Low blood pressure during pregnancy risks
Low Blood Pressure During Pregnancy: What You Should Know
Low Blood Pressure During Pregnancy: What You Should Know- Health Conditions
- Featured
- Breast Cancer
- IBD
- Migraine
- Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
- Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Type 2 Diabetes
- Articles
- Acid Reflux
- ADHD
- Allergies
- Alzheimer's & Dementia
- Bipolar Disorder
- Cancer
- Crohn's Disease
- Chronic Pain
- Cold & Flu
- COPD
- Depression
- Fibromyalgia
- Heart Disease
- High Cholesterol
- HIV
- Hypertension
- IPF
- Osteoarthritis
- Psoriasis
- Skin Disorders and Care
- STDs
- Featured
- Discover
- Wellness Topics
- Nutrition
- Fitness
- Skin Care
- Sexual Health
- Women's Health
- Mental Well-Being
- Sleep
- Product Reviews
- Vitamins & Supplements
- Sleep
- Mental Health
- Nutrition
- At-Home Testing
- CBD
- Men’s Health
- Original Series
- Fresh Food Fast
- Diagnosis Diaries
- You’re Not Alone
- Present Tense
- Video Series
- Youth in Focus
- Healthy Harvest
- No More Silence
- Future of Health
- Wellness Topics
- Plan
- Health Challenges
- Mindful Eating
- Sugar Savvy
- Move Your Body
- Gut Health
- Mood Foods
- Align Your Spine
- Find Care
- Primary Care
- Mental Health
- OB-GYN
- Dermatologists
- Neurologists
- Cardiologists
- Orthopedists
- Lifestyle Quizzes
- Weight Management
- Am I Depressed? A Quiz for Teens
- Are You a Workaholic?
- How Well Do You Sleep?
- Tools & Resources
- Health News
- Find a Diet
- Find Healthy Snacks
- Drugs A-Z
- Health A-Z
- Health Challenges
- Connect
- Breast Cancer
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease
- Psoriatic Arthritis
- Migraine
- Multiple Sclerosis
- Psoriasis
Medically reviewed by Debra Rose Wilson, Ph. D., MSN, R.N., IBCLC, AHN-BC, CHT — By Julie Marks on June 16, 2019
Overview
Having low blood pressure during pregnancy is common. Most of the time, this condition won’t cause major problems, and blood pressure will return to prepregnancy levels after you give birth. In some cases, however, very low blood pressure can be dangerous for mom and baby.
Effects of pregnancy on blood pressure
If you’re pregnant, your doctor or nurse will likely check your blood pressure at every prenatal visit.
Blood pressure is the force of your blood as it pushes against artery walls while your heart pumps. It can go up or down at certain times of the day, and it may change if you’re feeling excited or nervous.
Your blood pressure reading reveals important information about the health of you and your baby. It can also be a way for your doctor to determine if you have another condition that needs to be checked out, like preeclampsia.
Changes that happen in your body during pregnancy can affect your blood pressure.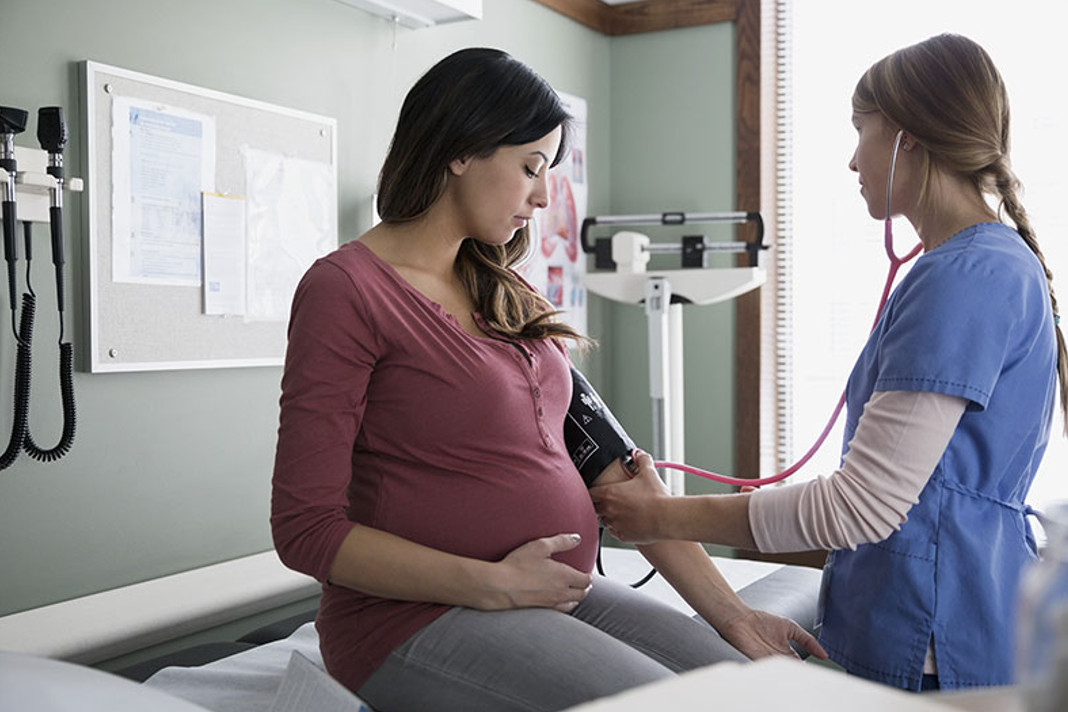 When carrying a baby, your circulatory system expands quickly, which may cause a drop in blood pressure.
When carrying a baby, your circulatory system expands quickly, which may cause a drop in blood pressure.
It’s common for your blood pressure to lower in the first 24 weeks of pregnancy.
Other factors that can contribute to low blood pressure include:
- dehydration
- anemia
- internal bleeding
- prolonged bed rest
- certain medications
- heart conditions
- endocrine disorders
- kidney disorders
- infections
- nutritional deficiencies
- allergic reaction
What’s considered low?
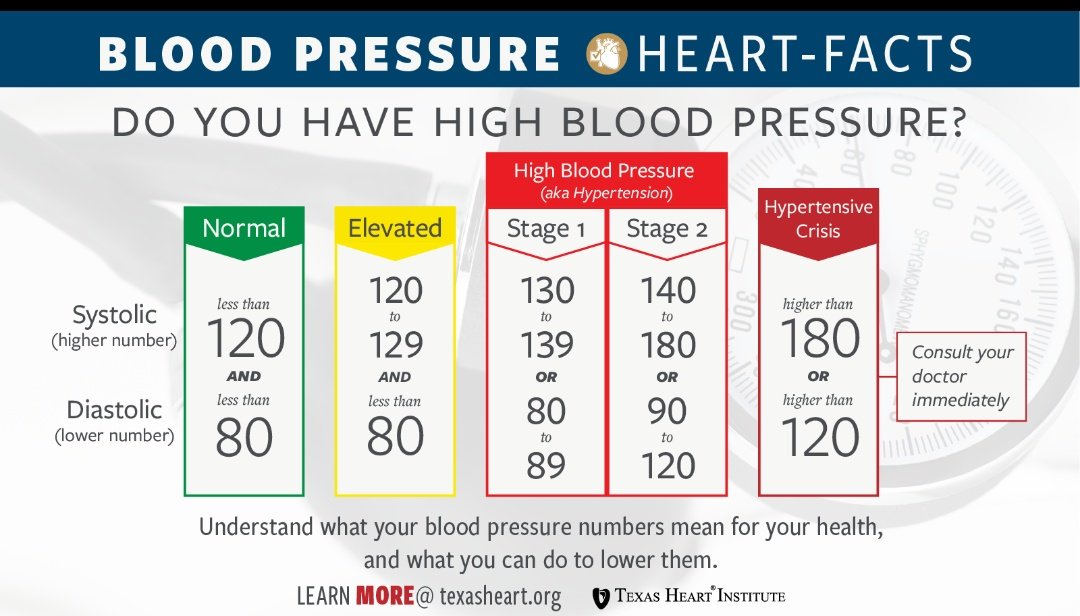
Current guidelines define a normal blood pressure reading as less than 120 mm Hg systolic (the top number) over 80 mm Hg diastolic (the bottom number).
Doctors typically determine you have low blood pressure if your reading is below 90/60 mm Hg.
Some people have low blood pressure their whole lives and have no signs of it.
Dangers of low blood pressure during pregnancy
Generally, low blood pressure during pregnancy isn’t a cause for concern unless you experience symptoms. Big drops may be the sign of a serious, or even life-threatening, problem.
Big drops may be the sign of a serious, or even life-threatening, problem.
Extremely low blood pressure can lead to falls, organ damage, or shock.
Low blood pressure may also be a sign of ectopic pregnancy, which happens when a fertilized egg implants outside of a woman’s uterus.
Does blood pressure affect the baby?
A large amount of research has been conducted on how high blood pressure during pregnancy affects babies, but data on the effects of low blood pressure is limited.
Some studies have suggested that low blood pressure during pregnancy may lead to problems, such as stillbirth and low birth weight. However, other research has shown additional risk factors are to blame for these outcomes.
More research is needed to understand the impact of low prenatal blood pressure on the health of a baby.
Symptoms of low blood pressure
Signs and symptoms of low blood pressure may include:
- dizziness
- lightheadedness, especially when standing or sitting up
- fainting
- nausea
- tiredness
- blurred vision
- unusual thirst
- clammy, pale, or cold skin
- rapid or shallow breathing
- lack of concentration
Call your healthcare provider if you develop any symptoms of low blood pressure during pregnancy.
Diagnosis
Low blood pressure is diagnosed with a simple test.
Your doctor or nurse will place an inflatable cuff around your arm and use a pressure-measuring gauge to calculate your blood pressure.
This test can be performed in your doctor’s office, but you can also buy your own device and measure your blood pressure at home.
If you have low blood pressure throughout your pregnancy, your doctor might order more tests to rule out other conditions.
Treatment
Generally, you won’t require treatment for low blood pressure during pregnancy.
Doctors typically don’t recommend medications for pregnant women unless symptoms are serious or complications are likely.
Your blood pressure will probably start to rise on its own during your third trimester.
Self-care for low blood pressure during pregnancy
If you do experience symptoms of low blood pressure, such as dizziness, you might want to try the following:
- Avoid getting up quickly when you’re seated or lying down.

- Don’t stand for long periods of time.
- Eat small meals throughout the day.
- Don’t take very hot baths or showers.
- Drink more water.
- Wear loose clothing.
It’s also a good idea to eat a healthy diet and take your prenatal supplements during your pregnancy to prevent symptoms of low blood pressure.
Postpartum blood pressure
Your blood pressure should return to your pre-pregnancy levels after you give birth.
Medical professionals will check your blood pressure often in the hours and days after you deliver your baby. Also, your doctor will probably check your blood pressure at your postnatal office visits.
Outlook
Low blood pressure during pregnancy is normal. The condition usually isn’t something to be concerned about unless you have symptoms.
If you do experience bothersome symptoms of low blood pressure, let your doctor know.
For more pregnancy guidance and weekly tips tailored to your due date, sign up for our I’m Expecting newsletter.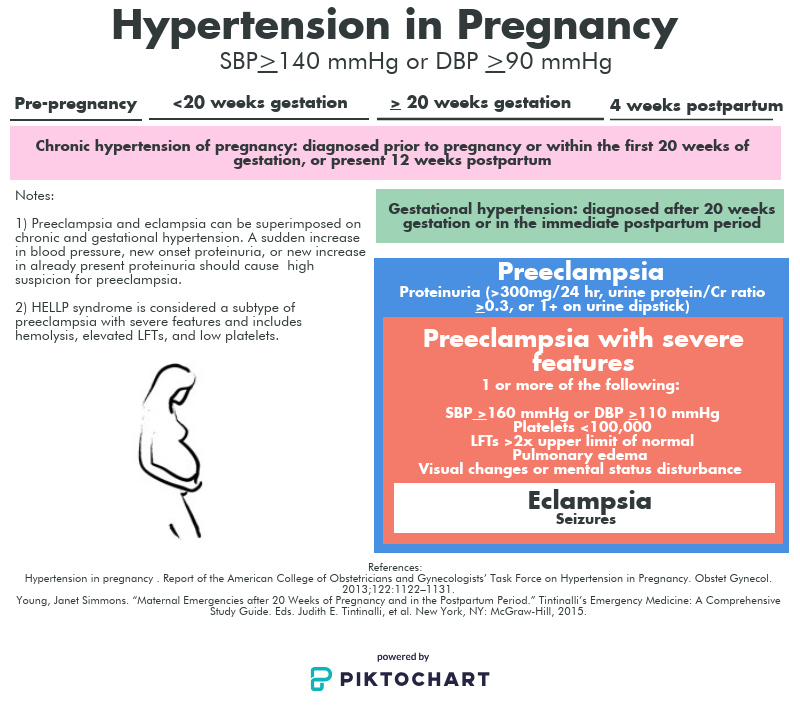
Last medically reviewed on June 17, 2019
- Parenthood
- Pregnancy
- Pregnancy Health
How we reviewed this article:
Healthline has strict sourcing guidelines and relies on peer-reviewed studies, academic research institutions, and medical associations. We avoid using tertiary references. You can learn more about how we ensure our content is accurate and current by reading our editorial policy.
- Chen A, et al. (2007). Does low maternal blood pressure during pregnancy increase the risk of perinatal death?
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2225167/ - Hypotension. (n.d.).
nhlbi.nih.gov/health/health-topics/topics/hyp - Low blood pressure - when blood pressure is too low. (2016).
heart.org/en/health-topics/high-blood-pressure/the-facts-about-high-blood-pressure/low-blood-pressure-when-blood-pressure-is-too-low - Mayo Clinic Staff.
 (2018). High blood pressure (hypertension).
(2018). High blood pressure (hypertension).
mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/high-blood-pressure/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20373417 - Mayo Clinic Staff. (2018). Low blood pressure (hypotension).
mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/low-blood-pressure/symptoms-causes/syc-20355465 - Steer P, et al. (2004). Maternal blood pressure in pregnancy, birth weight, and perinatal mortality in first births: Prospective study. DOI:
10.1136/bmj.38258.566262.7C - Understanding blood pressure readings. (2017).
heart.org/en/health-topics/high-blood-pressure/understanding-blood-pressure-readings - Warland J, et al. (2008). Maternal blood pressure in pregnancy and stillbirth: A case-control study of third-trimester stillbirth. DOI:
10.1055/s-2008-1075031 - Zhang J, et al. (2001). Low blood pressure during pregnancy and poor perinatal outcomes: An obstetric paradox. DOI:
10.1093/aje/153.7.642
Our experts continually monitor the health and wellness space, and we update our articles when new information becomes available.
Current Version
Jun 17, 2019
Written By
Julie Marks
Edited By
Ruby Thompson
Medically Reviewed By
Debra Rose Wilson, PhD, MSN, RN, IBCLC, AHN-BC, CHT
Share this article
Medically reviewed by Debra Rose Wilson, Ph.D., MSN, R.N., IBCLC, AHN-BC, CHT — By Julie Marks on June 16, 2019
related stories
Abnormal Blood Pressure During Pregnancy
What Causes Dizziness in Pregnancy?
Why Does My Blood Pressure Fluctuate?
What's Causing Your Pregnancy Headaches & Dizziness?
Why Twins Don’t Have Identical Fingerprints
Read this next
Abnormal Blood Pressure During Pregnancy
Medically reviewed by Judith Marcin, M.D.
Learn how pregnancy affects blood pressure and what you can do to prevent abnormal blood pressure levels during pregnancy.
READ MORE
What Causes Dizziness in Pregnancy?
Medically reviewed by Valinda Riggins Nwadike, MD, MPH
Dizziness is a common symptom of pregnancy, and it may occur for a variety of reasons.
 You should always discuss this symptom with your doctor or…
You should always discuss this symptom with your doctor or…READ MORE
Why Does My Blood Pressure Fluctuate?
Medically reviewed by Deborah Weatherspoon, Ph.D., MSN
Find out when fluctuating blood pressure is normal and when it may signal an underlying condition.
READ MORE
What's Causing Your Pregnancy Headaches & Dizziness?
Medically reviewed by Joan K. Lingen, MD
Getting a headache every once in a while during the first few months of pregnancy is common and is usually caused by altered hormone levels and…
READ MORE
Why Twins Don’t Have Identical Fingerprints
Medically reviewed by Alana Biggers, M.D., MPH
Identical twins are the same in so many ways, but does that include having the same fingerprints? There's conflicting information out there so we look…
READ MORE
Doula vs.
 Midwife: What’s the Difference?
Midwife: What’s the Difference?Medically reviewed by Meredith Wallis, MS, APRN, CNM, IBCLC
What is the difference between a doula and a midwife? Do I need to choose? Read on to learn more about the similarities and differences.
READ MORE
Your Guide to a Pregnancy-Safe Skin Care Routine
When you're expecting, pregnancy-safe skin care can help ensure the health of you and your baby. We'll tell you what to avoid — and some good…
READ MORE
Can Ectopic Pregnancy Be Diagnosed With Ultrasound?
Medically reviewed by Valinda Riggins Nwadike, MD, MPH
Ectopic pregnancy is a serious condition that requires accurate and swift diagnosis. Ultrasound for ectopic pregnancy diagnosis is just one tool your…
READ MORE
Is It Safe to Consume Flaxseeds During Pregnancy?
Given the inconclusive and conflicting stances about eating flaxseeds during pregnancy, it might be better to err on the side of caution.

READ MORE
Pregnancy After Miscarriage: Answers to Your Questions
Medically reviewed by Amanda Kallen, MD
Getting pregnant after a miscarriage can be an emotional experience, filled with joy but also anxiety and guilt. Learn more about pregnancy after…
READ MORE
Low blood pressure during pregnancy
Skip to main content
Back
Many women experience low blood pressure, defined as below 90/60, while they’re expecting a baby. This is not usually a problem, doesn’t normally require medication, and will start returning to its previous level during the third trimester. Your doctor will monitor your blood pressure throughout the pregnancy.
Low blood pressure during pregnancy happens because your body secretes hormones, and progesterone in particular, which help to relax the walls of your blood vessels and increase the flow of blood to you and your baby.
Occasionally, low blood pressure may be indicative of some other problem. It may be the result of an ectopic pregnancy, in which a fertilised egg becomes implanted outside your uterus. And if it’s very low, it may cause falls, or shock, in which your brain and other vital organs don’t get enough blood to work properly.
Low blood pressure has a variety of symptoms. If you experience any of these, you should mention them to your doctor.
- Dizziness
- Nausea
- Weakness
- Fatigue and sleepiness
- Fainting
- Rapid heartbeat
- Confusion and inability to concentrate
- Blurry vision
- Pale, clammy skin
Can low blood pressure harm your baby?
We know a lot less about the effects of low blood pressure on babies than the effects of high pressure. Some research suggests that it may lead to stillbirth and low birth weight, but this correlation is difficult to establish because there are so many other variables and risk factors involved during pregnancy. In the vast majority of cases, low blood pressure at this time is nothing to worry about.
In the vast majority of cases, low blood pressure at this time is nothing to worry about.
Is there anything you can do to deal with low blood pressure when you’re pregnant?
Although medication is not normally needed when this happens, there are some simple changes you can make that may reduce the likelihood of its happening.
Take it easy. Try to slow down, avoid making sudden movements, and don’t stand up too quickly. If you do feel faint or dizzy, lie down on your left side, which may help to increase the blood flow to your heart.
Drink lots of water. As well as preventing dehydration, this increases your blood volume, and thus your blood pressure.
Eat a healthy diet. Your doctor may also recommend that you increase your salt intake, though it’s important not to overdo this.
References:
www.bounty.com/pregnancy-and-birth/pregnancy/pregnancy-other-conditions/low-blood-pressure-in-pregnancy
www.healthline. com/health/pregnancy/low-blood-pressure-during-pregnancy#risks
com/health/pregnancy/low-blood-pressure-during-pregnancy#risks
www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/320303.php
Your browser's JavaScript functionality is turned off. Please enable JavaScript for full functionality of this site.
Pregnancy and low blood pressure | Mamovedia
Every pregnant woman who has already registered with the antenatal clinic knows that pressure control is a mandatory procedure during each visit to the doctor. Measuring the pressure of a pregnant woman is very important, since any deviation from the normal state can cause irreparable harm to the health of the unborn baby.
Most often, women have low blood pressure or hypotension. In the event that a woman had low blood pressure even before pregnancy, and at the same time she feels good while carrying a baby, then you should not worry. In addition, many women in the early stages of pregnancy experience a decrease in pressure and this is due to the action of hormones on the body.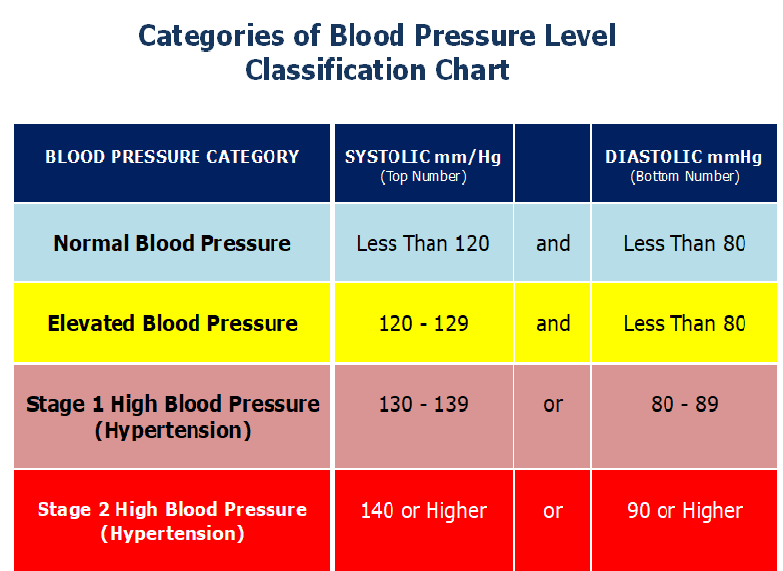 nine0003
nine0003
Every woman should know that it often happens that a decrease in pressure is observed against the background of anemia, therefore, if low blood pressure is detected, a pregnant woman needs to check the level of hemoglobin in the blood.
A dangerous condition is one in which, against the background of low blood pressure, a woman experiences frequent dizziness, lethargy, weakness, and nausea. In this case, it is not worth the risk, but you need to urgently consult a doctor.
The danger of low blood pressure during pregnancy lies in the fact that there is a deterioration in blood flow to certain body structures, such as the placenta and the brain. In this case, a woman has a fairly high risk of miscarriage. nine0003
If a pregnant woman feels dizzy, weak, weak, she should lie down and listen to her feelings. In this case, it is necessary to remove the pillow from under the head and put it under the legs. Thus, the blood flow to the head will increase somewhat. In addition, sweet tea can help.
In addition, sweet tea can help.
During pregnancy, a woman should not go hungry. Even if the expectant mother has toxicosis, it is still necessary to eat, but in very small portions.
Walking and reasonable exercise are excellent remedies for low blood pressure in pregnant women. nine0003
What can cause low blood pressure during pregnancy? As noted earlier, one of the causes of low blood pressure is a sharp change in the hormonal background in the body of a pregnant woman. In addition, a decrease in pressure can be caused by various diseases, for example, stomach ulcers, infections, allergies, diseases of the adrenal glands and the thyroid gland.
The main symptoms of low blood pressure in pregnant women are nausea, general weakness, drowsiness, fatigue, frequent dizziness, frequent darkening of the eyes, ringing and noise in the ears, fainting, a feeling of lack of air. nine0003
Of course, each woman has her own norm of blood pressure, which is in the range from 90 to 60 to 140 to 90. Normal is the pressure at which the pregnant woman feels good and does not experience any discomfort.
Normal is the pressure at which the pregnant woman feels good and does not experience any discomfort.
Some women mistakenly believe that low blood pressure cannot harm the baby. But in vain, because low pressure can provoke a violation of the full delivery of all the necessary nutrients and oxygen to the fetus.
A pregnant woman may experience placental insufficiency if her blood pressure is low. That is why, during pregnancy, a sharp decrease in pressure should not be allowed in order not to harm the health of the unborn baby.
In no case should you take various pharmaceutical preparations to normalize blood pressure without first consulting a doctor. This is due to the fact that some of the components that are contained in such preparations can not only increase pressure, but also the tone of the uterus. nine0003
The best way to normalize blood pressure during pregnancy is to use safer methods such as drinking sweet black tea or tomato juice. In addition, parsley greens well raises the pressure.
As for coffee, it is better to refrain from drinking it while carrying a baby.
To normalize blood pressure during pregnancy, a rational daily routine, high-quality and balanced nutrition, good sleep, and walks in the fresh air are best suited. nine0003
A pregnant woman should see a doctor if she experiences fainting, dizziness, chronic fatigue, increased thirst or feeling short of breath.
Pregnancy and blood pressure
Pressure and pregnancy
Pregnancy is a period when a woman's body uses all its potential, all its reserves to provide everything necessary for the full bearing of a child.
Blood pressure is one of the main parameters of blood flow intensity in the body. During the period of bearing a baby, a woman’s body is faced with the need to provide oxygen and nutrition not only for herself, but also for her unborn child. A change in the level of pressure during pregnancy becomes an indicator of disturbances in the functioning of the body that threaten the health of a woman and a child, and can also complicate the course of childbirth.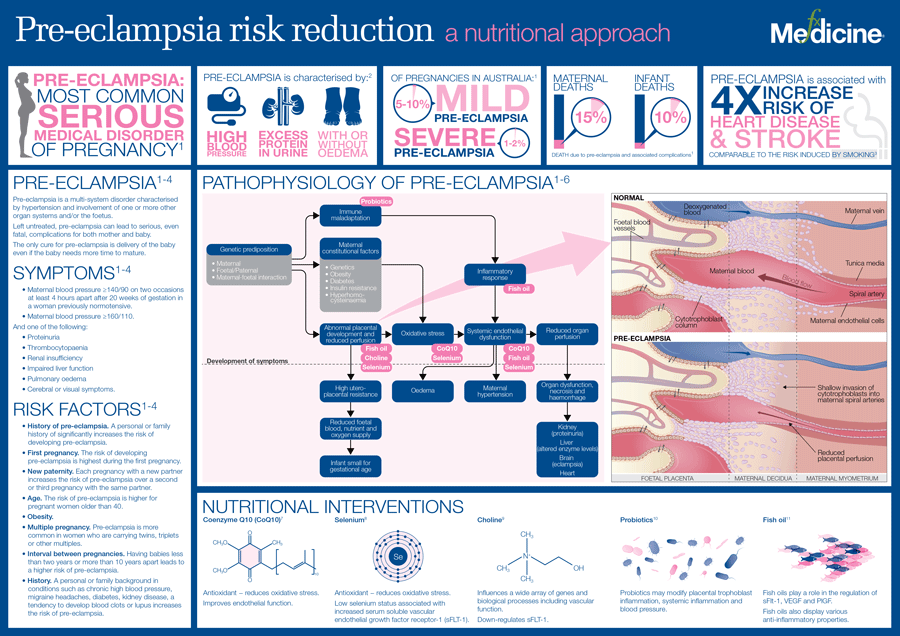 nine0003
nine0003
When blood pressure is measured
At each appointment with an obstetrician-gynecologist or therapist in the antenatal clinic of the expectant mother, blood pressure must be measured. But visits to the doctor's office should not be limited. It is necessary to independently measure this indicator in the morning and in the evening, so that the results can be compared, they must be recorded daily in a special notebook. Particular attention to their pressure should be shown by those women who previously had toxicosis of pregnancy, miscarriages, miscarriages. Women with hypertension, overweight, neurocircular and vegetovascular dystonia, diseases of the kidneys, heart, blood vessels should be on a special account, and measure pressure as often as recommended by the doctor. nine0003
nine0003
The hourly measurement of blood pressure in at-risk pregnant women is called 24-hour monitoring. It is done three times during the entire period of pregnancy. The first time - at the very beginning of pregnancy, to identify a woman's tendency to hypertension, the second time - at 24-28 weeks of pregnancy, to identify a predisposition to preeclampsia or late toxicosis of pregnant women, the third time - before childbirth, to determine the degree of risk to the woman and the fetus , as well as to resolve the issue of the method of obstetrics. nine0003
If there are problems with pressure in a pregnant woman, then it is necessary to visit a cardiologist and a therapist who can advise what needs to be done to solve the problem of pressure during pregnancy.
Types of blood pressure monitors
There are two types of blood pressure monitors (blood pressure monitor) - mechanical and electronic.
- Mechanical blood pressure monitor used by physicians.
 It gives the most accurate results. You can learn how to use a mechanical tonometer at home. However, taking blood pressure on your own is very difficult, so if you want to use this type of blood pressure monitor, you will need an assistant. nine0061
It gives the most accurate results. You can learn how to use a mechanical tonometer at home. However, taking blood pressure on your own is very difficult, so if you want to use this type of blood pressure monitor, you will need an assistant. nine0061 - Electronic blood pressure monitor is easier to use. It is enough to put the cuff on your arm and press the button. The device itself will do the rest, and you will only have to read the results on the electronic scoreboard. An electronic tonometer shows the value of blood pressure and pulse, memorizing the indicators. There are blood pressure monitors, the cuff of which can be worn on the shoulder, on the wrist and even on the finger. For the home, the most suitable device is the cuff of which is worn on the shoulder. Wrist or finger gauges can be used to measure blood pressure at work or while traveling. nine0061
Correct measurement of blood pressure
Do not immediately panic about high or low blood pressure during pregnancy, you need to make sure that the measurement is correct.
There are several important rules for the correct determination of blood pressure:
- Before measuring, sit down and rest for a couple of minutes, think about something pleasant. Stress is one of the factors in the short-term increase in pressure.
- Place the cuff on your bare arm or thin fabric. It must be sized. nine0061
- Measure pressure on both arms.
- Never round the received numbers and write them down.
- It is not recommended to determine the level of blood pressure after a meal or after exercise.
Blood pressure during pregnancy: norm and deviations
Blood pressure is the pressure force of blood flow on the wall of blood vessels. It is measured in millimeters of mercury (mm Hg) and is written in two numbers separated by a slash. nine0003
The first digit shows the pressure at the moment of maximum contraction of the heart (systolic blood pressure), and the second - at the time of its complete relaxation (diastolic blood pressure). If blood pressure is normal, we can safely say that the mother’s cardiovascular system is doing its job, which means that all organs receive a sufficient amount of oxygen and nutrients brought with the bloodstream.
If blood pressure is normal, we can safely say that the mother’s cardiovascular system is doing its job, which means that all organs receive a sufficient amount of oxygen and nutrients brought with the bloodstream.
Outside of pregnancy, normal blood pressure ranges from 100/60 to 130/80 mmHg. Art. During pregnancy, the pressure may differ slightly from the original: if it is 10% lower or higher than usual, then such changes are still within the normal range. If the pressure is lower or higher than usual by 15–20% or more, then we are dealing with arterial hypotension (low blood pressure) or arterial hypertension (high blood pressure). It is desirable for a woman to know her usual level of pressure, which was before pregnancy, so that the doctor can draw the right conclusions. nine0003
1.1 What is the danger of changes in blood pressure
During pregnancy, nutrients and oxygen are constantly supplied to the fetus through the vasculature of the placenta, and the products of its vital activity are returned to the mother.
This exchange is only possible at an optimum pressure level. Changes in blood pressure in one direction or the other can have adverse effects.
Under reduced pressure, transport deteriorates and the amount of substances needed by the child decreases, which can lead to fetal growth retardation syndrome. And a significant increase in blood pressure can cause damage to microvessels, foci of hemorrhages are formed, which can lead to placental abruption. That is why during pregnancy it is so important to control blood pressure and keep it at an optimal level. nine0003
Normal blood pressure during pregnancy
The norms of blood pressure accepted in general medicine range from 100/60 to 120/80 mm Hg. But during pregnancy, these indicators may change somewhat. Usually in the early stages (the entire 1st trimester and up to 20 weeks), these numbers slightly decrease, which is associated with a change in the hormonal background of the whole organism and a restructuring of metabolic processes.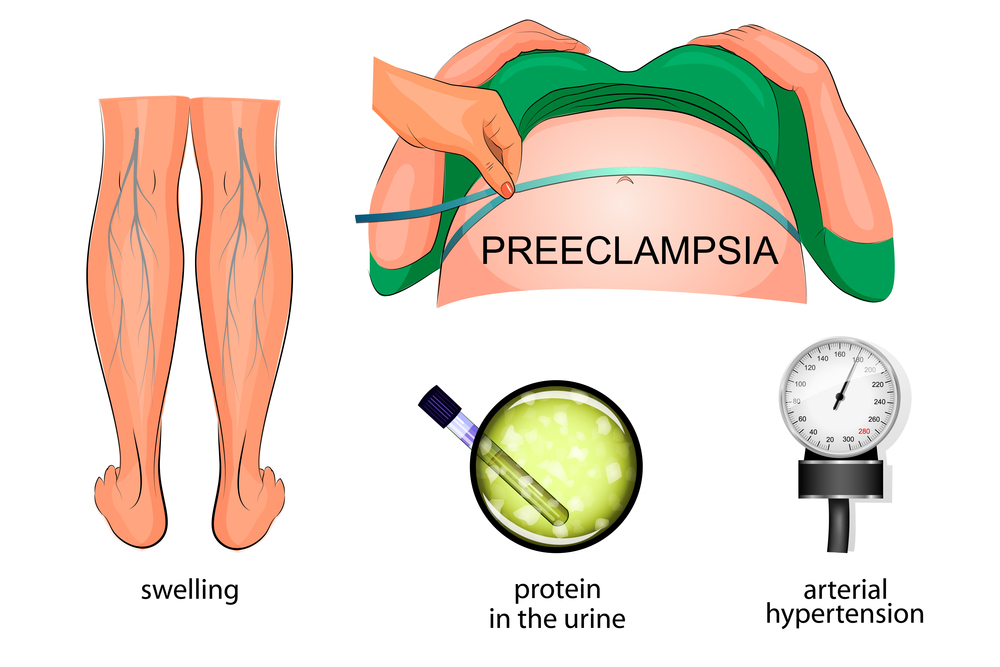
Later, as the fetus grows and develops more intense blood flow to feed it, the pressure may increase relative to "non-pregnant" values. Because of this, the average norms for expectant mothers lie in a wider range - from 105/60 to 139/89 mmHg
Significant deviations from this range upwards are called gestational hypertension, and downwards are called hypotension.
Low blood pressure during pregnancy or hypotension
In the first months of pregnancy, the hormonal background of the expectant mother undergoes significant changes, works with a great load, creating a favorable background for the development of the child, and these changes are often accompanied by a decrease in blood pressure, hypotension.
1.1.1 Possible causes of hypotension
Sometimes it is impossible to determine the cause that provoked the appearance of such a disorder, but the following may play a role in its development:
- Hormonal changes;
- NDC for hypotonic type;
- Infectious diseases;
- Liver pathology;
- Taking certain medications;
- Features of woman's emotionality.
Pregnancy hypotension is often not perceived as a serious threat to the health and progress of pregnancy. However, it can be a serious pathogenic factor that provokes various disorders of the course of pregnancy:
- Termination of pregnancy
- Fetal growth retardation
- Oxygen starvation baby
- Weak labor activity
- Possible bleeding after separation of the placenta
- Relaxation of the uterus after childbirth and rebleeding
1.1.2 Main symptoms of hypotension:
- Nausea, vomiting
- Headache
- Tinnitus
- Shortness of breath
- Dizziness
- Increased fatigue
- Drowsiness
- Pale skin
- Increased perspiration
- Loss of consciousness
1.1.3 How to increase blood pressure or what to do with low blood pressure
As a general rule, women with low blood pressure are not hospitalized unless there is a risk to the baby. Expectant mothers are observed by an obstetrician-gynecologist, a therapist and, if necessary, a cardiologist. Most often, in the third trimester, the pressure returns to normal. nine0003
Expectant mothers are observed by an obstetrician-gynecologist, a therapist and, if necessary, a cardiologist. Most often, in the third trimester, the pressure returns to normal. nine0003
Pregnant women should follow these guidelines:
- Get at least 8 hours of sleep (optimally 9-10 hours) and rest during the day if possible.
- Spend more time outdoors (at least 2 hours a day).
- Food should be taken in small portions, but throughout the day.
- Moderate physical activity recommended - do prenatal gymnastics; if possible, swim. nine0061
- Useful water procedures - shower, douche, contrast foot baths, as well as massage; physiotherapy (electrosleep, salt-coniferous and mineral baths) and acupuncture are successfully used for treatment.
- If necessary, doctors can prescribe drug therapy: usually, pregnant women are prescribed herbal preparations that increase the tone of the autonomic nervous system, such as extracts of eleutherococcus, radiols, tinctures of magnolia vine, aralia, zamaniha in combination with sedatives (valerian, motherwort), as well as drugs based on caffeine.
 nine0061
nine0061
If a pregnant woman has lost consciousness due to a sudden drop in blood pressure, the first thing to do is to lay her horizontally on her side and call an ambulance. Then open the door or window, unfasten the collar, give a sniff of ammonia. You can massage the area between the nose and lip or act on the fingertips on the hands.
High blood pressure during pregnancy or hypertension
Arterial hypertension is a disease characterized by a persistent increase in blood pressure. The changes that occur in the body during pregnancy predispose to the development of hypertension and therefore pregnant women are at a higher risk of developing hypertension than the general population. Arterial hypertension is a risk factor for various complications of pregnancy and ranks second in the list of causes of maternal death. At the same time, the diagnosis and treatment of arterial hypertension in pregnant women requires a special approach. nine0003
If before pregnancy you noted that your blood pressure was higher than normal, took pills, visited the appropriate doctors, be prepared that this problem will come up now. And, most likely, it will manifest itself with greater force.
And, most likely, it will manifest itself with greater force.
Remember: now the situation is completely different, you do not need to take the same pills as before pregnancy.
Forms of arterial hypertension during pregnancy
Arterial hypertension of pregnancy is an increase in blood pressure during pregnancy. It is regarded as a persistent increase in systolic blood pressure above 140 mm Hg. and diastolic blood pressure above 90 mmHg in women with normal blood pressure before pregnancy. Women with such an increase in pressure require close medical supervision.
There are several types of arterial hypertension during pregnancy:
- Chronic hypertension is characterized by the presence of high blood pressure before pregnancy and its persistence after pregnancy.
- Arterial hypertension of pregnancy is a persistent increase in blood pressure that develops after the 20th week of pregnancy, which disappears at the end of pregnancy. nine0061
- Pre-eclampsia/eclampsia is a severe impairment of the cardiovascular system and kidneys during pregnancy, which includes: hypertension and impaired renal function.

In pregnant women, arterial hypertension occurs with a frequency of 4-8%, which is a very high figure, especially if you take into account the young age of most expectant mothers. During pregnancy, the woman's body adapts to new conditions of functioning, which include ensuring the life and development of the fetus. On the part of the cardiovascular system in the body of a pregnant woman, the following changes occur:
- An increase in the volume of circulating blood and the appearance of a placental circulatory system is necessary for the nutrition and development of the child. In pregnant women, the volume of circulating blood increases by 25-30%, which, in addition to ensuring the nutrition of the child, allows women to lose part of the blood during childbirth, without significant damage to health.
- Increased heart rate.
- An increase in intra-abdominal pressure, an increase in the diaphragm and a change in the position of the heart in the chest due to a significant increase in the size of the uterus.
 nine0061
nine0061 - Gradual weight gain in a pregnant woman.
Possible other causes of high blood pressure
- Exercise
- Drinking strong tea or coffee
- Chronic stress, fatigue, lack of sleep, emotional stress
- Smoking, alcohol abuse
- Unbalanced diet, lack of vitamins and minerals
- Obesity, overweight
- Multiple pregnancy
- Lack of physical activity
- Diseases of the thyroid gland
- Diseases of the adrenal glands
- Diabetes mellitus
- Head, brain and spinal cord injuries
- Encephalitis
- Myelitis
- Diseases of the heart and blood vessels
- Renal dysfunction
- Hereditary predisposition
Main symptoms of hypertension:
- Headache
- Nausea, vomiting
- Dizziness, weakness, impotence
- Redness of the skin of the hands and face
- Noise or ringing in the ears
- Visual impairment
- Edema
- Urinary protein excretion
- Convulsions
High blood pressure can cause complications such as retinal detachment or retinal haemorrhage, which can lead to partial or complete loss of vision. nine0003
nine0003
If blood pressure began to rise in the second or third trimester of pregnancy, then we are probably dealing with a serious complication of pregnancy - preeclampsia.
Preeclampsia is a special condition that occurs only during pregnancy and ends with its completion. The manifestations of preeclampsia are varied, but the classic symptoms are:
- arterial hypertension
- edema
- proteinuria (protein in urine)
With preeclampsia, there is a violation of microcirculation in all vital organs: the blood supply to the brain worsens, kidney failure develops, the blood becomes viscous, and the resulting microthrombi disrupt the work of all organs and systems. Of particular danger is such damage to the vessels of the placenta and the brain. The most severe manifestation of preeclampsia - eclampsia - convulsive seizures, ending in a cerebral coma.
But preeclampsia often begins with a pathological increase in body weight. Expectant mothers often wonder why this doctor pays such attention to weight. Well, think about it, added a couple of extra pounds. nine0003
Expectant mothers often wonder why this doctor pays such attention to weight. Well, think about it, added a couple of extra pounds. nine0003
But after all, such an increase is due to fluid retention in the body, or the so-called latent edema.
And if treatment is not started in time, all manifestations of preeclampsia will not be long in coming. If there was an increase in blood pressure before the onset of pregnancy, then its successful course is possible only with good preparation and the correct selection of drugs that reduce pressure. With uncomplicated hypertension and a slight increase in pressure, only non-drug measures are sufficient. nine0003
More about preeclampsia
Treatment and prevention of arterial hypertension during pregnancy
Treatment of arterial hypertension during pregnancy is a complex and responsible task. Therefore, the basis of any type of treatment should be close cooperation between the patient and the doctor.
In the treatment of arterial hypertension in pregnancy, as well as in the treatment of arterial hypertension, the following methods are used: non-drug treatment and drug treatment. nine0003
nine0003
Non-drug treatment, i.e. treatment without drugs, is the most appropriate treatment for hypertension during pregnancy, since many of the drugs used in the treatment of this disease can be dangerous to the fetus.
What to do with pressure, how to reduce pressure during pregnancy
Non-drug treatment and prevention of arterial hypertension includes:
- Diet. The main requirements for the diet of women suffering from hypertension are a reduction in the consumption of table salt, coffee, tea, and the rejection of bad habits. The allowable amount of salt per day for patients with hypertension is 5 grams, while the calculation must include not only the salt with which we season food, but also the salt contained in various foods. nine0061
- Physical activity. Moderate physical activity has a positive effect on the general condition of the body, promotes fat burning, normalizes metabolism, improves blood supply to internal organs and the fetus, increases muscle tone and helps to establish the correct position of the fetus in the uterus.
 For the treatment and prevention of arterial hypertension during pregnancy, daily physical activity in the form of gymnastics (preferably with an instructor), hiking in the fresh air, and swimming are recommended. nine0061
For the treatment and prevention of arterial hypertension during pregnancy, daily physical activity in the form of gymnastics (preferably with an instructor), hiking in the fresh air, and swimming are recommended. nine0061 - Maintain normal body weight. The common expression that during pregnancy a woman "should eat for two" is not true. In fact, an "energy supplement" during pregnancy should not exceed 350 kcal. At the same time, maintaining normal body weight during pregnancy is extremely important for maintaining the health of the pregnant woman herself and her child (obesity contributes to the development of hypertension and diabetes). The normal weight gain of a pregnant woman by the end of pregnancy should not exceed 12 kg. nine0061
Drug treatment of hypertension during pregnancy should be carried out under the supervision of a specialist doctor and only with safe drugs.
- With a single slight increase in pressure, treatment begins with the appointment of sedative natural drugs, for example: valerian, motherwort, novopassitis and others.