-12 months - 4-5 feedings per day
If a child has at least some deviations in development, a lag in weight gain, then you should definitely consult with a pediatrician to draw up a baby nutrition plan!
Most doctors and infant nutritionists agree that “free” (on demand) feeding is optimal for a baby. To meet the needs of the child, it is important for parents to listen to the child. However, when a child is bottle-fed, you should pay attention to some nuances. Already in the first days of life, babies show their individual character - one eats in moderation, the other can overeat. Therefore, when feeding with milk formulas, it is recommended to stick to the golden mean and choose a partially limited "free mode", when there are no restrictions on the time and frequency of feeding, but the volume of the mixture eaten is controlled.
However, when a child is bottle-fed, you should pay attention to some nuances. Already in the first days of life, babies show their individual character - one eats in moderation, the other can overeat. Therefore, when feeding with milk formulas, it is recommended to stick to the golden mean and choose a partially limited "free mode", when there are no restrictions on the time and frequency of feeding, but the volume of the mixture eaten is controlled.
From the first days of the transition to artificial feeding, it is important to carefully monitor the reactions of the baby and record them. The best option is to keep a child's food diary, where you need to write down all the nuances associated with feeding: time, amount of food, baby's reactions after feeding. If necessary, such a diary will help you and your baby's pediatrician adjust the schedule and volume of feedings, as well as understand the possible causes of problems with nutrition and growth.
After a year, the time comes to transfer the child to a diet that is closest to what is eaten in the family.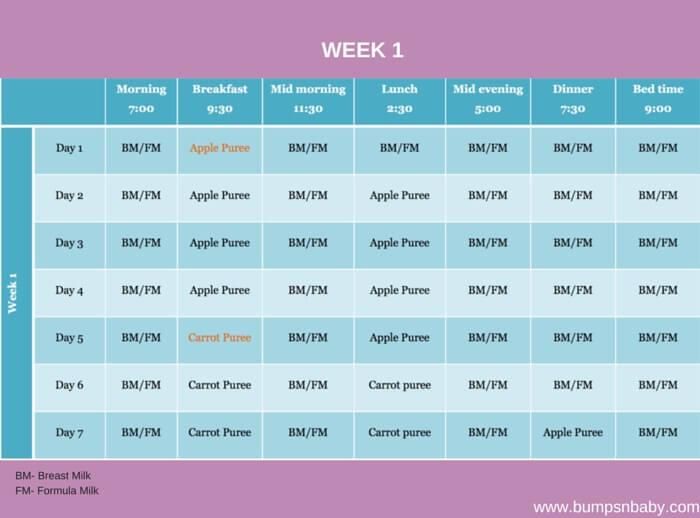 And then the question arises of when to give up formula milk. If up to a year a child is breastfed or artificially fed and does not particularly need regular milk, then after a year it becomes an important source of nutrients: calcium, phosphorus, vitamins, proteins, fats and carbohydrates. But even the best cow's milk in its original form is not suitable for feeding young children. Why?
And then the question arises of when to give up formula milk. If up to a year a child is breastfed or artificially fed and does not particularly need regular milk, then after a year it becomes an important source of nutrients: calcium, phosphorus, vitamins, proteins, fats and carbohydrates. But even the best cow's milk in its original form is not suitable for feeding young children. Why?
It's all about the large amount of casein - a protein that is difficult to digest and thereby increases the load on the child's digestive systems, which do not produce enough hydrochloric acid and enzymes to digest casein.
The ideal option for children from one year old is special baby milk or a milk drink that will provide the child's body with all the necessary nutrients, helping to occur a natural transition and adaptation to the next, adult, stage of nutrition. Valio specialists have developed a special baby milk Valio Baby 3, which can be used with mixed and artificial feeding. It is ideal for children from one year old, who become more mobile and active every day. You can also learn more about the correct complementary foods menu in our blog.
It is ideal for children from one year old, who become more mobile and active every day. You can also learn more about the correct complementary foods menu in our blog.
5 1
FoodShare:
Author: Reetta Tikanmäki
Palm oil in baby food
Infant milk formulas are made from cow's milk. However, in terms of fat composition, it differs significantly from that of the mother.
Read
Author: Ivargizova Oksana
How to choose milk formula for a baby
Breast milk is the best food for a newborn baby. It contains all the necessary nutritional components that fully meet the needs of the child and are necessary for his healthy and harmonious development.
It contains all the necessary nutritional components that fully meet the needs of the child and are necessary for his healthy and harmonious development.
Read
Show all
Baby menu at 9 months
6-12 months
Article
5/5 1 reviews
Although breast milk or formula remains the mainstay of infant nutrition at this age, a 9-month-old baby's menu becomes more varied with new complementary foods. The correct diet of the child is the basis of his harmonious development, good health and good mood. But how to organize a diet, what can be given at this age and how much should a child eat at one meal?
8 min. for reading Feb.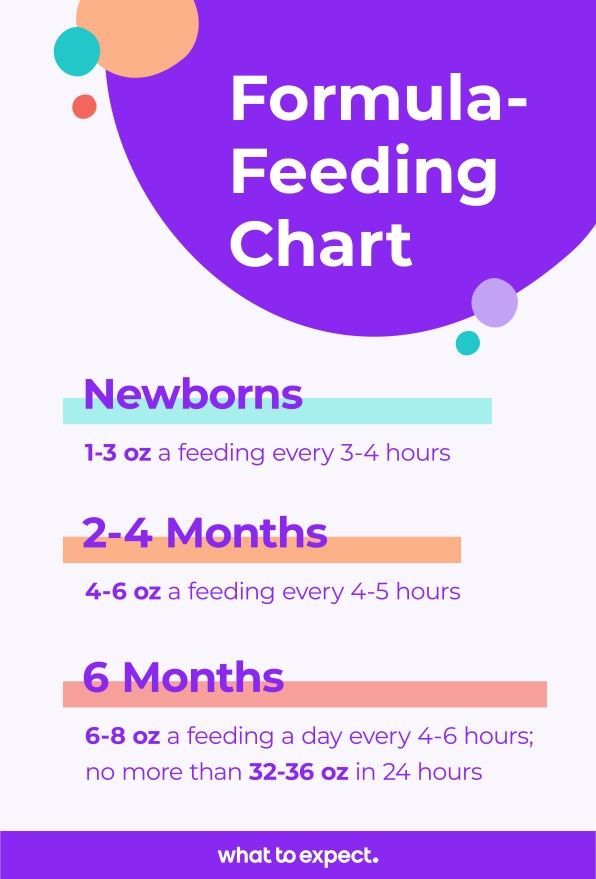 17, 2022
17, 2022
The correct diet for a nine-month-old baby includes 5 meals: a day the baby receives liquid food twice and thick food three times. This is due to the fact that mashed potatoes and cereals take longer to digest than milk, so they give the baby a longer energy supply. Feeding is usually carried out at intervals of 4 hours. If the baby asks to eat 2-3 hours after liquid food, offer her a baby snack, fruit or vegetable (in small pieces or in the form of a puree).
A 9-month-old baby's daily diet includes many healthy foods and drinks that provide essential nutrients such as vitamins, proteins, carbohydrates, fats and minerals. In addition to milk and infant formula, the following products can be given to a child:
- Fruits and vegetables in the form of puree (apple, pear, cauliflower, etc.)
- Fruit juices and compotes without sugar.
- Meat in various forms.
- Fish.
- Kashi from various cereals.
- Chicken or quail egg yolk.

- Children's fresh cottage cheese.
- Children's low-fat kefir.
- Children's cookies, croutons, bread.
Read also: The baby refuses new foods
According to WHO recommendations, by the 9th month, all of the above products should already be on the menu. If something from the food is still unfamiliar to your child, it is recommended to gradually add it to the diet.
Start with smaller portions and see how your child reacts to the new food. If there is no allergic reaction to the product, you can increase the volume and add it to new dishes. New complementary foods are recommended to be introduced at intervals of 5-7 days. An indicative table for one day will help to create an optimal diet for health. It also shows how much formula or milk the baby should eat per day.
* infant formula.
**Dairy-free porridge should be diluted with breast milk or infant formula given to the baby. Milk porridge is diluted with water.
| I feeding 6 hours | Breast milk or formula for infants with cow's milk protein intolerance | 200 ml |
| II feeding 10 hours | Dairy-free porridge* | 180 g |
| Vegetable oil < | about 1 tsp | |
| Fruit puree (apple, pear) | 70 g | |
| III feeding 14 hours | Vegetable puree or pureed soup | 180 g |
| Vegetable oil | about 1 tsp | |
| Meat puree (rabbit, turkey) | 50 g | |
| Fruit juice | 70 g | |
| IV feeding 18 hours | Fruit puree | 50 g |
| Vegetable puree or dairy-free porridge | 180 g | |
| Vegetable oil | about 1 tsp | |
| Meat puree | 50 g | |
| V feeding 22 hours | Breast milk or formula for infants with cow's milk protein intolerance | 200 ml |
*dairy-free porridge should be diluted with breast milk or it is safe for children with allergies to cow's milk proteins.
** you can eat porridge or vegetables, so you can eat grass - porridge with vegetables.
1st day
| First breakfast | Breast milk or formula |
| Second breakfast | Buckwheat porridge with pumpkin, juice |
| Lunch | Pumpkin steam cutlets, veal puree |
| Snack | Rusks or baby biscuits, yoghurt |
| Dinner | Cauliflower puree |
| Second dinner | Breast milk or formula |
2nd day
| First breakfast | Breast milk or formula |
| Second breakfast | Oatmeal, berry juice |
| Lunch | Steamed fish, rice, fruit compote |
| Snack | Vegetable puree |
| Dinner | Vegetable puree |
| Second supper | Breast milk or formula |
3rd day
| First breakfast | Breast milk or formula |
| Second breakfast | Semolina porridge, quail egg yolk |
| Lunch | Steamed zucchini, boiled veal, apple compote |
| Snack | Pumpkin and apple puree |
| Dinner | Curd casserole with carrots |
| Second supper | Breast milk or formula |
Fourth day
| First breakfast | Breast milk or formula |
| Second breakfast | Rice porridge, fruit puree |
| Lunch | Mashed potatoes or turkey meatball soup |
| Snack | Carrot Apple Juice |
| Dinner | Kefir |
| Second supper | Breast milk or formula |
5th day
| First breakfast | Breast milk or formula |
| Second breakfast | Oatmeal and apple puree |
| Lunch | Cream soup with chicken and vegetables |
| Snack | Carrot juice |
| Dinner | Cauliflower puree, crackers or bread |
| Second supper | Breast milk or formula |
6.
 Sixth day
Sixth day | First breakfast | Breast milk or formula |
| Second breakfast | Rice porridge, half yolk (chicken egg) |
| Lunch | Vegetable soup with chicken breast, juice |
| Snack | Baked apple |
| Dinner | Spinach mashed potatoes |
| Second supper | Breast milk or formula |
7th day
| First breakfast | Breast milk or formula |
| Second breakfast | Millet porridge, croutons |
| Lunch | Steamed chicken cutlets, vegetable puree |
| Snack | Apple juice |
| Dinner | Curd with fruits |
| Second dinner | Breast milk or formula |
Parents need to gradually accustom the child to eating solid food, because now he is moving to a new level of development: more teeth appear, so the baby can now chew food. If this is not done in a timely manner, a baby may refuse solid food in a year. Changing the consistency of dishes favorably affects the development of the digestive system.
If this is not done in a timely manner, a baby may refuse solid food in a year. Changing the consistency of dishes favorably affects the development of the digestive system.
No need to grind fish and potatoes in a blender - just put the food on a plate and mash well with a fork. Meat can be offered in the form of meatballs to develop chewing skills. It can be turkey, rabbit, veal, beef, chicken. The norm of meat for one meal is 60-70 g.
It is quite normal if at first large pieces in a dish cause discontent in a child or even a gag reflex - he will soon get used to it. Sometimes it happens the other way around - the baby willingly tries the pieces, but refuses pureed food. Treat your baby with apple slices, bread, crackers or baby snacks. But the meat is still better to grind thoroughly.
At this age, consumption of mother's milk or adapted formula decreases. There are only two feedings per day - in the morning and in the evening. Everything else is "adult" food. Ideally, the baby should sleep through the night and get up at 06:00-07:00. If the little one wakes up at night, it is already possible to gradually wean him from feeding at night (provided that he is gaining weight normally). You can consult with your pediatrician about this.
Ideally, the baby should sleep through the night and get up at 06:00-07:00. If the little one wakes up at night, it is already possible to gradually wean him from feeding at night (provided that he is gaining weight normally). You can consult with your pediatrician about this.
Please note that uneaten food (already cooked) must not be stored and reheated. It is also not recommended to add sugar and salt to the dish.
If you give your child ready-made baby puree, we recommend that you do not feed him immediately from a jar, but pour the right amount onto a plate. In this case, the rest can be stored in the refrigerator for another 24 hours.
Find out more: Baby Portion
Pay attention to the quality of food you cook: appearance, smell and expiration date. It is better to use seasonal vegetables and fruits, and shop in trusted places.
Wash food thoroughly under running water before cooking. You can also use special children's products for washing fruits and vegetables.
All products must be brought to full readiness, and then thoroughly crushed to the desired consistency, so that the baby can comfortably chew small pieces. After eating, wash the dishes with a special detergent.
How to properly feed a 9-month-old baby if he refuses food and does not eat the foods you suggest?
Poor appetite is one of the indicators of a baby's health. The problem may concern the digestive tract, glucose levels, central nervous system. The feeling of hunger appears when the level of sugar in the blood decreases. But for this you need to take breaks between meals. Also, the smell of food affects the appetite - it causes the release of gastric juice.
How to restore your appetite:
- observe the diet;
- develop a delicious menu for a baby at 9 months;
- Serve dishes beautifully and set the table;
- ventilate the room before eating;
- let the baby use cutlery.
See also: Baby doesn't eat well, how to feed?
In order for the baby to eat willingly, he must be in a good mood. Try to avoid stressful and nervous situations, feed him in a calm, comfortable atmosphere.
Try to avoid stressful and nervous situations, feed him in a calm, comfortable atmosphere.
If the baby refuses to eat or eats very slowly, do not rush or force him to eat. Also, do not force the little one to eat foods that he refuses. Otherwise, in the future, he will have a negative attitude towards the feeding process, refuse to eat any food at all. He can even feel sick and vomit only with one kind of food.
Important
Games and cartoons during meals do not really improve appetite. On the contrary, in this way you only teach the baby to eat without noticing the dishes.
With the help of our tips, you can create a menu for a child at 9 months for every day, which will meet the requirements of a healthy diet and preferences of the baby
1. What should not be given to a child at 9 months?
It is not recommended to give cow's milk until the age of one. It contains too much calcium, which overloads the kidneys, and protein, which is poorly digested.