Internal organs during pregnancy
How a Woman's Organs Shift During Pregnancy to Make Room for a Baby
How a Woman's Organs Shift During Pregnancy to Make Room for a BabyJump to
- Main content
- Search
- Account
US Markets Loading... H M S In the news
Chevron iconIt indicates an expandable section or menu, or sometimes previous / next navigation options. HOMEPAGEScience
Save Article IconA bookmarkShare iconAn curved arrow pointing right.During the approximately 40 weeks of pregnancy, a woman's body undergoes some significant changes.
As the fetus grows, it occupies more and more space inside the mother. This is the cause of the obvious pregnancy bump, but just expanding outward isn't enough — her internal organs are also put under a significant amount of pressure, which can cause some discomfort.
That movement can also be pretty dramatic to look at. In the GIF below, which we spotted when it was recently tweeted out by the UK publication Scienmag, you can see those nine months of change sped up to just a few seconds.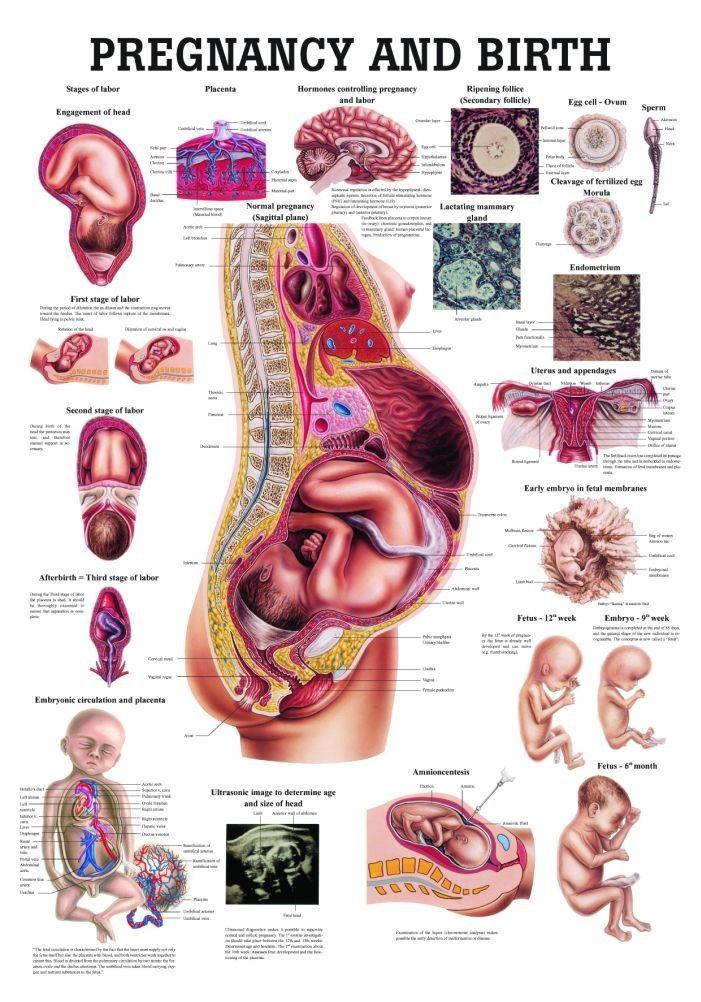
—Science (@scienmag) February 23, 2017
The GIF is from an ongoing exhibit at Chicago's Museum of Science + Industry which shows the "impact of a pregnancy on a mother's body as she adjusts physically and mentally to the changes inside her."
If you go to the museum's website, you can actually play with an interactive slider that shows what's happening throughout pregnancy. During weeks 29 through 32, for example, they note that organs are being squeezed.
In the YouTube video below, you can see a slower version of the interactive, beginning near the start of pregnancy and going through birth.
Sign up for notifications from Insider! Stay up to date with what you want to know.
Subscribe to push notifications
Read next
LoadingSomething is loading.Thanks for signing up!
Access your favorite topics in a personalized feed while you're on the go.
Pregnancy Pregnant HealthMore...
How your body changes during pregnancy
How your body changes during pregnancy | BabyCenter- Community
- Getting Pregnant
- Pregnancy
- Baby Names
- Baby
- Toddler
- Child
- Health
- Family
- Courses
- Registry Builder
- Baby Products
Advertisement
1:17 min
Watch how your body changes and makes room for your developing baby during pregnancy.
Join your birth club and find other parents due when you are.
Join
Advertisement | page continues below
Inside pregnancy: Weeks 1 to 9
1:57 min
Inside pregnancy: Weeks 10 to 14
2:04 min
Inside pregnancy: Weeks 15 to 20
2:00 min
Inside pregnancy: Weeks 21 to 27
1:27 min
Inside pregnancy: Weeks 28 to 37
1:54 min
Inside pregnancy: Girl or boy?
1:58 min
Your baby's senses during pregnancy
2:04 min
My pregnancy week by week
2
weeks
pregnant
3
weeks
pregnant
4
weeks
pregnant
5
weeks
pregnant
6
weeks
pregnant
7
weeks
pregnant
8
weeks
pregnant
9
weeks
pregnant
10
weeks
pregnant
11
weeks
pregnant
12
weeks
pregnant
13
weeks
pregnant
14
weeks
pregnant
15
weeks
pregnant
16
weeks
pregnant
17
weeks
pregnant
18
weeks
pregnant
19
weeks
pregnant
20
weeks
pregnant
21
weeks
pregnant
22
weeks
pregnant
23
weeks
pregnant
24
weeks
pregnant
25
weeks
pregnant
26
weeks
pregnant
27
weeks
pregnant
28
weeks
pregnant
29
weeks
pregnant
30
weeks
pregnant
31
weeks
pregnant
32
weeks
pregnant
33
weeks
pregnant
34
weeks
pregnant
35
weeks
pregnant
36
weeks
pregnant
37
weeks
pregnant
38
weeks
pregnant
39
weeks
pregnant
40
weeks
pregnant
41
weeks
pregnant
Advertisement
Physiological changes in the body during pregnancy
From the very first days of pregnancy, a woman's body undergoes profound transformations.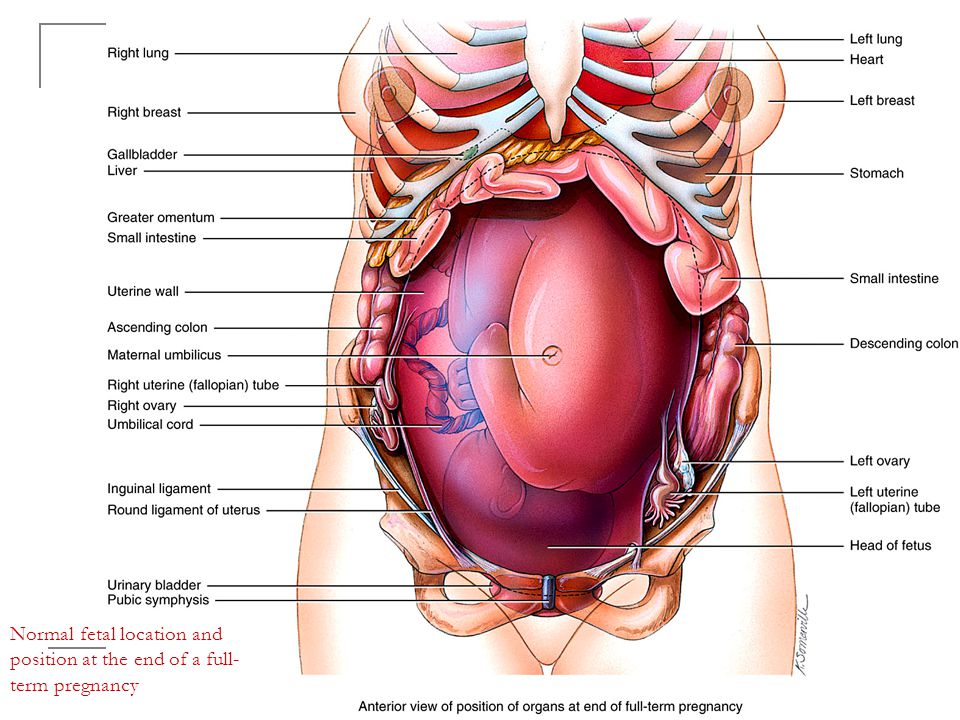 These transformations are the result of the coordinated work of almost all body systems, as well as the result of the interaction of the mother's body with the child's body. During pregnancy, many internal organs undergo significant restructuring. These changes are adaptive in nature, and, in most cases, are short-lived and completely disappear after childbirth. Consider the changes in the basic systems of the vital activity of a woman's body during pregnancy.
These transformations are the result of the coordinated work of almost all body systems, as well as the result of the interaction of the mother's body with the child's body. During pregnancy, many internal organs undergo significant restructuring. These changes are adaptive in nature, and, in most cases, are short-lived and completely disappear after childbirth. Consider the changes in the basic systems of the vital activity of a woman's body during pregnancy.
The respiratory system during pregnancy works hard. The respiratory rate increases. This is due to an increase in the need of the mother and fetus for oxygen, as well as in the limitation of the respiratory movements of the diaphragm due to an increase in the size of the uterus, which occupies a significant space of the abdominal cavity.
The mother's circulatory system during pregnancy has to pump more blood to ensure an adequate supply of nutrients and oxygen to the fetus. In this regard, during pregnancy, the thickness and strength of the heart muscles increase, the pulse and the amount of blood pumped by the heart in one minute increase.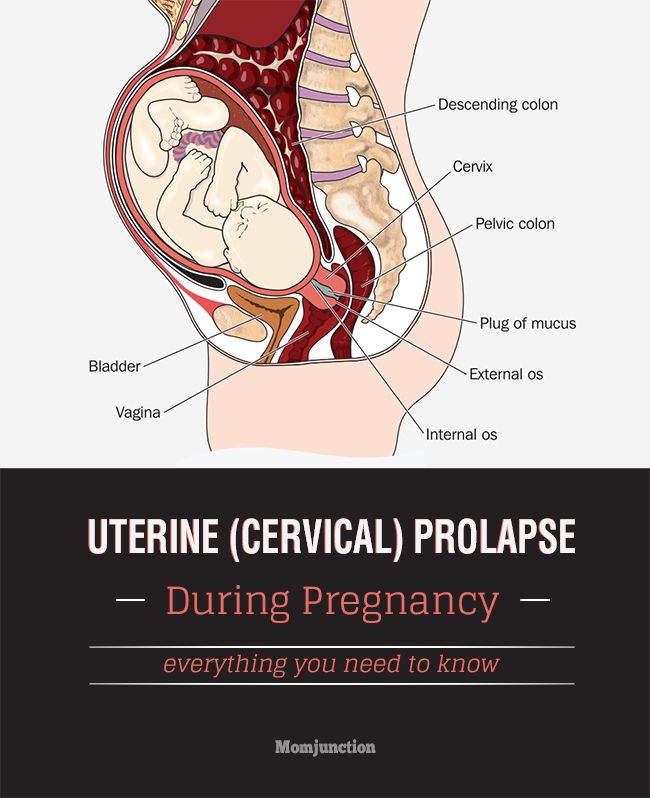 In addition, the volume of circulating blood increases. In some cases, blood pressure increases. The tone of blood vessels during pregnancy decreases, which creates favorable conditions for increased supply of tissues with nutrients and oxygen. During pregnancy, the network of vessels of the uterus, vagina, and mammary glands decreases sharply. On the external genitalia, in the vagina, lower extremities, there is often an expansion of the veins, sometimes the formation of varicose veins. Heart rate decreases in the second half of pregnancy. It is generally accepted that the rise in blood pressure over 120-130 and a decrease to 100 mm Hg. signal the occurrence of pregnancy complications. But it is important to have data on the initial level of blood pressure.
In addition, the volume of circulating blood increases. In some cases, blood pressure increases. The tone of blood vessels during pregnancy decreases, which creates favorable conditions for increased supply of tissues with nutrients and oxygen. During pregnancy, the network of vessels of the uterus, vagina, and mammary glands decreases sharply. On the external genitalia, in the vagina, lower extremities, there is often an expansion of the veins, sometimes the formation of varicose veins. Heart rate decreases in the second half of pregnancy. It is generally accepted that the rise in blood pressure over 120-130 and a decrease to 100 mm Hg. signal the occurrence of pregnancy complications. But it is important to have data on the initial level of blood pressure.
And changes in the blood system. During pregnancy, blood formation increases, the number of red blood cells, hemoglobin, plasma and bcc increases. BCC by the end of pregnancy increases by 30-40%, and erythrocytes by 15-20%.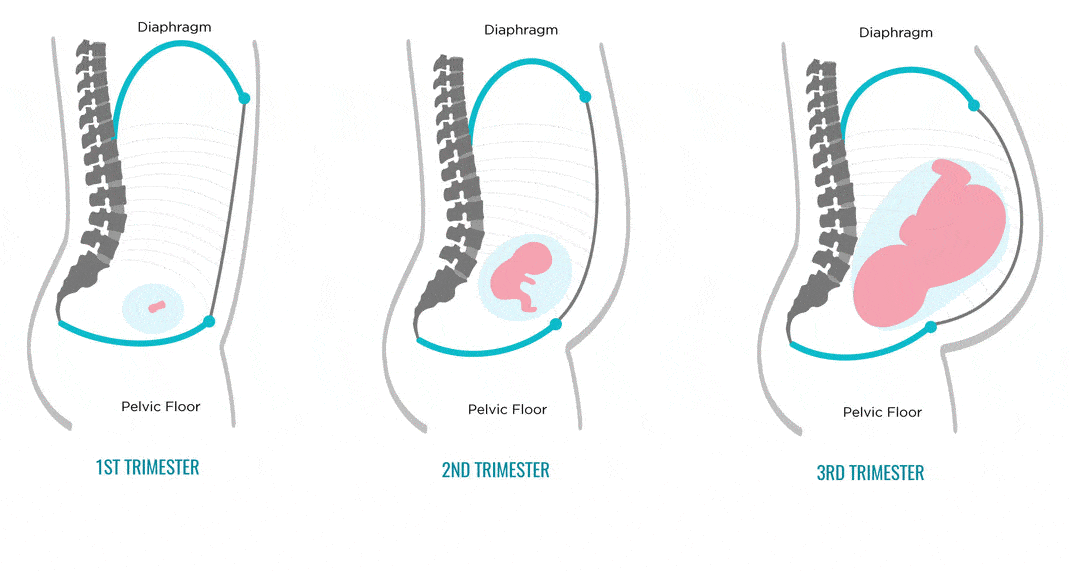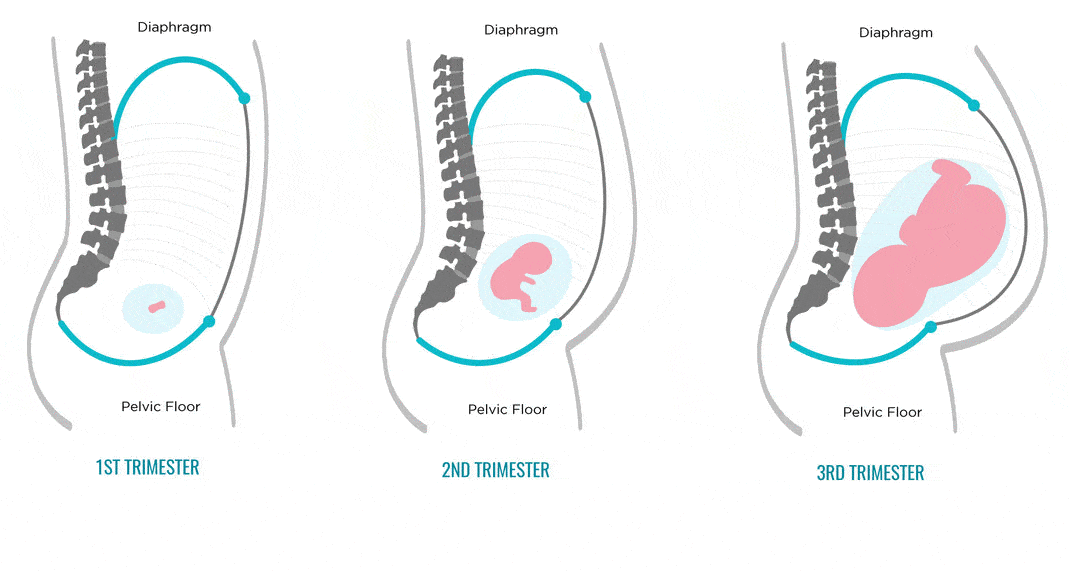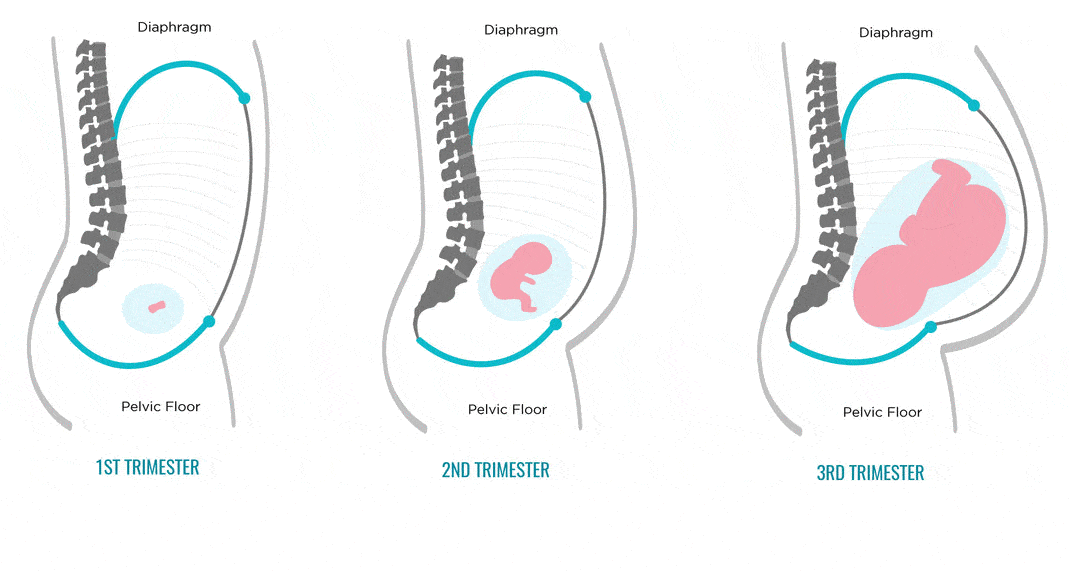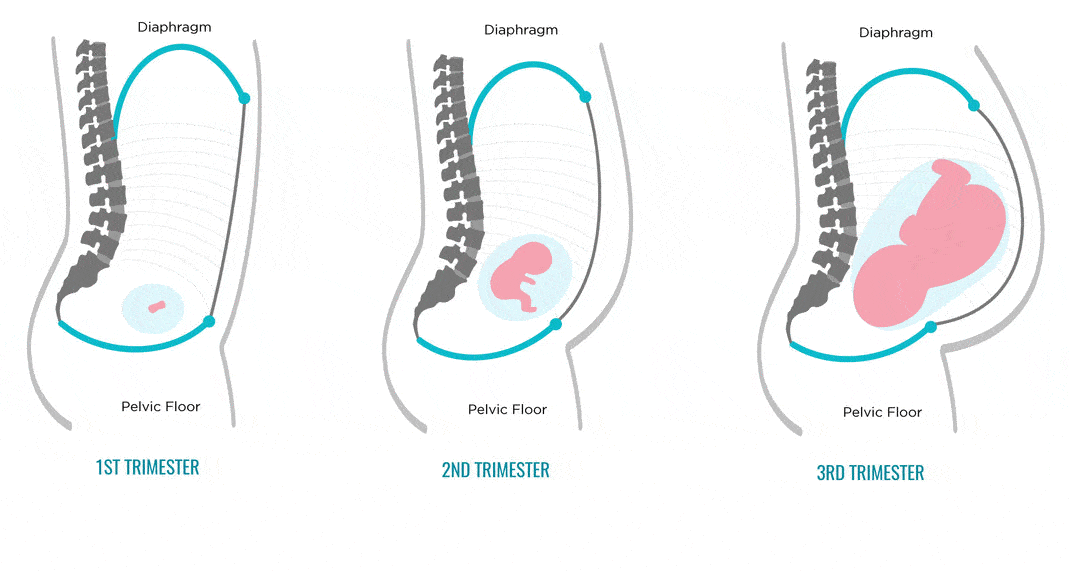 Many healthy pregnant women have a slight leukocytosis. ESR during pregnancy increases to 30-40. Changes occur in the coagulation system that contribute to hemostasis and prevent significant blood loss during childbirth or placental abruption and in the early postpartum period.
Many healthy pregnant women have a slight leukocytosis. ESR during pregnancy increases to 30-40. Changes occur in the coagulation system that contribute to hemostasis and prevent significant blood loss during childbirth or placental abruption and in the early postpartum period.
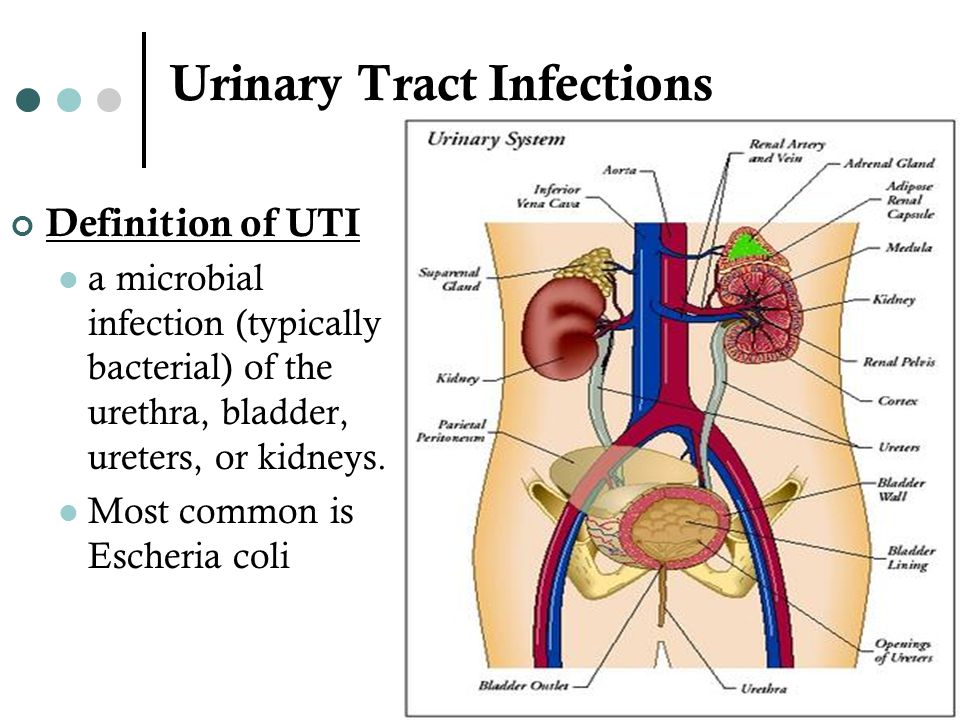
Kidneys work hard during pregnancy. They secrete decay products of substances from the body of the mother and fetus (the waste products of the fetus pass through the placenta into the mother's blood).
Changes in the digestive system are represented by increased appetite (in most cases), cravings for salty and sour foods. In some cases, there is an aversion to certain foods or dishes that were well tolerated before the onset of pregnancy. Due to the increased tone of the vagus nerve, constipation may occur.
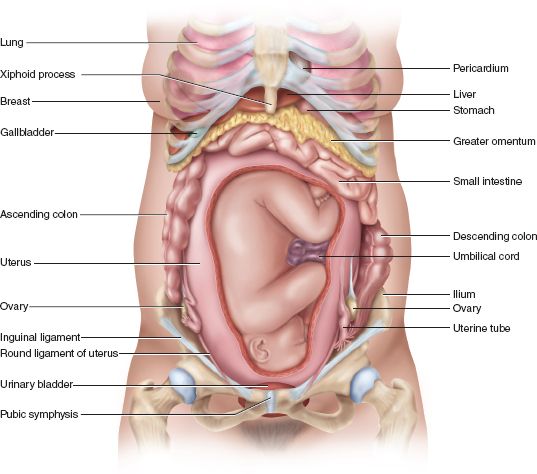
The most significant changes, however, occur in the genitals of pregnant women. These changes prepare the woman's reproductive system for childbirth and breastfeeding.
The uterus of a pregnant woman increases significantly in size. Its mass increases from 50 g - at the beginning of pregnancy to 1200 g - at the end of pregnancy. The volume of the uterine cavity by the end of pregnancy increases by more than 500 times! The blood supply to the uterus is greatly increased. In the walls of the uterus, the number of muscle fibers increases. The cervix is filled with thick mucus that clogs the cavity of the cervical canal. The fallopian tubes and ovaries also increase in size. In one of the ovaries, there is a "corpus luteum of pregnancy" - a place for the synthesis of hormones that support pregnancy. Walls vaginas will loosen and become more elastic. External genitalia (labia minor and major), also increase in size and become more elastic. The tissues of the perineum are loosened. In addition, there is an increase in mobility in the joints of the pelvis and a divergence of the pubic bones.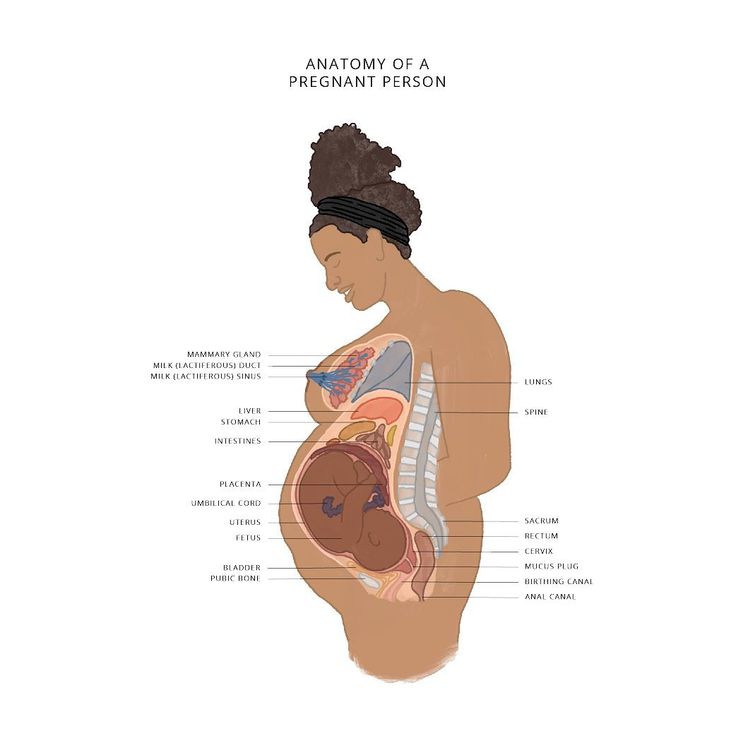 The changes in the genital tract described above are of extremely important physiological significance for childbirth. Loosening the walls, increasing the mobility and elasticity of the genital tract increases their throughput and facilitates the movement of the fetus through them during childbirth.
The changes in the genital tract described above are of extremely important physiological significance for childbirth. Loosening the walls, increasing the mobility and elasticity of the genital tract increases their throughput and facilitates the movement of the fetus through them during childbirth.
Skin in the genital area and in the midline of the abdomen usually becomes darker in color. Sometimes "stretch marks" form on the skin of the lateral parts of the abdomen, which turn into whitish stripes after childbirth.
Mammary glands increase in size, become more elastic, tense. When pressing on the nipple, colostrum (first milk) is released.
Changes in the bone skeleton and muscular system . An increase in the concentration of the hormones relaxin and progesterone in the blood contributes to the leaching of calcium from the skeletal system. This helps to reduce the rigidity of the joints between the bones of the pelvis and increase the elasticity of the pelvic ring. Increasing the elasticity of the pelvis is of great importance in increasing the diameter of the internal bone ring in the first stage of labor and further reducing the resistance of the birth tract to fetal movement in the second stage of labor. Also, calcium, washed out of the mother's skeletal system, is used to build the skeleton of the fetus.
Increasing the elasticity of the pelvis is of great importance in increasing the diameter of the internal bone ring in the first stage of labor and further reducing the resistance of the birth tract to fetal movement in the second stage of labor. Also, calcium, washed out of the mother's skeletal system, is used to build the skeleton of the fetus.
It should be noted that calcium compounds are washed out of all bones of the maternal skeleton (including the bones of the foot and spine). As shown earlier, a woman's weight increases during pregnancy by 10 -12 kg. This additional load against the background of a decrease in bone stiffness can cause foot deformity and the development of flat feet. A shift in the center of gravity of the body of a pregnant woman due to an increase in the weight of the uterus can lead to a change in the curvature of the spine and the appearance of pain in the back and pelvic bones. Therefore, for the prevention of flat feet, pregnant women are advised to wear comfortable shoes with low heels. It is advisable to use insoles that support the arch of the foot. For the prevention of back pain, special physical exercises are recommended that can unload the spine and sacrum, as well as wearing a comfortable bandage. Despite an increase in calcium loss by the bones of the skeleton of a pregnant woman and an increase in their elasticity, structure and bone density (as is the case with osteoporosis in older women).
It is advisable to use insoles that support the arch of the foot. For the prevention of back pain, special physical exercises are recommended that can unload the spine and sacrum, as well as wearing a comfortable bandage. Despite an increase in calcium loss by the bones of the skeleton of a pregnant woman and an increase in their elasticity, structure and bone density (as is the case with osteoporosis in older women).
Changes in the nervous system . In the first months of pregnancy and at the end of it, there is a decrease in the excitability of the cerebral cortex, which reaches its greatest degree by the time of the onset of childbirth. By the same period, the excitability of the receptors of the pregnant uterus increases. At the beginning of pregnancy, there is an increase in the tone of the vagus nerve, in connection with which various phenomena often occur: changes in taste and smell, nausea, increased salivation, etc.
Active endocrine glands there are significant changes that contribute to the proper course of pregnancy and childbirth. Changes in body weight. By the end of pregnancy, a woman's weight increases by about 10-12 kg. This value is distributed as follows: fetus, placenta, membranes and amniotic fluid - approximately 4.0 - 4.5 kg, uterus and mammary glands -1.0 kg, blood - 1.5 kg, intercellular (tissue) fluid - 1 kg , an increase in the mass of adipose tissue of the mother's body - 4 kg.
Changes in body weight. By the end of pregnancy, a woman's weight increases by about 10-12 kg. This value is distributed as follows: fetus, placenta, membranes and amniotic fluid - approximately 4.0 - 4.5 kg, uterus and mammary glands -1.0 kg, blood - 1.5 kg, intercellular (tissue) fluid - 1 kg , an increase in the mass of adipose tissue of the mother's body - 4 kg.
Ultrasound of internal organs during pregnancy in St. Petersburg
When monitoring pregnant women, ultrasound is of great importance. During the examination of the internal organs, various anomalies are detected that interfere with the normal development of the fetus. If you do not conduct an ultrasound during this period, there is a risk of not noticing the pathology and not taking action in time.
Since ultrasound examination is harmless, doctors advise to undergo it as a preventive measure. Thanks to this, it is possible to detect many diseases at an early stage and not allow them to go into the acute stage.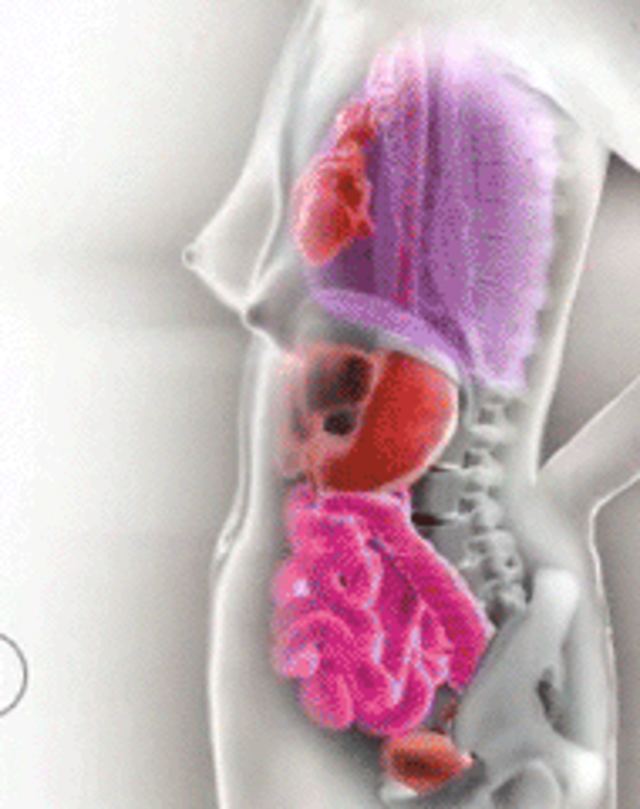
Ultrasound of the heart during pregnancy
Ultrasound of the heart during pregnancy is mandatory in several cases:
- shortness of breath;
- chest pain;
- tachycardia;
- heart disease;
- undergone heart surgery.
Color Doppler ultrasound is able to detect blood flow disturbances. The health of the heart and vascular system is of great importance for the fetus, and in case of any deviations, the doctor will prescribe a course of treatment, preventing the development of the disease.
Ultrasound of the abdominal organs during pregnancy
Examination of the abdominal cavity also plays an important role in the health of the child and mother. Ultrasound of the abdominal organs during pregnancy includes a set of studies - while studying the spleen, gallbladder, liver and other organs.
Any abnormalities such as liver stones, tumors, ulcers and cysts are noted during the procedure.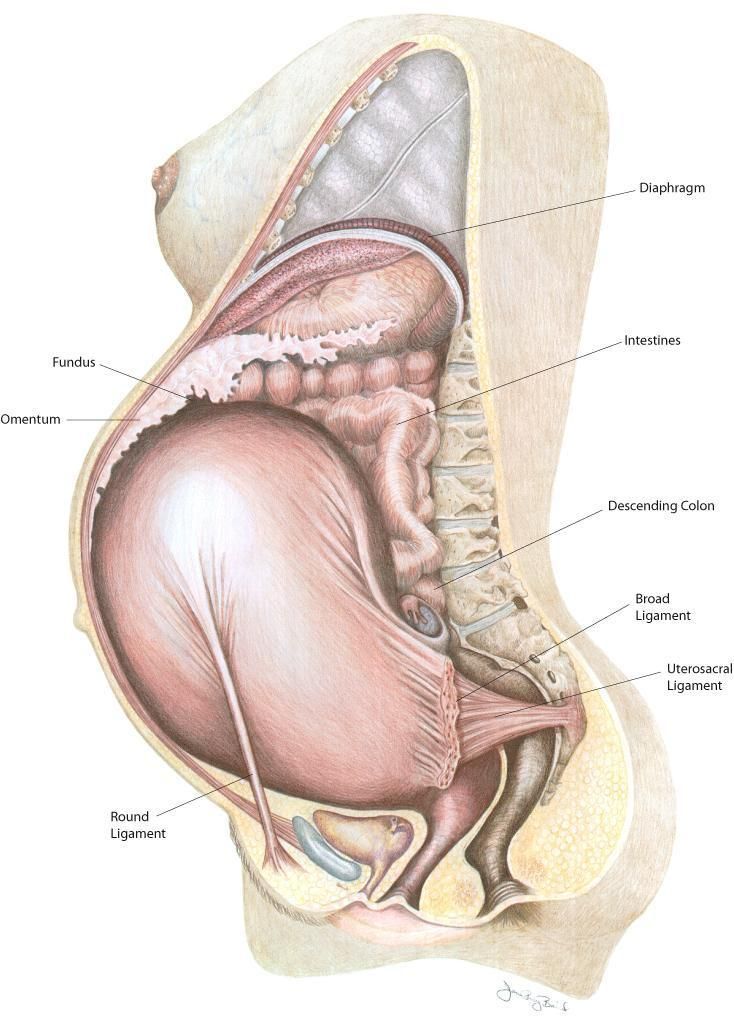 If incipient or chronic diseases are detected, the doctor, after making a diagnosis, will prescribe a treatment that will help get rid of the disease, but at the same time will not harm the fetus.
If incipient or chronic diseases are detected, the doctor, after making a diagnosis, will prescribe a treatment that will help get rid of the disease, but at the same time will not harm the fetus.
Ultrasound of the kidneys during pregnancy
In the examination during pregnancy, special attention is paid to the ultrasound examination of the kidneys.
In the presence of kidney stones various symptoms appear:
- renal colic;
- blood in urine;
- nausea and vomiting;
- chills and high fever.
Ultrasound of the kidneys during pregnancy will allow you to identify the disease before the onset of alarming symptoms and cure it in time.
In addition to the examination of the kidneys during pregnancy, it is recommended to undergo an examination of the genitourinary system, mammary glands, adrenal glands and thyroid gland. All this will show the general condition of the organs and, based on this information, will allow drawing conclusions and prescribing the correct treatment.