Morning sickness prevention
Morning sickness | March of Dimes
Morning sickness is when you have nausea and vomiting during pregnancy. Even though it’s called morning sickness, it can happen any time of day.
Morning sickness usually starts at about 6 weeks of pregnancy and goes away in the second trimester.
Lots of pregnant women have morning sickness. It usually doesn’t cause harm to you or your baby.
Hyperemesis gravidarum is severe nausea and vomiting that needs treatment (sometimes in a hospital) to help you get better.
If your morning sickness is severe or if it goes into your fourth month of pregnancy, tell your health care provider right away.
What is morning sickness?
Morning sickness (also called nausea and vomiting of pregnancy, or NVP) is nausea (feeling sick to your stomach) and vomiting that happens in the first few months of pregnancy. Even though it's called morning sickness, it can last all day and happen any time of day.
At least 7 in 10 pregnant women have morning sickness in the first trimester (first 3 months) of pregnancy. It usually starts at about 6 weeks of pregnancy and is at its worst at about 9 weeks. Most women feel better in their second trimester, but some have morning sickness throughout pregnancy. If you have morning sickness, tell your health care provider.
Mild morning sickness doesn’t harm you or your baby. But if nausea and vomiting becomes severe (called hyperemesis gravidarum), it can cause serious problems during pregnancy. You may need to stay in the hospital for treatment.
What is hyperemesis gravidarum?
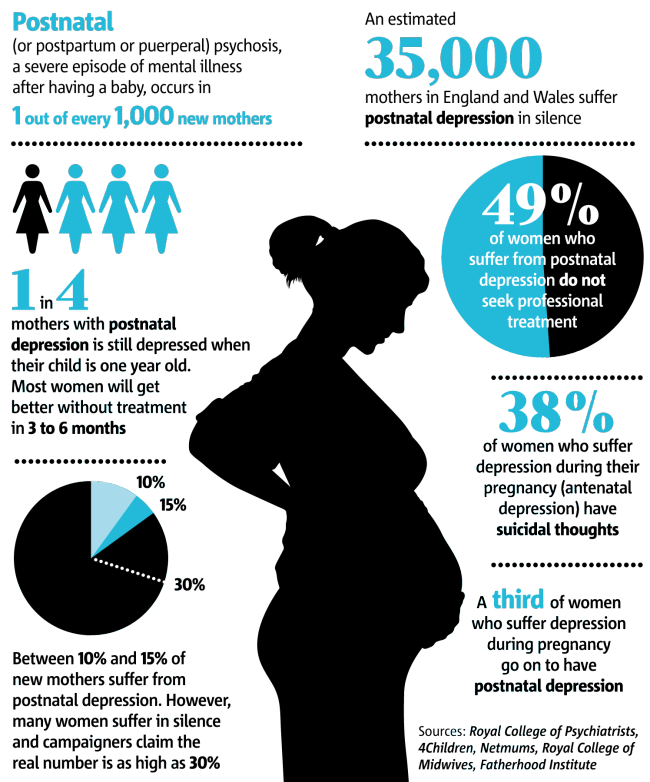
About 3 in 100 women may have hyperemesis gravidarum. This is extreme, excessive nausea and vomiting during pregnancy. It can cause you to lose weight and become dehydrated (not have enough water in your body). It can start early in pregnancy and last the entire pregnancy. If you have hyperemesis gravidarum, you need treatment to help keep you and your baby safe.
You may be at risk for hyperemesis gravidarum if you:
- Are pregnant for the first time.
- Are pregnant with a girl.
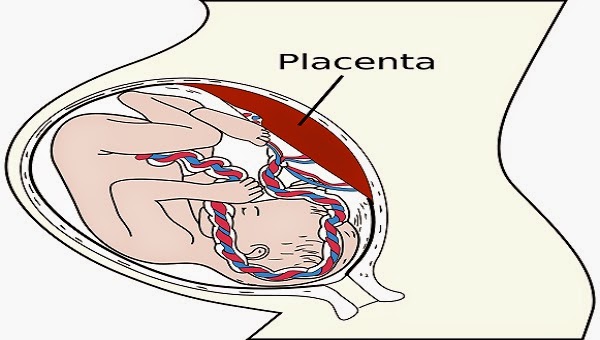
- Are pregnant with multiples (twins, triplets or more). Being pregnant with more than one baby may increase your risk for severe morning sickness because you may have a large placenta and increased pregnancy hormones. The placenta grows in your uterus (womb) and supplies your babies with food and oxygen through the umbilical cord.
- Had mild or severe morning sickness in a previous pregnancy, or your mother or sister had severe morning sickness during pregnancy. Take your family health history to help you find out about health conditions that run in your family. This is a record of any health conditions and treatments that you or your family members have had.
- Have motion sickness or migraines. A migraine is a severe headache that may make you sensitive to bright lights and sound.
- Are overweight.
- Have trophoblastic disease, a condition that leads to abnormal cell growth in the uterus (womb).

Signs and symptoms of hyperemesis gravidarum include:
- Vomiting more than 3 to 4 times a day
- Vomiting that makes you dizzy or lightheaded
- Vomiting that makes you dehydrated. Signs and symptoms of dehydration include feeling thirsty, dry mouth, a fast heart beat or making little to no urine.
- Losing more than 10 pounds in pregnancy
If you have hyperemesis gravidarum, your provider may treat you with medicine to help relieve your nausea and vomiting. You may need treatment in a hospital with intravenous (also called IV) fluids. IV fluids go through a needle into your vein. They help you stay hydrated and can give you nutrients that you usually get from food. If you continue to lose weight, you may need a feeding tube to make sure you’re getting enough nutrients for you and your baby.
What causes morning sickness?
We don’t know for sure what causes morning sickness. It may be caused by low blood sugar or increased pregnancy hormones. Morning sickness may be worse if you’re stressed or overly tired, if you eat certain foods or if you’re traveling (if you often have motion sickness).
Morning sickness may be worse if you’re stressed or overly tired, if you eat certain foods or if you’re traveling (if you often have motion sickness).
Can you prevent or relieve morning sickness?
Yes. Here’s what you can do to help you feel better and even prevent morning sickness:
- Take a prenatal vitamin before you get pregnant. Talk to your health care provider about which one to take. Sometimes vitamins can upset your stomach, so take it with a snack.
- Keep snacks by your bed. Eat a few crackers before you get up in the morning to help settle your stomach.
- Eat 5 or 6 small meals each day instead of 3 larger meals.
- Eat foods that are low in fat and easy to digest, like cereal, rice and bananas. Don’t eat spicy or fatty foods.
- Eat healthy snacks between meals. This can help keep your stomach from being empty and helps prevent nausea. Try snacks that are high in protein, like milk or yogurt.
- Drink plenty of fluids, especially water.

- Avoid smells that upset your stomach.
You may have heard about these ways to prevent or relieve morning sickness. Talk to your provider before trying any of these:
- Acupressure and acustimulation (also called electrical nerve stimulation) wristbands. These involve putting pressure on or stimulating certain points of the body (called pressure points) to help prevent nausea.
- Acupuncture. This is a kind of treatment in which thin needles are put into your skin. If you’re thinking about acupuncture to help with morning sickness, tell your provider and find an acupuncturist who is trained to work with pregnant women.
- Ginger. Ginger is an herb (plant) used in cooking and medicine. Ginger ale, tea or candies may help relieve morning sickness.
Even if it’s legal where you live for either personal or medical use, it’s not safe to use marijuana to treat morning sickness. No amount of marijuana has been proven safe to use during pregnancy. If you’re thinking of using marijuana to help with morning sickness, talk to your provider about other treatments that are safer for your baby.
If you’re thinking of using marijuana to help with morning sickness, talk to your provider about other treatments that are safer for your baby.
Is there medical treatment for morning sickness?
Yes. If you can’t relieve morning sickness on your own or if you have severe nausea and vomiting of pregnancy, your provider may treat you with these medicines:
- Vitamin B6 and doxylamine. Your provider may treat you with these medicines separately or together. You can get vitamin B6 and doxylamine over-the-counter (OTC), which means you don’t need a prescription for them from your provider. Doxylamine is found in some OTC sleep aids (medicines that help you sleep). Or your provider may prescribe you a medicine that combines them.
- Antiemetic drugs. These are drugs that help prevent vomiting. If Vitamin B6 and doxylamine don’t work, your provider may prescribe an antiemetic drug for you. Not all are safe to use during pregnancy, so talk to your provider to make sure the medicine is a good choice for you.

Talk to your provider before you take any medicine during pregnancy, even medicine to help treat morning sickness.
When should you call your health care provider about morning sickness?
For most women, morning sickness is mild and goes away over time. But call your provider if:
- Your morning sickness continues into your 4th month of pregnancy.
- You lose more than 2 pounds.
- Your vomit is brown in color or has blood in it. If so, call your provider right away.
- You vomit more than 3 times a day and can’t keep food or fluids down.
- Your heart beats faster than usual.
- You’re tired or confused.
- You’re making much less urine than usual or no urine at all.
Last reviewed: September, 2020
Morning Sickness: Causes, Treatments, and Prevention
Morning Sickness: Causes, Treatments, and PreventionMedically reviewed by Valinda Riggins Nwadike, MD, MPH — By Euna Chi, MD on August 25, 2019
Overview
Morning sickness is a common symptom of pregnancy and is marked by nausea and occasional vomiting. Despite the name, morning sickness can cause discomfort at any time of the day.
Despite the name, morning sickness can cause discomfort at any time of the day.
Morning sickness usually happens within the first four months of pregnancy and is often the first sign that a woman is pregnant.
There are various ways to alleviate morning sickness, and complications are rare.
Causes of morning sickness
There’s no one cause of morning sickness during pregnancy, and severity varies among women. Increased hormone levels during the first few weeks of pregnancy is among the most common causes. Reduced blood sugar is another common cause of morning sickness.
Other factors can worsen morning sickness. These include:
- having twins or triplets
- excessive fatigue
- emotional stress
- frequent traveling
Morning sickness can vary between pregnancies. While you may have had severe morning sickness during one pregnancy, in future pregnancies it may be very mild.
Possible complications of morning sickness
Nausea and vomiting can easily cause a loss of appetite. Many pregnant women worry that this will harm their babies. Mild morning sickness is generally not harmful.
Many pregnant women worry that this will harm their babies. Mild morning sickness is generally not harmful.
Women who experience morning sickness well beyond the first 3 to 4 months of their pregnancies should speak with their doctor. Also seek help if you aren’t gaining any weight during pregnancy.
Morning sickness is usually not severe enough to hinder fetal growth and development. For some pregnant women, nausea causes them to experience severe vomiting and weight loss.
This condition is called hyperemesis gravidarum. It causes electrolyte imbalances and unintentional weight loss. If left untreated, this condition may eventually harm your baby.
Call your doctor immediately if you experience:
- inability to keep food down
- weight loss of 2 pounds or more
- fever
- infrequent urination with small quantities of dark-colored urine
- lightheadedness or dizziness
- fast heartbeat
- severe nausea within the second trimester
- blood in your vomit
- frequent headaches
- abdominal pain
- spotting, or bleeding
Severe bouts of morning sickness generally require hospitalization. Hyperemesis gravidarum often requires intravenous (IV) fluids for rehydration.
Hyperemesis gravidarum often requires intravenous (IV) fluids for rehydration.
Treatment for morning sickness
Your doctor may prescribe supplements or medications to alleviate nausea and to help you retain foods and fluids. Medications your doctor may prescribe include:
- antihistamines: to help with nausea and motion sickness
- phenothiazine: to help calm severe nausea and vomiting
- metoclopramide (Reglan): to help the stomach move food into the intestines and help with nausea and vomiting
- antacids: to absorb stomach acid and help prevent acid reflux
Do not take these medications on your own without first talking with your doctor.
Some people find that alternative remedies may also help relieve morning sickness. Make sure you only try these after first discussing them with your doctor. These remedies include:
- vitamin B-6 supplements
- prenatal vitamins
- ginger products, including ginger ale, ginger tea, and ginger drops
- saltine crackers
- acupuncture
- hypnosis
Tests for morning sickness
Based on your symptoms, your doctor may order some tests to make sure that you and your baby are safe. These include:
These include:
Urine tests
Urine tests can determine whether you’re dehydrated.
Blood chemistry tests
Your doctor may order blood chemistry tests that include:
- complete blood count (CBC)
- comprehensive metabolic panel
- comprehensive metabolic panel (Chem-20), to measure the electrolytes in your blood.
These tests will determine whether you’re:
- dehydrated
- malnourished, or deficient in certain vitamins
- anemic
Ultrasound
Ultrasound uses sound waves to produce images of your baby. The doctor then uses these images and sounds to check that your baby is developing at a healthy rate.
Preventing morning sickness
Taking the following steps may help prevent or minimize nausea:
- Drink plenty of water.
- Drink water before and after meals.
- Take naps.
- Ventilate your home and workspace to eliminate scents that make you nauseous.
- Avoid spicy foods.

- Eat small meals.
- Avoid fatty foods.
- Take vitamins at night.
- Avoid cigarette smoke.
If none of these preventative measures works, or if you experience morning sickness beyond the first 3 to 4 months of your pregnancy, it’s important that you speak with your doctor.
Also, be sure to talk to your doctor before starting any medications or alternative remedies to discuss these options.
Last medically reviewed on August 26, 2019
- Parenthood
- Pregnancy
How we reviewed this article:
Healthline has strict sourcing guidelines and relies on peer-reviewed studies, academic research institutions, and medical associations. We avoid using tertiary references. You can learn more about how we ensure our content is accurate and current by reading our editorial policy.
- Bustos
M, et al. (2018). Nausea and vomiting of pregnancy-what’s new? DOI:
10.1016/j. autneu.2016.05.002
autneu.2016.05.002 - Mayo
Clinic Staff. (2018). Preeclampsia.
mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/preeclampsia/symptoms-causes/syc-20355745 - Metoclopramide [Fact sheet]. (2018).
mothertobaby.org/fact-sheets/metoclopramide/pdf/ - Morning sickness: Nausea and vomiting of pregnancy. (n.d.).
acog.org/~/media/For%20Patients/faq126.pdf?dmc=1&ts=20120706T1713504525 - Routine
tests during pregnancy. (2017).
acog.org/Patients/FAQs/Routine-Tests-During-Pregnancy?IsMobileSet=false
Share this article
Medically reviewed by Valinda Riggins Nwadike, MD, MPH — By Euna Chi, MD on August 25, 2019
related stories
When Does Morning Sickness Start?
Can You Get Morning Sickness at Night?
The Peak of Your Morning Sickness
Vomiting During Pregnancy
Hyperemesis Gravidarum
Read this next
When Does Morning Sickness Start?
Medically reviewed by Valinda Riggins Nwadike, MD, MPH
Is that nausea you're feeling actually morning sickness? Learn more about when morning sickness starts, when it ends, and how to manage the symptoms…
READ MORE
Can You Get Morning Sickness at Night?
Medically reviewed by Debra Sullivan, Ph.
 D., MSN, R.N., CNE, COI
D., MSN, R.N., CNE, COIWe explain morning sickness at night and ways to manage this pregnancy symptom.
READ MORE
The Peak of Your Morning Sickness
Medically reviewed by Fernando Mariz, MD
Morning sickness is very common during pregnancy, but when does it peak? Learn about what to expect, and get tips on minimizing this type of nausea.
READ MORE
Vomiting During Pregnancy
Medically reviewed by Valinda Riggins Nwadike, MD, MPH
Nausea and vomiting during pregnancy are an unfortunate reality for many. Understanding the causes — from morning sickness to illness to hyperemesis…
READ MORE
Hyperemesis Gravidarum
Hyperemesis gravidarum (HG) is an extreme form of morning sickness that causes severe nausea and vomiting during pregnancy.
 Learn treatment options…
Learn treatment options…READ MORE
Pregnancy After Miscarriage: Answers to Your Questions
Medically reviewed by Amanda Kallen, MD
Getting pregnant after a miscarriage can be an emotional experience, filled with joy but also anxiety and guilt. Learn more about pregnancy after…
READ MORE
What Is a Nurse Midwife and How to Tell If They Are Right for You
Medically reviewed by Meredith Wallis, MS, APRN, CNM, IBCLC
A nurse midwife is a nurse with education, training, and certification to provide prenatal, delivery, and women's care.
READ MORE
Your 6-Week Ultrasound: What to Expect
Medically reviewed by Valinda Riggins Nwadike, MD, MPH
We'll tell you all about the 6-week ultrasound, including why your doctor may have ordered it, what the risks are, and what it means if no heartbeat…
READ MORE
Does Swaddling Increase the Risk of SIDS?
Medically reviewed by Mia Armstrong, MD
Is swaddling safe, or is it a risk factor for SIDS? Here's what the most recent research says.

READ MORE
How to Relieve and Prevent Hip Pain During Pregnancy
Medically reviewed by Holly Ernst, PA-C
Hip pain is a common complication of pregnancy. Here are stretches, other home remedies, causes, and what you can do to prevent it.
READ MORE
Why nausea in the morning on an empty stomach - causes and how to treat at home
Most often, pregnant women face nausea in the morning on an empty stomach, due to intoxication, but it is not uncommon for this problem to occur in males or even children
Do not worry too much if you have encountered such a problem once, it is likely that this is a banal poisoning. But, if nausea in the morning on an empty stomach does not go away, you should immediately consult a doctor. Some people are used to dealing with this problem with folk remedies and medicines and they really get better, but it is worth considering that most likely the disease or pathology itself continues to develop. And as a result, it will turn into a more serious form. That is why it is so important to consult a doctor who will find out the cause of morning sickness and prescribe the most effective treatment.
And as a result, it will turn into a more serious form. That is why it is so important to consult a doctor who will find out the cause of morning sickness and prescribe the most effective treatment.
Possible diseases
Most often, morning sickness on an empty stomach may indicate the presence of the following diseases: unpleasant symptoms. This is due to inflammatory processes in the duodenum 12. The patient can also be tormented by: burning, bloating during and after eating, heartburn.
 Accompanying symptoms are pain in the right hypochondrium and excessive gas formation.
Accompanying symptoms are pain in the right hypochondrium and excessive gas formation. Other causes of nausea in the morning
After excluding the above diseases from the list of causes, the following causes can be considered:
- Pregnancy. Intoxication and nausea in the morning is often found in pregnant women, especially in the early stages. This is a normal reaction of the body to significant changes and hormonal changes. It is very important to completely exclude drugs for the treatment of the digestive tract during pregnancy. These funds can have an extremely negative impact on the health of the patient, the unborn child and the course of pregnancy. Therefore, you will have to endure this ailment and get by with folk remedies, but be sure to consult your doctor.
- Migraine. Morning sickness on an empty stomach may precede a severe headache. You will most likely still feel a lot of noise and increased sensitivity to smells.
- High blood pressure (hypertension).
 The problem of morning sickness can be accompanied by headache and dizziness. If you do not pay attention to these symptoms in a timely manner, you risk starting this disease, which in turn can lead to a stroke.
The problem of morning sickness can be accompanied by headache and dizziness. If you do not pay attention to these symptoms in a timely manner, you risk starting this disease, which in turn can lead to a stroke. - Cardiovascular disease - rarely, nausea on an empty stomach occurs with heart failure or developing myocardial infarction. If nausea is accompanied by pain, a feeling of heaviness and tightness behind the sternum, numbness or tingling in one half of the body, it is necessary to seek medical help as soon as possible, as this may be an incipient myocardial infarction.
- Increased intracranial pressure - Nausea and regurgitation in infants can occur when pressure increases inside the ventricles of the brain.
What to do if you feel sick in the morning
It is important to understand that regular morning sickness is a signal of the presence of a pathology or disease and it is highly undesirable to self-medicate. Be sure to consult a doctor for an examination, but if you don’t have such an opportunity at the moment, there are several effective ways that will help reduce or temporarily get rid of this problem:
- Medicines.
 You need to be very careful and you must be sure that morning sickness is not the cause of pregnancy or an intestinal disease.
You need to be very careful and you must be sure that morning sickness is not the cause of pregnancy or an intestinal disease. - Ginger root, mint and lemon drinks. You can make infusions of these products for maximum effect, simply by adding them to a glass and boiling water, after 15 minutes you will have a very effective and safe (in the absence of allergies) remedy for morning sickness. YOU can also just add them to hot tea.
- Medicinal collection - if nausea relentlessly torments you in the morning, you can try a collection of mint, oak bark and celandine. To prepare the drink, take 1 tsp of mint leaves, dried oak bark and chopped celandine, pour 0.5 l of boiling water and boil in a water bath for 10 minutes. After the broth is cooled and filtered, take 1 tablespoon 3-5 times a day before meals.
- During pregnancy. There are some little tricks you can use. For example, do not get out of bed quickly, drink plenty of fluids. Eliminate fatty and heavy foods from your diet.
 Eat small meals several times a day.
Eat small meals several times a day.
causes, treatment, prevention. How to get rid of nausea?
Causes of nausea
Nausea may indicate the presence of diseases, but in some cases it occurs in apparently healthy people. This unpleasant sensation is more common in women, but men have their own risk factors.
Non-disease causes of nausea include the following situations.
- Overeating and eating fatty foods. This is due to the inability of the body to process a large amount of "heavy" food.
- Psychogenic reactions: stress, neurosis, anxiety. With psychogenic nausea, it is enough to feel an unpleasant smell or see something unpleasant, to remember the emotions experienced.
- Motion sickness or motion sickness. This type of nausea is associated with irritation of the receptors of the vestibular apparatus during movement.
- Pregnancy. Nausea during pregnancy is one of the first manifestations of toxicosis. Morning sickness most often appears at 6-7 weeks and most often stops at 12-13 weeks.

- Exposure to toxic fumes from chemicals, smoke, etc.
- Side effects of drugs. Nausea may manifest as an adverse reaction of the body to certain medications, such as antibiotics, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, corticosteroids, etc.
- Sunstroke or heat stroke.
- Increased body temperature.
Nausea can be a symptom of many gastrointestinal disorders. These include:
- diseases requiring urgent surgical intervention: acute pancreatitis, appendicitis, intestinal obstruction, peritonitis;
- chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract: gastritis, enteritis, colitis, gastroesophageal reflux disease, ulcerative colitis, peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum, irritable bowel syndrome, chronic cholecystitis;
- intestinal infections - salmonellosis, dysentery, enterovirus, rotavirus infections, helminthiases, food poisoning, etc.;
- liver diseases - hepatitis, cirrhosis;
- foreign body of the esophagus, stomach;
- food allergy.

Nausea may develop in some diseases of other organs and systems.
- Traumatic brain injuries, brain tumors, encephalitis, meningitis, stroke, etc.
- Diseases of the inner ear: labyrinthitis, Meniere's disease.
- Diseases of the cardiovascular system: myocardial infarction, hypertension.
- Diseases of the endocrine system: phenylketonuria (impaired amino acid metabolism), diabetic ketoacidosis (abnormal carbohydrate metabolism, in which acetone accumulates in the blood), thyrotoxicosis (excess thyroid hormones).
- Renal failure.
- Migraine.
- When receiving chemotherapy.
Nausea treatment
Since nausea is most often a symptom of an illness, it is important to identify and eliminate the underlying cause. If the cause is not associated with the disease, it is necessary to eliminate the harmful factors.
Tablets
Different medications may be used depending on the underlying cause.
- For motion sickness or motion sickness, the antihistamine Dramina.
- For nausea associated with the work of the gastrointestinal tract - Motilium, Cerucal. These drugs improve the motility of the stomach and intestines and contribute to the rapid evacuation of food.
- With neurogenic nausea - sedatives (tincture of valerian, motherwort), tranquilizers.
With nausea and vomiting, it is important to drink plenty of fluids in order to restore fluid loss and normalize the balance of water and electrolytes in the body.
We tell you what is actually the most common cause of stomach gastritis, what are the symptoms of the disease and what is the modern approach to effective treatment
Folk remedies
Mineral water, for example, Borjomi, Narzan, Essentuki, Jermuk, helps to eliminate the feeling of nausea, you can also try tea with lemon. Also eliminates discomfort 1 teaspoon of soda dissolved in a glass of water.
Folk remedies for nausea include a decoction of dill seeds, potato juice, and an infusion of basil leaves.
Prevention
Prevention of nausea is based on the elimination of its causes. It is necessary to follow certain rules of prevention.
- More time outdoors during pregnancy.
- Eat little and often.
- Avoid fatty and fried foods.
- Drink more fluids.
Frequently asked questions and answers
Why is nausea dangerous?
Nausea is characterized by a peculiar feeling of pressure in the epigastrium and an unpleasant sensation in the mouth. It may be accompanied by pallor of the face, salivation, dizziness, low blood pressure, general weakness, and sometimes pre-syncope.
Nausea can be a manifestation of acute and chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (stomach diseases, pancreatitis, etc.), but it also occurs with hypertensive crises, toxicosis of pregnant women, kidney failure, with sun or heat stroke, motion sickness or "seasickness" and other diseases.
Sometimes even healthy people may experience nausea as a reaction to unpleasant odors, even to the memory of them.