Leukorrhea third trimester
What to Expect, Fetal Development
Written by Stephanie Watson
In this Article
- What Is the Third Trimester?
- New Fetal Development
- Third Trimester Changes in Your Body
- Red Flag Symptoms
- Third Trimester Tips for Twins
What Is the Third Trimester?
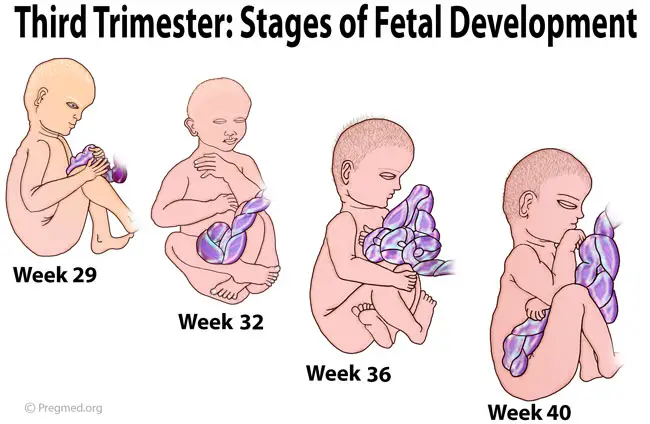
The third trimester is the last phase of your pregnancy. It lasts from weeks 29 to 40, or months 7, 8, and 9. During this trimester, your baby grows, develops, and starts to change position to get ready for birth.
Now that you've reached the third trimester, you're in the home stretch of your pregnancy. You've only got a few more weeks to go, but this part of your pregnancy can be the most challenging.
New Fetal Development
In the third trimester, your baby keeps growing. By the end, a full-term baby usually is between 19 and 21 inches long and between 6 and 9 pounds.
Your baby begins to turn itself head-down to get ready for delivery. At week 36, the baby’s head should begin to move into your pelvic area, also called lightening. It will stay in this down-facing position for the last 2 weeks of your pregnancy.
Your baby develops in other important ways in the third trimester. During this phase, it’s able to:
- Open its eyes and see
- Hear
- Suck on its thumb
- Cry
- Smile
Your baby’s brain continues to develop. Its lungs and kidneys mature. It gains muscle tone and about 16% body fat. The bones at the top of its skull are soft to ease delivery. Most babies have blue eyes at this stage, and they’ll stay that color until a few days or weeks after they’re born. It also has nails on its toes and reaching to the ends of its fingers. If it’s a boy, the testes have descended into the scrotum.
During the third trimester, the vernix caseosa, a protective coating, covers your fetus’ skin. Soft body hair called the lanugo falls out and is almost gone by the end of week 40.
Third Trimester Changes in Your Body
- Abdominal achiness. As your baby grows, it takes up more room in your abdomen. This can cause you to have some aches and discomfort. You may find it hard to get comfortable when you’re in bed at night trying to go to sleep. You may even feel like it’s harder to take deep breaths.
- Backache. The extra weight you've gained puts added pressure on your back, making it feel achy and sore. You might also feel discomfort in your pelvis and hips as your ligaments loosen to prepare for labor. To ease the pressure on your back, try to practice good posture. Sit up straight and use a chair that provides good back support. At night, sleep on your side with a pillow tucked between your legs. Wear low-heeled, comfortable shoes with good arch support. To ease back pain, use a heating pad. Ask your doctor whether it's OK for you to take acetaminophen.
- Bleeding. Some light bleeding toward the end of your pregnancy might be a sign that labor is starting.
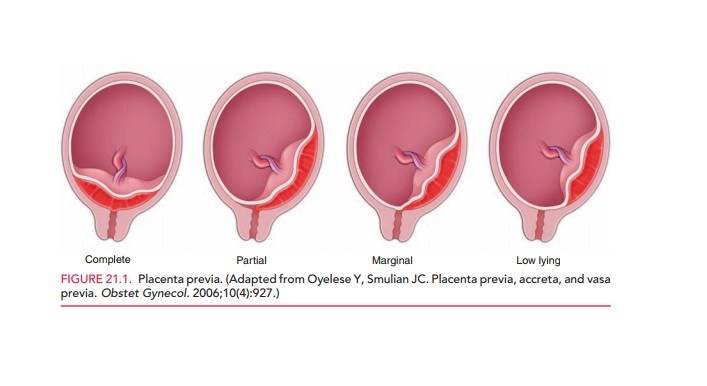
 But spotting may sometimes be a sign of a serious problem, including placenta previa (the placenta grows low and covers the cervix), placental abruption (separation of the placenta from the uterine wall), or preterm labor. Call your doctor as soon as you notice any bleeding.
But spotting may sometimes be a sign of a serious problem, including placenta previa (the placenta grows low and covers the cervix), placental abruption (separation of the placenta from the uterine wall), or preterm labor. Call your doctor as soon as you notice any bleeding. - Braxton-Hicks contractions. You might start to feel mild contractions, which are warm-ups to prepare your uterus for the real labor to come. Braxton-Hicks contractions often aren't as intense as real labor contractions, but they may feel a lot like labor and can eventually progress to it. One main difference is that real contractions gradually get closer and closer together -- and more intense. If you're red in the face and out of breath after your contractions, or they're coming regularly, call your doctor.
- Breast enlargement and leaking. By the end of your pregnancy, your breasts will have grown by as much as 2 pounds. Make sure you're wearing a supportive bra so your back doesn't suffer.
 Close to your due date, you may start to see a yellowish fluid leaking from your nipples. This substance, called colostrum, will nourish your baby in the first few days after birth.
Close to your due date, you may start to see a yellowish fluid leaking from your nipples. This substance, called colostrum, will nourish your baby in the first few days after birth. - Vivid dreams. It’s common to have more vivid dreams or nightmares in your third trimester. This can disrupt your sleep. Your wild dreams are likely caused by changes in hormone levels from pregnancy.
- Clumsiness. You may feel clumsy or out of balance during the third trimester. You may drop things. Part of the reason is that you’ve gained weight in your belly area. That makes it harder to balance your body.
- Discharge. You might see more vaginal discharge during the third trimester. If the flow is heavy enough to soak through your panty liners, call your doctor. Close to your delivery date, you might see a thick, clear, or slightly blood-tinged discharge. This is your mucus plug, and it's a sign that your cervix has begun dilating in preparation for labor.
 If you experience a sudden rush of fluid, it may mean that your water has broken (although only about 8% of pregnant women have their water break before contractions begin). Call your doctor as soon as possible after your water breaks.
If you experience a sudden rush of fluid, it may mean that your water has broken (although only about 8% of pregnant women have their water break before contractions begin). Call your doctor as soon as possible after your water breaks. - Fatigue. You might have been feeling energetic in your second trimester, but are weary now. Carrying extra weight, waking up several times during the night to go to the bathroom, and dealing with the anxiety of preparing for a baby can all take a toll on your energy level. Eat healthy food and get regular exercise to give yourself a boost. When you feel tired, try to take a nap, or at least sit down and relax for a few minutes. You need to reserve all your strength now for when your baby arrives and you're really not getting any sleep.
- Frequent urination. Now that your baby is bigger, its head may be pressing down on your bladder. That extra pressure means you'll have to go to the bathroom more frequently -- including several times each night.
 You might also find that you're leaking urine when you cough, sneeze, laugh, or exercise. To relieve the pressure and prevent leakage, go to the bathroom whenever you feel the urge and urinate completely each time. Avoid drinking fluids right before bedtime to cut down on unwanted late-night bathroom visits. Wear a panty liner to absorb any leakage. Let your doctor know if you have any pain or burning with urination. These can be signs of a urinary tract infection.
You might also find that you're leaking urine when you cough, sneeze, laugh, or exercise. To relieve the pressure and prevent leakage, go to the bathroom whenever you feel the urge and urinate completely each time. Avoid drinking fluids right before bedtime to cut down on unwanted late-night bathroom visits. Wear a panty liner to absorb any leakage. Let your doctor know if you have any pain or burning with urination. These can be signs of a urinary tract infection. - Heartburn and constipation. They're caused by extra production of the hormone progesterone, which relaxes certain muscles -- including the muscles in your esophagus that normally keep food and acids down in your stomach, and the ones that move digested food through your intestines. To relieve heartburn, try eating more frequent, smaller meals throughout the day and avoid greasy, spicy, and acidic foods (like citrus fruits). For constipation, increase your fiber intake and drink extra fluids to keep things moving more smoothly.
 If your heartburn or constipation is really bothering you, talk to your doctor about what medications may be safe for you to take for symptom relief.
If your heartburn or constipation is really bothering you, talk to your doctor about what medications may be safe for you to take for symptom relief. - Hemorrhoids. Hemorrhoids are actually varicose veins -- swollen veins that form around the anus. These veins enlarge during pregnancy because extra blood is flowing through them and the weight of pregnancy increases the amount of pressure to the area. To relieve the itch and discomfort, try sitting in a warm tub or sitz bath. Ask your doctor whether you can also try an over-the-counter hemorrhoid ointment or stool softener.
- Sciatica. Nerve pain that shoots from your lower back to your buttocks and down your leg is more likely in the third trimester. Sciatica may be caused by hormone changes during pregnancy, or because your baby’s growing body presses against the sciatic nerve. Sciatica pain may come and go or be constant. Yoga, massage, or physical therapy are ways to relieve the pain, but it usually goes away after your baby is born.

- Shortness of breath. As your uterus expands, it rises up until it sits just under your rib cage, leaving less room for your lungs to expand. That added pressure on your lungs can make it more difficult to breathe. Exercising can help with shortness of breath. You can also try propping up your head and shoulders with pillows while you sleep.
- Spider and varicose veins. Your circulation has increased to send extra blood to your growing baby. That excess blood flow can cause tiny red veins, known as spider veins, to appear on your skin. Spider veins may get worse in your third trimester, but they should fade once your baby is born. Pressure on your legs from your growing baby may also cause some surface veins in your legs to become swollen and blue or purple. These are called varicose veins. They should improve within a few months after you deliver. Although there's no way to avoid varicose veins, you can prevent them from getting worse by:
- Getting up and moving throughout the day
- Wearing support hose
- Propping up your legs whenever you have to sit for long periods.
- Stretch marks. You may develop stretch marks on your breasts, butt, tummy, or thighs. Stretch marks are a type of scar that happens when your skin stretches during pregnancy. Not everyone gets them. If you do, they may be red, purple, pink, or brown in color.
- Swelling. Your rings might be feeling tighter these days, and you may also notice that your ankles and face are looking bloated. Mild swelling is the result of excess fluid retention (edema). To reduce swelling, put your feet up on a stool or box whenever you sit for any length of time, and elevate your feet while you sleep. If you have sudden onset of swelling though, seek medical attention immediately as it may be a sign of preeclampsia, a dangerous pregnancy complication.
- Weight gain. Aim for a weight gain of 1/2 pound to 1 pound a week during your third trimester. By the end of your pregnancy, you should have put on a total of about 25 to 35 pounds (your doctor may have recommended that you gain more or less weight if you started out your pregnancy underweight or overweight).
 The extra pounds you've put on are made up of the baby's weight, plus the placenta, amniotic fluid, increased blood and fluid volume, and added breast tissue. If your baby seems to be too small or too big based on the size of your belly, your doctor will do an ultrasound to check the baby’s growth.
The extra pounds you've put on are made up of the baby's weight, plus the placenta, amniotic fluid, increased blood and fluid volume, and added breast tissue. If your baby seems to be too small or too big based on the size of your belly, your doctor will do an ultrasound to check the baby’s growth.
Red Flag Symptoms
Any of these symptoms could be a sign that something is wrong with your pregnancy. Don't wait for your regular prenatal visit to talk about it. Call your doctor right away if you experience:
- Severe abdominal pain or cramps
- Severe nausea or vomiting
- Bleeding
- Severe dizziness
- Pain or burning during urination
- Rapid weight gain (more than 6.5 pounds per month) or too little weight gain
Third Trimester Tips for Twins
Expecting twins? You might want to add these things to your third trimester to-do list:
- Go stroller shopping. Side-by-side or tandem? Take a few double strollers for a test drive to see which type feels best to you.
 Look for one that's easy to open and maneuver.
Look for one that's easy to open and maneuver. - Get breastfeeding tips. Breastfeeding two babies is more of a challenge than one, but you can definitely do it. Ask your doctor ahead of time for tips.
- Check your iron. Ask your doctor if you need to take iron supplements. As a mom-to-be of twins, you're four times more likely to have iron-deficiency anemia.
- Know the signs of preeclampsia. Carrying twins doubles your risk of this serious condition. Tell your doctor right away if you have a headache, trouble seeing, or sudden weight gain.
- Find a support group. Start looking for groups of moms of multiples in your area. You may appreciate exchanging tips and getting support from other moms in the same boat.
- Create a schedule. Read up on how to get your twins on the same sleeping and eating schedule.
 Learning some tips now may save your sanity when you have two newborns.
Learning some tips now may save your sanity when you have two newborns.
Health & Pregnancy Guide
- Getting Pregnant
- First Trimester
- Second Trimester
- Third Trimester
- Labor and Delivery
- Pregnancy Complications
- All Guide Topics
What to Expect, Fetal Development
Written by Stephanie Watson
In this Article
- What Is the Third Trimester?
- New Fetal Development
- Third Trimester Changes in Your Body
- Red Flag Symptoms
- Third Trimester Tips for Twins
What Is the Third Trimester?
The third trimester is the last phase of your pregnancy. It lasts from weeks 29 to 40, or months 7, 8, and 9. During this trimester, your baby grows, develops, and starts to change position to get ready for birth.
Now that you've reached the third trimester, you're in the home stretch of your pregnancy. You've only got a few more weeks to go, but this part of your pregnancy can be the most challenging.
You've only got a few more weeks to go, but this part of your pregnancy can be the most challenging.
New Fetal Development
In the third trimester, your baby keeps growing. By the end, a full-term baby usually is between 19 and 21 inches long and between 6 and 9 pounds.
Your baby begins to turn itself head-down to get ready for delivery. At week 36, the baby’s head should begin to move into your pelvic area, also called lightening. It will stay in this down-facing position for the last 2 weeks of your pregnancy.
Your baby develops in other important ways in the third trimester. During this phase, it’s able to:
- Open its eyes and see
- Hear
- Suck on its thumb
- Cry
- Smile
Your baby’s brain continues to develop. Its lungs and kidneys mature. It gains muscle tone and about 16% body fat. The bones at the top of its skull are soft to ease delivery. Most babies have blue eyes at this stage, and they’ll stay that color until a few days or weeks after they’re born. It also has nails on its toes and reaching to the ends of its fingers. If it’s a boy, the testes have descended into the scrotum.
It also has nails on its toes and reaching to the ends of its fingers. If it’s a boy, the testes have descended into the scrotum.
During the third trimester, the vernix caseosa, a protective coating, covers your fetus’ skin. Soft body hair called the lanugo falls out and is almost gone by the end of week 40.
Third Trimester Changes in Your Body
- Abdominal achiness. As your baby grows, it takes up more room in your abdomen. This can cause you to have some aches and discomfort. You may find it hard to get comfortable when you’re in bed at night trying to go to sleep. You may even feel like it’s harder to take deep breaths.
- Backache. The extra weight you've gained puts added pressure on your back, making it feel achy and sore. You might also feel discomfort in your pelvis and hips as your ligaments loosen to prepare for labor. To ease the pressure on your back, try to practice good posture. Sit up straight and use a chair that provides good back support.
 At night, sleep on your side with a pillow tucked between your legs. Wear low-heeled, comfortable shoes with good arch support. To ease back pain, use a heating pad. Ask your doctor whether it's OK for you to take acetaminophen.
At night, sleep on your side with a pillow tucked between your legs. Wear low-heeled, comfortable shoes with good arch support. To ease back pain, use a heating pad. Ask your doctor whether it's OK for you to take acetaminophen. - Bleeding. Some light bleeding toward the end of your pregnancy might be a sign that labor is starting. But spotting may sometimes be a sign of a serious problem, including placenta previa (the placenta grows low and covers the cervix), placental abruption (separation of the placenta from the uterine wall), or preterm labor. Call your doctor as soon as you notice any bleeding.
- Braxton-Hicks contractions. You might start to feel mild contractions, which are warm-ups to prepare your uterus for the real labor to come. Braxton-Hicks contractions often aren't as intense as real labor contractions, but they may feel a lot like labor and can eventually progress to it. One main difference is that real contractions gradually get closer and closer together -- and more intense.
 If you're red in the face and out of breath after your contractions, or they're coming regularly, call your doctor.
If you're red in the face and out of breath after your contractions, or they're coming regularly, call your doctor. - Breast enlargement and leaking. By the end of your pregnancy, your breasts will have grown by as much as 2 pounds. Make sure you're wearing a supportive bra so your back doesn't suffer. Close to your due date, you may start to see a yellowish fluid leaking from your nipples. This substance, called colostrum, will nourish your baby in the first few days after birth.
- Vivid dreams. It’s common to have more vivid dreams or nightmares in your third trimester. This can disrupt your sleep. Your wild dreams are likely caused by changes in hormone levels from pregnancy.
- Clumsiness. You may feel clumsy or out of balance during the third trimester. You may drop things. Part of the reason is that you’ve gained weight in your belly area. That makes it harder to balance your body.
- Discharge. You might see more vaginal discharge during the third trimester.
 If the flow is heavy enough to soak through your panty liners, call your doctor. Close to your delivery date, you might see a thick, clear, or slightly blood-tinged discharge. This is your mucus plug, and it's a sign that your cervix has begun dilating in preparation for labor. If you experience a sudden rush of fluid, it may mean that your water has broken (although only about 8% of pregnant women have their water break before contractions begin). Call your doctor as soon as possible after your water breaks.
If the flow is heavy enough to soak through your panty liners, call your doctor. Close to your delivery date, you might see a thick, clear, or slightly blood-tinged discharge. This is your mucus plug, and it's a sign that your cervix has begun dilating in preparation for labor. If you experience a sudden rush of fluid, it may mean that your water has broken (although only about 8% of pregnant women have their water break before contractions begin). Call your doctor as soon as possible after your water breaks. - Fatigue. You might have been feeling energetic in your second trimester, but are weary now. Carrying extra weight, waking up several times during the night to go to the bathroom, and dealing with the anxiety of preparing for a baby can all take a toll on your energy level. Eat healthy food and get regular exercise to give yourself a boost. When you feel tired, try to take a nap, or at least sit down and relax for a few minutes. You need to reserve all your strength now for when your baby arrives and you're really not getting any sleep.
- Frequent urination. Now that your baby is bigger, its head may be pressing down on your bladder. That extra pressure means you'll have to go to the bathroom more frequently -- including several times each night. You might also find that you're leaking urine when you cough, sneeze, laugh, or exercise. To relieve the pressure and prevent leakage, go to the bathroom whenever you feel the urge and urinate completely each time. Avoid drinking fluids right before bedtime to cut down on unwanted late-night bathroom visits. Wear a panty liner to absorb any leakage. Let your doctor know if you have any pain or burning with urination. These can be signs of a urinary tract infection.
- Heartburn and constipation. They're caused by extra production of the hormone progesterone, which relaxes certain muscles -- including the muscles in your esophagus that normally keep food and acids down in your stomach, and the ones that move digested food through your intestines.
 To relieve heartburn, try eating more frequent, smaller meals throughout the day and avoid greasy, spicy, and acidic foods (like citrus fruits). For constipation, increase your fiber intake and drink extra fluids to keep things moving more smoothly. If your heartburn or constipation is really bothering you, talk to your doctor about what medications may be safe for you to take for symptom relief.
To relieve heartburn, try eating more frequent, smaller meals throughout the day and avoid greasy, spicy, and acidic foods (like citrus fruits). For constipation, increase your fiber intake and drink extra fluids to keep things moving more smoothly. If your heartburn or constipation is really bothering you, talk to your doctor about what medications may be safe for you to take for symptom relief. - Hemorrhoids. Hemorrhoids are actually varicose veins -- swollen veins that form around the anus. These veins enlarge during pregnancy because extra blood is flowing through them and the weight of pregnancy increases the amount of pressure to the area. To relieve the itch and discomfort, try sitting in a warm tub or sitz bath. Ask your doctor whether you can also try an over-the-counter hemorrhoid ointment or stool softener.
- Sciatica. Nerve pain that shoots from your lower back to your buttocks and down your leg is more likely in the third trimester.
 Sciatica may be caused by hormone changes during pregnancy, or because your baby’s growing body presses against the sciatic nerve. Sciatica pain may come and go or be constant. Yoga, massage, or physical therapy are ways to relieve the pain, but it usually goes away after your baby is born.
Sciatica may be caused by hormone changes during pregnancy, or because your baby’s growing body presses against the sciatic nerve. Sciatica pain may come and go or be constant. Yoga, massage, or physical therapy are ways to relieve the pain, but it usually goes away after your baby is born. - Shortness of breath. As your uterus expands, it rises up until it sits just under your rib cage, leaving less room for your lungs to expand. That added pressure on your lungs can make it more difficult to breathe. Exercising can help with shortness of breath. You can also try propping up your head and shoulders with pillows while you sleep.
- Spider and varicose veins. Your circulation has increased to send extra blood to your growing baby. That excess blood flow can cause tiny red veins, known as spider veins, to appear on your skin. Spider veins may get worse in your third trimester, but they should fade once your baby is born. Pressure on your legs from your growing baby may also cause some surface veins in your legs to become swollen and blue or purple.
 These are called varicose veins. They should improve within a few months after you deliver. Although there's no way to avoid varicose veins, you can prevent them from getting worse by:
These are called varicose veins. They should improve within a few months after you deliver. Although there's no way to avoid varicose veins, you can prevent them from getting worse by:- Getting up and moving throughout the day
- Wearing support hose
- Propping up your legs whenever you have to sit for long periods.
- Stretch marks. You may develop stretch marks on your breasts, butt, tummy, or thighs. Stretch marks are a type of scar that happens when your skin stretches during pregnancy. Not everyone gets them. If you do, they may be red, purple, pink, or brown in color.
- Swelling. Your rings might be feeling tighter these days, and you may also notice that your ankles and face are looking bloated. Mild swelling is the result of excess fluid retention (edema). To reduce swelling, put your feet up on a stool or box whenever you sit for any length of time, and elevate your feet while you sleep. If you have sudden onset of swelling though, seek medical attention immediately as it may be a sign of preeclampsia, a dangerous pregnancy complication.

- Weight gain. Aim for a weight gain of 1/2 pound to 1 pound a week during your third trimester. By the end of your pregnancy, you should have put on a total of about 25 to 35 pounds (your doctor may have recommended that you gain more or less weight if you started out your pregnancy underweight or overweight). The extra pounds you've put on are made up of the baby's weight, plus the placenta, amniotic fluid, increased blood and fluid volume, and added breast tissue. If your baby seems to be too small or too big based on the size of your belly, your doctor will do an ultrasound to check the baby’s growth.
Red Flag Symptoms
Any of these symptoms could be a sign that something is wrong with your pregnancy. Don't wait for your regular prenatal visit to talk about it. Call your doctor right away if you experience:
- Severe abdominal pain or cramps
- Severe nausea or vomiting
- Bleeding
- Severe dizziness
- Pain or burning during urination
- Rapid weight gain (more than 6.
 5 pounds per month) or too little weight gain
5 pounds per month) or too little weight gain
Third Trimester Tips for Twins
Expecting twins? You might want to add these things to your third trimester to-do list:
- Go stroller shopping. Side-by-side or tandem? Take a few double strollers for a test drive to see which type feels best to you. Look for one that's easy to open and maneuver.
- Get breastfeeding tips. Breastfeeding two babies is more of a challenge than one, but you can definitely do it. Ask your doctor ahead of time for tips.
- Check your iron. Ask your doctor if you need to take iron supplements. As a mom-to-be of twins, you're four times more likely to have iron-deficiency anemia.
- Know the signs of preeclampsia. Carrying twins doubles your risk of this serious condition. Tell your doctor right away if you have a headache, trouble seeing, or sudden weight gain.

- Find a support group. Start looking for groups of moms of multiples in your area. You may appreciate exchanging tips and getting support from other moms in the same boat.
- Create a schedule. Read up on how to get your twins on the same sleeping and eating schedule. Learning some tips now may save your sanity when you have two newborns.
Health & Pregnancy Guide
- Getting Pregnant
- First Trimester
- Second Trimester
- Third Trimester
- Labor and Delivery
- Pregnancy Complications
- All Guide Topics
causes, meaning and methods of treatment of white discharge during pregnancy * Clinic Diana in St. Petersburg
Leukorrhea of pregnant women: causes, significance and methods of treatment of white discharge during pregnancy
White vaginal discharge is normal during pregnancy and is not usually a cause for concern unless there are other symptoms.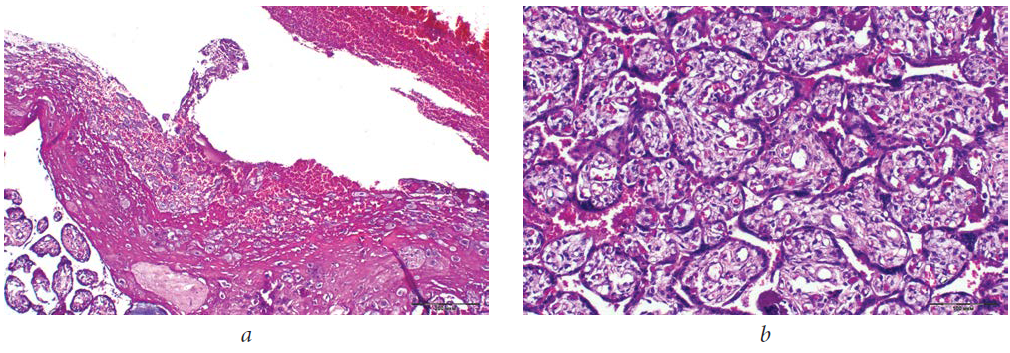 What does normal discharge look like in pregnant women? How to detect violations?
What does normal discharge look like in pregnant women? How to detect violations?
Characteristics of normal discharge in pregnant women
Contents of the article
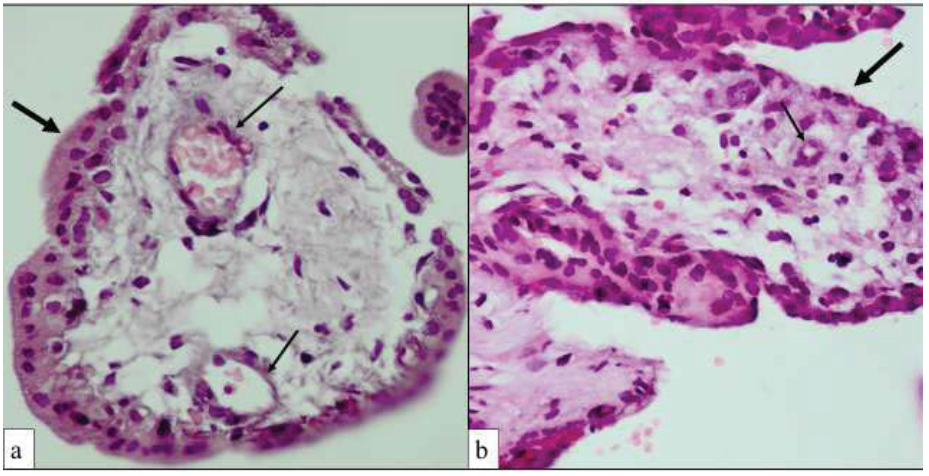
Leukorrhea gravidarum does not differ from the usual physiological leukorrhea, manifesting itself in the form of vaginal discharge, having the following characteristics:
- intense white or translucent color;
- no odor;
- liquid consistency;
- no strange symptoms;
- moderately abundant (depending on the hormonal background or the influence of other factors).
All women, pregnant or not, experience vaginal discharge that begins a year or two before puberty and ends after menopause. The amount of such secretions varies over time and in response to many factors. For example, it increases just before the start of the menstrual cycle, but even during the nine months of pregnancy, it is normal to notice an increase in the amount of discharge.
Thus, in general, leucorrhoea gravidarum is a natural manifestation of hormonal activity and the health of the genital area, which does not pose a danger to the health of a woman and an unborn child. In fact, the presence of leucorrhea is associated with the need to lubricate and protect the internal mucous membrane of the vagina, which is very useful at the beginning and end of pregnancy.
Leukorrhea gravidarumWhen does white discharge appear in pregnant women?
Leukorrhea during pregnancy can occur as early as the first few weeks as estrogen production increases. But the discharge is more pronounced as the date of birth approaches.
How long does it take?
The leucorrhoea during pregnancy, closely related to the concentration of estrogen in the bloodstream, often persists until delivery. It should be noted, inter alia, that for the same reason, newborn girls may experience leukorrhea for a short time after birth, caused by exposure of the uterus to maternal estrogens.
What should be done so that white discharge does not turn into pathological?
Contraindicated during pregnancy:
- tampons with the potential to cause infections and inflammation;
- vaginal douches not specifically ordered by a gynecologist because they may alter the physiological bacterial flora of the vagina;
- self-medication of any or suspected vaginal infections, even in the case of ordinary candidal infection.
If necessary, panty liners may be used, preferably made of cotton, and it is recommended to inform the gynecologist of any change in the type of discharge.
In case of heavy blood loss or possible rupture of the membranes, urgently go to the emergency room.
When to go to the gynecologist?
In case of doubt about discharge, it is always recommended to consult your gynecologist. This is strictly necessary in special cases where normal vaginal discharge is accompanied by:
- profuse mucus,
- traces of amniotic fluid,
- blood,
- Associated and indicative symptoms of infection such as bad smell, itching or burning in the vaginal area or when urinating, yellow-green color, cottage cheese-like texture.

These events require gynecological monitoring due to possible signs of the following conditions:
- Mucosal plug prolapse (coincides with the prenatal phase). Normal white discharge becomes more profuse, pinkish and more gel-like in consistency and may cause a woman some discomfort. Early loss of the mucosal plug can cause preterm labor.
- Premature rupture of membranes. It is not always possible for a woman to distinguish between normal vaginal mucus (leucorrhoea or hydrorrhea) and loss of amniotic fluid. Usually the latter is especially abundant and looks like water. In the pharmacy, you can buy pads that change color in case of amniotic fluid loss, but the last word in terms of diagnosis always and without fail belongs to the gynecologist.
- Infections . Signs of a possible intimate infection are itching, burning, irritation of the vagina, increased intimate discharge, and changes in color, texture, or smell.
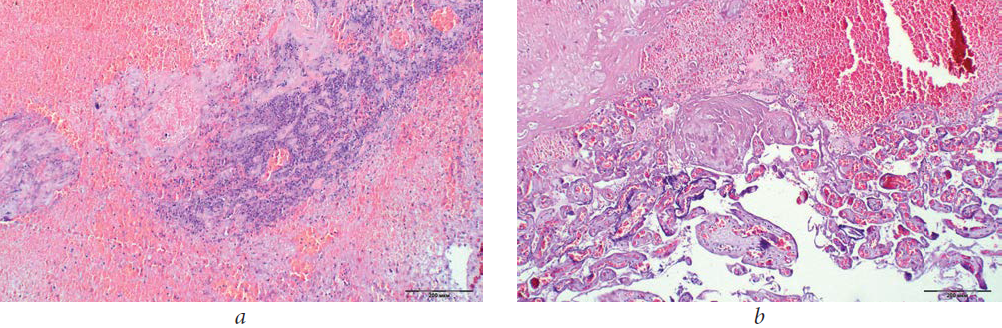 It is very important to recognize these signs during pregnancy, because some infections can be dangerous for the fetus and therefore require adequate and timely treatment.
It is very important to recognize these signs during pregnancy, because some infections can be dangerous for the fetus and therefore require adequate and timely treatment. - Threatened abortion or incipient miscarriage . There is a loss of bright red blood, often mixed with clots and accompanied by abdominal cramps.
Bleeding during pregnancy should always be reported to the gynecologist.
[dcb id=9583]
Tags: leucorrhoea, pregnancy, discharge from women, infections, threatened miscarriage
description, features, recommendations, contraindications, what you need to know
Often, expectant mothers, discovering discharge in the third trimester of pregnancy, begin to panic. Panic is a thankless task. In addition, in most cases it is absolutely groundless. In order to understand what to go to the doctor with and what to stay at home with, we propose to classify the secretion that occurs in the later stages and understand its varieties in detail.
Ideally
To begin with, let's figure out which picture can be considered a reference. This is a light or slightly whitish discharge, which is evidence that the mother is healthy. Doctors call this phenomenon the term "leucorrhea". They are present at each stage of bearing a baby, being the "brainchild" of hormones that are rampant in the mother's body. Closer to the expected date of birth, the secrets secreted by the reproductive system will become more abundant and liquid. They owe their "evolution" to estrogen. The ideal situation is one in which whites do not cause inconvenience, are not accompanied by itching and do not have an unpleasant odor. You can cope with whites with the help of ordinary daily pads. Nothing over the top.
Deciphering brown mucus
Have you found a brownish secretion on your underwear that scares you not only with its painful appearance, but also with the unpleasant smell of raw meat? Go to the doctor! A brown tint is evidence that blood clots have got into the mucus. The doctor will be able to recognize their nature and determine whether there is a need for hospitalization. In most cases, this is necessary. Brown secretion is a direct road to the hospital ward, sometimes until the very birth.
The doctor will be able to recognize their nature and determine whether there is a need for hospitalization. In most cases, this is necessary. Brown secretion is a direct road to the hospital ward, sometimes until the very birth.
Both in the early and later stages, with the help of brown leucorrhea (the medical name for the phenomenon under discussion), the female body seems to say: the vessels that feed the uterus regularly lose blood. Of course, in such situations, the baby's blood loss is out of the question, however, due to constant bleeding, the baby clearly lacks oxygen. Hospitalization in such cases is necessary in order to protect the expectant mother from stress, as well as carefully monitor her condition.
Brown discharge in the third trimester of pregnancy may indicate placenta previa. After analyzing them, the specialist will come to a conclusion regarding when exactly the little person decides to leave his comfortable home and appear in this world. Based on the results of the analysis, a caesarean section is prescribed, because since the placenta has blocked the way for the baby, you will have to use the emergency exit.
Is yellow and green a sign of danger?
It is enough to look at the photo of discharge during pregnancy in the third trimester or listen to the stories of "experienced colleagues" to understand: leukorrhea that appears from the genital tract can be not only white or brown. It may be greenish or yellowish. The appearance of leucorrhea of such shades on panties is a loud call: go to the gynecologist!
It is not uncommon for yellow and green "symptoms" to indicate the presence of a venereal infection in the mother's body. Explicit yellowness is a sign of gonorrhea. If yellow mucus almost instantly degenerated into green discharge, an acute inflammation occurs in the female body or an infection rampages. But do not make independent premature conclusions, because "green" can also occur in the process of taking antibiotics. And in such situations, leukorrhea is just evidence of a malfunction in the microflora.
Often yellowish discharge in the 3rd trimester of pregnancy is not mucus at all, but urine stains. You should not be afraid. It's just that you are faced with a very delicate, but very common problem - leakage. Urine comes out drop by drop when mom laughs or sneezes. Fighting the problem will not work, just as it will not work and control it. With the advent of the baby, everything will pass, as if it never happened.
You should not be afraid. It's just that you are faced with a very delicate, but very common problem - leakage. Urine comes out drop by drop when mom laughs or sneezes. Fighting the problem will not work, just as it will not work and control it. With the advent of the baby, everything will pass, as if it never happened.
To sum up
What should be remembered by women who are carrying a baby in order not to torment their nervous system in vain and calmly enjoy the best period in their lives? First, what be
Light discharge during pregnancy in the third trimester is absolutely normal. Provided that whites do not have an unpleasant odor and are not accompanied by burning.
If the expected date of birth is close, abundant mucus may be a uterine plug that has successfully exited, opening the way for the baby. The discovery of a cork indicates only one thing: within two or three days you will become a mother. A brownish secretion just before the due date indicates that the meeting with the baby is closer than ever: there are only a couple of hours left before the start!
Vaginal secretion that is neither white nor beige is a signal.