Teeth in toddlers how many
Teeth development in children - Better Health Channel
The development of primary teeth begins while the baby is in the womb. At about 5 weeks' gestation, the first buds of primary teeth appear in the baby's jaws. At birth, the baby has a full set of 20 primary teeth (10 in the upper jaw, 10 in the lower jaw) hidden under the gums. Primary teeth are also known as baby teeth, milk teeth or deciduous teeth.
Types of teeth
The names of the different types of teeth are:
- Incisors – the front teeth located in the upper and lower jaws. Each incisor has a thin cutting edge. The upper and lower incisors come together like a pair of scissors to cut the food.
- Canines – the pointy teeth on both sides of the incisors in the upper and lower jaws; used to tear food.
- Premolars – which have flat surfaces to crush food.
- Molars – these are larger than premolars towards the back of the mouth, with broad, flat surfaces that grind food.
Teething
'Eruption' refers to the tooth breaking through the gum line. In babies, tooth eruption is also called teething. The timing of tooth eruption differs from child to child. For example, one child may cut their first tooth when only a few months old, while another may not start teething until they are 12 months old or more.
The exact timing may be different from child to child but the order of tooth development is more consistent.
Generally, the average child has their full set of 20 primary teeth by the age of 3 years.
Managing the teething process
Babies’ immune systems start to change when they are around 6 months old. Along with the tendency to put things in their mouths, this makes them more prone to illnesses. Symptoms of common childhood illnesses such as changes in sleep and eating patterns, fussiness, rash, drooling, runny nose and diarrhoea are often linked to teething when that might not be the cause. If your child has these symptoms, speak to your child’s doctor about other possible causes such as bacterial, viral or middle ear infections.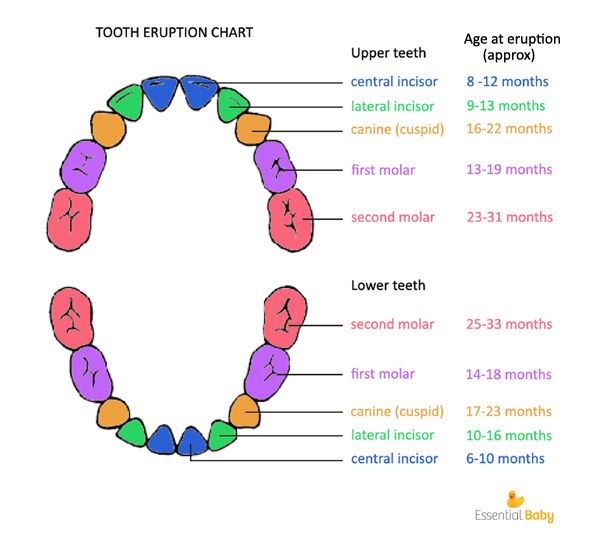
Teething takes about 8 days, which includes 4 days before and 3 days after the tooth comes through the gum. (You may see a blue-grey bubble on the gum where the tooth is about to appear. This is called an eruption cyst and will usually go away without treatment.) During this time, it can be tough to keep children comfortable.
Some tips include:
- Massage – gently massage the gum with clean fingers or a soft, wet cloth.
- Chilled (not frozen) teething rings or rusks – pressure from a cold object can relieve discomfort from teething. Do not sterilise plastic teething rings in boiling water or dishwater, unless specified by the manufacturer. Be sure to check product information before buying teething rings. Avoid the ones that use a plastic softener called 'diisononyl phthalate'.
- Unsweetened teething rusks or sugar-free teething biscuits – these can be given to infants over 6 months who have started eating solids.
- Pain-relieving medications – paracetamol works well for children.
 Ibuprofen may also help, but it is not as well tolerated by children.
Ibuprofen may also help, but it is not as well tolerated by children. - Dry the drool – the skin around the mouth, particularly the chin area, can become irritated. Gently wipe this away with a soft cloth throughout the day.
Some treatments should be used with caution or not at all. These include:
- Teething necklaces – amber is believed by some people to release healing oil on contact with warm skin. The oil is thought to be soothing or help to reduce pain. Although amber teething strings or necklaces are designed to be worn around the neck, wrist or ankle, they have been incorrectly used to chew on. The ACCC has issued a product safety statement about amber teething necklaces, warning of possible choking and strangulation hazards. Parents are asked to consider other less risky ways of providing relief from teething.
- Teething gels – common teething gels contain 8.7–9.0% of the ingredient choline salicylate. Salicylate is related to aspirin. The use of aspirin for children younger than 16 is not recommended because in some children it has been known to cause Reye's syndrome – a rare but potentially lethal condition that can cause liver and brain damage.
 Although there has not been a reported case of Reye's syndrome associated with the use of teething gels, the general advice is that it is a risk not worth taking when there are other things available.
Although there has not been a reported case of Reye's syndrome associated with the use of teething gels, the general advice is that it is a risk not worth taking when there are other things available.
Teething gels containing benzocaine are also not recommended for use in children. Research also suggests that teething gels may not relieve teething pain, rather the act of massaging it into the gum is what helps.
Caring for baby teeth
Some parents may feel that caring for baby (primary) teeth isn't as important as caring for adult (permanent) teeth, simply because baby teeth fall out.
However, baby teeth are very important. They allow children to chew food and speak properly, and they reserve the spaces in the gums for future adult teeth.
Tooth decay in baby teeth
Tooth decay is preventable. The risk of developing dental decay can be significantly reduced by good oral hygiene habits and a healthy diet from a young age.
Decayed baby teeth need to be treated by a dental practitioner. In some cases, specialist treatment in a hospital under a general anaesthetic is needed. If neglected, decayed baby teeth can lead to mouth pain, dental abscesses (a boil or swelling resulting from infected teeth), and problems with the surrounding teeth. Severe decay in baby teeth can affect eating and sleep, which can slow growth.
In some cases, specialist treatment in a hospital under a general anaesthetic is needed. If neglected, decayed baby teeth can lead to mouth pain, dental abscesses (a boil or swelling resulting from infected teeth), and problems with the surrounding teeth. Severe decay in baby teeth can affect eating and sleep, which can slow growth.
If a baby molar is lost too early due to severe decay, adjacent baby teeth may drift into the gap and create spacing problems for the adult tooth when it comes through.
Watch this Australian Dental Association video about caring for children’s oral health.
Loss of baby teeth
From the age of about 6 years, baby teeth start to become 'wobbly' and fall out to make way for adult teeth. It is perfectly normal for a child to lose their first tooth up to a year or 2 earlier or later than 6 years of age. Girls generally lose teeth earlier than boys. The first tooth to fall out is usually located in the front of the lower jaw.
Losing baby teeth can be unsettling and painful for young children. Suggestions for parents include:
Suggestions for parents include:
- Reassure your child that losing baby teeth is a natural process and new adult teeth will come in their place. It's normal for gums to be tender and bleed a little, although some children experience little or no discomfort while losing their teeth.
- Use cold packs or over-the-counter anti-inflammatory or pain-relieving medication to help relieve loose tooth pain. Ask your dentist or pharmacist for recommendations on appropriate medication for your child.
- Make use of the Tooth Fairy. This myth has lasted a long time with good reason! The idea of getting some money or another reward in exchange for a tooth might soften the idea of tooth loss for your child.
Permanent teeth
Permanent teeth are also known as adult teeth or secondary teeth. The permanent teeth start to develop in the jaws at birth and continue after a child is born. By about 21 years, the average person has 32 permanent teeth, including 16 in the upper jaw and 16 in the lower jaw. (In some cases, the third molars – commonly called wisdom teeth – do not develop or do not erupt so some people only have a set of 28 permanent teeth.)
(In some cases, the third molars – commonly called wisdom teeth – do not develop or do not erupt so some people only have a set of 28 permanent teeth.)
At about the age of 6 years, the first permanent molar teeth erupt. These 4 molars (2 in each jaw) come out behind the child's baby teeth. Other permanent teeth, such as the incisors, canines, and premolars, erupt into the gaps in the gum left by baby teeth that are lost.
As with baby teeth, the timing for when the permanent teeth come through can differ. Generally, the order of and rough timeline for each type of permanent tooth is:
- First molars – between 6 and 7 years.
- Central incisors – between 6 and 8 years.
- Lateral incisors – between 7 and 8 years.
- Canine teeth – between 9 and 13 years.
- Premolars – between 9 and 13 years.
- Second molars – between 11 and 13 years.
- Third molars (wisdom teeth) – between the ages of 17 and 21 years, if at all.
Mouthguards protect children's teeth
Mouthguards help protect teeth and prevent dental injuries, particularly when playing and training for contact sports. All children playing contact sports should wear a custom-fitted mouthguard, even primary school-age children. Custom-fitted mouthguards are comfortable, allow speech and do not restrict breathing. Learn more about mouthguards.
All children playing contact sports should wear a custom-fitted mouthguard, even primary school-age children. Custom-fitted mouthguards are comfortable, allow speech and do not restrict breathing. Learn more about mouthguards.
Where to get help
- Your dentist
- Australian Dental Association ‘Find a Dentist’ or Tel. (03) 8825 4600
- Dental Health Services Victoria Tel. (03) 9341 1000 or 1800 833 039 outside Melbourne metro - provides public dental services through the Royal Dental Hospital of Melbourne and community dental clinics, for eligible people.
- Maternal and Child Health Line (24 hours) Tel. 13 22 29
- NURSE-ON-CALL (24 hours, 7 days) Tel. 1300 60 60 24 – for expert health information and advice
- Royal Children's Hospital (Dentistry) Tel. (03) 9345 5344
Teeth development in children - Better Health Channel
The development of primary teeth begins while the baby is in the womb. At about 5 weeks' gestation, the first buds of primary teeth appear in the baby's jaws. At birth, the baby has a full set of 20 primary teeth (10 in the upper jaw, 10 in the lower jaw) hidden under the gums. Primary teeth are also known as baby teeth, milk teeth or deciduous teeth.
At birth, the baby has a full set of 20 primary teeth (10 in the upper jaw, 10 in the lower jaw) hidden under the gums. Primary teeth are also known as baby teeth, milk teeth or deciduous teeth.
Types of teeth
The names of the different types of teeth are:
- Incisors – the front teeth located in the upper and lower jaws. Each incisor has a thin cutting edge. The upper and lower incisors come together like a pair of scissors to cut the food.
- Canines – the pointy teeth on both sides of the incisors in the upper and lower jaws; used to tear food.
- Premolars – which have flat surfaces to crush food.
- Molars – these are larger than premolars towards the back of the mouth, with broad, flat surfaces that grind food.
Teething
'Eruption' refers to the tooth breaking through the gum line. In babies, tooth eruption is also called teething. The timing of tooth eruption differs from child to child. For example, one child may cut their first tooth when only a few months old, while another may not start teething until they are 12 months old or more.
The exact timing may be different from child to child but the order of tooth development is more consistent.
Generally, the average child has their full set of 20 primary teeth by the age of 3 years.
Managing the teething process
Babies’ immune systems start to change when they are around 6 months old. Along with the tendency to put things in their mouths, this makes them more prone to illnesses. Symptoms of common childhood illnesses such as changes in sleep and eating patterns, fussiness, rash, drooling, runny nose and diarrhoea are often linked to teething when that might not be the cause. If your child has these symptoms, speak to your child’s doctor about other possible causes such as bacterial, viral or middle ear infections.
Teething takes about 8 days, which includes 4 days before and 3 days after the tooth comes through the gum. (You may see a blue-grey bubble on the gum where the tooth is about to appear. This is called an eruption cyst and will usually go away without treatment. ) During this time, it can be tough to keep children comfortable.
) During this time, it can be tough to keep children comfortable.
Some tips include:
- Massage – gently massage the gum with clean fingers or a soft, wet cloth.
- Chilled (not frozen) teething rings or rusks – pressure from a cold object can relieve discomfort from teething. Do not sterilise plastic teething rings in boiling water or dishwater, unless specified by the manufacturer. Be sure to check product information before buying teething rings. Avoid the ones that use a plastic softener called 'diisononyl phthalate'.
- Unsweetened teething rusks or sugar-free teething biscuits – these can be given to infants over 6 months who have started eating solids.
- Pain-relieving medications – paracetamol works well for children. Ibuprofen may also help, but it is not as well tolerated by children.
- Dry the drool – the skin around the mouth, particularly the chin area, can become irritated. Gently wipe this away with a soft cloth throughout the day.
Some treatments should be used with caution or not at all. These include:
These include:
- Teething necklaces – amber is believed by some people to release healing oil on contact with warm skin. The oil is thought to be soothing or help to reduce pain. Although amber teething strings or necklaces are designed to be worn around the neck, wrist or ankle, they have been incorrectly used to chew on. The ACCC has issued a product safety statement about amber teething necklaces, warning of possible choking and strangulation hazards. Parents are asked to consider other less risky ways of providing relief from teething.
- Teething gels – common teething gels contain 8.7–9.0% of the ingredient choline salicylate. Salicylate is related to aspirin. The use of aspirin for children younger than 16 is not recommended because in some children it has been known to cause Reye's syndrome – a rare but potentially lethal condition that can cause liver and brain damage. Although there has not been a reported case of Reye's syndrome associated with the use of teething gels, the general advice is that it is a risk not worth taking when there are other things available.

Teething gels containing benzocaine are also not recommended for use in children. Research also suggests that teething gels may not relieve teething pain, rather the act of massaging it into the gum is what helps.
Caring for baby teeth
Some parents may feel that caring for baby (primary) teeth isn't as important as caring for adult (permanent) teeth, simply because baby teeth fall out.
However, baby teeth are very important. They allow children to chew food and speak properly, and they reserve the spaces in the gums for future adult teeth.
Tooth decay in baby teeth
Tooth decay is preventable. The risk of developing dental decay can be significantly reduced by good oral hygiene habits and a healthy diet from a young age.
Decayed baby teeth need to be treated by a dental practitioner. In some cases, specialist treatment in a hospital under a general anaesthetic is needed. If neglected, decayed baby teeth can lead to mouth pain, dental abscesses (a boil or swelling resulting from infected teeth), and problems with the surrounding teeth. Severe decay in baby teeth can affect eating and sleep, which can slow growth.
Severe decay in baby teeth can affect eating and sleep, which can slow growth.
If a baby molar is lost too early due to severe decay, adjacent baby teeth may drift into the gap and create spacing problems for the adult tooth when it comes through.
Watch this Australian Dental Association video about caring for children’s oral health.
Loss of baby teeth
From the age of about 6 years, baby teeth start to become 'wobbly' and fall out to make way for adult teeth. It is perfectly normal for a child to lose their first tooth up to a year or 2 earlier or later than 6 years of age. Girls generally lose teeth earlier than boys. The first tooth to fall out is usually located in the front of the lower jaw.
Losing baby teeth can be unsettling and painful for young children. Suggestions for parents include:
- Reassure your child that losing baby teeth is a natural process and new adult teeth will come in their place. It's normal for gums to be tender and bleed a little, although some children experience little or no discomfort while losing their teeth.
- Use cold packs or over-the-counter anti-inflammatory or pain-relieving medication to help relieve loose tooth pain. Ask your dentist or pharmacist for recommendations on appropriate medication for your child.
- Make use of the Tooth Fairy. This myth has lasted a long time with good reason! The idea of getting some money or another reward in exchange for a tooth might soften the idea of tooth loss for your child.
Permanent teeth
Permanent teeth are also known as adult teeth or secondary teeth. The permanent teeth start to develop in the jaws at birth and continue after a child is born. By about 21 years, the average person has 32 permanent teeth, including 16 in the upper jaw and 16 in the lower jaw. (In some cases, the third molars – commonly called wisdom teeth – do not develop or do not erupt so some people only have a set of 28 permanent teeth.)
At about the age of 6 years, the first permanent molar teeth erupt. These 4 molars (2 in each jaw) come out behind the child's baby teeth.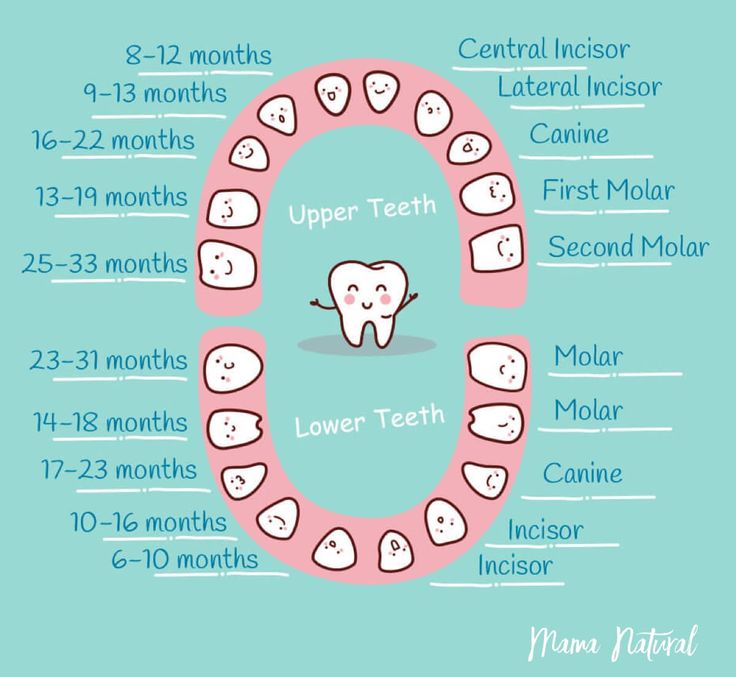 Other permanent teeth, such as the incisors, canines, and premolars, erupt into the gaps in the gum left by baby teeth that are lost.
Other permanent teeth, such as the incisors, canines, and premolars, erupt into the gaps in the gum left by baby teeth that are lost.
As with baby teeth, the timing for when the permanent teeth come through can differ. Generally, the order of and rough timeline for each type of permanent tooth is:
- First molars – between 6 and 7 years.
- Central incisors – between 6 and 8 years.
- Lateral incisors – between 7 and 8 years.
- Canine teeth – between 9 and 13 years.
- Premolars – between 9 and 13 years.
- Second molars – between 11 and 13 years.
- Third molars (wisdom teeth) – between the ages of 17 and 21 years, if at all.
Mouthguards protect children's teeth
Mouthguards help protect teeth and prevent dental injuries, particularly when playing and training for contact sports. All children playing contact sports should wear a custom-fitted mouthguard, even primary school-age children. Custom-fitted mouthguards are comfortable, allow speech and do not restrict breathing. Learn more about mouthguards.
Learn more about mouthguards.
Where to get help
- Your dentist
- Australian Dental Association ‘Find a Dentist’ or Tel. (03) 8825 4600
- Dental Health Services Victoria Tel. (03) 9341 1000 or 1800 833 039 outside Melbourne metro - provides public dental services through the Royal Dental Hospital of Melbourne and community dental clinics, for eligible people.
- Maternal and Child Health Line (24 hours) Tel. 13 22 29
- NURSE-ON-CALL (24 hours, 7 days) Tel. 1300 60 60 24 – for expert health information and advice
- Royal Children's Hospital (Dentistry) Tel. (03) 9345 5344
First teeth - articles from the specialists of the clinic "Mother and Child"
Bogorad Maria Vladimirovna
Ophthalmologist, Ophthalmologist for children
Clinic "Mother and Child" Kuntsevo, Clinical Hospital Lapino-1
When to expect
The milk teeth of the future baby are laid at the 7-8th week of intrauterine development, and the permanent ones - at the end of the 4th month of pregnancy. In total, 20 milk teeth are laid in a child, while permanent ones - 32. To provide the crumbs with a Hollywood smile, the expectant mother needs to eat right throughout all nine months of pregnancy. There are no calcium preparations that would be 100% absorbed, so it is very important to draw “natural” calcium from food, especially cottage cheese. And, of course, the most pregnant woman needs to cure all her teeth - now there are very sparing technologies for this.
In total, 20 milk teeth are laid in a child, while permanent ones - 32. To provide the crumbs with a Hollywood smile, the expectant mother needs to eat right throughout all nine months of pregnancy. There are no calcium preparations that would be 100% absorbed, so it is very important to draw “natural” calcium from food, especially cottage cheese. And, of course, the most pregnant woman needs to cure all her teeth - now there are very sparing technologies for this.
The eruption of the first milk teeth in most cases begins at the 3-8th month of a baby's life and ends closer to three years. But it also happens that children are born already with one or two teeth, or teeth can erupt in the first weeks of life. Often the timing of teething depends on genetic characteristics, but much more - on other factors. They affect the teeth and diseases of the crumbs (for example, with rickets, frequent SARS and dyspepsia, teeth erupt later). It is worth paying attention to the nature of nutrition, the quality of drinking water, even the climate! In northern residents, teeth erupt on average a little later than in southerners. Sometimes teething is delayed, and the first tooth appears closer to the year. Usually there is nothing wrong with this. It is believed that not so much the timing as the order of teething speaks about the health of the child. If it is broken, pay attention to this fact and show the baby to a pediatric dentist.
Sometimes teething is delayed, and the first tooth appears closer to the year. Usually there is nothing wrong with this. It is believed that not so much the timing as the order of teething speaks about the health of the child. If it is broken, pay attention to this fact and show the baby to a pediatric dentist.
The process has begun
Profuse salivation indicates that the teething process has begun. In addition, the baby begins to pull into his mouth everything that only comes to his hand. This means that the gums itch, causing him discomfort. Trying to relieve itching, the baby instinctively acts correctly - micro-massage of the gums improves microcirculation in them, teeth erupt easier and faster. During this period, provide the child with teethers: hypoallergenic silicone toys filled with water. The teether should not be cooled in the freezer - only in the refrigerator: otherwise the crumb will get hurt on a hard surface. If the gums are very swollen, and the baby is crying in pain, use special dental gels that have a mild local anesthetic effect.
For most children, the process of teething goes fairly smoothly. There may be short periods of anxiety, violations of the regime of the day and nutrition. Sometimes even teething is accompanied by diarrhea, runny nose, cough and fever. And during the period of the appearance of teeth, the baby is vulnerable to all kinds of infections. The immunity of the crumbs decreases these days, and it is easier to “pick up” the virus, so it’s not worth writing off the worsening of the condition only on the teeth. If a child has a fever when a tooth is cut, it is necessary to look for another inflammatory focus in the body.
At 6 months old the baby usually boasts central lower incisors. This is an excuse to start brushing your teeth. Why so early? Milk teeth are small and sharp, have an uneven wavy edge, are close to each other and, as a rule, have a yellowish tint. These teeth have a low degree of mineralization. Their enamel and dentin are very thin. All this contributes to the rapid emergence and spread of caries.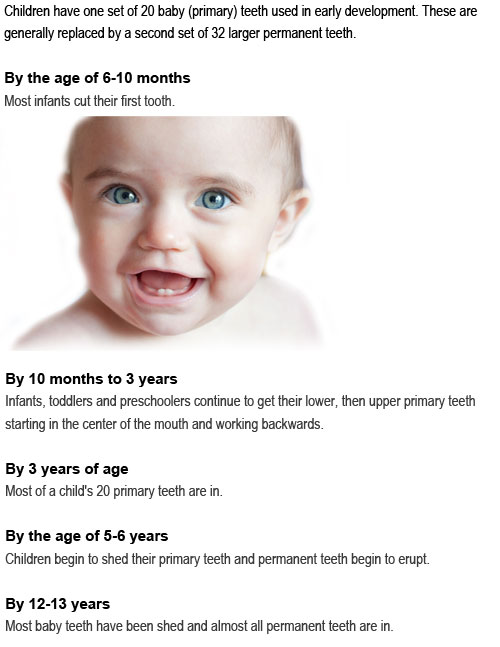 In order to prevent it, you need to brush your teeth regularly: for this, you can use various massage brushes that not only teach the child to hygiene, but also facilitate the process of teething. Teeth are immediately taught to clean correctly - from the gums to the edge, slightly "sweeping", semicircular movements, and in no case horizontal. If possible, brush your teeth after every meal (and at least twice a day). Is there no such possibility? Give the baby a drink - the water will wash away the remnants of food.
In order to prevent it, you need to brush your teeth regularly: for this, you can use various massage brushes that not only teach the child to hygiene, but also facilitate the process of teething. Teeth are immediately taught to clean correctly - from the gums to the edge, slightly "sweeping", semicircular movements, and in no case horizontal. If possible, brush your teeth after every meal (and at least twice a day). Is there no such possibility? Give the baby a drink - the water will wash away the remnants of food.
At 8 months the upper central incisors usually erupt. In 9 months the upper lateral incisors appear. At 11 months and the lower lateral incisors are already in place in many children! By , the baby has eight normal teeth . But there may not be a single one - delayed teething occurs in 25% of cases with normal psychomotor development of the child. In extremely rare cases, the absence of teeth is associated with adentia - the absence of their rudiments.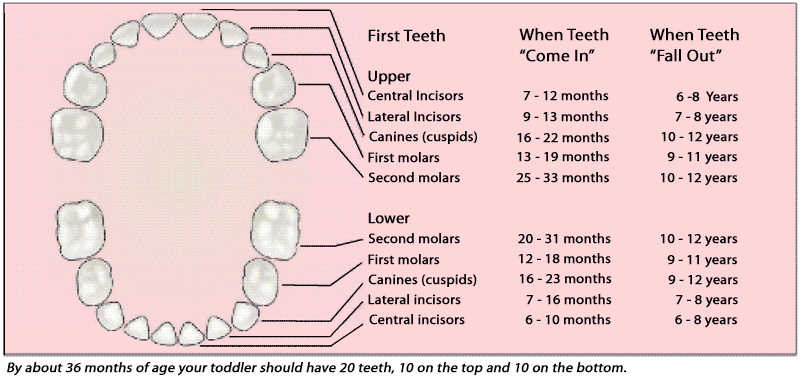 You can check this with a pediatric dentist using the radiovisiography method. By 13–15 months , first the upper first molars appear, and then the lower ones.
You can check this with a pediatric dentist using the radiovisiography method. By 13–15 months , first the upper first molars appear, and then the lower ones.
From the age of one, the baby's teeth can be brushed with children's toothpaste and a special children's brush. The service life of the brush is no more than 2 months, even if it looks like new. Many babies swallow delicious pasta. You should not be afraid of this if it is childish and its quantity is no more than a pea. Of course, up to 2–2.5 years, brushing your teeth should be done with the help of, and then under the vigilant control of your mother.
B 18 months fangs erupt. Usually these teeth cause more problems than others, their eruption is more painful, and this process is often accompanied by malaise. At 20 months the second molars erupt. And sometimes already at this age, the mother may notice the first problems. Doctors reassure: carious milk teeth are not a reason to worry that permanent ones will also be bad. As practice shows, there are no regularities here. Of course, if parents do not neglect the prevention of diseases and dental hygiene. At 2.5 years old, the baby normally has a full set of milk teeth. There are 20 of them - 10 on each jaw .
As practice shows, there are no regularities here. Of course, if parents do not neglect the prevention of diseases and dental hygiene. At 2.5 years old, the baby normally has a full set of milk teeth. There are 20 of them - 10 on each jaw .
Milk teeth do not last long - soon they will fall out and permanent ones will appear in their place. Usually the change of teeth begins at about 5-6 years and lasts until 20, when the wisdom teeth erupt.
From the age of 6 months, it is obligatory to come for preventive examinations twice a year. When this becomes a habit, the baby will not be afraid of doctors, and by the age of 7–8 (when a visit to the clinic can no longer be avoided) he will sit in the dental chair quite calmly
In order for the baby's teeth to grow strong and healthy, you need to start taking care of them almost before conception. And it is also better to get to know the dentist early
Terms of eruption and loss of milk teeth
| Upper teeth | |||
| Tooth name | Eruption period | Eruption procedure | Drop time |
| Central cutter | 8 months - 1 year | 2 | 6-7 years old |
| Side cutter | 9 months - 1 year 2 months | 3 | 7-8 years old |
| Fang | 1 year 3 months - 1 year 10 months | 7 | 10-12 years old |
| First molar | 1 year - 1 year 6 months | 5 | 9-11 years old |
| Second molar | 2 years - 2 years 8 months | 10 | 10-12 years old |
| Lower teeth | |||
| Central cutter | 6 months -10 months | 1 | 6–7 years old |
| Side cutter | 10 months -1 year 4 months | 4 | 7-8 years old |
| Fang | 1 year 4 months - 2 years | 8 | 9-12 years old |
| First molar | 1 year 2 months - 1 year 7 months | 6 | 9-11 years old |
| Second molar | 1 year 10 months - 2 years 8 months | 9 | 10-12 years old |
Make an appointment
to the doctor - Bogorad Maria Vladimirovna
Clinical Hospital Lapino-1 "Mother and Child" Clinic "Mother and Child" Kuntsevo
Pediatric Ophthalmology for ChildrenOphthalmology
By clicking on the submit button, I consent to the processing of personal data
Attention! Prices for services in different clinics may vary.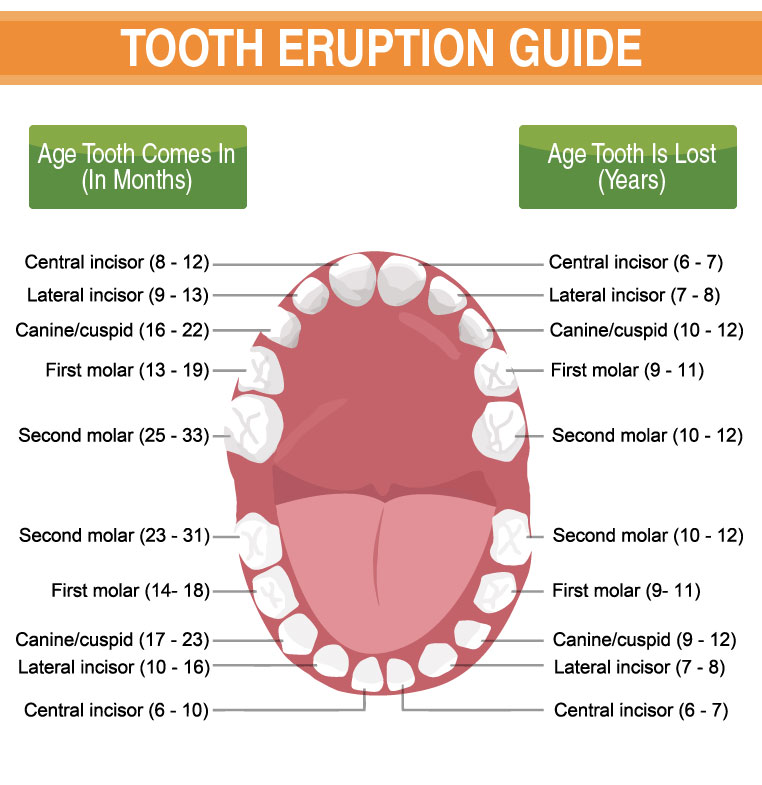 To clarify the current cost, select a clinic
To clarify the current cost, select a clinic
Lapino-1 Clinical Hospital "Mother and Child"Clinic "Mother and Child" KuntsevoClinic "Mother and Child" Novogireevo
All directionsAnesthesia in dentistrySpecialist consultations (adults)
01.
Anesthesia in dentistry
02.
Specialist consultations (adults)
Nothing found
The administration of the clinic takes all measures to timely update the price list posted on the website, however, in order to avoid possible misunderstandings, we advise you to clarify the cost of services and the timing of the tests by calling
Timing of teething - Article
Author:
Marbery Gedrean | Checked by: Shteba Victoria Petrovna | Last revised: October 18, 2020.
Most parents are very concerned about how teething (and gums) affects their babies in everyday life. Although we cannot fully predict exactly how each baby will react to their first tooth. However, we can learn about teething symptoms and how to soothe your baby during this difficult time. In general, the more we know about teething, the better we can help our babies get through it. Let's figure it out.
Timing of teething
One of the most common questions parents ask is, “How long does it take for babies to teeth?”. It is useful to know both the time frame for the appearance of the first tooth and the time frame in which all teeth erupt. In general, teething is an ongoing process that occurs between the ages of 6 and 24 months. Although your baby has twenty milk teeth that will appear within two years, teething, fortunately, only causes pain and irritation at the time when the tooth is about to break through the gum. It is not known exactly how long it will take for a tooth to fully erupt, but on average experts say it can erupt within 1-7 days per tooth. However, teething symptoms usually only last a couple of days, so if a baby experiences discomfort for an extended period of time, it's safe to assume it's not teething.
However, teething symptoms usually only last a couple of days, so if a baby experiences discomfort for an extended period of time, it's safe to assume it's not teething.
Teething timeline
Most babies erupt their first teeth between 6 and 7 months of age, but this may happen sooner or later. In general, your baby's teeth are likely to appear in the following timeline windows:
6-7 months
During this time, the first teeth begin to erupt. The first teeth to erupt are usually the lower central incisors, which are the two middle teeth at the bottom. Children at this age become more active. They begin to grab and pull objects towards them, transfer objects from one hand to the other, and may even begin to crawl. It's important to keep an eye on small objects within your baby's reach, as he'll want to put everything in his mouth during teething!
8 to 13 months
Between 8 and 12 months your baby will have upper central incisors.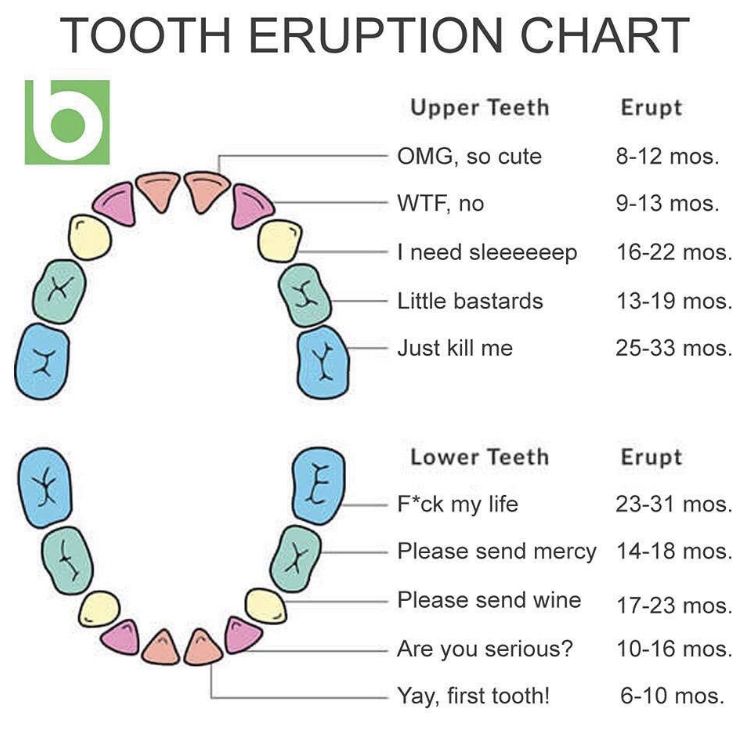 In addition, sometime between 9 and 13 months they will have upper and lower teeth next to their upper central incisors (these are called lower and upper lateral incisors). In addition to teething, it is important to understand that other important milestones in gross motor development are also achieved during this developmental window. Most babies are able to sit up, stand up unassisted, take their first steps, pick up and throw objects, roll a ball, and grasp objects.
In addition, sometime between 9 and 13 months they will have upper and lower teeth next to their upper central incisors (these are called lower and upper lateral incisors). In addition to teething, it is important to understand that other important milestones in gross motor development are also achieved during this developmental window. Most babies are able to sit up, stand up unassisted, take their first steps, pick up and throw objects, roll a ball, and grasp objects.
13 to 20 months
Typically, between 13 and 16 months of age, your baby's first molars come in at about the same time. Shortly thereafter, their fangs will appear in both the top and bottom rows, between about 16 and 20 months.
20 to 30 months
At the final stage of teething, the back teeth or second molars appear in the bottom row of the baby. While most teething symptoms appear the same in both toddlers and babies, there are some differences as your baby grows older. First of all, your baby can now tell you about their discomfort and pain, unlike non-verbal babies. On the other hand, many toddlers will not show any signs of discomfort and will not complain of pain at all during the passage of molars. For other babies, the pain can be significantly worse because their first molars are larger than their other molars. They may even complain of a headache or jaw pain!
First of all, your baby can now tell you about their discomfort and pain, unlike non-verbal babies. On the other hand, many toddlers will not show any signs of discomfort and will not complain of pain at all during the passage of molars. For other babies, the pain can be significantly worse because their first molars are larger than their other molars. They may even complain of a headache or jaw pain!
Toys that can help
Teethers - Teething toys that help to significantly relieve the symptoms of teething in children, while keeping them occupied during play. Because teething babies are always looking for something they can chew on, teething toys are specifically designed to soothe gums and temporarily ease teething.
“6 months? But my 3 month old is teething right now!”
Some babies start teething early at 6 months - and usually it's a little thing you don't have to worry about!
Many babies begin to drool more often and explore their world by bringing their hand to their mouth to chew at about 3-4 months.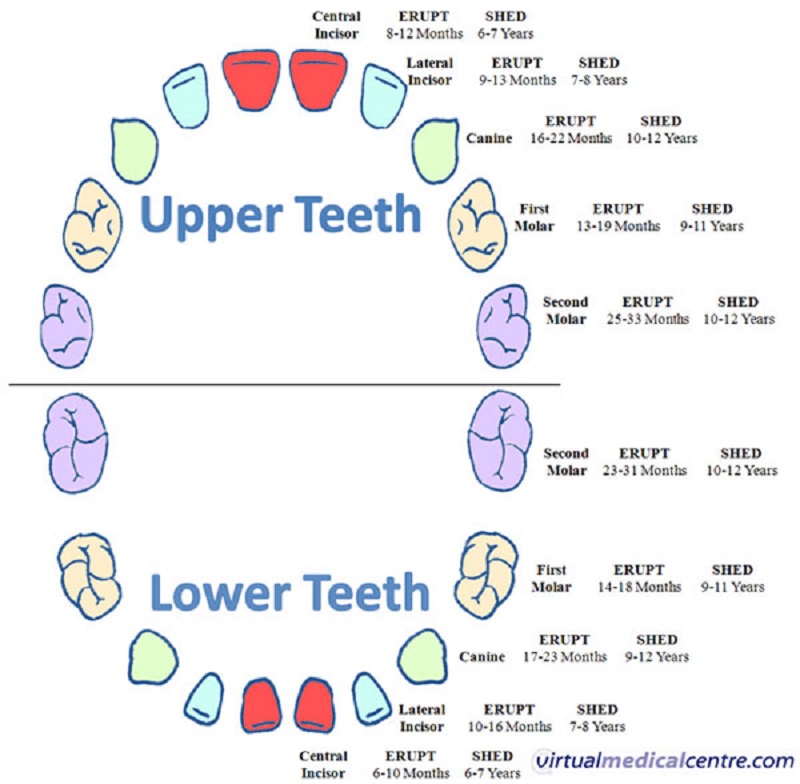 This is completely normal and is often accompanied by teething after some time.
This is completely normal and is often accompanied by teething after some time.
If you suspect that your little bundle of joy, which can be much less joyful during gum pain attacks, is teething, look for symptoms such as:
- saliva, the surest sign;
- capriciousness - unfortunately, also a frequent indicator of common childhood worries;
- slight temperature increase approx. 37.2 - 38 °C.
The bottom two teeth usually show up first, so keep an eye on this area and be prepared to be over-the-top when they show up.
When your child has their first teeth, you can use a small, soft-bristled toothbrush. You can also wipe your child's gums daily with a clean, damp cloth.
Remember that your child's pediatrician is your ally! Let him know about your child's teeth at your next appointment. The doctor can make sure that everything is in order and, if necessary, recommend visiting a pediatric dentist.
It's really impossible to tell exactly how long teething lasts, but fortunately, regardless of your baby's age or stage of teething, one of the best ways to help your little one is to provide a variety of fun and lovable teething toys.