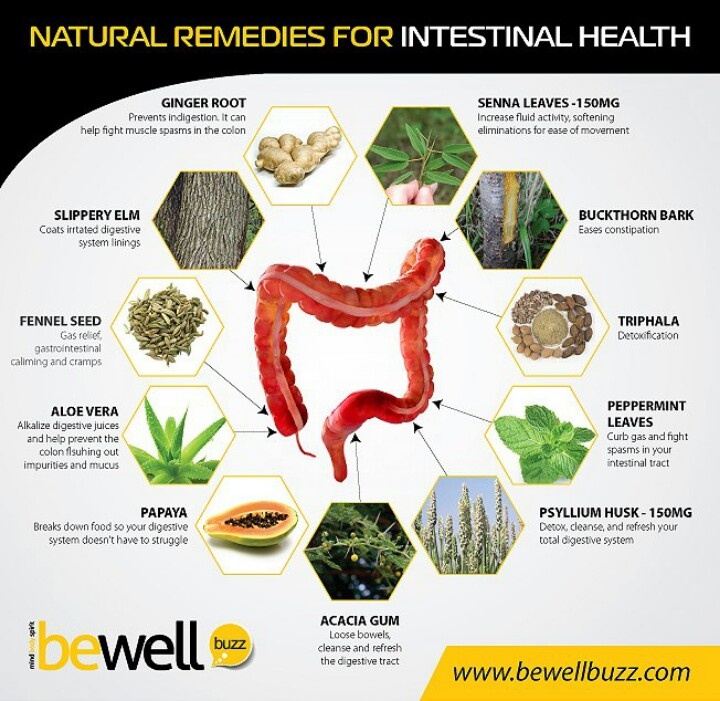
Problems in conceiving
Having trouble conceiving | Jean Hailes
Endometriosis
Endometriosis is a common and often painful condition that affects approximately ten per cent of women. It occurs when the tissue that normally lines the uterus (the endometrium) grows outside the lining of the uterus. The misplaced tissue commonly grows on the uterine (fallopian) tubes, the ovaries or the tissue lining the pelvis (the peritoneum).
How does endometriosis affect fertility?
It is thought that around 30% of women with endometriosis are infertile, however further research is needed to confirm this.
In mild endometriosis there is no obvious reason why infertility occurs. It may be because the endometriosis cells release chemicals that interfere with the ability to conceive or affect early normal development of the embryo.
In moderate to severe endometriosis, scarring may cause interference with ovulation and the passage of the egg along the tube because of damage or blockage. It can also prevent the sperm from reaching the egg.
Not all women with endometriosis are infertile. Many women have children without difficulty, have already had children before they are diagnosed, or eventually have a successful pregnancy.
Treatment options
Surgical treatment of endometriosis, such as an operation called a laparoscopy to remove the endometriosis, is believed to increase the chances of pregnancy.
In an operation using laparoscopy the overall pregnancy rate was approximately 42% of women with endometriosis [1]. Approximately 45% of women will develop a recurrence of endometriosis after laparoscopic surgery for endometriosis [2].
If surgical treatment is unsuccessful, in vitro fertilisation (IVF) treatments may also be considered. However, before trying this form of treatment it is important that your endometriosis is properly treated, as the oestrogen levels involved may flare up any existing endometriosis.
Adenomyosis
Adenomyosis is a condition of the uterus (womb) where the cells which normally form a lining on the inside of the uterus also grow in the muscle wall of the uterus. If adenomyosis is centred in one area, it can lead to a mass of adenomyosis called an adenomyoma.
If adenomyosis is centred in one area, it can lead to a mass of adenomyosis called an adenomyoma.
Adenomyosis is only seen in women in their reproductive years because its growth requires oestrogen. After menopause, adenomyosis lessens because of the lack of oestrogen.
Does adenomyosis affect fertility?
Studies suggest there may be changes in the ability of the uterine muscles to contract appropriately. Also, these endometrial cells inside the muscle may release body chemicals which lead to subfertility.
Fibroids
Fibroids (also known as uterine fibromyomas, leiomyomas or myomas) are non-cancerous growths or lumps of muscle tissue that form within the walls of the uterus (womb).
Fibroids can vary in size ranging from the size of a pea to the size of a rock melon or larger.
It is not known exactly why fibroids occur. However, we do know that the female hormones, oestrogen (estrogen) and progesterone play a significant role in stimulating the growth of fibroids.
Fibroids occur in women of reproductive age, growing at varying rates until the onset of menopause, when they tend to decrease in size and may slowly shrink in size due to the loss of oestrogen and progesterone.
Do fibroids affect fertility?
Infertility is not a common problem for women with fibroids, less than 3% of women may have fertility problems as a result of fibroids. Fibroids can interfere with implantation of the embryo into the uterus, increase the risk of miscarriage or impact the progress of labour depending on the size and position.
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
PCOS is the most common endocrine (hormonal) disorder in women. Symptoms include menstrual problems such as irregular periods and anovulation (lack of ovulation), high androgen (testosterone) levels which can cause male patterned hair growth and acne and metabolic problems which cause weight gain and an increased risk of type 2 diabetes.
PCOS and fertility
One of the first things you may have been told when diagnosed with PCOS was that the condition can affect your ability to have children. Whilst this is true for some women who have PCOS, 60% of women with PCOS become pregnant naturally. Some women may experience reduced fertility or it may take longer to conceive.
Whilst this is true for some women who have PCOS, 60% of women with PCOS become pregnant naturally. Some women may experience reduced fertility or it may take longer to conceive.
In women with PCOS the hormone changes that can cause irregular cycles may also affect ovulation and therefore affect fertility. Lack of ovulation is the most common cause of infertility in PCOS. An anovulatory cycle is a menstrual cycle in which ovulation fails to occur. This means that you do bleed but do not release an egg or ovulate.
In addition, body weight has an impact on fertility for women especially for those with PCOS.
Further help
There are many things you can do to improve your fertility and treatments are available if you have difficulty conceiving. See your doctor to first discuss treatment of your PCOS symptoms tailored to your individual needs. This might include some changes to lifestyle and/or medication.
Premature & early menopause
Premature menopause
Premature menopause is when the final period occurs before a woman is 40. The reason for premature menopause may be because:
The reason for premature menopause may be because:
- your periods stopped spontaneously but early (premature ovarian failure)
- you have had surgery to remove both ovaries (oophorectomy)
- chemotherapy has caused ovaries to fail
Early menopause
Early menopause is when the final period occurs before a woman is 45. Again the reasons may be spontaneous, surgical or chemical.
Effect on fertility
With premature and early menopause, the ovaries run out of eggs earlier than expected and they are unable to produce an egg or the hormones required for pregnancy.
Very rarely, (about a 2-5% lifetime chance), a woman may have a spontaneous pregnancy after a diagnosis of premature/early menopause.
Sometimes, premature/early menopause is diagnosed when a woman has sought help for fertility. If the ovaries fail to respond to the hormones used to produce eggs or if eggs fail to fertilise, these may be signs of premature/early menopause developing.
For a woman who has gone through premature/early menopause, depending on her circumstance her options for having children include:
- a donor egg
- surrogacy with a donor egg
- adoption
To explore the best option for you, ask your doctor for a referral to a fertility specialist who is a member of one of the in vitro fertilisation (IVF) clinics.
Fertility & chemotherapy
If you have been diagnosed with cancer and premature/early menopause is likely to occur because of treatment for cancer, there are some things you can do before you have the treatment.
Before chemotherapy and/or radiotherapy, you could investigate your options for trying to preserve eggs for conception. There are a number of options including:
- egg preservation
- ovarian preservation
- ovarian biopsy and freezing
Egg preservation
This takes place before chemotherapy.
The ovaries are hormonally stimulated to produce eggs and the eggs are then collected.
If you have a male partner, the eggs can be fertilised with your partner's sperm and the embryos are then frozen. When you are ready for pregnancy, the embryos are transferred into the uterus.
If you do not have a partner, the unfertilised eggs may be frozen. When you are ready for pregnancy, the eggs are thawed and a male partner's sperm or donor sperm is used to fertilise them. (This technology is still in development and sadly the success is limited).
Ovarian preservation
Some women are given therapy with a GnRH agonist – a hormone that causes a chemical reaction to control the ovary and eggs temporarily. This therapy is given during chemotherapy. After the chemotherapy stops, the GnRH agonist stops and the menstrual cycle should return. This therapy is not well developed or researched.
Ovarian biopsy & freezing
This procedure takes place before chemotherapy starts. A piece of ovary is excised (cut away) and frozen. After the chemotherapy is complete, the ovarian tissue is transplanted under skin and with hormone stimulation, eggs are collected. This technique has recently shown some success although is still in the research phase.
This technique has recently shown some success although is still in the research phase.
Thyroid problems
Your thyroid is a small bowtie or butterfly-shaped gland, located in your neck, wrapped around the windpipe. The thyroid gland takes iodine (mostly found in foods such as seafood and salt) to produce thyroid hormones. Two key thyroid hormones are triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4). These hormones help oxygen get into cells and regulate the body's metabolism. The thyroid hormones also affect other important functions of the body such as growth.
There are number of factors that can put you at a higher risk of thyroid disease:
- A personal history of autoimmune conditions, including Type 1 diabetes
- If you have grown up in an area that was iodine deficient
- If you have been exposed to head and neck radiation in the past
Thyroid conditions affect women five times more often than men.
If the thyroid is underactive, symptoms of hypothyroidism may occur. An overactive thyroid gland produces excess thyroid hormones and is called hyperthyroidism.
An overactive thyroid gland produces excess thyroid hormones and is called hyperthyroidism.
How a problem thyroid affects fertility and pregnancy
According to Dr Jennifer Wong, a consultant endocrinologist at Monash Health, a number of health problems are associated with a problematic thyroid:
- Decreased fertility making it much harder to become pregnant
- Increased risk of miscarriage
- Increased risk of pre-term or early delivery
- Hypertension (high blood pressure)
- Premature birth
Diagnosing thyroid dysfunction
It is very important to detect thyroid problems in women pre-pregnancy and during the first 12 weeks of pregnancy as the foetus is dependent on the mother's thyroid hormone in the first trimester.
A simple, specific blood test will determine whether you have thyroid dysfunction. You can see your doctor for this test.
Thyroid treatment
If you are diagnosed with a thyroid condition, treatment is quite easy and manageable.
Premature & early menopause
Premature menopause
Premature menopause is when the final period occurs before a woman is 40. The reason for premature menopause may be because:
- your periods stopped spontaneously but early (premature ovarian failure)
- you have had surgery to remove both ovaries (oophorectomy)
- chemotherapy has caused ovaries to fail
Early menopause
Early menopause is when the final period occurs before a woman is 45. Again the reasons may be spontaneous, surgical or chemical.
Effect on fertility
With premature and early menopause, the ovaries run out of eggs earlier than expected and they are unable to produce an egg or the hormones required for pregnancy.
Very rarely, (about a 2-5% lifetime chance), a woman may have a spontaneous pregnancy after a diagnosis of premature/early menopause.
Sometimes, premature/early menopause is diagnosed when a woman has sought help for fertility. If the ovaries fail to respond to the hormones used to produce eggs or if eggs fail to fertilise, these may be signs of premature/early menopause developing.
If the ovaries fail to respond to the hormones used to produce eggs or if eggs fail to fertilise, these may be signs of premature/early menopause developing.
For a woman who has gone through premature/early menopause, depending on her circumstance her options for having children include:
- a donor egg
- surrogacy with a donor egg
- adoption
To explore the best option for you, ask your doctor for a referral to a fertility specialist who is a member of one of the in vitro fertilisation (IVF) clinics.
Turner's syndrome
The most common genetic cause of infertility in women is Turner's syndrome.
Turner's syndrome is a chromosomal condition that alters development in females. This condition occurs in about 1 in 2,500 female births worldwide.
It is caused by the complete or partial lack of one of the X chromosomes (female sex chromosome). This results in a range of complications, including stunted growth and development, deafness, an increased risk of heart and kidney problems and infertility. Women with this condition tend to be shorter than average and are usually unable to conceive a child because of an absence of ovarian function.
Women with this condition tend to be shorter than average and are usually unable to conceive a child because of an absence of ovarian function.
The majority of women with Turner's syndrome are infertile. There are two types of Turner's syndrome – XO who never have periods and XX/XO Mosaic who can have periods but have an early menopause. Spontaneous pregnancies (less than 5% of women) are associated with a high risk of miscarriage, and chromosomal and congenital abnormalities.
Pregnancy can be achieved at present through IVF technology with donor egg or embryo.
Due to early menopause, women with Turner Mosaic syndrome should not delay exploring their pregnancy options for too long, if this is possible.
Counselling regarding fertility and pregnancy is highly recommended for all women with Turner's syndrome.
Infertility - NHS
Infertility is when a couple cannot get pregnant (conceive) despite having regular unprotected sex.
Around 1 in 7 couples may have difficulty conceiving.
About 84% of couples will conceive naturally within a year if they have regular unprotected sex (every 2 or 3 days).
For couples who have been trying to conceive for more than 3 years without success, the likelihood of getting pregnant naturally within the next year is 1 in 4, or less.
Getting help
Some people get pregnant quickly, but for others it can take longer. It's a good idea to see a GP if you have not conceived after a year of trying.
Women aged 36 and over, and anyone who's already aware they may have fertility problems, should see their GP sooner.
They can check for common causes of fertility problems and suggest treatments that could help.
Infertility is usually only diagnosed when a couple have not managed to conceive after a year of trying.
There are 2 types of infertility:
- primary infertility – where someone who's never conceived a child in the past has difficulty conceiving
- secondary infertility – where someone has had 1 or more pregnancies in the past, but is having difficulty conceiving again
Read more about how infertility is diagnosed.
Treating infertility
Fertility treatments include:
- medical treatment for lack of regular ovulation
- surgical procedures such as treatment for endometriosis, repair of the fallopian tubes, or removal of scarring (adhesions) within the womb or abdominal cavity
- assisted conception such as intrauterine insemination (IUI) or IVF
The treatment offered will depend on what's causing the fertility problems and what's available from your local integrated care board (ICB).
Private treatment is also available, but it can be expensive and there's no guarantee it will be successful.
It's important to choose a private clinic carefully. You can ask a GP for advice, and should make sure you choose a clinic that's licensed by the Human Fertilisation and Embryology Authority (HFEA).
Some treatments for infertility, such as IVF, can cause complications.
For example:
- multiple pregnancy – if more than 1 embryo is placed in the womb as part of IVF treatment there's an increased chance of having twins; this may not seem like a bad thing, but it significantly increases the risk of complications for you and your babies
- ectopic pregnancy – the risk of having an ectopic pregnancy is slightly increased if you have IVF
Read more about how infertility is treated.
What causes infertility?
There are many possible causes of infertility, and fertility problems can affect either partner. But in a quarter of cases it is not possible to identify the cause.
Common causes of infertility include:
- lack of regular ovulation (the monthly release of an egg)
- poor quality semen
- blocked or damaged fallopian tubes
- endometriosis – where tissue that behaves like the lining of the womb (the endometrium) is found outside the womb
Risk factors
There are also several factors that can affect fertility.
These include:
- age – fertility declines with age
- weight – being overweight or obese (having a BMI of 30 or over) reduces fertility; in women, being overweight or severely underweight can affect ovulation
- sexually transmitted infections (STIs) – several STIs, including chlamydia, can affect fertility
- smoking – can affect fertility: smoking (including passive smoking) affects your chance of conceiving and can reduce semen quality; read more about quitting smoking
- alcohol – the safest approach is not to drink alcohol at all to keep risks to your baby to a minimum.
 Drinking too much alcohol can also affect the quality of sperm (the chief medical officers for the UK recommend adults should drink no more than 14 units of alcohol a week, which should be spread evenly over 3 days or more)
Drinking too much alcohol can also affect the quality of sperm (the chief medical officers for the UK recommend adults should drink no more than 14 units of alcohol a week, which should be spread evenly over 3 days or more) - environmental factors – exposure to certain pesticides, solvents and metals has been shown to affect fertility, particularly in men
- stress – can affect your relationship with your partner and cause a loss of sex drive; in severe cases, stress may also affect ovulation and sperm production
There's no evidence to suggest caffeinated drinks, such as tea, coffee and colas, are associated with fertility problems.
Page last reviewed: 18 February 2020
Next review due: 18 February 2023
Fomin's clinic — a network of multidisciplinary clinics
If pregnancy does not occur within six months of active sexual life, then this is one of the signs of infertility. But don't panic. This does not mean at all that you have infertility, perhaps it is enough for you, for example, to adjust your diet. Second, infertility is treated. Well, you should not immediately cheat yourself on the subject of IVF. Remember, infertility is not the same as IVF.
But don't panic. This does not mean at all that you have infertility, perhaps it is enough for you, for example, to adjust your diet. Second, infertility is treated. Well, you should not immediately cheat yourself on the subject of IVF. Remember, infertility is not the same as IVF.
Infertility is a diagnosis that 10% of women all over the world have to live with: according to statistics, every fourth married couple is infertile. In this article we will talk about what female infertility is, how to live with it and whether it can be overcome.
Female infertility is a diagnosis made after a year of unsuccessful attempts to have children, subject to regular sex with a partner without contraception. If a woman is older than 35 years, the diagnosis is made faster - after 6 months. After 35 years, the ability to conceive gradually decreases, so older women should not delay treatment.
However, one should not rush to sad conclusions either. According to statistics, even completely healthy couples under the age of 30 manage to conceive a child in the first three months only in 20-37% of cases. At the same time, after six months, pregnancy occurs already in 80% of couples. Until a year has passed from the first attempt, there is no need to worry, be examined, and even more so, to be treated.
At the same time, after six months, pregnancy occurs already in 80% of couples. Until a year has passed from the first attempt, there is no need to worry, be examined, and even more so, to be treated.
Pregnancy depends on many reasons - in order for the "stars to align" and all the factors to coincide, sometimes it takes some time.
For example, it is known that the easiest way to get pregnant is to make love 3-4 times a week. But a break of more than 5 days can adversely affect the quality of spermatozoa.
In addition, much depends on the lifestyle of parents - stress and heavy workload reduce fertility in both men and women. It's no surprise that many successful pregnancies have started during family vacations.
If less than 6-12 months have passed since the first attempt, you can try several "life hacks":
Choose the best time to conceive. According to some reports, the day of ovulation and 2-3 days before it are best suited for conception. To find out when ovulation occurs, a urinary express test for luteinizing hormone will help - a day or two before ovulation it will become positive.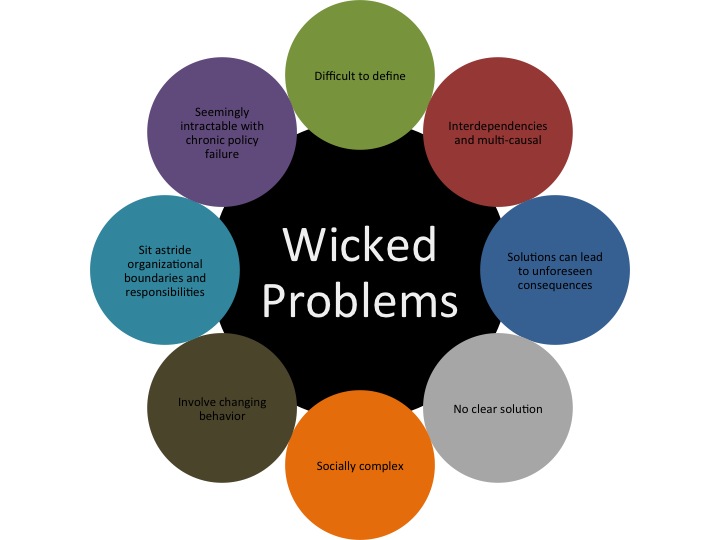 However, calculating the optimal time is not always the best option.
However, calculating the optimal time is not always the best option.
I always oppose the calculation of the optimal time for conception, because because of this, sex begins on a schedule in a couple's life, and this is one continuous stress. It seems to me that it is more reasonable to have sex 2-3 times a week during the entire cycle.
Kosolapova Inna Vladimirovna, gynecologist-reproductologist of the Fomina Clinic, chief physician
Do not use lubricants. Water-based, oil-based and silicone-based lubricants reduce sperm survival. But lubricants based on hydroxyethylcellulose have less effect on sperm survival - so if there is a lack of lubrication, you can continue to use them.
Stop dieting. Good nutrition is the key to a successful pregnancy. But don't overeat either. There is evidence that a body mass index (BMI) of 19 is ideal for pregnancy.-thirty. In women who have a BMI greater or less, the time to conception increases.
You can calculate your BMI manually by dividing your weight by your height squared. Alternatively, you can use the built-in calculator on the website of the medical organization, or download a special application.
Alternatively, you can use the built-in calculator on the website of the medical organization, or download a special application.
Quit smoking and alcohol. Smoking increases the risk of infertility by 1.6 times. It is also better not to abuse alcohol - eat more than 20 grams of ethanol per day, the risks of "earning" infertility increase by 60%.
On the other hand, the position of the body during sex, based on the available data, does not affect the result in any way. The "missionary" position is suitable for conception just like any other.
If more than a year has passed and nothing helps, it's time to see a doctor. The diagnosis of "infertility" has the right to make only an obstetrician-gynecologist (reproductologist).
It is important to understand that infertility is not only a woman's problem. According to statistics, in the absence of children in a third of cases, the mother is “to blame”, in a third - the father, and in another third of cases the cause of infertility cannot be established. This means that with the diagnosis of "infertility" it is necessary to examine both partners.
This means that with the diagnosis of "infertility" it is necessary to examine both partners.
Male infertility is diagnosed by a urologist/andrologist. But if you go to a family planning center, a reproductive specialist can make a diagnosis.
Most often, female infertility is associated with problems in the reproductive system: in the ovaries, fallopian (or fallopian) tubes, through which the egg passes from the ovaries to the uterus, and in the uterus itself. To figure out what exactly “broke down” in the female reproductive system, the doctor will collect an anamnesis, carefully examine the patient and prescribe tests. We talk more about this in the article "Diagnostics of female infertility".
Infertility is treated, and quite successfully — according to statistics, after diagnosis and therapy, children appear in 50% of women (without the use of assisted reproductive technologies: IVF, etc.). On the other hand, success depends on many factors, from the age and history of previous pregnancies to problems with the partner's sperm. Many factors influence the possibility of getting pregnant, so it can be difficult to predict the result.
Many factors influence the possibility of getting pregnant, so it can be difficult to predict the result.
If the problem is overweight or underweight, it is often enough to normalize the weight for a successful pregnancy. True, much more often the problem is associated with sex hormones - in this situation, the doctor will select the appropriate medication. And if the problem is in the obstruction of the fallopian tubes or in the uterus itself, surgery may be required.
In vitro fertilization (IVF) is available for patients for whom these treatments are not suitable or have not worked.
The essence of IVF is that the patient's ovaries are stimulated with the help of hormones, then the egg is taken and fertilized with the husband's sperm, then the embryo is "grown" for some time in a special incubator and transplanted into the mother's uterus. A baby is born in the same way as other children conceived "naturally".
In Russia, the IVF procedure can be done free of charge under the CHI policy. However, it is important to understand that this is a complex treatment method that requires serious preparation and gives the best result until the age of 40-45. It is difficult to predict how successful IVF will be. According to statistics, the procedure ends with the birth of a live and healthy baby in about 27% of cases.
However, it is important to understand that this is a complex treatment method that requires serious preparation and gives the best result until the age of 40-45. It is difficult to predict how successful IVF will be. According to statistics, the procedure ends with the birth of a live and healthy baby in about 27% of cases.
At the same time, IVF success rates vary greatly not only in different countries, but also in different clinics in the same city. There are clinics in which in 30-40% of cases it is possible to achieve a positive result on the first try.
Very often, mothers are concerned about possible health problems that may occur in children conceived through IVF. But in recent times there has been much less cause for concern than 20 years ago.
When the method was first created, all viable embryos that were obtained after fertilization were placed into the uterus of mothers “just in case”. If everyone took root, the mother often gave birth to twins or triplets, and sometimes “quadruples”. It is much harder to bear several children than one - and after all, mothers already had problems with pregnancy, otherwise IVF would simply not have been required.
It is much harder to bear several children than one - and after all, mothers already had problems with pregnancy, otherwise IVF would simply not have been required.
Today, the goal of the procedure is the birth of one healthy baby, so mothers transfer only one, maximum two of the best embryos. As a result, most children born after IVF do not differ much from their peers.
- Female infertility is as common as male infertility. If you can’t get pregnant within a year, you need to be examined, and sometimes treated together with your spouse.
- Infertility is a complex diagnosis that can have many causes. However, after treatment, about half of women successfully become pregnant and give birth to healthy babies (without IVF).
- IVF is a fairly effective way to give birth to a healthy baby. However, this method (like any other) has pros and cons, so you need to make a decision after consulting with an obstetrician-gynecologist or reproductologist.
Subscribe to us
Causes of infertility in women
Treatment of infertility
If a woman is faced with the problem of conceiving, it is natural to ask herself what is the reason for this? Read on to find out what can affect fertility and should you seek medical help to get pregnant?
Myth
- MYTH: Infertility is more often due to problems in women than in men.
- TRUTH: Infertility occurs with the same frequency in both women and men. Approximately 1/3 of couples experience infertility in the man, 1/3 in the woman, and 1/3 in both partners. 1
Is it my fault?
Difficulties with the onset of pregnancy are observed quite often. On average, 9% of the total population has this problem. 2
There are many factors that can cause infertility, so you should not focus on “whose fault it is”.
- Approximately 1/3 of infertile couples are caused by a female factor 1
- In 1/3 of couples with infertility, the cause is male factor 1
- In 1/3 of couples with infertility, the cause is a mixed (male and female) factor 1
Infertility is not a permanent condition, and it does not mean that you will never have children. You may just need specialist help to achieve your pregnancy goal.
You may just need specialist help to achieve your pregnancy goal.
What are the causes of female infertility?
After you and your partner have undergone a reproductive test, the doctor will be able to make a diagnosis that will explain the causes of infertility.
Unfortunately, in some cases it is not possible to determine a specific factor, so the diagnosis of "infertility of unknown etiology" can be made. In some cases, the doctor may recommend the passage of more advanced and modern methods of infertility treatment - assisted reproductive technologies (ART).
- With increasing age, reproductive function begins to decline
- A healthy 30-year-old woman is approximately 20% likely to become pregnant every month 3
- However, a healthy 40-year-old woman is approximately 5% likely to become pregnant per month 3
- As you age, you are more likely to need ART procedures to get pregnant
- Problems with ovulation occur in approximately 25% of cases associated with infertility 4
- In order for a woman to get pregnant safely, ovulation (release of an egg from an ovary) must take place monthly
- Ovulation may not occur if the woman has irregular or absent periods, and if the woman is overweight or underweight
- Drugs are commonly prescribed to treat ovulation problems 4
- 25-35% of cases of female infertility are associated with obstruction or functional insufficiency of the fallopian tubes 6
- Fallopian tubes are extremely sensitive to damaging factors
- Obstruction of the fallopian tubes may result from a previous infection or surgery on the abdominal organs
- Blockage of the fallopian tubes can prevent the passage of spermatozoa to the egg.
 If fertilization has occurred, then obstruction makes it difficult for the development of the embryo and its passage into the uterine cavity
If fertilization has occurred, then obstruction makes it difficult for the development of the embryo and its passage into the uterine cavity - Obstruction of the fallopian tubes in some cases can be cured with surgical methods. In case of failure of surgical treatment, an in vitro fertilization (IVF) procedure may be required
- 30-50% of women with endometriosis suffer from infertility 7
- Endometriosis - a disease in which the endometrium (the tissue lining the uterine cavity) is found in the ovaries, fallopian tubes, on the outer surface of the uterus, and in other parts of the body 1
- Endometrium can cause painful, heavy, irregular menses, scarring and adhesions 5
- Laparoscopic intervention to help diagnose endometriosis
- Drugs and/or surgery are used to treat endometriosis. After therapy, it is possible to move on to ART
- Approximately 5-10% of fertility problems are due to fibroid tumors (fibroids or leiomyomas)
- These are benign neoplasms consisting of muscle and connective tissue that develop in and around the uterus
- They may change the shape of the uterus or fallopian tubes or cause blockage of the fallopian tubes
- These tumors can make it difficult for sperm to reach the egg or prevent implantation of the embryo in the uterus
- The exact cause of fibroid tumors is unknown, and the severity of any symptoms usually depends on their location, size, and number
- Fibroids are treated with drugs and/or surgery.
 After therapy, it is possible to move on to ART
After therapy, it is possible to move on to ART
- 70-80% of women with PCOS may experience infertility 9
- PCOS leads to an increase in the volume of the ovaries, as well as the growth of numerous small cysts on the thickened surface of the ovaries 4
- This can lead to irregular menstruation, which in turn affects fertility 4
- Ultrasound is used to diagnose PCOS
- The most common treatments for PCOS are drugs and/or surgery. After therapy, it is possible to proceed to ART
- 3% to 8% of female infertility cases may be due to cervical pathology 10
- The glands located in the cervix secrete a secret (mucus) that helps the sperm to move through the genital tract 11
- Some women do not produce enough secretion, it may be too dense and viscous, or contain antibodies (protein molecules) that inhibit the activity of spermatozoa 11
4
- Cervical mucus problems can be corrected with drug therapy / either by transferring sperm directly to the uterus by insemination / or by using IVF, which ensures conception outside the female body
- Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) such as chlamydia or gonorrhea can cause pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) 5
- PID causes blockage of the fallopian tubes and increases the risk of ectopic pregnancy 8.
 12
12 - An ectopic pregnancy occurs when the implantation of the embryo occurs outside the uterus 12
- Tubal obstruction can be treated with surgery, if unsuccessful, ART may be required
- Menopause is a natural process that women go through when childbearing ends and menstruation stops
- Some women go through early menopause before age 40
- If a woman goes through early menopause, then for the onset of pregnancy it is necessary to resort to assisted reproductive technologies (ART), including the use of donor eggs
Are oral contraceptives causing my infertility?
MYTH: Taking oral contraceptives for several years increases the risk of infertility.
TRUE: Studies have not found an association between infertility and contraceptive use over a long period of time.
Like many women, you may have used oral or other hormonal contraceptives for several years to prevent unwanted pregnancies.