What causes vasospasm
Vasospasm | Cedars-Sinai
ABOUT DIAGNOSIS TREATMENT
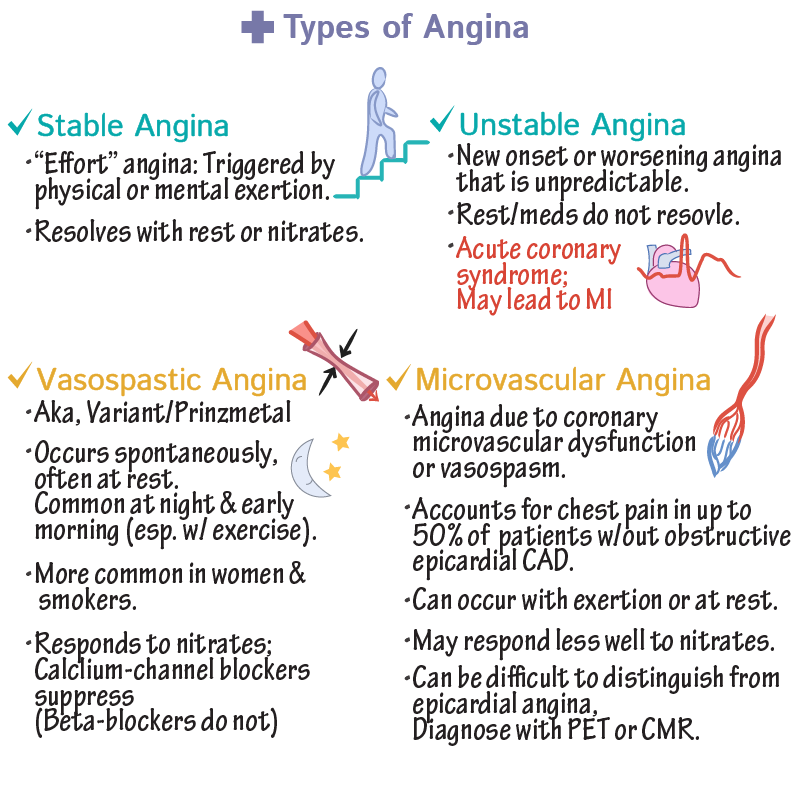
Overview
A vasospasm is the narrowing of the arteries caused by a persistent contraction of the blood vessels, which is known as vasoconstriction. This narrowing can reduce blood flow.
Vasospasms can affect any area of the body including the brain (cerebral vasospasm) and the coronary artery (coronary artery vasospasm).
When the vasospasm occurs in the brain, it is often due to a subarachnoid hemorrhage after a cerebral aneurysm has ruptured.
Symptoms
Symptoms of a vasospasm can vary depending on the area of the body affected. When the condition occurs in the brain symptoms may include:
- Fever
- Neck stiffness
- Confusion
- Difficulty with speaking
- Weakness on one side of the body
Patients who have experienced a cerebral vasospasm often also have stroke-like symptoms:
- Numbness or weakness of the face, arm or leg, especially on one side of the body
- Confusion
- Trouble speaking
- Trouble seeing in one or both eyes
- Trouble walking
- Dizziness, loss of balance or coordination
- Severe headache with no known cause
When the condition occurs in the arms or legs, symptoms include:
- Sharp pain, often described as burning or stinging, at the affected area
- Finger or toe turning purple or blue
When a vasospasm develops in the coronary artery, the main symptom is chest pain often described as constricting, crushing, pressure, squeezing or tightness.
Causes and Risk Factors
Patients who have experienced hemorrhagic stroke are at an increased risk of developing a cerebral vasospasm. Patients with atherosclerosis, a condition where fatty deposits build up and harden on the inside of the arteries, are at an increased risk of developing coronary artery vasospasms.
Patients with Rynaud's Phenomenon are also at an increased risk of developing vasospasms in the toes or fingers.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of a vasospasm usually begins with a physical exam and a review of the patient’s medical history and symptoms. For vasospasms that are minor, this is often adequate to diagnose the condition. For more severe conditions other diagnostic tools will be used.
Imaging tests, including magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and computed tomography (CT) angiography, are used to diagnosed the condition and observe the area affected by the reduced blood flow.
Other tests look exclusively at the blood vessels within the body.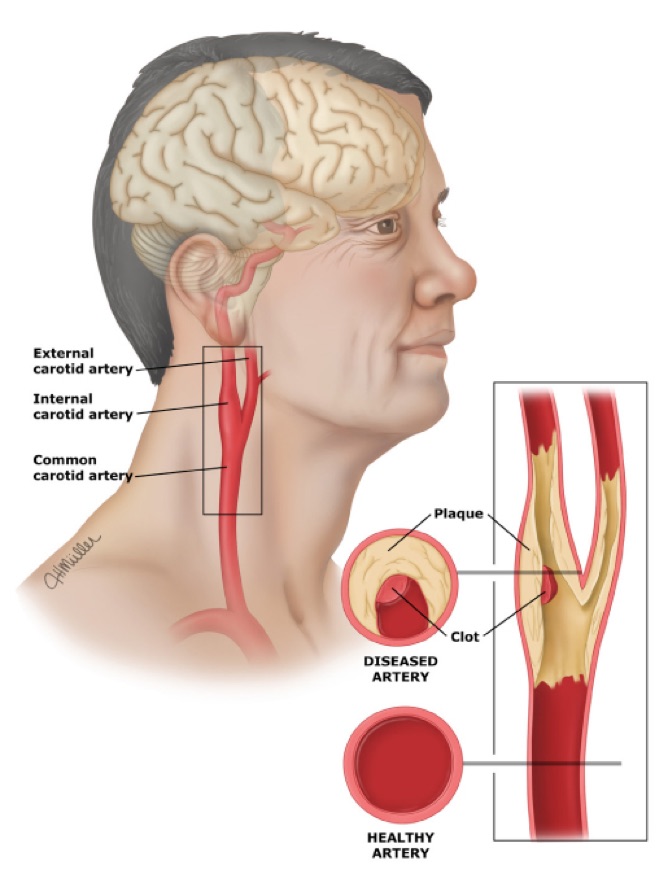 An angiogram may be used to view the arteries. A transcranial Doppler (TCD) ultrasound is used to measure the blood that is flowing through the arteries at the base of the brain.
An angiogram may be used to view the arteries. A transcranial Doppler (TCD) ultrasound is used to measure the blood that is flowing through the arteries at the base of the brain.
If the vasospasm is in the coronary artery an electrocardiogram (ECG) or an echocardiogram may also be used to diagnose the condition.
Treatment
Treatment of vasospasms depends on the severity of the condition and the area of the body it is affecting.
For patients who have experienced a mild form of the condition affecting one of the body's extremities, such as a finger or toe, treatment will focus on preventing episodes of vascular constriction. This may include avoiding cold air, vibration and emotional stress. Lifestyle changes to improve circulation, such as stopping smoking, also will be recommended.
For more severe cases affecting the coronary artery, treatment will focus on minimizing chest pain and preventing a heart attack. Both of these goals can be achieved through medication such as nitroglycerin, long-acting nitrates, calcium channel-blockers or beta-blockers.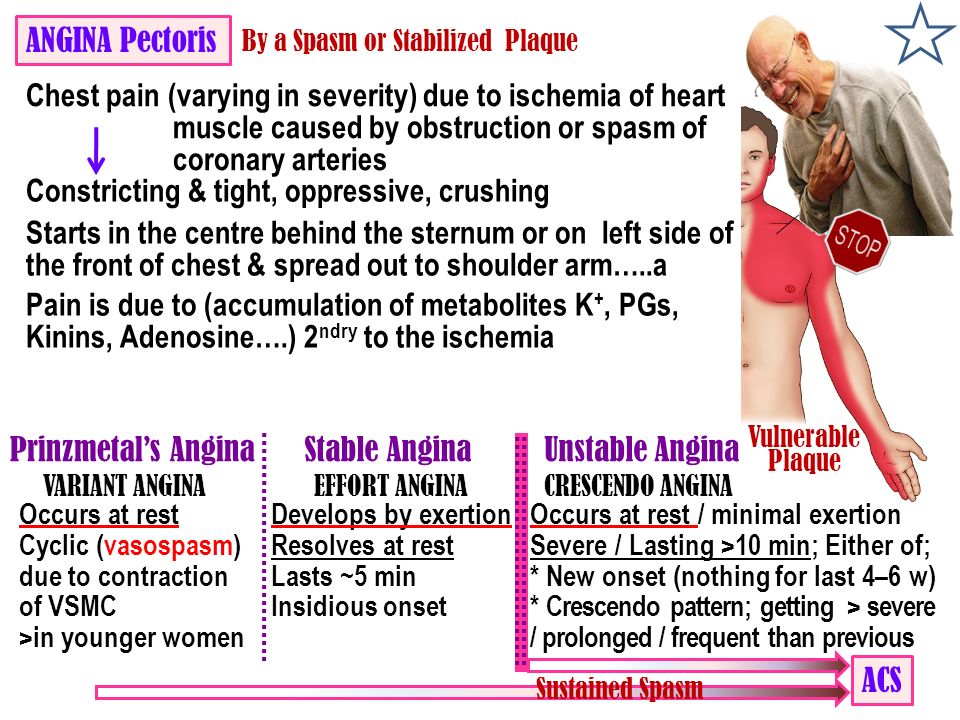
Treatment for vasospasms caused by bleeding inside the skull will vary depending on what caused it, where it is and how large it is. Treatment will usually focus on treating the bleeding first, which may involve interventional radiology or neurosurgery to treat abnormal or leaky blood vessels. The knowledgeable and highly trained staff at Cedars-Sinai's Department of Neurosurgery and the Neurovascular Center will work with each patient to determine the best treatment option.
For patients who have experienced a stroke, the Stroke Program at Cedars-Sinai provides a multidisciplinary treatment approach focused on three areas: stroke prevention, immediate stroke treatment and post-stroke rehabilitation.
© 2000-2022 The StayWell Company, LLC. All rights reserved. This information is not intended as a substitute for professional medical care. Always follow your healthcare professional's instructions.
Narrowed Arteries Affect the Brain, Heart and Hands
Written by WebMD Editorial Contributors
Medically Reviewed by Dan Brennan, MD on June 08, 2021
Humans rely on blood vessels called arteries to carry oxygen-rich blood to all parts of our bodies. Vasospasm occurs when an artery suddenly narrows and the blood supply is drastically reduced. It most often happens in the brain or in the heart. The results can be serious. Sometimes the term vasospasm is used to describe the narrowing of small blood vessels in the hands.
Vasospasm occurs when an artery suddenly narrows and the blood supply is drastically reduced. It most often happens in the brain or in the heart. The results can be serious. Sometimes the term vasospasm is used to describe the narrowing of small blood vessels in the hands.
What Is a Cerebral Vasospasm?
"Vaso" means vessel. A spasm is a sudden muscular contraction. A vasospasm is a sudden contraction of the muscular walls of a blood vessel. In some cases, we know what causes the muscles to contract. Other times it's a mystery.
Cerebral relates to the brain. A cerebral vasospasm almost always follows another major event inside the skull, called a subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH). This is a kind of stroke that happens when a blood vessel on the surface of the brain breaks. Blood fills the space between the skull and the brain. It leaks beneath the arachnoid membrane.
Subarachnoid hemorrhage or SAH is most often caused by an aneurysm. An aneurysm is a weak place in a blood vessel often resulting in a balloon-like bulge.
SAH is the most dangerous type of stroke. You might survive the stroke but then have a cerebral vasospasm, which puts your health and life at risk for a second time.
Signs, Diagnosis, and Treatment of Cerebral Vasospasm
Doctors closely follow people who have had a SAH, watching for signs of cerebral vasospasm. These signs include:
- Stiff neck
- One-sided paralysis
- Impaired speech
- Confusion
Cerebral vasospasm usually occurs in the two weeks following the SAH. Doctors use various imaging tests to diagnose vasospasm. One diagnostic tool is cerebral angiography, which is an X-ray with contrast dye. It is invasive and carries some risk. The transcranial Doppler (TCD) is a type of non-invasive ultrasound. Doctors can do it at your bedside.
Doctors sometimes use medicines called calcium channel blockers to protect the brain following a SAH. In case of vasospasm, doctors may use triple-H therapy, a combination of steps that increase blood flow to the brain. The aim is to open the narrowed blood vessels.
The aim is to open the narrowed blood vessels.
What is Coronary Artery Vasospasm?
Vasospasm can also occur in an artery that supplies blood to the heart. When one of these arteries suddenly narrows, the body reacts immediately. Pain may strike the jaw, chest, arm, and back, feeling much like a heart attack. In a healthy individual, vasospasm may not be serious. In someone with coronary artery disease, it can cause a heart attack or otherwise damage the heart.
Vasospasm happens when something disrupts the chemical messengers that control the heart. Causes include:
- Stress or anxiety
- Hyperventilation
- Transitioning from sleep to wakefulness
- Some legal drugs, such as medications for migraine
- Illegal drugs such as cocaine and amphetamines
- Some herbal supplements, like bitter orange
The pain from coronary artery vasospasm is sometimes called variant angina. It can feel like classic angina pectoris, the chest pain and pressure that some people have during exercise.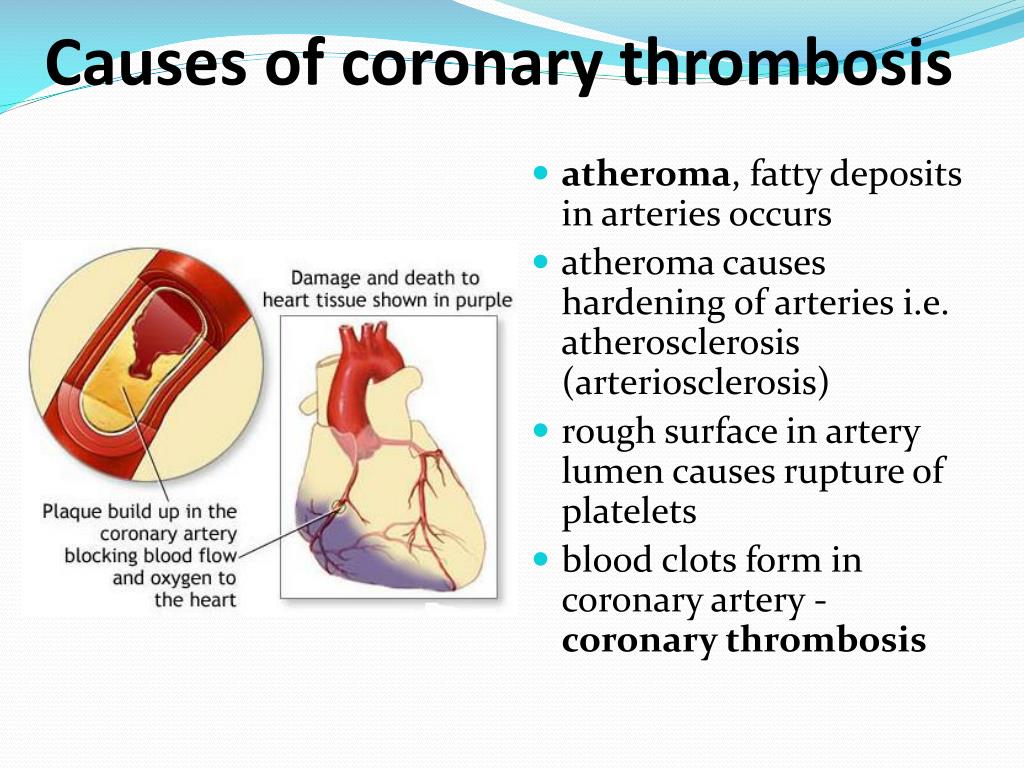 Variant angina occurs when you are resting, most often at night.
Variant angina occurs when you are resting, most often at night.
Diagnosis of Coronary Artery Vasospasm
Doctors often find it hard to distinguish between coronary artery vasospasm and other forms of heart disease. The process often involves ruling out other heart conditions that could cause the symptoms.
Doctors sometimes use angiography to look at the arteries. When a person has had a heart attack, the doctor may see a blocked artery. If a person has coronary artery disease, the doctor may see a partially closed artery. With vasospasm, the arteries sometimes look completely clear.
Diagnosis is more difficult when a person with heart disease has an attack that appears to be vasospasm. Doctors can confirm a diagnosis of vasospasm by using certain drugs to trigger a spasm. Some cardiologists are not trained in these procedures or are uncomfortable using them.
Treatment of Coronary Artery Vasospasm
Immediate treatment of coronary artery vasospasm involves using a medication called nitroglycerin to open up the artery.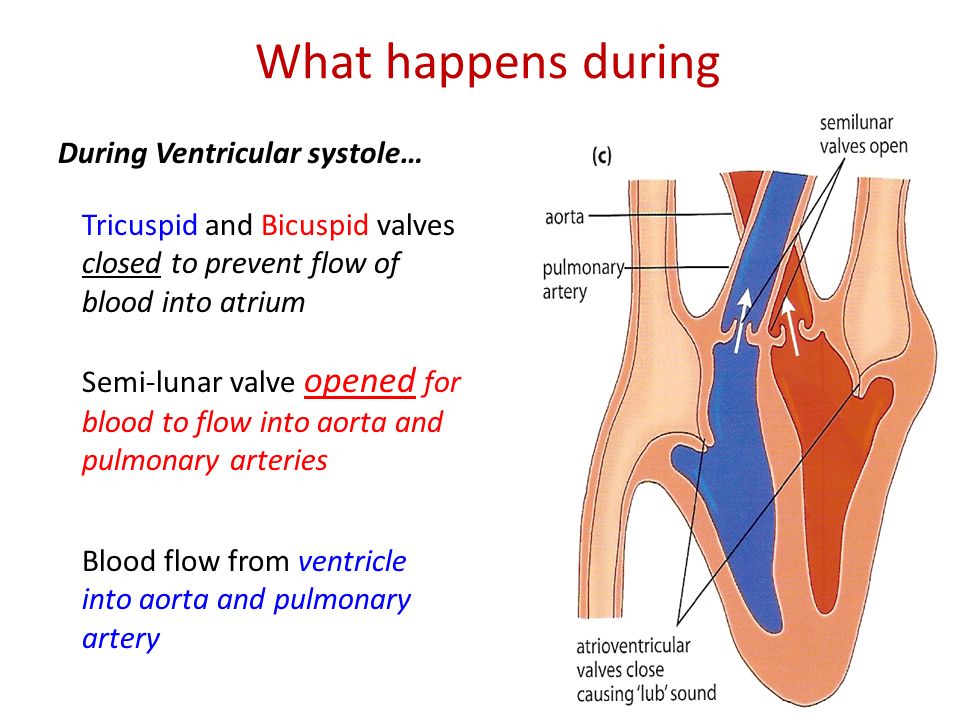 To prevent future attacks, doctors sometimes recommend timed-release nitroglycerin taken at bedtime, since many attacks occur at night. They may also prescribe calcium channel blockers or other drugs that relax the arteries.
To prevent future attacks, doctors sometimes recommend timed-release nitroglycerin taken at bedtime, since many attacks occur at night. They may also prescribe calcium channel blockers or other drugs that relax the arteries.
Vasospasm and Raynaud Syndrome
Vasospasm of the heart and brain happens in large arteries. But the term vasospasm is sometimes used for a syndrome in which smaller arteries constrict, called Raynaud syndrome. This condition causes abnormal sensations and color changes in the hands. These changes usually occur in response to cold.
The hands may turn white, blue, or red. They may burn, prickle, or feel cold. Low temperatures usually trigger these reactions, but emotional stress may be a trigger as well. Other extremities, such as the toes and nose, may also be affected.
Most cases of Raynaud syndrome occur in women aged 15 to 40. A few other conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis, may cause Raynaud syndrome. In about 80% of cases, doctors are unable to discover a cause. Doctors usually diagnose Raynaud syndrome based on a physical examination. Other tests aren't usually needed.
Doctors usually diagnose Raynaud syndrome based on a physical examination. Other tests aren't usually needed.
If you have Raynaud syndrome, you should avoid getting too cold. In cold weather, you should always wear coats, hats, and mittens. You may need to use mittens on your hands when taking food out of the freezer. Smoking should be avoided because nicotine constricts blood vessels. In some cases, doctors may prescribe calcium channel blockers.
Causes of exacerbation of cardiovascular diseases in winter
Why colds are dangerous for the heart, and how to protect yourself from heart attack and stroke in winter will be told by the chief freelance specialist cardiologist of the Ministry of Health of Chuvashia, chief physician of the Republican Cardiological Dispensary Irina Petrovna Efimova.
The winter season is increasingly full of surprises in the form of short-term rise in temperature, followed by severe frosts, with unpredictable rainfall. Such temperature fluctuations adversely affect the general state of health. Even in the absence of any serious illness. Why? Because, most often, they are accompanied by significant changes in atmospheric pressure. The most predisposed to a painful reaction to the weather, especially people with cardiovascular diseases. Age also plays a role. More sensitive to the weather people after 40-50 years old, suffering from atherosclerosis of cerebral vessels. Statistics show that in winter the number of heart attacks and other acute conditions of the cardiovascular system increases by 35-40%!
Such temperature fluctuations adversely affect the general state of health. Even in the absence of any serious illness. Why? Because, most often, they are accompanied by significant changes in atmospheric pressure. The most predisposed to a painful reaction to the weather, especially people with cardiovascular diseases. Age also plays a role. More sensitive to the weather people after 40-50 years old, suffering from atherosclerosis of cerebral vessels. Statistics show that in winter the number of heart attacks and other acute conditions of the cardiovascular system increases by 35-40%!
According to experts, the main reasons for this may be the following.
Deterioration of blood circulation. Cold causes constriction of blood vessels, which limits blood flow to the heart. In addition, when inhaling cold air, a spasm of the coronary arteries can be observed.
Wrong diet. If in summer and autumn our body receives all the necessary vitamins and microelements, then in winter this does not happen. The main food in winter is meat, flour dishes and sweets, which we drink with tea or coffee to keep warm. Such a diet raises blood pressure, increasing the risk of developing heart accidents.
The main food in winter is meat, flour dishes and sweets, which we drink with tea or coffee to keep warm. Such a diet raises blood pressure, increasing the risk of developing heart accidents.
Sedentary lifestyle. In winter, we move much less, which leads to the accumulation of extra pounds. Excess weight weakens the work of all organs, primarily the heart and blood vessels.
Oxygen deficiency. This problem is directly related to the previous one. Due to the fact that in winter we spend little time outdoors and rarely ventilate the rooms, our body experiences a constant lack of oxygen, which adversely affects the condition of the heart and blood vessels.
Decreased immunity . A decrease in physical activity, a violation of the diet, combined with frequent temperature changes when going outside, in heated rooms, in transport, especially in warm winter clothes ... - all this leads to a noticeable decrease in immunity.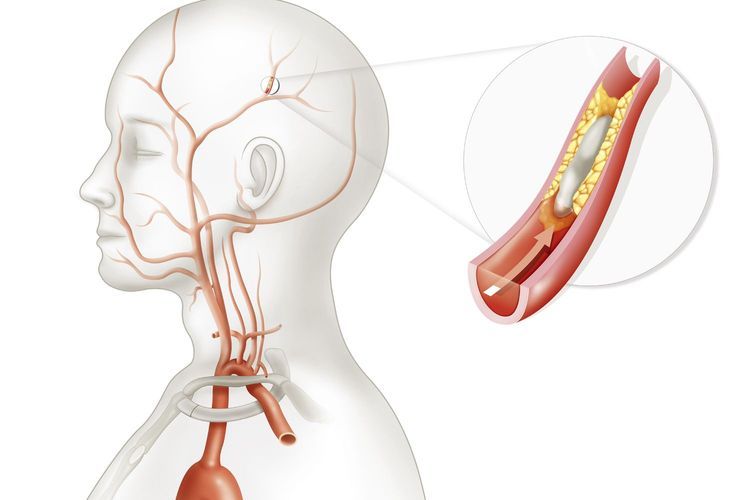 Against this background, the likelihood of respiratory and other diseases increases. This also adversely affects the state of heart health.
Against this background, the likelihood of respiratory and other diseases increases. This also adversely affects the state of heart health.
Incorrect medication. Reduced daylight hours, drowsiness and fatigue, which are often overcome in winter, lead to the fact that the cores forget to take the pills prescribed to them.
High blood pressure. In winter, constant blood pressure readings can be increased by several points, which puts additional stress on the heart.
Increased cholesterol levels. Due to the excessive fatty and high-calorie foods that we eat in winter, the level of cholesterol in the blood rises, contributing to the development of atherosclerosis, myocardial infarction and coronary heart disease.
Vitamin D deficiency. The main source of vitamin D is ultraviolet rays, which are so lacking in winter. Vitamin D has a strengthening effect on the heart and blood vessels, and its deficiency in the cores can provoke exacerbations of diseases.
Excessive exercise. According to doctors, sometimes the development of heart attacks and strokes in men in winter can be associated with intensive snow removal, pulling out a car stuck in a snowdrift ... All this greatly overloads the cardiovascular system, which in such conditions can fail.
How to protect the heart from the cold? Knowing all of the above, we can protect our body, and especially the cardiovascular system, from "winter" troubles. And it's easy. It is only important to observe certain preventive measures:
This is, firstly, proper nutrition. To maintain normal heart function in winter, it is important to enrich the diet with healthy foods. These are fatty varieties of fish for the prevention of atherosclerosis. Seasonal vegetables and fruits. Among them, garlic is very useful - a powerful remedy for hypertension. The antiviral properties of garlic have been known for a long time. However, few people know that garlic is also an excellent remedy for high blood pressure. Avocado - a source of fatty acids and potassium, grapefruit for the normal functioning of the heart muscle. Cereal crops - a blow to cholesterol. You will bring invaluable benefits to your body if you replace white bread with whole grains, and also introduce unprocessed cereals into your diet. Cereals contain a large amount of fiber, which prevents the absorption of bad cholesterol. Berries are a storehouse of minerals and nutrients. Dark chocolate is a treat for heart health. So, regular consumption of dark chocolate prevents the appearance of blood clots, and also improves the functioning of red blood cells. I would also like to note flaxseed oil - it is a powerful preventive measure against many cardiovascular diseases. It is flaxseed oil that contains the most omega-3 acids, which “mercilessly” clean our blood vessels from stale cholesterol.
However, few people know that garlic is also an excellent remedy for high blood pressure. Avocado - a source of fatty acids and potassium, grapefruit for the normal functioning of the heart muscle. Cereal crops - a blow to cholesterol. You will bring invaluable benefits to your body if you replace white bread with whole grains, and also introduce unprocessed cereals into your diet. Cereals contain a large amount of fiber, which prevents the absorption of bad cholesterol. Berries are a storehouse of minerals and nutrients. Dark chocolate is a treat for heart health. So, regular consumption of dark chocolate prevents the appearance of blood clots, and also improves the functioning of red blood cells. I would also like to note flaxseed oil - it is a powerful preventive measure against many cardiovascular diseases. It is flaxseed oil that contains the most omega-3 acids, which “mercilessly” clean our blood vessels from stale cholesterol.
Outdoor walks. Every day at least 40-60 minutes should be devoted to walks in the fresh air, even if it is very cold outside. For those who suffer from heart disease, it is better to refrain from walking in severe frosts. But that doesn't mean you shouldn't be outdoors. When weather permits, a half-hour walk is a must, especially before bed. Such patients, first of all, are required to follow the recommendations of the attending physician. As a rule, they must constantly take prescribed drugs. In addition, you need to have drugs with you that quickly expand the coronary vessels in case an angina attack occurs. And, of course, you should dress warmly enough.
For those who suffer from heart disease, it is better to refrain from walking in severe frosts. But that doesn't mean you shouldn't be outdoors. When weather permits, a half-hour walk is a must, especially before bed. Such patients, first of all, are required to follow the recommendations of the attending physician. As a rule, they must constantly take prescribed drugs. In addition, you need to have drugs with you that quickly expand the coronary vessels in case an angina attack occurs. And, of course, you should dress warmly enough.
Warm clothes and footwear. Clothing and footwear must be warm and comfortable at the same time. Under no circumstances should you sweat in the cold. It is recommended to use the principle of layering: several thin blouses are better than one thick sweater. Preference should be given to products made from natural materials. In any case, those clothes that come into contact with the body should not be synthetic. Synthetics do not breathe, create increased humidity, cool quickly and transfer this cold to the body. Naturally, people with coronary heart disease should not leave the house in the cold without gloves and a headgear. When exposed to cold, a spasm of the capillary vessels of the skin occurs, and reflexively the same spasm occurs in the coronary vessels. This fact has been repeatedly confirmed experimentally: when the palms are cooled, the coronary circulation is disturbed. In a healthy person, the narrowing is quickly replaced by an expansion of the coronaries, but in a patient, an attack of angina pectoris may occur. Without a headgear, the mechanism of action of cold is the same as with the cooling of the palms: capillary spasm causes a similar reaction in the coronary vessels.
Naturally, people with coronary heart disease should not leave the house in the cold without gloves and a headgear. When exposed to cold, a spasm of the capillary vessels of the skin occurs, and reflexively the same spasm occurs in the coronary vessels. This fact has been repeatedly confirmed experimentally: when the palms are cooled, the coronary circulation is disturbed. In a healthy person, the narrowing is quickly replaced by an expansion of the coronaries, but in a patient, an attack of angina pectoris may occur. Without a headgear, the mechanism of action of cold is the same as with the cooling of the palms: capillary spasm causes a similar reaction in the coronary vessels.
And most importantly: adherence to the regimen of medications prescribed by doctors and prompt medical attention if the condition worsens.
Be healthy and take care of your heart!
Vasospasm (angiospasm) - symptoms and treatment
Learn about additional research
January 17, 2021
37037
Causes of vasospasm
Varieties of angiospasm are classified according to their localization:
- in the limbs;
- in the main arteries;
- in the brain.
A separate variant of the pathology is angiospasm of the coronary vessels.
Causes of vasospasm
Spasm of blood vessels occurs in the presence of several factors that affect the development of this disease:
- Smoking. A bad habit provokes vasoconstriction, and therefore another negative factor, for example, a common cold, can lead to spasm.
- Alcohol abuse.
- Improper sleep and wake patterns.
- Physical and mental overload.
- Excessive consumption of coffee and tea.
- Intoxication with toxic substances containing carbon sulphide compounds and lead.
- Inflammation of blood vessels.
- Violations of nervous regulation.
The last reason includes a whole group of factors of an internal and external nature (neurosis, malfunctions of the endocrine system, etc.).
Profile "Lipid status" in Moscow
from 1 w.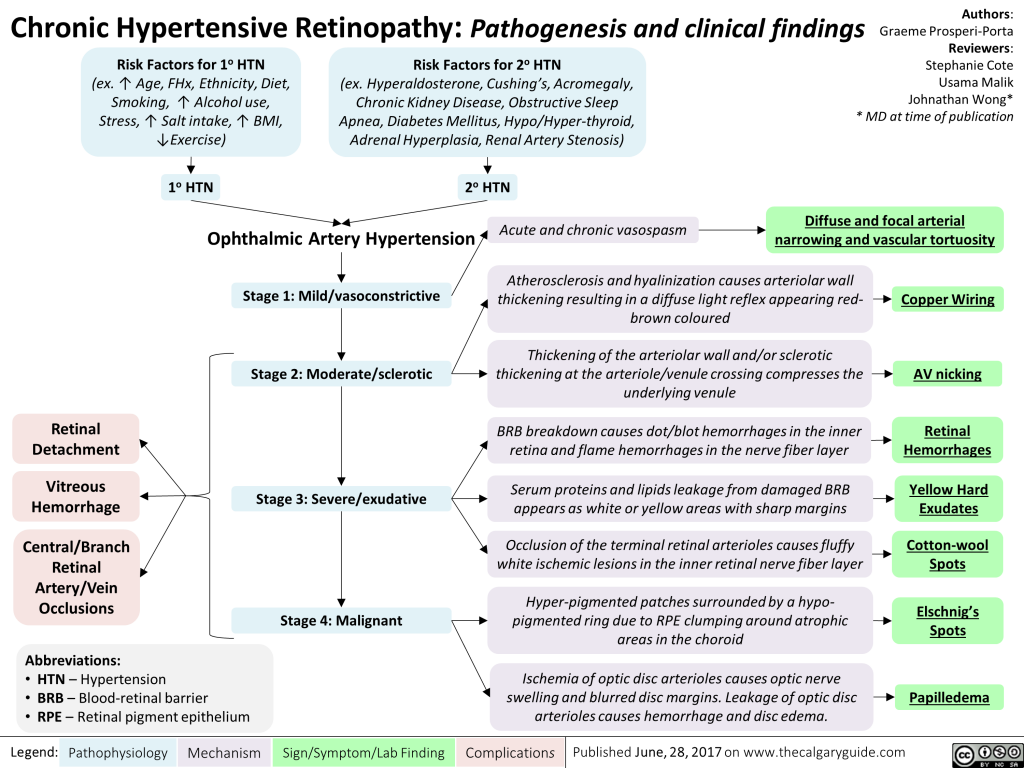 d.
d.
from 2810 ₽
Cardiorisk profile in Moscow
from 1 w.d.
from 9930 ₽
Thrombosis profile in Moscow
from 1 - 5 w.d.
from 4530 ₽
Symptoms of vasospasm
If the cause of angiospasm was the narrowing of the capillaries, the external manifestation will be noticeable to the naked eye: the affected area of the body acquires an alabaster (white) shade. So, Raynaud's disease is characterized by the so-called white finger syndrome. It is associated with bleeding of the phalanges. The fingers lose their sensitivity. Another symptom is livedo reticularis. With angiospasm, areas with a characteristic bluish tinge appear on the skin of the thighs and ankles. Sometimes the symptom is supplemented by a mesh pattern. The skin of the affected area becomes cold and pale. Angiospasm can lead to edema and subsequent tissue necrosis.
If there is a narrowing of the vessels of the main artery, a characteristic symptom is the so-called commander's foot. The presentation is similar to Raynaud's disease, but affects the entire lower limb. The leg becomes cold, its skin becomes whitish. With prolonged angiospasm, the limb may turn blue, and its incomplete paralysis occurs.
The presentation is similar to Raynaud's disease, but affects the entire lower limb. The leg becomes cold, its skin becomes whitish. With prolonged angiospasm, the limb may turn blue, and its incomplete paralysis occurs.
Coronary spasm is similar in its symptoms to angina pectoris. There is a paroxysmal pain behind the sternum, which does not weaken, even if the body is at rest.
Cerebral angiospasm occurs with atherosclerosis of cerebral vessels. But the cause of the symptom can be not only this pathology. Angiospasm is also possible with damage to various parts of the brain.
How to determine vasospasm
Manifestations of angiospasm are similar to ischemic ones, especially if the disease develops on the basis of obstructive angiopathy. To establish a complete clinical picture based on the symptoms of the patient, it is necessary to conduct a number of studies. Under the influence of thermal stimuli and pharmacological agents, the dynamics of blood flow is analyzed. With the help of these studies, areas with angiospasm are detected. Plethysmography, rheography, local temperature measurement are also used.
With the help of these studies, areas with angiospasm are detected. Plethysmography, rheography, local temperature measurement are also used.
Treatment of vasospasm
Therapy that is prescribed to stop or prevent angiospasm often coincides with the treatment of the disease that causes the symptom. If the patient smokes or drinks alcohol, he should definitely give up these bad habits. When foci of chronic infection are detected, they are sanitized. If, along with angiospasm, a patient is diagnosed with high blood pressure, antihypertensive drugs are prescribed.
In some cases, drugs are used that contain vasoactive calcium channel blockers. The choice of medicine should take into account the individual characteristics of the body.
Peripheral spasm requires additional therapy, which includes rubbing and warming of diseased limbs, as well as novocaine blockade. In some cases, surgical intervention is required - resection of the sympathetic nerve trunk, alcoholization of the sympathetic nerves.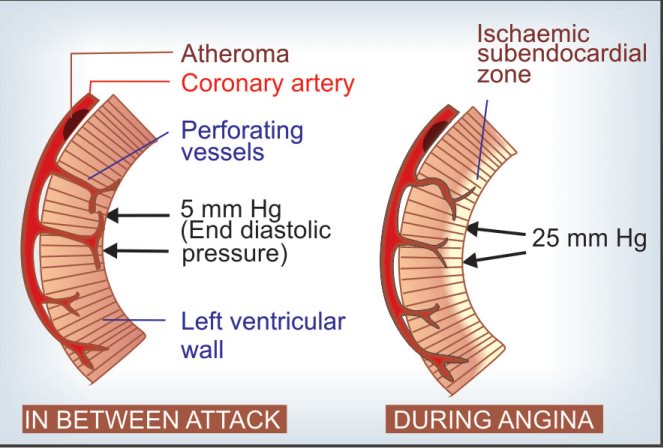
general practitioner
Covid-19
Coronavirus, RNA (SARS-CoV-2, PCR) smear, quality
Determination of SARS-CoV-2 RNA by PCR.
Certificate of results in two languages: English, Russian.
Pre-order of the test is available on the website
Covid-19
Post-vaccination antibodies to SARS-CoV-2-IgG, to the spike (S) protein
The test is used to detect the immune response of the body after vaccination against COVID-19.
Certificate of results in two languages: English, Russian.
Pre-order analysis is available on the website
Covid-19
High-quality antibodies to SARS-CoV-2 spike (S) protein, IgM
An analysis for IgM antibodies to coronavirus in Moscow laboratories allows you to quickly diagnose the asymptomatic course of the disease in the first days after infection.
Ask a question
Your name Mandatory field
Mail for feedback Mandatory field
Question text Mandatory field
I agree to the processing of personal data and have read the user agreement
You may be interested
Research and diagnostics
Tests
Covid-19 Dr. Fooke specific IgG (food allergens) Hla typing ImmunoCAP allergen diagnostic panels (IgE specific) Allergens of animals and birds (ige specific)
Fooke specific IgG (food allergens) Hla typing ImmunoCAP allergen diagnostic panels (IgE specific) Allergens of animals and birds (ige specific)
Doctors
Ultrasound doctor Gynecologist Dermatologist Cardiologist Nurse Neurologist Nutritionist Pediatrician Therapist Endocrinologist
Articles
20.07.2021 17:28:00
PSA (Prostate specific antigen) analysis - indications, preparation, interpretation
The article discusses in detail the PSA blood test for men. The study allows for the primary diagnosis of cancer and other pathologies of the prostate gland. According to official figures, more than five hundred thousand men a year are faced with this diagnosis.







/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/9892303/tpc5.png)



