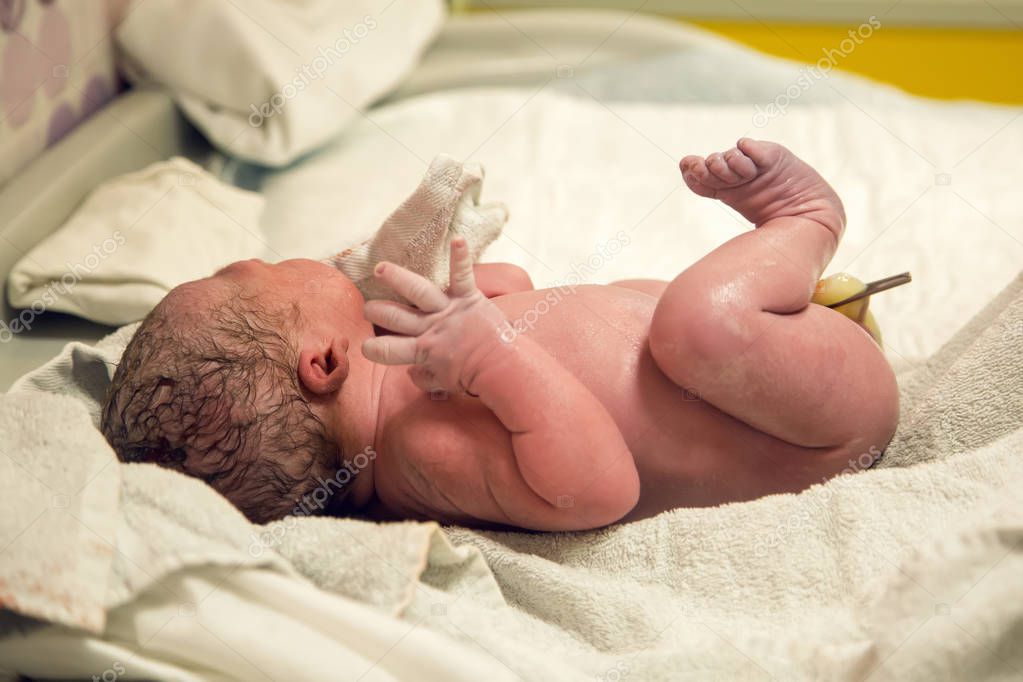
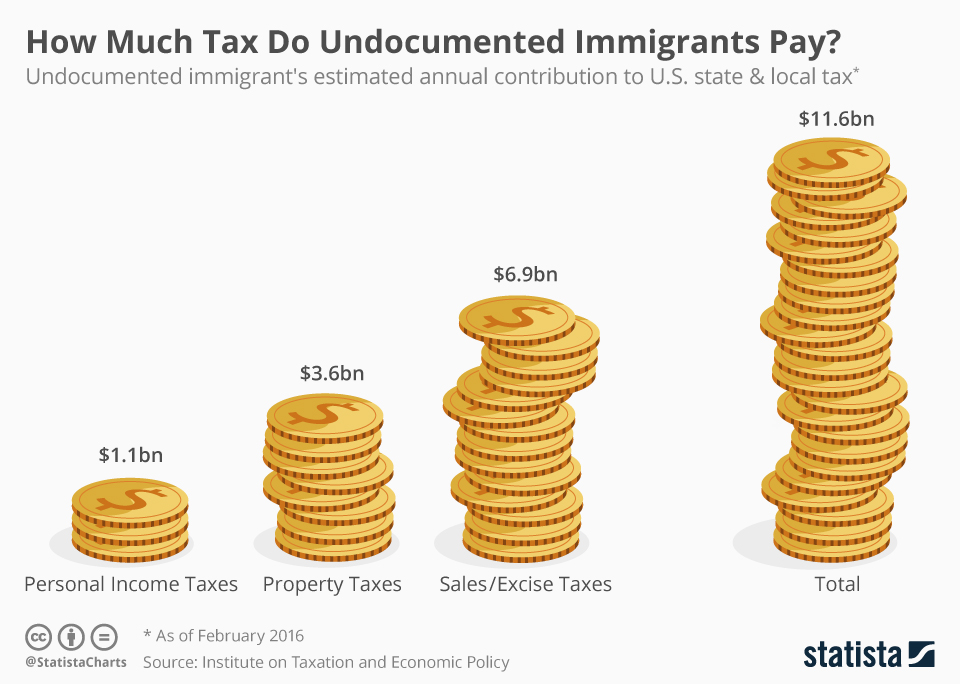
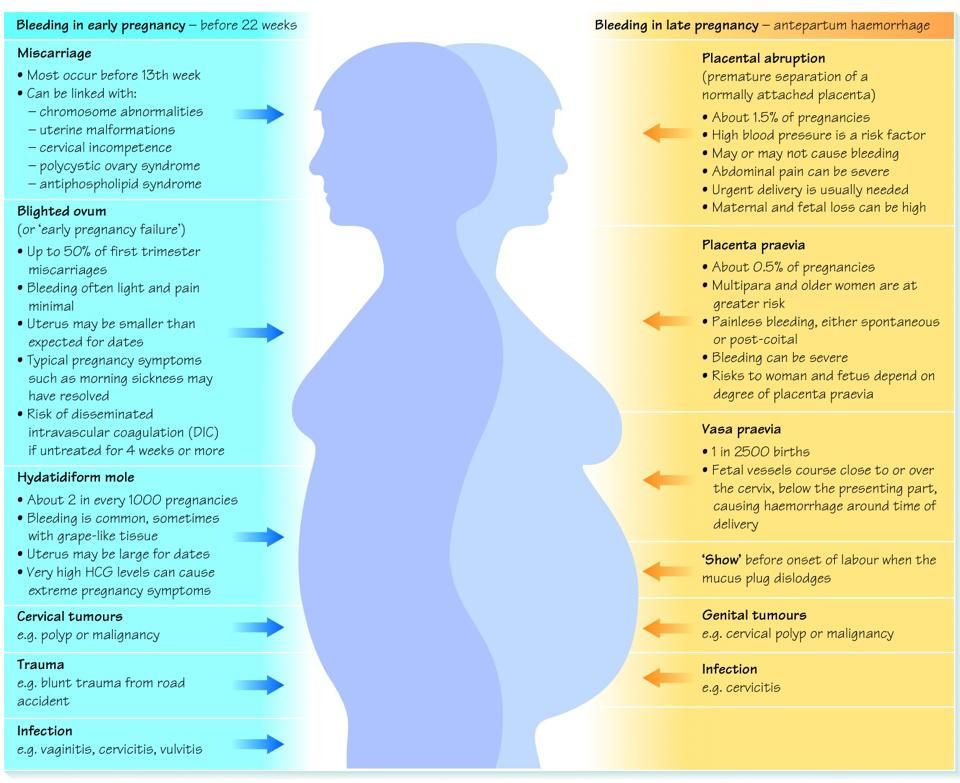
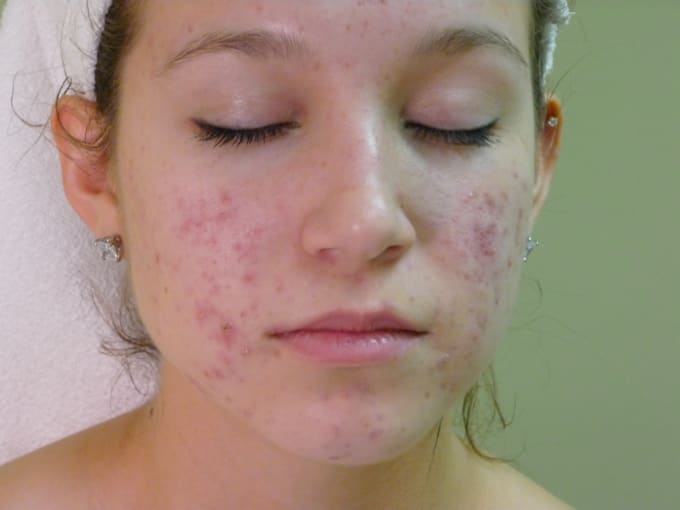
Newborn baby after birth
Baby's first 24 hours | Pregnancy Birth and Baby
Baby's first 24 hours | Pregnancy Birth and Baby beginning of content5-minute read
Listen
The first day of your new baby’s life is thrilling and exhausting for both of you. This page explains what your newborn baby can sense, and how the umbilical cord and placenta can be managed. It has general information for you if you have had a healthy, full-term pregnancy – 37 to 42 weeks’ gestation.
What will my newborn baby look like?
When your baby is born, their skin might be blue and mottled. They are likely to be covered in amniotic fluid, blood and vernix, which is a cheesy white substance. This is normal.
Their skin will start to become pink as they start to breathe — which is about a minute after birth. Your baby’s hands and feet may still appear blueish for several hours.
The amniotic fluid and the vernix are there because they were there in the womb. They are important for your baby to be able to smell and taste after birth. These familiar things help your baby to feel secure outside the womb.
Birth of the placenta and cutting the umbilical cord
After you have given birth to your baby, you will have more contractions that will help you deliver the placenta. Once this happens, the umbilical cord, which is connected to the placenta, will be clamped in two places and cut. Your support person might be invited to cut the cord.
Skin-to-skin contact
After a normal vaginal birth, your newborn baby will be put on your chest for skin-to-skin contact. Your baby needs sleep and food, and they need to feel secure and warm, so they need to feel your skin.
Doing this simple thing:
- reduces newborn crying
- helps start and sustain breastfeeding
- helps maintain your baby’s body temperature
After this first contact, they will be weighed, measured and observed to make sure they are healthy.
If you have a caesarean section, ask your midwife to make sure your baby has skin-to-skin contact with you as early as possible. It may be possible for you or your partner to hold your baby-skin-to skin in theatre and in recovery.
Feeding
Babies start to show signs of wanting to feed soon after birth and usually attach and suck at the breast about 50 minutes after birth. They may then breastfeed for an hour or more. Put your baby against your chest, and they will probably find your breast and start feeding. If that doesn’t happen, you can ask your midwife or a lactation consultant for help.
The first milk you make is called 'colostrum'. It’s thick and often yellowish, rather than pure white. It’s the ideal milk for your baby. Normally a small amount is produced — your baby’s tummy is just the size of a marble.
If they haven’t fed an hour or so after birth, try again a couple of hours later. You can also express some colostrum to feed to your baby on a spoon.
Weighing and measuring
After skin-to-skin contact and the first breastfeed, your midwife might offer to weigh your baby, and measure your baby’s length and head circumference. Your baby doesn’t need to be washed for at least 24 hours.
Vitamin K
At the time of weighing, your midwife will also offer to give your baby a vitamin K injection to prevent bleeding from vitamin K deficiency.
Cord blood collection if you are Rh negative
If your blood group is Rh negative, some blood will be taken from the umbilical cord to determine whether your baby’s blood group is compatible.
Sleeping
Your baby will stay with you so you can bond and respond easily to their needs. They’ll probably sleep soon after their first feed, and that might last 6 hours or so. They will probably sleep for more than half of their first day in the world.
Apgar scores
One of the main observations made after birth is called an Apgar score. It assesses your baby’s adjustment to life outside the womb.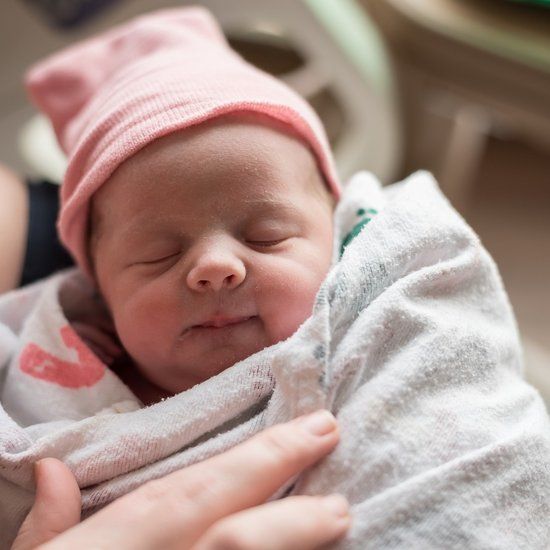 The Apgar score is measured at 1 minute and 5 minutes after birth while the baby is on your chest. Sometimes it is measured again at 10 minutes after birth.
The Apgar score is measured at 1 minute and 5 minutes after birth while the baby is on your chest. Sometimes it is measured again at 10 minutes after birth.
It records your baby’s heart rate, breathing, colour, muscle tone and reflexes. The maximum score is 10. A score of 7 or above usually means your baby is doing well. It is not an ability or intelligence test, and it doesn’t predict your baby’s health later in life.
What will my newborn baby see, hear, smell, taste and feel?
Your baby has been listening to your voice for the last half of your pregnancy and will recognise it when you speak to them after birth. Your partner or support person’s voice may also be familiar if they have also been talking near your baby. Your baby will feel secure when they hear your voices and may respond by turning their head towards you. Your baby will also be able to hear your heart beating as they did in the womb.
Your baby’s vision is blurred at birth but they will be able to focus on your face from about 30 centimetres away. This is called the ‘cuddle distance’. It is roughly the distance from your breast to your face. Your baby will make the connection between what they hear and what they see.
This is called the ‘cuddle distance’. It is roughly the distance from your breast to your face. Your baby will make the connection between what they hear and what they see.
Your baby will smell and taste the amniotic fluid and your colostrum, which has a similar flavour.
Urine and meconium
Within the first 24 hours your baby will probably pass urine and meconium (newborn faeces) at least once. Meconium is black and sticky. Your baby’s poo will change colour and consistency over the next few days.
More information
You can call Pregnancy, Birth and Baby, 7 days a week on 1800 882 436 to speak with a maternal child health nurse to find out more.
Sources:
Cochrane (Early skin-to-skin contact for mothers and their healthy newborn infants), National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) (NICE Guideline CG37: Postnatal care up to 8 weeks after birth), World Health Organization (WHO) (Recommendations on newborn health), Raising Children Network (After baby is born: what to expect in the first few hours), Australian Breastfeeding Association (Breastfeeding timeline)Learn more here about the development and quality assurance of healthdirect content.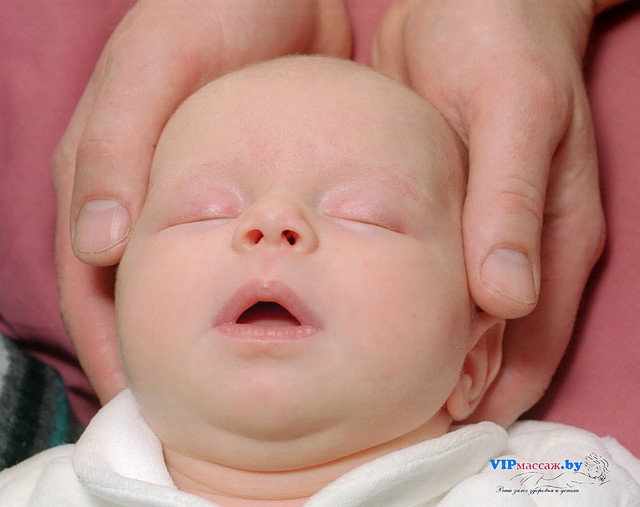
Last reviewed: September 2022
Back To Top
Related pages
- Mum's first few days after giving birth
- Mum's first 24 hours after birth
- Your baby in the first few days
- Birth injury (to the baby)
- What is kangaroo care?
Need more information?
Newborn clothes & dressing a newborn | Raising Children Network
How many clothes does a newborn need? And what newborn clothes are best? Get answers to these questions and more in our guide to dressing a newborn.
Read more on raisingchildren.net.au website
Newborns behaviour | Raising Children Network
Newborn behaviour baffling you? Here's all you need on newborns behaviour with articles, videos and resources on crying, colic and more.
Read more on raisingchildren.net.au website
Dressing a newborn
When dressing your newborn, here are a few things to consider, like which clothes to use, how to dress them and making sure the change table is safe.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Newborn bloodspot screening - MyDr.com.au
Newborn screening tests can detect rare but serious genetic or metabolic disorders in newborn babies.
Read more on myDr website
Newborn essentials
Here is a newborn's essentials checklist including vaccinations and immunisations, health checks, nappy changing and breastfeeding and bottle feeding.
Read more on Pregnancy, Birth & Baby website
Wind, burping & newborn babies in pictures | Raising Children Network
Newborns might have wind from swallowing air when crying or feeding. Burping can help newborns get rid of wind. See how to burp your newborn – in pictures
Burping can help newborns get rid of wind. See how to burp your newborn – in pictures
Read more on raisingchildren.net.au website
Newborns development | Raising Children Network
Want to track newborns development? Here's all you need on newborn development with articles, videos and resources on growth, relationships and more.
Read more on raisingchildren.net.au website
Is my newborn safe? - MyDr.com.au
Dr Norman Swan explains the risks of COVID-19 to your newborn.
Read more on myDr website
Newborns sleep | Raising Children Network
Need help understanding newborn sleep? Here’s all you need on newborn sleep with articles, videos and resources on safe sleep, sleep habits, tiredness and more.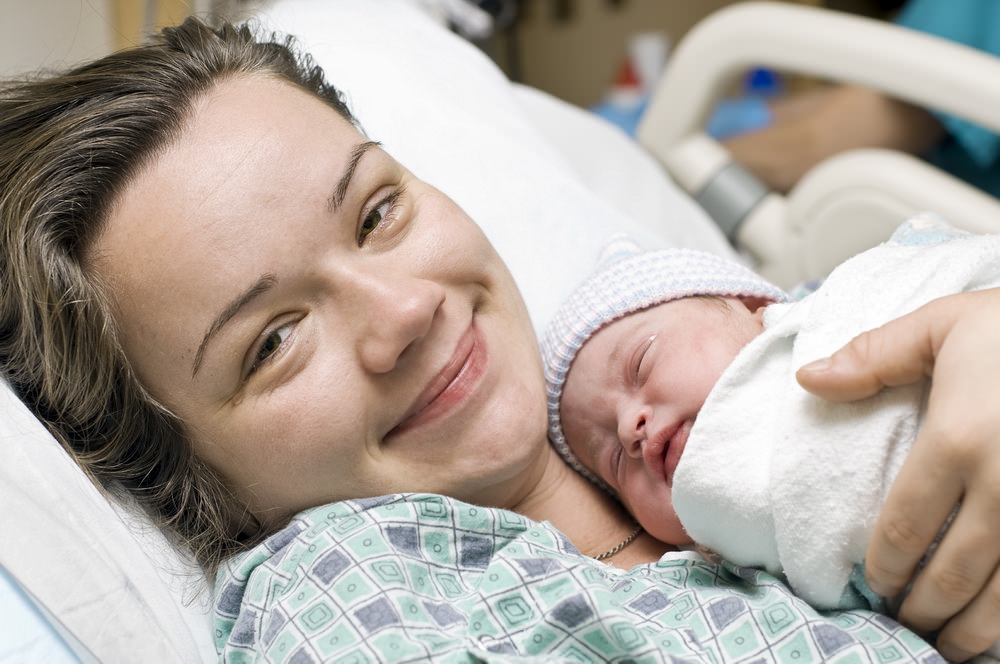
Read more on raisingchildren.net.au website
Newborns safety | Raising Children Network
Newborn safety stressing you? Here’s all you need on newborns safety with articles, videos and resources on first aid, CPR, equipment, car seats and more.
Read more on raisingchildren.net.au website
Disclaimer
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is not responsible for the content and advertising on the external website you are now entering.
OKNeed further advice or guidance from our maternal child health nurses?
1800 882 436
Video call
- Contact us
- About us
- A-Z topics
- Symptom Checker
- Service Finder
- Linking to us
- Information partners
- Terms of use
- Privacy
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is funded by the Australian Government and operated by Healthdirect Australia.
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby is provided on behalf of the Department of Health
Pregnancy, Birth and Baby’s information and advice are developed and managed within a rigorous clinical governance framework. This website is certified by the Health On The Net (HON) foundation, the standard for trustworthy health information.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
This information is for your general information and use only and is not intended to be used as medical advice and should not be used to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any medical condition, nor should it be used for therapeutic purposes.
The information is not a substitute for independent professional advice and should not be used as an alternative to professional health care. If you have a particular medical problem, please consult a healthcare professional.
Except as permitted under the Copyright Act 1968, this publication or any part of it may not be reproduced, altered, adapted, stored and/or distributed in any form or by any means without the prior written permission of Healthdirect Australia.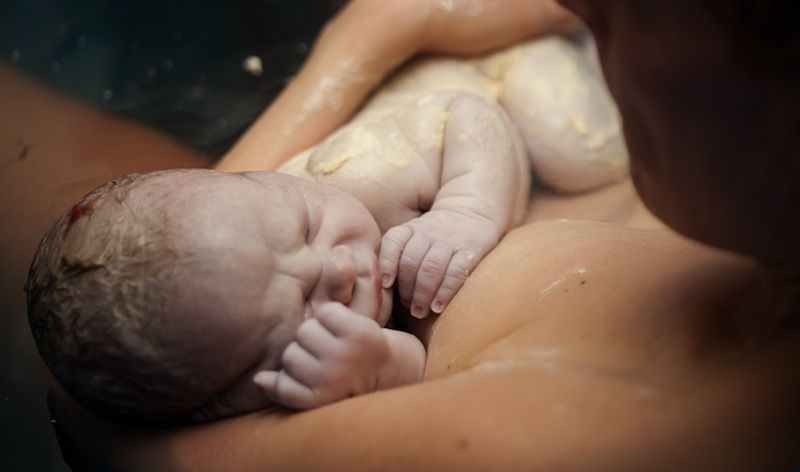
Support this browser is being discontinued for Pregnancy, Birth and Baby
Support for this browser is being discontinued for this site
- Internet Explorer 11 and lower
We currently support Microsoft Edge, Chrome, Firefox and Safari. For more information, please visit the links below:
- Chrome by Google
- Firefox by Mozilla
- Microsoft Edge
- Safari by Apple
You are welcome to continue browsing this site with this browser. Some features, tools or interaction may not work correctly.
What happens to a newborn baby in the hospital?
What happens to a newborn baby in the hospital right after birth?
There's a flurry of activity in the delivery room in the seconds, minutes, and hours after your baby's birth. If you've had a vaginal delivery and you and your baby are in good condition, you'll immediately have skin-to-skin contact with your newborn.
Medical staff place your baby directly onto your abdomen and dry them there. (Newborn babies don't have the ability to control their temperature well, so after a baby is born it's important to keep them warm and dry.) Your baby is covered with a warm towel or blanket and given a cap to keep their head warm.
Skin-to-skin contact also helps keep your newborn warm and lets the two of you start bonding as well. (Don't worry if you can't hold your baby right away due to one of you needing immediate medical care – there will be plenty of time for bonding later.)
The following things also take place immediately or soon after your baby's birth:
The umbilical cord is cut – but not immediately
Your doctor or midwife clamps the umbilical cord in two places and then cuts – or has your partner cut – between the two clamps.
Traditionally in the United States, the cord was cut almost immediately after birth. However, research shows that delayed cord clamping – which allows extra blood to flow from the placenta to the baby – lowers the risk of iron-deficiency anemia in infancy. The American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) and the American College of Obstetrics and Gynecology recommend delaying cord clamping for at least 30 to 60 seconds.
The American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) and the American College of Obstetrics and Gynecology recommend delaying cord clamping for at least 30 to 60 seconds.
Blood is collected
If your blood is type O or Rh negative, blood is collected from the cord to identify your baby's blood type. That's because if your child's blood type is incompatible with yours, it can cause an increased risk of jaundice and hemolytic anemia (a type of anemia caused by red blood cells being destroyed faster than they are created).
If you're banking your newborn's cord blood, that will be collected at this time too.
Suction is used, if needed
Your doctor may have suctioned your baby's mouth and nose before the delivery of their shoulders. If your baby still seems to have too much fluid in their mouth or nose, the doctor may repeat the process again after birth.
Apgar assessment
At one and five minutes after birth, an Apgar assessment is done to evaluate your newborn's heart rate, breathing, muscle tone, reflex response, and color. Your doctor should be able to do these simple assessments while your baby is resting on your belly, so you can stay together.
Your doctor should be able to do these simple assessments while your baby is resting on your belly, so you can stay together.
ID bands and footprints
A nurse puts matching ID bands on you, your newborn, and your partner minutes after the delivery (and certainly before taking your baby out of the room for any reason). These bands are checked and matched every time you and your baby are separated or reunited.
The hospital will explain its security procedures to you, including the protocol and form of ID needed for a staff member to take your baby from your room.
Most hospitals routinely make two copies of your newborn's footprints – one for their hospital record and the other as a keepsake for you. If they don't usually do this but it's something you'd like, you can ask for a set to take home.
Eye drops
Antibiotic ointment or drops are placed in your baby's eyes soon after birth. (This may be postponed for up to an hour so that you can breastfeed.) This is required by law in the U. S. to help prevent eye infections, some of which can cause blindness. These infections are caused by bacteria that your baby could have been exposed to during birth, such as gonorrhea or chlamydia.
S. to help prevent eye infections, some of which can cause blindness. These infections are caused by bacteria that your baby could have been exposed to during birth, such as gonorrhea or chlamydia.
Weight and other measurements are taken
Your baby is weighed, and their length and head circumference are measured.
Vitamin K shot
An injection of vitamin K helps your newborn's blood clot normally and protects them from a rare but dangerous bleeding disorder.
Hepatitis B shot
Your baby should get their first dose of the hepatitis B vaccine before being discharged from the hospital.
- If you're a hepatitis B carrier or your status is unknown, your baby should be vaccinated within 12 hours of birth.
- Babies of mothers who are known hepatitis B carriers will receive an injection of hepatitis B immune globulin (HBIG) – which provides short-term protection – within 12 hours of birth.
- If your hepatitis B status is unknown, your blood will be drawn for testing, and if you're found to be positive, your child should receive a dose of HBIG as soon as possible.

Baby's first exam
Your baby gets a complete pediatric exam within 24 hours, followed by daily exams after that as long as you're in the hospital. If your newborn is in your room when the doctor is doing rounds, the doctor does the exam there and reviews the findings with you. If your child is in the NICU or nursery, the doctor will do the exam there and then come to your room to talk about the findings.
Circumcision
If you've decided that you want your newborn boy to be circumcised in the hospital, it's usually done a day or two after birth.
When do you start breastfeeding after your baby's birth?
Babies tend to be very alert right after birth, making it a good time to begin breastfeeding if you're both willing. In fact, the AAP recommends that healthy, full-term infants "be placed and remain in direct skin-to-skin contact with their mothers immediately after delivery until the first feeding is accomplished."
Most babies begin to nurse within the first hour or so, given the opportunity.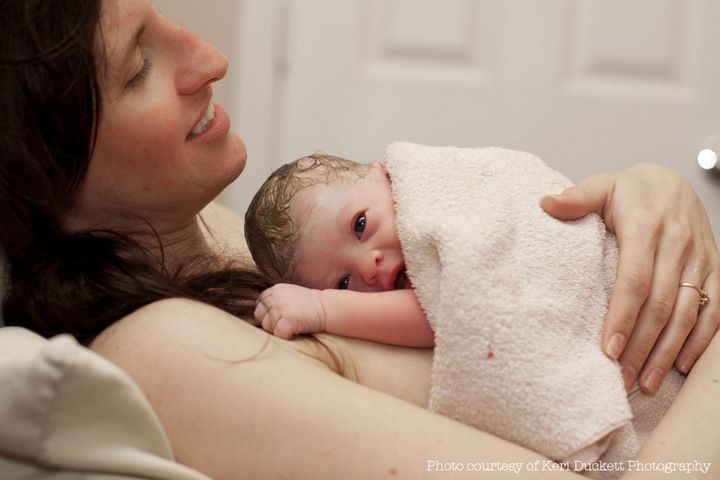 There's no need to panic if your newborn seems to have trouble finding or staying on your nipple right after birth – they may just lick your nipple at first.
There's no need to panic if your newborn seems to have trouble finding or staying on your nipple right after birth – they may just lick your nipple at first.
Don't be shy about asking for help with breastfeeding while you're still in the birth room (or recovery room, if you had a c-section). Later, when you get to the postpartum unit, there may be a lactation consultant for one-on-one coaching or group breastfeeding support. (It's a good idea to find out ahead of time what resources will be available.) If you're uncertain about anything, ask for help.
What happens after your baby's birth if you have a c-section?
If you have a c-section, your baby is handed to a nurse or doctor as soon as they're delivered and taken to a radiant warmer. They're dried off, their mouth and nasal passages are suctioned, an Apgar assessment is done, and they'll get any other attention they need.
In many hospitals, if you and your newborn are doing well, they are swaddled in a warm blanket and placed on your upper chest for a bit — or they can be brought to your partner, who will likely be sitting near your head.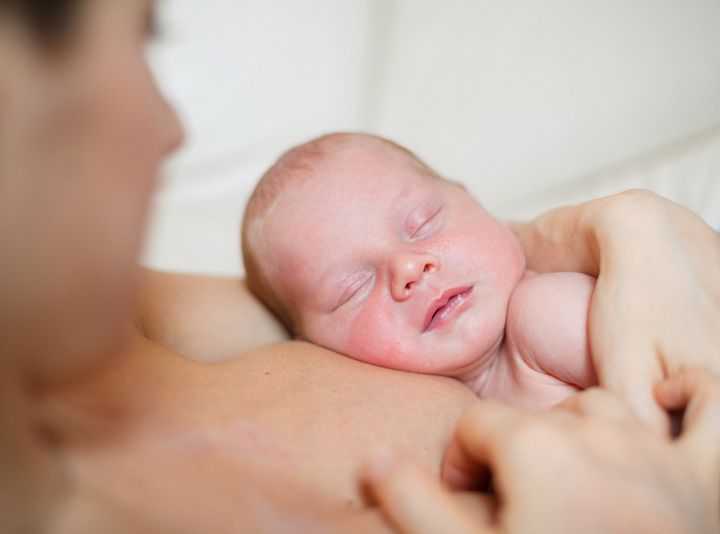 Your partner can hold your baby while you're being stitched up, and you can touch and talk to them while you're still in the operating room.
Your partner can hold your baby while you're being stitched up, and you can touch and talk to them while you're still in the operating room.
Afterward, your newborn goes to the well-baby nursery briefly – your partner may be able to go with them – while you head to the recovery room. In the nursery, their vital signs are taken, and they are weighed and measured.
As soon as possible, the two of you will be reunited and you can have skin-to-skin contact. If you plan to breastfeed, this is a good time to start.
What happens after your baby's birth if there are complications?
If there are any birth complications or your baby has any immediate health problems at birth, things happen quickly. The doctor cuts the cord, and your baby is dried off and placed on a radiant warmer. The warmer allows your baby to be left naked without getting cold so that the medical team can do whatever is necessary.
If your baby needs further care after being stabilized, they may be taken to a neonatal intensive care unit (NICU). But if they're doing well and need no further care, they are swaddled in a warm blanket and brought to you.
But if they're doing well and need no further care, they are swaddled in a warm blanket and brought to you.
What tests does a newborn baby in the hospital get?
Blood test: All states require newborn screening tests. Your baby's heel is pricked and a few drops of blood are taken to test for metabolic, genetic, and endocrine problems. Because some signs of the conditions don't show up until the second day of life or later, it's best to do this on day two or three, but no later than day seven. If you and your baby leave the hospital within 24 hours of birth, you'll be given instructions about following up to have the tests completed.
Pulse oximetry (pulse ox): The amount of oxygen in your baby's blood is measured using painless sensors on the hands and feet to check for the possibility of a congenital heart defect.
Hearing tests: Your newborn's hearing should be checked before you leave the hospital.
HIV: If your HIV status is unknown, your baby's cord blood may be tested for the virus.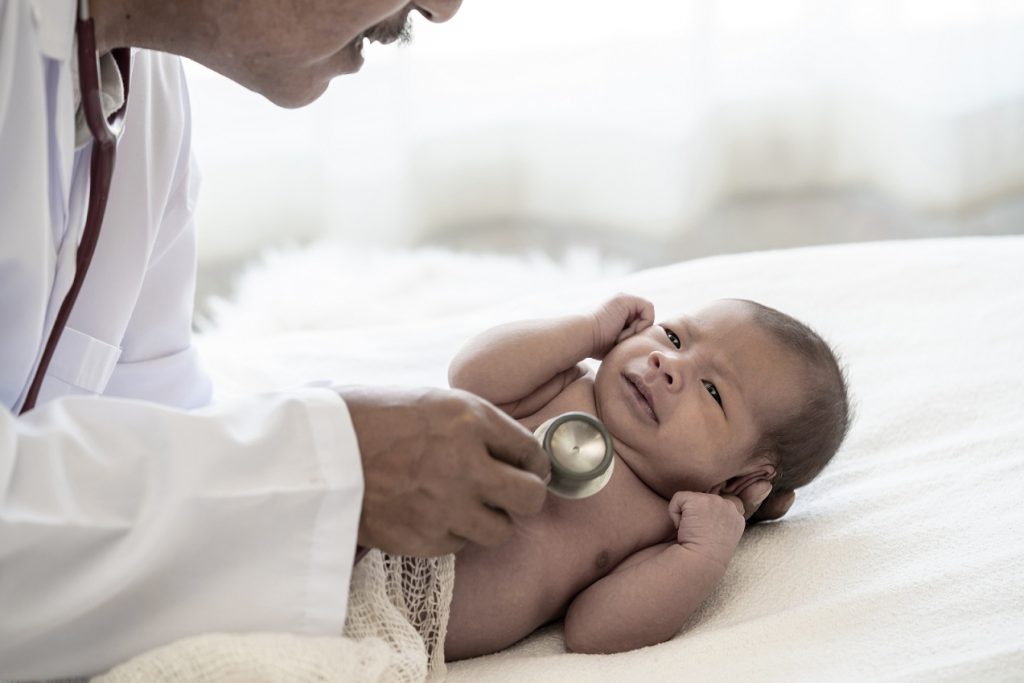 (Some states require this.)
(Some states require this.)
Does a newborn baby get a bath in the hospital?
Yes, your baby will most likely receive a bath while you're in the hospital, but it may not happen as soon as you think. Babies have traditionally been given their newborn bath not long after birth, but research is showing there are advantages to waiting at least 12 hours. A delayed bath:
- Promotes breastfeeding. The amniotic fluid that remains on your newborn may provide breastfeeding cues for them. Researchers theorize this may be one reason why delayed bathing in hospitals resulted in increased breastfeeding rates. One study found that delaying a healthy newborn bath for more than 12 hours after birth resulted in a greater rate of exclusive breastfeeding in the hospital and increased rates of mothers planning to breastfeed (either exclusively or in combination with formula) after leaving the hospital.
- Keeps your baby warm and reduces stress. Longer skin-to-skin contact with you reduces your baby's stress level and keeps them warm.
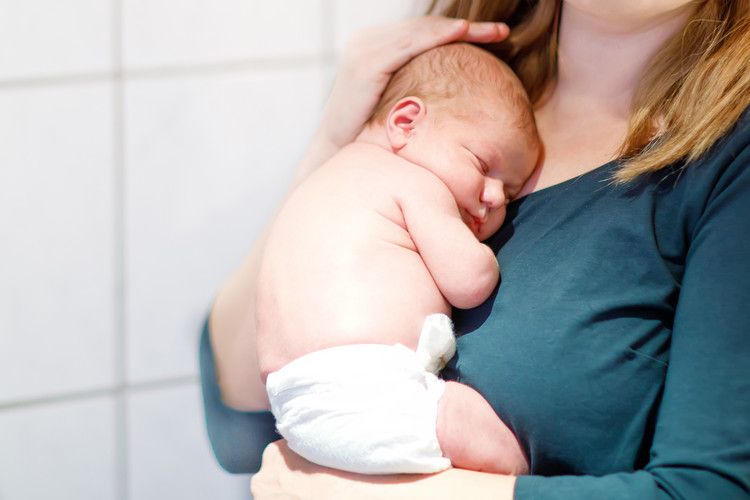 To keep a newborn warm, the World Health Organization (WHO) recommends delaying a baby's first bath for at least six hours and ideally 24 hours after birth. (Because babies have a hard time regulating their temperatures, baths can easily chill and physically stress them.)
To keep a newborn warm, the World Health Organization (WHO) recommends delaying a baby's first bath for at least six hours and ideally 24 hours after birth. (Because babies have a hard time regulating their temperatures, baths can easily chill and physically stress them.) - Protects your baby's skin. The waxy white vernix that coats your baby protects and moisturizes their skin and keeps them warm. There's no need to rush to wash it off.
- Cultivates good bacteria. Delayed bathing may help a baby develop their microbiome – their normal bacterial flora – which researchers think may play a part in disease prevention.
Ask what the hospital's usual procedure is for bathing newborns, and request a delay if you prefer that. Baths usually take place in the nursery, where the baby is put under radiant heat for warmth.
Depending on your hospital's policy, you may be able to watch and even participate in your newborn's first bath. Some parents find that the hands-on experience gives them more confidence bathing their baby once they get home, especially if it's their firstborn.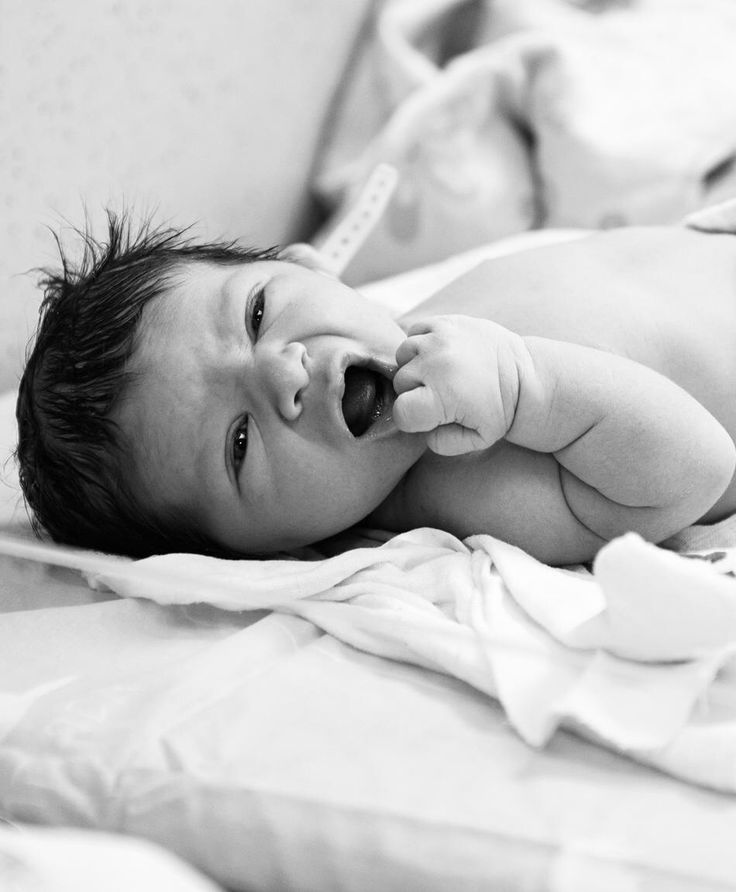
Where does a newborn baby sleep in the hospital?
Where your baby sleeps in the hospital – whether it's in your room or in the nursery – is usually up to you. Different hospitals have different policies, so it's good to ask in advance what your hospital's is. That way, you can be prepared to voice your preference if it's different from what the hospital typically does.
Overall, there's been a shift away from healthy newborns spending time in the nursery. Instead, your baby can stay in a bassinet by your bed. This arrangement is called rooming in. That said, the nursery is a resource for you, so don't feel bad if you use it.
Rooming in has benefits for you and your baby:
- If you're breastfeeding, it's easier to learn your baby's feeding cues and begin to establish a feeding routine from the start. In fact, the World Health Organization recommends rooming in because research shows it supports successful breastfeeding.
- You can practice caring for your newborn and ask questions about what's normal while you have medical experts available to help you.

- Research shows that both moms and babies sleep better.
- Babies tend to cry less, be more content, and have lower stress hormones.
- You have more opportunities to bond and have skin-to-skin contact with your baby.
Moms sometimes have their baby spend time in the nursery because they:
- Feel better knowing they'll be monitored while they sleep
- Had a c-section or other medical complication and need some extra help
- Want to spend some time alone with their other children
- Just need a break
When it comes to rooming in or having your baby spend some time in the nursery, the most important factor is what works best for your family.
When do you go home after a baby is born?
After an uncomplicated vaginal delivery, you're likely to stay in the hospital for 24 to 48 hours. If you have an uncomplicated c-section, you'll probably be in the hospital for two to four days. Find out more about how long you may stay in the hospital after childbirth.
Your baby should have a checkup three to five days after birth, or one to two days after going home. The doctor may ask you to bring your newborn in again about two weeks after that. If your child has any health problems – such as unexpected newborn weight loss or jaundice – you may see the doctor more often in the first few weeks. You'll bring your baby in for well-child doctor visits at 1 month and 2 months of age.
Watch the videos
Three ways to burp your baby
How to hold a crying baby
Baby poop guide: 11 types of baby poop
Baby sleep: Tips for birth to 3 months
advertisement | page continues below
How a newborn baby changes - articles from the specialists of the clinic "Mother and Child"
Babin Evgeny Alexandrovich
Pediatric surgeon, Orthopedic traumatologist, Pediatric orthopedic surgeon
Mother and Child Clinic South-West, Mother and Child Clinic Kuntsevo,
The baby was born, and we expect him to look like beautiful and pink babies from advertising pictures. And he is some kind of red, then suddenly turned yellow, on the skin or a rash, or peeling. In addition, the weight is still unstable, the chair is incomprehensible - is the child healthy? Healthy, and all these changes are the so-called transient (transitional) states. Where do they come from, what do they look like and what to do with it all?
And he is some kind of red, then suddenly turned yellow, on the skin or a rash, or peeling. In addition, the weight is still unstable, the chair is incomprehensible - is the child healthy? Healthy, and all these changes are the so-called transient (transitional) states. Where do they come from, what do they look like and what to do with it all?
The child sat in the mother's stomach for nine months, swam in the water and received oxygen through the placenta. As soon as the baby was born, his world immediately became different: instead of water around him, air, the ambient temperature dropped from 36.6-37 ° C to 22-25 ° C, plus gravity, sounds, smells, bright light. And now you have to breathe (lungs) yourself, eat differently, and then also remove metabolic products. And just like that, it is not easy for a newborn to immediately switch from one lifestyle to another, it takes time. That is why, from the point of view of physiology, in the first month of life, “something happens all the time” with children, and much more often and brighter than in later life. These are the transitory (transitional, boundary) states. All of them surprise and even frighten young parents, especially since transition states appear and disappear very quickly. But for newborns, they are completely natural. What moms and dads see most often are transitional states of skin, stool, weight, plus or minus a couple more conditions.
These are the transitory (transitional, boundary) states. All of them surprise and even frighten young parents, especially since transition states appear and disappear very quickly. But for newborns, they are completely natural. What moms and dads see most often are transitional states of skin, stool, weight, plus or minus a couple more conditions.
How the skin changes
The child was born, and we see that he is all sort of bluish-purple, and then his skin color immediately turns red. On the second day after birth, the baby "blushes" the brightest. Doctors call this redness "erythema simple" and it appears due to the fact that the skin adapts to a new environment. Then the child's skin turns pale and by the end of the first week of life it becomes the pale pink color we are used to.
But that's not all. On the third or fifth day of life, the baby's skin may begin to peel off, especially on the abdomen and chest. What's this? Does the child lack vitamins, something with nutrition, is the air too dry in the house? No, this is also a transitional state - physiological peeling, and it is also associated with the fact that the skin is adapting to a new life..jpg) The skin flakes for about a week, and then everything goes away. You don't need to do anything with it. Of course, you can treat the skin with various softening lotions and creams, but there will be no significant effect from them. Very soon, the baby's skin will become smooth and soft on its own.
The skin flakes for about a week, and then everything goes away. You don't need to do anything with it. Of course, you can treat the skin with various softening lotions and creams, but there will be no significant effect from them. Very soon, the baby's skin will become smooth and soft on its own.
Most of all, parents are afraid of a rash on the baby's skin, which does not often, but sometimes still appears in the first week of life. This is the so-called toxic erythema - spots with grayish-yellow seals in the center. The rash is most often located on the extensor surfaces of the arms and legs around the joints, on the chest. Less often, such spots can be on the whole body (except for the palms, feet and mucous membranes). “Maybe it’s chickenpox, rubella, or some other disease?” parents are afraid. No, this is a kind of reaction of the skin of a newly born baby to its environment, especially to hypothermia, overheating, contact with clothes, food. Within one to three days, new spots may appear, but more often two or three days after the onset, they all disappear without a trace.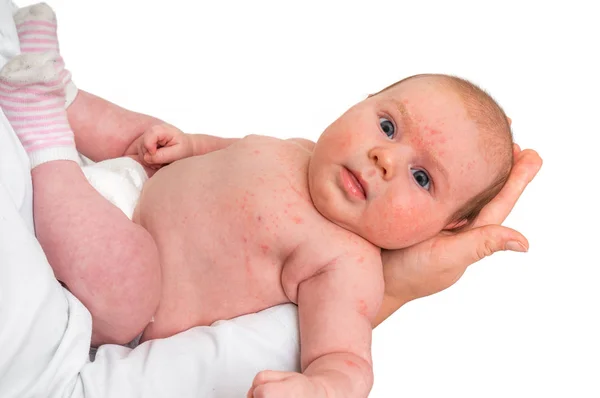 At the same time, the child’s well-being is not disturbed, the body temperature is normal and he does not need any medication. The only thing is that you need to take care of the bubbles on the skin: for example, gently blot them after bathing. And you also need to make sure that the bubbles do not rub and they do not burst (otherwise an infection may join them).
At the same time, the child’s well-being is not disturbed, the body temperature is normal and he does not need any medication. The only thing is that you need to take care of the bubbles on the skin: for example, gently blot them after bathing. And you also need to make sure that the bubbles do not rub and they do not burst (otherwise an infection may join them).
Physiological jaundice
The changes that are visible on the skin do not end there. Very often (in 60-70% of children) on the second or third day of life, the skin turns yellow, the maximum of yellowness occurs on the third or fourth day, and by the end of the first week it disappears. This is how physiological jaundice of a newborn is manifested - a condition in which the amount of bile pigment, bilirubin, increases in a child. In some children, jaundice is similar to a light tan (parents may not notice it), while in others, the skin will turn bright yellow. Very quickly, the level of bilirubin returns to normal and the skin color becomes normal again. If jaundice is mild and passes quickly, then no additional treatment is needed. But if jaundice does not disappear or the skin color is intense yellow, you should consult a doctor.
If jaundice is mild and passes quickly, then no additional treatment is needed. But if jaundice does not disappear or the skin color is intense yellow, you should consult a doctor.
Weight loss
Do you think the baby will immediately be born well-fed, with folds and cute roundness? No, right after birth, this is still far away. In the first days of life, an already not too well-fed newborn will lose even more weight. Such weight loss is a natural process, the so-called physiological weight loss. Weight decreases because immediately after birth, the baby loses part of the water through the skin, its umbilical cord dries out, meconium (the first feces) and urine are excreted, and also because the baby still eats a small amount of milk. Maximum weight loss usually occurs by the third or fifth day and is normally no more than 6-8% of birth weight. At this time, mother and baby are usually discharged from the hospital, but there is no need to worry. By the seventh or tenth day of life, a healthy baby will restore its previous parameters.
chair changes
On the first or second day, all newborns pass the original stool (meconium): it is thick, viscous and dark green in color. Time passes, the baby begins to receive colostrum, and on the third or fourth day of life, a transitional stool appears. Now areas of dark green color alternate with greenish and yellow ones, and some lumps, mucus are also visible in the stool. It all looks like some kind of intestinal disorder, but it's not. It's just that the gastrointestinal tract is moving to a new job, now it's ready to digest food. By the end of the first week of life, the stool in most children is yellow, similar to gruel, and it will continue to be so.
Warm-cold
A typical fear of all grandmothers is that the child is freezing! Yes, indeed, in newborns, the body temperature regulation processes are still imperfect, so babies easily cool down, but they also overheat just as easily. For example, if a newborn is dressed too warmly or placed next to a heating battery, he will quickly overheat, even if this is the usual temperature in the room.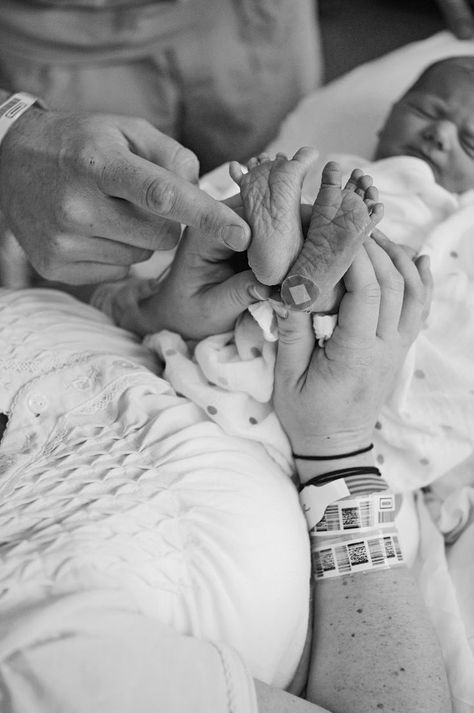 At the same time, the child easily loses heat when he is undressed for a long time or he lies in wet clothes. Therefore, in the room where there is a newborn, the air temperature should be adequate - 20-22 ° C. And if she rises higher, and the child is warmly dressed, then this will also not be good.
At the same time, the child easily loses heat when he is undressed for a long time or he lies in wet clothes. Therefore, in the room where there is a newborn, the air temperature should be adequate - 20-22 ° C. And if she rises higher, and the child is warmly dressed, then this will also not be good.
Sometimes, very rarely (in 1% of newborns), body temperature on the third or fifth day may temporarily rise to 38–39 °C. There are no other symptoms of the disease, the body temperature quickly returns to normal, but the parents have time to get scared. It’s difficult to figure out what it is - temporary hyperthermia or still a disease - it’s difficult, so it’s better to call a doctor.
Hormonal crisis
An uncommon occurrence, but it also occurs occasionally. In some children, on the third or fourth day of life, the mammary glands become engorged (in both girls and boys). They increase as much as possible by the seventh or eighth day, and liquid discharge may even appear from them.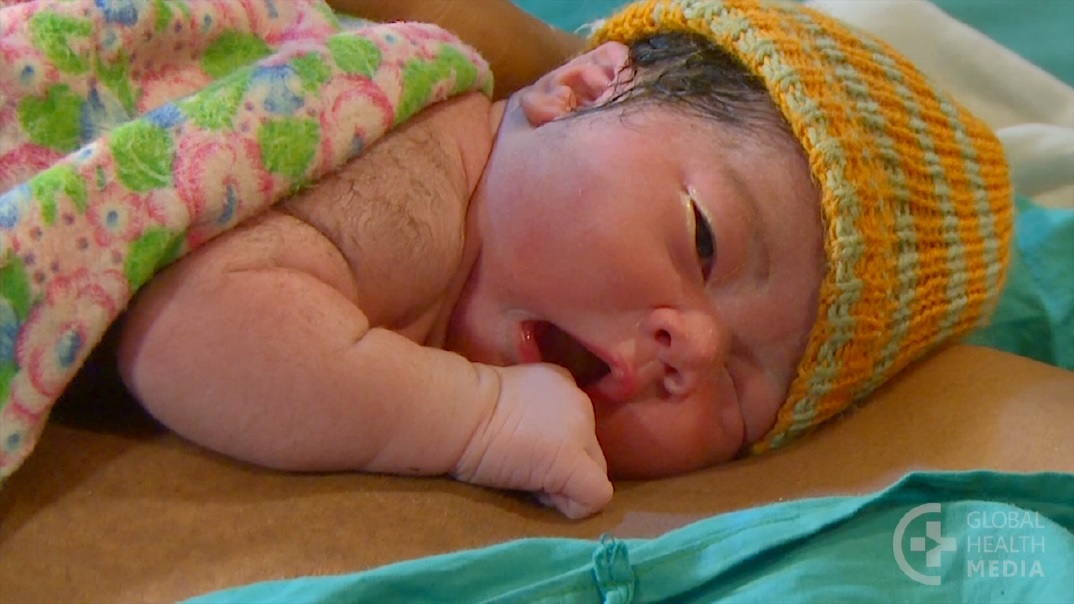 Some girls have very little bloody discharge from the vagina for a very short time. This is the so-called hormonal crisis - it occurs due to the action of maternal hormones - estrogens (they penetrate through the placenta during childbirth). At the peak of estrogen action, the signs of a hormonal crisis are maximum, then the hormones are removed from the body and the symptoms gradually disappear. Therefore, you don’t need to apply a cabbage leaf to your chest, make compresses with camphor or something else: everything will pass by itself.
Some girls have very little bloody discharge from the vagina for a very short time. This is the so-called hormonal crisis - it occurs due to the action of maternal hormones - estrogens (they penetrate through the placenta during childbirth). At the peak of estrogen action, the signs of a hormonal crisis are maximum, then the hormones are removed from the body and the symptoms gradually disappear. Therefore, you don’t need to apply a cabbage leaf to your chest, make compresses with camphor or something else: everything will pass by itself.
Usually, all these transitional states are pronounced in the first week of life, less often, but it happens that they drag on for up to three to four weeks. One more thing - it is not necessary that the child will show all transitional states, but almost everyone has physiological weight loss and transitional stools. And many of the transitional states are completely invisible to parents, but they also exist, they can simply be identified only by laboratory methods.
So we are not in a hurry to be frightened, noticing that the child’s skin suddenly began to peel off or he turned slightly yellow. We remember that he must adapt to a new life, that in the first time after birth, the baby has the right to some changes. Especially if, with all this, the baby is cheerful, calm and eats well. Well, if you are still somehow anxious, ask your pediatrician questions. He will definitely be able to put everything in its place.
Inset
The maximum weight loss in a newborn usually occurs by the third or fifth day and normally amounts to no more than 6-8% of body weight at birth.
From the point of view of physiology, in the first month of life, “something happens all the time” with children, and much more often and brighter than in later life. These are the transitory (transitional, boundary) states.
In infants, the body temperature regulation processes are still imperfect, so they easily become overcooled and overheated. In this regard, in the room where there is a newborn, the air temperature should be about - 20–22 ° C.
In this regard, in the room where there is a newborn, the air temperature should be about - 20–22 ° C.
Physiological jaundice of the newborn:
- occurs on the 2-3rd day of the baby's life, reaches a maximum on the 4-5th day, and disappears by the 10th day;
- the general condition of the child does not suffer;
- the level of bilirubin in the blood does not exceed 180 µmol/l.
Make an appointment
to the doctor - Babin Evgeny Alexandrovich
Clinic "Mother and Child" KuntsevoClinic "Mother and Child" South-West
Pediatric surgeryChildren Medical examinationSupervision of children at homeObservation of children with special needs
By clicking on the send button, I consent to the processing of personal data
Attention! Prices for services in different clinics may vary. To clarify the current cost, select a clinic
Clinical Hospital MD GROUPClinical Hospital Lapino-1 "Mother and Child"Children's Clinic KG "Lapino" on New Riga (branch)Clinic "Mother and Child" KuntsevoClinic "Mother and Child" SavelovskayaClinic "Mother and Child" South-WestClinic "Mother and Child" » Novogireevo
All directions
01.
Kinesiotherapy for children
02.
Specialist consultations (adults)
03.
Specialist consultations (children)
04.
Massage/manipulation for children
05.
Therapeutic research
Nothing found
The administration of the clinic takes all measures to timely update the price list posted on the website, however, in order to avoid possible misunderstandings, we advise you to clarify the cost of services and the timing of the tests by calling
Newborn
Newborn
Behind 9 months of joyful and a little anxious expectation, behind the exciting and always dramatic moment of childbirth, and finally, your meeting took place. You and your baby. You have a whole life ahead of you filled with happiness and love. For you, a young (or experienced) mother, behind the huge stress associated with childbirth, and looking at your child, do you guess that he experienced no less?
During childbirth, the fetus experiences an increasing load and hypoxia (oxygen starvation), passage through the mother's birth canal is associated with enormous pressure on soft tissues and bone skeleton for such a crumb. All these overloads are provided by wise nature by no means by chance. The fact is that after birth, the child's living conditions change radically, and in order to cope with the new requirements provided by life, the child needs birth stress. He needs to adapt to a much lower ambient temperature, to the manifestations of the laws of gravity (which he has not yet encountered), he has to cope with an incredible variety of all kinds of visual, auditory, vestibular and many other stimuli! Moreover, now the child needs to master fundamentally new types of breathing, blood circulation and nutrition, which are fundamentally different from those that he has successfully used for nine months. And what does it take to deal with the microbial environment?! In a word, for him all the most difficult is ahead. The first year of life is difficult, of which the first month is the most difficult, and in it the first seven days are always the most difficult. Early neonatal period. Here he is, a child who survived the period of exile (the so-called period of childbirth, when the actual birth of a child takes place).
All these overloads are provided by wise nature by no means by chance. The fact is that after birth, the child's living conditions change radically, and in order to cope with the new requirements provided by life, the child needs birth stress. He needs to adapt to a much lower ambient temperature, to the manifestations of the laws of gravity (which he has not yet encountered), he has to cope with an incredible variety of all kinds of visual, auditory, vestibular and many other stimuli! Moreover, now the child needs to master fundamentally new types of breathing, blood circulation and nutrition, which are fundamentally different from those that he has successfully used for nine months. And what does it take to deal with the microbial environment?! In a word, for him all the most difficult is ahead. The first year of life is difficult, of which the first month is the most difficult, and in it the first seven days are always the most difficult. Early neonatal period. Here he is, a child who survived the period of exile (the so-called period of childbirth, when the actual birth of a child takes place).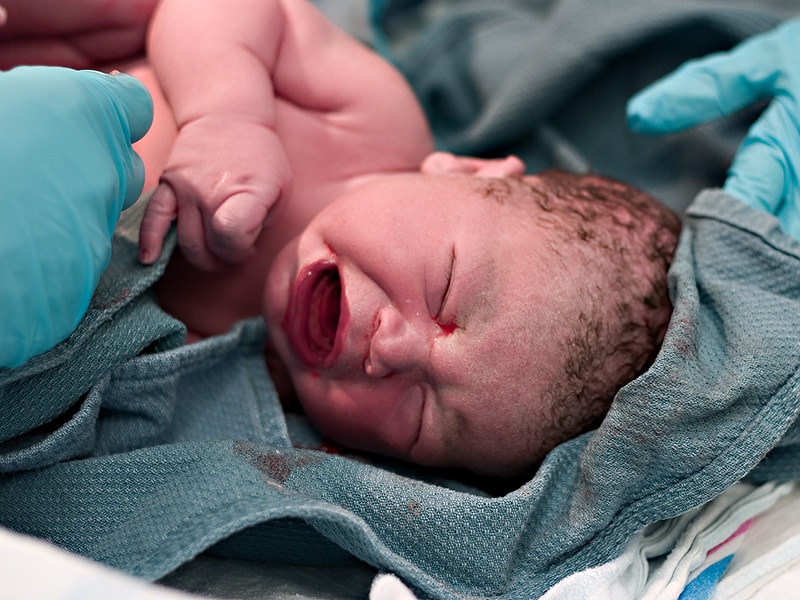 What does he feel at this moment? Is he aware of what is happening to him now Scientists - neurophysiologists cite data indicating the presence of some neuropsychic activity in the fetus as early as 32 - 34 weeks of intrauterine development. This speaks in favor of the fact that the child is able to realize the processes that occur to him at the time of birth. He experiences feelings that, with a certain degree of certainty, can be called fear. And if at the time of childbirth, in addition to quite natural stress, the child feels negativism from the mother (due to pain, fatigue), then this can serve as a basis for the development of childhood neuroses in the future, which are so hard to fight! When the incredibly stressful period of exile is over, and the mother, feeling relieved, relaxes, the umbilical cord is cut for the child. This moment is the starting point for the start of extrauterine respiration and blood circulation.
What does he feel at this moment? Is he aware of what is happening to him now Scientists - neurophysiologists cite data indicating the presence of some neuropsychic activity in the fetus as early as 32 - 34 weeks of intrauterine development. This speaks in favor of the fact that the child is able to realize the processes that occur to him at the time of birth. He experiences feelings that, with a certain degree of certainty, can be called fear. And if at the time of childbirth, in addition to quite natural stress, the child feels negativism from the mother (due to pain, fatigue), then this can serve as a basis for the development of childhood neuroses in the future, which are so hard to fight! When the incredibly stressful period of exile is over, and the mother, feeling relieved, relaxes, the umbilical cord is cut for the child. This moment is the starting point for the start of extrauterine respiration and blood circulation.
The child makes the first deep breath and scream, informing the world about his birth Having experienced severe stress, he can now afford to scream loudly for a long time, which contributes to better expansion of the lungs, expansion of the bronchi, and improvement of blood flow in the vital organs. At this moment, a complex and largely mysterious process of imprinting takes place - imprinting in the memory of the newborn of his environment. What will he remember? Of course, these details of the situation should be the hands of the mother, the smell of her skin, the sounds of her voice.
At this moment, a complex and largely mysterious process of imprinting takes place - imprinting in the memory of the newborn of his environment. What will he remember? Of course, these details of the situation should be the hands of the mother, the smell of her skin, the sounds of her voice.
So, the child breathes, cries, experiences temperature stimuli, his circulatory system is gradually reorganized to a new type of functioning, for the first time he receives nutrition through his mouth, and not through the umbilical cord. A baby, if the pregnancy proceeded without any special complications, is born with a sterile intestine, and its colonization with microorganisms occurs from the first seconds of life. Already when passing through the birth canal of the mother, the child gets acquainted with the microbial world. It is very important that the colonization of the intestines, skin and mucous membranes of the newborn occurs with the microflora of a healthy (well, as far as possible!) mother.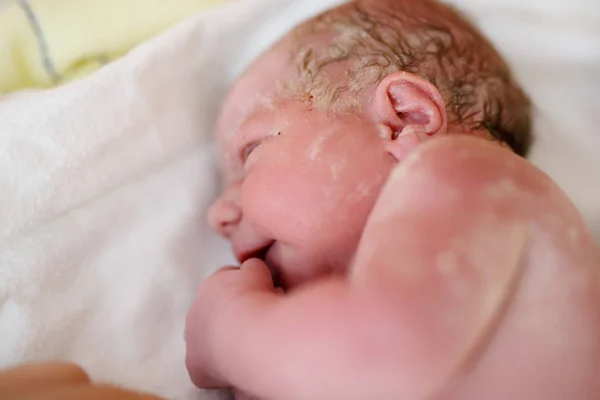 For this, it is also necessary that the baby receives precious drops of maternal colostrum, which, getting into the intestines, carry microbes there that normally inhabit the mother's skin. Not the worst start! But this is only the beginning + In general, talking about the functioning of the intestines of a newborn deserves special attention!
For this, it is also necessary that the baby receives precious drops of maternal colostrum, which, getting into the intestines, carry microbes there that normally inhabit the mother's skin. Not the worst start! But this is only the beginning + In general, talking about the functioning of the intestines of a newborn deserves special attention!
In the meantime, the newborn is passing primordial feces - meconium - a thick, viscous mass of dark green color (an extremely sticky substance!). This continues for three days. In the future, the stool changes its color and consistency, becomes more watery and frequent (up to 7-8 times a day). During this period, the child usually experiences the first troubles with digestion, which will haunt him for at least the first three to four months of life. His digestive tract learns to assimilate food, digest it, move it along the intestines. This process does not always go smoothly, there are breakdowns in the form of regurgitation, watery, rapid stools, and sometimes, on the contrary, constipation. These conditions belong to the category of borderline (that is, located on the border between health and disease, but they are transient and, with a favorable course of the early neonatal period, end happily. Due to the named digestive difficulties that a newborn baby has to face, by the third or fourth days of life, he loses up to 6% of the original body weight.
These conditions belong to the category of borderline (that is, located on the border between health and disease, but they are transient and, with a favorable course of the early neonatal period, end happily. Due to the named digestive difficulties that a newborn baby has to face, by the third or fourth days of life, he loses up to 6% of the original body weight.
Normally, with sufficient nutrition and the absence of diseases, the initial body weight should be restored by the 10th day of life. An important stage of adaptation to the conditions of extrauterine existence is the restructuring of the circulatory system. After tying the umbilical cord, the placental circulation ceases to function, which provided the fetus with blood enriched with oxygen and nutrients from the mother.
With the first breath and cry, the lungs expand and the pulmonary circulation is activated, which takes over the provision of blood circulation through the pulmonary vessels. Within a few minutes, the ductus arteriosus closes, and after two to three days, the foramen ovale located in the interatrial septum also closes. But in some cases, these intrauterine ( fetal) ducts continue to function for several days. On the third - fourth day of life, there is another moment of the adaptation period: a sexual crisis. It manifests itself by engorgement of the mammary glands, profuse mucous discharge from the vagina in girls, and even meager bloody discharge on the fifth to eighth day of life. The reason for the sexual crisis is that in the last weeks of intrauterine life, the fetus received quite a lot of estrogens (sex hormones responsible for the growth of the uterus and mammary glands) from the mother, whose body, in preparation for childbirth, increases their production the more, the closer the moment themselves childbirth. By the same time, 60-70% of newborns have transistorized (transient) jaundice due to an increase in the level of bilirubin in the blood. Moreover, the level of bilirubin in the blood rises in all newborns without exception.
But in some cases, these intrauterine ( fetal) ducts continue to function for several days. On the third - fourth day of life, there is another moment of the adaptation period: a sexual crisis. It manifests itself by engorgement of the mammary glands, profuse mucous discharge from the vagina in girls, and even meager bloody discharge on the fifth to eighth day of life. The reason for the sexual crisis is that in the last weeks of intrauterine life, the fetus received quite a lot of estrogens (sex hormones responsible for the growth of the uterus and mammary glands) from the mother, whose body, in preparation for childbirth, increases their production the more, the closer the moment themselves childbirth. By the same time, 60-70% of newborns have transistorized (transient) jaundice due to an increase in the level of bilirubin in the blood. Moreover, the level of bilirubin in the blood rises in all newborns without exception.
Jaundice (do not confuse with an infectious disease!) develops for several reasons, including due to the low functional ability of the liver, characteristic of this age, and also due to the breakdown of fetal erythrocytes (they are replaced by erythrocytes with "adult" hemoglobin ). Jaundice is very frightening for young mothers, and I want to emphasize that, like all transistor states, it is not a disease, but only a neonatologist observing a child can understand this.
Jaundice is very frightening for young mothers, and I want to emphasize that, like all transistor states, it is not a disease, but only a neonatologist observing a child can understand this.
The last thing I would like to tell you about here is the state of immunity of the newborn.
The immune system of the fetus begins to develop in early pregnancy. However, by the time of birth, she is still far from maturity. In addition, birth stress, getting from a sterile mother's womb into a world inhabited by microorganisms, weight loss in the first days of life, and the cessation of antibodies from the mother after umbilical cord ligation contribute to the development of an immunodeficiency state in a newborn. Even if the child is healthy, during this period he is extremely at risk of infection. The troubles associated with this can be avoided by early breastfeeding (colostrum contains a large number of immune bodies), as well as by a healthy microbial environment, which can be ensured by being in the same room with the child.