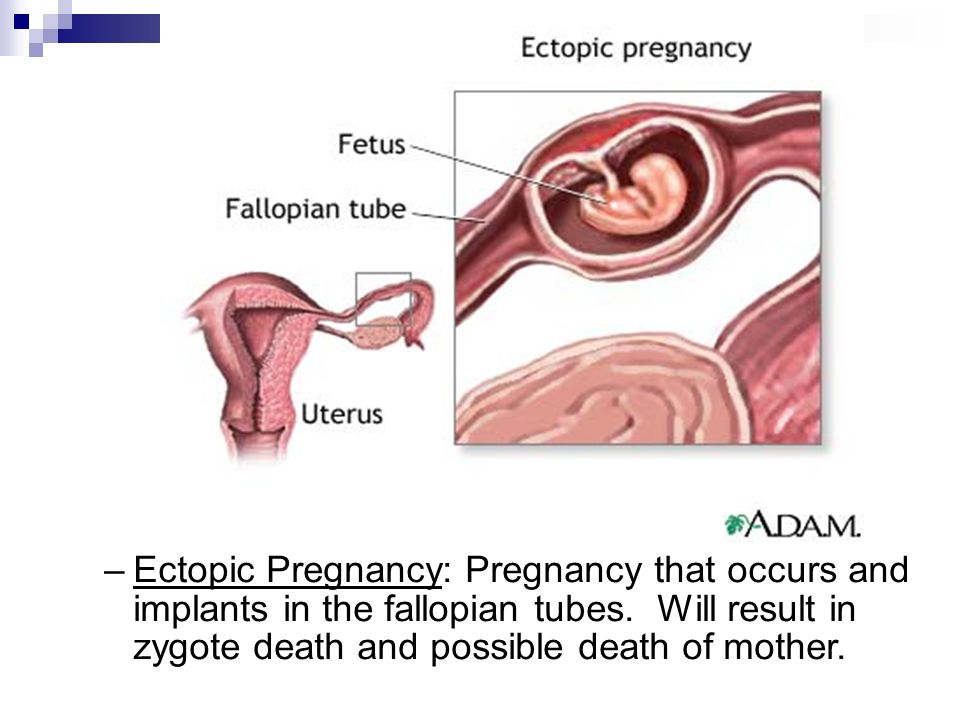
Bleeding during ectopic pregnancy
Ectopic pregnancy - Symptoms - NHS
Symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy usually develop between the 4th and 12th weeks of pregnancy.
Some women don't have any symptoms at first. They may not find out they have an ectopic pregnancy until an early scan shows the problem or they develop more serious symptoms later on.
Main symptoms
You may have an ectopic pregnancy if you miss a period, have a positive pregnancy test, and have other signs of pregnancy.
Contact your GP or call NHS 111 if you have a combination of any of these symptoms and you think you might be pregnant – even if you haven't had a positive pregnancy test.
Vaginal bleeding
Vaginal bleeding tends to be a bit different to your regular period. It often starts and stops, and may be watery and dark brown in colour.
Some women mistake this bleeding for a regular period and don't realise they're pregnant.
Vaginal bleeding during pregnancy is relatively common and isn't necessarily a sign of a serious problem, but you should seek medical advice if you experience it.
Tummy pain
You may experience tummy pain, typically low down on one side. It can develop suddenly or gradually, and may be persistent or come and go.
Tummy pain can have lots of causes, including stomach bugs and trapped wind, so it doesn't necessarily mean you have an ectopic pregnancy.
But you should get medical advice if you have it and think you might be pregnant.
Shoulder tip pain
Shoulder tip pain is an unusual pain felt where your shoulder ends and your arm begins.
It's not known exactly why it occurs, but it can be a sign of an ectopic pregnancy causing some internal bleeding, so you should get medical advice right away if you experience it.
Discomfort when going to the toilet
You may experience pain when going for a pee or poo. You may also have diarrhoea.
Some changes to your normal bladder and bowel patterns are normal during pregnancy, and these symptoms can be caused by urinary tract infections and stomach bugs.
But it's still a good idea to seek medical advice if you experience these symptoms and think you might be pregnant.
Symptoms of a rupture
In a few cases, an ectopic pregnancy can grow large enough to split open the fallopian tube. This is known as a rupture.
Ruptures are very serious, and surgery to repair the fallopian tube needs to be carried out as soon as possible.
Signs of a rupture include a combination of:
- a sharp, sudden and intense pain in your tummy
- feeling very dizzy or fainting
- feeling sick
Call 999 for an ambulance or go to your nearest accident and emergency (A&E) department immediately if you experience these symptoms.
Page last reviewed: 23 August 2022
Next review due: 23 August 2025
Ectopic Pregnancy (for Parents) - Nemours KidsHealth
What Is an Ectopic Pregnancy?
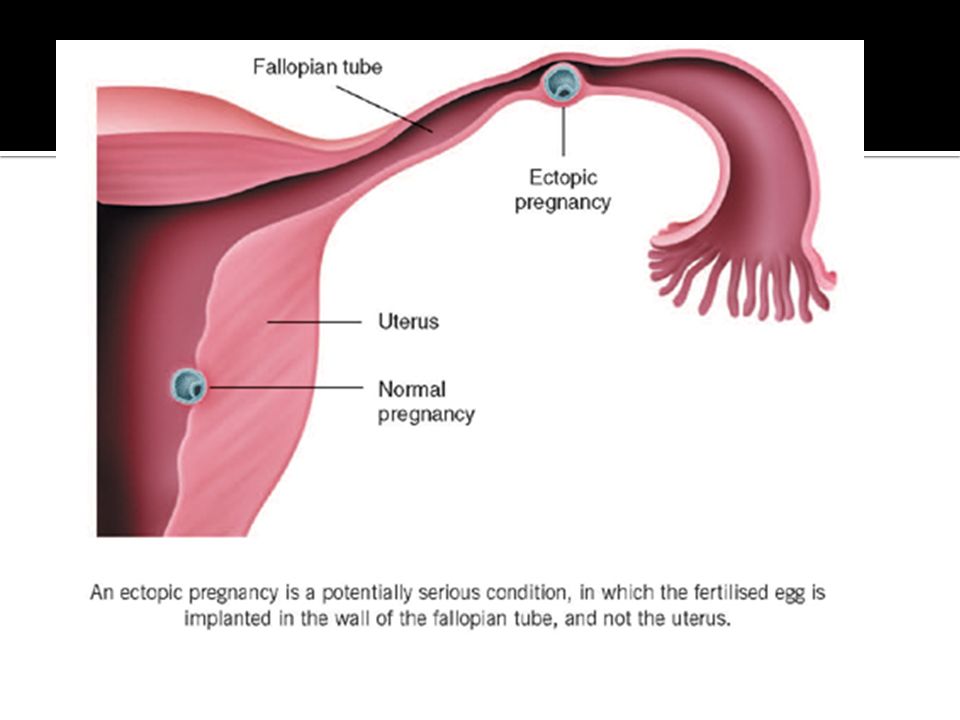
In a normal pregnancy, the fertilized egg implants and develops in the uterus. In an ectopic pregnancy, the egg implants somewhere other than the uterus — often, in the fallopian tubes. This is why ectopic pregnancies are commonly called "tubal pregnancies." The egg also can implant in the ovary, abdomen, or the cervix.
None of these areas has the right space or nurturing tissue for a pregnancy to develop. As the fetus grows, it will eventually burst the organ that contains it. This can cause severe bleeding and endanger the mother's life. A classical ectopic pregnancy does not develop into a live birth.
What Are the Signs & Symptoms of an Ectopic Pregnancy?
Ectopic pregnancy can be hard to diagnose because symptoms often are like those of a normal early pregnancy. These can include missed periods, breast tenderness, nausea, vomiting, tiredness, or frequent urination (peeing).
These can include missed periods, breast tenderness, nausea, vomiting, tiredness, or frequent urination (peeing).
Often, the first warning signs of an ectopic pregnancy are pain or vaginal bleeding. There might be pain in the pelvis, abdomen, or even the shoulder or neck (if blood from a ruptured ectopic pregnancy builds up and irritates certain nerves). The pain can range from mild and dull to severe and sharp. It might be felt on just one side of the pelvis or all over.
These symptoms also might happen with an ectopic pregnancy:
- vaginal spotting
- dizziness or fainting (caused by blood loss)
- low blood pressure (also caused by blood loss)
- lower back pain
What Causes an Ectopic Pregnancy?
An ectopic pregnancy usually happens because a fertilized egg couldn’t quickly move down the fallopian tube into the uterus. The tube can get blocked from an infection or inflammation. The tube can get blocked from:
- pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)
- endometriosis, when cells from the lining of the uterus implant and grow elsewhere in the body
- scar tissue from previous abdominal or fallopian surgeries
- rarely, birth defects that changed the shape of the tube
How Is an Ectopic Pregnancy Diagnosed?
If a woman might have an ectopic pregnancy, her doctor may do an ultrasound to see where the developing fetus is.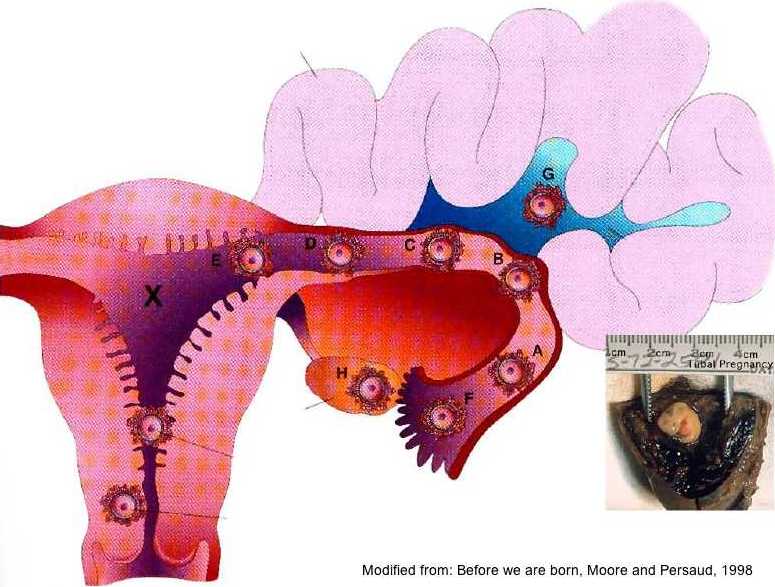 Often, pregnancies are too small to see on ultrasound until more than 5 or 6 weeks after a woman’s last menstrual period. If an external ultrasound can’t show the pregnancy, the doctor might do the test with a wand-like device in the vagina.
Often, pregnancies are too small to see on ultrasound until more than 5 or 6 weeks after a woman’s last menstrual period. If an external ultrasound can’t show the pregnancy, the doctor might do the test with a wand-like device in the vagina.
A woman might need testing every few days if the first tests can’t confirm or rule out an ectopic pregnancy.
How Is an Ectopic Pregnancy Treated?
How doctors treat an ectopic pregnancy depends on things like the size and location of the pregnancy.
Sometimes they can treat an early ectopic pregnancy with an injection of methotrexate, which stops the growth of the embryo. The tissue usually is then absorbed by the woman’s body.
If the pregnancy is farther along, doctors usually need to do surgery to remove the abnormal pregnancy.
Whatever treatment she gets, a woman will see her doctor regularly afterward to make sure her pregnancy hormone levels return to zero. This may take several weeks. An elevated level could mean that some ectopic tissue was missed. If so, she might need more methotrexate or surgery.
If so, she might need more methotrexate or surgery.
What About Future Pregnancies?
Most women who have had an ectopic pregnancy can have normal pregnancies in the future. Having had one ectopic pregnancy does increase a woman’s risk of having another one.
What Else Should I Know?
Any woman can have an ectopic pregnancy. But the risk is higher for women who are older than 35 and those who have had:
- PID
- a previous ectopic pregnancy
- surgery on a fallopian tube
- infertility problems or medicine to stimulate ovulation
Some birth control methods also can affect a woman's risk of ectopic pregnancy. Those who become pregnant while using an intrauterine device (IUD) might be more likely to have an ectopic pregnancy. Smoking and having multiple sexual partners also increase the risk of an ectopic pregnancy.
When Should I Call the Doctor?
If you believe you're at risk for an ectopic pregnancy, meet with your doctor to talk about your options before you become pregnant. If you are pregnant and have any concerns about the pregnancy being ectopic, talk to your doctor — it's important to find it early. Your doctor might want to check your hormone levels or schedule an early ultrasound to ensure that your pregnancy is developing normally.
If you are pregnant and have any concerns about the pregnancy being ectopic, talk to your doctor — it's important to find it early. Your doctor might want to check your hormone levels or schedule an early ultrasound to ensure that your pregnancy is developing normally.
Call your doctor right away if you're pregnant and having any pain, bleeding, or other symptoms of ectopic pregnancy.
Ectopic pregnancy - Adamant Medical Clinic
Ectopic pregnancy is a serious medical condition. This complication is very dangerous for a woman. If an ectopic pregnancy is not removed on time, there is a risk of intra-abdominal bleeding. And this, in turn, threatens the health and life of the patient. Therefore, noticing the early symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy, you should immediately see a doctor. This condition requires urgent medical attention.
The uterus is a muscular organ that exists to bear a child. However, sometimes the egg, having been fertilized, does not enter the uterine cavity, but is fixed in the ovaries, tubes or abdominal cavity.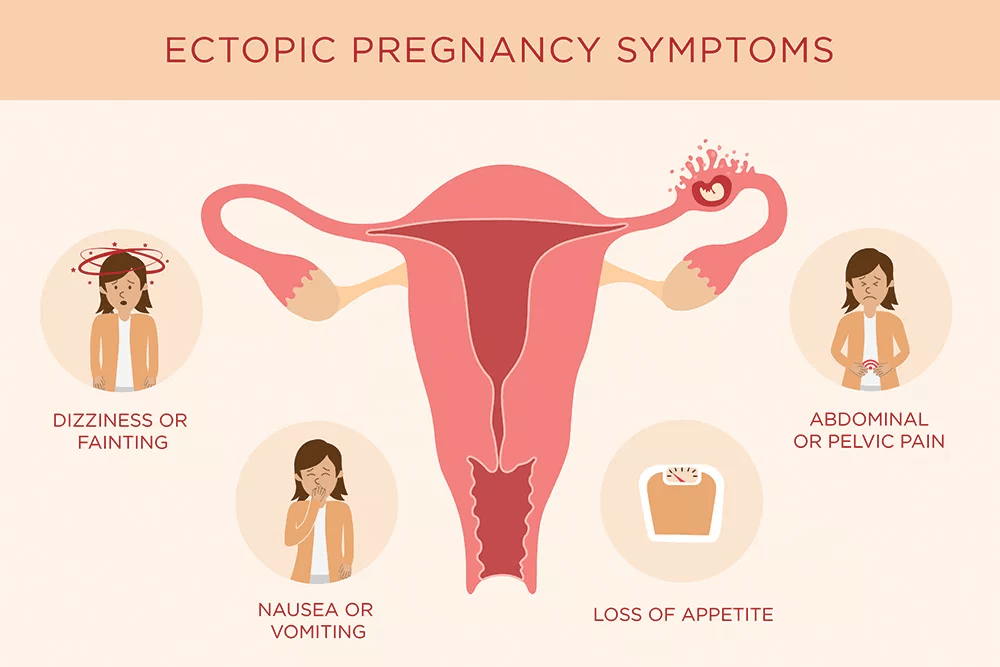 As a result, there are pains during an ectopic pregnancy and a rupture of an organ (for example, a fallopian tube) is possible.
As a result, there are pains during an ectopic pregnancy and a rupture of an organ (for example, a fallopian tube) is possible.
Why does an ectopic pregnancy occur?
Causes of ectopic pregnancy may be as follows:
- pelvic inflammatory disease, especially chronic
- endometriosis
- congenital malformation of the tubes
- IVF complication
The question of why an ectopic pregnancy occurs worries many women. However, it is possible to establish the true causes of an ectopic pregnancy only after a laparoscopic operation to remove it.
Symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy
Many women wonder how to distinguish an ectopic pregnancy from a normal one. Doctors recommend that you carefully monitor your condition and pay attention to the main symptoms of ectopic pregnancy:
- pain in ectopic pregnancy
- bleeding
Pain during an ectopic pregnancy is aching, cramping in nature. Painful sensations appear from the moment of attachment of the fetal egg. If a rupture occurs, bleeding begins, pain radiates to the anus, and can spread throughout the abdomen, a woman may feel pain during an ectopic pregnancy while urinating or trying to empty the intestines.
Painful sensations appear from the moment of attachment of the fetal egg. If a rupture occurs, bleeding begins, pain radiates to the anus, and can spread throughout the abdomen, a woman may feel pain during an ectopic pregnancy while urinating or trying to empty the intestines.
Bleeding during an ectopic pregnancy occurs in the abdominal cavity. However, due to a drop in hormone levels, uterine bleeding is often observed. The volume of allocations is usually meager. Bleeding during an ectopic pregnancy lasts a long time.
Both of these symptoms require immediate medical attention. Rarely, bleeding during an ectopic pregnancy is accompanied by fever, which signals the onset of the inflammatory process.
Early ectopic pregnancy: treatment
There is only one possible way to treat pathology - the removal of an ectopic pregnancy by surgery. However, before proceeding with the operation, doctors conduct a diagnosis. External signs of ectopic pregnancy must be confirmed by laboratory and instrumental methods of examination.
There are three ways that help to make a diagnosis:
1) pregnancy can be diagnosed if menstruation is delayed by 2-3 days. To do this, conduct a test for hCG. There are no signs of an ectopic pregnancy yet.
2) After one and a half to two weeks from the start of the delay, an ultrasound examination can be performed. If a fetal egg is not visualized in the area of \u200b\u200bthe uterus, a second appointment will be scheduled in a few days. If the same picture is observed at the second appointment, the doctor will suspect an ectopic pregnancy. Early symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy may be absent.
3) fetal heartbeat appears after 2.5-3 weeks. The first early symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy may already appear. On an ultrasound, a growing ovum will be seen in the tubes, ovaries, or abdomen.
Ectopic pregnancy is treated only surgically. At Adamant Medical Clinic, surgeries are performed laparoscopically. Often, a woman usually sees a specialist when symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy appear, and the fallopian tube is almost always removed during surgery.
The Department of Operative Gynecology of AMK has everything you need to perform the most complex operations. Our doctors are specialists with extensive experience. They know how to distinguish an ectopic pregnancy and are able to quickly and reliably make a diagnosis. If an operation is necessary, patients are guaranteed an individual approach. We use only modern techniques and materials that allow us to remove an ectopic pregnancy with a minimal risk of complications.
Ectopic pregnancy - causes and treatment
If the fixation and subsequent development of the ovum occurs outside the uterus, then the pregnancy is called ectopic (ectopic). It occurs in 2% of all pregnancies. The embryo can be fixed on the ovary, in the abdominal cavity, in the cervix, in the fallopian tubes. An ectopic pregnancy in the early stages is no different from a normal one.
An egg is released from the ovary during ovulation and enters the fallopian tube. Fertilization occurs when a sperm and an egg meet in the ampulla of the fallopian tube. Normally, at the end of the first week after fertilization, the embryo enters the uterine cavity and implantation occurs. A fertilized egg can develop normally only in the uterus.
Normally, at the end of the first week after fertilization, the embryo enters the uterine cavity and implantation occurs. A fertilized egg can develop normally only in the uterus.
Types
- tubal - the embryo develops in the fallopian tubes;
- abdominal - the embryo is attached to the walls of the peritoneum;
- ovarian - the embryo is attached to the walls of the cervix;
- cervical - the embryo is attached to the cavity of the ovary.
Very rare bilateral ectopic pregnancy, as well as heterotopic pregnancy (combination of uterine and ectopic). An ectopic pregnancy of any type is considered a medical emergency.
Let's take a look at tubal pregnancy next, because it is the most common and accounts for 98-99% of all pregnancies outside the uterus.
Signs of ectopic pregnancy
Until the fetal egg overstretches the wall of the fallopian tube, pregnancy is no different from normal and is characterized by standard signs:
- delayed menstruation;
- positive test;
- early toxicosis;
- drowsiness;
- breast enlargement and soreness;
- change in taste preferences.
.jpg)
During menstruation, scanty dark-colored blood discharge is possible. It is impossible for a woman to determine an ectopic pregnancy at home, and diagnostics and specialist advice are required.
Until a certain point, the fertilized egg develops normally. But the embryo grows and it ceases to have enough nutrients. At some point, he ruptures the fallopian tube and bleeding occurs. At the same time, the blood practically does not flow out, only small spotting discharges may appear, the main bleeding occurs in the abdominal cavity.
An ectopic pregnancy may show symptoms after 2 weeks of delayed menstruation. A woman may feel:
- weakness, dizziness;
- pain in rectum radiating to back;
- loss of appetite;
- pain in the lower abdomen, sometimes with nausea and vomiting;
- scanty spotting.
Particular attention should be paid to pain in the lower abdomen. This symptom is also characteristic of a normal uterine pregnancy. But in a normal pregnancy, the pain is temporary. With tubal, as a rule, the pain increases, intensifies and does not stop.
But in a normal pregnancy, the pain is temporary. With tubal, as a rule, the pain increases, intensifies and does not stop.
If you experience any of the symptoms listed, seek medical attention immediately. The condition can worsen sharply at any moment, which threatens the health and life of a woman.
Causes of ectopic pregnancy
Causes are all conditions that disrupt the movement of a fertilized egg into the uterine cavity:
- chronic inflammatory processes of the pelvic organs;
- violation of patency - the appearance of adhesions and scarring of tissues;
- violation of peristalsis of the fallopian tube
- the exit from the pipe is closed;
- pathology of the endometrium;
- transferred infectious diseases;
- congenital factor - pipes are twisted and very long;
- single fallopian tube.
Risk factors:
- history of ectopic pregnancy;
- adhesive process in the small pelvis;
- interventions on the fallopian tubes;
- intrauterine contraception;
- surgery;
- pregnancy after prolonged infertility, after IVF procedure;
- anatomical features;
- bad habits;
- age from 35 years;
- hormonal and endocrine disorders.

Diagnosis
It is very difficult to detect a tubal pregnancy during a routine gynecological examination. Methods for diagnosing ectopic pregnancy:
- beta-hCG test is the only biochemical indicator for diagnosing ectopic pregnancy. In a normal course, the increase in hCG should double every 2-3 days. Suspicion will be a sluggish increase in hCG, no more than 1.5 times every 2-3 days. A low rise in beta-hCG may be with an undeveloped uterine or ectopic pregnancy;
- An early ultrasound of an ectopic pregnancy should be transvaginal to determine where the embryo has attached. It is desirable to carry out for 5-7 days after the delay of menstruation.
Blood progesterone testing is not indicated for the diagnosis of tubal pregnancy. Only according to the beta-hCG data, it is impossible to make a diagnosis, it is necessary to do a transvaginal ultrasound.
Complications
Termination of an ectopic pregnancy usually occurs for 4-6 weeks and develops as a rupture of the tube or as a tubal abortion.
Signs of interruption by type of tube rupture:
- delayed menstruation;
- intra-abdominal bleeding, characterized by a sharp decrease in blood pressure, pallor, cold sweat, dizziness, fainting, nausea, vomiting;
- sharp and very severe pain in the abdomen.
May occur after 6 weeks of pregnancy. An extremely dangerous situation for a woman's life and require immediate surgical intervention.
Signs of interruption by type of tubal abortion:
- delayed menstruation;
- bleeding from labia;
- constant aching, dull pain in the lower abdomen, may radiate to the lower back, groin, rectum.
Tubal abortion takes a long time, without acute manifestations. With detachment of the fetal from the fallopian tube, blood enters the abdominal cavity in small portions and therefore there are no sharp symptoms. On gynecological examination, an increase in the size of the uterus and appendages, pain on palpation of the posterior fornix of the vagina is determined.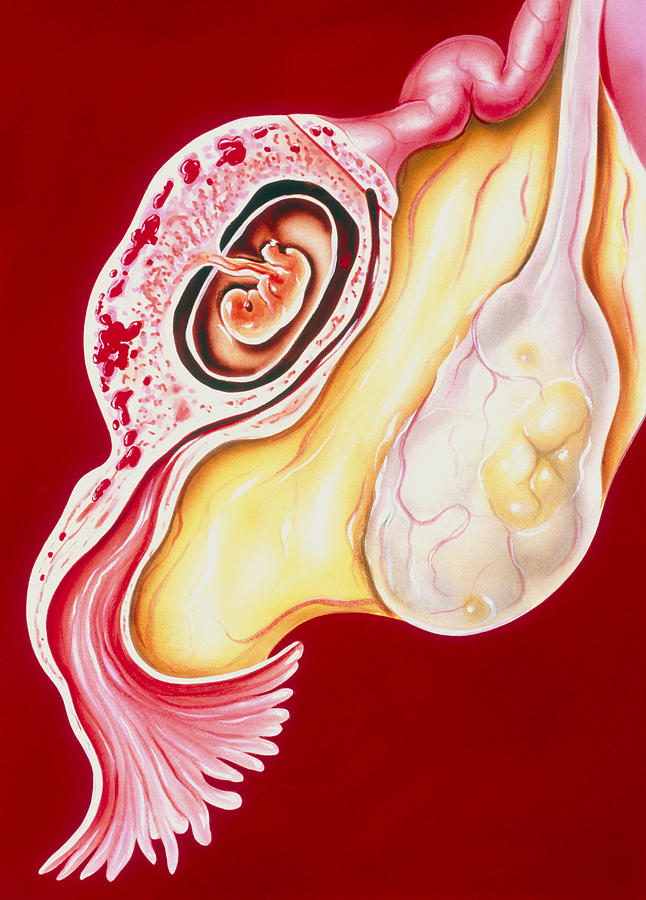
What complications can be:
- severe bleeding;
- repeated ectopic pregnancy;
- infertility.
Ectopic pregnancy and consequences
- probability of normal pregnancy and childbirth - about 50%;
- repeated ectopic pregnancy - about 20%;
- 15-20% miscarriages;
- 25% infertility.
Ectopic pregnancy, what treatment is used
If an ectopic pregnancy is suspected, a woman should be urgently hospitalized in a hospital, even if there are no complaints of well-being. The main threat is that the pregnancy can be terminated at any time.
The effectiveness of treatment is determined by timely diagnosis at an early stage and the choice of using laparoscopic access.
In the hospital, after 48-72 hours, repeat ultrasound, determine the level of beta-hCG and conduct a gynecological examination. If the increase in beta-hCG is less than 50% in 48-72 hours and the fetal egg is not detected, then the patient will be shown a diagnostic laparoscopy.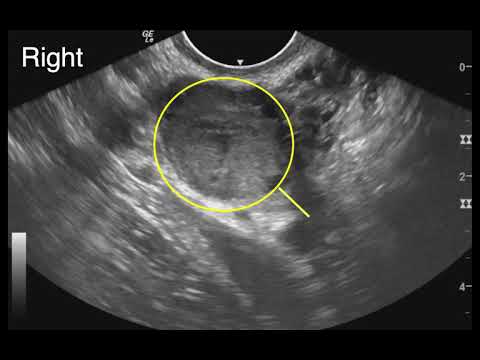 Such diagnostics will help not to wait for the rupture of the tube, blood loss and shock.
Such diagnostics will help not to wait for the rupture of the tube, blood loss and shock.
Currently in Russia, ectopic pregnancy is treated only surgically:
- radical (tubectomy) - removal of the tube along with ectopic pregnancy. It is used for rupture or overstretching of the pipe;
- organ-preserving (tubotomy) - the tube is cut and the fetal egg is removed. The method is used with timely detection and slight stretching of the pipe.
Only surgery can remove the fetal egg, which is attached outside the uterine cavity. The most common is laparoscopy. The surgeon removes the fetal egg and partially or completely the fallopian tube through small punctures. After 3 days, the woman is allowed to go home.
Opening of the abdominal cavity is usually used when laparoscopic access is difficult (pronounced adhesive process, a large amount of blood in the abdominal cavity, obesity).
The nature of the operation depends on the condition of the woman, the volume of blood loss, location and size of the ovum.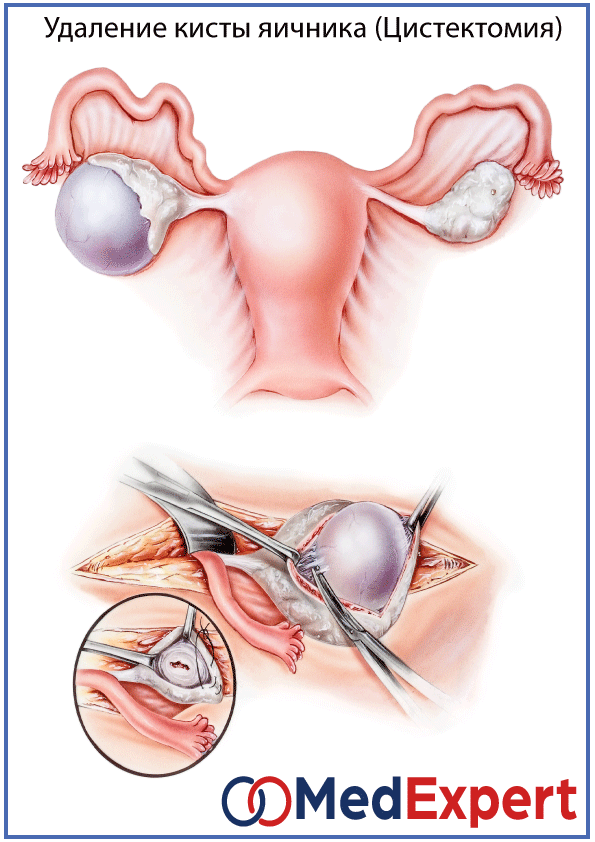 With laparoscopic access, the incidence of recurrent ectopic pregnancy is lower than with laparotomy.
With laparoscopic access, the incidence of recurrent ectopic pregnancy is lower than with laparotomy.
Recovery from an ectopic pregnancy
It is important to have a complete examination to understand the cause of an ectopic pregnancy and eliminate it. Observe physical and sexual rest for at least a month after surgery. Measures should be aimed at restoring reproductive function after surgery:
- prevention of adhesions - physiotherapy, reflexology, injections of longidase, lidase;
- oral contraceptives are recommended for the duration of rehabilitation therapy. As a rule, 6 months after an ectopic pregnancy, you can become pregnant again.
If a tubal pregnancy was diagnosed in time, the chances of conceiving and carrying a healthy child are quite high. When planning a pregnancy, be sure to consult a doctor.
How to avoid ectopic pregnancy
Prevention involves reducing the likelihood of occurrence of causes that lead to the development of ectopic pregnancy:
- timely treatment of inflammatory diseases of the genital organs;
- reliable contraception as abortion prevention;
- use of contraceptives strictly under medical supervision;
- pregnancy planning, complete examination;
- treatment of hormonal disorders.