Signs of miscarriage back pain
6 Early Miscarriage Symptoms - Signs of Pregnancy Loss
Let's get one thing straight: Carrying another living being inside of your body is no small feat, so it's totally understandable to feel on edge about it...or to worry about a miscarriage.
You're also not alone in your anxiety—according to one 2015 study published in the journal Obstetrics & Gynecology, 41 percent of women surveyed who'd had a miscarriage felt like they did something wrong—and many (incorrectly) believed that lifting heavy objects or being super-stressed may have caused their miscarriages.
In reality, miscarriages (a.k.a. a loss of pregnancy before 20 weeks) happen in about 10 percent of known pregnancies, according to the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG)—and half the time, those miscarriages are due to chromosomal abnormalities that can't be prevented.
Related Story
- 5 Women Share the Pain of Having a Miscarriage
While sometimes women can experience recurrent miscarriages (two or more consecutive pregnancy losses—a condition that needs to be checked out for an underlying cause like genetic defects or chronic conditions) most times, miscarriage is an isolated event. Couples will often go on to have successful pregnancies.
Still, that reassurance can only go so far—especially when faced with any twinge, bleeding, or cramping during pregnancy. If you’re worried at all, certainly reach out to your doctor who can tell you if you need to be examined. And, just because you notice some of these signs of early miscarriage doesn’t mean there’s anything wrong either.
That said, it doesn't hurt to be informed about potential red flags—here are the early miscarriage symptoms you should look out for when you're expecting.
1. You're bleeding pretty heavily.
While, yes, bleeding is a sign of a miscarriage, it depends on what kind of bleeding you're experiencing: Spotting, for example, might be completely normal. “As the fertilized egg burrows or implants into the uterus, you may see some spotting,” says Kecia Gaither, M.D., an ob-gyn and maternal fetal medicine specialist. You can also experience bleeding behind the developing placenta, she says.
You can also experience bleeding behind the developing placenta, she says.
Related Story
- Is Your Heavy Period a Sign of Something Serious?
Bright red blood and heavy bleeding, however, should sound alarm bells, says Gaither. If the pregnancy continues after some bleeding, it can be called a threatened miscarriage, and needs to be monitored by an ob-gyn, per the U.S. National Library of Medicine.
2. You're seeing very large blood clots and tissue.
While some bleeding and spotting might be normal (i.e., no cause for concern) during pregnancy, clotting of any kind should trigger you to call your ob-gyn. Some clots can even grow to be as big as a lemon, per Planned Parenthood.
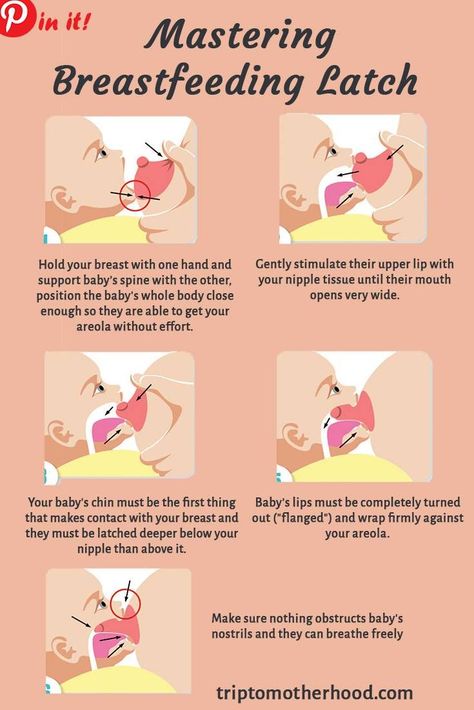
Your body may also pass other tissue (which will look a lot like heavy bleeding), or a light-pink vaginal fluid. Either way, if you're pregnant and you notice something off with what's coming out of your vagina, it's time to see a doc.
3. You have pain and cramping—like PMS.
When it comes to cramping, menstrual-like cramps can be totally normal as your uterus begins to expand, says Gaither. Other times, cramping can be a sign of an early miscarriage. “The cramping is from the uterus contracting trying to expel the pregnancy,” says Gaither.
Bleeding and cramping might also be signs of other pregnancy problems, like ectopic pregnancies (when a fertilized egg attaches itself somewhere outside of the uterus—usually to a fallopian tube). So if you're experiencing bleeding and cramping after learning you're pregnant, it's good to get checked out, regardless.
4. Your back is killing you.
Just like cramping, you may also feel a lower backache that can range from mild to severe discomfort. Though, again, this can be normal in a healthy pregnancy, too. The best advice is boring, but true: Always talk to your doctor if you’re concerned about your symptoms—they’re there to help you in every way they can.
5. Your ob-gyn doesn't find a heartbeat.
To be fair, this isn't a symptom—but that's because sometimes there aren't any symptoms with a miscarriage. It may also be as simple as not feeling pregnant anymore, according to Planned Parenthood.
Related Story
- 23 Best Pregnancy Apps, According To Ob-Gyns
In other situations, women can have a "nonviable pregnancy," says Gaither. (You may hear women also call it a missed miscarriage.) It happens when a pregnancy fails to progress, especially in the first trimester. You may notice that symptoms you felt before (nausea, for instance) have disappeared, though these may not go away until hormone levels have decreased, says Gaither.
6. You're late...and you're never late.
If your period usually comes like clockwork, but arrives a little late this time (and you’ve been having unprotected sex), you may have experienced a chemical pregnancy, says Gaither.
This usually happens without you even knowing about it (unless you're trying and you take a pregnancy test). Basically, a chemical pregnancy occurs when the egg and sperm meet, implant, and your body produces the hormone HCG, but things fail to develop further, says Gaither. Chemical pregnancies may make up 50 to 75 percent of all miscarriages, says the American Pregnancy Association.
Jessica Migala
Jessica Migala is a health writer specializing in general wellness, fitness, nutrition, and skincare, with work published in Women’s Health, Glamour, Health, Men’s Health, and more. She is based in the Chicago suburbs and is a mom to two little boys and rambunctious rescue pup.
Miscarriage Pain: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
According to the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG), miscarriage happens in at least 10 percent of clinically identified pregnancies. (Meaning, you actually knew you were pregnant; some miscarriages happen before you even miss your period.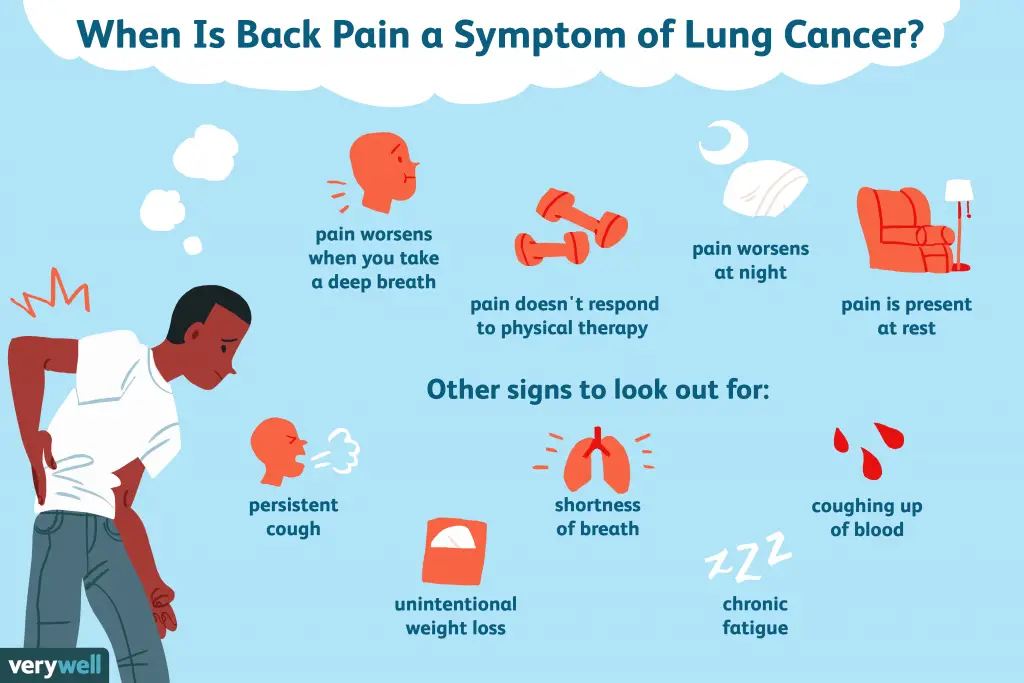 )
)
When miscarriage happens after you’ve already gotten a positive pregnancy test, it can be a physically and emotionally painful process.
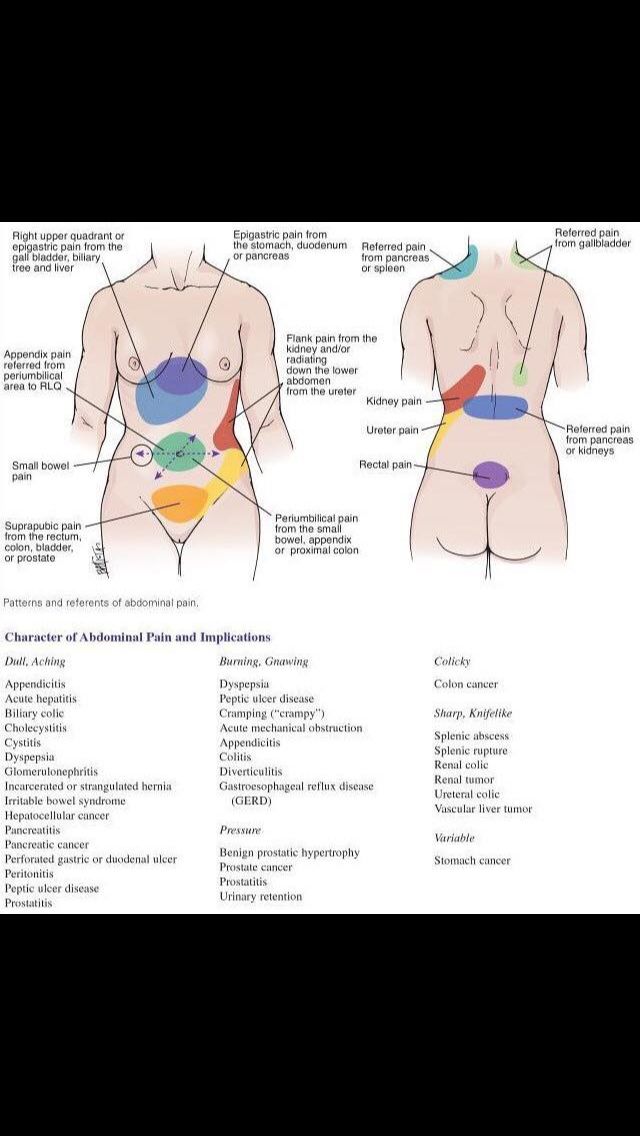
We can’t make miscarriage any easier, but we can help you understand what’s happening. For instance, although abdominal pain is one of the most frequent symptoms of a miscarriage, it’s not the only type of pain or discomfort you might feel.
Here’s a breakdown of seven types of pain you might have during a miscarriage and what you can do to relieve your symptoms.
Cramping with a miscarriage is usually caused by your uterus contracting. Just like during your period, your uterus contracts to push contents out. Since your uterus is mostly a muscle, these contractions feel like muscle cramps (in other words, they hurt).
You’ll usually feel these cramps on both sides of your lower abdomen or pelvic region. The cramps may come and go in waves or your pain may feel more constant. Unless your doctor has told you not to, you can treat your pain with over-the-counter (OTC) pain relievers like Motrin or Tylenol. You can also use a heating pad to ease cramping.
You can also use a heating pad to ease cramping.
During a normal menstrual cycle, your uterus builds up lining to prepare for a pregnancy. When the pregnancy can’t continue, the lining needs to be shed.
Because your body has been preparing for pregnancy, there will be more lining and tissue, so your bleeding will be heavier than a period. The further along you are in the pregnancy, the heavier it will be.
To absorb the bleeding, you’ll need to wear a pad. ACOG doesn’t recommend using tampons during a miscarriage. And because the bleeding may last longer and be heavier than a typical period, you may notice some discomfort from moisture accumulation.
Blood loss with a miscarriage
You can lose a significant amount of blood with a miscarriage. Stay in touch with your doctor during the process and call if you experience dizziness or excessive blood loss (e.g., soaking more than two maxi pads per hour for more than 2 hours in a row).
To combat any discomfort, change your pad frequently and clean the area gently with water, avoiding soap.
The change in the vaginal environment from bleeding may also cause a yeast or bacteria overgrowth that could lead to vaginal odor. If you notice any signs of a yeast infection such as itching, or if the discharge becomes very foul smelling, call a doctor.
Gastrointestinal symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea can be caused by hormone changes, as well as side effects from any medication you take to manage the miscarriage. Diarrhea can also be caused by the relaxing of the smooth muscle, just like you experience with a period.
To combat nausea symptoms, drink plenty of water and try to eat small meals consisting of bland, gentle-on-the-stomach foods. These can include:
- rice
- bananas
- oatmeal
- scrambled eggs
- plain grilled chicken
If your symptoms are making it hard for you to keep food down or stay hydrated, ask your doctor about taking an antinausea or antidiarrheal medication.
Similar to how your period cramps can lead to back pain, the uterine contractions during a miscarriage can cause back pain.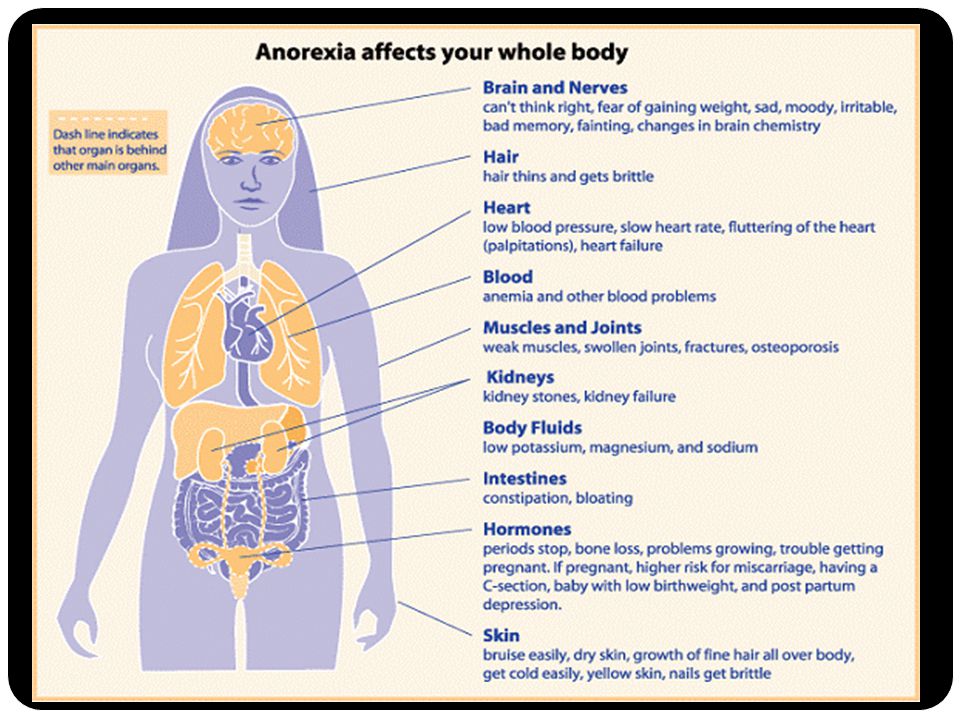 This is usually felt in the lower back and the pain can be mild, moderate, or severe.
This is usually felt in the lower back and the pain can be mild, moderate, or severe.
You can treat it just like you would your cramps — with pain relievers and heating pads — but if it’s really uncomfortable, don’t hesitate to ask your doctor what else you can do.
Shoulder pain is a symptom of ectopic pregnancy and it’s a serious medical emergency. If you have severe, one-sided pain, dizziness or fever, or pain affecting your rectum, pelvis, shoulder, or neck, call your doctor or get urgent medical care right away.
Ectopic pregnancy may not cause bleeding, so it can be a harder type of pregnancy to identify.
It’s normal to feel tired and weak with a miscarriage. You may also have a headache. If you experience excessive dizziness or feel like you may faint, tell your doctor or call your local urgent care center.
It’s also important to rest and drink plenty of water to manage these symptoms. Try to sleep, stay hydrated, and eat nutrient-dense foods.
No matter how far along in your pregnancy you are when you miscarry, you’re allowed to feel grief. Miscarriage emotions can be complicated and messy. You may feel both sad and relieved that it’s over, or you may feel intense and sometimes overwhelming grief.
Miscarriage emotions can be complicated and messy. You may feel both sad and relieved that it’s over, or you may feel intense and sometimes overwhelming grief.
No matter your situation, you might feel disappointed, hopeless, or scared to conceive again. You might experience anxiety, mood swings and irritability, and even depression.
Talking about your loss can help. Try turning to trusted friends and family members, social media groups, or a mental health professional. Miscarriage can also lead to clinical depression, similar to postpartum depression — so be sure to seek medical attention if you experience any symptoms.
The severity of your miscarriage symptoms will depend on how far along you are in your pregnancy and what type of miscarriage you have. Still, a miscarriage at any stage can be difficult because all bodies respond differently.
You may choose expectant management to let your body pass the tissue on its own, you might use medication that can speed up the process, or you may choose a surgical procedure called a dilation and curettage (D&C) to remove the contents of the uterus.
The bleeding that occurs with miscarriage can be different for everyone, too. In general, you can expect menstrual-like bleeding for about a week. After that, spotting can continue for several weeks — sometimes even until your next period. And when is that? Again, it varies: Your menstrual cycle can restart anywhere between 4 to 8 weeks after the miscarriage.
When to seek medical help
If you suspect you’re having a miscarriage, you should always consult with your doctor. Your provider will also stay in touch with you throughout the recovery process.
Depending on the timing of your miscarriage and how it’s managed, it may be 2 or 3 weeks before you’re feeling like yourself again physically. In some cases, your doctor may order an ultrasound to confirm that your uterus is clear of retained tissue.
For some people, the emotional pain of a miscarriage can last much longer. It’s important to remember that the stage of your pregnancy when you miscarried doesn’t matter: You experienced a loss, and loss naturally comes with feelings of grief.
Sometimes that grief can get too big for you to handle on your own. As with postpartum depression after a birth, symptoms of depression can develop after a miscarriage. In fact, according to a 2015 journal article, nearly 20 percent of women report symptoms of depression and/or anxiety after miscarriage.
If you think you might be depressed or are simply struggling to manage your emotional recovery after miscarriage, don’t be afraid or ashamed to reach out for support. A licensed mental health professional can help you process your loss and begin to heal.
You can also look for a miscarriage support group to connect with other people who have shared your experience. You can search or contact any of the following resources for local and online miscarriage support groups:
- Hope After Loss
- Share Pregnancy and Infant Loss Support
- Empty Cradle
- First Candle
- Empty Arms Bereavement Support
- The Compassionate Friends
- The Miscarriage Association (UK)
Miscarriage can be a difficult experience on your body, mind, and heart.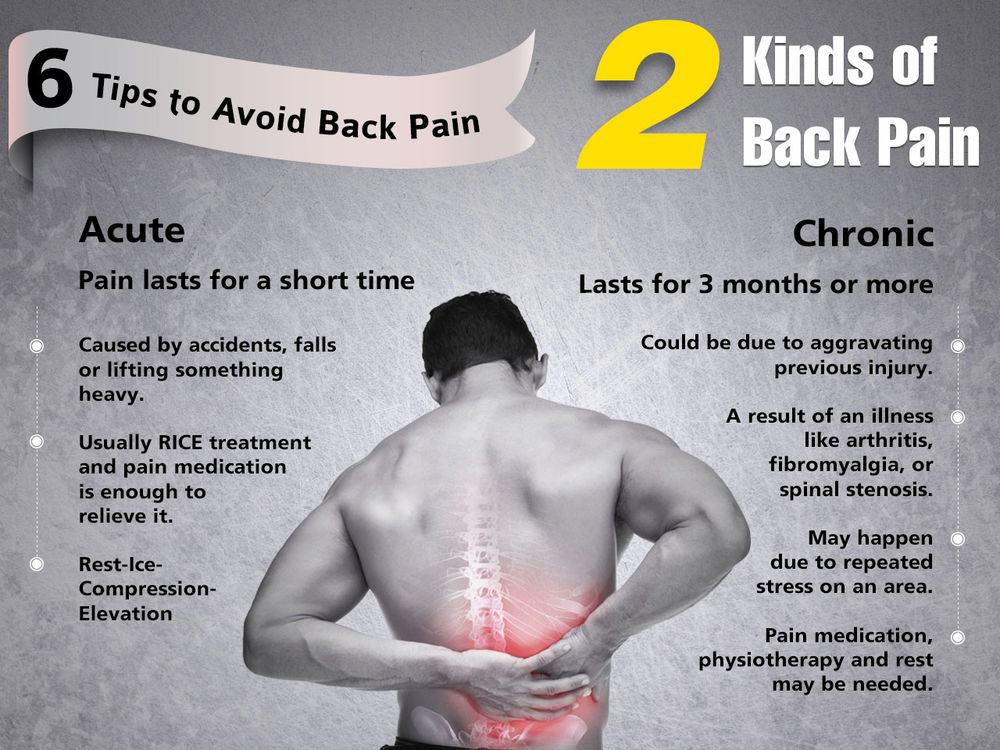 You can help ease physical symptoms with rest, fluids, OTC pain relievers — and stay in touch with your doctor if you have any complications.
You can help ease physical symptoms with rest, fluids, OTC pain relievers — and stay in touch with your doctor if you have any complications.
It’s also important to address the emotional pain of a miscarriage. Talking to a mental health professional or finding support from a local or online pregnancy loss group can help you take steps toward healing.
Miscarriage, symptoms - Health Clinic 365 Yekaterinburg
Causes of miscarriage
Questions to the doctor about miscarriage
Diagnosis of miscarriage
Treatment and prevention of miscarriage
According to statistics, 10 to 20% of all pregnancies end in miscarriage. However, the real numbers could be much higher, as a large number of miscarriages happen very early, and women are not even aware of their pregnancy. Most miscarriages happen due to abnormal development of the fetus. nine0003 Miscarriage is quite common, but this fact does not make things any easier. It is always difficult to cope with the realization that there was a pregnancy, but no child. Miscarriage symptoms . Most miscarriages occur before 12 weeks. Signs and symptoms of a miscarriage include: It is important to consider the fact that in early pregnancy, spotting or vaginal bleeding is quite common. In most cases, women who experience light bleeding during the first three months have an uneventful pregnancy thereafter. In some cases, even with heavy bleeding, the pregnancy does not end in a miscarriage. nine0003 Some women who have a miscarriage develop an infection in the uterus. This infection, also called septic miscarriage, can cause: When to see a doctor. Call your doctor if: You can put a piece of tissue to be isolated in a clean container and take it to your doctor for examination. It is unlikely that the study will give any accurate results, but if it is determined that the fragments of the excreted tissue are from the placenta, the doctor will be able to conclude that the symptoms that appear are not associated with the presence of a tubal (ectopic) pregnancy. nine0003 You can get more detailed information about miscarriage from the gynecologists of the Health 365 clinic in Yekaterinburg. Gynecologist, initial appointment 2300 i From the moment of conception, a woman's body is rebuilt. At the first appointment, the doctor will warn you about early symptoms that indicate a threatened miscarriage: Lower back pain may occur during the first trimester of pregnancy. It is often encountered by women in the later stages. Pulling the lower back during pregnancy can be due to various processes occurring in the body. Some of them create inconvenience, but do not pose a threat. Attachment of the ovum to the wall of the uterus occurs 5-7 days after fertilization, even before a woman notices a delay in menstruation and thinks about a possible pregnancy. The process may be accompanied by an increase in vaginal discharge. They are not white, but pink. Women often believe that menstruation begins. Due to the production of various hormones, a few days can pull the lower back. These sensations are caused by natural, not pathological changes in the body. They are harmless, do not require treatment and disappear after 5-6 days. After the attachment of the fetal egg in the uterus, the fetus begins to grow. He needs more nutrients and oxygen every day. To deliver them, the circulatory system begins to work differently, directing more blood to the uterus. Vessels from the pelvic area overflow, increase in volume and come into contact with the nerve endings in the lumbar region. There is a pulling pain. It is felt at 5-7 weeks of pregnancy. If the pain symptoms are not very pronounced, you can not worry. The body will rebuild, and the pain will pass without treatment. nine0003 During childbirth, the joints and ligaments in the spine and pelvis should be well stretched. The body prepares in advance for the upcoming work. He already at an early stage begins to produce the hormone relaxin, which softens the joints and ligaments. Due to a change in their density, it can pull the lower back. At the 9-10th week of pregnancy, the volume of the uterus already noticeably increases. At the end of the first and beginning of the second trimester, spontaneous uterine contractions may occur, resembling labor pains, but less intense. Drawing cramping pain is given in the lower back. They can periodically disturb 2-3 weeks. If there are no other dangerous symptoms, medication, restriction of motor activity is not required. Drawing back pain in pregnant women often occurs from natural causes. They do not pose a threat to the health of the expectant mother and the development of the fetus, do not require treatment. But it is necessary to tell the doctor about them in the antenatal clinic. He correlates them with other symptoms and will not miss the signs of an incipient miscarriage, other pathologies. Drawing pain in the lower back is often one of the signs of dangerous conditions: In case of missed pregnancy, threatened miscarriage, lower back pain is accompanied by bloody discharge from the vagina, cramping or constant aching pain in the lower abdomen. This is a dangerous condition. You need to immediately go to the hospital or call an ambulance. Do not refuse if the doctor suggests treatment in a hospital. To stop an incipient miscarriage, you need to administer drugs intravenously, limit physical activity, and constantly monitor the condition of the woman and fetus. nine0003 In case of miscarriage, examinations should be carried out to make sure that there are no particles of the fetus left in the uterus. Immunity in pregnant women is weakened. Hypothermia, malnutrition, increased stress can cause kidney disease. If the lower back is pulled during pregnancy on one side, on the right or on the left, check the functioning of the genitourinary system. Additional symptoms indicate problems with the kidneys: legs and arms swell, pressure and temperature rise, and pain occurs when urinating. Women with chronic kidney disease should be especially careful. They can worsen when the load on the diseased organ increases - in the second or third trimester, with a cold or eating salty, spicy, smoked, fatty foods. You cannot self-medicate. Taking the usual antibacterial drugs (Canephron, Levofloxacin, Furadonin) is undesirable for pregnant women. You need to see a nephrologist. Starting from 7-8 weeks, the hormone relaxin begins to be produced, softening the joints and ligaments. If before conception a woman suffered from osteochondrosis, scoliosis, kyphosis, an exacerbation of diseases is possible even in the first or second trimester. An additional risk factor is rapid weight gain. In women who have not previously suffered from osteochondrosis, it can develop in the later stages, when the spine is under a lot of stress due to a significant increase in body weight, a shift in the center of gravity, uterine pressure and softening of the joints and ligaments. The pain is pulling, exhausting, aggravated after a long stay in one position. With dystrophic tissue lesions, it can be felt on one side, left or right. Spinal problems can complicate childbirth. If you do not start treatment in a timely manner, do not engage in prevention, they will continue to progress after childbirth. If the production of the hormone relaxin is strongly activated, premature softening of the joints occurs, which can cause the pubic bones to diverge. This increases the risk of preterm birth. With the divergence of the pubic bones, the pain is shooting, sharp. She gives to the lower abdomen and lower back. There are swelling in the pubic area. To diagnose symphysitis, the doctor examines blood and urine tests, conducts an additional ultrasound examination, observes the dynamics of the development of the disease and decides on the possibility of natural childbirth or the need for a planned caesarean section. In the later stages, motor activity may be limited, strict bed rest is recommended. nine0003 Pregnancy increases the risk of complications from colds. Especially dangerous is the early period when the organs of the fetus are formed. A significant increase in temperature, infection, uncontrolled use of antibiotics can provoke serious pathologies. It is necessary to consult a doctor and start treatment at the first symptoms of a cold. Lower back pain and body aches can occur when the temperature rises. It passes if it is knocked down using traditional medicine recommended by a doctor. But if it hurts in the lower back on the right or left, the temperature rises to 39degrees, there was a strong cough, shortness of breath - pneumonia is possible. You need to call a doctor at home or an ambulance. If your lower back is pulling during pregnancy, do not take painkillers. If the pain is severe, but examinations have not shown dangerous pathologies, consult a doctor. After studying the causes and symptoms of pain, he will choose safe ways to alleviate the condition. In the first trimester, you need to be especially careful. A woman may still not know about pregnancy, but pain is already appearing. With a delay in menstruation, even for 2-3 days, you need to coordinate drug treatment with your doctor. The second trimester is the time when a woman intensively gains weight and the load on the musculoskeletal system increases, pressure on the internal organs. The doctor will advise you to wear a bandage for pregnant women and other non-drug ways to relieve and prevent pain. The third trimester - the body prepares for childbirth, the joints soften, the bones in the pelvic area diverge. If it pulls the lower back, the lower abdomen hurts, you need to lie down. If the pain intensifies, becomes cramping, childbirth may begin. If the period is less than 38 weeks, call the doctor who manages the pregnancy and describe the symptoms. nine0003 To reduce the risk of lower back pain, the development of diseases of the musculoskeletal system:  Try to deal with the situation psychologically and understand what could be causing the miscarriage, what increases the risk of it, and what type of treatment might be needed.
Try to deal with the situation psychologically and understand what could be causing the miscarriage, what increases the risk of it, and what type of treatment might be needed.
Prices
causes of pain in the early stages and in the second trimester
 The composition of the produced hormones changes, nutrients are distributed between the mother and the fetus. At an early stage, these changes are invisible to others. But the woman notices that menstruation did not begin at the appointed time. Taste preferences change, nausea appears in the morning, fatigue, drowsiness, irritability or unusual peace. If you notice signs of pregnancy, you need to see a doctor. A few days after the delay in menstruation, pregnancy can be confirmed by laboratory tests. The doctor will give advice on how to prevent the development of pathologies and bear a healthy child. nine0003
The composition of the produced hormones changes, nutrients are distributed between the mother and the fetus. At an early stage, these changes are invisible to others. But the woman notices that menstruation did not begin at the appointed time. Taste preferences change, nausea appears in the morning, fatigue, drowsiness, irritability or unusual peace. If you notice signs of pregnancy, you need to see a doctor. A few days after the delay in menstruation, pregnancy can be confirmed by laboratory tests. The doctor will give advice on how to prevent the development of pathologies and bear a healthy child. nine0003  It arises due to increased weight and a shift in the center of gravity. But in the first trimester, the weight and size of the abdomen change slightly. You need to analyze your condition and understand if there is a danger. nine0003
It arises due to increased weight and a shift in the center of gravity. But in the first trimester, the weight and size of the abdomen change slightly. You need to analyze your condition and understand if there is a danger. nine0003 Causes that do not cause concern
Attachment of the ovum to the uterus
 nine0003
nine0003 Changes in the circulatory system
Softening of the joints, ligaments
Uterine growth
 The woman feels that the lower abdomen has become more firm and convex. The growing uterus begins to come into contact with other organs. With increased sensitivity, its pressure can be felt at an early stage. But more often women experience discomfort, mild pressing back pain in the second trimester. nine0003
The woman feels that the lower abdomen has become more firm and convex. The growing uterus begins to come into contact with other organs. With increased sensitivity, its pressure can be felt at an early stage. But more often women experience discomfort, mild pressing back pain in the second trimester. nine0003 Braxton-Higgs contractions
 nine0003
nine0003 Dangerous conditions
Missed pregnancy, threatened miscarriage
 This can cause a life-threatening inflammatory process or further infertility. Requires the introduction of drugs that enhance uterine contraction, relieve inflammation, or surgical intervention.
This can cause a life-threatening inflammatory process or further infertility. Requires the introduction of drugs that enhance uterine contraction, relieve inflammation, or surgical intervention. Diseases of the genitourinary system
 He will prescribe a safe treatment. nine0003
He will prescribe a safe treatment. nine0003 Osteochondrosis
 nine0003
nine0003 Symphysitis
Colds
Prevention and treatment
 nine0003
nine0003 Prevention of pain in the lower back