Visible veins early pregnancy
Changes in Your Body During Pregnancy: First Trimester
Path to well being
How do I know I’m pregnant?
A missed period is often the first sign of pregnancy. You may have some other physical signs as well. These include mild cramping and a little bleeding when the fertilized egg implants itself in your uterus.
If you’ve missed your period and think you may be pregnant, you can take a home pregnancy test. These tests are very accurate if you take them a few days after you expected to get your period. Call your doctor if the test is positive.
Why do I feel so tired?
Feeling very tired is another common symptom of early pregnancy. Your body is working hard to adjust to all the new physical changes. This can cause extreme fatigue. You may need to sleep longer than usual at night. If possible, you can take short naps during the day. Your energy will most likely return in the second trimester of pregnancy.
What is morning sickness?
Morning sickness consists of nausea and vomiting. It is caused by pregnancy hormones. Many pregnant people have it to some degree in their first trimester. Despite what it sounds, morning sickness can occur at any time of day. Certain foods or smells might make you feel sick and sometimes vomit. Some people seem to feel sicker when their stomachs are empty. Morning sickness usually goes away by the second trimester.
There are over-the-counter vitamins and herbal supplements that may help with morning sickness. Taking vitamin B6 may help with nausea, even though it may not prevent vomiting. Ginger supplements also may relieve nausea.
What other changes can I expect during the first trimester?
Frequent urination. Towards the end of the first trimester, you will feel like urinating more often. This is because your growing uterus pushes on your bladder. You may even leak a little urine when you cough or sneeze.
Lightheadedness. Your body is working overtime to make extra blood to support your baby. This can cause you to feel dizzy or lightheaded. Hunger, weakness, or stress can cause these symptoms as well.
This can cause you to feel dizzy or lightheaded. Hunger, weakness, or stress can cause these symptoms as well.
Heartburn. The muscles that break down food become more relaxed during pregnancy. Hormone changes also slow down this process. Food also stays in your stomach longer to give your body more time to absorb nutrients. All these things can cause or worsen heartburn.
Constipation. You should be taking a daily prenatal vitamin that contains iron. The iron in the vitamin can lead to constipation. The slow process of breaking down food also can cause constipation, gas, and bloating. Your doctor may suggest taking fiber supplements or a stool softener to provide relief. Make sure you drink plenty of water (about eight glasses per day). Tell your doctor if you have severe problems. They may switch you to a different prenatal vitamin.
Visible veins. Your body makes extra blood and your heart pumps faster to meet the needs of pregnancy. This can cause the blue veins in your belly, breasts, and legs to become more noticeable. You may develop spider veins on your face, neck, or arms. These are tiny blood vessels that branch out from a central area, like the legs of a spider.
This can cause the blue veins in your belly, breasts, and legs to become more noticeable. You may develop spider veins on your face, neck, or arms. These are tiny blood vessels that branch out from a central area, like the legs of a spider.
Skin changes. You may notice that your skin looks more rosy and shiny. Some people call this a “pregnancy glow.” It is caused by increased blood circulation. Pregnancy hormones can cause extra oil on your skin. It may cause you to have flares of acne.
Breast changes. Most people notice changes in their breasts early in pregnancy. The hormones in your body change to prepare for breastfeeding. As this occurs, your breasts may feel tender and swollen. You might notice small bumps forming in the area around your nipples. Your breasts will continue to grow and change throughout your pregnancy. They may feel even bigger and fuller later on.
Vaginal changes. The lining of your vagina will become thicker and less sensitive. You may notice a thin, white discharge. This is normal during pregnancy. Mild vaginal bleeding (spotting) is also normal and common. However, you should call your doctor if you have vaginal bleeding. If the bleeding is heavy or painful, go to the emergency room.
You may notice a thin, white discharge. This is normal during pregnancy. Mild vaginal bleeding (spotting) is also normal and common. However, you should call your doctor if you have vaginal bleeding. If the bleeding is heavy or painful, go to the emergency room.
A growing belly. Your waistline will begin to expand as your baby and uterus grow larger. Depending on your size before pregnancy, you may not notice this change until the second trimester. It is normal to gain no or little weight in your first trimester.
Emotional symptoms. Your hormones are on overload during pregnancy. You might feel moody, forgetful, or unable to focus. Fatigue and stress can increase these symptoms.
Things to consider
Keep in mind that each pregnancy experience is unique. Even the same person may have different changes in their multiple pregnancies. For each change, your symptoms may be mild or severe. Do not worry if the changes do not happen at a certain time. Talk to your doctor if you have any concerns.
Talk to your doctor if you have any concerns.
When to see your doctor
Contact your doctor if you think or know you are pregnant. They will make an appointment to confirm your pregnancy and talk to you about prenatal care.
You should also contact your doctor if your morning sickness and vomiting are severe enough to cause weight loss.
Questions to ask your doctor
- Am I pregnant?
- How far along am I in my pregnancy?
- What kinds of physical and emotional changes should I expect?
- Are my symptoms normal?
- Are there any risks that I should be aware of?
- Which prenatal vitamin do you recommend I take?
Resources
American Academy of Family Physicians: Taking Care of You and Your Baby While You’re Pregnant
6 Pregnancy Symptoms You Can’t Miss
Have you been experiencing changes to your body, mood and sleep pattern? Have you been wondering whether it could be the early signs of pregnancy? Some women experience early signs, whilst some don’t have any indication at all.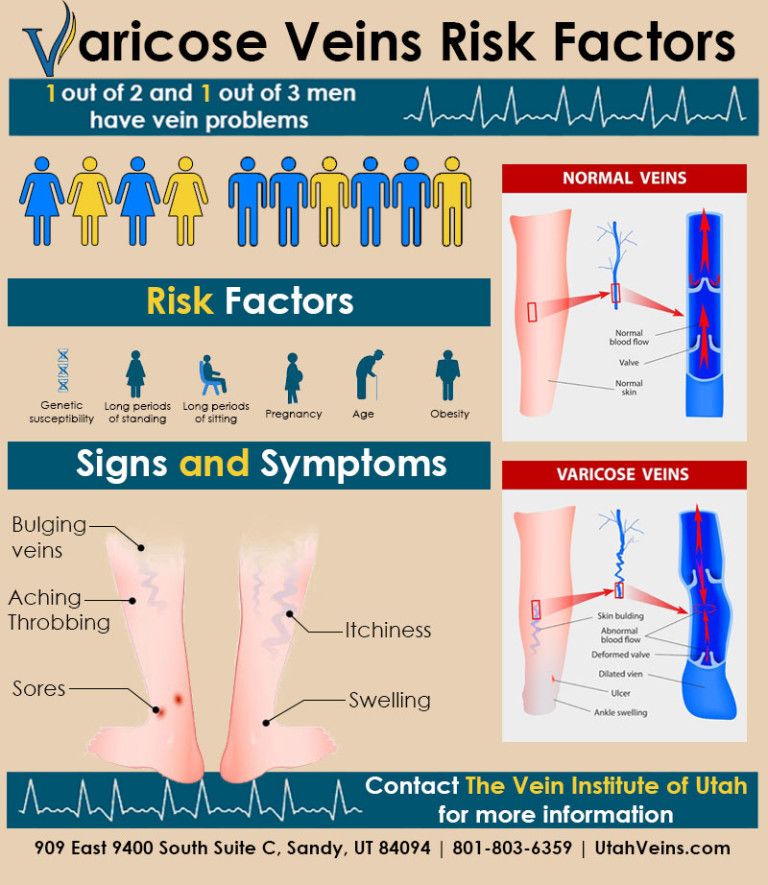 Remember that every woman is different, and no two journeys should be compared.
Remember that every woman is different, and no two journeys should be compared.
The only definite way of knowing if you’re pregnant is to take a pregnancy test, however it’s still good to be in the know. We’ve put together a reference list of what to look out for if you’re unsure:
1) Spotting and crampingEarly on, symptoms of menstruation and early signs of pregnancy are easily confused as they can be similar. If you have conceived, you may experience implantation bleeding, which is when the fertilised egg attaches itself to the uterus wall, which can cause cramps and spotting. Women often see this as their period starting, just in a more mild form. Cramping in the feet and legs is also considered an early sign of pregnancy. It occurs as a result of how your body is processing calcium.
The thickening of the vaginal walls can also lead to a milky discharge being excreted, which if odorless, is typically harmless and can be left to clear up on it’s own. However, if not odorless, pay a visit to your doctor.
However, if not odorless, pay a visit to your doctor.
Sudden changes in your mood can be one of the early signs of pregnancy. It could mean you are in the first trimester, causing your hormones to go haywire. Unexplainable crying, feelings of stress, and heightened emotions in general can all be early pregnancy symptoms. The rapid changes your body is undergoing will leave your hormone levels rocketing up and down, leaving you feeling not yourself. Although, as with all generalised symptoms, this may not be a display of pregnancy symptoms at all, and may be a sign of something else changing within your body.
Whether you are trying, or already are pregnant, conceiveplease™ Pre-conception and Pregnancy vitamins have been formulated to support pre-conception health and provide micronutrients important for the increasing needs of pregnancy. This may help your body to feel balanced in the face of early pregnancy symptoms.
3) Dizziness and faintingSome pregnancy symptoms can feel pretty unpleasant, or even scary, so it’s a good idea to read about them so you’re not caught off guard. Dizziness and fainting is one of the early signs of pregnancy, but can occur the whole way throughout too.
Dizziness and fainting is one of the early signs of pregnancy, but can occur the whole way throughout too.
The main cause of dizziness is due to the rising hormones causing your blood vessels to relax and widen. This is to increase blood flow to your baby, but it means blood returns more slowly to you. This causes your blood pressure to be lower than usual, which reduces the blood flow to your brain, resulting in temporary dizziness.
It can also be caused by low blood sugar levels that may occur due to changes in your metabolism. Women who are anemic or who have varicose veins may be more susceptible than others. During the second trimester, dizziness may be caused because your growing uterus puts pressure on blood vessels. Later, in the third trimester, it can be caused if you lie on your back, allowing the weight of the baby to press on your vena cava (a large vein that carries blood from your lower body to your heart). Maintaining a healthy diet, and ensuring your vitamin intake is sufficient via prenatal vitamins such as conceiveplease™ Pre-conception and Pregnancy vitamins may decrease these symptoms hugely.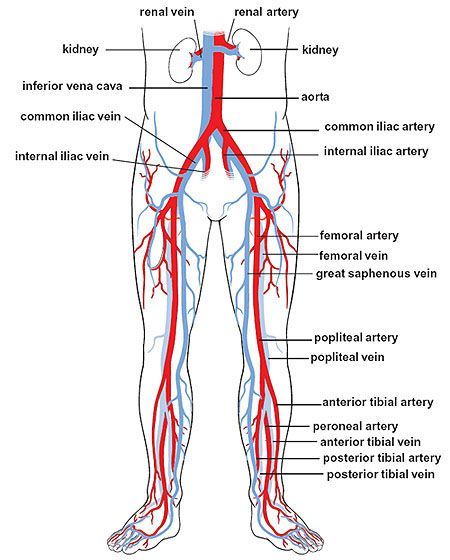
One of the most common pregnancy symptoms is a change in the look and feel of your breasts. They may grow larger, and feel tender or highly sensitive. The veins on your breasts may become more noticeable and your areola (nipples) may darken. These changes can start to occur as early as the first week after conception, although they can start as late as 12 weeks. Women with darker hair and darker complexions tend to notice more colour change than fairer skinned women.
Some women report to having sore and tingly breasts as an early pregnancy symptom in the first one or two weeks. Some even say their nipples become too sensitive to touch. The nipples may become more prominent and feel quite sensitive or even sore. Some pregnant women choose to start wearing a comfortable, supportive bra such as a sports bra without underwires to support their changing breasts.
Seeing prominent blue veins is amongst the more common pregnancy symptoms, with around 50% of women reporting it. Blood flow increases by about 20-40% during pregnancy as our veins are transporting blood, nutrients, and oxygen to your developing fetus. The increased blood volume makes the veins more visible under the skin.
Blood flow increases by about 20-40% during pregnancy as our veins are transporting blood, nutrients, and oxygen to your developing fetus. The increased blood volume makes the veins more visible under the skin.
Breast discomfort often subsides after a few weeks, although it may return in the later stages of pregnancy. If you have been experiencing any of these changes, whilst it is not definitively an early sign of pregnancy, it is extremely common in first trimester. If in doubt, the conceiveplease™ One Step HCG Urine Pregnancy Test is a quick, affordable, and sensitive test that helps you accurately determine if you are pregnant in the privacy of your own home.
5) InsomniaExperiencing sleep problems whilst pregnant is totally normal. Infact, insomnia is so common in the first trimester it’s considered something to look out for as one of the early signs of pregnancy. Between more frequent trips to the bathroom, huge changes in hormone levels, and pregnancy side-effects such as congestion and heartburn, you might be spending more time awake than asleep throughout the night. The good news: whilst insomnia isn’t fun, it won’t hurt your baby.
The good news: whilst insomnia isn’t fun, it won’t hurt your baby.
Physical and logistical causes aside, another big cause is stress. All the early signs of pregnancy can compound and cause anxiety about everything from the pregnancy, labour and generally becoming a parent! Being open about your feelings, developing a bedtime routine, exercising and staying comfortable are all things that can help you overcome those sleepless nights.
6) Increased body temperatureDid you know that feeling overheated for 2 weeks or more when you wake up in the morning may be an early sign of pregnancy. Following ovulation, your body temperature can be higher than normal. If it doesn’t regulate over the next couple of weeks, this can be considered an early pregnancy symptom.
You can use a basal body thermometer to track your first morning temperature, and you might notice that it rises around 1 degree when you conceive and stays elevated throughout your pregnancy. Though not definitely one of the early pregnancy symptoms (there are other reasons your temperature can rise), it could help you preempt your baby!
If you experienced any of these symptoms, only to receive an unwanted negative test result, don’t be disheartened. The conceiveplease™ Fertility Kit contains everything you need to aid you in your journey of natural conception. If you are confused about when an optimum time to have sex with your partner is, and would like to optimise your chances of conceiving naturally, the conceiveplease™ One Step Ovulation & Pregnancy Planning Kit is aimed at optimising natural conception, whilst our prenatal vitamins will keep both you and your partner healthy during the conception process.
The conceiveplease™ Fertility Kit contains everything you need to aid you in your journey of natural conception. If you are confused about when an optimum time to have sex with your partner is, and would like to optimise your chances of conceiving naturally, the conceiveplease™ One Step Ovulation & Pregnancy Planning Kit is aimed at optimising natural conception, whilst our prenatal vitamins will keep both you and your partner healthy during the conception process.
Varicose veins during pregnancy - what to do and how to treat varicose veins in the legs
Varicose veins are persistent and irreversible enlargement resulting from pathological changes in the walls and valves of blood vessels. The superficial veins in the legs most often expand, since they have increased pressure when standing and walking. Varicose veins during pregnancy is one of the diseases that can appear or progress during the period of gestation. Because of this, women get sick 4 times more often than men.
Causes
The following reasons contribute to the occurrence of varicose veins during pregnancy:
- Violation of the outflow of blood from the veins of the lower extremities. This is because the growing uterus presses on the inferior vena cava - a large abdominal vein that collects blood from the lower half of the trunk and lower extremities.
- During pregnancy, the blood is more viscous, flows more slowly, this also contributes to venous congestion.
- The increase in body weight during gestation increases the load on the legs.
The development of varicose veins is promoted by wearing high-heeled shoes, prolonged work in a standing position, lifting weights, and overweight.
Symptoms
The first symptom is a visible increase in the vessels of the lower extremities. The veins are blue or purple, tortuous, protrude above the surface of the skin, may be serpentine or knobby (nodular) in shape. At the initial stage of the disease, a woman is only concerned about a cosmetic defect.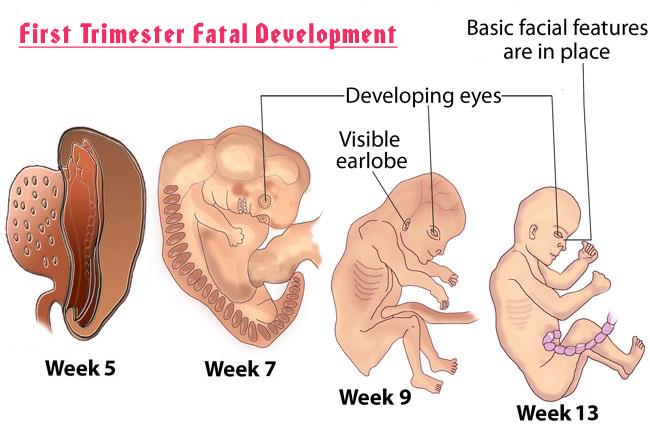
Other complaints follow. Edema appears, increasing in the evening and decreasing or completely disappearing after rest and a night's sleep. At night, convulsions may disturb. When walking, rapid fatigue is observed, there may be a feeling of fullness and pain.
Varicose veins of the lower extremities are observed in 50% of pregnant women, but not all of them suffer from true varicose veins, when irreversible changes appear in the venous wall. For most, the disease is functional in nature, that is, it is temporary, and after childbirth, when the factors that prevent normal venous outflow are eliminated, the tubes return to normal. This usually happens within a year.
Regression does not occur if the predisposition is independent of pregnancy. In this case, close relatives usually have varicose veins, or the woman herself had some symptoms even before conception.
Diagnostics
As you know, the “gold standard” for diagnosing pathology is ultrasound duplex scanning (USDS) of the veins of the lower extremities. This is a safe procedure for the expectant mother. Experienced obstetricians and gynecologists strongly recommend that pregnant women visit a phlebologist in the early stages of pregnancy, which contributes to the early prevention of complications of varicose veins in the postpartum period.
This is a safe procedure for the expectant mother. Experienced obstetricians and gynecologists strongly recommend that pregnant women visit a phlebologist in the early stages of pregnancy, which contributes to the early prevention of complications of varicose veins in the postpartum period.
Stockings for varicose veins during pregnancy
During pregnancy, it is recommended to wear special compression (anti-varicose) tights and stockings. They need to be put on in a prone position, slightly lifting the leg up. There are 4 compression classes (pressure levels):
- 18-21 mmHg
- 23-32 mmHg
- 33-48 mmHg
- over 49 mmHg
During pregnancy, it is recommended to use compression class 1-2. The third class of compression hosiery is used for the late stage of leg varicose veins, the fourth class - only for severe congenital anomalies of the venous system.
Tights should be specially designed for expectant mothers so that they do not put pressure on the growing belly, but support it.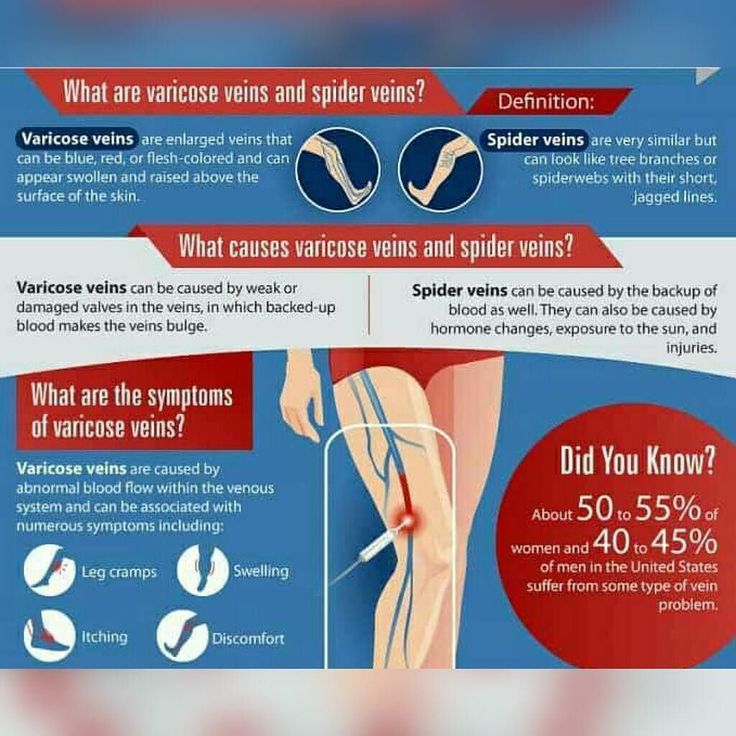
How much to wear?
After 20 weeks, you need to wear a bandage. It supports the uterus and reduces pressure on the large vessels of the abdominal cavity, thereby improving the outflow of blood from the lower half of the body.
Compression underwear and a bandage should be bought in pharmacies, it is important to choose the right size for them.
Exercise
It is recommended to attend gymnastics for pregnant women or do exercises at home. Particularly good prevention of varicose veins are classes in the pool. Sports strengthen the walls of blood vessels and improve blood flow. In addition, gymnastics is the prevention of overweight.
A contrast shower on the calf muscles is useful.
If you think you have a predisposition to varicose veins, you should avoid saunas and thermal treatments.
As often as possible, try to give your legs an elevated position. Don't sit cross-legged for long periods of time.
Wear comfortable shoes with small heels.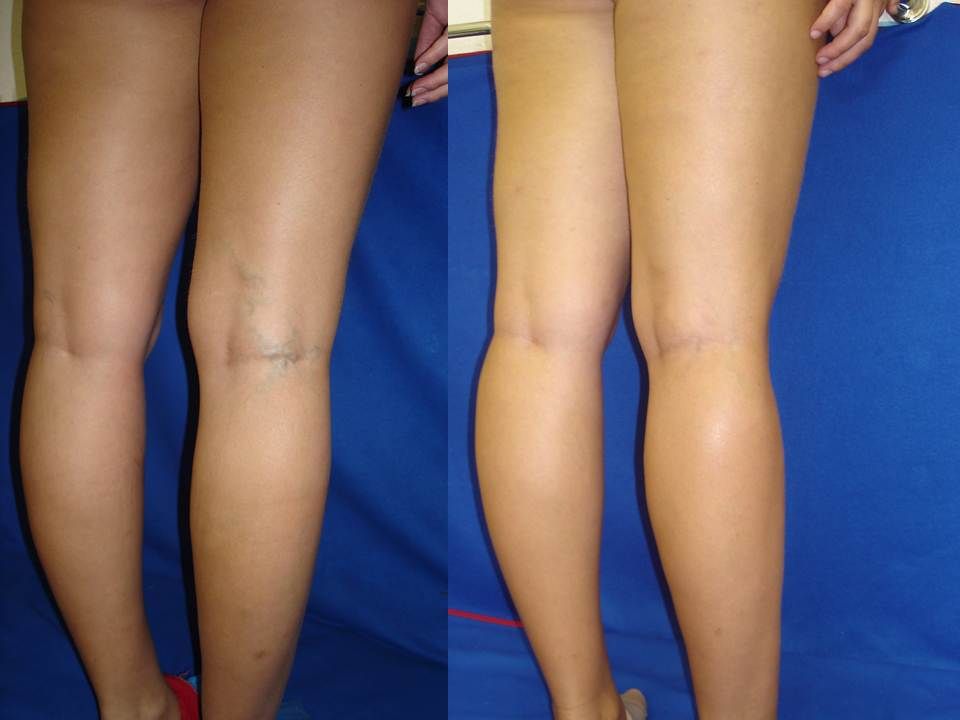
You can use creams for pregnant women "to relieve fatigue from the legs", such creams usually contain plant substances that, with regular use, strengthen the walls of superficial veins.
Treatment
Treatment of true varicose veins is surgical. During pregnancy, surgical treatment is carried out only for emergency indications, in view of the development of complications (thrombophlebitis).
A modern method of treatment is sclerotherapy, when a chemical substance is injected into the lumen of the vein, which leads to sclerosis and closure of its lumen. Endovasal methods are also minimally invasive treatments performed on an outpatient basis (described in the relevant sections of our website). They may be an alternative to surgical treatment. However, during pregnancy and lactation are also contraindicated.
All other methods are aimed only at preventing the disease from developing and temporarily reducing symptoms.
Most often, various ointments and gels are used, which are applied to the affected limb. For example, heparin-containing ointments reduce blood clotting and prevent the formation of blood clots. Venotonics (allowed only from the second trimester of pregnancy) have a decongestant and anti-inflammatory effect and strengthen the walls of blood vessels.
For example, heparin-containing ointments reduce blood clotting and prevent the formation of blood clots. Venotonics (allowed only from the second trimester of pregnancy) have a decongestant and anti-inflammatory effect and strengthen the walls of blood vessels.
The diagnostic equipment used in our center has been tested in ROSTEST and has an appropriate conclusion about the absence of contraindications for use in pregnant women and children.
In the medical center "Yuzhny" they are very kind to expectant mothers and experienced phlebologists are well versed in the methods of diagnosing CVI and the secrets of preserving your beautiful legs after childbirth.
Varicose veins during pregnancy - what to do and how to treat
Veins are actively involved in the complex 9-month pregnancy process, and their changes are significant. Even with complete medical supervision, there is a risk of developing venous insufficiency.
Pregnancy is accompanied by profound changes throughout the female body. One of the first effects of pregnancy is an increase in the load on the veins of the pelvis and lower extremities. Therefore, many pregnant women develop varicose veins, which sometimes disappear after childbirth. This varicose vein is accompanied by discomfort, a feeling of heaviness, pain when walking, but women are mainly concerned with noticeable skin changes and varicose coloration of the legs and ankles, which remain after pregnancy.
One of the first effects of pregnancy is an increase in the load on the veins of the pelvis and lower extremities. Therefore, many pregnant women develop varicose veins, which sometimes disappear after childbirth. This varicose vein is accompanied by discomfort, a feeling of heaviness, pain when walking, but women are mainly concerned with noticeable skin changes and varicose coloration of the legs and ankles, which remain after pregnancy.
From sickness to sickness
Many pregnant women are familiar with the feeling of malaise, accompanied by discomfort in the lower extremities. Functional chronic venous insufficiency is the first stage of venous disease with a feeling of heaviness in the lower extremities, sometimes with itching, paresthesias and, in some cases, convulsions, often nocturnal.
The possibility of thrombosis in pregnant women is 3-5 times higher than in other women. Sometimes blockage of the veins leads to their inflammation - thrombophlebitis.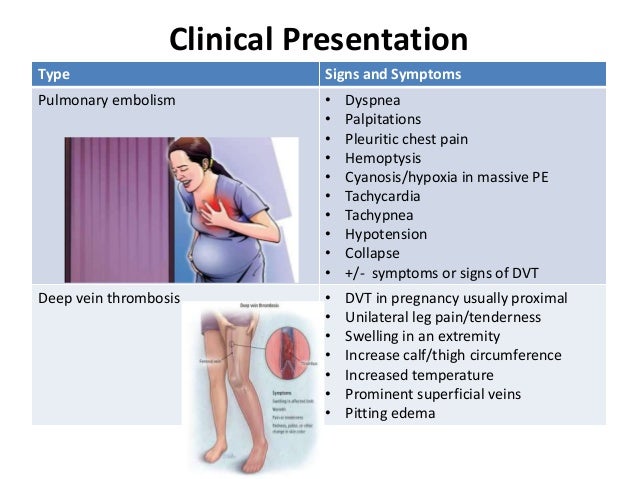 Blood clots that form in this case in the veins can cause a serious and dangerous disease - pulmonary embolism. In addition, the risk of developing thrombosis remains for another 1.5 months after childbirth, especially if they are severe.
Blood clots that form in this case in the veins can cause a serious and dangerous disease - pulmonary embolism. In addition, the risk of developing thrombosis remains for another 1.5 months after childbirth, especially if they are severe.
Should I go to the doctor?
There are five groups of factors that affect the body of a pregnant woman, which explain the need for observation by a phlebologist.
Mechanical factor
An enlarged uterus is a barrier to blood circulation, as it compresses the inferior vena cava, pressing it against the spinal column and iliac muscle. This is of particular importance at rest, when a sharp decrease in venous outflow can lead to postural shock, well known to gynecologists. The anatomical structure of the iliac vein, which crosses the right iliac artery, explains the high incidence of thrombosis of the left limb (Cocket's syndrome).
Circulatory factor
An increase in blood volume and outflow of blood from the heart leads to an increase in the load on the vessels, especially veins, and their expansion. This is especially important for the veins of the lower extremities and the vaginal area.
This is especially important for the veins of the lower extremities and the vaginal area.
Hormonal factors
Progesterone, due to its relaxing effect on smooth muscle fibers, leads not only to a decrease in the tone of the venous wall, but also to a decrease in the tone of the urethra, bladder and small intestine.
Hemostatic factors
Changes in the hemostasis system always occur in the direction of increased coagulability (increased fibrinogen and factor III levels, increased platelet activity and decreased fibrinolytic activity).
Hemorheological factors
Blood viscosity increases despite a decrease in hematocrit.
Other contributing factors
In addition to the above factors associated with pregnancy, there are other contributing factors such as family history, sedentary lifestyle, immobile posture while working, driving, too low or high thin heels, obesity, underfloor heating, hot baths, and multiple pregnancies with short intervals between them.