Diet for first trimester
Pregnancy Diet: 13 Foods to Eat While Pregnant
Pregnant? Hangry? Looking for a snack that will make your tummy and your baby happy? You’re probably hearing it a lot: Eating nutritious foods while pregnant is essential.
We’re here to make your pantry into a one-stop shop of healthy and delicious foods that will give your baby the best start to life.
When building your healthy eating plan, you’ll want to focus on whole foods that give you higher amounts of the good stuff you’d need when not pregnant such as:
- protein
- vitamins and minerals
- healthy types of fat
- complex carbohydrates
- fiber and fluids
Here are 13 super nutritious foods to eat when you’re pregnant to help make sure you’re hitting those nutrient goals.
During pregnancy, you need to consume extra protein and calcium to meet the needs of your growing little one. Dairy products like milk, cheese, and yogurt should be on the docket.
Dairy products contain two types of high-quality protein: casein and whey. Dairy is the best dietary source of calcium, and provides high amounts of phosphorus, B vitamins, magnesium, and zinc.
Yogurt, especially Greek yogurt, contains more calcium than most other dairy products and is especially beneficial. Some varieties also contain probiotic bacteria, which support digestive health.
If you’re lactose intolerant, you may also be able to tolerate yogurt, especially probiotic yogurt. Check with your doctor to see if you can test it out. A whole world of yogurt smoothies, parfaits, and lassi could be waiting.
This group of food includes lentils, peas, beans, chickpeas, soybeans, and peanuts (aka all kinds of fabulous recipe ingredients!).
Legumes are great plant-based sources of fiber, protein, iron, folate, and calcium — all of which your body needs more of during pregnancy.
Folate is one of the most essential B vitamins (B9). It’s very important for you and baby, especially during the first trimester, and even before.
You’ll need at least 600 micrograms (mcg) of folate every day, which can be a challenge to achieve with foods alone. But adding in legumes can help get you there along with supplementation based on your doctor’s recommendation.
But adding in legumes can help get you there along with supplementation based on your doctor’s recommendation.
Legumes are generally very high in fiber, too. Some varieties are also high in iron, magnesium, and potassium. Consider adding legumes to your diet with meals like hummus on whole grain toast, black beans in a taco salad, or a lentil curry.
Sweet potatoes are not only delicious cooked about a thousand ways, they’re also rich in beta carotene, a plant compound that is converted into vitamin A in your body.
Vitamin A is essential for baby’s development. Just watch out for excessive amounts of animal-based sources of vitamin A, such as organ meats, which can cause toxicity in high amounts.
Thankfully, sweet potatoes are an ample plant-based source of beta carotene and fiber. Fiber keeps you full longer, reduces blood sugar spikes, and improves digestive health (which can really help if that pregnancy constipation hits).
For a fab brekky, try sweet potatoes as a base for your morning avocado toast.
Smoked on a whole wheat bagel, teriyaki grilled, or slathered in pesto, salmon is a welcome addition to this list. Salmon is rich in essential omega-3 fatty acids that have a host of benefits.
These are found in high amounts in seafood, and help build the brain and eyes of your baby and can even help increase gestational length.
But wait: Have you been told to limit your seafood intake due to the mercury and other contaminants found in high mercury fish? You can still eat fatty fish like salmon.
Here are the high mercury fish to avoid:
- swordfish
- shark
- king mackerel
- marlin
- bigeye tuna
- tilefish from the Gulf of Mexico
Plus, salmon is one of the very few natural sources of vitamin D, which is lacking for most of us. It’s important for bone health and immune function.
Those incredible, edible eggs are the ultimate health food, as they contain a little bit of almost every nutrient you need. A large egg contains about 80 calories, high-quality protein, fat, and many vitamins and minerals.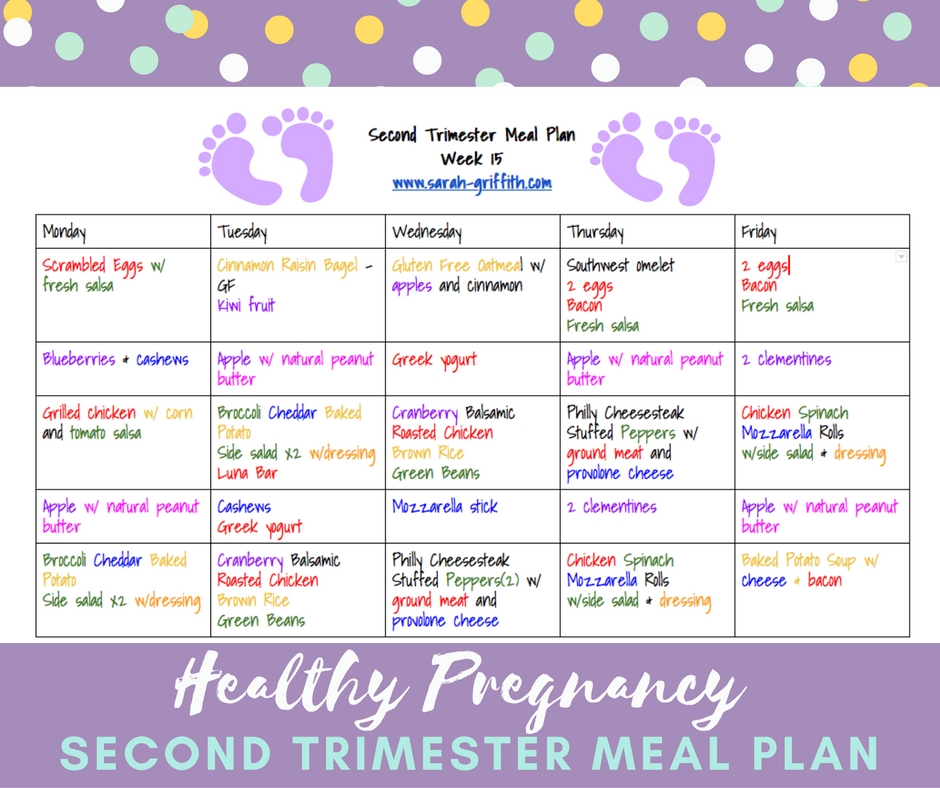
Eggs are a great source of choline, a vital nutrient during pregnancy. It’s important in baby’s brain development and helps prevent developmental abnormalities of the brain and spine.
A single whole egg contains roughly 147 milligrams (mg) of choline, which will get you closer to the current recommended choline intake of 450 mg per day while pregnant (though more studies are being done to determine if that is enough).
Here are some of the healthiest ways to cook eggs. Try them in spinach feta wraps or a chickpea scramble.
No surprise here: Broccoli and dark, green vegetables, such as kale and spinach, pack in so many of the nutrients you’ll need. Even if you don’t love eating them, they can often be squirreled into all kinds of dishes.
Benefits include fiber, vitamin C, vitamin K, vitamin A, calcium, iron, folate, and potassium. They’re a bonanza of green goodness.
Adding in servings of green veggies is an efficient way to pack in vitamins and fend off constipation due to all that fiber. Vegetables have also been linked to a reduced risk of low birth weight.
Vegetables have also been linked to a reduced risk of low birth weight.
Try this kale eggs Florentine recipe or blend some spinach into a green smoothie and you won’t even know it’s in there.
Lean beef, pork, and chicken are excellent sources of high-quality protein. Beef and pork are also rich in iron, choline, and other B vitamins — all of which you’ll need in higher amounts during pregnancy.
Iron is an essential mineral that is used by red blood cells as a part of hemoglobin. You’ll need more iron since your blood volume is increasing. This is particularly important during your third trimester.
Low levels of iron during early and mid-pregnancy may cause iron deficiency anemia, which increases the risk of low birth weight and other complications.
It can be hard to cover your iron needs with meals alone, especially if you develop an aversion to meat or are vegetarian or vegan. However, for those who can, eating lean red meat regularly may help increase the amount of iron you’re getting from food.
Pro tip: Pairing foods that are rich in vitamin C, such as oranges or bell peppers, along with iron-rich foods may also help increase absorption.
Toss some vitamin C-rich tomato slices on that turkey burger or whip up this steak and mango salad.
Berries hold a lot of goodness in their tiny packages like water, healthy carbs, vitamin C, fiber, and antioxidants.
Berries have a relatively low glycemic index value, so they should not cause major spikes in blood sugar.
Berries are also a great snack, as they contain both water and fiber. They provide a lot of flavor and nutrition, but with relatively few calories.
Some of the best berries to eat while pregnant are blueberries, raspberries, goji berries, strawberries, and acai berries. Check out this blueberry smoothie for some inspiration.
Unlike their refined counterparts, whole grains are packed with fiber, vitamins, and plant compounds. Think oats, quinoa, brown rice, wheat berries, and barley instead of white bread, pasta, and white rice.
Some whole grains, like oats and quinoa, also contain a fair amount of protein. They also hit a few buttons that are often lacking in pregnant people: B vitamins, fiber, and magnesium.
There are so many ways to adds whole grains to any meal, but we’re especially liking this quinoa and roasted sweet potato bowl.
Avocados are an unusual fruit because they contain a lot of monounsaturated fatty acids. This makes them taste buttery and rich — perfect for adding depth and creaminess to a dish.
They’re also high in fiber, B vitamins (especially folate), vitamin K, potassium, copper, vitamin E, and vitamin C.
Because of their high content of healthy fats, folate, and potassium, avocados are a great choice during pregnancy (and always).
The healthy fats help build the skin, brain, and tissues of your little one, and folate may help prevent neural tube defects, developmental abnormalities of the brain and spine such as spina bifida.
Potassium may help relieve leg cramps, a side effect of pregnancy for some women. In fact, avocados contain more potassium than bananas.
In fact, avocados contain more potassium than bananas.
Try them as guacamole, in salads, in smoothies, and on whole wheat toast, but also as a substitute for mayo or sour cream.
Dried fruit is generally high in calories, fiber, and various vitamins and minerals. One piece of dried fruit contains the same amount of nutrients as fresh fruit, just without all the water and in a much smaller form.
One serving of dried fruit can provide a large percentage of the recommended intake of many vitamins and minerals, including folate, iron, and potassium.
Prunes are rich in fiber, potassium, and vitamin K. They’re natural laxatives and may be very helpful in relieving constipation. Dates are high in fiber, potassium, iron, and plant compounds.
However, dried fruit also contains high amounts of natural sugar. Make sure to avoid the candied varieties, which contain even more sugar.
Although dried fruit may help increase calorie and nutrient intake, it’s generally not recommended to consume more than one serving at a time.
Try adding a small portion to a trail mix with nuts and seeds for an on-the-go protein- and fiber-filled snack.
Fish liver oil is made from the oily liver of fish, most often cod. It’s rich in the omega-3 fatty acids EPA and DHA, which are essential for fetal brain and eye development.
Supplementing with fish oil may help protect against preterm delivery and may benefit fetal eye development.
Fish liver oil is also very high in vitamin D, of which many people don’t get enough. It may be highly beneficial for those who don’t regularly eat seafood or supplement with omega-3 or vitamin D.
A single serving (1 tablespoon or 15 milliliters) of fish liver oil provides more than the recommended daily intake of omega-3, vitamin D, and vitamin A.
However, it’s not recommended to consume more than one serving per day, as too much preformed vitamin A can be dangerous for your baby. High levels of omega-3 may also have blood-thinning effects.
Low mercury fish like salmon, sardines, canned light tuna, or pollock can also help get you to your omega-3 goals.
Say it with me: We all have to stay hydrated. And pregnant folks especially. During pregnancy, blood volume increases by about 45 percent.
Your body will channel hydration to your baby, but if you don’t watch your water intake, you may become dehydrated yourself.
Symptoms of mild dehydration include headaches, anxiety, tiredness, bad mood, and reduced memory.
Increasing your water intake may also help relieve constipation and reduce your risk of urinary tract infections, which are common during pregnancy.
General guidelines recommend that pregnant women drink about 80 ounces (2.3 liters) of water daily. But the amount you really need varies. Check with your doctor for a recommendation based on your specific needs.
Keep in mind that you also get water from other foods and beverages, such as fruit, vegetables, coffee, and tea.
Pro tip: Try keeping a reusable water bottle on hand so that you can quench your thirst throughout the day.
Your growing baby is just waiting to slurp up all those nutrient-dense foods from a well-rounded eating plan of whole grains, fruits and veggies, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
There’s a whole world of delicious options that give you and your baby everything you’ll need. Keep your healthcare team informed of your eating choices and let them guide you on a plan with any necessary supplements.
This list should be a good start towards a healthy, well-nourished pregnancy.
Quick tips for foods to eat when pregnant
- Dairy products, especially yogurt, are a great choice. They help you meet increased protein and calcium needs.
- Legumes are super sources of folate, fiber, and many other nutrients. Folate is a very important nutrient during pregnancy.
- Sweet potatoes are an excellent source of beta carotene, which your body transforms into vitamin A. Vitamin A is important for the growth and differentiation of cells in your growing baby.
- Salmon contains the essential omega-3 fatty acids EPA and DHA, which are important for brain and eye development in your growing baby. It’s also a natural source of vitamin D.

- Whole eggs are incredibly nutritious and a great way to increase your overall nutrient intake. They also contain choline, an essential nutrient for brain health and development.
- Broccoli and leafy greens contain most of the nutrients that you’ll need. They’re also rich in fiber, which may help prevent or treat constipation.
- Lean meat is a good source of high-quality protein. Beef and pork are also rich in iron, choline, and B vitamins, all of which are important nutrients during pregnancy.
- Berries contain water, carbs, vitamin C, fiber, vitamins, antioxidants, and plant compounds. They may help you increase your nutrient and water intake.
- Whole grains are packed with fiber, vitamins, and plant compounds. They’re also rich in B vitamins, fiber, and magnesium.
- Avocados contain high amounts of monounsaturated fatty acids, fiber, folate, and potassium. They may help relieve leg cramps, too.
- Dried fruit may be highly beneficial for pregnant women since they’re small and nutrient-dense.
Just make sure to limit your portions and avoid candied varieties, to prevent excess sugar intake.
- Drinking water is important as your blood volume increases during pregnancy. Adequate hydration may also help prevent constipation and urinary tract infections.
Pregnancy Diet: 13 Foods to Eat While Pregnant
Pregnant? Hangry? Looking for a snack that will make your tummy and your baby happy? You’re probably hearing it a lot: Eating nutritious foods while pregnant is essential.
We’re here to make your pantry into a one-stop shop of healthy and delicious foods that will give your baby the best start to life.
When building your healthy eating plan, you’ll want to focus on whole foods that give you higher amounts of the good stuff you’d need when not pregnant such as:
- protein
- vitamins and minerals
- healthy types of fat
- complex carbohydrates
- fiber and fluids
Here are 13 super nutritious foods to eat when you’re pregnant to help make sure you’re hitting those nutrient goals.
During pregnancy, you need to consume extra protein and calcium to meet the needs of your growing little one. Dairy products like milk, cheese, and yogurt should be on the docket.
Dairy products contain two types of high-quality protein: casein and whey. Dairy is the best dietary source of calcium, and provides high amounts of phosphorus, B vitamins, magnesium, and zinc.
Yogurt, especially Greek yogurt, contains more calcium than most other dairy products and is especially beneficial. Some varieties also contain probiotic bacteria, which support digestive health.
If you’re lactose intolerant, you may also be able to tolerate yogurt, especially probiotic yogurt. Check with your doctor to see if you can test it out. A whole world of yogurt smoothies, parfaits, and lassi could be waiting.
This group of food includes lentils, peas, beans, chickpeas, soybeans, and peanuts (aka all kinds of fabulous recipe ingredients!).
Legumes are great plant-based sources of fiber, protein, iron, folate, and calcium — all of which your body needs more of during pregnancy.
Folate is one of the most essential B vitamins (B9). It’s very important for you and baby, especially during the first trimester, and even before.
You’ll need at least 600 micrograms (mcg) of folate every day, which can be a challenge to achieve with foods alone. But adding in legumes can help get you there along with supplementation based on your doctor’s recommendation.
Legumes are generally very high in fiber, too. Some varieties are also high in iron, magnesium, and potassium. Consider adding legumes to your diet with meals like hummus on whole grain toast, black beans in a taco salad, or a lentil curry.
Sweet potatoes are not only delicious cooked about a thousand ways, they’re also rich in beta carotene, a plant compound that is converted into vitamin A in your body.
Vitamin A is essential for baby’s development. Just watch out for excessive amounts of animal-based sources of vitamin A, such as organ meats, which can cause toxicity in high amounts.
Thankfully, sweet potatoes are an ample plant-based source of beta carotene and fiber. Fiber keeps you full longer, reduces blood sugar spikes, and improves digestive health (which can really help if that pregnancy constipation hits).
Fiber keeps you full longer, reduces blood sugar spikes, and improves digestive health (which can really help if that pregnancy constipation hits).
For a fab brekky, try sweet potatoes as a base for your morning avocado toast.
Smoked on a whole wheat bagel, teriyaki grilled, or slathered in pesto, salmon is a welcome addition to this list. Salmon is rich in essential omega-3 fatty acids that have a host of benefits.
These are found in high amounts in seafood, and help build the brain and eyes of your baby and can even help increase gestational length.
But wait: Have you been told to limit your seafood intake due to the mercury and other contaminants found in high mercury fish? You can still eat fatty fish like salmon.
Here are the high mercury fish to avoid:
- swordfish
- shark
- king mackerel
- marlin
- bigeye tuna
- tilefish from the Gulf of Mexico
Plus, salmon is one of the very few natural sources of vitamin D, which is lacking for most of us. It’s important for bone health and immune function.
It’s important for bone health and immune function.
Those incredible, edible eggs are the ultimate health food, as they contain a little bit of almost every nutrient you need. A large egg contains about 80 calories, high-quality protein, fat, and many vitamins and minerals.
Eggs are a great source of choline, a vital nutrient during pregnancy. It’s important in baby’s brain development and helps prevent developmental abnormalities of the brain and spine.
A single whole egg contains roughly 147 milligrams (mg) of choline, which will get you closer to the current recommended choline intake of 450 mg per day while pregnant (though more studies are being done to determine if that is enough).
Here are some of the healthiest ways to cook eggs. Try them in spinach feta wraps or a chickpea scramble.
No surprise here: Broccoli and dark, green vegetables, such as kale and spinach, pack in so many of the nutrients you’ll need. Even if you don’t love eating them, they can often be squirreled into all kinds of dishes.
Benefits include fiber, vitamin C, vitamin K, vitamin A, calcium, iron, folate, and potassium. They’re a bonanza of green goodness.
Adding in servings of green veggies is an efficient way to pack in vitamins and fend off constipation due to all that fiber. Vegetables have also been linked to a reduced risk of low birth weight.
Try this kale eggs Florentine recipe or blend some spinach into a green smoothie and you won’t even know it’s in there.
Lean beef, pork, and chicken are excellent sources of high-quality protein. Beef and pork are also rich in iron, choline, and other B vitamins — all of which you’ll need in higher amounts during pregnancy.
Iron is an essential mineral that is used by red blood cells as a part of hemoglobin. You’ll need more iron since your blood volume is increasing. This is particularly important during your third trimester.
Low levels of iron during early and mid-pregnancy may cause iron deficiency anemia, which increases the risk of low birth weight and other complications.
It can be hard to cover your iron needs with meals alone, especially if you develop an aversion to meat or are vegetarian or vegan. However, for those who can, eating lean red meat regularly may help increase the amount of iron you’re getting from food.
Pro tip: Pairing foods that are rich in vitamin C, such as oranges or bell peppers, along with iron-rich foods may also help increase absorption.
Toss some vitamin C-rich tomato slices on that turkey burger or whip up this steak and mango salad.
Berries hold a lot of goodness in their tiny packages like water, healthy carbs, vitamin C, fiber, and antioxidants.
Berries have a relatively low glycemic index value, so they should not cause major spikes in blood sugar.
Berries are also a great snack, as they contain both water and fiber. They provide a lot of flavor and nutrition, but with relatively few calories.
Some of the best berries to eat while pregnant are blueberries, raspberries, goji berries, strawberries, and acai berries. Check out this blueberry smoothie for some inspiration.
Check out this blueberry smoothie for some inspiration.
Unlike their refined counterparts, whole grains are packed with fiber, vitamins, and plant compounds. Think oats, quinoa, brown rice, wheat berries, and barley instead of white bread, pasta, and white rice.
Some whole grains, like oats and quinoa, also contain a fair amount of protein. They also hit a few buttons that are often lacking in pregnant people: B vitamins, fiber, and magnesium.
There are so many ways to adds whole grains to any meal, but we’re especially liking this quinoa and roasted sweet potato bowl.
Avocados are an unusual fruit because they contain a lot of monounsaturated fatty acids. This makes them taste buttery and rich — perfect for adding depth and creaminess to a dish.
They’re also high in fiber, B vitamins (especially folate), vitamin K, potassium, copper, vitamin E, and vitamin C.
Because of their high content of healthy fats, folate, and potassium, avocados are a great choice during pregnancy (and always).
The healthy fats help build the skin, brain, and tissues of your little one, and folate may help prevent neural tube defects, developmental abnormalities of the brain and spine such as spina bifida.
Potassium may help relieve leg cramps, a side effect of pregnancy for some women. In fact, avocados contain more potassium than bananas.
Try them as guacamole, in salads, in smoothies, and on whole wheat toast, but also as a substitute for mayo or sour cream.
Dried fruit is generally high in calories, fiber, and various vitamins and minerals. One piece of dried fruit contains the same amount of nutrients as fresh fruit, just without all the water and in a much smaller form.
One serving of dried fruit can provide a large percentage of the recommended intake of many vitamins and minerals, including folate, iron, and potassium.
Prunes are rich in fiber, potassium, and vitamin K. They’re natural laxatives and may be very helpful in relieving constipation. Dates are high in fiber, potassium, iron, and plant compounds.
However, dried fruit also contains high amounts of natural sugar. Make sure to avoid the candied varieties, which contain even more sugar.
Although dried fruit may help increase calorie and nutrient intake, it’s generally not recommended to consume more than one serving at a time.
Try adding a small portion to a trail mix with nuts and seeds for an on-the-go protein- and fiber-filled snack.
Fish liver oil is made from the oily liver of fish, most often cod. It’s rich in the omega-3 fatty acids EPA and DHA, which are essential for fetal brain and eye development.
Supplementing with fish oil may help protect against preterm delivery and may benefit fetal eye development.
Fish liver oil is also very high in vitamin D, of which many people don’t get enough. It may be highly beneficial for those who don’t regularly eat seafood or supplement with omega-3 or vitamin D.
A single serving (1 tablespoon or 15 milliliters) of fish liver oil provides more than the recommended daily intake of omega-3, vitamin D, and vitamin A.
However, it’s not recommended to consume more than one serving per day, as too much preformed vitamin A can be dangerous for your baby. High levels of omega-3 may also have blood-thinning effects.
Low mercury fish like salmon, sardines, canned light tuna, or pollock can also help get you to your omega-3 goals.
Say it with me: We all have to stay hydrated. And pregnant folks especially. During pregnancy, blood volume increases by about 45 percent.
Your body will channel hydration to your baby, but if you don’t watch your water intake, you may become dehydrated yourself.
Symptoms of mild dehydration include headaches, anxiety, tiredness, bad mood, and reduced memory.
Increasing your water intake may also help relieve constipation and reduce your risk of urinary tract infections, which are common during pregnancy.
General guidelines recommend that pregnant women drink about 80 ounces (2.3 liters) of water daily. But the amount you really need varies. Check with your doctor for a recommendation based on your specific needs.
Check with your doctor for a recommendation based on your specific needs.
Keep in mind that you also get water from other foods and beverages, such as fruit, vegetables, coffee, and tea.
Pro tip: Try keeping a reusable water bottle on hand so that you can quench your thirst throughout the day.
Your growing baby is just waiting to slurp up all those nutrient-dense foods from a well-rounded eating plan of whole grains, fruits and veggies, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
There’s a whole world of delicious options that give you and your baby everything you’ll need. Keep your healthcare team informed of your eating choices and let them guide you on a plan with any necessary supplements.
This list should be a good start towards a healthy, well-nourished pregnancy.
Quick tips for foods to eat when pregnant
- Dairy products, especially yogurt, are a great choice. They help you meet increased protein and calcium needs.
- Legumes are super sources of folate, fiber, and many other nutrients.
Folate is a very important nutrient during pregnancy.
- Sweet potatoes are an excellent source of beta carotene, which your body transforms into vitamin A. Vitamin A is important for the growth and differentiation of cells in your growing baby.
- Salmon contains the essential omega-3 fatty acids EPA and DHA, which are important for brain and eye development in your growing baby. It’s also a natural source of vitamin D.
- Whole eggs are incredibly nutritious and a great way to increase your overall nutrient intake. They also contain choline, an essential nutrient for brain health and development.
- Broccoli and leafy greens contain most of the nutrients that you’ll need. They’re also rich in fiber, which may help prevent or treat constipation.
- Lean meat is a good source of high-quality protein. Beef and pork are also rich in iron, choline, and B vitamins, all of which are important nutrients during pregnancy.
- Berries contain water, carbs, vitamin C, fiber, vitamins, antioxidants, and plant compounds.
They may help you increase your nutrient and water intake.
- Whole grains are packed with fiber, vitamins, and plant compounds. They’re also rich in B vitamins, fiber, and magnesium.
- Avocados contain high amounts of monounsaturated fatty acids, fiber, folate, and potassium. They may help relieve leg cramps, too.
- Dried fruit may be highly beneficial for pregnant women since they’re small and nutrient-dense. Just make sure to limit your portions and avoid candied varieties, to prevent excess sugar intake.
- Drinking water is important as your blood volume increases during pregnancy. Adequate hydration may also help prevent constipation and urinary tract infections.
Diet for pregnant women for weight loss
While expecting a baby, a woman experiences not only hormonal and physical changes in her body. It is important for her to rebuild some eating habits in favor of more correct ones. When carrying a fetus, the consumption of valuable vitamins and trace elements increases, so you need to replenish their reserves all the time. Let's talk about what a pregnant woman's diet can be and how to make nutrition complete.
Let's talk about what a pregnant woman's diet can be and how to make nutrition complete.
Website editor
Tags:
diets
protein diet
diet table
How to lose weight during pregnancy
Diet for pregnant women
If you follow the rules of nutrition during pregnancy, the diet will keep the weight normal and will not harm the baby. Here are the basic principles of the diet for expectant mothers and draw up an approximate menu.
Contents of the article
Diet during pregnancy must solve a large number of problems. First, you need to provide your body and the developing body of the child with all the necessary substances. Secondly, to minimize the symptoms of toxicosis, reduce the burden on the liver and stomach. And, thirdly, to avoid excessive weight gain in the expectant mother. We tell you what a safe diet for pregnant women consists of for weight loss.
And, thirdly, to avoid excessive weight gain in the expectant mother. We tell you what a safe diet for pregnant women consists of for weight loss.
Is it safe to lose weight during pregnancy?
Pregnant women are generally not advised to lose weight or follow a strict diet during pregnancy. But as part of a balanced diet, the expectant mother can safely lose a few pounds during the first trimester. The main thing is to stick to a healthy diet and avoid fatty and sugary foods. Only in this case, after giving birth, you will quickly return to your previous shape.
Diet for pregnant women - general recommendations
There is a diet for pregnant women for the 1st, 2nd and 3rd trimesters to reduce weight, but due to the competent construction of the diet, and not a complete rejection of food. We will talk about the nutritional features at each stage of fetal development. However, there are general rules that should be observed during the entire course of pregnancy.
However, there are general rules that should be observed during the entire course of pregnancy.
- Eat 5-6 times a day in small portions.
- The last meal should be no later than 3 hours before bedtime.
- Avoid alcohol, fried, smoked, coffee and fast food.
- Consume a diet predominantly of fruits, nuts, vegetable broths, cereals, lean fish.
- Take vitamin complexes.
Pregnancy Diet - 1st Trimester
In the first trimester of pregnancy, the fetus is formed from the embryo, the brain and internal organs begin to develop. During this period, you need to approach the preparation of the diet most seriously.
The body of the future mother should receive enough protein and folic acid. And a diet for pregnant women should take into account such important points. These substances are rich in foods such as lean meat and eggs, legumes, lettuce, whole grain bread, cheese, cottage cheese, celery, cabbage, liver, apples.
Diet menu for the 1st trimester of pregnancy
Our great-grandmothers' favorite saying that it's time to eat for two should encourage you to eat better, better, not more. Adjust your diet so as not to harm yourself or your child. In the early stages, a diet for pregnant women is especially important, so be sure to consult a doctor. He will be able to suggest which products to add and which should be excluded.
Monday
- Breakfast: buckwheat with yogurt, apple juice with celery.
- Second breakfast: cottage cheese.
- Lunch: vegetable soup, wholemeal bread.
- Afternoon snack: peach.
- Dinner: salad with salmon and avocado.
- Late dinner: berry juice.
Tuesday
- Breakfast: cottage cheese with berries, tea.
- Second breakfast: dry biscuits, freshly squeezed juice.

- Lunch: pumpkin puree soup.
- Snack: apples.
- Dinner: steamed turkey meatball.
- Late dinner: yogurt.
Wednesday
- Breakfast: oatmeal with milk.
- Second breakfast: bread with butter.
- Lunch: fish soup.
- Snack: cottage cheese with low-fat sour cream.
- Dinner: liver, buckwheat.
- Late dinner: seaweed salad.
Thursday
- Breakfast: sugar-free granola with milk.
- Second breakfast: yogurt.
- Lunch: weak meat broth with egg.
- Snack: vegetable salad.
- Dinner: stewed cabbage, rice.
- Late dinner: fruit drink.
Friday
- Breakfast: bread with tomatoes and cream cheese.
- Second breakfast: pear.
- Lunch: pasta with meat hedgehog.

- Snack: almonds.
- Dinner: baked potatoes with herbs and butter.
- Before going to bed: herbal tea, fermented baked milk.
Saturday
- Breakfast: cottage cheese pancakes 5%, green tea.
- Second breakfast: prunes.
- Lunch: chicken soup, bread.
- Snack: cabbage and carrot salad.
- Dinner: cucumber and tomato salad.
- Late dinner: a glass of milk.
Sunday
- Breakfast: millet porridge, juice.
- Second breakfast: orange.
- Lunch: vegetable soup with tomatoes, peppers and Brussels sprouts.
- Snack: pear.
- Dinner: steamed fish cake and vegetables.
- Late dinner: kefir.
Diet for Pregnancy - 2nd Trimester
In the second trimester of pregnancy (from 13 to 28 weeks), pay attention to vitamin D and calcium (they are absorbed only in conjunction). Include dairy products, spinach, eggs, sea fish, cod liver, butter in your diet. Pregnant women may experience swelling, so the diet for every day should include a decrease in the amount of salt consumed.
Include dairy products, spinach, eggs, sea fish, cod liver, butter in your diet. Pregnant women may experience swelling, so the diet for every day should include a decrease in the amount of salt consumed.
Get into the habit of regular walks in the fresh air, even during the cold season. Consume potentially allergenic foods with caution: citrus fruits, red berries, nuts. In the second trimester, the load on the liver of a pregnant woman increases, so exclude fatty and fried foods.
Pregnancy diet - 3rd trimester
During this period (from 28 weeks to the end of the 40th), the baby grows more actively than in the previous two. Mom puts on weight more noticeably, the body prepares for childbirth. The diet of a pregnant woman in the 3rd trimester involves a menu with a restriction of simple carbohydrates. This does not mean that the diet should be aimed at losing weight and losing weight. It's more about a balanced diet.
During pregnancy, strict restrictions should be avoided, and even more so, you should not starve yourself. Just like in the second trimester, watch your calcium intake. To exclude edema, fatigue and toxicosis, try to give up fatty meat.
Protein Diet for Pregnancy
Following the principles of this diet helps to return to its former shape almost immediately after childbirth. The protein diet for pregnant women is based on the main rule - the daily protein intake should be 120 grams. However, in addition to protein foods, a future mother can consume up to 400 grams of carbohydrates per day.
It is also important to consider what not to eat during pregnancy. Banned are chocolates, cakes, sugar, white bread and fast food. There are other basic rules:
- Distribute food throughout the day. The optimal number of meals is 5 times a day. Five meals a day includes three main meals and two light snacks.

- Keep breaks between meals at 3.5 hours.
- Drink enough water per day, but in small portions during the day, not at night.
Benefits of a protein diet for pregnant women
- You eat a varied diet and don't feel hungry because protein takes a long time to digest.
- You eat enough protein, which is an important micronutrient for the body.
- You don't completely eliminate carbohydrates. The diet includes fruits, vegetables and cereals. The only thing you cut out of your life is fast-digesting carbohydrates like white bread and sweets. Simple carbohydrates just negatively affect the digestion of pregnant women and lead to constipation. As a rule, these are empty calories with no nutritional value.
The cons of a protein diet for pregnant women for weight loss
- The protein diet may not suit you, as it does not adjust much depending on the trimester.
 Before starting a diet, you should consult a doctor.
Before starting a diet, you should consult a doctor. - As part of the diet for pregnant women, general recommendations are given for each day, which you adhere to, missing individual indicators.
- Some sources state that in the first trimester it is necessary to consume 60-90 grams of protein per day, and from the 5th month of pregnancy - increase the daily rate to 120 grams. To determine the optimal amount, contact your doctor.
It should be noted that in excess of protein can overload the body and lead to undesirable consequences. It provokes increased work of the kidneys, necessary for the removal of their decay products. Lack of fiber and an excess of proteins - let it lead to stomach problems in the form of bloating, heaviness, heartburn, and so on.
Daily protein diet menu for pregnant women - 1st trimester
- Breakfast: oatmeal and dried fruits (literally a few pieces) and rosehip broth.

- Snack: any fruit, medium-fat cottage cheese no more than 100 grams and 1 tablespoon of curdled milk.
- Lunch: chicken broth soup, steamed vegetables up to 200 grams and 1 piece of lean fish for a couple.
- Snack: natural yogurt (1 cup) and an apple.
- Dinner: Mixed vegetable omelette and a slice of whole grain bread.
Daily protein diet menu for pregnant women - 2nd trimester
- Breakfast: whole grain bread slice, hard boiled egg and green tea.
- Snack: 1 glass of fermented baked milk and a small banana.
- Lunch: broccoli soup, rice with chicken (200 grams), grated carrot salad with sour cream
- Snack: a handful of hazelnuts and 5 pieces of dried apricots.
- Dinner: fresh vegetable salad and a handful of cottage cheese.
- Snack: a glass of low-fat yogurt.
Daily protein diet menu for pregnant women - 3rd trimester
- Breakfast: rice milk porridge with dried fruits, raisins and fruit drink.

- Snack: diet syrniki with oatmeal and pear.
- Lunch: fresh cabbage soup and grilled fish with vegetable stew (medium portions).
- Snack: 1 cup yogurt, a slice of whole grain bread, an apple.
- Dinner: fresh vegetable salad and steamed turkey with 50 grams of buckwheat.
- Snack: low-fat kefir 1 cup.
Diet number 9 for pregnant women
Diet (table) number 9 for pregnant women with diabetes provides for fractional meals with a break between meals of 2.5 hours. This mode will avoid spikes in blood sugar. One serving should not exceed 150 g. It is based on the recommendations of the Soviet gastroenterologist Pevzner.
When following table number 9, it is necessary to limit the amount of carbohydrates to 200-300 g per day. Two meals should be rich in protein. The total calorie content of the diet should not exceed 2500 kcal. At its core, diet number 9for pregnant women with gestational diabetes is somewhat similar to the principle of nutrition, in which protein predominates. Gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) manifests itself during the period of bearing a child and is limited by the duration of pregnancy, that is, sugar rises only in these months.
Gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) manifests itself during the period of bearing a child and is limited by the duration of pregnancy, that is, sugar rises only in these months.
When following the Pregnancy Diet 9, sugar and simple carbohydrates should be excluded from the diet. Limit your intake of pasta, starchy vegetables and legumes, fried foods, fatty foods, smoked foods, and salt.
Diet table number 9in case of diabetes, pregnant women are obliged to exclude sugar and simple carbohydrates: even from 100 g of pasta, the glucose level can jump up to 8 units. Now the woman's body is under tremendous stress: hormones block insulin, and the pancreas must produce more of it than in any other state.
High blood sugar can affect both the mother's well-being and the baby's health. Diet table number 9 for gestational diabetes in pregnant women takes into account the preparation of a balanced menu that helps to cope with unpleasant symptoms. We recommend regular visits to the doctor during pregnancy so that he can track the dynamics of the baby's development and adjust therapeutic nutrition for diabetes.
We recommend regular visits to the doctor during pregnancy so that he can track the dynamics of the baby's development and adjust therapeutic nutrition for diabetes.
It is not worth neglecting the doctor's recommendations, because diabetes during pregnancy can harm both the mother and the child. In rare cases, the disease can lead to miscarriage.
Diet table number 9 for GDM in pregnant women is also suitable for weight loss, because you control the amount of carbohydrates and reduce sugar in the diet. What do you need to know about the power plan? We share the basic principles of the 9th table.
Keep a food diary
To lose weight and improve your health, you need to control the percentage of carbohydrates and sugar in the diet. The easiest way to do this is with a diary. Write down every meal regularly so that the doctor can adjust the menu based on the results of the tests. If the sugar level jumps sharply, the specialist will know what is the reason.
If the sugar level jumps sharply, the specialist will know what is the reason.
Control carbohydrates
Diet table number 9 for pregnant women is a menu for every day with a minimum amount of carbohydrate foods. If they are present, they should be evenly distributed throughout the day. This way you avoid sudden spikes in blood sugar after eating. Doctors recommend reducing portions to small and medium and do not forget about healthy snacks.
Bet on foods with a low glycemic index
A diet for high sugar in a pregnant woman necessarily includes foods that do not cause large drops in blood glucose levels. Choose healthy, low-GI carbohydrate foods such as vegetables, beans, low-fat dairy, berries, and whole grain snacks.
Include lean proteins such as tofu, chicken, fish, and eggs, as well as healthy fats in your diet. The list includes nuts, avocados and olive oil.
Keep yourself away from foods that are low in nutrients. Sweets, sugary drinks, ice cream and fast food - these foods are prohibited for diabetics. And no compromises, because you need to think not about momentary pleasures, but about the health of both of you.
In order for the diet table No. 9 for pregnant women to be suitable for weight loss (under the supervision of a doctor), you need to follow other important rules:
- Control your daily calories. It is calculated from the individual characteristics of the body (35 kcal per 1 kilogram of mother's weight), but does not exceed 2000 calories per day. Half of the diet is healthy carbohydrate meals, 20% is protein foods, and the rest is unsaturated fats.
- Do not exceed the allowed daily allowance of salt - 12 grams.
- Drink the required amount of water, at least 2 liters.
- Eat small meals up to 6-7 times a day. Try to maintain a pause between meals at 2 hours.

- Replace sugar with sweeteners.
- Steam or simmer food. Fried foods are completely excluded. Meat and vegetables can be baked.
- Smoked and fried foods are prohibited.
- Priority is given to foods high in fiber.
If you are on a diet for pregnant women with diabetes and are overweight, be sure to keep an eye on the increase. Get on the scale every week and periodically take urine and blood tests. Of course, don't forget your home blood glucose meter. People with diabetes should definitely have a device in their first aid kit.
Diet 9 table for pregnant women - menu
Monday
- Breakfast: vegetable salad, porridge, boiled egg.
- Second breakfast: kissel.
- Lunch: liver with puree, chicken broth, juice.
- Afternoon snack: peach.
- Dinner: chicken breast, cabbage salad with carrots.

- Late dinner: curdled milk.
Tuesday
- Breakfast: cottage cheese, oatmeal, vegetable juice.
- Second breakfast: kefir.
- Lunch: boiled salmon, buckwheat, lean cabbage soup.
- Snack: apple.
- Dinner: boiled egg, vinaigrette.
- Late supper: fermented baked milk.
Wednesday
- Breakfast: chicory drink, yogurt, barley porridge.
- Second breakfast: milk.
- Lunch: baked turkey, vegetarian borscht, fruit.
- Snack: orange.
- Dinner: steamed fish cake, vegetables.
- Late dinner: kefir.
Thursday
- Breakfast: millet porridge, cottage cheese, tea.
- Second breakfast: kefir.
- Lunch: boiled chicken, soup, compote.
- Snack: jelly.
- Dinner: cabbage rolls, boiled meat.

- Late dinner: curdled milk.
Friday
- Breakfast: boiled egg, vegetable salad.
- Second breakfast: vegetable juice.
- Lunch: boiled veal, stewed cabbage, soup.
- Snack: pear.
- Dinner: boiled fish, vegetable casserole.
- Late dinner: yogurt.
Saturday
- Breakfast: buckwheat porridge with yogurt.
- Second breakfast: kissel.
- Lunch: stewed rabbit, baked potatoes, fish soup.
- Snack: kefir.
- Dinner: barley, boiled fish.
- Late dinner: apple.
Sunday
- Breakfast: buckwheat, boiled egg.
- Second breakfast: an apple.
- Lunch: rice, steamed beef cutlets, mushroom soup.
- Afternoon snack: fermented baked milk.
- Dinner: mashed potatoes with fish, vegetables.

- Late dinner: curdled milk.
Consult your doctor regularly, do not hesitate to ask questions about pregnancy - there can be no trifles in such a topic. Try to follow a healthy lifestyle. Eliminate harmful foods from the diet and add healthy foods to the menu based on the recommendations of experts.
Diet for pregnant women for weight loss - nutritionist's advice: video
youtube
Click and watch
Nutrition for a pregnant woman
So, your plans and decisions to have a baby have come true - you are pregnant! But this news causes you a double feeling: - on the one hand, a feeling of joy, and on the other hand, a feeling of certain fear and even fear of unknown trials for your life and the fate of the unborn baby. What will he be like? - healthy, beautiful, happy?...
And it largely depends on the woman herself, on what lifestyle she will lead during pregnancy and, most importantly, how she will eat.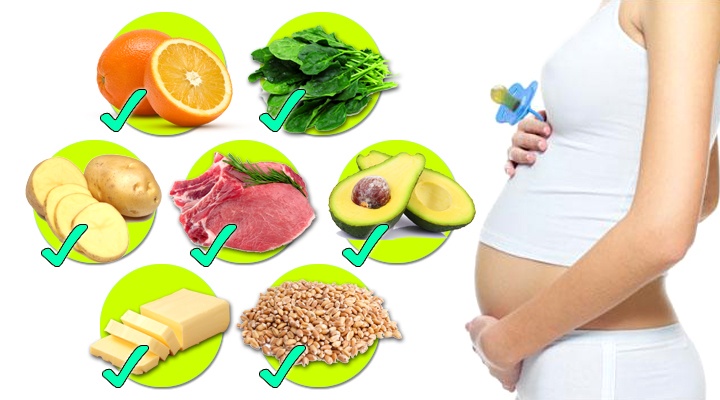
Nutrition of a woman in different periods of pregnancy
The main thing in the menu of a future mother is variety. She should consume foods from all food groups: meat, fish, vegetables and fruits, dairy products, bread and cereals.
A woman's nutrition during pregnancy can be roughly divided into three periods (trimesters).
If before pregnancy a woman ate normally, felt comfortable, did not experience allergies to any products, then it is not worth changing her diet at an early stage of the first trimester of pregnancy.
During this period, all organs and systems in the child's body are formed, tissues are formed. The body needs complete proteins and vitamins: lean meat (rabbit, chicken, turkey), fish and seafood, dairy products. Be sure to eat rice, fresh or frozen vegetables, seasonal fruits. In the first trimester, many expectant mothers are still working. No matter how difficult it is to control your diet in the workplace, you need to do it - find time for a full breakfast and lunch.
In the first trimester of pregnancy, there is an active restructuring of the body and adaptation to a new state. During this period, it is recommended to switch to a low-calorie diet, which includes more fruits, juices, decoctions of dried fruits, including rose hips. At the very beginning of pregnancy, especially if toxicosis torments, more frequent, but less plentiful meals are recommended.
Always keep a hematogen, a bag of nuts or dried fruit in your pocket to have a snack on the street. If your condition does not allow you to eat regular food, you should pay attention to baby food. Baby products literally save expectant mothers suffering from severe toxicosis. These are boxed cereals, children's curds, cookies and fruit purees.
In the first trimester, special attention must be paid to the quality of products. Gradually abandon sauces, semi-finished products and canned food containing harmful chemical additives. Do not forget that the placenta freely accumulates and passes chemistry. The importance of products containing folic acid is great, without it intensive metabolism is impossible, its deficiency can cause developmental abnormalities. Folic acid is found in greens, nuts, white cabbage and broccoli, beets, legumes, and eggs.
The importance of products containing folic acid is great, without it intensive metabolism is impossible, its deficiency can cause developmental abnormalities. Folic acid is found in greens, nuts, white cabbage and broccoli, beets, legumes, and eggs.
According to nutritionists, the diet of pregnant women should be 300 kcal / day higher than that of non-pregnant women, but in the first trimester there is no need to increase the energy value of the diet at all; in the second trimester, an additional 340 kcal / day is required; in the third trimester - 452 kcal / day. Pregnant women generally get enough calories, and more than 80% of women achieve and even exceed the required weight gain. These extra calories benefit the fetus. An underweight woman should gain 16–20 kg during her entire pregnancy, an overweight woman about 7 kg, and a normal body weight of 11–12 kg.
In the second trimester there are active jumps in the height and weight of the baby and uterus, so the caloric content of the diet needs to be increased.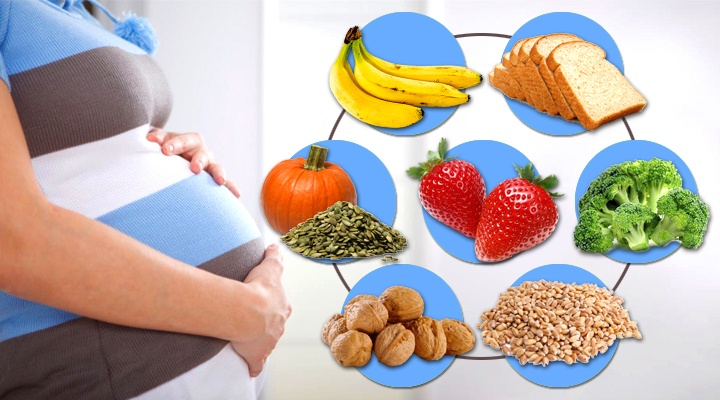 It is desirable to eat more and better. At this time, the need for trace elements increases: iron, magnesium, zinc, selenium, calcium, potassium. The child creates his own "reserve" of trace elements using the mother's resource, which means that the mother should have enough of them for two.
It is desirable to eat more and better. At this time, the need for trace elements increases: iron, magnesium, zinc, selenium, calcium, potassium. The child creates his own "reserve" of trace elements using the mother's resource, which means that the mother should have enough of them for two.
Very often in pregnant women in the second trimester hemoglobin drops, this is a normal physiological phenomenon, if it is not threatening to health. You can increase hemoglobin by eating red meat, chicken, fish, dried fruits, pomegranates, green vegetables and fresh herbs, buckwheat, citrus fruits (oranges, grapefruits, pomelo, lemons), rosehip and berry infusions.
In the second trimester, a pregnant woman should limit the intake of smoked and fried foods, as well as salt in her diet. In no case should you limit the liquid. Pure water is the best drink for a pregnant woman, and water should be consumed up to 2-2.5 liters per day. Water is a natural drink for the body, it does not cause complications and has no contraindications. Edema is caused not by water, but by salt, which we not only add in its pure form, but also consume with canned food, mayonnaise, cheese, and sausage. The absence of salt is not harmful, it is naturally found in many products: vegetables, bread, so the diet will not remain completely without it. Excess salt disrupts metabolism.
Edema is caused not by water, but by salt, which we not only add in its pure form, but also consume with canned food, mayonnaise, cheese, and sausage. The absence of salt is not harmful, it is naturally found in many products: vegetables, bread, so the diet will not remain completely without it. Excess salt disrupts metabolism.
During this period, you can increase the calorie content of food. Childbirth must be approached physically strong. It is better to eat meat and fish in the morning, for breakfast and lunch, and for dinner, prepare dairy and vegetable dishes: cheesecakes, stewed vegetables, cottage cheese and vegetable casseroles. It is necessary to minimize the intake of canned food, smoked meats, pickles and marinades, hot spices and fatty foods. Frequent walks in the air, physical activity are recommended.
In the third trimester, it is necessary to reduce the calorie content of foods at the expense of confectionery and flour products, eat less fatty meat, as well as cheese and sour cream.
By the end of this period, many experts advise pregnant women to give up meat altogether in order to increase tissue elasticity and prevent ruptures.
During the entire period of pregnancy, special attention should be paid to the combination of products. If you combine foods wisely, you can ensure more efficient absorption of food. If the food is digested poorly, then this can lead to rotting and fermentation of products and the formation of substances harmful to the body of the mother and child. In addition, the fermentation process is accompanied by gas formation, which can lead to flatulence (bloating) and discomfort. This is especially harmful in the last stages of pregnancy.
Try not to take the first, second and third course at the same time; this overflows the stomach and presses on the fetus, the food is poorly digested and poorly absorbed. Eat little and often. It is not recommended to eat immediately before starting work, a long walk, before charging and immediately after it; it is advisable to rest for 10 minutes before eating.
Eat only when you are hungry, try not to snack on the go. Follow the diet, eat at about the same time.
Proper preparation of food will help to maximize the useful substances contained in the products. Do not overcook food, try not to reheat the same dish several times, it is better to set aside only the portion that will be used. Cook in the most gentle way: baking, steaming, stewing. Avoid frying, boiling in large amounts of water, with this method of processing products, many useful substances are lost. If possible, do not cook for several days at once. Do not use aluminum cookware when cooking. Remember that for a pregnant woman, it is not calories that are important, but the quality of food, its naturalness, primarily a “living cell” (whole cereals, raw vegetables and fruits, fresh meat and dairy products).
What can harm the pregnant woman and the fetus
Smoking and alcohol – quit smoking from the first days of pregnancy, if you have smoked before, avoid "passive" smoking, and do not consume alcoholic beverages in any doses.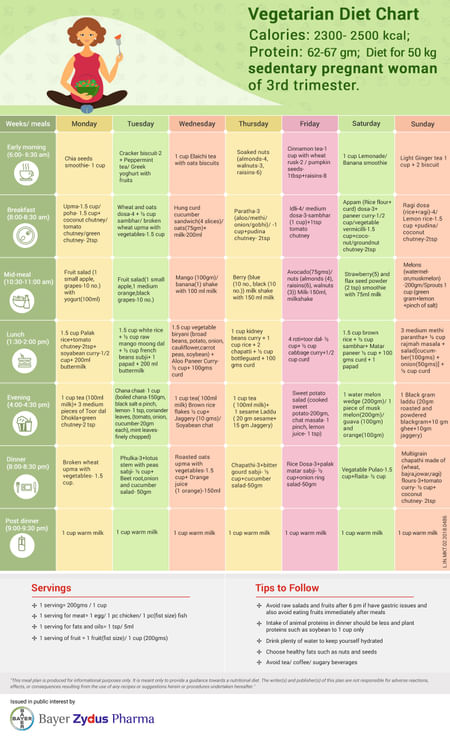
Lack of vitamins and microelements in the body - their absence or deficiency can lead to irreparable consequences. So, for example, iodine deficiency can lead to mental retardation of a child, folic acid deficiency - to severe fetal deformities, calcium deficiency - to a violation of the formation of the child's skeleton, iron deficiency - to anemia and a delay in the physical and neuropsychic development of the child. It is necessary to consult a doctor, perhaps he will recommend switching to iodized salt, as well as supplementing your diet with a vitamin-mineral complex and folic acid.
Excess weight is the risk of having a large child, which means the risk of complications during childbirth and the child's tendency to become obese at an older age.
The use of food additives (sauces, seasonings such as vegeta, bouillon cubes), exotic fruits, semi-finished products, carbonated drinks - the risk of allergies and anomalies in a child, unfortunately, increases.
Recommended for pregnant women:
- Do not eat hot dogs and other snacks containing meat that has not been heated on fire or boiled in boiling water.