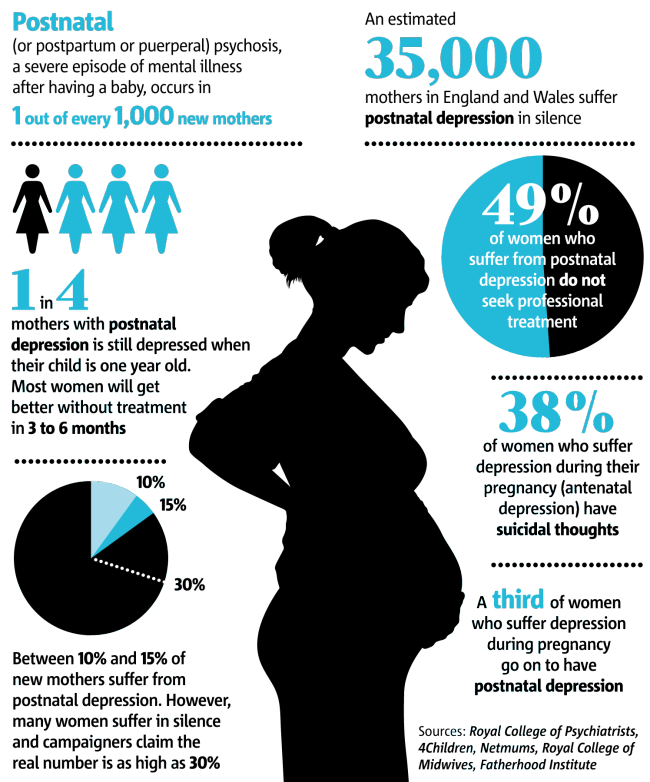
Reason for ectopic pregnancy
Ectopic Pregnancy: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatments
Ectopic Pregnancy: Symptoms, Causes, and TreatmentsMedically reviewed by Debra Rose Wilson, Ph.D., MSN, R.N., IBCLC, AHN-BC, CHT — By Marissa Selner on January 8, 2018
What is an ectopic pregnancy?
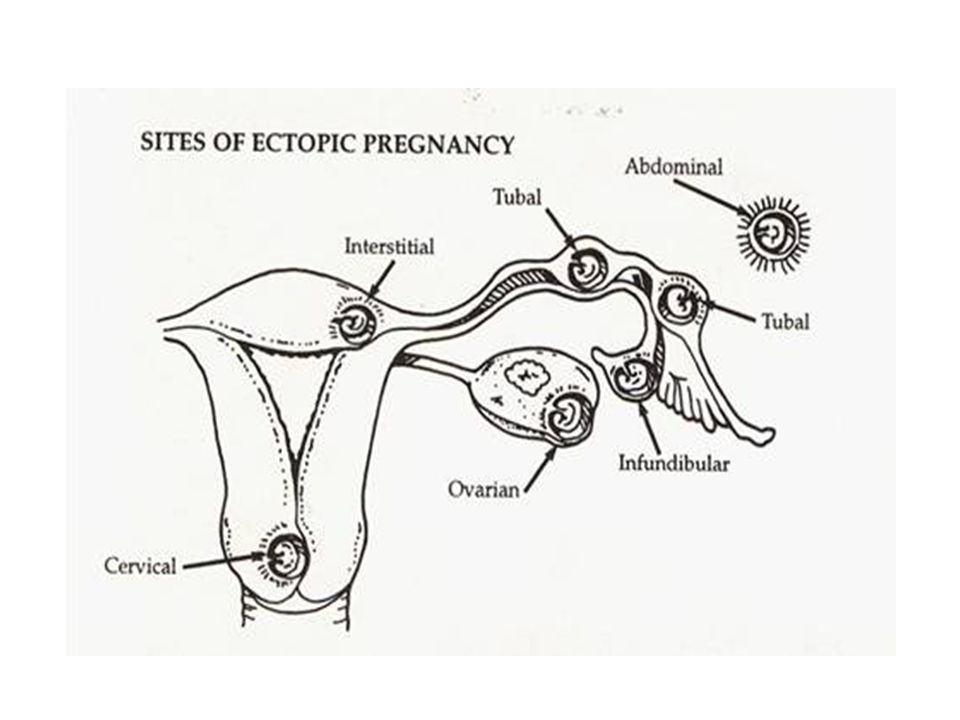
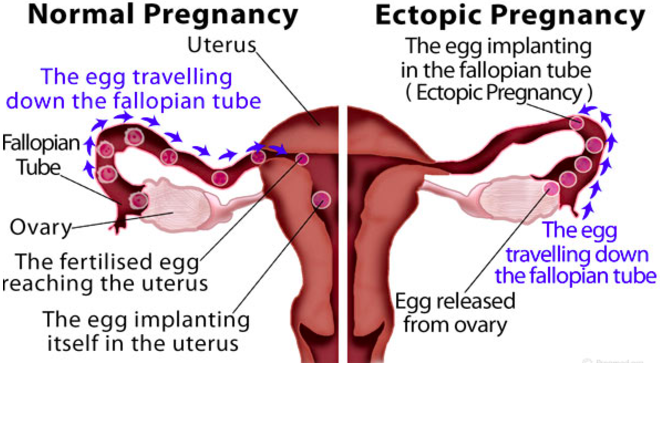
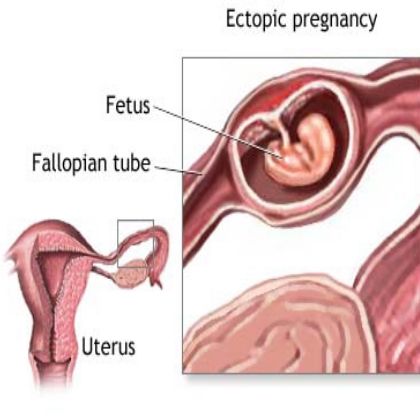
From fertilization to delivery, pregnancy requires a number of steps in a woman’s body. One of these steps is when a fertilized egg travels to the uterus to attach itself. In the case of an ectopic pregnancy, the fertilized egg doesn’t attach to the uterus. Instead, it may attach to the fallopian tube, abdominal cavity, or cervix.
While a pregnancy test may reveal a woman is pregnant, a fertilized egg can’t properly grow anywhere other than the uterus. According to the American Academy of Family Physicians (AAFP), ectopic pregnancies occur in about 1 out of every 50 pregnancies (20 out of 1,000).
An untreated ectopic pregnancy can be a medical emergency. Prompt treatment reduces your risk of complications from the ectopic pregnancy, increases your chances for future, healthy pregnancies, and reduces future health complications.
What causes an ectopic pregnancy?
The cause of an ectopic pregnancy isn’t always clear. In some cases, the following conditions have been linked with an ectopic pregnancy:
- inflammation and scarring of the fallopian tubes from a previous medical condition, infection, or surgery
- hormonal factors
- genetic abnormalities
- birth defects
- medical conditions that affect the shape and condition of the fallopian tubes and reproductive organs
Your doctor may be able to give you more specific information about your condition.
Who is at risk for an ectopic pregnancy?
All sexually active women are at some risk for an ectopic pregnancy. Risk factors increase with any of the following:
- maternal age of 35 years or older
- history of pelvic surgery, abdominal surgery, or multiple abortions
- history of pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)
- history of endometriosis
- conception occurred despite tubal ligation or intrauterine device (IUD)
- conception aided by fertility drugs or procedures
- smoking
- history of ectopic pregnancy
- history of sexually transmitted diseases (STDs), such as gonorrhea or chlamydia
- having structural abnormalities in the fallopian tubes that make it hard for the egg to travel
If you have any of the above risk factors, talk to your doctor.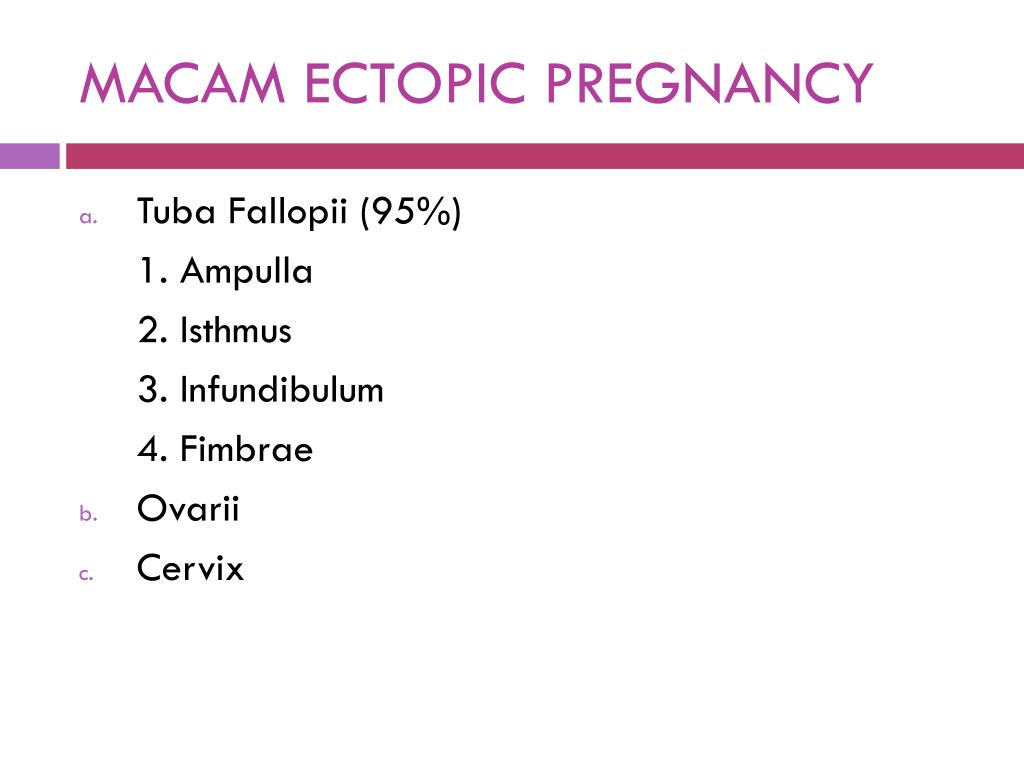 You can work with your doctor or a fertility specialist to minimize the risks for future ectopic pregnancies.
You can work with your doctor or a fertility specialist to minimize the risks for future ectopic pregnancies.
What are the symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy?
Nausea and breast soreness are common symptoms in both ectopic and uterine pregnancies. The following symptoms are more common in an ectopic pregnancy and can indicate a medical emergency:
- sharp waves of pain in the abdomen, pelvis, shoulder, or neck
- severe pain that occurs on one side of the abdomen
- light to heavy vaginal spotting or bleeding
- dizziness or fainting
- rectal pressure
You should contact your doctor or seek immediate treatment if you know that you’re pregnant and have any of these symptoms.
Diagnosing an ectopic pregnancy
If you suspect you may have an ectopic pregnancy, see your doctor immediately. Ectopic pregnancies can’t be diagnosed from a physical exam. However, your doctor may still perform one to rule out other factors.
Another step to diagnosis is a transvaginal ultrasound. This involves inserting a special wand-like instrument into your vagina so that your doctor can see if a gestational sac is in the uterus.
Your doctor may also use a blood test to determine your levels of hCG and progesterone. These are hormones that are present during pregnancy. If these hormone levels start to decrease or stay the same over the course of a few days and a gestational sac isn’t present in an ultrasound, the pregnancy is likely ectopic.
If you’re having severe symptoms, such as significant pain or bleeding, there may not be enough time to complete all these steps. The fallopian tube could rupture in extreme cases, causing severe internal bleeding. Your doctor will then perform an emergency surgery to provide immediate treatment.
Treating ectopic pregnancy
Ectopic pregnancies aren’t safe for the mother. Also, the embryo won’t be able to develop to term. It’s necessary to remove the embryo as soon as possible for the mother’s immediate health and long-term fertility. Treatment options vary depending on the location of the ectopic pregnancy and its development.
Treatment options vary depending on the location of the ectopic pregnancy and its development.
Medication
Your doctor may decide that immediate complications are unlikely. In this case, your doctor can prescribe several medications that could keep the ectopic mass from bursting. According to the AAFP, one common medication for this is methotrexate (Rheumatrex).
Methotrexate is a drug that stops the growth of rapidly dividing cells, such as the cells of the ectopic mass. If you take this medication, your doctor will give it to you as an injection. You should also get regular blood tests to ensure that the drug is effective. When effective, the medication will cause symptoms that are similar to that of a miscarriage. These include:
- cramping
- bleeding
- the passing of tissue
Further surgery is rarely required after this occurs. Methotrexate doesn’t carry the same risks of fallopian tube damage that come with surgery. You won’t be able to get pregnant for several months after taking this medication, however.
Surgery
Many surgeons suggest removing the embryo and repairing any internal damage. This procedure is called a laparotomy. Your doctor will insert a small camera through a small incision to make sure they can see their work. The surgeon then removes the embryo and repairs any damage to the fallopian tube.
If the surgery is unsuccessful, the surgeon may repeat a laparotomy, this time through a larger incision. Your doctor may also need to remove the fallopian tube during surgery if it’s damaged.
Home care
Your doctor will give you specific instructions regarding the care of your incisions after surgery. The chief goals are to keep your incisions clean and dry while they heal. Check them daily for infection signs, which could include:
- bleeding that won’t stop
- excessive bleeding
- foul-smelling drainage from the site
- hot to the touch
- redness
- swelling
You can expect some light vaginal bleeding and small blood clots after surgery. This can occur up to six weeks after your procedure. Other self-care measures you can take include:
This can occur up to six weeks after your procedure. Other self-care measures you can take include:
- don’t lift anything heavier than 10 pounds
- drink plenty of fluids to prevent constipation
- pelvic rest, which means refraining from sexual intercourse, tampon use, and douching
- rest as much as possible the first week postsurgery, and then increase activity in the next weeks as tolerated
Always notify your doctor if your pain increases or you feel something is out of the ordinary.
Prevention
Prediction and prevention aren’t possible in every case. You may be able to reduce your risk through good reproductive health maintenance. Have your partner wear a condom during sex and limit your number of sexual partners. This reduces your risk for STDs, which can cause PID, a condition that can cause inflammation in the fallopian tubes.
Maintain regular visits with your doctor, including regular gynecological exams and regular STD screenings.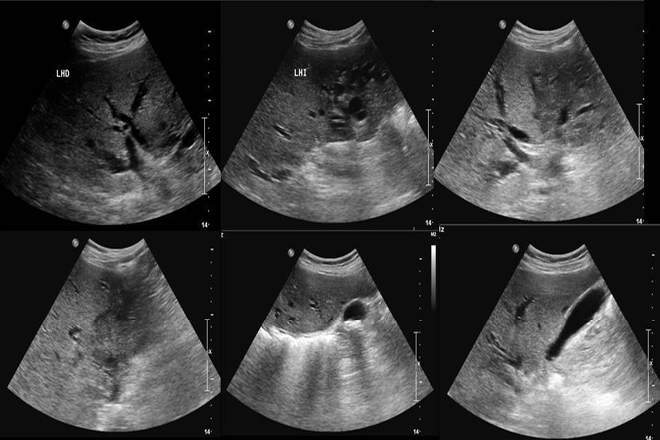 Taking steps to improve your personal health, such as quitting smoking, is also a good preventive strategy.
Taking steps to improve your personal health, such as quitting smoking, is also a good preventive strategy.
What’s the long-term outlook?
The long-term outlook after an ectopic pregnancy depends on whether it caused any physical damage. Most people who have ectopic pregnancies go on to have healthy pregnancies. If both fallopian tubes are still intact, or even just one, the egg can be fertilized as normal. However, if you have a preexisting reproductive problem, that can affect your future fertility and increase your risk of future ectopic pregnancy. This is especially the case if the preexisting reproductive problem has previously led to an ectopic pregnancy.
Surgery may scar the fallopian tubes, and it can make future ectopic pregnancies more likely. If the removal of one or both fallopian tubes is necessary, speak to your doctor about possible fertility treatments. An example is in vitro fertilization that involves implanting a fertilized egg into the uterus.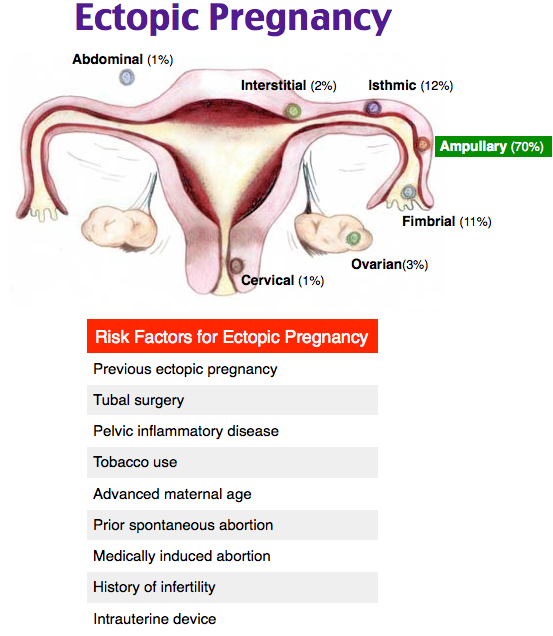
Pregnancy loss, no matter how early, can be devastating. You can ask your doctor if there are available support groups in the area to provide further support after loss. Take care of yourself after this loss through rest, eating healthy foods, and exercising when possible. Give yourself time to grieve.
Remember that many women go on to have healthy pregnancies and babies. When you’re ready, talk to your doctor about ways you can ensure that your future pregnancy is a healthy one.
Last medically reviewed on January 8, 2018
- Parenthood
- Pregnancy
- Pregnancy Complications
How we reviewed this article:
Healthline has strict sourcing guidelines and relies on peer-reviewed studies, academic research institutions, and medical associations. We avoid using tertiary references. You can learn more about how we ensure our content is accurate and current by reading our editorial policy.
- Cleveland Clinic Staff. (2014). Ectopic pregnancy.
my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases_conditions/hic_Ectopic_Pregnancy - Ectopic pregnancy. (2017).
acog.org/Patients/FAQs/Ectopic-Pregnancy - Gyn onc home care after your laparotomy. (2017).
uwhealth.org/healthfacts/gyn-onc/6081.pdf - Mayo Clinic Staff. (2015). Ectopic pregnancy.
mayoclinic.com/health/ectopic-pregnancy/DS00622 - Perkins KM, et al. (2015). Risk of ectopic pregnancy associated with assisted reproductive technology in the United States, 2001-2011.
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4315158/
Our experts continually monitor the health and wellness space, and we update our articles when new information becomes available.
Current Version
Jan 8, 2018
By
Marissa Selner
Edited By
Frank Crooks
Medically Reviewed By
Debra Rose Wilson, PhD, MSN, RN, IBCLC, AHN-BC, CHT
Share this article
Medically reviewed by Debra Rose Wilson, Ph. D., MSN, R.N., IBCLC, AHN-BC, CHT — By Marissa Selner on January 8, 2018
D., MSN, R.N., IBCLC, AHN-BC, CHT — By Marissa Selner on January 8, 2018
related stories
7 Causes for a False-Positive Pregnancy Test
Causes of a Negative Pregnancy Test with No Period
Pregnancy After Tubal Ligation: Know the Symptoms
What You Should Know About Blocked Fallopian Tubes
Depression After a Miscarriage
Read this next
7 Causes for a False-Positive Pregnancy Test
Reputable home pregnancy tests can be accurate, but they aren’t foolproof and can cause confusion. Here are 7 reasons you may receive a false-positive…
READ MORE
Causes of a Negative Pregnancy Test with No Period
Medically reviewed by Michael Weber, MD
If you miss your period but get a negative pregnancy test, there are a number of possible explanations. Here's what might be going on.
READ MORE
Pregnancy After Tubal Ligation: Know the Symptoms
Medically reviewed by Debra Rose Wilson, Ph.D., MSN, R.N., IBCLC, AHN-BC, CHT
If you've undergone a tubal ligation procedure, it's unlikely but still possible that you'll become pregnant. Here's what to watch for.
READ MORE
What You Should Know About Blocked Fallopian Tubes
Medically reviewed by Deborah Weatherspoon, Ph.D., MSN
Blocked fallopian tubes can affect fertility, but with treatment, some women can go on to have healthy pregnancies.
READ MORE
Depression After a Miscarriage
Medically reviewed by Janine Kelbach, RNC-OB
It’s not uncommon to experience depression after the sudden loss of a pregnancy. Learn how to cope with the depression associated with miscarriage.

READ MORE
Pregnancy Complications
Medically reviewed by Michael Weber, MD
Sometimes a pregnant woman’s existing health conditions can contribute to problems, and other times new conditions arise because of body and hormonal…
READ MORE
Pregnancy After Miscarriage: Answers to Your Questions
Medically reviewed by Amanda Kallen, MD
Getting pregnant after a miscarriage can be an emotional experience, filled with joy but also anxiety and guilt. Learn more about pregnancy after…
READ MORE
What Is a Nurse Midwife and How to Tell If They Are Right for You
Medically reviewed by Meredith Wallis, MS, APRN, CNM, IBCLC
A nurse midwife is a nurse with education, training, and certification to provide prenatal, delivery, and women's care.
READ MORE
Your 6-Week Ultrasound: What to Expect
Medically reviewed by Valinda Riggins Nwadike, MD, MPH
We'll tell you all about the 6-week ultrasound, including why your doctor may have ordered it, what the risks are, and what it means if no heartbeat…
READ MORE
Does Swaddling Increase the Risk of SIDS?
Medically reviewed by Mia Armstrong, MD
Is swaddling safe, or is it a risk factor for SIDS? Here's what the most recent research says.
READ MORE
Ectopic Pregnancy: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatments
Ectopic Pregnancy: Symptoms, Causes, and TreatmentsMedically reviewed by Debra Rose Wilson, Ph.D., MSN, R.N., IBCLC, AHN-BC, CHT — By Marissa Selner on January 8, 2018
What is an ectopic pregnancy?
From fertilization to delivery, pregnancy requires a number of steps in a woman’s body. One of these steps is when a fertilized egg travels to the uterus to attach itself. In the case of an ectopic pregnancy, the fertilized egg doesn’t attach to the uterus. Instead, it may attach to the fallopian tube, abdominal cavity, or cervix.
One of these steps is when a fertilized egg travels to the uterus to attach itself. In the case of an ectopic pregnancy, the fertilized egg doesn’t attach to the uterus. Instead, it may attach to the fallopian tube, abdominal cavity, or cervix.
While a pregnancy test may reveal a woman is pregnant, a fertilized egg can’t properly grow anywhere other than the uterus. According to the American Academy of Family Physicians (AAFP), ectopic pregnancies occur in about 1 out of every 50 pregnancies (20 out of 1,000).
An untreated ectopic pregnancy can be a medical emergency. Prompt treatment reduces your risk of complications from the ectopic pregnancy, increases your chances for future, healthy pregnancies, and reduces future health complications.
What causes an ectopic pregnancy?
The cause of an ectopic pregnancy isn’t always clear. In some cases, the following conditions have been linked with an ectopic pregnancy:
- inflammation and scarring of the fallopian tubes from a previous medical condition, infection, or surgery
- hormonal factors
- genetic abnormalities
- birth defects
- medical conditions that affect the shape and condition of the fallopian tubes and reproductive organs
Your doctor may be able to give you more specific information about your condition.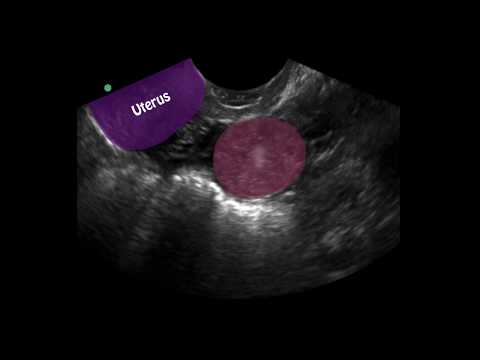
Who is at risk for an ectopic pregnancy?
All sexually active women are at some risk for an ectopic pregnancy. Risk factors increase with any of the following:
- maternal age of 35 years or older
- history of pelvic surgery, abdominal surgery, or multiple abortions
- history of pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)
- history of endometriosis
- conception occurred despite tubal ligation or intrauterine device (IUD)
- conception aided by fertility drugs or procedures
- smoking
- history of ectopic pregnancy
- history of sexually transmitted diseases (STDs), such as gonorrhea or chlamydia
- having structural abnormalities in the fallopian tubes that make it hard for the egg to travel
If you have any of the above risk factors, talk to your doctor. You can work with your doctor or a fertility specialist to minimize the risks for future ectopic pregnancies.
What are the symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy?
Nausea and breast soreness are common symptoms in both ectopic and uterine pregnancies. The following symptoms are more common in an ectopic pregnancy and can indicate a medical emergency:
The following symptoms are more common in an ectopic pregnancy and can indicate a medical emergency:
- sharp waves of pain in the abdomen, pelvis, shoulder, or neck
- severe pain that occurs on one side of the abdomen
- light to heavy vaginal spotting or bleeding
- dizziness or fainting
- rectal pressure
You should contact your doctor or seek immediate treatment if you know that you’re pregnant and have any of these symptoms.
Diagnosing an ectopic pregnancy
If you suspect you may have an ectopic pregnancy, see your doctor immediately. Ectopic pregnancies can’t be diagnosed from a physical exam. However, your doctor may still perform one to rule out other factors.
Another step to diagnosis is a transvaginal ultrasound. This involves inserting a special wand-like instrument into your vagina so that your doctor can see if a gestational sac is in the uterus.
Your doctor may also use a blood test to determine your levels of hCG and progesterone. These are hormones that are present during pregnancy. If these hormone levels start to decrease or stay the same over the course of a few days and a gestational sac isn’t present in an ultrasound, the pregnancy is likely ectopic.
These are hormones that are present during pregnancy. If these hormone levels start to decrease or stay the same over the course of a few days and a gestational sac isn’t present in an ultrasound, the pregnancy is likely ectopic.
If you’re having severe symptoms, such as significant pain or bleeding, there may not be enough time to complete all these steps. The fallopian tube could rupture in extreme cases, causing severe internal bleeding. Your doctor will then perform an emergency surgery to provide immediate treatment.
Treating ectopic pregnancy
Ectopic pregnancies aren’t safe for the mother. Also, the embryo won’t be able to develop to term. It’s necessary to remove the embryo as soon as possible for the mother’s immediate health and long-term fertility. Treatment options vary depending on the location of the ectopic pregnancy and its development.
Medication
Your doctor may decide that immediate complications are unlikely. In this case, your doctor can prescribe several medications that could keep the ectopic mass from bursting. According to the AAFP, one common medication for this is methotrexate (Rheumatrex).
According to the AAFP, one common medication for this is methotrexate (Rheumatrex).
Methotrexate is a drug that stops the growth of rapidly dividing cells, such as the cells of the ectopic mass. If you take this medication, your doctor will give it to you as an injection. You should also get regular blood tests to ensure that the drug is effective. When effective, the medication will cause symptoms that are similar to that of a miscarriage. These include:
- cramping
- bleeding
- the passing of tissue
Further surgery is rarely required after this occurs. Methotrexate doesn’t carry the same risks of fallopian tube damage that come with surgery. You won’t be able to get pregnant for several months after taking this medication, however.
Surgery
Many surgeons suggest removing the embryo and repairing any internal damage. This procedure is called a laparotomy. Your doctor will insert a small camera through a small incision to make sure they can see their work. The surgeon then removes the embryo and repairs any damage to the fallopian tube.
The surgeon then removes the embryo and repairs any damage to the fallopian tube.
If the surgery is unsuccessful, the surgeon may repeat a laparotomy, this time through a larger incision. Your doctor may also need to remove the fallopian tube during surgery if it’s damaged.
Home care
Your doctor will give you specific instructions regarding the care of your incisions after surgery. The chief goals are to keep your incisions clean and dry while they heal. Check them daily for infection signs, which could include:
- bleeding that won’t stop
- excessive bleeding
- foul-smelling drainage from the site
- hot to the touch
- redness
- swelling
You can expect some light vaginal bleeding and small blood clots after surgery. This can occur up to six weeks after your procedure. Other self-care measures you can take include:
- don’t lift anything heavier than 10 pounds
- drink plenty of fluids to prevent constipation
- pelvic rest, which means refraining from sexual intercourse, tampon use, and douching
- rest as much as possible the first week postsurgery, and then increase activity in the next weeks as tolerated
Always notify your doctor if your pain increases or you feel something is out of the ordinary.
Prevention
Prediction and prevention aren’t possible in every case. You may be able to reduce your risk through good reproductive health maintenance. Have your partner wear a condom during sex and limit your number of sexual partners. This reduces your risk for STDs, which can cause PID, a condition that can cause inflammation in the fallopian tubes.
Maintain regular visits with your doctor, including regular gynecological exams and regular STD screenings. Taking steps to improve your personal health, such as quitting smoking, is also a good preventive strategy.
What’s the long-term outlook?
The long-term outlook after an ectopic pregnancy depends on whether it caused any physical damage. Most people who have ectopic pregnancies go on to have healthy pregnancies. If both fallopian tubes are still intact, or even just one, the egg can be fertilized as normal. However, if you have a preexisting reproductive problem, that can affect your future fertility and increase your risk of future ectopic pregnancy. This is especially the case if the preexisting reproductive problem has previously led to an ectopic pregnancy.
This is especially the case if the preexisting reproductive problem has previously led to an ectopic pregnancy.
Surgery may scar the fallopian tubes, and it can make future ectopic pregnancies more likely. If the removal of one or both fallopian tubes is necessary, speak to your doctor about possible fertility treatments. An example is in vitro fertilization that involves implanting a fertilized egg into the uterus.
Pregnancy loss, no matter how early, can be devastating. You can ask your doctor if there are available support groups in the area to provide further support after loss. Take care of yourself after this loss through rest, eating healthy foods, and exercising when possible. Give yourself time to grieve.
Remember that many women go on to have healthy pregnancies and babies. When you’re ready, talk to your doctor about ways you can ensure that your future pregnancy is a healthy one.
Last medically reviewed on January 8, 2018
- Parenthood
- Pregnancy
- Pregnancy Complications
How we reviewed this article:
Healthline has strict sourcing guidelines and relies on peer-reviewed studies, academic research institutions, and medical associations. We avoid using tertiary references. You can learn more about how we ensure our content is accurate and current by reading our editorial policy.
We avoid using tertiary references. You can learn more about how we ensure our content is accurate and current by reading our editorial policy.
- Cleveland Clinic Staff. (2014). Ectopic pregnancy.
my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases_conditions/hic_Ectopic_Pregnancy - Ectopic pregnancy. (2017).
acog.org/Patients/FAQs/Ectopic-Pregnancy - Gyn onc home care after your laparotomy. (2017).
uwhealth.org/healthfacts/gyn-onc/6081.pdf - Mayo Clinic Staff. (2015). Ectopic pregnancy.
mayoclinic.com/health/ectopic-pregnancy/DS00622 - Perkins KM, et al. (2015). Risk of ectopic pregnancy associated with assisted reproductive technology in the United States, 2001-2011.
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4315158/
Our experts continually monitor the health and wellness space, and we update our articles when new information becomes available.
Current Version
Jan 8, 2018
By
Marissa Selner
Edited By
Frank Crooks
Medically Reviewed By
Debra Rose Wilson, PhD, MSN, RN, IBCLC, AHN-BC, CHT
Share this article
Medically reviewed by Debra Rose Wilson, Ph. D., MSN, R.N., IBCLC, AHN-BC, CHT — By Marissa Selner on January 8, 2018
D., MSN, R.N., IBCLC, AHN-BC, CHT — By Marissa Selner on January 8, 2018
related stories
7 Causes for a False-Positive Pregnancy Test
Causes of a Negative Pregnancy Test with No Period
Pregnancy After Tubal Ligation: Know the Symptoms
What You Should Know About Blocked Fallopian Tubes
Depression After a Miscarriage
Read this next
7 Causes for a False-Positive Pregnancy Test
Reputable home pregnancy tests can be accurate, but they aren’t foolproof and can cause confusion. Here are 7 reasons you may receive a false-positive…
READ MORE
Causes of a Negative Pregnancy Test with No Period
Medically reviewed by Michael Weber, MD
If you miss your period but get a negative pregnancy test, there are a number of possible explanations. Here's what might be going on.
READ MORE
Pregnancy After Tubal Ligation: Know the Symptoms
Medically reviewed by Debra Rose Wilson, Ph.D., MSN, R.N., IBCLC, AHN-BC, CHT
If you've undergone a tubal ligation procedure, it's unlikely but still possible that you'll become pregnant. Here's what to watch for.
READ MORE
What You Should Know About Blocked Fallopian Tubes
Medically reviewed by Deborah Weatherspoon, Ph.D., MSN
Blocked fallopian tubes can affect fertility, but with treatment, some women can go on to have healthy pregnancies.
READ MORE
Depression After a Miscarriage
Medically reviewed by Janine Kelbach, RNC-OB
It’s not uncommon to experience depression after the sudden loss of a pregnancy. Learn how to cope with the depression associated with miscarriage.

READ MORE
Pregnancy Complications
Medically reviewed by Michael Weber, MD
Sometimes a pregnant woman’s existing health conditions can contribute to problems, and other times new conditions arise because of body and hormonal…
READ MORE
Pregnancy After Miscarriage: Answers to Your Questions
Medically reviewed by Amanda Kallen, MD
Getting pregnant after a miscarriage can be an emotional experience, filled with joy but also anxiety and guilt. Learn more about pregnancy after…
READ MORE
What Is a Nurse Midwife and How to Tell If They Are Right for You
Medically reviewed by Meredith Wallis, MS, APRN, CNM, IBCLC
A nurse midwife is a nurse with education, training, and certification to provide prenatal, delivery, and women's care.
READ MORE
Your 6-Week Ultrasound: What to Expect
Medically reviewed by Valinda Riggins Nwadike, MD, MPH
We'll tell you all about the 6-week ultrasound, including why your doctor may have ordered it, what the risks are, and what it means if no heartbeat…
READ MORE
Does Swaddling Increase the Risk of SIDS?
Medically reviewed by Mia Armstrong, MD
Is swaddling safe, or is it a risk factor for SIDS? Here's what the most recent research says.
READ MORE
Ectopic pregnancy. The reasons. Symptoms. Treatment.
Services and prices
Primary reception of gynecologist
dated 1700 ₽
Repeated gynecologist
dated 1400 ₽
Primary reception of a surgeon-gynecologist
2000 ₽
9000 pregnancy is a condition in which a fetus can begin to develop outside the uterus. Unfortunately, in this case, the embryo cannot be saved. It is necessary to start treatment as soon as possible, as the woman's condition can quickly worsen.
Unfortunately, in this case, the embryo cannot be saved. It is necessary to start treatment as soon as possible, as the woman's condition can quickly worsen. Unfortunately, an ectopic pregnancy is almost the same as a normal one. But this problem can lead to many unpleasant consequences, so you need to contact a specialist at the first suspicion.
Causes of ectopic pregnancy
- Adnexitis. After various inflammatory processes, adhesions may remain, which can prevent the egg from being in the uterus.
- Violation of nerve conduction, in which there are problems with the transport of the egg through the tubes into the uterine cavity.
- Various anomalies in the tubes that form in utero.
- Hormonal diseases that negatively affect the activity of the whole organism.
- Operations after which adhesions may form.
- If a woman has only one tube, this can also prevent the egg from reaching the uterine cavity.
Symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy
An ectopic pregnancy begins in the same way as a normal one - toxicosis, swollen mammary glands, lack of menstruation.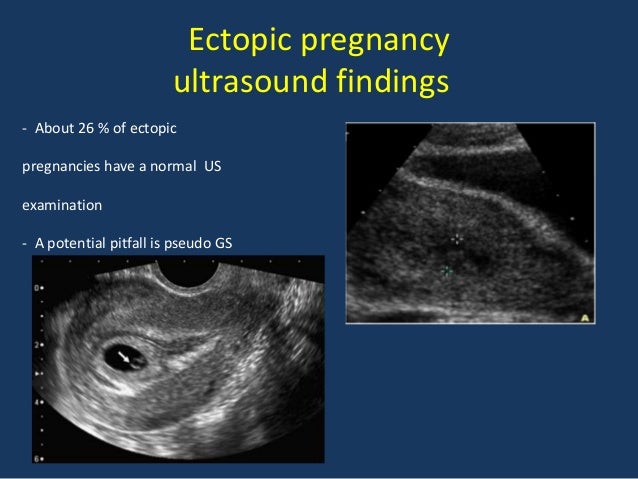 However, in the future, pathological symptoms may occur that are not characteristic of a normal pregnancy:
However, in the future, pathological symptoms may occur that are not characteristic of a normal pregnancy:
- Cramping pain in the lumbar region. When a pipe breaks, the pain is so sharp that a person can lose consciousness.
- Brown discharge that may occur over a number of days.
- Urge to empty the bowels.
- Rectal pain may occur.
Treatment
In case of ectopic pregnancy, the main method of treatment is surgery. It could be:
- Fallopian tube incision. During the operation, the fetal egg is removed.
- Vacuum extraction.
- Complete pipe removal. Produced during an interrupted pregnancy.
Treatment with conservative methods is used only at the earliest stages. Such treatment is possible only if there are no pronounced symptoms.
Prevention of pathology
One of the most dangerous consequences of an ectopic pregnancy is infertility, so the following rules must be followed:
- Treat existing diseases under the supervision of a specialist - a gynecologist.

- Monitor the hormonal background, take tests on the advice of a specialist.
- Have regular gynecological examinations.
Take care of yourself, dear mothers! We wish you all an easy pregnancy and healthy babies!
Back to the list of articles
Ectopic pregnancy - signs, causes, symptoms, treatment and prevention
Ectopic pregnancy
Contents
- What is an ectopic pregnancy and how does it develop?
- Signs and symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy
- Causes of an ectopic pregnancy
- Diagnosis of an ectopic pregnancy
- Treatment of an ectopic pregnancy
- Consequences of an ectopic pregnancy
- Why should you visit the Mama Papa Ya clinic?
After fertilization, the ovum sequentially moves through the cilia of the epithelium along the fallopian tube and attaches to the inner surface of the uterus.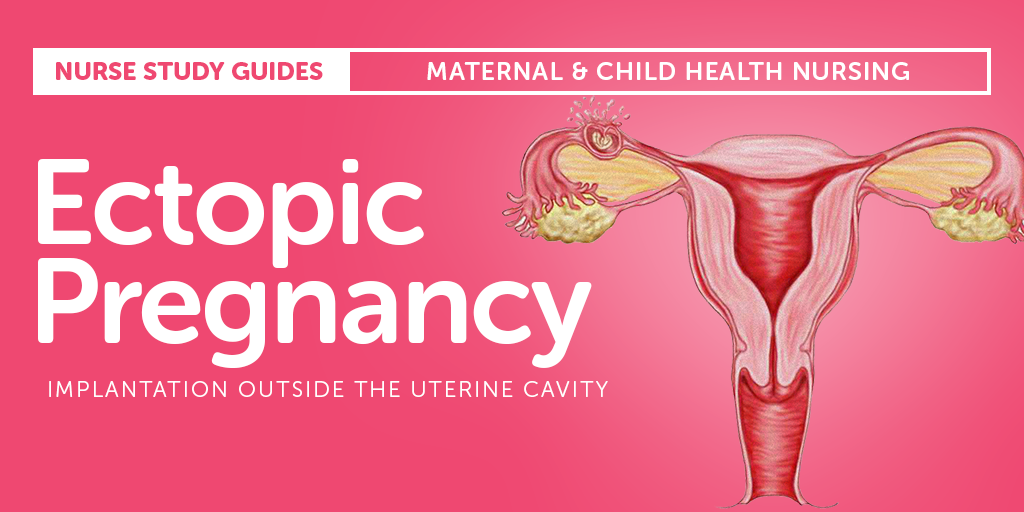 Symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy occur when such implantation occurs outside the surface of the endometrium. This happens in 2% of all conceptions.
Symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy occur when such implantation occurs outside the surface of the endometrium. This happens in 2% of all conceptions.
What is an ectopic pregnancy and how does it develop?
In this condition, the egg is attached not in the uterus, but in the fallopian tube, on the surface of the peritoneum or cervix. At this time, a home pregnancy test will be positive, but the fetal egg will not be able to fully develop and will inevitably die.
Early symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy are a medical emergency. Prompt treatment reduces a woman's risk of complications and increases her chance of having a baby in the future.
Signs and symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy
When a patient develops an ectopic pregnancy, early signs are normal. Observed:
- delayed menstruation;
- breast tenderness;
- fatigue;
- nausea;
- frequent urination.
Later signs of ectopic pregnancy appear after 6 to 8 weeks of delayed menstruation:
- slight discharge of blood from the vagina;
- abdominal or pelvic pain.

With further development, the following signs and symptoms of ectopic pregnancy occur:
- pain in the lower abdomen, aggravated by movement; at first, it may suddenly appear on one side, and then spread to the entire pelvic area;
- severe vaginal bleeding;
- soreness during intercourse or gynecological examination;
- dizziness or fainting due to internal bleeding;
- pale skin, cold sweat, shortness of breath, weak rapid pulse, impaired consciousness (signs of shock).
Causes of ectopic pregnancy
The most common type of pathology is tubal, in which a fertilized egg develops in the fallopian tube. Causes of an ectopic pregnancy in this case include:
- smoking: it interferes with the ability of the fallopian tube to move the embryo into the uterine cavity;
- an inflammatory disease such as gonorrhea or chlamydia that has caused a scar in the tubal cavity;
- surgery on fallopian tube;
- previous ectopic pregnancy.
Pathology risk factors:
- woman's age over 35;
- surgery for diseases of the abdominal organs;
- multiple abortions;
- endometriosis;
- malformations of the fallopian tubes;
- pregnancy due to the use of an intrauterine device.
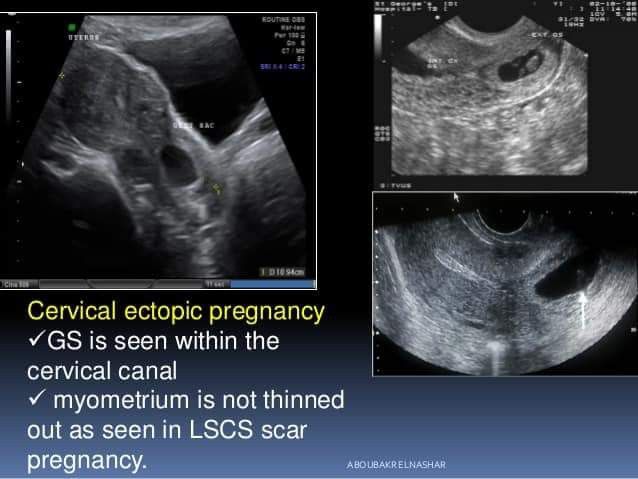
Diagnosis of ectopic pregnancy
At the beginning of its development, such a pregnancy proceeds as normal, and its termination resembles a spontaneous abortion. How to recognize an ectopic pregnancy? It is very difficult to do this on your own, since such a measureable sign as basal temperature during ectopic pregnancy is not informative - the schedule before the loss of the embryo is the same as during normal gestation.
Diagnosis of ectopic pregnancy is carried out using the following methods:
- gynecological examination, revealing the absence of signs of uterine pregnancy and pathological formation, for example, in the tube;
- Ultrasound, which makes it possible to determine the pathology from 1 - 2 weeks of delayed menstruation, when a fetal egg is not found in the uterus;
- analysis for hCG with an interval of 48 hours, normally the indicator doubles during this time, with an ectopic pregnancy, its increase in the blood is not so great.
Treatment of ectopic pregnancy
A child cannot develop outside the uterus, and the spontaneous interruption of such a pathological process is dangerous for a woman's life. Therefore, the treatment of ectopic pregnancy is only surgical:
- salpingostomy - a longitudinal incision of the tube with subsequent restoration of its wall;
- salpingectomy - removal of part of the tube when it is ruptured.
Both operations can be performed laparoscopically or laparotomically.
There is also a medication method of treatment - methotrexate. It is used only in the earliest stages when the operation is impossible.
Consequences of an ectopic pregnancy
Generally, the consequences of an ectopic pregnancy are relatively favorable: although a woman's ability to conceive is reduced by about 40%, she can still carry and give birth to a child. Another negative factor is the increased risk of recurrence of such a pathology.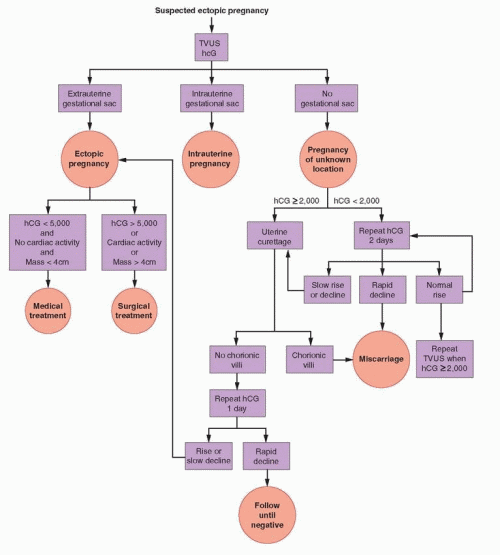
Recovery from an ectopic pregnancy occurs during the next menstrual cycle. Much more harm to a woman is brought not by physical, but by psychological trauma. Full rehabilitation requires the support of relatives, communication on appropriate forums, and sometimes individual and group psychotherapy.
The negative consequences of an ectopic pregnancy can be reduced if the causes of the disease are immediately looked for and eliminated.
Why should you visit the Mama Papa Ya clinic?
The network of medical clinics "Mama Papa Ya", whose branches are located in Moscow and other cities, offers medical services at affordable prices that will help to avoid the development of pathology or diagnose it in time:
- consultation of a qualified gynecologist on pregnancy planning;
- individual pregnancy management program “Waiting for you, baby!”;
- tests necessary for expectant mothers, including determining the level of hCG;
- gynecological ultrasound for the diagnosis of the disease at an early stage.
All consultations and procedures are carried out at a convenient time for the patient, without waiting and queues.
If you miss your period, we recommend that you take a home pregnancy test and, regardless of the results, make an appointment with a gynecologist. This can be done by calling the nearest clinic or on the website.
Reviews
Good clinic, good doctor! Raisa Vasilievna can clearly and easily explain what the essence of the problem is. If something is wrong, she talks about everything directly, not in a veiled way, as other doctors sometimes do. I don't regret that I went to her.
Anna
I want to express my gratitude to the staff of the clinic Mom, Dad, me. The clinic has a very friendly atmosphere, very friendly and cheerful staff and highly qualified specialists. Thank you very much! I wish prosperity to your clinic.
Anonymous user
Today I removed a mole on my face at the dermatologist Kodareva I.A. Doctor is very thorough! Correct! Thanks a lot! Administrator Borshchevskaya Julia is friendly, clearly fulfills her duties.
Belova E.M.
Today I was served in the clinic, I was satisfied with the staff, as well as the gynecologist. Everyone treats patients with respect and care. We thank them very much and continue to prosper.
Anonymous user
The Mama Papa Ya clinic in Lyubertsy is very good. The team is friendly and responsive. I recommend this clinic to all my friends. Thanks to all doctors and administrators. I wish the clinic prosperity and many adequate clients.
Iratiev V.V.
Visited the clinic "Mama Papa Ya" with a child. I needed a consultation with a pediatric cardiologist. I liked the clinic. Good service doctors. We didn't stand in line, everything was the same price.
Evgenia
I liked the first visit. I was carefully examined, additional examinations were prescribed, and good recommendations were given. I will continue the treatment further, I liked the conditions in the clinic.
Kristina
The doctor carefully examined my husband, ordered an ECG and made a preliminary diagnosis.