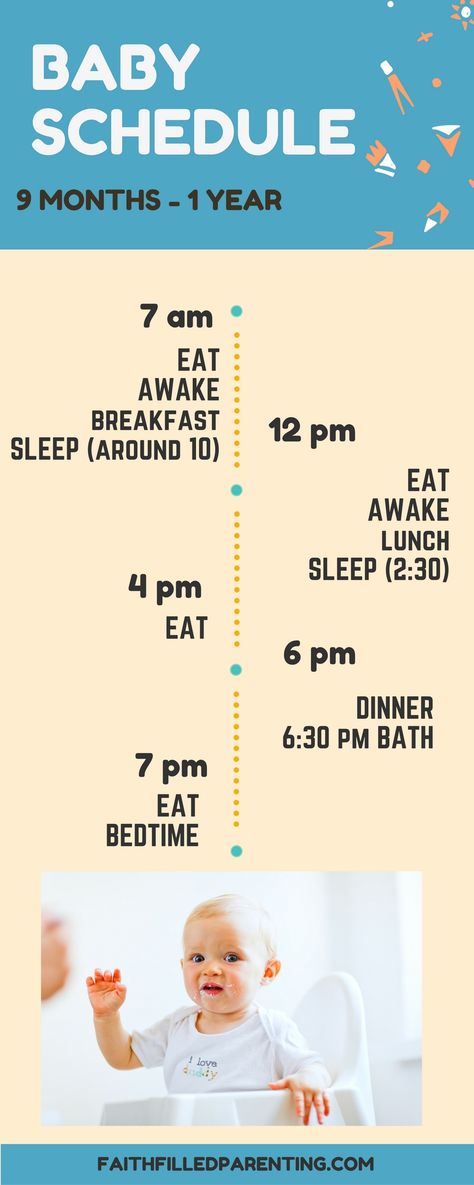
Warning signs of labor
Contractions and signs of labor
Donate
Contact
Events
DONATE
- Home >
- Pregnancy >
- Labor & birth > Contractions and signs of labor
Topics
In This Topic
KEY POINTS
Learning the signs of labor before your due date can help you feel ready for your baby’s birth.
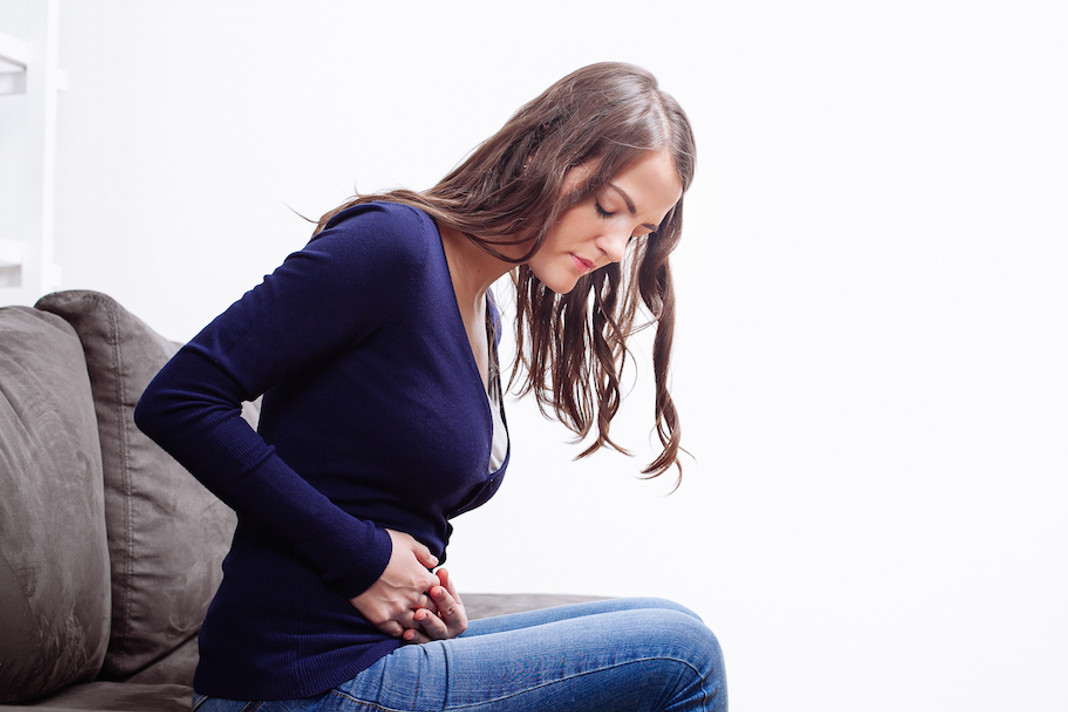
Signs of labor include strong and regular contractions, pain in your belly and lower back, a bloody mucus discharge and your water breaking.
If you think you’re in labor, call your health care provider.
Not all contractions mean you're in true labor. Learning the difference between true and false labor can help you know when it’s the real thing.
What is labor?
Labor (also called childbirth) is the process of your baby leaving the uterus (womb). You’re in labor when you have regular contractions that cause your cervix to change. Contractions are when the muscles of your uterus get tight and then relax. Contractions help push your baby out of your uterus. Your cervix is the opening to the uterus that sits at the top of the vagina. When labor starts, your cervix dilates (opens up).
As you get closer to your due date, learning the signs of labor can help you feel ready for labor and birth. If you have any signs of labor, call your health care provider.
What are the signs of labor?
You know you’re in true labor when:
- You have strong and regular contractions.
 A contraction is when the muscles of your uterus tighten up like a fist and then relax. Contractions help push your baby out. When you’re in true labor, your contractions last about 30 to 70 seconds and come about 5 to 10 minutes apart. They’re so strong that you can’t walk or talk during them. They get stronger and closer together over time.
A contraction is when the muscles of your uterus tighten up like a fist and then relax. Contractions help push your baby out. When you’re in true labor, your contractions last about 30 to 70 seconds and come about 5 to 10 minutes apart. They’re so strong that you can’t walk or talk during them. They get stronger and closer together over time. - You feel pain in your belly and lower back. This pain doesn't go away when you move or change positions.
- You have a bloody (brownish or reddish) mucus discharge. This is called bloody show.
- Your water breaks. Your baby has been growing in amniotic fluid (the bag of waters) in your uterus. When the bag of waters breaks, you may feel a big rush of water. Or you may feel just a trickle.
If you think you’re in labor, call your health care provider, no matter what time of day or night. Your provider can tell you if it’s time to head for the hospital. To see for sure that you’re in labor, your health care provider measures your cervix.
To see for sure that you’re in labor, your health care provider measures your cervix.
What are signs that you may be close to starting labor?
You may be close to starting labor if:
- Your baby drops or moves lower into your pelvis. This is called lightening. It means that your baby is getting ready to move into position for birth. It can happen a few weeks or even just a few hours before your labor begins.
- You have an increase in vaginal discharge that’s clear, pink or slightly bloody. This is called show or bloody show. It can happen a few days before labor starts or at the beginning of labor.
- At a prenatal checkup, your health care provider tells you that your cervix has begun to efface (thin) and dilate (open). Before labor, your cervix is about 3.5 to 4 centimeters long. When it’s fully dilated (open) for labor, it’s 10 centimeters. Once labor starts, contractions help open your cervix.
- You have the nesting instinct.
 This is when you want to get things organized in your home to get ready for your baby. You may want to do things like cook meals or get the baby’s clothes and room ready. Doing these things is fine as long as you’re careful not to overdo it. You need your energy for labor and birth.
This is when you want to get things organized in your home to get ready for your baby. You may want to do things like cook meals or get the baby’s clothes and room ready. Doing these things is fine as long as you’re careful not to overdo it. You need your energy for labor and birth.
If you have any of these signs, you may start labor soon. Learn the signs of labor so you know when to call your provider.
What are false labor and Braxton-Hicks contractions?
Not all contractions mean you’re in labor. You may have contractions on and off before true labor starts. These contractions are called false labor or Braxton-Hicks contractions. They soften and thin the cervix to help your body get ready for labor and birth. You may feel them in the weeks right before your due date. Learning the differences between true labor contractions and false labor contractions can help you know when you’re really in labor.
It can be hard to tell the difference between true labor and false labor. When you first feel contractions, time them. Write down how much time it takes from the start of one contraction to the start of the next. Make a note of how strong the contractions feel. Keep a record of your contractions for 1 hour. Walk or move around to see if the contractions stop when you change positions.
When you first feel contractions, time them. Write down how much time it takes from the start of one contraction to the start of the next. Make a note of how strong the contractions feel. Keep a record of your contractions for 1 hour. Walk or move around to see if the contractions stop when you change positions.
What is preterm labor?
Preterm labor is labor that begins too early, before 37 weeks of pregnancy. Premature babies (born before 37 weeks of pregnancy) can have health problems at birth and later in life. If you’re not to 37 weeks of pregnancy and you have signs or symptoms of preterm labor, call your provider. Getting help quickly is the best thing you can do. Learn about risk factors for preterm labor and what you can do to help reduce your risk.
What are stages of labor?
Stages of labor include the whole process of labor, from your first contractions (stage 1) to pushing (stage 2) to delivery of the placenta (stage 3) after your baby is born. Learning about the stages of labor can help you know what to expect during labor and birth.
Learning about the stages of labor can help you know what to expect during labor and birth.
Last reviewed: December, 2018
') document.write('
Nutrition, weight & fitness
') document.write('') }
') document.write('
Prenatal care
') document.write('') }
Early signs & symptoms of labor: What to watch for
As you approach the end of your pregnancy, your excitement is probably reaching its peak. And it’s easy to wonder if every unusual sensation in your body is a sign that the big day is right around the corner.
The signs and symptoms of labor are unique for just about every mom-to-be. But as you get closer to welcoming your little one, it helps to be prepared and know what physical symptoms to expect and when.
Below, we’ll go over some symptoms that labor is coming soon but hasn’t started yet. And we’ll provide some tell-tale signs that it’s time to grab your bags – because labor is about to begin.
Signs that labor is coming soon but hasn’t started yet
A normal pregnancy lasts about 37 to 42 weeks from the date of your last period, so once you enter the later 30s, your body is starting to gear up for the main event. The following changes don’t necessarily mean it’s time to go to the hospital, but they are signs that the big day is approaching:
Dilation and other cervical changes
Some of the biggest changes your body goes through before labor may be identified during cervical exams. As you get closer to labor, your cervix can start to soften and efface (get thinner). These changes allow your cervix to then dilate (open and grow wider), which will be necessary to deliver your baby.
Starting around week 36, your doctor or midwife may check for changes to your cervix and the position of your baby. It’s important to remember that these changes progress differently for everyone. Progress might start slowly and then increase rapidly just before labor, or vice versa.
It’s important to remember that these changes progress differently for everyone. Progress might start slowly and then increase rapidly just before labor, or vice versa.
It’s also normal to begin labor and not have a lot of changes yet. Once labor truly begins, your cervix will continue to dilate until you reach 10 centimeters and are considered fully dilated. Full dilation is what’s needed to start delivery.
Braxton Hicks contractions
Braxton Hicks are mild contractions that happen irregularly and become more common in the third trimester of pregnancy. You might experience Braxton Hicks contractions well before other signs of approaching labor show up. They tend to become stronger and more frequent as you get closer to your due date. But is this cramping a sign of labor? Not in the same way that regular contractions are (we’ll get to that below). And not everyone notices Braxton Hicks contractions.
Aches, pains and looser joints
Throughout your pregnancy, the hormone relaxin will loosen the ligaments in your body, particularly those in your pelvis. This will help your body stretch and flex during delivery, but you may feel discomfort or pain in your pelvic area. As your due day approaches, it’s also common to feel a bit wobbly, particularly in your hips and lower back. This is because the muscles around your joints now need to work harder to keep those areas stable.
This will help your body stretch and flex during delivery, but you may feel discomfort or pain in your pelvic area. As your due day approaches, it’s also common to feel a bit wobbly, particularly in your hips and lower back. This is because the muscles around your joints now need to work harder to keep those areas stable.
Stomach issues
Stomach trouble isn’t out of the ordinary at any point during pregnancy. But it could intensify late in your third trimester, leading you to wonder, “Is nausea a sign that labor is approaching?” The answer is, sort of. Your baby is still growing and competing for space with everything else in your abdomen. As a result, you may experience indigestion and heartburn. But these issues can be with you for weeks or months.
However, a bout of diarrhea at the end of pregnancy can often be a sign that labor is 24 to 48 hours away. But those numbers can vary.
Lightening
As mentioned above, one of the things that doctors may check for during cervical exams is the position of the baby. This is in part because as you get closer to your due date, your baby will most likely settle into your pelvic area, which is referred to as the baby “dropping” or lightening.
This is in part because as you get closer to your due date, your baby will most likely settle into your pelvic area, which is referred to as the baby “dropping” or lightening.
Lightening often takes place two to four weeks before labor for first-time mothers. Mothers who have given birth before may not experience lightening until much closer to labor.
Your baby’s new position may put added pressure on your pelvis and bladder. So you may be used to frequent urination as a pregnancy symptom, but even more frequent urination is a potential sign of labor to come.
However, lightening sometimes makes it feel easier to breathe. And it could also reduce heartburn thanks to less pressure on the stomach and organs.
Nesting instincts
Many mothers-to-be experience a burst of energy in the weeks before they deliver and an urge to get things done along with it. The science isn’t clear on why, but there are theories that it could be instinct or the result of peaking estrogen.
Whatever their cause, these “nesting instincts” may take the form of planning for labor, organizing or cleaning house, and doing other activities that help prepare for the baby’s arrival. If you experience this, just be sure not to spend all your energy on it. You’re going to want as much energy as possible going into labor.
Questions or concerns about labor signs? Our 24/7 BabyLine is free for our members and patients.
The first signs that labor may be starting
While signs that labor is approaching can vary a lot from person to person, some of the signs that labor is actually beginning tend to be more universal.
You start to experience real contractions
Uterine contractions are your body’s way of getting your baby into position so you can push the baby out. The first stage of labor is generally defined as when you start experiencing true contractions.
What do contractions feel like?
Early labor contractions are mild and irregular, lasting for hours or days. But as you progress towards active labor, true contractions become more intense. They’re often compared to menstrual cramps or the severe gut pain that might be related to gas or an intestinal issue.
But as you progress towards active labor, true contractions become more intense. They’re often compared to menstrual cramps or the severe gut pain that might be related to gas or an intestinal issue.
One of the main ways to tell true contractions apart from Braxton Hicks contractions is that normal contractions happen at regular intervals that become more frequent over time. You can track your contraction intervals either by using an app or phone, or by using a stopwatch and charting the start time and duration of each contraction on a piece of paper.
False labor vs. real labor
These key differences can help you tell when to go to the hospital for contractions.
| True labor | False labor |
|---|---|
| Contractions happen at regular intervals | Contractions happen irregularly |
| Contraction intensity increases | Contraction intensity is relatively consistent |
| The time between contractions shortens | The time between contractions doesn’t shorten |
| Discomfort remains regardless of position or movement | Changing position or moving around often relieves discomfort |
You feel consistent pain in your belly and lower back
Once contractions have truly begun, you’ll feel pain in your abdomen as a result. In addition, your baby’s head may put pressure on your lower back. So is this back pain a sign of labor? It can be. When labor is starting, pain can move in waves from your back to your front.
In addition, your baby’s head may put pressure on your lower back. So is this back pain a sign of labor? It can be. When labor is starting, pain can move in waves from your back to your front.
You lose your mucus plug and experience “bloody show”
What does losing your mucus plug mean? The mucus plug is a protective accumulation of mucus in the opening of the cervix, and as your cervix dilates, this “plug” may be passed into the vagina and discharged before labor starts.
Vaginal discharge containing this mucus may be thicker and have a pink or red color to it. This is due to bleeding from the cervix as it changes. When mucus and blood are discharged together, it’s referred to as “bloody show.” It’s worth noting that the mucus plug is often lost in the days leading up to labor, but it can also happen earlier or later depending on when you actually start to dilate and efface.
Your water breaks
During pregnancy, your baby is surrounded by amniotic fluid, which helps protect them from bacteria. Around the beginning of labor, the sac containing this fluid often ruptures. This can take the form of a sudden gush or a slow trickle of fluid from your vagina, but it isn’t always obvious. So if you suspect that your water may have broken, call your care team or head to the hospital. It may take contractions or your baby applying pressure before your water breaks.
Around the beginning of labor, the sac containing this fluid often ruptures. This can take the form of a sudden gush or a slow trickle of fluid from your vagina, but it isn’t always obvious. So if you suspect that your water may have broken, call your care team or head to the hospital. It may take contractions or your baby applying pressure before your water breaks.
What to watch for: Signs of preterm labor
Labor is considered preterm if it starts three or more weeks before your due date. If you haven’t reached week 37 and you believe that you may be experiencing signs that labor is starting, call your care team immediately.
What to do if you suspect that you’re in labor
The most common signs that it’s time to go to the hospital are water breaking or regular contractions that are five minutes apart for at least an hour (if it’s your first baby). If you live farther away from the hospital or this is not your first baby, your doctor or care team may give you other instructions.
Labor is yours alone. Listen to your body and don’t be afraid to go to the hospital early if you have any concerns. And in the meantime, if you have any planning left to do, we’re here to help.
Harbingers of childbirth - How to understand that it is time to go to the hospital?
January 10, 2017
Alekseeva Inna
Obstetrician-gynecologist, Doctor of the highest category
Subscribe to our Instagram! Useful information about pregnancy and childbirth from leading obstetricians and gynecologists in Moscow and foreign experts: https://www.instagram.com/roddompravda/
Tips and opinions from leading children's specialists: https://www.instagram.com/emc.child/
Every pregnant woman with excitement and joy awaits the upcoming birth. The closer the cherished date, the more attentively the expectant mother listens to the changes taking place in her body and in the behavior of the baby. Of course, the expectant mother wants to know by what signs it is possible to understand that childbirth is just around the corner.
Of course, the expectant mother wants to know by what signs it is possible to understand that childbirth is just around the corner.
It is customary to call the harbingers of childbirth external, really tangible changes in the body, which are direct preparation for the onset of labor. The tissues of the birth canal - the cervix, vagina, vulva, perineum - become quite elastic, extensible, but at the same time - very strong and resistant to tearing. The cervix is located in the center of the vaginal vault, shortens by almost half its normal length and softens significantly. The cervical canal - the lumen of the cervix connecting the uterine cavity with the vagina - opens slightly, as a result, the diameter of the cervical canal is approximately 2-2.5 cm. Of course, such a significant "perestroika" takes more than one day.
Female sex hormones are responsible for preparing for childbirth. During the nine months of pregnancy, progesterone "reigns" in the body of the expectant mother. It ensures the normal tone of the uterus (relaxed state of the muscles), the production of cervical mucus - a mucous plug in the cervix that protects the fetus from infection. The amount of progesterone during pregnancy largely determines the normal development and growth of the fetus, the necessary concentration of nutrients and oxygen in the mother's blood, as well as their timely and uninterrupted delivery to the baby.
It ensures the normal tone of the uterus (relaxed state of the muscles), the production of cervical mucus - a mucous plug in the cervix that protects the fetus from infection. The amount of progesterone during pregnancy largely determines the normal development and growth of the fetus, the necessary concentration of nutrients and oxygen in the mother's blood, as well as their timely and uninterrupted delivery to the baby.
Shortly before childbirth, the production of progesterone decreases markedly, it is replaced by estrogens - female sex hormones. The increase in estrogen in the blood is caused by the need to prepare the body for the upcoming birth. It is these hormones that are responsible for the elasticity and patency of the birth canal. The rate of cervical dilatation in the first stage of labor depends on them. In the second period, when the cervix is fully opened and the fetus passes through the birth canal, it is also very important how elastic and extensible the walls of the vagina are - this will largely determine the duration of the straining period. Finally, the onset of labor itself depends on the level of estrogen: contractions occur as a result of a nerve impulse that is caused by a certain level (“peak”) of estrogen accumulation.
Finally, the onset of labor itself depends on the level of estrogen: contractions occur as a result of a nerve impulse that is caused by a certain level (“peak”) of estrogen accumulation.
These changes are normal and do not require an unscheduled visit to the doctor or hospitalization. Harbingers of childbirth are manifestations of a planned restructuring in the body of a future mother, the “finishing touches” of preparation for the upcoming joyful event.
The absence of clearly perceptible changes on the eve of the expected date of birth is also not a pathology. Not all expectant mothers note those changes in well-being that are commonly called harbingers. However, this does not mean that there is no preparation. In some cases, the “final preparations” go unnoticed by the pregnant woman. Therefore, do not worry or urgently contact a specialist.
The appearance of any of the "harbingers" indicates the likelihood of the development of regular labor activity over the next two hours - two weeks. None of the sensations described gives a 100% guarantee that a woman will become a mother within the next 24 hours. Hormonal changes before childbirth begin approximately two weeks before the expected birth. Theoretically, during these two weeks, at any time, a pregnant woman can notice certain changes in her state of health. Consequently, the absence of labor activity an hour, a day, or even a week after the first noted changes is not a pathology and does not require special medical advice.
None of the sensations described gives a 100% guarantee that a woman will become a mother within the next 24 hours. Hormonal changes before childbirth begin approximately two weeks before the expected birth. Theoretically, during these two weeks, at any time, a pregnant woman can notice certain changes in her state of health. Consequently, the absence of labor activity an hour, a day, or even a week after the first noted changes is not a pathology and does not require special medical advice.
- Scarlet discharge from the genital tract in any amount.
- Severe abdominal pain.
- Increased blood pressure (above 130/80 mmHg).
- An increase in body temperature to 37.5 ° C and above.
- Increased heart rate (more than 100 beats per minute).
- Severe headache, vomiting, blurred vision.
- Significant increase in edema.
- Absence, sharp decrease, sharp increase in fetal movements.
- Suspicion of amniotic fluid leakage.
Weight loss . Shortly before the expected date of delivery, the expectant mother may notice some “weight loss”. Weight loss during this period is associated with the removal of excess fluid from the body, that is, a general decrease in edema. The more pronounced the fluid retention during pregnancy, the more mass the pregnant woman will “lose” on the eve of childbirth. During pregnancy, water is retained in the body of all expectant mothers to a greater or lesser extent. The reason is progesterone - a hormone whose main function is to support the processes of pregnancy. Before childbirth, progesterone is replaced by estrogen. It is estrogen that removes excess fluid from the body. The first results are visible on the hands, feet and legs. Depending on the severity of edema, weight loss before childbirth varies from 0.5 to 2.5 kg.
Change of stool. Increased frequency and change in the consistency of physiological functions on the eve of childbirth is also associated with an increase in estrogen levels and the removal of fluid from the body of the future mother. Similar changes in the body of a non-pregnant woman are observed during menstruation. The chair can become more frequent up to 2-3 times a day, at the same time there may be some liquefaction of the feces. More frequent urge to defecate, a sharp change in the color and smell of feces, combined with nausea and vomiting, is a reason for consulting a doctor - food poisoning can be masked under such "harbingers".
Fundal prolapse. Shortly before delivery, the baby presses the presenting part (most often the head) against the lower segment of the uterus and pulls it down, pressing against the entrance to the small pelvis. The fetus "groups", taking the most advantageous position for itself at the time of the onset of contractions. As a result of such "preparations" from the side of the fetus, the uterus "sags", and its upper part - the bottom - ceases to exert pressure on the internal organs. After lowering the bottom of the uterus, the pregnant woman has no shortness of breath (it becomes easier to breathe, there is a feeling of a full breath). If in the last month the expectant mother had belching, heartburn, a feeling of heaviness in the stomach after eating, these phenomena disappear when the bottom of the uterus descends. However, lowering down to the pelvic area, the uterus will put more pressure on the internal organs located there. The pelvic organs, in particular, include the bladder. It is located directly in front of the uterus, in its lower part. Behind the uterus, at a distance of several centimeters, there is an ampulla of the rectum - the output section of the intestine. It is not difficult to guess what the result of pressure on the bladder and rectum will be: the urge to go to the toilet before childbirth can become noticeably more frequent.
Isolation of the mucous plug. During pregnancy, the glands of the mucous membrane of the cervical canal (the lumen of the cervix) secrete a special secret. It is a thick, sticky, jelly-like mass that forms a kind of cork. The mucous plug completely fills the cervical canal, preventing the penetration of bacterial flora from the vagina into the uterine cavity. Thus, cervical mucus, or the mucous plug of the cervix, protects the fetus from ascending infection. Before childbirth, when the cervix begins to soften under the influence of estrogen, the cervical canal opens slightly and the cervical mucus contained in it can be released. In this case, the expectant mother may find small clots of yellowish-brownish mucus, transparent, jelly-like, odorless. The mucous plug can stand out at once or depart in parts during the day. In the latter case, slight discomfort is sometimes noted in the form of "sipping" in the lower abdomen, reminiscent of sensations before or during menstruation. However, most often, the release of the mucous plug is not accompanied by tangible changes in the well-being of the expectant mother. After the discharge of the mucous plug, it is not recommended to visit the pool, swim in the reservoirs and in the bath. When immersed in water, it fills the vagina; thus, in the absence of a mucous plug, the risk of infection of the fetus and membranes through the ajar cervix increases.
Thus, cervical mucus, or the mucous plug of the cervix, protects the fetus from ascending infection. Before childbirth, when the cervix begins to soften under the influence of estrogen, the cervical canal opens slightly and the cervical mucus contained in it can be released. In this case, the expectant mother may find small clots of yellowish-brownish mucus, transparent, jelly-like, odorless. The mucous plug can stand out at once or depart in parts during the day. In the latter case, slight discomfort is sometimes noted in the form of "sipping" in the lower abdomen, reminiscent of sensations before or during menstruation. However, most often, the release of the mucous plug is not accompanied by tangible changes in the well-being of the expectant mother. After the discharge of the mucous plug, it is not recommended to visit the pool, swim in the reservoirs and in the bath. When immersed in water, it fills the vagina; thus, in the absence of a mucous plug, the risk of infection of the fetus and membranes through the ajar cervix increases.
Training contractions. Training or false contractions are called such contractions that appear shortly before childbirth and are not actually labor activity, since they do not lead to the opening of the cervix. A contraction is essentially a single contraction of the uterine wall; this contraction usually lasts a few seconds. At the time of the contraction, the expectant mother feels a gradually increasing and then gradually decreasing tension in the abdomen. If at this moment you put your hand on your stomach, you can notice that the stomach becomes very hard, but after the contraction it completely relaxes and becomes soft again. In addition to involuntary tension of the uterus, other changes in the well-being of the expectant mother during false contractions are usually not noted. It is not difficult to distinguish training fights from real ones. In most cases, false contractions are weak, painless, irregular or alternating at a significant interval (30 minutes or more). Labor pains, on the contrary, are distinguished by regularity and a gradual increase in intensity. Unlike false contractions, real contractions lead to a visible result - the opening of the cervix. In doubtful cases, a simple obstetric examination will be enough to make an accurate diagnosis. In other cases, training contractions, like all harbingers of childbirth, do not require a visit to a doctor or hospitalization. False contractions may recur for several hours and then stop. Most often, they disturb a pregnant woman in the evening and morning hours for several days.
Labor pains, on the contrary, are distinguished by regularity and a gradual increase in intensity. Unlike false contractions, real contractions lead to a visible result - the opening of the cervix. In doubtful cases, a simple obstetric examination will be enough to make an accurate diagnosis. In other cases, training contractions, like all harbingers of childbirth, do not require a visit to a doctor or hospitalization. False contractions may recur for several hours and then stop. Most often, they disturb a pregnant woman in the evening and morning hours for several days.
Discomfort. In the last weeks before giving birth, many pregnant women report discomfort in the lower abdomen and in the area of the sacrum (the area slightly below the waist). Such changes in
the well-being of the expectant mother is caused by sprain of the pelvic ligaments and increased blood flow to the pelvic organs. Usually these minor sensations, described as a feeling of "light languor" in the lower abdomen, are comparable to similar phenomena in the period before or during menstruation. Discomfort, like training contractions, more often disturbs the expectant mother in the morning and evening hours. The level of discomfort is minimal, it should not worry the expectant mother and does not require medical intervention.
Discomfort, like training contractions, more often disturbs the expectant mother in the morning and evening hours. The level of discomfort is minimal, it should not worry the expectant mother and does not require medical intervention.
All harbingers of childbirth can appear during the last two weeks before childbirth, their presence, as well as their absence, is the norm and does not require a visit to a doctor. It is important to learn to listen to changes in your body, not to be afraid of changes in well-being associated with prenatal preparation, and most importantly, to have time to mentally and physically prepare for the most important event - the birth of a baby.
Subscribe to our Instagram. You will find useful information about pregnancy and childbirth from leading EMC obstetricians and gynecologists.
false or real / “Waiting for a baby”
February
Shortly before the birth, the expectant mother may be disturbed by training contractions, rhythmic contractions of the uterus, which quickly pass and appear occasionally. How to distinguish them from real contractions, and why they are needed, we will try to find out.
How to distinguish them from real contractions, and why they are needed, we will try to find out.
For the first time, the phenomenon of temporary contractions was described by the English doctor John Braxton Hicks. That is why they are called - Braxton Hicks contractions or false, training contractions, precursor contractions. In his scientific work of 1872, he argued that these contractions are short-term (from half a minute to 2 minutes) contractions of the muscles of the uterus, which are felt by a pregnant woman as an increase in the tone of the uterus. They appear after the 20th week of pregnancy. And during the day they happen often, but the expectant mother in the daytime may not even notice them. However, as time goes on, they intensify, becoming more and more obvious.
WHAT FALSE PARTS ARE FOR
The uterus is a muscular organ. And like any muscle that has to perform the work allotted to it in the body, it needs training. After all, if she hangs for all forty weeks like a bag, she will not cope with the load in childbirth.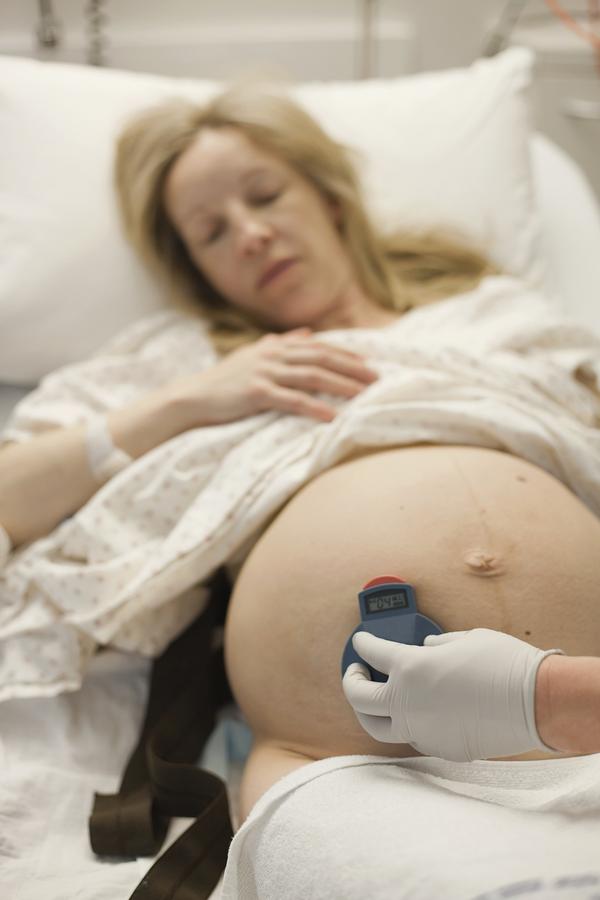 Thus, the purpose of training or false contractions is to prepare the uterus and cervix for childbirth. That is why one of the names of training bouts is contractions harbingers - harbingers of an approaching birth.
Thus, the purpose of training or false contractions is to prepare the uterus and cervix for childbirth. That is why one of the names of training bouts is contractions harbingers - harbingers of an approaching birth.
ARE FALSE PARTS PAINFUL
As a rule, false contractions are painless, but with increasing duration they become more noticeable and bring more discomfort. However, in all women, they manifest themselves in different ways, someone does not feel them at all, and someone does not sleep at night, tossing and turning and trying to find a comfortable position for sleeping. It all depends on the pain threshold. The main thing in this situation is to stop being nervous about this and calm yourself with the thought that such training is necessary for the most important upcoming event - the birth of your crumbs. And to calm down a little and sleep better, ask your doctor to prescribe a sedative for you and get a special pillow for expectant and nursing mothers. With her, falling asleep and experiencing the discomfort of the last weeks of pregnancy will be much easier!
HOW TO LIVE WITH FREQUENT PARTS
Some moms-to-be complain that their Braxton Hicks contractions are frequent and cause significant discomfort, even when they are doing housework or other light physical activities. In such a situation, obstetricians are advised to lie down or vice versa, take an easy walk, in any case, change the type of activity. If training contractions bother you a lot, it is recommended to drink a glass of water, juice or herbal tea, calm down and get some rest. Ask someone close to give you a massage. Lie in silence. And to also benefit from training fights, try doing breathing exercises: practice breathing techniques in childbirth in practice.
In such a situation, obstetricians are advised to lie down or vice versa, take an easy walk, in any case, change the type of activity. If training contractions bother you a lot, it is recommended to drink a glass of water, juice or herbal tea, calm down and get some rest. Ask someone close to give you a massage. Lie in silence. And to also benefit from training fights, try doing breathing exercises: practice breathing techniques in childbirth in practice.
HOW TO DIFFERENTIATE TRAINING FROM BIRTH
The most important thing to understand is that real contractions are much more painful than Braxton Hicks contractions. You will understand it right away. In addition, the contractions that bring you closer to childbirth are more regular. The contractions begin in the lower back, spread to the front of the abdomen, and occur every 10 minutes (or more than 5 contractions per hour). Then they occur with an interval of about 30-70 seconds and over time the intervals between them are reduced. Some women describe the sensations of labor pains as severe menstrual cramps, or sensations during diarrhea, when the pain rolls in waves in the abdomen. These contractions, unlike false ones, continue even after a change in position and when walking, constantly intensifying. As soon as you feel all these symptoms, call your ob-gyn - hour X has arrived. If in doubt, also do not be afraid to disturb the doctor. The doctor will ask you a few questions that will help him determine the type of contractions and eliminate all your doubts and worries. After all, it is always better to consult a doctor and trust his professional experience.
Some women describe the sensations of labor pains as severe menstrual cramps, or sensations during diarrhea, when the pain rolls in waves in the abdomen. These contractions, unlike false ones, continue even after a change in position and when walking, constantly intensifying. As soon as you feel all these symptoms, call your ob-gyn - hour X has arrived. If in doubt, also do not be afraid to disturb the doctor. The doctor will ask you a few questions that will help him determine the type of contractions and eliminate all your doubts and worries. After all, it is always better to consult a doctor and trust his professional experience.
You should seek help if:
• you have more than four contractions an hour and they happen regularly
• contractions are accompanied by pain in the lower spine
• contractions are accompanied by watery or bloody vaginal discharge
• the contractions are so strong that it is very difficult for you to endure them
• there is a marked change in the child's movement, or less than 10 movements every 2 hours
• you think your waters have started to break
Alla Misyutina, Medical Consultant, Independent Laboratory INVITRO
Dear women, during labor, the body needs a lot of oxygen, so proper breathing is very important. A large influx of oxygen into the blood of mother and baby alleviates the condition of the crumbs, which during childbirth experiences oxygen starvation. Special breathing techniques help to properly open the birth canal and make contractions and attempts as effective as possible.
A large influx of oxygen into the blood of mother and baby alleviates the condition of the crumbs, which during childbirth experiences oxygen starvation. Special breathing techniques help to properly open the birth canal and make contractions and attempts as effective as possible.
Different types of breathing should be used at different stages of labor.
• During "false" contractions, breathing should be deep and slow. During the period when the contractions become more intense, it is necessary to use "pain-relieving breathing". This breathing is slow, deep, the inhalation is done through the nose, it should be longer than the exhalation through the mouth. More details: inhale is done at the expense of 1-2-3-4, and exhale - at the expense of 1-2-3-4-5-6. With the help of such breathing: mom relaxes, distracts from pain, focuses on the score; the baby receives as much as possible, so he needs oxygen.
• In breaks from contractions, you need to rest and breathe evenly without any effort, so that you can then easily follow the doctor's recommendations.
• During attempts, you need to exhale all the air from the lungs, then take a deep breath and push for up to 6-9 seconds. Quickly exhale all the air, quickly take a deep breath and again hold your breath for 6-9 seconds, and so on - about three times per attempt.
• In breaks from attempts to rest and breathe deeply, evenly and relaxed.
• It is very important to only push on the perineum and never push on the head. In this case, all efforts are wasted and will appear in the form of burst vessels in the eyes and on the face.
• In the period after the birth of the head, it is necessary to stop pushing and breathing shallowly, some call this breathing “dog-like”, deep breathing can harm both mom and baby. Then everything goes on as usual, the main thing is to obey the doctor.
• After the baby was born, within half an hour the last stage of labor begins - the birth of the placenta. Special breathing is no longer required, at the doctor's command, push a little into the perineum and EVERYTHING! Dear women, pain during childbirth is good, it means that your baby will be born soon. There is no need to resist the pain, this is a mistake that brings a woman and a child nothing but fatigue. On the contrary, it is necessary to concentrate and help in every possible way to give birth to a healthy baby.
There is no need to resist the pain, this is a mistake that brings a woman and a child nothing but fatigue. On the contrary, it is necessary to concentrate and help in every possible way to give birth to a healthy baby.
BIRTH PASSES
So, you have decided that this is no longer a “teaching”, but the beginning of childbirth. In addition to contractions, the onset of labor can be indicated by the outflow of amniotic fluid and the passage of a mucous plug that closes the lumen of the cervix. The mucous plug can also come off 2-3 days before delivery. However, her departure does not always mean that it is time to go to the hospital. During pregnancy, the cervix is tightly closed. With the onset of labor pains, its opening begins: the cervix of the uterus gradually expands to 10-12 cm in diameter (full disclosure). The birth canal is preparing to "release" the child from the womb. Intrauterine pressure increases during contractions as the uterus shrinks. And in the end, this leads to rupture of the fetal bladder and the outflow of part of the amniotic fluid.
The first, preparatory, period of labor for women giving birth for the first time takes an average of 12 hours, and 2-4 hours less for those who have second births. At the beginning of the second stage of labor, contractions join the contractions - contractions of the muscles of the abdominal wall and diaphragm. In addition to the fact that different muscle groups are involved in contractions and attempts, they have one more important difference: contractions are an involuntary and uncontrollable phenomenon, neither their strength nor frequency depend on the woman in labor, while attempts to a certain extent obey her will , it can delay or strengthen them. Therefore, at this stage of childbirth, a lot depends on the expectant mother and her ability to quickly and correctly follow the commands of the obstetrician taking delivery. And most importantly - to tune in correctly and not allow panic and thoughts about something bad. Obstetricians and gynecologists recommend that mothers perceive childbirth as a holiday, a baby's birthday.