Want surrogate mother
Apply to Become a Surrogate
Will I Be Matched to a Couple or Intended Parent In My state? Will I Have to Relocate?
Most likely, your intended parent(s) might live somewhere else in the U.S. or even abroad! We help lots of international intended parents. That said, many intended parents love to visit for you and your family for a few OB appointments if they can, and of course, they come to your state to support you with delivery. You would not need to re-locate states during the journey if you live in a surrogacy-friendly state, although there is some travel involved to your intended parents’ IVF clinic. During the surrogate pregnancy, you would see your local OBGYN and have cycling monitoring appointments for the cycling injections, which prepare your body for the embryo transfer. We match you carefully based on legal concerns for surrogacy statutes state-by-state, personality, pregnancy preferences, and more.
Does a Surrogate Mother Use Her Own Eggs for a Surrogacy Journey?
No, not in the case of “gestational surrogacy. ” In gestational surrogacy, a gestational surrogate never uses her own eggs. In a gestational surrogacy journey, a surrogate or her partner are never biologically related to the baby or babies. The exception is if they are doing a “traditional surrogacy” journey, which we are not involved in at all. Also, because a gestational surrogate is not the mother or parent to the baby (the intended mother or intended father is!), we refrain from using the term “surrogate mother” to be in sync with current standards.
How Long Does It Take for a Surrogate to Be Matched With Intended Parents?
It can range from 2 weeks to several months. Our match process depends on your matching preferences for intended parents, how quickly we get forms back from you, and how quickly we can help obtain your pregnancy and delivery medical records. We also do a thorough virtual in-home interview to meet you and your family, which is one of our last pieces of the puzzle before introducing you to your potential intended parents!
Do I Need to See My OBGYN to Be Approved to Be a Surrogate?
Possibly. You can wait until after applying with us to see your OB/GYN if needed. When we request your pregnancy medical records on your behalf, we also request an OBGYN form for your OB to fill out to approve you to be a surrogate. If you have not seen your OBGYN in a while, they may want you to come in for an appointment before they will agree to fill out the surrogate form. Also, depending on when you had your last pap smear, you might need to complete an updated pap smear result from your doctor. Again, that would be after you apply!
You can wait until after applying with us to see your OB/GYN if needed. When we request your pregnancy medical records on your behalf, we also request an OBGYN form for your OB to fill out to approve you to be a surrogate. If you have not seen your OBGYN in a while, they may want you to come in for an appointment before they will agree to fill out the surrogate form. Also, depending on when you had your last pap smear, you might need to complete an updated pap smear result from your doctor. Again, that would be after you apply!
I’m Nervous About Needles for the IVF Injections. Help!
It’s completely normal to feel nervous as a new surrogate. We have lots of tips and tricks for the cycling medications! Some surrogates feel it’s easier to do the shots themselves, while other surrogates always have a partner or friend help them. The IVF clinic will teach you how to do the IVF injections. We also have many previous surrogates who can help you as well! Once you become a CFC surrogate, you will be invited to our CFC Surrogate Support Facebook Group, which is an incredible way to meet other amazing surrogates and get advice about your surrogacy journey.
Are Your Intended Parents In The Room With You for the Embryo Transfer?
Yes, sometimes. Sometimes intended parents are able to fly or drive in for the embryo transfer. By this time in the process, you will have had the chance to connect and develop your relationship with your intended parents or parent. Intended parents will typically stand near their surrogate’s head during the embryo transfer for privacy – It can be a wonderful bonding experience! Other times, intended parents can attend the embryo transfer via Skype or FaceTime. They may be waiting to come visit you later on during the pregnancy for an OBGYN appointment or ultrasound.
Does a Surrogate Have to Deliver In a Hospital?
No. At Creative Family Connections, we understand that surrogates and intended parents have preferences that can align for a wonderful journey! A surrogate with CFC can work with an OBGYN or midwife for their surrogate pregnancy. We require that all CFC surrogates deliver in a birthing center or hospital. If a higher level of care were required, a plan would be in place well in advance through our birth plan. If there is no Level III NICU nearby, exceptions can be made for a Level II NICU for a singleton delivery. We provide a large amount of surrogate support in coordinating with your hospital or birthing center. Around the 20th week of pregnancy, we create a detailed surrogate and intended parent birth plan to outline all the details. Labor & delivery nurses and staff, as well as hospital social workers have said that our birth plan is extremely helpful so that birthing staff knows about the surrogacy journey delivery in advance. We help coordinate all the details so that you and the intended parents can have a beautiful birth experience that is as smooth as possible!
If a higher level of care were required, a plan would be in place well in advance through our birth plan. If there is no Level III NICU nearby, exceptions can be made for a Level II NICU for a singleton delivery. We provide a large amount of surrogate support in coordinating with your hospital or birthing center. Around the 20th week of pregnancy, we create a detailed surrogate and intended parent birth plan to outline all the details. Labor & delivery nurses and staff, as well as hospital social workers have said that our birth plan is extremely helpful so that birthing staff knows about the surrogacy journey delivery in advance. We help coordinate all the details so that you and the intended parents can have a beautiful birth experience that is as smooth as possible!
Are Mental Health Services Covered For Surrogates?
Yes. Our surrogacy contract sets funds aside just for mental health services in the event that they are wanted during the journey! If you have health insurance that will cover part of the costs, the intended parent(s) would pay for the remainder up to a certain amount based on the contract. Some surrogates feel they want counseling and mental health support for the journey and other surrogates don’t. We absolutely want mental health services to be available for surrogates if they would like it! There is also a psychological evaluation for a surrogate and her partner/spouse (if applicable – we love single mom surrogates too!) where you discuss the surrogacy journey in detail. That surrogate psychological evaluation is paid for by the intended parent(s).
Some surrogates feel they want counseling and mental health support for the journey and other surrogates don’t. We absolutely want mental health services to be available for surrogates if they would like it! There is also a psychological evaluation for a surrogate and her partner/spouse (if applicable – we love single mom surrogates too!) where you discuss the surrogacy journey in detail. That surrogate psychological evaluation is paid for by the intended parent(s).
Can a Surrogate Breastfeed the Baby or Babies?
No, but a surrogate can pump breastmilk for intended parents, a local hospital, or Preemies Milk Bank! Per The American Society of Reproductive Medicine guidelines, it is advised that a surrogate not breastfeed the baby due to attachment considerations, however, you can definitely pump breastmilk post-delivery for a surrogacy journey! This is all discussed in detail in your surrogacy contract, but it is also a flexible arrangement. Sometimes intended parents are so appreciative of receiving breastmilk to bottle feed their baby/babies, while others prefer to stick to baby formula. Sometimes surrogates and intended parents arrange to ship breastmilk for several weeks or several months (at no cost to you). International intended parents typically switch to formula once they are back home, but it is possible to ship abroad! If intended parents are interested in receiving breastmilk, there is a $250 per week stipend as a thank you to all the time and dedication it takes to pump regularly. Read about one of our surrogate pumping stories here.
Sometimes surrogates and intended parents arrange to ship breastmilk for several weeks or several months (at no cost to you). International intended parents typically switch to formula once they are back home, but it is possible to ship abroad! If intended parents are interested in receiving breastmilk, there is a $250 per week stipend as a thank you to all the time and dedication it takes to pump regularly. Read about one of our surrogate pumping stories here.
Is Surrogate Compensation Taxable?
We do not send surrogates a W2 or 1099 tax form. While we are experts in all things surrogacy, we are not tax experts, so we advise you to speak with a tax professional or CPA. A surrogate’s base compensation is deposited into monthly pregnancy payments upon heartbeat confirmation via an ultrasound. (At that point, you also receive $250 per month to assist with mileage to doctors’ appointments, prenatal vitamins, etc.)
Have a specific surrogacy question?
Contact us and we’d be happy to help!What It Is and How Does Surrogacy Work
Written by Rebecca Buffum Taylor
Medically Reviewed by Jennifer Robinson, MD on November 04, 2021
In this Article
- What Is a Surrogate Mother?
- Who Uses Surrogates?
- Finding a Surrogate
- How to Choose a Surrogate
- Using a Surrogate
- Legal Issues With Surrogates
There's still some controversy about using a surrogate mother to have a baby. The legal process is also tricky because it varies from state to state. Even so, whether it's because of fertility problems or other reasons, surrogacy is an option for you and your partner. Find out how it works and see if it's right for you.
The legal process is also tricky because it varies from state to state. Even so, whether it's because of fertility problems or other reasons, surrogacy is an option for you and your partner. Find out how it works and see if it's right for you.
What Is a Surrogate Mother?
There are two kinds:
Traditional surrogate. It's a woman who gets artificially inseminated with the father's sperm. They then carry the baby and deliver it for you and your partner to raise.
A traditional surrogate is the baby's biological mother. That's because it was their egg that was fertilized by the father's sperm. Donor sperm can also be used.
Gestational surrogates. A technique called "in vitro fertilization" (IVF) now makes it possible to gather eggs from the mother (or an egg donor), fertilize them with sperm from the father (or a sperm donor), and place the embryo into the uterus of a gestational surrogate.
The surrogate then carries the baby until birth. They don't have any genetic ties to the child because it wasn't their egg that was used.
A gestational surrogate is called the "birth mother." The biological mother, though, is still the woman whose egg was fertilized.
In the U.S., gestational surrogacy is less complex legally. That's because both intended parents have genetic ties to the baby. As a result, gestational surrogacy has become more common than a traditional surrogate. About 750 babies are born each year using gestational surrogacy.
Who Uses Surrogates?
If you're a woman, you may consider a surrogate for several reasons:
- Medical problems with your uterus
- You had a hysterectomy that removed your uterus
- Conditions that make pregnancy impossible or risky for you, such as severe heart disease
You may want to think about surrogacy if you tried but couldn't get pregnant with a variety of assisted-reproduction techniques, such as IVF.
Surrogates have also made parenthood an option for people who might not be able to adopt a child, perhaps because of their age or marital status.
If gay men decide to use a traditional surrogate, one of them uses their sperm to fertilize the surrogate's egg through artificial insemination. The surrogate then carries the baby and gives birth.
A gay couple might also choose an egg donor, fertilize that donated egg, and then have the embryo implanted in a gestational surrogate to carry until birth.
Finding a Surrogate
There are several ways you can find a surrogate mother:
Friends or family. Sometimes you can ask a friend or relative to be a surrogate for you. It's somewhat controversial. But because of the high cost of surrogacy and the complex legal issues it raises about parental rights, a tried-and-tested family relationship can be simpler to manage.
The American Society for Reproductive Medicine accepts certain family ties as acceptable for surrogates. It generally discourages surrogacy, though, if the child would carry the same genes as a child born of incest between close relatives.
A surrogacy agency. Most people use one to arrange a gestational surrogate. There are about 100 agencies now operating in the U.S. They act as go-betweens.
An agency helps you find a surrogate and make arrangements. It also collects any fees that get passed between you and the surrogate, such as paying for their medical expenses.
How to Choose a Surrogate
Right now there aren't any regulations about who can be a surrogate mother. But experts agree on a few points about how to select one.
You should choose surrogates who:
- Are at least 21 years old
- Have already given birth to at least one healthy baby so they understand firsthand the medical risks of pregnancy and childbirth and the emotional issues of bonding with a newborn
- Have passed a psychological screening by a mental health professional to uncover any issues with giving up the baby after birth
- Sign a contract about their role and responsibilities in the pregnancy, such as prenatal care and agreeing to give you the baby after birth
Using a Surrogate
The American Society for Reproductive Medicine says surrogates should get a medical exam to check that they are likely to have a healthy, full-term pregnancy. The organization suggests they get tests that check for infectious diseases such as syphilis, gonorrhea, chlamydia, HIV, cytomegalovirus, and hepatitis B and C.
The organization suggests they get tests that check for infectious diseases such as syphilis, gonorrhea, chlamydia, HIV, cytomegalovirus, and hepatitis B and C.
Surrogates should get tests to make sure they have immunity to measles, rubella (German measles), and chickenpox. Also, you may want to ask that they get a medical procedure to visually "map" the uterus, which can help the doctor check their potential to carry a pregnancy. Surrogate mothers should have their own doctor during pregnancy rather than use yours.
The cost of surrogacy can range from $80,000 to $120,000. A lot of different things go into the price, such as whether the surrogates have their own medical insurance or whether you need to buy a surrogacy-pregnancy policy for them.
Legal Issues With Surrogates
Parental rights aren't guaranteed after a surrogate pregnancy. The law continues to change as reproductive technology and the very definition of a "parent" changes.
There isn't a federal law on surrogacy and state laws vary. After a surrogate pregnancy in some states, you may still have to pass adoption proceedings to gain legal custody of the child. In other states, a "declaration of parentage" before birth lets you avoid having to "adopt" the baby.
After a surrogate pregnancy in some states, you may still have to pass adoption proceedings to gain legal custody of the child. In other states, a "declaration of parentage" before birth lets you avoid having to "adopt" the baby.
To protect your rights as parents-to-be -- and the rights of the child you're hoping to have -- hire an attorney who specializes in reproductive law in your state. They can write a surrogacy contract that clearly spells out what everyone needs to do.
A contract like that may help if legal issues come up after birth. It can also outline agreements about a variety of possible scenarios with the pregnancy, such as what happens if there are twins or triplets.
Infertility & Reproduction Guide
- Overview
- Symptoms
- Diagnosis & Tests
- Treatment & Care
- Support & Resources
Surrogate motherhood: case studies.

Any risk has a degree of probability of occurrence, as well as non-occurrence.
The task of the participants in the process is to take all possible measures to reduce the likelihood of such events occurring.
Registration of documents in the registry office.
At the moment, the current legislation does not contain an exhaustive and clear list of requirements for the content and form of documents required for submission to the registry office.
After giving birth and signing all the necessary documents, the surrogate mother was preparing for discharge, and the genetic parents went to the registry office.
Employees of the district registry office informed about the need to provide a copy of the license of the clinic where IVF was done, as well as a special certificate.
Genetic parents were forced to look for an option to quickly obtain a certified copy of the clinic's license and resolve the issue with the execution of other documents.
The difficulty was that the IVF procedure was carried out in St. Petersburg, and the registry office in which it was supposed to perform registration actions in Moscow.
Registration of documents in the maternity hospital.
There was no lawyer in the maternity hospital who could provide qualified assistance in preparing the necessary documents.
As a result, the chief physician, fearing the possibility of being involved in a lawsuit, initially refused to certify the signature of the surrogate mother, and then demanded that the agreement between the genetic parents and the surrogate mother be provided, as well as other documents, some of which, in the opinion of the chief physician, should have been mandatory notarized.
The chief doctor's demands were outside the legal field and were justified solely by his inner convictions.
With the help of a lawyer, the genetic parents urgently filed a complaint with a higher supervisory authority, whose employees promptly responded to the appeal and explained in an accessible form to the chief doctor the specifics of his performance of his official duties.
Brother and sister were born 24 days apart.
After repeated unsuccessful attempts to treat infertility, it was decided to increase the likelihood of pregnancy by transferring (implanting) embryos to 2 surrogate mothers.
As a result, both surrogate mothers became pregnant, and one of them had a multiple pregnancy, which caused premature birth.
The doctors refused to induce premature labor or perform a caesarean section of the second surrogate mother to synchronize the date of birth of the children, because. there was no medical indication for this.
As a result, the difference in date of birth between two siblings and a sister was 24 days.
The registry office staff explained that they would be happy to help, but the Family Code of the Russian Federation does not provide for the possibility of changing the date of birth in order to preserve family and medical secrets for children born by a surrogate mother, in contrast to similar cases when children are adopted from an orphanage. Understanding that every time parents present birth certificates at work, in kindergarten, school or when traveling abroad, parents will be forced to answer questions that are not pleasant for them, and also fearing for possible psychological trauma for children, it was decided to apply to one from the district courts of Moscow.
Understanding that every time parents present birth certificates at work, in kindergarten, school or when traveling abroad, parents will be forced to answer questions that are not pleasant for them, and also fearing for possible psychological trauma for children, it was decided to apply to one from the district courts of Moscow.
The court satisfied the demands of the parents and ordered the registry office to “synchronize” the dates of birth of the children.
A surrogate mother tried to sell HER child.
Crime reports are replete with reports of parents trying to sell their children, but this story is fundamentally different from the rest - the decision to “sell” the child was made before the onset of pregnancy!
Having entered the global Internet, the woman found an advertisement for a married couple looking for a surrogate mother.
The day before the embryo transfer procedure, the doctor saw on the ultrasound picture that the surrogate mother was already pregnant!
The surrogate mother did not invent fables and immediately told the truth - she was haunted by the thought that pregnancy might not occur as a result of embryo transfer and then she would not be able to earn money, but the idea came right away - guaranteed to get pregnant naturally, and a partner was found fast…
Confirming the full awareness of the committed actions, the “surrogate” mother said: "I understand that in fact I would give birth to my own child, and they (the married couple) would think that genetically this is their child . .. and I would still give it to them."
.. and I would still give it to them."
When asked that, in fact, she wanted to sell her own child, the already former surrogate mother answered with silence.
An attempt by a surrogate mother to return the children 2 years after birth..
2 years after the birth of the twins, the surrogate mother was very “upset” when she learned that the genetic parents were not married.
The surrogate mother formalized her “disorder” in the form of a statement of claim to challenge motherhood.
The fact is that the employees of the registry office, referring to the content of Part 4 of Art. 51 of the Family Code of the Russian Federation consider that a man and a woman must be married until the transfer of the embryo to a surrogate mother.
If a marriage certificate was issued after the embryo transfer or was not issued at all, genetic parents will definitely face serious difficulties in obtaining a birth certificate.
Of course, the very fact of the influence of marital status on the possibility of infertility treatment is a violation of the Constitutional rights of genetic parents who do not want or are not able to register a marriage.
This is confirmed by the content of Art. 35 of the Federal Law "On the protection of the health of citizens".
The court that considered the case denied the surrogate mother her claims and retained parental rights for genetic parents.
Agreement with a surrogate mother.
One of the common causes of disputes and conflict situations between genetic parents and a surrogate mother is an agreement that does not meet special requirements.
In fact, the contract has clear signs of a contract for the provision of services.
At the same time, it must be remembered that the contract should not violate the rights and freedoms of a citizen and, of course, should contain mechanisms for resolving the most common situations in such processes.
Before starting preparations for the transfer of the surrogate mother's embryo, the genetic parents asked for a legal review of the contract drawn up by a lawyer working for a company headed by one of the genetic parents.
The subject of the agreement was the agreement of the parties that the genetic parents pay a fee to the surrogate mother for agreeing to record the genetic parents in the birth certificate as the father and mother of the child born by the surrogate mother. In fact, the genetic parents and the surrogate mother unintentionally signed a "heartfelt confession" to human trafficking.
Another contract, which fell into my hands, obliged the surrogate mother to sign an agreement to register the quote: "the rights of genetic parents to a child born by a surrogate mother."
Thus, the contract infringed on the inalienable right of the surrogate mother to independently decide on the issue of signing documents, and the child was considered as a thing subject to transfer by assignment of the right. Such conditions are not valid, with all the ensuing legal consequences.
Most of the contracts drawn up by lawyers who do not specialize in such matters, as well as contracts posted on the Internet, do not contain a number of essential conditions.
Pins:
Each of these situations occurred solely because of the confidence of genetic parents in the presence of sufficient knowledge and understanding of the features of "Surrogate motherhood".
Therefore, I recommend that genetic parents, be sure to contact a specialist, at least for an oral consultation and drawing up an agreement with a surrogate mother.
You should not hope that the information posted on thematic sites and forums will be reliable, sufficient, and most importantly, applicable in a particular individual situation.
How to find a surrogate mother in Russia
Future parents faced with the need to find a surrogate mother have several options for resolving this situation.
To fully understand the issue, consider each of them.
Search for a surrogate mother
The first thing that comes to mind when the question arises is: “Where can I find a surrogate mother?” This is an opportunity to use the help of friends or relatives.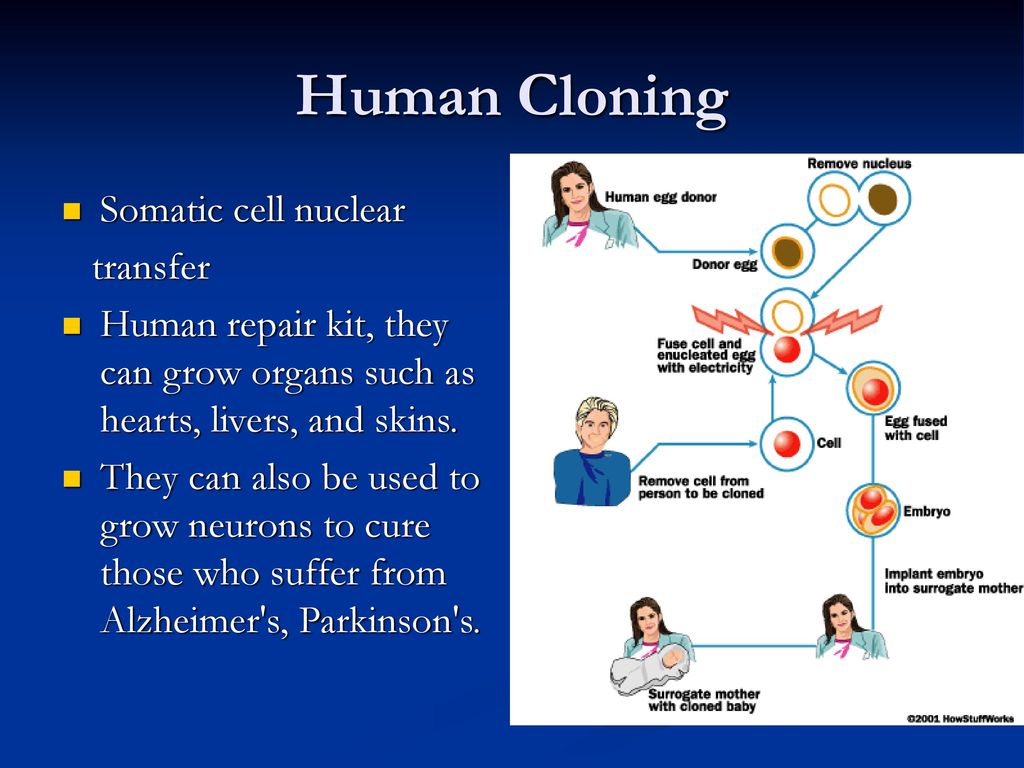 This is ideal, however, not the most common option. The fact is that a woman who is suitable for the candidacy of a surrogate mother must meet a whole list of medical requirements.
This is ideal, however, not the most common option. The fact is that a woman who is suitable for the candidacy of a surrogate mother must meet a whole list of medical requirements.
Requirements for a surrogate mother
A surrogate mother, according to the current instructions of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation, must meet the following requirements: be between the ages of 20 and 35 and have at least one healthy child of her own. The surrogate mother must be completely healthy, physically and mentally, which is confirmed by examination data from specialists.
In the field of reproductive health, a surrogate mother in Lipetsk should not have a history of miscarriages, premature births, caesarean sections, or experience in using an intrauterine device. Compliance with all these requirements will reduce the risks and minimize possible complications during IVF and later during pregnancy.
Another option is to search for a surrogate mother on the Internet. It would seem that it could be easier to enter a search query: “I am looking for a surrogate mother in Russia” or “Surrogate motherhood, announcements”, and a list of names of surrogate mothers, announcements and prices will immediately appear, which will seem to customers more economical than when concluding a contract in surrogacy clinic. Finding a surrogate mother on the Internet is easy and seemingly cheap. However, you should not ignore other costs that you will inevitably encounter. Namely: payment for travel, sometimes the candidate's relocation, her accommodation and a full examination. If the first woman does not fit for health reasons, does not pass an interview with a psychologist, then you will also have to pay similar costs for the second, third, and so on.
It would seem that it could be easier to enter a search query: “I am looking for a surrogate mother in Russia” or “Surrogate motherhood, announcements”, and a list of names of surrogate mothers, announcements and prices will immediately appear, which will seem to customers more economical than when concluding a contract in surrogacy clinic. Finding a surrogate mother on the Internet is easy and seemingly cheap. However, you should not ignore other costs that you will inevitably encounter. Namely: payment for travel, sometimes the candidate's relocation, her accommodation and a full examination. If the first woman does not fit for health reasons, does not pass an interview with a psychologist, then you will also have to pay similar costs for the second, third, and so on.
Next, it will be necessary to draw up and sign a legally competent contract, which will clearly spell out the rights and obligations of the parties, the costs of a lawyer will again fall on future parents. You need to be prepared for the fact that in addition to finding a good IVF clinic and a maternity hospital, you yourself will have to constantly resolve all domestic, legal issues, control the well-being of the surrogate mother and timely intake of drugs prescribed by the attending physician. Here we must not forget that the whole process from start to finish takes about one year.
You need to be prepared for the fact that in addition to finding a good IVF clinic and a maternity hospital, you yourself will have to constantly resolve all domestic, legal issues, control the well-being of the surrogate mother and timely intake of drugs prescribed by the attending physician. Here we must not forget that the whole process from start to finish takes about one year.
Also, during the entire IVF procedure and ongoing pregnancy, it will be necessary to document many current moments, keep all receipts for tests, products, medicines and doctor visits, all this may be needed in case of litigation about the born child. After all, we must not forget that in Russia the genetic parents of a child born and born by a surrogate mother can be entered in his birth certificate as legal parents only with the consent of the surrogate mother. Announcements will not give you a guarantee that in the future she will not refuse to provide such consent, because no one vouches for her services. Not to mention that there is a black list of surrogate mothers and intermediaries who make money on other people's troubles in a fraudulent way.
Not to mention that there is a black list of surrogate mothers and intermediaries who make money on other people's troubles in a fraudulent way.
The best option for surrogacy
Therefore, future parents who are looking for a surrogate mother in Russia, after weighing all the pros and cons, most often turn to IVF agencies and clinics, which, in addition to professionalism, provide guarantees of their services, in including surrogacy services. And in any case, this outweighs the illusory opportunity to save on reducing the cost of a surrogate mother and her unborn child.
The cost of surrogate motherhood
The cost of surrogate motherhood in Lipetsk is determined on a case-by-case basis and is specified in the contract between the surrogate mother and the biological parents. The cost of services includes medical and legal support of the program, the expenses of the surrogate mother during pregnancy and the final compensation.