What causes yeast infection of the mouth
Oral thrush - Symptoms and causes
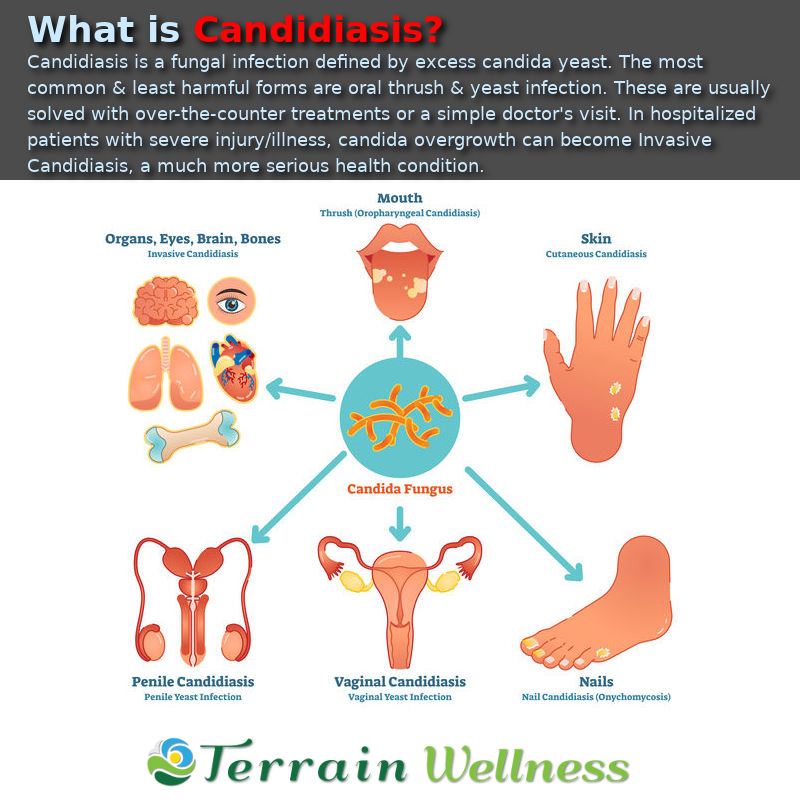
Overview
Oral thrush
Oral thrush
Oral thrush produces slightly raised, creamy white, sore patches in your mouth or on your tongue.
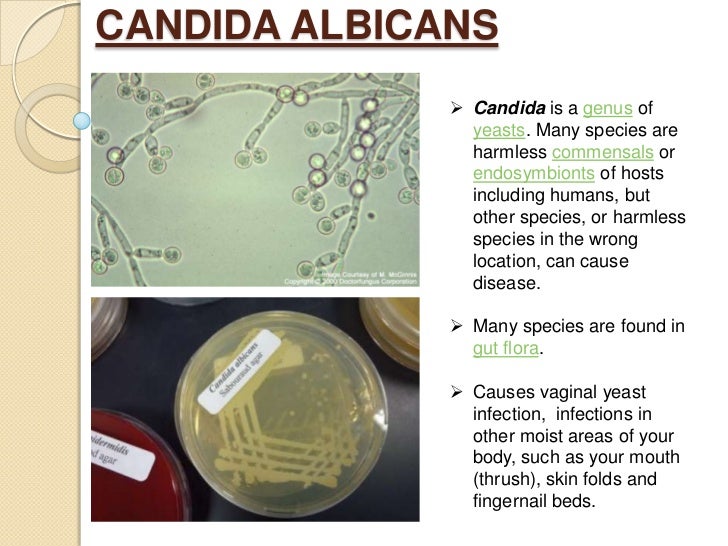
Oral thrush — also called oral candidiasis (kan-dih-DIE-uh-sis) — is a condition in which the fungus Candida albicans accumulates on the lining of your mouth. Candida is a normal organism in your mouth, but sometimes it can overgrow and cause symptoms.
Oral thrush causes creamy white lesions, usually on your tongue or inner cheeks. Sometimes oral thrush may spread to the roof of your mouth, your gums or tonsils, or the back of your throat.
Although oral thrush can affect anyone, it's more likely to occur in babies and older adults because they have reduced immunity; in other people with suppressed immune systems or certain health conditions; or people who take certain medications. Oral thrush is a minor problem if you're healthy, but if you have a weakened immune system, symptoms may be more severe and difficult to control.
Products & Services
- Book: Mayo Clinic Book of Home Remedies
Symptoms
Children and adults
Initially, you may not even notice symptoms of oral thrush. Signs and symptoms may include:
- Creamy white lesions on your tongue, inner cheeks, and sometimes on the roof of your mouth, gums and tonsils
- Slightly raised lesions with a cottage cheese-like appearance
- Redness, burning or soreness that may be severe enough to cause difficulty eating or swallowing
- Slight bleeding if the lesions are rubbed or scraped
- Cracking and redness at the corners of your mouth
- A cottony feeling in your mouth
- Loss of taste
- Redness, irritation and pain under dentures (denture stomatitis)
In severe cases, usually related to cancer or a weakened immune system from HIV/AIDS, the lesions may spread downward into your esophagus — the long, muscular tube stretching from the back of your mouth to your stomach (Candida esophagitis). If this occurs, you may experience difficulty swallowing and pain or feel as if food is getting stuck in your throat.
If this occurs, you may experience difficulty swallowing and pain or feel as if food is getting stuck in your throat.
Infants and breast-feeding mothers
In addition to the distinctive white mouth lesions, infants may have trouble feeding or be fussy and irritable. They can pass the infection to their mothers during breast-feeding. The infection may then pass back and forth between the mother's breasts and the baby's mouth.
Women whose breasts are infected with candida may experience these signs and symptoms:
- Unusually red, sensitive, cracked or itchy nipples
- Shiny or flaky skin on the darker, circular area around the nipple (areola)
- Unusual pain during nursing or painful nipples between feedings
- Stabbing pains deep within the breast
When to see a doctor
If you or your child develops white lesions inside the mouth, see your doctor or dentist.
Thrush is uncommon in healthy older children, teenagers and adults, so if thrush develops, see your doctor to determine if further evaluation is needed to check for an underlying medical condition or other cause.
Request an Appointment at Mayo Clinic
From Mayo Clinic to your inbox
Sign up for free, and stay up to date on research advancements, health tips and current health topics, like COVID-19, plus expertise on managing health. Click here for an email preview.
To provide you with the most relevant and helpful information, and understand which information is beneficial, we may combine your email and website usage information with other information we have about you. If you are a Mayo Clinic patient, this could include protected health information. If we combine this information with your protected health information, we will treat all of that information as protected health information and will only use or disclose that information as set forth in our notice of privacy practices. You may opt-out of email communications at any time by clicking on the unsubscribe link in the e-mail.
You may opt-out of email communications at any time by clicking on the unsubscribe link in the e-mail.
Causes
Normally, your immune system works to repel harmful invading organisms, such as viruses, bacteria and fungi, while maintaining a balance between "good" and "bad" microbes that normally inhabit your body. But sometimes these protective mechanisms fail, increasing the number of candida fungus and allowing an oral thrush infection to take hold.
The most common type of candida fungus is Candida albicans. Several factors, such as a weakened immune system, can increase your risk of oral thrush.
Risk factors
You may have an increased risk of oral thrush infection if any of these issues apply:
- Weakened immunity. Oral thrush is more likely to occur in infants and older adults due to reduced immunity. Some medical conditions and treatments can suppress your immune system, such as cancer and its treatments, organ transplantation and required drugs that suppress the immune system, and HIV/AIDS.
- Diabetes. If you have untreated diabetes or the disease isn't well-controlled, your saliva may contain large amounts of sugar, which encourages the growth of candida.
- Vaginal yeast infections. Vaginal yeast infections are caused by the same fungus that causes oral thrush. You can pass the infection to your baby.
- Medications. Drugs such as prednisone, inhaled corticosteroids, or antibiotics that disturb the natural balance of microorganisms in your body can increase your risk of oral thrush.
- Other oral conditions. Wearing dentures, especially upper dentures, or having conditions that cause dry mouth can increase the risk of oral thrush.
Complications
Oral thrush is seldom a problem for healthy children and adults.
For people with lowered immunity, such as from cancer treatment or HIV/AIDS, thrush can be more serious. Untreated oral thrush can lead to more-serious systemic candida infections. If you have a weakened immune system, thrush may spread to your esophagus or other parts of your body.
If you have a weakened immune system, thrush may spread to your esophagus or other parts of your body.
Prevention
These measures may help reduce your risk of developing candida infections:
- Rinse your mouth. If you need to use a corticosteroid inhaler, be sure to rinse your mouth with water or brush your teeth after taking your medication.
- Brush your teeth at least twice a day and floss daily or as often as your dentist recommends.
- Check your dentures. Remove your dentures at night. Make sure dentures fit properly and don't cause irritation. Clean your dentures daily. Ask your dentist for the best way to clean your type of dentures.
- See your dentist regularly, especially if you have diabetes or wear dentures. Ask your dentist how often you need to be seen.
- Watch what you eat. Try limiting the amount of sugar-containing foods you eat. These may encourage the growth of candida.

- Maintain good blood sugar control if you have diabetes. Well-controlled blood sugar can reduce the amount of sugar in your saliva, discouraging the growth of candida.
- Treat a vaginal yeast infection as soon as possible.
- Treat dry mouth. Ask your doctor about ways to avoid or treat your dry mouth.
By Mayo Clinic Staff
Related
Associated Procedures
Products & Services
Thrush: Symptoms, Causes & Treatment
Overview
A thrush infection in your mouth looks like cottage cheese — raised, white lesions that may bleed when you scrape them.What is thrush?
Thrush is a fungal (yeast) infection that can grow in your mouth, throat and other parts of your body. With oral thrush (oral candidiasis), you may develop white, raised, cottage cheese-like lesions (spots) on your tongue and cheeks. Thrush can quickly become irritated and cause mouth pain and redness.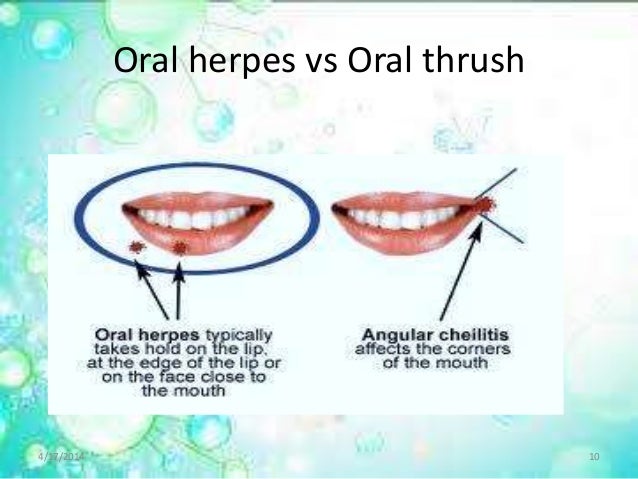
Thrush happens when there’s an overgrowth of Candida, a type of fungus. Another name for thrush in your mouth or throat is oropharyngeal candidiasis.
Healthcare providers treat thrush with antifungal medication. If your immune system is healthy, thrush is a minor problem that goes away a couple of weeks after you start treatment.
Who can get thrush?
While thrush can affect anyone, some people are more at risk, including:
- Babies under 1 month old.
- Toddlers.
- Adults aged 65 or over.
- People with weakened immune systems (where symptoms are harder to control).
Symptoms and Causes
What are the symptoms of thrush?
Thrush usually develops suddenly. A common sign is the presence of creamy white, slightly raised lesions in your mouth — usually on your tongue or inner cheeks. You may also have lesions on the roof of your mouth, gums, tonsils or back of your throat.
Other symptoms may include:
- Redness and soreness inside and at the corners of your mouth.

- Loss of sense of taste (ageusia).
- Cottony feeling in your mouth.
The lesions can hurt and may bleed a little when you scrape them or brush your teeth. In severe cases, the lesions can spread into your esophagus and cause:
- Pain or difficulty swallowing.
- A feeling that food gets stuck in your throat or mid-chest area.
- Fever, if the infection spreads beyond your esophagus.
Thrush can spread to other parts of your body, including your lungs, liver and skin. This happens more often in people with cancer, HIV or other conditions that weaken the immune system.
What causes thrush?
Most people have small amounts of the Candida fungus in their mouth, digestive tract and skin. When illnesses, stress or medications disturb this balance, the fungus grows out of control and causes thrush.
Medications that can make yeast flourish and cause infection include:
- Corticosteroids.
- Antibiotics.
- Birth control pills.
Is thrush contagious?
Thrush can be contagious to those at risk (like people with weakened immune systems or who take certain medications). In people with healthy immune systems, it’s unusual to pass thrush through kissing or other close contact. In most cases, thrush isn’t particularly contagious (meaning, it doesn’t spread from person to person), but it is transmittable (meaning, you can catch it in other ways).
If you’re worried about getting thrush from another person who has it, avoid coming into contact with their saliva (spit). It’s smart to wash your hands as often as possible if you’re near someone who has thrush.
What are the risk factors for thrush?
Candida infection is more likely to develop in babies and people with:
- Diabetes.
- Anemia.
- HIV/AIDS (thrush in your esophagus — or swallowing tube — is common in this group).
- Cancer.
- Dry mouth (xerostomia).
- Pregnancy (due to the hormonal changes that occur).

- Smoking.
- Ill-fitting dentures.
What are the complications of thrush?
Thrush rarely causes complications in people with healthy immune systems. But if you have a weakened immune system, Candida can enter your bloodstream and spread to other areas of your body, such as your eyes, brain or heart. This type of infection is serious and may lead to septic shock, a life-threatening condition.
Diagnosis and Tests
How is thrush diagnosed?
A healthcare provider can usually tell right away if you have thrush by looking for the distinctive white lesions on your mouth, tongue or cheeks. Lightly brushing the lesions away reveals a reddened, tender area that may bleed slightly. A microscopic exam of tissue from a lesion can confirm whether or not you have thrush.
If thrush extends into your esophagus, your healthcare provider might:
- Take a throat culture (swab the back of your throat with sterile cotton and study the microorganisms under a microscope).

- Perform an endoscopy of your esophagus, stomach and small intestine (examine the lining of these areas with a lighted camera mounted on the tip of a flexible tube).
- Take X-rays of your esophagus.
Management and Treatment
How is thrush treated?
The typical treatment for thrush is antifungal medications:
Antifungal medications
Healthcare providers usually prescribe antifungals (like nystatin) to treat thrush. These medicines are available in tablets, lozenges or liquids that are “swished” around in your mouth before swallowing. Usually, you need to take these medications for 10 to 14 days. Your healthcare provider will recommend specific treatment based on your age and the cause of the infection.
Kids and adults with healthy immune systems typically respond well to antifungal treatment. But thrush symptoms may be more severe and harder to treat in those with weakened immune systems.
How soon after treatment will I feel better?
Antifungals can clear up thrush in one to two weeks. You may need to continue the medication for a few more days to kill any fungus that’s left behind.
You may need to continue the medication for a few more days to kill any fungus that’s left behind.
Prevention
How can I lower my risk for thrush?
You can do these things to reduce your risk for thrush:
- Practice good oral hygiene. Brush your teeth at least twice a day and floss at least once a day.
- Avoid certain mouthwashes or sprays. Some of these products can destroy the normal balance of microorganisms in your mouth. Talk to your dentist or doctor about which ones are safe to use.
- See your dentist regularly. This is especially important if you have diabetes or wear dentures.
- Limit the amount of sugar and yeast-containing foods you eat. Foods such as bread, beer and wine encourage Candida growth.
- Avoid smoking and other tobacco use. Ask your healthcare provider about ways to help you quit smoking.
Outlook / Prognosis
What can I expect if I have thrush?
With treatment, thrush usually goes away within one to two weeks. But if your symptoms linger or get worse, let your healthcare provider know.
But if your symptoms linger or get worse, let your healthcare provider know.
Living With
When should I see my healthcare provider?
If you develop signs or symptoms of thrush — such as soreness, bleeding or raised white areas inside your mouth — schedule an appointment with a healthcare provider.
If you’ve already taken antifungals for thrush but your symptoms return, call your provider right away. It could indicate a more serious infection.
Frequently Asked Questions
Are there any home remedies for oral thrush?
You’ll need antifungal medication to clear up thrush. But you might try some of these home remedies to ease your symptoms:
- Swish with warm saltwater.
- Take probiotics.
- Eat yogurt that contains healthy bacteria.
Why is thrush a concern during breastfeeding (chestfeeding)?
Because infants are more at risk, getting or giving thrush during breastfeeding (chestfeeding) is a concern among parents. It’s a common breastfeeding issue, and in some cases, treatment can be tricky.
It’s a common breastfeeding issue, and in some cases, treatment can be tricky.
If your baby has thrush, they can pass the infection to you during breastfeeding. Likewise, if you develop a thrush infection around your breasts or nipples, you can pass the infection to your baby.
If you and your baby both have thrush, it’s important to receive treatment at the same time to prevent an ongoing exchange of the infection.
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Thrush is a fungal infection that affects your mouth, throat and other areas of your body. It’s an uncomfortable and inconvenient condition. But in people with healthy immune systems, it’s easily treatable with antifungal medications. People with compromised immune systems may have a more difficult time getting rid of thrush. If you develop thrush symptoms, contact your healthcare provider. Prompt treatment can get you back on track and feeling better.
Oral candidiasis (thrush) - symptoms and treatment
Oral candidiasis is an inflammatory disease that develops against the background of damage to the mucous membranes by fungi of the genus Candida.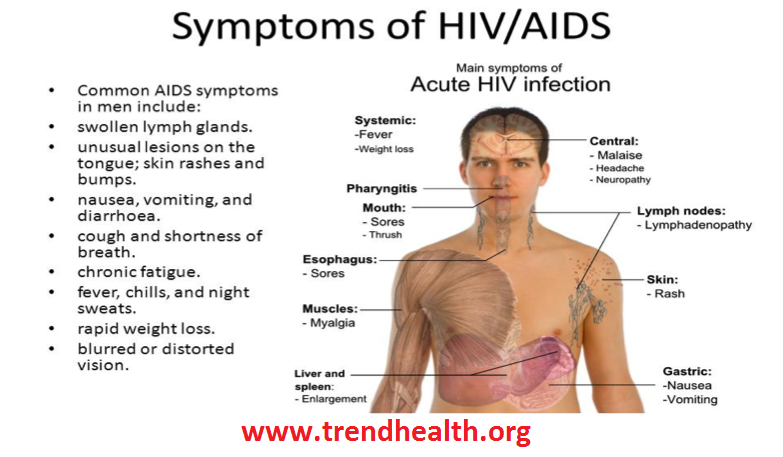 This is usually associated with a deterioration in local and general immunity. According to studies, up to 90% of the adult population is carriers of this fungus, but the disease most often does not develop, since under normal conditions the pathogen does not act aggressively.
This is usually associated with a deterioration in local and general immunity. According to studies, up to 90% of the adult population is carriers of this fungus, but the disease most often does not develop, since under normal conditions the pathogen does not act aggressively.
Causes of candidiasis
Thrush in the mouth in an adult is a mucosal lesion that may indicate serious health problems. For the reproduction of the fungus, special conditions are necessary. Most often, the disease occurs in patients who neglect oral hygiene. The presence of caries, inflammatory gum disease increases the chances of developing fungal inflammation. This is due to the fact that a large number of pathogenic microorganisms depletes the defense mechanisms.
The second group of reasons is the weakening of the immune system due to a number of diseases and conditions:
-
HIV, diabetes mellitus;
-
oncological diseases;
-
dystrophy, deficiency of vitamins, minerals;
-
surgeries, severe infections, etc.
There are also specific reasons for the development of thrush. It may appear after prolonged and powerful antibiotic therapy. The use of antibiotics leads to the destruction of beneficial flora and imbalance. This causes the active reproduction of Candida.
Oral candidiasis also develops against the background of inhaled corticosteroids. Usually the lesion has the appearance of erythema and appears in areas where the drug has come into contact with the mucosa: in the palate, tongue.
Features of the diet affect the likelihood of developing candidiasis. So, the predominance of carbohydrates predisposes to the activity of the fungus. The growth of Candida and its attachment to the mucosa are enhanced in the presence of sugars.
Bad habits increase the chances of developing leukoplakia, lichen planus and other diseases. Especially when it comes to smoking. Candidiasis often develops in patients with tongue piercings.
The presence of removable dentures is also a risk factor if the patient does not follow the rules of hygiene. In the absence of high-quality cleansing, the prosthesis is covered with a biofilm, which contains a lot of fungi. Disinfection is the main measure for the prevention of the disease and part of the complex treatment for progressive oral candidiasis. If the patient does not remove the structure at night, this also increases the likelihood of developing the disease. The mucous membrane remains without oxygen for a long time, is not washed by saliva - these conditions are suitable for the development of fungi and anaerobic microorganisms. The prosthesis can injure the mucous membranes if it does not fit. Microtraumas weaken local defenses and contribute to the onset of the development of a fungal infection. Injuries can also be associated with sharp chipped teeth and fillings, chemical and thermal burns.
In the absence of high-quality cleansing, the prosthesis is covered with a biofilm, which contains a lot of fungi. Disinfection is the main measure for the prevention of the disease and part of the complex treatment for progressive oral candidiasis. If the patient does not remove the structure at night, this also increases the likelihood of developing the disease. The mucous membrane remains without oxygen for a long time, is not washed by saliva - these conditions are suitable for the development of fungi and anaerobic microorganisms. The prosthesis can injure the mucous membranes if it does not fit. Microtraumas weaken local defenses and contribute to the onset of the development of a fungal infection. Injuries can also be associated with sharp chipped teeth and fillings, chemical and thermal burns.
Dryness of the oral cavity due to decreased salivation, changes in the viscosity of saliva, its composition is one of the causes of candidiasis. This may be due to other diseases, so it is important to find out the causes of dryness in order to effectively deal with the consequences.
Oral candidiasis is more common in children. The immaturity of the immune system, the colonization of the oral cavity by Candida from the vaginal canal of the mother during natural childbirth lead to the fact that the disease develops in early infancy. However, older children can also suffer from an illness, which is associated with a weakening of the immune forces.
Types of oral candidiasis and symptoms
Manifestations of oral candidiasis may vary from patient to patient. This is due to the degree of damage to the mucous membranes, as well as the specific type of disease. There are four forms:
-
acute pseudomembranous;
-
acute atrophic;
-
chronic atrophic;
-
chronic hyperplastic.
Although the treatment regimen for all forms is almost the same, the symptoms can vary significantly. Let's consider them in more detail.
Acute pseudomembranous candidiasis
This form of oral candidiasis may be asymptomatic. There is slight discomfort due to a white film or small plaques rising above the mucosa. With a mild course, one or more plaques appear, they are easily removed by scraping, and the mucosal area under them has a bright red color. In severe cases, large plaques appear in large numbers. They can merge, forming large areas of damage. Sometimes the symptoms cover the entire mucous membrane. When the plaques thicken, their removal becomes problematic. A severe course is more typical for infants, as well as in adult patients after antibiotic therapy, corticosteroids, immunosuppressants.
There is slight discomfort due to a white film or small plaques rising above the mucosa. With a mild course, one or more plaques appear, they are easily removed by scraping, and the mucosal area under them has a bright red color. In severe cases, large plaques appear in large numbers. They can merge, forming large areas of damage. Sometimes the symptoms cover the entire mucous membrane. When the plaques thicken, their removal becomes problematic. A severe course is more typical for infants, as well as in adult patients after antibiotic therapy, corticosteroids, immunosuppressants.
Acute and chronic atrophic candidiasis
Acute atrophic candidiasis is accompanied by severe burning. There may be no white plaque, and the mucous membrane becomes bright red. Many patients report a metallic, sour, salty, or bitter taste in their mouths. A characteristic manifestation of the disease is dry mouth. This form of the disease is often associated with drug therapy.
In chronic atrophic candidiasis, redness and burning are less pronounced. Usually the disease develops against the background of the installation and wearing of prostheses.
Usually the disease develops against the background of the installation and wearing of prostheses.
Chronic hyperplastic candidiasis
This form of the disease is typical for adults. Oral thrush can spread to the mucous membranes of the cheeks, the corners of the mouth and lips, the back of the tongue, and the soft palate. One of the symptoms is the appearance of white plaques that tend to merge with each other. As the disease progresses, their surface becomes rough, rough. Over time, the elements may turn yellow. Formations merge with mucous membranes and it is impossible to remove them.
Diagnostic methods
Treatment by a general dentist. Diagnosis begins with an examination and a detailed survey: the doctor will find out what drugs you have taken recently, whether there are chronic and infectious diseases. A cytological examination of plaque taken from the mucosa is mandatory. This is important because the accumulation of non-fungal flora can be easily confused with a fungal infection.
Scraping is performed in the morning, on an empty stomach, it is not necessary to brush your teeth before the procedure. On the eve, it is important to refuse to eat foods rich in carbohydrates so as not to provoke the growth of pathogenic flora. Studies allow not only to accurately determine the pathogen and type of Candida fungus, but also to find out the sensitivity of fungi to the main antifungal drugs. Based on the results of the tests, the doctor will determine the fungus in the oral cavity and prescribe medication.
Features of treatment
The basis of treatment is systemic and local antifungal drugs. Today they are widely represented on the pharmaceutical market, but it is important to know that the level of Candida fungus resistance to fixed assets is growing every year. For example, resistance to drugs such as Fluconazole is almost complete. Previously, this remedy was used in almost all cases of the disease, but today doctors are forced to revise standard treatment regimens.
Treatment of thrush in the mouth in adults is selected individually. The choice of a systemic antifungal agent is based on the type of pathogen, the patient's condition and the individual characteristics of his health. There are agents to which the infection has minimal resistance. The doctor may prescribe drugs based on nystatin, imidazole derivatives, etc.
In addition, local funds must be used:
-
mouth rinses;
-
gels and suspensions for application to affected areas;
-
topical lozenges and lozenges;
-
irrigation solutions and aerosols;
-
ointments for laying in the oral cavity on a cotton-gauze swab, etc.
Your healthcare provider may prescribe an over-the-counter antiseptic or mild saline rinse. Usually, solutions based on iodine, chlorhexidine, potassium permanganate, gentian violet, sodium tetraborate in glycerin are used. Some pills the doctor may recommend laying on the cheek.
Conditions for effective treatment
Effective treatment of oral thrush involves addressing the underlying cause. It is very important to sanitize the oral cavity: to cure teeth destroyed by caries, to remove non-viable teeth and roots that can no longer be restored. These are chronic foci of inflammation, so simultaneous sanitation will shorten the treatment time. Tartar and plaque should also be removed. This is especially true in cases of candidal stomatitis associated with trauma to the gums with sharp edges of hard dental deposits.
Patients with removable dentures should be retrained in hygiene and disinfection of prosthetic structures. If the time of using the prosthesis comes to an end, it is important to replace it in a timely manner. Treatment of candidiasis will be useless if a person uses the prosthesis incorrectly and again creates conditions for the reproduction of fungi in the oral cavity.
Unsuitable crowns, bridges and other structures are also subject to replacement. It is also important to eliminate enamel chips, which become a source of injury to the gums, mucous membranes of the cheeks and tongue.
It is also important to eliminate enamel chips, which become a source of injury to the gums, mucous membranes of the cheeks and tongue.
Smokers should, if possible, reduce their smoking episodes or give up smoking habits. If the disease developed while taking corticosteroids, it is important to explain the rules of treatment: you should rinse your mouth with plenty of warm water after spraying the drug.
In the treatment of oral candidiasis that has developed against the background of antibiotic therapy, measures should be taken to restore the normal microflora of the intestine and oral cavity. It may be necessary to consult another narrow specialist or therapist: you will need to take probiotics and prebiotics.
For all patients treated for candidiasis, a few general guidelines apply:
-
maintaining oral hygiene;
-
refusal of food rich in carbohydrates;
-
Refusal of sugary drinks.
It is necessary to exclude from the diet food that can irritate the mucous membranes: dishes cooked with vinegar, marinades, spicy, peppery foods, smoked meats, sour fruits and berries. Also, you can not eat confectionery, pastries with yeast, sugar. It is better to give preference to warm dishes. It is necessary to observe such a diet for another 1.5-2 months after recovery.
Also, you can not eat confectionery, pastries with yeast, sugar. It is better to give preference to warm dishes. It is necessary to observe such a diet for another 1.5-2 months after recovery.
In some cases, it is advisable to use toothpastes with glucose oxidase, lysozyme, lactoferrin. They improve the protective forces of the oral mucosa and can be part of a comprehensive prevention of inflammation. The choice of toothpaste must be agreed with the doctor, he will recommend the best remedy, and also tell you which brush is suitable.
Possible complications
If treatment is started late or incorrectly selected, acute oral candidiasis can be transformed into chronic or complicated by the transition to an invasive process that is difficult to treat.
Prevention of candidiasis
Specific prophylaxis of candidiasis in the oral cavity is carried out only in the presence of HIV infection, the patient undergoing radiation therapy, immunosuppressive or antibiotic therapy. In the absence of these risk factors, the doctor will make recommendations for a specific case.
In the absence of these risk factors, the doctor will make recommendations for a specific case.
Prevention of fungal diseases in patients with diabetes mellitus, bronchial asthma, chronic systemic diseases involves control of the underlying pathology. It is important to regularly see a doctor of your profile, take the prescribed funds.
If antibiotic therapy is necessary, the following rules must be followed:
-
take antibiotics only as directed by your doctor;
-
observe a sufficient duration of the course of treatment - do not cancel self-prescribed drugs when relief occurs;
-
if a long course of treatment is needed or if repeated antibiotic therapy is required, take the prescribed antifungal agents for prophylaxis.
When treating asthma, ask your doctor about using nebulizers. After inhalation, it is important to rinse the mouth in order to prevent the negative effects of the drug components on the mucous membranes.
If oral candidiasis often recurs, it is better to undergo a comprehensive examination: a standard medical examination or use specific diagnostic methods that the doctor will select. Fungal infections of the mucous membranes can be a manifestation of an underlying disease that you do not know about. Consult a therapist to find out the exact causes and take action in time.
Thrush in the mouth in adults: symptoms, treatment - ROOTT
Causes Types Danger Treatment Remedial measures Drugs against thrush
Oral candidiasis (thrush) is an infectious disease of the mucous membranes. It is caused by a fungus of the genus Candida.
Mucous membranes are covered with whitish plaques resembling curd mass. Patients have unpleasant sensations in the mouth, a burning sensation. Eating, sometimes even speaking, becomes painful. Patients complain of dry mouth and bad breath.
Thrush is very common in infants but is easily tolerated and heals quickly. It often occurs in people with dentures, those taking corticosteroids, or undergoing chemotherapy.
Causes of the disease
Yeast fungi are present in the body of any person. Under the influence of certain factors, they begin to multiply uncontrollably.
Thrush in the mouth is caused by:
- Hormonal changes, e.g. during pregnancy
- Taking certain medications
- Weakening of immunity due to illness
- Inadequate oral hygiene
- Mucosal injuries
- High carbohydrate diet
- Taking contraceptives
- Smoking
- Candidiasis is contagious, it can be transmitted through shared utensils, kissing.
Classification
Symptoms of thrush manifest themselves in different ways, depending on the form of the disease. In dentistry, the following forms of candidiasis are distinguished:
- Acute pseudomembranous - Mild form: the only symptom is the presence of plaque. If you scrape it off, a swollen, reddened mucous membrane is visible. - Moderate: plaque is difficult to remove, there are unpleasant sensations while eating.
 The submandibular lymph nodes are enlarged. - Severe form: extensive, off-white plaque. Signs of tissue infiltration. Plaques are removed with difficulty, bleeding mucous membrane is visible under them.
The submandibular lymph nodes are enlarged. - Severe form: extensive, off-white plaque. Signs of tissue infiltration. Plaques are removed with difficulty, bleeding mucous membrane is visible under them. - Acute atrophic Mucosa red, painful to touch, smooth. The plaque is dense, covers the cheeks from the inside, tongue, palate. The mouth is dry. There are teeth marks on the tongue. There may be a bitter, sour, metallic taste in the mouth. The acute course can become chronic, usually in patients with removable dentures. Therefore, its second name is prosthetic stomatitis. Under the prosthesis, the mucous membrane is dry, red. There is almost no plaque, but the pain syndrome is pronounced. On the back of the tongue papillae atrophy. This leads to a change in taste sensations. Sometimes atrophic candidiasis is called erythematous ("erythema" - redness).
- Chronic hyperplastic It occurs only in adults, mainly in smokers. The coating is dirty gray, located in the corners of the lips, on the tongue.
 It scrapes off badly, has an unpleasant smell. The plaques merge, covering the mucosa almost completely. Saliva changes: it becomes viscous and foams. The most common such thrush in men.
It scrapes off badly, has an unpleasant smell. The plaques merge, covering the mucosa almost completely. Saliva changes: it becomes viscous and foams. The most common such thrush in men.
Why is thrush dangerous? But candida is a yeast-like fungus, and, therefore, is capable of rapid reproduction, like any yeast. From the mucous membranes of the mouth, thrush can spread to the throat. This causes changes in the voice, makes it hoarse. Spreading to the esophagus, it provokes inflammation of the esophageal mucosa (esophagitis), making it painful for food to pass through it.
Untreated hyperplastic candidiasis develops into malignant neoplasms.
Most importantly, the reproduction of the fungus indicates a malfunction in the body's defenses.
Only a doctor is able to prescribe the necessary examination and, based on its results, prescribe the appropriate treatment for a fungal infection.
How to treat thrush
Successful treatment requires an accurate diagnosis.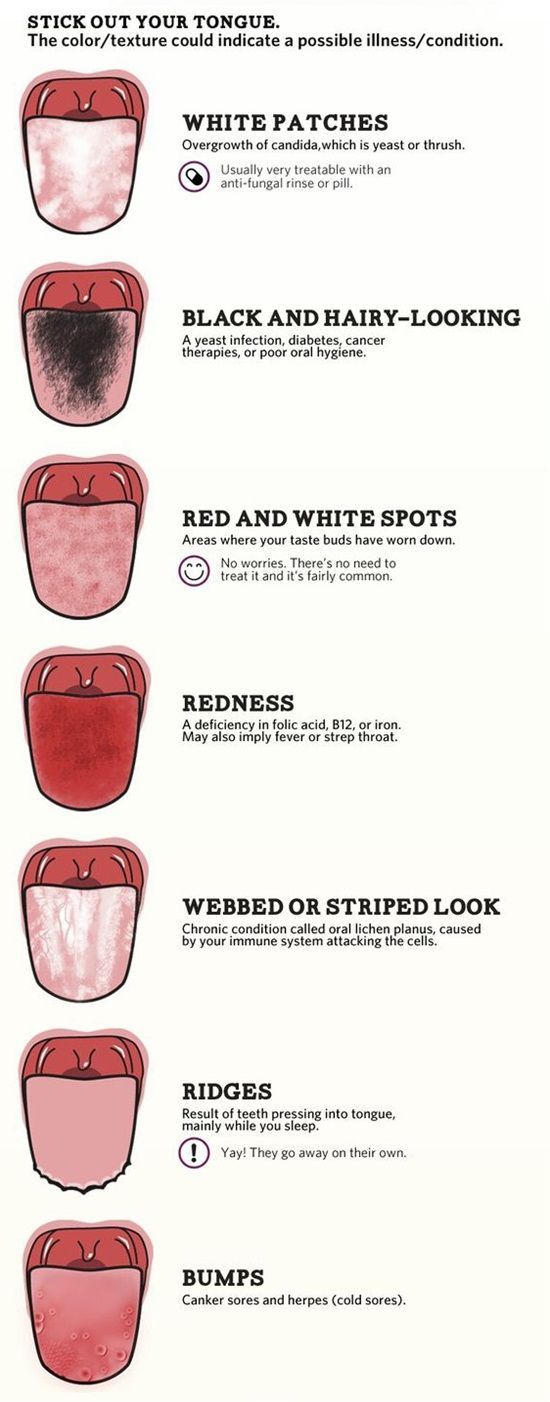 For this, a number of laboratory tests are prescribed. Bacteriological culture is mandatory. He will not only confirm the thrush, but also determine which type of fungus caused it. This is important when prescribing drugs. After a clinical examination, the dentist may recommend blood glucose or HIV tests.
For this, a number of laboratory tests are prescribed. Bacteriological culture is mandatory. He will not only confirm the thrush, but also determine which type of fungus caused it. This is important when prescribing drugs. After a clinical examination, the dentist may recommend blood glucose or HIV tests.
Consultations with narrow specialists are recommended:
- Endocrinologist To make sure there are no endocrine disorders.
- Allergist To detect sensitivity to dentures.
- Therapist To clarify the nature of somatic diseases.
Treatment of thrush in adults and children should be comprehensive and include activities aimed at strengthening general immunity, teaching adequate oral hygiene, and changing the diet.
Algorithm of therapeutic measures
- For the best result, the intervention begins with the sanitation of the oral cavity. Carious teeth are treated by replacing the affected tissues with filling material.
 Remove hard plaque and tartar from enamel. Plaque is a hotbed of infection, it is necessary to get rid of it.
Remove hard plaque and tartar from enamel. Plaque is a hotbed of infection, it is necessary to get rid of it. - Eliminate factors that provoke candidiasis. Replace dentures if they cause an allergic reaction or do not fit well. Stop the exacerbation of common diseases. Take steps to improve your hormone levels. Conduct activities that increase immunity.
- Administer antifungals based on culture results. Prescribed antihistamines, restorative agents, immunomodulators.
- Give recommendations on the normalization of the microflora in the oral cavity.
To prevent relapses, it is useful to establish regular hygiene, exclude foods rich in fast carbohydrates and sugars from the diet. Restorative activities include physical activity and stress-reducing activities (hobbies). It is important not to take medicines uncontrollably, according to recommendations from the Internet or from friends.
Thrush medicines
- Candidiasis medicines come in various forms:
- Suspensions (Diflucan, Amphotericin B)
- Tablets (Nystatin, Flucanosole, Itriconazole)
- Gels (Mikanozol)
A good effect in candidiasis is brought by rinsing with antiseptic agents: Chlorhexidine, Miramistin.