Round scaly patch on skin
Discoid eczema | nidirect
Discoid eczema, also known as nummular or discoid dermatitis, is a long-term skin condition. It causes skin to become itchy, reddened, swollen and cracked in circular or oval patches. See your pharmacist or GP if you think you may have discoid eczema so they can recommend a suitable treatment.
Symptoms of discoid eczema
Circular or oval patches of eczema
Circular or oval patches of eczema can affect any part of the body, although they don't usually affect the face or scalp.
They start as a group of small red spots or bumps on the skin which join up to form larger pink, red or brown patches that can range from a few millimetres to several centimetres in size.
Blistering
At first, these patches of eczema are often swollen, blistered (covered with small fluid-filled pockets) and ooze fluid.
Itchiness and pain
The patches also tend to be very itchy, particularly at night.
Dry, crusty, cracked and flaky skin patches
Over time, the patches may become dry, crusty, cracked and flaky. the centre of the patch also sometimes clears, leaving a ring of discoloured skin that can be mistaken for ringworm.
Discoid eczema causes circular or oval patches of eczema on the skinYou may just have one patch of discoid eczema, but most people get several patches. The skin between the patches is often dry.
Patches of discoid eczema can sometimes become infected.
Signs of an infection can include:
- the patches oozing a lot of fluid
- a yellow crust developing over the patches
- the skin around the patches becoming red, hot, swollen, and tender or painful
- feeling sick
- chills
- feeling unwell
When to get medical advice
See your pharmacist or GP if you think you may have discoid eczema so they can recommend a suitable treatment.
You should also seek medical advice if you think your skin may be infected.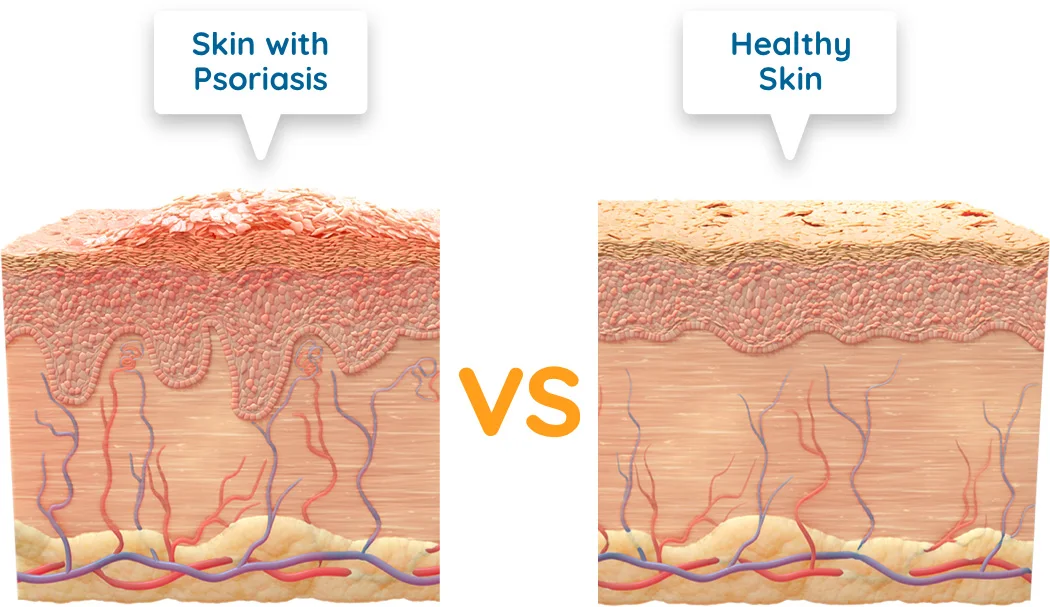 You may need treatment.
You may need treatment.
Your GP should be able to make a diagnosis just by examining the affected areas of skin. In some cases they may also ask questions or arrange some tests to rule out other conditions.
Your GP may refer you to a dermatologist (a doctor who specialises in managing skin conditions) if they're unsure of the diagnosis or if you need patch testing.
Causes of discoid eczema
The cause of discoid eczema is unknown, although it may occur as a result of having particularly dry skin.
Dry skin means your skin can't provide an effective barrier against substances that come into contact with it. This could allow a previously harmless substance, such as soap, to irritate (damage) your skin.
It's important to look carefully at all the chemicals in cosmetics and toiletries that may have come into contact with your skin. Contact dermatitis, a type of eczema caused by coming into contact with a particular irritant, may have a role in discoid eczema.
Some people with discoid eczema also have a history of atopic eczema, which often occurs in people who are prone to asthma and hay fever. However, unlike atopic eczema, discoid eczema doesn't seem to run in families.
Other possible triggers
An outbreak of discoid eczema may sometimes be triggered by a minor skin injury, such as an insect bite or a burn.
Some medicines may also be associated with discoid eczema, as patches of eczema can appear in people taking:
- interferon and ribavirin – when they're used together to treat hepatitis C
- tumour necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) blockers – used to treat some types of arthritis
- statins (cholesterol-lowering medication) – which can cause dry skin and rashes
Dry environments and cold climates can make discoid eczema worse, and sunny or humid (damp) environments may make your symptoms better.
Treating discoid eczema
Discoid eczema is usually a long-term problem. But medications are available to help relieve the symptoms and keep the condition under control.
Without treatment, discoid eczema can last for weeks, months or even years. It may also keep recurring – often in the same area that was affected previously.
Treatments used include:
- emollients – moisturisers applied to the skin to stop it becoming dry
- topical corticosteroids – ointments and creams applied to the skin that can help relieve severe symptoms
- antihistamines – medications that can reduce itching and help you sleep better
There are also things you can do yourself to help, such as avoiding all the irritating chemicals in soaps, detergents, bubble baths and shower gels.
Additional medication can be prescribed if your eczema is infected or particularly severe.
Occasionally, areas of skin affected by discoid eczema can be left permanently discoloured after the condition has cleared up.
Other types of eczema
Eczema is the name for a group of skin conditions that cause dry, irritated skin. Other types of eczema include:
- atopic eczema (also called atopic dermatitis) – the most common type of eczema, it often runs in families and is linked to other conditions such as asthma and hay fever
- contact dermatitis – a type of eczema that occurs when the body comes into contact with a particular substance
- varicose eczema – a type of eczema that most often affects the lower legs and is caused by problems with the flow of blood through the leg veins
- Discoid eczema
Help improve this page - send your feedback
You must have JavaScript enabled to use this form.
report a problem
leave feedback
ask a question
Report a problemWhich problem did you find on this page? (Tick all that apply)
A link, button or video is not working
There is a spelling mistake
Information is missing, outdated or wrong
I can't find what I'm looking for
Another issue
Messages
Tell us more about the problem you're having with the nidirect website.
Enter your feedback
What is your question about?Choose a topic for your question: - Select -AnglingBenefitsBirth certificatesBlue BadgeCareersCompensation due to a road problemChild MaintenanceCivil partnership certificatesCoronavirus (COVID-19)COVID vaccination certificateCriminal record checks (AccessNI)Death certificatesEducational Maintenance AllowanceEmployment rightsHigh Street Spend Local SchemeMarriage certificatesMotoringnidirect accountPassportsPenalty Charge NoticesPensionsPRONI - historical recordsRates or property valuationProblems with roads and streetsSmartpassMy question is about something else
What to do next
Discoid eczema - NHS
Discoid eczema, also known as nummular or discoid dermatitis, is a long-term (chronic) skin condition that causes skin to become itchy, swollen and cracked in circular or oval patches.
Without treatment, discoid eczema can last for weeks, months or even years. It may also keep coming back – often in the same area that was affected previously.
Symptoms of discoid eczema
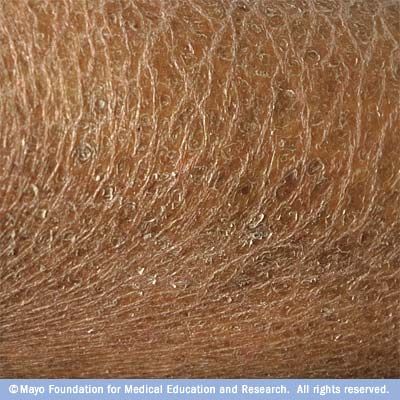
Discoid eczema causes distinctive circular or oval patches of eczema. It can affect any part of the body, although it does not usually affect the face or scalp.
Credit:
Phanie / Alamy Stock Photo https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo-nummular-eczema-72432322.html?pv=1&stamp=2&imageid=98CEB49C-1F7D-44C0-860A-2DCA2646A698&p=218214&n=0&orientation=0&pn=1&searchtype=0&IsFromSearch=1&srch=foo%3dbar%26st%3d0%26pn%3d1%26ps%3d100%26sortby%3d2%26resultview%3dsortbyPopular%26npgs%3d0%26qt%3dE5RG4J%26qt_raw%3dE5RG4J%26lic%3d3%26mr%3d0%26pr%3d0%26ot%3d0%26creative%3d%26ag%3d0%26hc%3d0%26pc%3d%26blackwhite%3d%26cutout%3d%26tbar%3d1%26et%3d0x000000000000000000000%26vp%3d0%26loc%3d0%26imgt%3d0%26dtfr%3d%26dtto%3d%26size%3d0xFF%26archive%3d1%26groupid%3d%26pseudoid%3d%7bA883FDE5-7F3D-4472-81F5-B61111916852%7d%26a%3d%26cdid%3d%26cdsrt%3d%26name%3d%26qn%3d%26apalib%3d%26apalic%3d%26lightbox%3d%26gname%3d%26gtype%3d%26xstx%3d0%26simid%3d%26saveQry%3d%26editorial%3d1%26nu%3d%26t%3d%26edoptin%3d%26customgeoip%3d%26cap%3d1%26cbstore%3d1%26vd%3d0%26lb%3d%26fi%3d2%26edrf%3d0%26ispremium%3d1%26flip%3d0%26pl%3d
The first sign of discoid eczema is usually a group of small spots or bumps on the skin. These then quickly join up to form larger patches that can range from a few millimetres to several centimetres in size.
These then quickly join up to form larger patches that can range from a few millimetres to several centimetres in size.
On lighter skin these patches will be pink or red. On darker skin these patches can be a dark brown or they can be paler than the skin around them.
Initially, these patches are often swollen, blistered (covered with small fluid-filled pockets) and ooze fluid. They also tend to be very itchy, particularly at night.
Over time, the patches may become dry, crusty, cracked and flaky. The centre of the patch also sometimes clears, leaving a ring of discoloured skin that can be mistaken for ringworm.
You may just have 1 patch of discoid eczema, but most people get several patches. The skin between the patches is often dry.
Patches of discoid eczema can sometimes become infected. Signs of an infection can include:
- the patches oozing a lot of fluid
- a yellow crust developing over the patches
- the skin around the patches becoming hot, swollen and tender or painful
- feeling sick
- feeling hot or shivery
- feeling unwell
When to seek medical advice
See a pharmacist or GP if you think you may have discoid eczema. They can recommend a suitable treatment.
They can recommend a suitable treatment.
You should also seek medical advice if you think your skin may be infected. You may need to use an antibiotic cream or, in severe cases, take antibiotics as a tablet or capsule.
A GP should be able to make a diagnosis just by examining the affected areas of skin. In some cases they may also ask questions or arrange some tests to rule out other conditions.
A GP may refer you to a doctor who specialises in skin conditions (dermatologist) if they're unsure of the diagnosis or if you need a patch test.
Causes of discoid eczema
The cause of discoid eczema is unknown, although it may happen as a result of having particularly dry skin.
When your skin is very dry it cannot provide an effective barrier against substances that come into contact with it. This could allow a previously harmless substance, such as soap, to irritate your skin.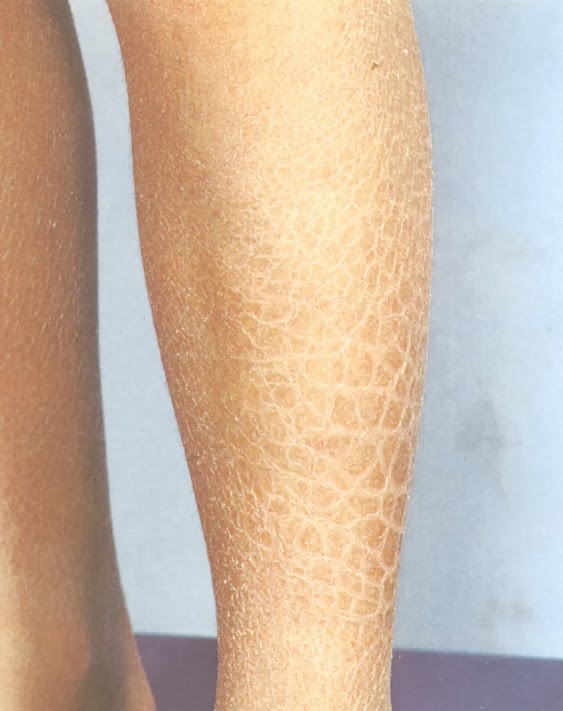
It's important to look carefully at all the chemicals in cosmetics and toiletries that may have come into contact with your skin. Contact dermatitis, a type of eczema caused by coming into contact with a particular irritant, may have a role in discoid eczema.
Some people with discoid eczema also have a history of atopic eczema, which often happens in people who are prone to asthma and hay fever. However, unlike atopic eczema, discoid eczema does not seem to run in families.
Other possible triggers
An outbreak of discoid eczema may sometimes be triggered by a minor skin injury, such as an insect bite or a burn.
Some medicines may also be associated with discoid eczema, as patches of eczema can appear in people taking:
- interferon and ribavirin – when they're used together to treat hepatitis C
- tumour necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) blockers – used to treat some types of arthritis
- statins (cholesterol-lowering medicine) – which can cause dry skin and rashes
Dry environments and cold climates can make discoid eczema worse, and sunny or damp (humid) environments may make your symptoms better.
Treating discoid eczema
Discoid eczema is usually a long-term problem, but medicines are available to help relieve the symptoms and keep the condition under control.
Treatments include:
- emollients – moisturisers applied to the skin to stop it becoming dry
- topical corticosteroids – ointments and creams containing a steroid that are applied to the skin and may relieve severe symptoms
- antihistamines – medicines that can reduce itching
There are also things you can do yourself to help, such as avoiding all the irritating chemicals in soaps, detergents, bubble baths and shower gels.
Additional medicine can be prescribed if your eczema is infected or particularly severe.
Occasionally, areas of skin affected by discoid eczema can be left permanently discoloured after the condition has cleared up.
Find out more about treating discoid eczema.
Other types of eczema
Eczema is the name for a group of skin conditions that cause dry, irritated skin. Other types of eczema include:
- atopic eczema (also called atopic dermatitis) – the most common type of eczema, it often runs in families and is linked to other conditions such as asthma and hay fever
- contact dermatitis – a type of eczema that happens when the skin comes into contact with a particular substance
- varicose eczema – a type of eczema that usually affects the lower legs and is caused by problems with the flow of blood through the leg veins
Page last reviewed: 30 October 2019
Next review due: 30 October 2022
Plaques on the skin - causes, diseases, diagnosis and treatment
- INVITRO
- Library
- Symptoms
- Plaques on the skin
Fungus
Allergy
Psoriasis
Keratoma
Mycosis
Nevus
Melanoma
27481 November 16
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section should not be used for self-diagnosis or self-treatment. In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, only the attending physician should prescribe diagnostic tests.
 For diagnosis and proper treatment, you should contact your doctor. nine0031 For a correct assessment of the results of your analyzes in dynamics, it is preferable to do studies in the same laboratory, since different laboratories may use different research methods and units of measurement to perform the same analyzes.
For diagnosis and proper treatment, you should contact your doctor. nine0031 For a correct assessment of the results of your analyzes in dynamics, it is preferable to do studies in the same laboratory, since different laboratories may use different research methods and units of measurement to perform the same analyzes. Plaques on the skin: the causes of occurrence, in what diseases they occur, diagnosis and methods of treatment.
Definition
A plaque is a pathological element with clear edges that rises above the skin surface or merges with it, more than 5 mm in size. nine0013In dermatology, many types of plaques are distinguished - about 70 diseases occur with the formation of these elements, which makes the plaque one of the most common rashes.
Plaque varieties
The shape of the plaques are round, oval and irregular in shape. Over time, the shape, surface and appearance of this element may change.
Due to the occurrence of plaques, they can be both a manifestation of skin diseases and a symptom of diseases of internal organs and systems (autoimmune reactions, liver diseases, oncological processes, allergic reactions). nine0013
Plaques are dry, smooth, red, brown, gray-white, etc.
Possible causes of plaques
Dry plaques on the skin in adults may be a manifestation of the following diseases: plaques with severe itching.
- Allergic reactions are characterized by the appearance on the skin of smooth dry plaques, pink spots, blisters, which are very itchy and cause severe discomfort. They can develop both when the skin comes into contact with the allergen, and when it gets on the mucous membranes (for example, with urticaria, hay fever, food and contact allergies). nine0004
- Psoriasis is a chronic non-infectious skin disease in which scaly dry plaques form on the elbows, knees, scalp, prone to fusion and accompanied by mild itching.

- Dry plaques form on the skin if it is exposed to stress for a long time with the loss of its protective functions.
- Diseases of the digestive tract, accompanied by malabsorption syndrome (impaired absorption of vitamins and trace elements in the small intestine), chronic diseases of the liver and other organs, in which substances that are not normally present in the dermis accumulate, also lead to the appearance of dry plaques. nine0004
- Solar keratoma is a precancerous condition, which is characterized by the presence of many light grayish plaques on the skin.
- Drug toxidermia is an allergic reaction accompanied by the appearance of elements in the form of plaques on the skin. In severe cases, Lyell's syndrome or Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis, may develop.
 nine0004
nine0004 - Dühring's dermatitis (herpetiform) is a chronic skin disease with no established etiology, which is characterized by recurrent appearance of a rash of various morphologies on the skin, accompanied by severe skin itching and burning.
- Mycosis fungoides is a primary T-cell lymphoma of the skin, a malignant lymphoid lesion, primarily of the skin. Itchy red plaques appear on the skin, resembling eczema. In the initial stages, they respond well to treatment with hormonal ointments, but the disease itself requires more complex therapy. nine0004
- In children, the appearance of red spots and plaques on the skin is most often associated with an allergic reaction to food.
- Becker's nevus is an anomaly in the development of the dermis, when dark plaques with an uneven surface appear on the skin, on which hair can begin to grow over time.
 nine0004
nine0004 - Pigmentary nevus - "birthmark", may rise above the skin, has a brown or dark color.
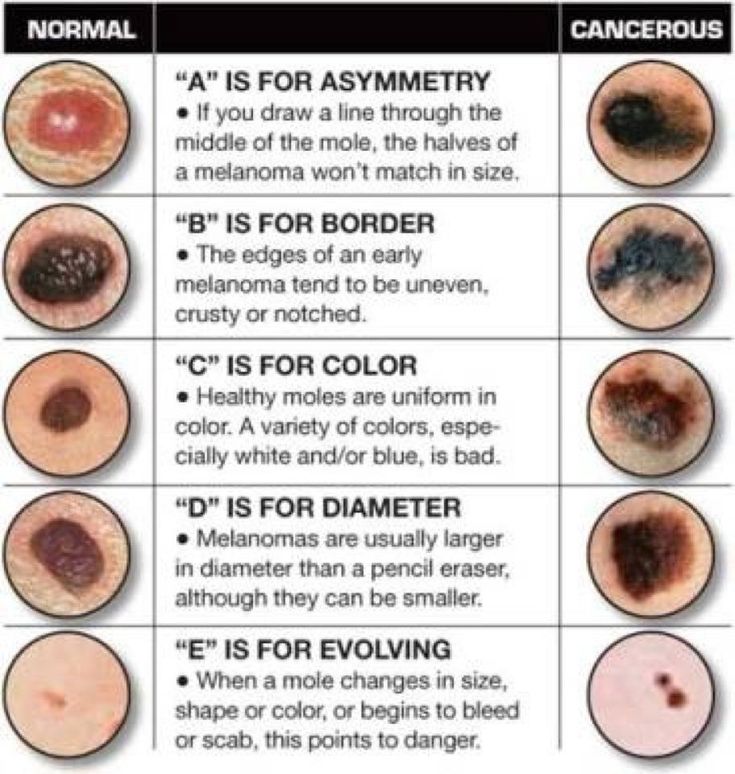
- Melanoma is the most malignant skin tumor characterized by rapid metastasis. It develops mainly from nevi and moles. If the nature of the surface, the boundaries of the mole change, its size increases, bleeding occurs, you should immediately contact a dermatologist or oncologist to exclude the development of melanoma. nine0009 Basal cell skin cancer is more often localized on the head, face, neck, does not metastasize, is characterized by slow growth.
- Senile keratoma occurs in elderly people, most likely due to a lack of vitamins, an abundance of animal fats consumed, skin sensitivity to ultraviolet radiation due to a violation of its protective functions. Typical localization - face, neck, open areas of the body.
- Seborrheic keratoma is a yellowish plaque on the skin that eventually transforms into a dark brown growth that tends to flake off, itch severely, crack, bleed, and can serve as an entryway for infection.
 nine0004
nine0004 - change in the shape of the plaque - the edges have become uneven;
- change in the surface of the plaque - cracks, ulcerations appeared;
- change in the size of the plaque - it began to grow rapidly above the surface of the skin or actively spread through it;
- discoloration of the plaque - in cases of malignancy, an uneven color of the formation is usually observed with areas of darker and lighter shades;
- the appearance of bleeding - both contact and spontaneous; nine0004
- enlargement of regional (nearby) lymph nodes.
- Clinical guidelines.
 Dermatitis herpetiformis // Russian Society of Dermatovenerologists and Cosmetologists. 2016.
Dermatitis herpetiformis // Russian Society of Dermatovenerologists and Cosmetologists. 2016. - Clinical guidelines. Urticaria in children // Union of Pediatricians of Russia; Russian Association of Allergists and Clinical Immunologists. 2018.
- Clinical guidelines. Toxidermia // Russian Society of Dermatovenerologists and Cosmetologists. 2016.
- Clinical guidelines. Familial hypercholesterolemia // National Society for the Study of Atherosclerosis. 2018.
-
Cholesterol plaques
5933 November 18th
-
Hepatic colic
3679 09 November
- nine0012 Laryngeal edema
2855 07 November
- non-specific - allergic reactions to household chemicals, laundry soap, cosmetic products, dehydration due to cold and wind;
- specific - then the spots become a manifestation of dermatological diseases.
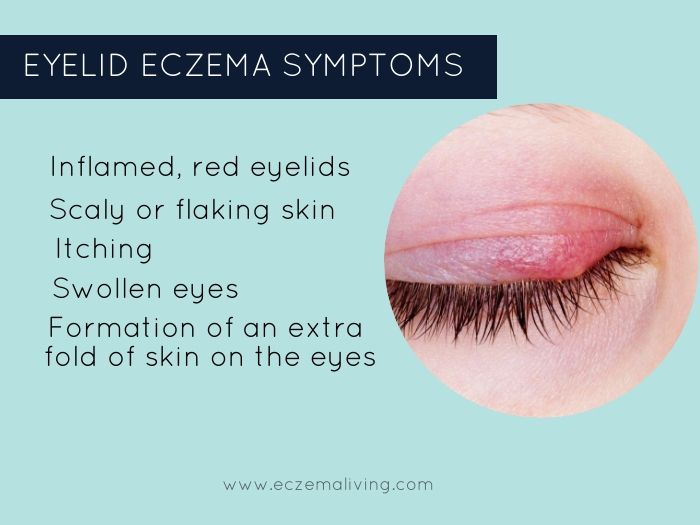
- dry skin;
- peeling and redness of the eyelids;
- dry skin-colored plaques on the trunk and extensor areas of the body;
- cracks.
The appearance of red plaques on the skin indicates their good blood supply. Possible causes of this condition may be the following nosologies:
Brown plaques occur when melanin is deposited in the affected area of the dermis, which causes a brown (dark) color. Possible causes may be the following diseases:
Which doctors to contact
With the formation of plaques on the skin, it is necessary to contact a dermatologist to determine the causes of the appearance of this element of the rash.
Plaque diagnostics and examinations
For the diagnosis of fungal skin lesions, scraping from the affected area is used for subsequent microscopic examination.
The development of an allergic reaction requires seeking medical help to identify the allergen, prescribing antihistamines, and sometimes hormonal drugs. In clinical cases of allergy, along with skin tests, analyzes are performed using various sets of common allergens and triggers: a panel for respiratory allergens, for food allergens, and for a combination of both. nine0031
Respiratory Panel
Synonyms: Comprehensive Respiratory Allergen Test Panel; Respiratory allergens panel, Allergen respiratory profile, Allergy testing. Brief description of the study "Panel respira...
Brief description of the study "Panel respira...
Up to 5 business days
Available with house call
5 515 RUB nine0013
In garbage
Food Panel, IgE
Food Allergen Panel: hazelnut, peanut, Walnut, almond, cow's milk, egg white, egg ...
Up to 5 business days
Available with house call
5 515 RUB
In garbage
Food and Respiratory Panel
Panel different allergens: A mixture of grass allergens: fragrant spikelet; perennial rye; timothy; rye cultivated; Woolly buckthorn (GP3) IgE . .. nine0013
.. nine0013
Up to 5 business days
Available with house call
5 515 RUB
In garbage
In psoriasis, seeing a dermatologist and rheumatologist can help reduce the symptoms of the disease if appropriate therapy is prescribed. For the diagnosis, it is usually sufficient to examine, determine, the skin manifestations of psoriasis are so characteristic, but if necessary, a differential diagnosis is carried out, including a clinical blood test, feces for the presence of worm eggs and protozoa, and a histological examination of the skin. nine0013
Clinical blood test: general analysis, leukoformula, ESR (with microscopy of a blood smear in the presence of pathological changes)
Synonyms: Complete blood count, UAC. Full blood count, FBC, Complete blood count (CBC) with differential white blood cell count (CBC with diff), Hemogram. Brief description of the study CBC: general...
Full blood count, FBC, Complete blood count (CBC) with differential white blood cell count (CBC with diff), Hemogram. Brief description of the study CBC: general...
Up to 1 business day
Available with house call
RUB 810
In garbage
Fecal test for helminth eggs
Synonyms: Feces on worm eggs; Analysis of feces for eggs of worms. Ova and Parasite Exam; O&P; Stool O&P test. Brief description of the study "Analysis of feces for eggs of helminths&ra...
Up to 1 business day
Available with house call
RUB 570
In garbage
Fecal analysis for protozoa (PRO stool)
Synonyms: Analysis of faeces for protozoa. Parasite Exam, feces; Parasitic Examination, fecal. Brief description of the study "Analysis of feces for protozoa" Fecal analysis for ...
Parasite Exam, feces; Parasitic Examination, fecal. Brief description of the study "Analysis of feces for protozoa" Fecal analysis for ...
Up to 1 business day
Available with house call
RUB 570
In garbage
Histological examination of biopsy material and material obtained during surgical interventions (endoscopic material; tissues of the female reproductive system; skin, soft tissues; hematopoietic and lymphoid tissue; bone and cartilage tissue)
Taking biomaterial is paid separately. According to the requirements of paragraph 17 of the Rules for conducting pathological and anatomical studies, approved. Order of the Ministry of Health of Russia. ..
..
Up to 5 business days
Available with house call
2 880 RUB
In garbage nine0013
Diseases of the stomach and intestines can also lead to plaque formation on the skin. To identify the pathology of the gastrointestinal tract, it is enough to refer to therapist or gastroenterologist, conduct a number of endoscopic examinations (gastroscopy, and, if necessary, colonoscopy), ultrasound of the abdominal organs, perform some screening blood tests for diseases of the liver, intestines, stomach.
Gastroscopy
Examination of the mucosa of the upper gastrointestinal tract with the possibility of biopsy or endoscopic removal of small pathological ...
RUB 4,440 Sign up
Colonoscopy
Endoscopic examination of the colon to look for abnormalities, perform biopsies, and remove small polyps and tumors.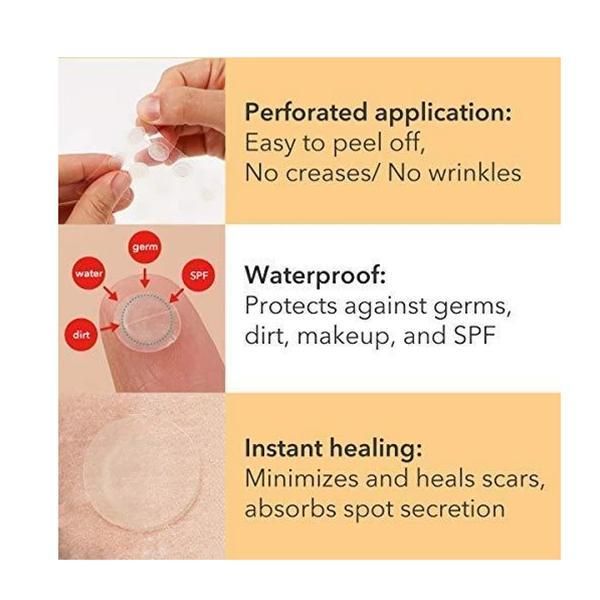
RUB 5,740 Sign up
Comprehensive ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs (liver, gallbladder, pancreas, spleen)
Scanning of the internal organs of the abdominal cavity to assess its functional state and the presence of pathology.
RUB 2,890 Sign up
Liver function tests: screening
Up to 1 business day
Available with house call
RUB 1,935
In garbage
Diagnosis of celiac disease: intolerance to cereal proteins (gluten)
Up to 8 working days
Available with house call
7 520 RUB nine0013
In garbage
Gastropanel
Up to 9 working days
Available with house call
RUB 4,760
In garbage
To clarify the diagnosis of keratoma, a skin biopsy is performed and epithelium scraping is performed, followed by microscopic and histochemical examination.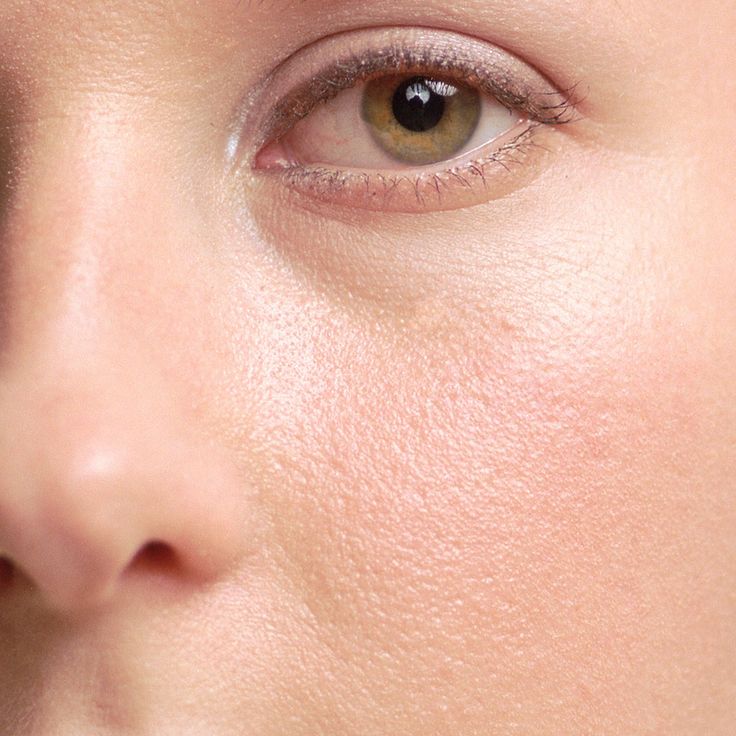 nine0013
nine0013
Histological examination of biopsy material and material obtained during surgical interventions (endoscopic material; tissues of the female reproductive system; skin, soft tissues; hematopoietic and lymphoid tissue; bone and cartilage tissue)
Taking biomaterial is paid separately. According to the requirements of paragraph 17 of the Rules for conducting pathological and anatomical studies, approved. Order of the Ministry of Health of Russia...
Up to 5 business days
Available with house call
2 880 RUB
In garbage
Examination of scrapings and impressions of tumors and tumor-like formations
Material for research.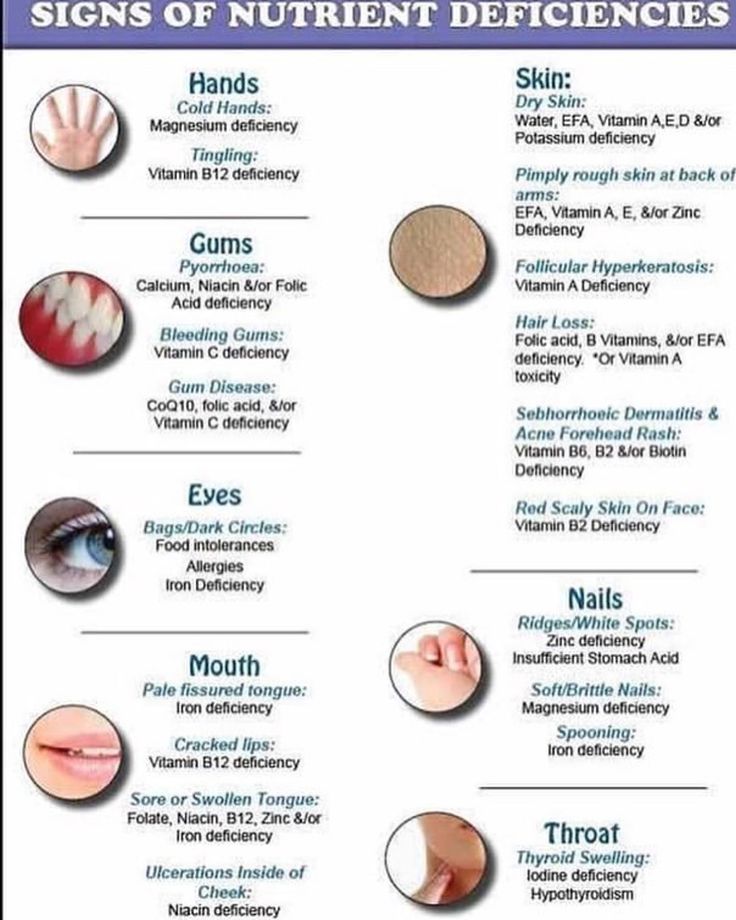 Imprints and scrapings are obtained from pathological lesions of the skin and mucous membranes (except for the cervix and cervical canal). Relative to test...
Imprints and scrapings are obtained from pathological lesions of the skin and mucous membranes (except for the cervix and cervical canal). Relative to test...
Up to 2 working days
Available with house call
RUB 1,030
In garbage
If atypical cells are detected in scrapings or biopsies, immediately contact oncologist.
If xanthoma appears on the skin, it is recommended to consult a cardiologist, take blood tests for lipid profile and blood glucose levels, and screen for diabetes. nine0013
Lipid profile screening
Up to 1 business day
Available with house call
1 355 RUB
In garbage
Glucose (in the blood) (Glucose)
Research material Serum or blood plasma. If it is not possible to centrifuge the sample 30 minutes after collection for serum/plasma separation...
If it is not possible to centrifuge the sample 30 minutes after collection for serum/plasma separation...
Up to 1 business day
Available with house call
335 RUB
In garbage
Diabetes management: advanced
Up to 1 business day
Available with house call
RUB 5 820
In garbage
What should I do if plaque appears on the skin?
Any newly appeared neoplasms should be shown to a dermatologist. Their cosmetic removal without prior consultation with a specialist is fraught with serious consequences.
Their cosmetic removal without prior consultation with a specialist is fraught with serious consequences.
In addition, there are symptoms that require immediate medical attention:
Plaque treatment
When plaques of an allergic nature appear on the skin, antihistamines are prescribed, in cases of a severe course of the disease, glucocorticosteroids. In addition, it is important to follow a hypoallergenic diet.
In addition, it is important to follow a hypoallergenic diet.
Mycotic plaques require antifungal drugs, both local (ointments, creams) and systemic (tablets). Taking these drugs is associated with a high risk of side effects, and therefore it is possible only after consulting a doctor, accurate verification of the diagnosis and confirmation of the etiology of the disease. nine0013
Treatment of psoriasis is multi-stage and complex, it involves constant monitoring by a rheumatologist, taking cytostatics and other drugs, using ointments and shampoos to improve skin condition, using antihistamines to reduce itching, including physiotherapy and a hypoallergenic diet in the treatment regimen.
When confirming the presence of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, properly selected therapy can stop the appearance of new plaques on the skin, as well as prevent the development of complications of the underlying disease. nine0013
Sources:
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section should not be used for self-diagnosis or self-treatment. In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, only the attending physician should prescribe diagnostic tests. For diagnosis and proper treatment, you should contact your doctor.
For a correct assessment of the results of your analyzes in dynamics, it is preferable to do studies in the same laboratory, since different laboratories may use different research methods and units of measurement to perform the same analyzes. nine0013
nine0013
Recommendations
Show more
Colds
Allergy
nine0012 SARSLaryngitis
Hypothyroidism
Rhinitis
Papillomatosis
Stenosis of the larynx
Voice disorders
Depending on the degree of preservation of the voice, its disorders are divided into two large groups. Functional voice changes are more often temporary, while voice changes due to organic damage to the vocal apparatus are more persistent.
Functional voice changes are more often temporary, while voice changes due to organic damage to the vocal apparatus are more persistent.
More
Nevus
nine0012 MelanomaChanges in a mole
Moles: causes of appearance, in which diseases changes occur, diagnosis and methods of treatment.
More
Allergy
Myocardial infarction
nine0012 ArrhythmiaPulmonary embolism (PE)
Massive blood loss
Burn
Decreased blood pressure
Arterial hypotension - an abnormal decrease in blood pressure (BP) less than 100/60 mm Hg. Art., accompanied by dizziness, blurred vision, decreased mental abilities and fainting. In different people, low blood pressure can vary within fairly wide limits. nine0013
Art., accompanied by dizziness, blurred vision, decreased mental abilities and fainting. In different people, low blood pressure can vary within fairly wide limits. nine0013
More
Gastritis
Diarrhea
Flatulence
Dysbacteriosis
nine0012 AllergyWorms
Ascites
Bloating
In most cases, bloating is associated with flatulence - excessive accumulation of gases in the intestines. Bloating (enlargement) of the abdomen can be due to various reasons.
Bloating (enlargement) of the abdomen can be due to various reasons.
More nine0013
Allergy
Laryngitis
Edema
Quincke's edema
Tracheostomy
nine0012 ChokingCough
Lump in throat
Laryngeal stenosis
Shortness of breath
Edema of the larynx
Edema of the larynx: causes, in which diseases it occurs, diagnosis and methods of treatment. nine0013
nine0013
More
Nothing found
Try editing your query or select a doctor or service from the list.
Doctor not found
Try changing your query or select doctor from the list
Medical office not found
Try changing your query or select medical office from the list
Therapist Traumatologist-orthopedist Endocrinologist Urologist Gynecologist Ultrasound doctor Cardiologist Pediatrician
No results found
Try changing your query
Thank you!
You have successfully made an appointment
Detailed information has been sent to your e-mail
Dry spots on the skin: three common dermatological diseases
July 5, 2020
Dry spots on the skin are a common dermatological symptom that can indicate both a temporary failure and a violation of the barrier functions of the epidermis, and a skin disease. It all depends on the size of the spots, the clarity of their boundaries, as well as the duration of their presence on the skin. nine0013
It all depends on the size of the spots, the clarity of their boundaries, as well as the duration of their presence on the skin. nine0013
The causes of dryness can be divided into two large groups:
Sometimes a person may notice that dry spots appear on his skin after a certain event occurs, for example, after washing clothes with his hands. Then the reason is obvious and easy to eliminate. But if dry spots on the skin do not go away, itch, peel off, you should consult a doctor. nine0013
Dry spots with scales
Pink raised dry spots on the body and head may indicate psoriasis. With this dermatological pathology in humans, raised plaques appear on the skin - psoriatic papules. They protrude above the surface of the skin, cause intense itching and flake, tend to spread and merge.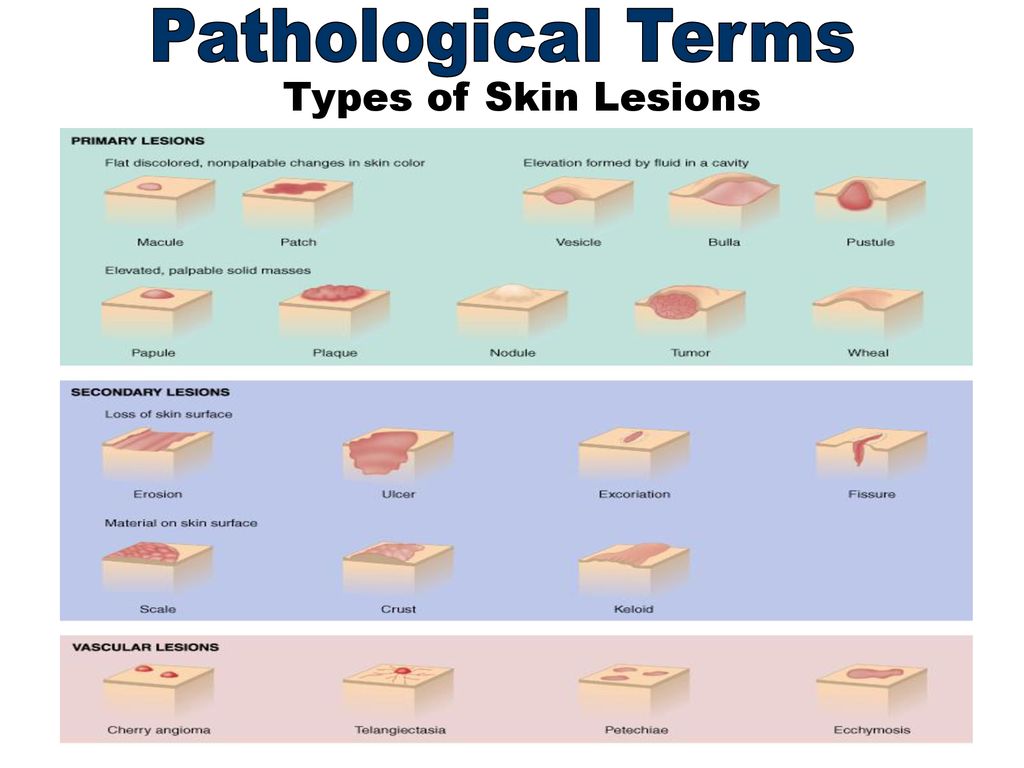
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune disease in which rashes are most often localized on the elbows, head, knees and groin. Dry pink spots covered with white scales are foci of chronic inflammation. Under the influence of internal autoimmune processes, epidermal cells divide several times faster than necessary. As a result, small scales are constantly separated from dying skin cells. nine0013
Atopic dermatitis and its difference from psoriasis
Atopic dermatitis can also cause dry patches on the body. And as with psoriasis, they cause itching. Due to the increased sensitivity of the skin to environmental factors, the mechanisms of its self-regulation are violated, including the barrier function. That is, an allergy is a trigger for atopic dermatitis, but the tendency to such a skin reaction is genetically laid down.
Most often, atopic dermatitis occurs in children. The disease has a chronic course, when exacerbations are replaced by periods of remission. Here are the typical signs of atopic dermatitis:
Here are the typical signs of atopic dermatitis:
It is difficult for a person who does not have a medical education to distinguish psoriasis from atopic dermatitis, but a doctor can easily make a differential diagnosis. There are several differences that may speak in favor of a particular pathology. Atopic dermatitis often affects children, psoriasis can debut in adulthood. Psoriatic plaques are raised above the skin, and scales can be seen. Dry spots in atopic dermatitis are flat. It is also important to consider typical localization. nine0013
Useful links: State Center of Urology in Moscow - Clinic of Urology named after R. M. Fronshtein of the First Moscow State Medical University named after I.M. Sechenov
Dry eczema
Sometimes white, dry, scaly patches on the skin of the legs can indicate dry eczema.