Symptoms of uterine infection after miscarriage
Miscarriage | Sparrow
Overview
Miscarriage is the spontaneous loss of a pregnancy before the 20th week. About 10 to 20 percent of known pregnancies end in miscarriage. But the actual number is likely higher because many miscarriages occur very early in pregnancy — before you might even know about a pregnancy.
The term "miscarriage" might suggest that something went wrong in the carrying of the pregnancy. But this is rarely true. Most miscarriages occur because the fetus isn't developing as expected.
Miscarriage is a relatively common experience — but that doesn't make it any easier. Take a step toward emotional healing by understanding what can cause a miscarriage, what increases the risk and what medical care might be needed.
Symptoms
Most miscarriages occur before the 12th week of pregnancy.
Signs and symptoms of a miscarriage might include:
- Vaginal spotting or bleeding
- Pain or cramping in your abdomen or lower back
- Fluid or tissue passing from your vagina
If you have passed fetal tissue from your vagina, place it in a clean container and bring it to your health care provider's office or the hospital for analysis.
Most women who have vaginal spotting or bleeding in the first trimester go on to have successful pregnancies.
Causes
Problems with the genes or chromosomes
Most miscarriages occur because the fetus isn't developing as expected. About 50 percent of miscarriages are associated with extra or missing chromosomes. Most often, chromosome problems result from errors that occur by chance as the embryo divides and grows — not problems inherited from the parents.
Chromosome problems might lead to:
- Blighted ovum. Blighted ovum occurs when no embryo forms.
- Intrauterine fetal demise. In this situation, an embryo forms but stops developing and dies before any symptoms of pregnancy loss occur.
-
Molar pregnancy and partial molar pregnancy. With a molar pregnancy, both sets of chromosomes come from the father. A molar pregnancy is associated with abnormal growth of the placenta; there is usually no fetal development.
A partial molar pregnancy occurs when the mother's chromosomes remain, but the father provides two sets of chromosomes. A partial molar pregnancy is usually associated with abnormalities of the placenta, and an abnormal fetus.
Molar and partial molar pregnancies are not viable pregnancies. Molar and partial molar pregnancies can sometimes be associated with cancerous changes of the placenta.
Maternal health conditions
In a few cases, a mother's health condition might lead to miscarriage. Examples include:
- Uncontrolled diabetes
- Infections
- Hormonal problems
- Uterus or cervix problems
- Thyroid disease
What does NOT cause miscarriage
Routine activities such as these don't provoke a miscarriage:
- Exercise, including high-intensity activities such as jogging and cycling.
- Sexual intercourse.
- Working, provided you're not exposed to harmful chemicals or radiation.
 Talk with your doctor if you are concerned about work-related risks.
Talk with your doctor if you are concerned about work-related risks.
Risk factors
Various factors increase the risk of miscarriage, including:
- Age. Women older than age 35 have a higher risk of miscarriage than do younger women. At age 35, you have about a 20 percent risk. At age 40, the risk is about 40 percent. And at age 45, it's about 80 percent.
- Previous miscarriages. Women who have had two or more consecutive miscarriages are at higher risk of miscarriage.
- Chronic conditions. Women who have a chronic condition, such as uncontrolled diabetes, have a higher risk of miscarriage.
- Uterine or cervical problems. Certain uterine conditions or weak cervical tissues (incompetent cervix) might increase the risk of miscarriage.
- Smoking, alcohol and illicit drugs. Women who smoke during pregnancy have a greater risk of miscarriage than do nonsmokers.
 Heavy alcohol use and illicit drug use also increase the risk of miscarriage.
Heavy alcohol use and illicit drug use also increase the risk of miscarriage. - Weight. Being underweight or being overweight has been linked with an increased risk of miscarriage.
- Invasive prenatal tests. Some invasive prenatal genetic tests, such as chorionic villus sampling and amniocentesis, carry a slight risk of miscarriage.
Complications
Some women who miscarry develop an infection in the uterus. This is also called a septic miscarriage. Signs and symptoms of this infection include:
- Fever
- Chills
- Lower abdominal tenderness
- Foul-smelling vaginal discharge
Prevention
Often, there's nothing you can do to prevent a miscarriage. Simply focus on taking good care of yourself and your baby:
- Seek regular prenatal care.
- Avoid known miscarriage risk factors — such as smoking, drinking alcohol and illicit drug use.
- Take a daily multivitamin.

- Limit your caffeine intake. A recent study found that drinking more than two caffeinated beverages a day appeared to be associated with a higher risk of miscarriage.
If you have a chronic condition, work with your health care team to keep it under control.
Diagnosis
Your health care provider might do a variety of tests:
- Pelvic exam. Your health care provider might check to see if your cervix has begun to dilate.
- Ultrasound. During an ultrasound, your health care provider will check for a fetal heartbeat and determine if the embryo is developing as it should be. If a diagnosis can't be made, you might need to have another ultrasound in about a week.
- Blood tests. Your health care provider might check the level of the pregnancy hormone, human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG), in your blood and compare it to previous measurements. If the pattern of changes in your HCG level is abnormal, it could indicate a problem.
 Your health care provider might check to see if you're anemic — which could happen if you've experienced significant bleeding — and may also check your blood type.
Your health care provider might check to see if you're anemic — which could happen if you've experienced significant bleeding — and may also check your blood type. - Tissue tests. If you have passed tissue, it can be sent to a lab to confirm that a miscarriage has occurred — and that your symptoms aren't related to another cause.
- Chromosomal tests. If you've had two or more previous miscarriages, your health care provider may order blood tests for both you and your partner to determine if your chromosomes are a factor.
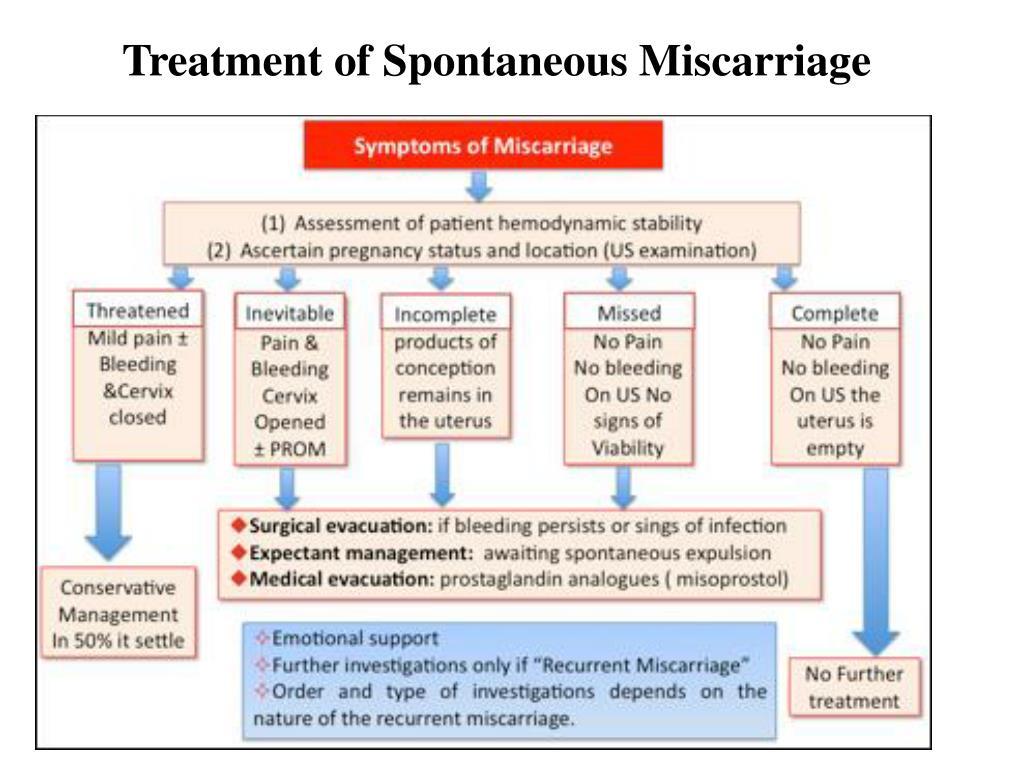
Possible diagnoses include:
- Threatened miscarriage. If you're bleeding but your cervix hasn't begun to dilate, there is a threat of miscarriage. Such pregnancies often proceed without any further problems.
- Inevitable miscarriage. If you're bleeding, cramping and your cervix is dilated, a miscarriage is considered inevitable.
- Incomplete miscarriage.
 If you pass fetal or placental material but some remains in your uterus, it's considered an incomplete miscarriage.
If you pass fetal or placental material but some remains in your uterus, it's considered an incomplete miscarriage. - Missed miscarriage. In a missed miscarriage, the placental and embryonic tissues remain in the uterus, but the embryo has died or was never formed.
- Complete miscarriage. If you have passed all the pregnancy tissues, it's considered a complete miscarriage. This is common for miscarriages occurring before 12 weeks.
- Septic miscarriage. If you develop an infection in your uterus, it's known as a septic miscarriage. This can be a severe infection and demands immediate care.
Treatment
Threatened miscarriage
For a threatened miscarriage, your health care provider might recommend resting until the bleeding or pain subsides. Bed rest hasn't been proved to prevent miscarriage, but it's sometimes prescribed as a safeguard. You might be asked to avoid exercise and sex, too. Although these steps haven't been proved to reduce the risk of miscarriage, they might improve your comfort.
Although these steps haven't been proved to reduce the risk of miscarriage, they might improve your comfort.
In some cases, it's also a good idea to postpone traveling — especially to areas where it would be difficult to receive prompt medical care. Ask your health care provider if it would be wise to delay any upcoming trips you've planned.
Miscarriage
With ultrasound, it's now much easier to determine whether an embryo has died or was never formed. Either finding means that a miscarriage will definitely occur. In this situation, you might have several choices:
- Expectant management. If you have no signs of infection, you might choose to let the miscarriage progress naturally. Usually this happens within a couple of weeks of determining that the embryo has died. Unfortunately, it might take up to three or four weeks. This can be an emotionally difficult time. If expulsion doesn't happen on its own, medical or surgical treatment will be needed.
- Medical treatment. If, after a diagnosis of certain pregnancy loss, you'd prefer to speed the process, medication can cause your body to expel the pregnancy tissue and placenta. The medication can be taken by mouth or by insertion in the vagina. Your health care provider might recommend inserting the medication vaginally to increase its effectiveness and minimize side effects such as nausea and diarrhea. For about 70 to 90 percent of women, this treatment works within 24 hours.
- Surgical treatment. Another option is a minor surgical procedure called suction dilation and curettage (D&C). During this procedure, your health care provider dilates your cervix and removes tissue from the inside of your uterus. Complications are rare, but they might include damage to the connective tissue of your cervix or the uterine wall. Surgical treatment is needed if you have a miscarriage accompanied by heavy bleeding or signs of an infection.
Physical recovery
In most cases, physical recovery from miscarriage takes only a few hours to a couple of days. In the meantime, call your health care provider if you experience heavy bleeding, fever or abdominal pain.
You may ovulate as soon as two weeks after a miscarriage. Expect your period to return within four to six weeks. You can start using any type of contraception immediately after a miscarriage. However, avoid having sex or putting anything in your vagina — such as a tampon — for two weeks after a miscarriage.
Future pregnancies
It's possible to become pregnant during the menstrual cycle immediately after a miscarriage. But if you and your partner decide to attempt another pregnancy, make sure you're physically and emotionally ready. Ask your health care provider for guidance about when you might try to conceive.
Miscarriage is usually a one-time occurrence. Most women who miscarry go on to have a healthy pregnancy after miscarriage. Less than 5 percent of women have two consecutive miscarriages, and only 1 percent have three or more consecutive miscarriages.
Less than 5 percent of women have two consecutive miscarriages, and only 1 percent have three or more consecutive miscarriages.
If you experience multiple miscarriages, generally two or three in a row, consider testing to identify any underlying causes. Such causes could include problems with the uterus, blood clotting or chromosomes. If the cause of your miscarriages can't be identified, don't lose hope. About 60 to 80 percent of women with unexplained repeated miscarriages go on to have healthy pregnancies.
Coping and support
Emotional healing can take much longer than physical healing. Miscarriage can be a heart-wrenching loss that others around you might not fully understand. Your emotions might range from anger and guilt to despair. Give yourself time to grieve the loss of your pregnancy, and seek help from loved ones.
You'll likely never forget your hopes and dreams surrounding this pregnancy, but in time acceptance might ease your pain. Talk to your health care provider if you're feeling profound sadness or depression.
Preparing for an appointment
If you have signs or symptoms of miscarriage, contact your health care provider right away. Depending on the circumstances, you might need immediate medical care.
Here's some information to help you get ready for your appointment, and what to expect from your health care provider.
What you can do
Before your appointment, you might want to:
- Ask about pre-appointment restrictions. In most cases you'll be seen immediately. If that's not the case, ask whether you should restrict your activities while you wait for your appointment.
- Find a loved one or friend who can join you for your appointment. Fear and anxiety might make it difficult to focus on what your health care provider says. Take someone along who can help remember all the information.
- Write down questions to ask your health care provider. That way, you won't forget anything important that you want to ask, and you can make the most of your time with your health care provider.

Below are some basic questions to ask your health care provider about miscarriage:
- What are the treatment options?
- What kinds of tests do I need?
- Can I continue to do my usual activities?
- What signs or symptoms should prompt me to call you or go to the hospital?
- Do you know what caused my miscarriage?
- What are my chances for a successful future pregnancy?
In addition to the questions you've prepared, don't hesitate to ask other questions during your appointment — especially if you need clarification or you don't understand something.
What to expect from your health care provider
Your health care provider is likely to ask you a number of questions, too. For example:
- When was your last menstrual period?
- Were you using any contraceptive methods at the time you likely conceived?
- When did you first notice your signs or symptoms?
- Have your symptoms been continuous or occasional?
- Compared with your heaviest days of menstrual flow, is your bleeding more, less or about the same?
- Have you had a miscarriage before?
- Have you had any complications during a previous pregnancy?
- Do you have any other health conditions?
- Do you know your blood type?
Content From Mayo Clinic Updated:
© 1998-2022 Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research (MFMER). All rights reserved. Terms of Use
All rights reserved. Terms of Use
1.800.SPARROW
1.517.364.1000
Donate to Sparrow
Unsupported Browser! This website will offer limited functionality in this browser. We only support the recent versions of major browsers like Chrome, Firefox, Safari, and Edge.
Recovering from a miscarriage - HSE.ie
While your body is recovering from a miscarriage, you are likely to have:
- bleeding from your vagina
- stomach cramps and pain
When to get urgent medical help
These symptoms could mean that some of the pregnancy tissue is still in your womb.
They could also be signs of an infection, especially if you also:
- feel feverish - a temperatures above 38°C (100.4°F)
- have flu-like symptoms like a sore throat, fever and muscle ache
You should go to the hospital if you are feeling unwell or feverish in the days after your miscarriage
Infection
Infection happens in about 2% of women who have had a miscarriage (2 in every 100 women). Infection can be treated with antibiotics.
Infection can be treated with antibiotics.
Sepsis
If your infection is not treated, sometimes serious complications like sepsis can occur. Sepsis is a very severe infection. It is caused by germs (usually bacteria) getting into your bloodstream.
Sepsis can cause organ damage and even death. It is very important to get medical help urgently if you think you may have an infection.
Do not use tampons
Do not use tampons or moon cups, as these could cause infection. It is safe to use sanitary towels or pads.
Your next period
Your next period will usually be 4 to 6 weeks after a miscarriage.
Emotions after a miscarriage
A miscarriage can be devastating for you and for your partner. The amount of emotional pain you feel is unique to you, and you may find it changes from time to time.
Sometimes, you may feel you are doing fine, but a sudden memory could trigger emotions. Feelings such as guilt, shock and anger are common. There is no right or wrong way to feel after a miscarriage.
Try to be open about your feelings and to communicate with your partner, family or friends.
Talk to your GP if you feel you are not coping. Remember your partner may have different ways of coping with the miscarriage.
Support
The loss of a pregnancy through miscarriage affects people in different ways. It can be a very distressing and emotional experience. You may need lots of support afterwards from your partner, family or friends.
Your GP can give you support during your physical and emotional recovery.
Your maternity hospital may offer support such as:
- chaplaincy or pastoral care
- clinical midwife specialist in bereavement and loss
The Pregnancy and Infant Loss in Ireland website has information and advice for parents.
Returning to work after a miscarriage
Your return to work depends on how you feel physically and emotionally.
If you can, rest for a few days before returning to work. Discuss this with your doctor in the hospital or with your GP.
You can get full maternity leave if you have a stillbirth or miscarriage after week 24 of your pregnancy.
Find out what benefits and entitlements you can get after a miscarriage or stillbirth.
Sex after a miscarriage
You can have sex again as soon as you feel ready. Make sure to wait until you feel well and until the pain and bleeding has reduced.
Remember you could get pregnant in the first month after a miscarriage. This can happen before your period returns. If this is not what you want, talk to your GP about contraception.
Future pregnancies
You can try for another baby as soon as you and your partner feel physically and emotionally ready.
Chances of another miscarriage
Most women will have a successful pregnancy after miscarriage. Having one or two miscarriages does not mean you are at higher risk for miscarriage in the future.
If you have 3 miscarriages, there might be a medical reason. Some medical conditions make it more likely to miscarry. Speak with your GP about treatment options.
Miscarriage. What to do after a miscarriage?
When a woman finds out about her pregnancy, she changes her rhythm of life, especially if the pregnancy is desired. However, depending on many circumstances, miscarriage , that is, a natural termination of pregnancy, may occur. Statistics say that up to 20 percent of pregnancies end in pathological abortions. Often a woman may not know that she was pregnant, as a miscarriage sometimes occurs at a very early stage and seems to be just a normal delay in menstruation followed by heavy discharge.
If a woman finds out that she is pregnant and wants to become a mother, she should be very attentive to her condition. The threat of miscarriage often occurs in the early stages of pregnancy and therefore it is necessary to know what symptoms and signs precede a sudden miscarriage.
Signs
The main sign of a suspected miscarriage is bleeding from the uterus. They happen not abundant, pale scarlet or gray-brown. The discharge most often gradually increases and is characterized by sudden spasms or pulling pains in the lower abdomen. These symptoms may last for some time.
The pains are often so mild that the woman simply does not pay attention to them. They are able to be interrupted, and the woman simply forgets about them, especially if the discharge also stopped, and before that they were insignificant. Meanwhile, the very first symptoms should alert you and you should urgently go to the gynecologist for examination and consultation. Even if the process has stopped, after a few days you can feel a sharp deterioration in health, and then you can no longer save the life of the unborn child. Be sure to pay attention to what exactly comes out with the discharge, if there are tissue fragments, it means that miscarriage has already occurred. Therefore, one should not hesitate to go to the doctor, the fetus may come out, in whole or in parts, there may be white particles or a round gray bubble. When the body is completely cleansed, the pain will subside, but before that it may continue for some time.
Even if the process has stopped, after a few days you can feel a sharp deterioration in health, and then you can no longer save the life of the unborn child. Be sure to pay attention to what exactly comes out with the discharge, if there are tissue fragments, it means that miscarriage has already occurred. Therefore, one should not hesitate to go to the doctor, the fetus may come out, in whole or in parts, there may be white particles or a round gray bubble. When the body is completely cleansed, the pain will subside, but before that it may continue for some time.
Terms of miscarriages
A miscarriage is classified as early if it occurred before twelve weeks from the onset of pregnancy. Starting from the 22nd week, if a spontaneous miscarriage has occurred, it is considered late. If the termination of pregnancy occurred before thirty-seven weeks, then this is already called premature birth. All subsequent fetal rejections are called term births and are generally considered normal, since during this period, mostly able-to-survive children are born. In modern medicine, children born after 22 weeks are nursed and subsequently do not differ from those born at term with normal weight.
In modern medicine, children born after 22 weeks are nursed and subsequently do not differ from those born at term with normal weight.
Types of miscarriages
Specialists have identified several types of miscarriages.
- Complete or inevitable - characterized by pain in the lower back and dilatation of the cervix, hemorrhages from it. The fetal membrane necessarily bursts, and the pregnancy is terminated. The fetus comes out of the uterus, and all discomfort in the form of pain and bleeding stops.
- Miscarriage is different in that the fetus died, but remained in the mother's body. This can be detected by a doctor when examining a woman and when listening to the fetal heartbeat.
- Repeated miscarriage is rare, it occurs only some time after the first and can occur up to three times in a row in the early stages.
Causes of spontaneous abortion
The vast majority of women, having learned about their pregnancy, want to give birth to a healthy baby. And if there is a spontaneous miscarriage , then for a failed mother this is a real tragedy. Many, having experienced an abortion, try to conceive a child faster again, but first you need to know the reasons for what happened in order to save the fetus in the future. According to statistics, the largest number of miscarriages occurs precisely in the early stages.
And if there is a spontaneous miscarriage , then for a failed mother this is a real tragedy. Many, having experienced an abortion, try to conceive a child faster again, but first you need to know the reasons for what happened in order to save the fetus in the future. According to statistics, the largest number of miscarriages occurs precisely in the early stages.
There are several reasons for this:
- Violations in genetics.
This is the most common cause of miscarriage. This is not due to heredity, it is a consequence of the mutation of parent germ cells, which accidentally ended up in unfavorable conditions. This is also the influence of radiation, poisoning, viruses, that is, temporary situations that affected the quality of germ cells. The body thus gets rid of a weak non-viable fetus. It is impossible and unnecessary to prevent such spontaneous abortion. It is only necessary, having decided to become pregnant, to try to cleanse your body of possible harmful influences.
- Hormonal disorders
The cause of miscarriage at a very early stage also lies in the lack of the hormone progesterone, or in the fact that a woman has an excess of male sex hormones that suppress the production of estrogen and progesterone in her body. In this case, the fetus can be saved medically by administering the necessary medicines to the woman. The work of the adrenal glands, as well as the thyroid gland, affects the production of hormones, so a lot depends on the work of these glands throughout the pregnancy process.
- Immunological causes .
In this case, the vitality of the fetus is directly affected by the Rh conflict. The embryo will inherit the positive Rh of the man, and if the partner has a negative Rh, then her body simply rejects cells that are foreign to him. A similar situation can be prevented by injecting the expectant mother with a variety of progesterone, a process called immunomodulation.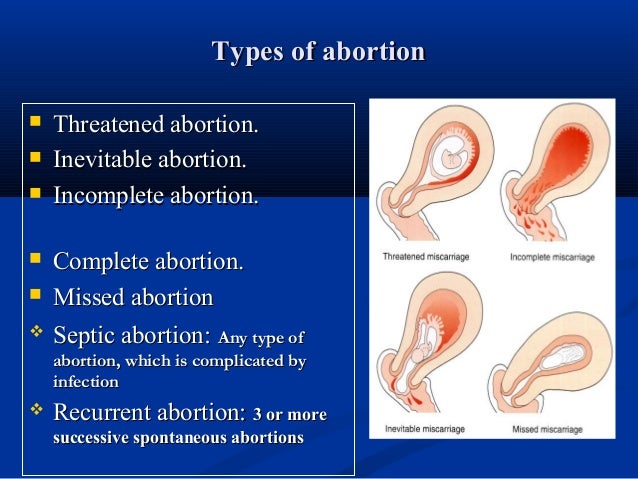
Sexually transmitted infections such as toxoplasmosis, syphilis, trichomoniasis, chlamydia and others are of great danger. External infection: bacteria and viruses infect the fetal membranes, and the body will inevitably reject the embryo. Therefore, before becoming pregnant, you should be examined to know for sure that there are no infections, and if the result is positive, undergo treatment.
In addition, all inflammatory processes, various diseases of the internal organs, which are accompanied by a persistent high temperature, can also lead to unexpected rejection of the fetus. Rubella is especially dangerous, and viral hepatitis is common. But even a sore throat, mild pneumonia, appendicitis sometimes play a key role and lead to a miscarriage, so the expectant mother must undergo a thorough examination even before the child is conceived, and then beware of all kinds of infections and weakening of the body.
- Medical abortion.
If a woman had an abortion in a hospital and then became pregnant and decided to give birth, there is a danger that she will have a miscarriage. Abortion is a stress factor for the body, ovarian dysfunction is often observed, inflammatory processes in the female genital organs can begin, and all this will lead, at best, to miscarriage and subsequent repeated miscarriages, and at worst, to infertility. Therefore, you need to think very seriously before going for an abortion.
- Medicines and certain herbs.
It is advisable for a pregnant woman not to take any medication at all, especially during the first three calendar months. Medicines and herbs can cause various defects in the fetus, which in turn will lead to its rejection. Analgesics and uncontrolled hormonal contraceptives are especially dangerous. Parsley and nettle should be eaten with caution - they cause a high tone of the uterus, which in turn can reject the fetus.
- Stress.
It is no coincidence that in ancient times, pregnant women were protected from unrest, they were created comfortable conditions, and they tried to give as many positive emotions as possible. Now the direct dependence of the health of the unborn baby on the mental state during pregnancy has already been proven. Any stress, fear and overstrain can cause an unexpected termination of pregnancy. If you have a problem (death of a loved one, divorce, etc.), you need to find sedatives with the help of a doctor, they will help you cope with this period.
- Unhealthy lifestyle.
Of course, the intake of alcoholic beverages, an unhealthy lifestyle, smoking, even coffee consumption in large quantities, improper diet - all this can lead to a transient miscarriage. Therefore, the expectant mother should prioritize and change her rhythm of life in advance in order to give birth to a healthy child.
- Sexual intercourse, falling, heavy lifting.
All of these factors can affect the fetus, so you should protect yourself and your baby by avoiding these activities.
What to do after a miscarriage?
Having experienced the tragedy of losing a child, parents often intend to immediately conceive a new baby, but they are afraid that everything will happen again. In this case, you do not need to make independent decisions, but consult a doctor. And first of all, it is necessary to identify the cause that led to the miscarriage. For this, the expectant mother needs to undergo as thorough an examination as possible.
If no obvious cause is found, the fetus most likely has a chromosomal abnormality. In this case, you should not worry, since the next conception will occur with a different set of chromosomes, which means that there will be no repeated miscarriage. If the miscarriage was repeated, it is necessary to contact a geneticist and conduct a study of the set of chromosomes of both parents.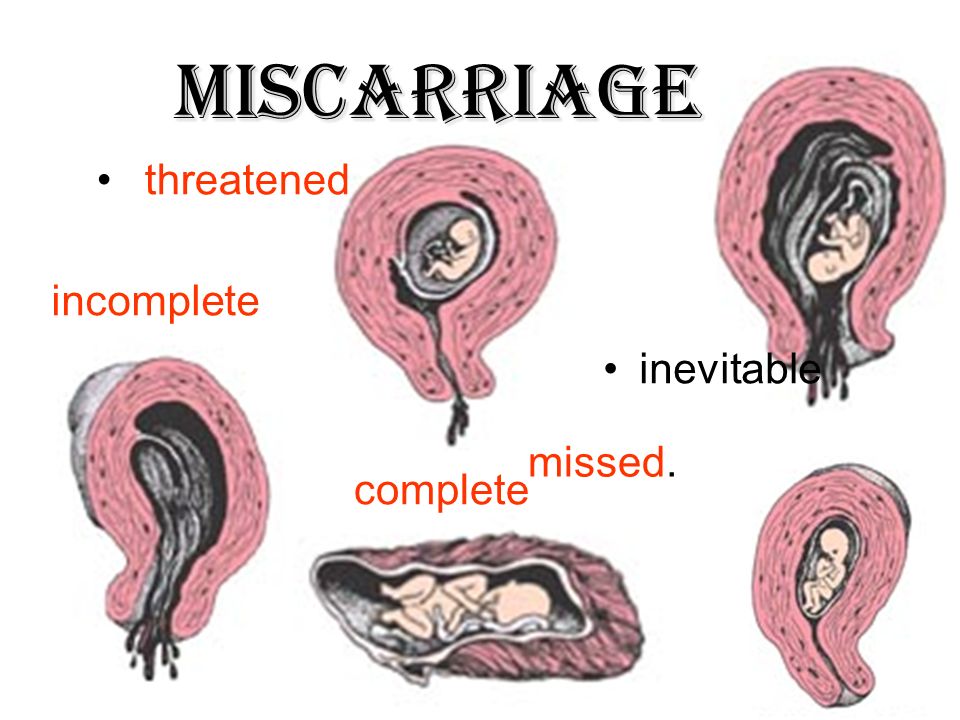 If it turns out that the cause was an infection, then it is necessary to fully recover. If we are talking about sexual infections, then both parents need to undergo therapy. It is necessary to take tests for hormonal studies, hemostasis systems and determine the immune status.
If it turns out that the cause was an infection, then it is necessary to fully recover. If we are talking about sexual infections, then both parents need to undergo therapy. It is necessary to take tests for hormonal studies, hemostasis systems and determine the immune status.
After a miscarriage, should be treated, if necessary, and pause between conceptions. During pregnancy, you should not take medications to prevent re-spontaneous pathological termination of pregnancy. Therefore, you can become pregnant only after the end of the course of treatment. If the cause was hormonal abnormalities, then the expectant mother should take special drugs to stabilize the background, and at this time she should never become pregnant. During the pause, you need to choose contraceptives with the help of a doctor. You can go to a specialized clinic where you will be prescribed a full course of rehabilitation.
The first week after a miscarriage women often experience pain in the lower abdomen, heavy bleeding, so you should refrain from sexual intercourse with a man. If there is severe bleeding, acute pain in the lower abdomen, convulsions, high fever, palpitations, nausea, vomiting, then you should immediately consult a doctor to identify the cause of this condition. It is necessary to plan a subsequent pregnancy not earlier than three months after this situation, but preferably six months later. Until that time, it is worth reconsidering your outlook on life, giving up hard work, eating right and wisely, taking vitamins, exercising, losing weight if you are overweight, stop smoking, drinking alcohol, think over your daily routine.
If there is severe bleeding, acute pain in the lower abdomen, convulsions, high fever, palpitations, nausea, vomiting, then you should immediately consult a doctor to identify the cause of this condition. It is necessary to plan a subsequent pregnancy not earlier than three months after this situation, but preferably six months later. Until that time, it is worth reconsidering your outlook on life, giving up hard work, eating right and wisely, taking vitamins, exercising, losing weight if you are overweight, stop smoking, drinking alcohol, think over your daily routine.
It is very important during this recovery period to have a positive attitude and confidence that the next attempt will be successful. This is harder to do than to say, because after a miscarriage the woman is in a depressed state and is afraid of a repetition of the situation. You can’t get hung up on your problem, during this period it’s better to do some favorite thing, relax, change the situation, travel, visit the city more often. The modern ecological situation in cities has a bad effect on women's health, so private trips to nature, a trip to the sea, to friends in another city can distract from painful thoughts. An important role in this case is played by the woman's relatives and, above all, the husband, who can surround her with care and attention, creating peace of mind.
The modern ecological situation in cities has a bad effect on women's health, so private trips to nature, a trip to the sea, to friends in another city can distract from painful thoughts. An important role in this case is played by the woman's relatives and, above all, the husband, who can surround her with care and attention, creating peace of mind.
You may need to contact a counseling psychologist or psychotherapist. Yoga classes, self-education, visiting theaters, exhibitions and temples have a very beneficial effect on the psyche of a woman and help to distract from her problems. Helping others who have a difficult life situation, caring for the sick can also have a beneficial psychological effect and help you look at your problems from the outside.
Remember, the human body is a self-healing system, it just needs a little help.
Treatment and prevention of miscarriage
Miscarriage. Symptoms
Causes of a miscarriage
Questions to ask your doctor about a miscarriage
Diagnosis of a miscarriage
If there is a risk of a miscarriage, your doctor may recommend rest until the bleeding or pain stops. Your doctor may also recommend that you abstain from sports and sexual activity. It is better not to travel, and especially not to travel to places where it is difficult to get emergency medical care.
Your doctor may also recommend that you abstain from sports and sexual activity. It is better not to travel, and especially not to travel to places where it is difficult to get emergency medical care.
Thanks to the widespread use of ultrasound, it is much easier these days to know if an embryo has died or not formed at all, and to know for sure that a miscarriage will occur. In this case, there are several options:
Expectant tactics. Before ultrasound was used in early pregnancy, most women had no idea that they were going to have a miscarriage. Some women allow the process to develop naturally. Usually a miscarriage occurs a few weeks after the death of the embryo is established. Unfortunately, this process can take three to four weeks. From an emotional point of view, this can be quite a difficult period.
Conservative treatment for miscarriage. If, after diagnosing a miscarriage, a woman decides to speed up the process, then the removal of the embryonic tissue and placenta from the body can be provoked by taking certain drugs. Some medications are taken by mouth, but your doctor may prescribe intravaginal medications to increase their effectiveness and reduce the risk of side effects such as nausea, abdominal pain, and diarrhea. Most likely, a miscarriage will occur at home. The time of action of the drug may vary. You may also need more than one dose of the drug. In 70% of cases, the drug begins to act within a day, and a miscarriage occurs in the next few days or weeks.
Some medications are taken by mouth, but your doctor may prescribe intravaginal medications to increase their effectiveness and reduce the risk of side effects such as nausea, abdominal pain, and diarrhea. Most likely, a miscarriage will occur at home. The time of action of the drug may vary. You may also need more than one dose of the drug. In 70% of cases, the drug begins to act within a day, and a miscarriage occurs in the next few days or weeks.
Surgical treatment. Another treatment option is vacuum aspiration and curettage. During this procedure, the doctor opens the cervix and, using a special device, gently sucks tissue from the uterus. Sometimes a special metal surgical instrument with a loop at the end (curette) is used to scrape the walls of the uterus after vacuum aspiration. Complications are rare, but the connective tissue of the cervix or the wall of the uterus may be damaged.
In the event of an unavoidable miscarriage, surgery is necessary to stop the bleeding.
Lifestyle and home care
Physical recovery
In most cases, physical recovery from a miscarriage takes a few hours to a few days. It will take 4-6 weeks to return to a normal lifestyle. During this period, if you experience heavy bleeding, fever, chills or severe pain, you should contact your doctor. These signs and symptoms may indicate an infection. For two weeks after a miscarriage, you should not have sex, use tampons, or flush your vagina.
Subsequent pregnancy
It is possible to become pregnant during your period immediately after a miscarriage. If you and your partner decide to try for a baby, make sure you are emotionally and physically ready for it. The doctor may recommend to postpone this process until the next menstruation, and maybe even more.
More than three miscarriages in a row should be investigated to determine the underlying causes, such as uterine abnormalities, coagulation problems, or abnormalities at the chromosomal level. In some cases, the doctor will suggest that you get tested after two miscarriages in a row, but two miscarriages still may not have hidden medical reasons. If the cause of miscarriages cannot be determined, do not lose hope. 60-70% of women who have had consecutive miscarriages can become pregnant in the future, even without treatment.
In some cases, the doctor will suggest that you get tested after two miscarriages in a row, but two miscarriages still may not have hidden medical reasons. If the cause of miscarriages cannot be determined, do not lose hope. 60-70% of women who have had consecutive miscarriages can become pregnant in the future, even without treatment.
How to cope with illness and where to find support
Psychological recovery can take much longer than physical recovery. A miscarriage is a painful loss that others will not be able to fully understand. You can experience completely different feelings: from anger to despair. Give yourself time to process this grief and find support from loved ones. Don't blame yourself for what happened. You may not be able to forget all the hopes and dreams you had for this pregnancy, but over time, acceptance will ease the pain. Talk to your healthcare provider if you are experiencing deep sadness or depression.
Prevention
With so many possible causes of miscarriage, there is simply no way to prevent it.