Define surrogate mother
What It Is and How Does Surrogacy Work
Written by Rebecca Buffum Taylor
Medically Reviewed by Jennifer Robinson, MD on November 04, 2021
In this Article
- What Is a Surrogate Mother?
- Who Uses Surrogates?
- Finding a Surrogate
- How to Choose a Surrogate
- Using a Surrogate
- Legal Issues With Surrogates
There's still some controversy about using a surrogate mother to have a baby. The legal process is also tricky because it varies from state to state. Even so, whether it's because of fertility problems or other reasons, surrogacy is an option for you and your partner. Find out how it works and see if it's right for you.
What Is a Surrogate Mother?
There are two kinds:
Traditional surrogate. It's a woman who gets artificially inseminated with the father's sperm. They then carry the baby and deliver it for you and your partner to raise.
A traditional surrogate is the baby's biological mother. That's because it was their egg that was fertilized by the father's sperm. Donor sperm can also be used.
Gestational surrogates. A technique called "in vitro fertilization" (IVF) now makes it possible to gather eggs from the mother (or an egg donor), fertilize them with sperm from the father (or a sperm donor), and place the embryo into the uterus of a gestational surrogate.
The surrogate then carries the baby until birth. They don't have any genetic ties to the child because it wasn't their egg that was used.
A gestational surrogate is called the "birth mother." The biological mother, though, is still the woman whose egg was fertilized.
In the U.S., gestational surrogacy is less complex legally. That's because both intended parents have genetic ties to the baby. As a result, gestational surrogacy has become more common than a traditional surrogate. About 750 babies are born each year using gestational surrogacy.
Who Uses Surrogates?
If you're a woman, you may consider a surrogate for several reasons:
- Medical problems with your uterus
- You had a hysterectomy that removed your uterus
- Conditions that make pregnancy impossible or risky for you, such as severe heart disease
You may want to think about surrogacy if you tried but couldn't get pregnant with a variety of assisted-reproduction techniques, such as IVF.
Surrogates have also made parenthood an option for people who might not be able to adopt a child, perhaps because of their age or marital status.
If gay men decide to use a traditional surrogate, one of them uses their sperm to fertilize the surrogate's egg through artificial insemination. The surrogate then carries the baby and gives birth.
A gay couple might also choose an egg donor, fertilize that donated egg, and then have the embryo implanted in a gestational surrogate to carry until birth.
Finding a Surrogate
There are several ways you can find a surrogate mother:
Friends or family. Sometimes you can ask a friend or relative to be a surrogate for you. It's somewhat controversial. But because of the high cost of surrogacy and the complex legal issues it raises about parental rights, a tried-and-tested family relationship can be simpler to manage.
The American Society for Reproductive Medicine accepts certain family ties as acceptable for surrogates. It generally discourages surrogacy, though, if the child would carry the same genes as a child born of incest between close relatives.
It generally discourages surrogacy, though, if the child would carry the same genes as a child born of incest between close relatives.
A surrogacy agency. Most people use one to arrange a gestational surrogate. There are about 100 agencies now operating in the U.S. They act as go-betweens.
An agency helps you find a surrogate and make arrangements. It also collects any fees that get passed between you and the surrogate, such as paying for their medical expenses.
How to Choose a Surrogate
Right now there aren't any regulations about who can be a surrogate mother. But experts agree on a few points about how to select one.
You should choose surrogates who:
- Are at least 21 years old
- Have already given birth to at least one healthy baby so they understand firsthand the medical risks of pregnancy and childbirth and the emotional issues of bonding with a newborn
- Have passed a psychological screening by a mental health professional to uncover any issues with giving up the baby after birth
- Sign a contract about their role and responsibilities in the pregnancy, such as prenatal care and agreeing to give you the baby after birth
Using a Surrogate
The American Society for Reproductive Medicine says surrogates should get a medical exam to check that they are likely to have a healthy, full-term pregnancy. The organization suggests they get tests that check for infectious diseases such as syphilis, gonorrhea, chlamydia, HIV, cytomegalovirus, and hepatitis B and C.
The organization suggests they get tests that check for infectious diseases such as syphilis, gonorrhea, chlamydia, HIV, cytomegalovirus, and hepatitis B and C.
Surrogates should get tests to make sure they have immunity to measles, rubella (German measles), and chickenpox. Also, you may want to ask that they get a medical procedure to visually "map" the uterus, which can help the doctor check their potential to carry a pregnancy. Surrogate mothers should have their own doctor during pregnancy rather than use yours.
The cost of surrogacy can range from $80,000 to $120,000. A lot of different things go into the price, such as whether the surrogates have their own medical insurance or whether you need to buy a surrogacy-pregnancy policy for them.
Legal Issues With Surrogates
Parental rights aren't guaranteed after a surrogate pregnancy. The law continues to change as reproductive technology and the very definition of a "parent" changes.
There isn't a federal law on surrogacy and state laws vary.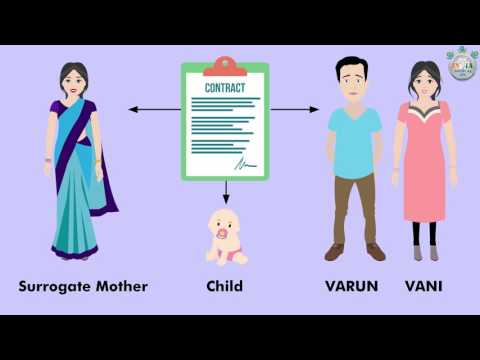 After a surrogate pregnancy in some states, you may still have to pass adoption proceedings to gain legal custody of the child. In other states, a "declaration of parentage" before birth lets you avoid having to "adopt" the baby.
After a surrogate pregnancy in some states, you may still have to pass adoption proceedings to gain legal custody of the child. In other states, a "declaration of parentage" before birth lets you avoid having to "adopt" the baby.
To protect your rights as parents-to-be -- and the rights of the child you're hoping to have -- hire an attorney who specializes in reproductive law in your state. They can write a surrogacy contract that clearly spells out what everyone needs to do.
A contract like that may help if legal issues come up after birth. It can also outline agreements about a variety of possible scenarios with the pregnancy, such as what happens if there are twins or triplets.
Infertility & Reproduction Guide
- Overview
- Symptoms
- Diagnosis & Tests
- Treatment & Care
- Support & Resources
Surrogate mother Definition & Meaning
- Top Definitions
- Quiz
- Examples
- British
This shows grade level based on the word's complexity.
Save This Word!
This shows grade level based on the word's complexity.
noun
a person who acts in the place of another person's biological mother.
an animal that is given another's offspring to raise.
Medicine/Medical. a woman who helps a couple to have a child by carrying to term an embryo conceived by the couple and transferred to her uterus, or by being inseminated with the man's sperm and either donating the embryo for transfer to the woman's uterus or carrying it to term.
QUIZ
SHALL WE PLAY A "SHALL" VS. "SHOULD" CHALLENGE?
Should you take this quiz on “shall” versus “should”? It should prove to be a quick challenge!
Question 1 of 6
Which form is commonly used with other verbs to express intention?
Compare embryo transfer.
Origin of surrogate mother
First recorded in 1975–80
Words nearby surrogate mother
surreptitious, surreptitiously, surrey, surrogacy, surrogate, surrogate mother, surround, surrounding, surroundings, surround sound, surround theater
Dictionary.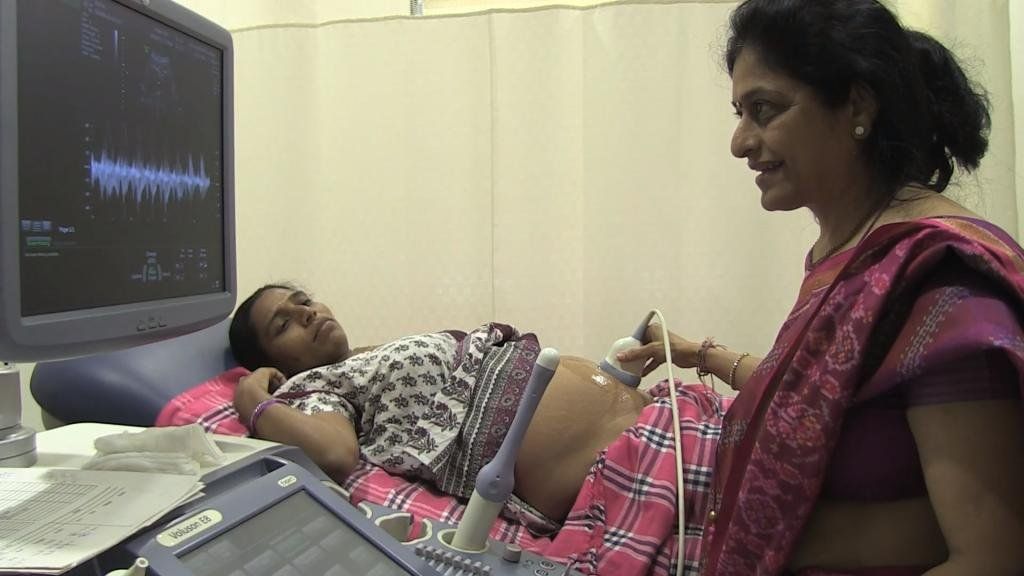 com Unabridged Based on the Random House Unabridged Dictionary, © Random House, Inc. 2022
com Unabridged Based on the Random House Unabridged Dictionary, © Random House, Inc. 2022
How to use surrogate mother in a sentence
Betty opened her family’s doors to me and she always looked out for me like a surrogate mother.
Locked up in the Land of Liberty: Part I|Yariel Valdés González|July 7, 2021|Washington Blade
Catch the two together in the new comedy movie Together Together about a single man’s quest for a surrogate mother, and catch Notaro at the virtual OZY Fest 2021 this weekend.
The Funniest Listens of the Week|Tracy Moran|May 13, 2021|Ozy
Taraji manages to bring an equal measure of truth to the mother in her character.
‘Empire’ Review: Hip-Hop Musical Chairs with an Insane Soap Opera Twist|Judnick Mayard|January 8, 2015|DAILY BEAST
Three on-the-record stories from a family: a mother and her daughters who came from Phoenix.
I Tried to Warn You About Sleazy Billionaire Jeffrey Epstein in 2003|Vicky Ward|January 7, 2015|DAILY BEAST
But my sources, my young women and their mother, heroically held firm.

I Tried to Warn You About Sleazy Billionaire Jeffrey Epstein in 2003|Vicky Ward|January 7, 2015|DAILY BEAST
I thought about the mother, her fear of the dark, of the harm she feared might come to her daughters.
I Tried to Warn You About Sleazy Billionaire Jeffrey Epstein in 2003|Vicky Ward|January 7, 2015|DAILY BEAST
Meanwhile two kids were taken from their mother when she flew back to the UK from Turkey.
Britain May Spy on Preschoolers Searching for Potential Jihadis|Nico Hines|January 7, 2015|DAILY BEAST
There was no doubt thought of his own loss in this question: yet there was, one may hope, a germ of solicitude for the mother too.
Children's Ways|James Sully
"The Smoker," and "Mother and Daughter," a triptych, are two of her principal pictures.
Women in the fine arts, from the Seventh Century B.C. to the Twentieth Century A.D.|Clara Erskine Clement
Now first we shall want our pupil to understand, speak, read and write the mother tongue well.

The Salvaging Of Civilisation|H. G. (Herbert George) Wells
The mother's lips could not finish the charge she was about to put upon her innocent child.
The Pastor's Fire-side Vol. 3 of 4|Jane Porter
The Authorised Version has: “And as a mother shall she meet him, and receive him as a wife married of a virgin.”
Solomon and Solomonic Literature|Moncure Daniel Conway
British Dictionary definitions for surrogate mother
surrogate mother
noun
a woman who bears a child on behalf of a couple unable to have a child, either by artificial insemination from the man or implantation of an embryo from the woman
Derived forms of surrogate mother
surrogacy (ˈsʌrəɡəsɪ), nounCollins English Dictionary - Complete & Unabridged 2012 Digital Edition © William Collins Sons & Co. Ltd. 1979, 1986 © HarperCollins Publishers 1998, 2000, 2003, 2005, 2006, 2007, 2009, 2012
Surrogacy program
The surrogacy program is offered to those women who, due to health reasons, cannot carry a pregnancy on their own.
The legislation of Russia allows such type of ART as surrogate motherhood, but with some restrictions. It is impossible to resort to the services of a surrogate mother only because of the desire to avoid pregnancy and childbirth. The list of indications for the program is determined by the order of the Russian Federation dated August 30, 2012 No. 107n "On the procedure for using assisted reproductive technologies, contraindications and restrictions on their use." The main indications are:
Some patients with these indications may have genetically related children (that is, it is possible to obtain their own oocytes for embryo cultivation with the help of hormonal stimulation), others additionally use the oocyte donor program. But in all cases, the surrogate mother is not an egg donor.
Medical surrogacy
The main difference between surrogate motherhood and egg donation is that the surrogate mother is transferred an embryo that does not genetically belong to her. By law, a surrogate mother cannot be an egg donor at the same time.
By law, a surrogate mother cannot be an egg donor at the same time.
A surrogate mother always bears a child that is genetically alien to her. The embryo can be cultured from the egg of a future mother or an anonymous donor.
More information for those wishing to become a surrogate mother
Despite the fact that during the entire period of pregnancy the embryo (then the fetus) develops in the body of a surrogate mother, it does not inherit any of its external features. If future parents can choose the most suitable donor (hair color, eye color, height, as well as nationality) when donating eggs, then these factors do not matter when choosing a surrogate mother.
Legal aspect in Russia
In Russia, surrogacy is legal and regulated by law. At the same time, the situation remains when certain medical aspects are not yet clearly spelled out in the law. All conditions in the contract that future parents and the surrogate mother sign with the clinic must be in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation.
In particular, the law says that the mother of a child is automatically recognized as the woman who gave birth to him.
When a child is born by a surrogate mother (despite the fact that he is not genetically related to her and there are documents from the reproduction clinic that confirm the fact of embryo transfer), only with the consent of the surrogate mother, the data of biological parents can be indicated in the birth certificate.
In practice, this is implemented as follows: in the near future after the birth of the child, the surrogate mother signs permission to have the data of biological parents entered into the birth certificate. Together with this document and the agreement with the clinic, parents apply to the registry office, where they issue a birth certificate. After that, according to the law, the biological parents of the child are endowed with full rights and obligations, and the surrogate mother is released from them.
Due to the fact that surrogate motherhood programs have been used in Russia for a long time, this procedure has already become routine in the registry offices. A single person can also be a biological parent, in which case only the mother or only the father is indicated on the birth certificate.
A single person can also be a biological parent, in which case only the mother or only the father is indicated on the birth certificate.
What disputes are possible?
In order to avoid any disputes, an agreement is drawn up, which describes in detail the rights and obligations of the parties and all possible situations.
Number of embryos transferred. Now, thanks to the success of IVF programs (especially in cryoprotocols), one embryo is most often transferred, but in some cases, at the request of the parents and with the consent of the surrogate mother, two.
A variant of the development of multiple pregnancy. In about 1% of cases, after the transfer of one embryo, its division may occur in the first days, and as a result, twins will be born. The contract should indicate whether the size of the surrogate mother's fee will increase in this case and by how much.
Surrogate mother's lifestyle: the contract will stipulate the obligation to follow the doctor's recommendations, visit the clinic chosen by the parents to monitor the pregnancy.
The possibility of having a child with congenital defects. Despite the fact that pre-implantation screening is carried out, and then several screenings during pregnancy, there are diseases that can neither be prevented nor diagnosed in early pregnancy. They are far from always associated with the lifestyle of a pregnant woman or her health (or the health of biological parents) and often occur spontaneously.
One of the key ways to avoid conflict situations is detailed counseling of all program participants before it starts and explanation of all possible consequences.
If it is not possible to resolve the conflict peacefully, one has to go to court: today the courts in the Russian Federation have a practice of resolving such disputes.
More information for those wishing to become a surrogate mother
Requirements for a surrogate mother
Before starting the program, a surrogate mother undergoes an examination:
01
Blood test for HIV, RW (syphilis), viral hepatitis B and C, TORCH infection.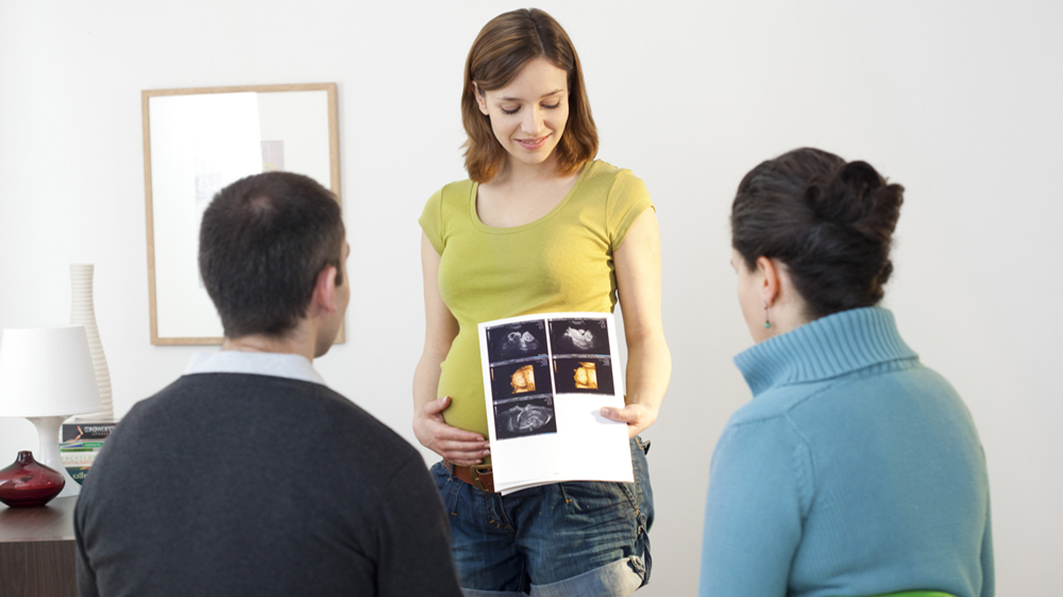
02
Screening for STIs (sexually transmitted infections).
03
Fluorography.
04
Ultrasound of the pelvic organs.
05
Oncocytology of scraping from the cervix, smear for the degree of purity of the vagina.
06
Determination of blood group and Rh factor.
07
General and biochemical blood tests, coagulogram.
08
Urinalysis.
09
ECG.
10
Examination by a general practitioner and conclusion that there are no chronic diseases and contraindications to pregnancy.
11
Examination and conclusion of a psychiatrist.
How embryo transfer works
Embryo transfer
Embryo transfer is a fairly quick (about 30 minutes) procedure, it does not require anesthesia or a long stay in the clinic. By agreement of all participants in the program, two embryos can be transferred, but no more, since multiple pregnancy carries a high risk to the health of children.
After the transfer, hormonal support is prescribed, as in any IVF protocol. It is possible to diagnose the onset of pregnancy approximately on the 12th - 14th day after the transfer: you need to donate blood for hCG. An ultrasound is scheduled approximately on the 21st day after the transfer - an earlier ultrasound is not informative.
Multiple pregnancy: what to do?
Two embryo transfers are currently only allowed if the parents are ready to have two children. This is due to the fact that cryopreservation can significantly increase the chances of successful implantation of all transferred embryos. The surrogate mother must agree to the transfer of two embryos, having received all the information about the risks of a multiple pregnancy.
What if only one embryo was transferred but a multiple pregnancy develops? This case should be discussed in advance and spelled out in the contract.
-
Either the pregnancy is kept as multiple, the parents are preparing for the birth of two children, the surrogate mother receives an additional payment.

-
Or, by decision of the parents, a reduction procedure (removal of one of the embryos) is carried out at an early stage of pregnancy, which carries certain risks for the remaining embryo.
Pregnancy management
Future parents choose a pregnancy clinic where a surrogate mother should be observed. The number of appointments, a set of tests and examinations is standard, as in the management of a naturally occurring pregnancy. At the request of the parents, additional studies can be prescribed, for example, NIPT is a non-invasive prenatal test, in which at the 9-11th week of pregnancy, fetal DNA can be isolated from the blood of a pregnant woman and with an accuracy of 99.99% determine the sex of the child and the presence of a number of diseases.
Monthly payment
In addition to the basic payment (after the birth of the child), the surrogate mother receives a monthly payment - this condition is prescribed in the contract.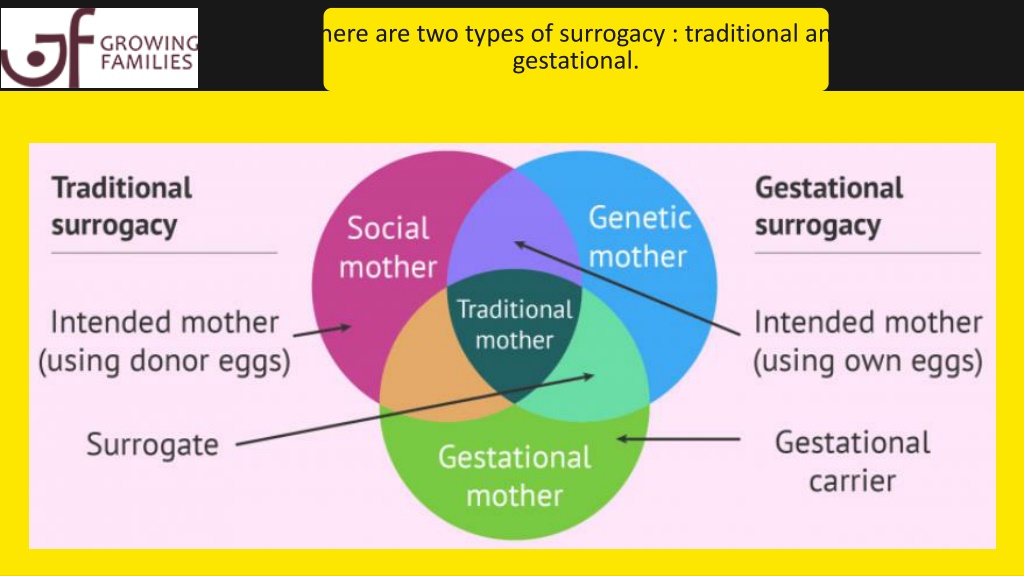
Delivery by a surrogate mother
Future parents choose a clinic or a maternity hospital for childbirth. In most cases, when there is no indication for a caesarean section, childbirth takes place naturally. The child is transferred to future parents immediately after birth. The consent of the surrogate mother to the transfer of the child to the biological parents is also issued.
If you have any questions related to participation in the surrogacy program, please contact the clinic.
Become a surrogate mother
Surrogacy. Aimed Clinic
Aymed Clinic uses the latest generation combined laser for embryo hatching. In women of older reproductive age, a high percentage of embryo implantation
with the embryo itself. An egg obtained from a woman suffering from infertility is fertilized with the sperm of her husband, and then the resulting embryo is placed in the uterus of the so-called surrogate mother.
In what cases it is worth turning to surrogate motherhood
One of the most common reasons why today people resort to the services of surrogate mothers is the complete absence of the uterus. The absence of a uterus in a woman can be a congenital pathology, in particular, with the Rakitansky-Kustner syndrome. Also, this organ can be removed surgically if there are vital indications. Such indications may be, for example, extensive bleeding during a caesarean section. There are other groups of patients who are shown this assisted reproductive technology. These are women with an increased risk of miscarriage, as well as patients who have diseases in which pregnancy and childbirth are completely contraindicated. An example is severe heart disease. Quite often, women who have undergone many unsuccessful IVF attempts for inexplicable reasons turn to such technology as surrogate motherhood.
The absence of a uterus in a woman can be a congenital pathology, in particular, with the Rakitansky-Kustner syndrome. Also, this organ can be removed surgically if there are vital indications. Such indications may be, for example, extensive bleeding during a caesarean section. There are other groups of patients who are shown this assisted reproductive technology. These are women with an increased risk of miscarriage, as well as patients who have diseases in which pregnancy and childbirth are completely contraindicated. An example is severe heart disease. Quite often, women who have undergone many unsuccessful IVF attempts for inexplicable reasons turn to such technology as surrogate motherhood.
How the procedures work
The technology is based on the same principles as in cycles that use a donor egg. The woman who receives the egg, that is, the biological mother, goes through an IVF cycle. At the same time, the future surrogate mother undergoes the procedure of preparation for implantation. Preparation is carried out with estrogen preparations, as well as progesterone.
Preparation is carried out with estrogen preparations, as well as progesterone.
Egg retrieval is a fairly simple outpatient procedure using light anesthesia. The resulting eggs are fertilized and cultured for several days. On the appointed day of transfer, embryos with the highest implantation potential are placed in the uterine cavity of the surrogate mother. The number of embryos placed in the uterine cavity directly depends on the age of the biological mother, as well as on the quality of the embryos themselves.
The pregnancy rate also depends on the age of the biological mother. If donor eggs are used, if the condition of the uterus of the woman who is to carry the pregnancy, and the quality of the donor eggs are optimal, then the effectiveness of the treatment can be very high. The highest in reproductive medicine. That is, from 70 to 75 percent.
Who can be a surrogate mother
A woman who is ready to bear a pregnancy can act on humanitarian grounds. For example, this may be a close relative of an infertile couple or a friend, a good friend. But many more women will decide to take such a step only for financial reasons. That is, for a monetary reward.
For example, this may be a close relative of an infertile couple or a friend, a good friend. But many more women will decide to take such a step only for financial reasons. That is, for a monetary reward.
In accordance with Russian law, the candidate must not be older than 35 years of age and must have at least one child of her own. Also, in accordance with the law, a woman who is ready to endure a pregnancy must sign an agreement to register her child born to her in the name of biological (genetic) parents. After that, the registry office can issue a birth certificate to the couple who used this reproductive technology, in their names.
An agreement is made between an infertile couple and a woman who is ready to bear the pregnancy. The biological mother is always present at the birth and takes care of the newborn. Taking special hormonal preparations, she can even prepare for lactation and provide breastfeeding to the baby.
Aimed Medical Center carries out all procedures related to the preliminary selection of candidates and their examination.
Today, the price of surrogacy is quite high, and to make sure that a woman who is ready to carry a pregnancy meets all the requirements, the specialists of our clinic conduct an extended medical examination. A psychiatric examination of future surrogate mothers is also carried out. Survey data is provided to infertile couples. After a suitable candidate is selected, all necessary contracts and documents are signed. The IVF cycle begins. After the birth of a child, the clinic's specialists assist in the preparation of all documents necessary to obtain a birth certificate. The certificate is issued in the name of the biological parents.
Indications for in vitro fertilization within the framework of the surrogacy program:
- Congenital or acquired absence of the uterus;
- Deformation of the uterine cavity or deformation of the cervix, possible with malformations or acquired as a result of past diseases. Adhesions in the uterine cavity that are not amenable to therapy;
- Genital or extragenital pathologies that make pregnancy impossible, as well as pathologies that are a contraindication to pregnancy;
- Failures in in vitro fertilization attempts, with repeated receipt of high-quality embryos, when their transfer to the uterine cavity does not lead to pregnancy.

Surrogacy: price and legal aspects
More recently, on January 1, 2012, a new law "On the basics of protecting the health of citizens" came into force. The new law defines the circle of persons who have the right to use this reproductive technology, as well as the criteria for women who are ready to bear a "foreign" child.
According to the law, biological parents do not have the right to choose the gender of their unborn child. Now not only persons who are in a legal marriage can resort to the services of surrogates, but also couples who are in a civil marriage, and single women.
However, the law, as before, does not oblige a woman who has carried a child to give it to its biological parents. And the law does not oblige the biological parents to accept the child. The risk is great for each of the parties, which means that there is something more important than the price of surrogacy. It is important to choose the right clinic that will help you make the right choice and provide legal support. Working with a medical center that helps you get all the paperwork right, you can feel confident.
Working with a medical center that helps you get all the paperwork right, you can feel confident.
Requirements for women who are ready to bear a child to whom they are not genetically related are determined by law. In addition, according to the law, such a woman can also act as an egg donor, that is, at the same time be both a surrogate mother and a biological one.
Stages and volumes of examination of women who are about to carry a pregnancy:
- It is necessary to undergo fluorography;
- The conclusion of the therapist is provided that the state of health allows the woman to bear the pregnancy, that there are no contraindications. Like fluorography, such a certificate is valid for 1 year;
- You need to undergo an examination and get a conclusion from a psychiatrist;
- Blood typing and Rh factor will also be required;
- A blood test is given for HIV, RW and HBsAg, for antibodies to hepatitis C. Tests are valid for three months;
- A clinical blood test is also given, which is valid for a month;
- Hemostasiogram required;
- Complete urinalysis;
- You also need to pass smears for flora;
- Cervical scraping being cytologic;
- A biochemical blood test will also be needed;
- Gynecological examination in progress;
- Pelvic ultrasound required;
- The material of the cervical canal and vagina, urethra is examined for gonorrhea, microplasma and ureaplasma, CMV and HSV, chlamydia;
- Antibodies to taxoplasma and herpes virus, rubella measles and cytomegalovirus are determined.

Necessary examinations for a married couple:
- Fluorography;
- Blood test for HIV, for RW and HBsAg, for antibodies to hepatitis C. Tests are valid for three months;
- Analysis of blood type and Rh factor.
Examinations for the biological mother before IVF:
- Therapeutic examination, obtaining a health report;
- Gynecological examination;
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs;
- Complete blood count, including clotting time;
- Urinalysis;
- Flora smears and cytology of cervical scrapings will be required;
- Ultrasound of the thyroid gland and ultrasound of the mammary glands;
- Flora examination of cervical canal materials;
- Blood hormones: LH and FSH, estradiol and prolactin, TSH and T4 free;
- CA125 if repeat IVF is required.
Examinations of the father:
- Spermogram.
Stages of the program for surrogate motherhood:
- At the first stage, the menstrual cycles of mothers, biological and surrogate, are synchronized.

/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/9892303/tpc5.png)